

BioNoticias

4ª semana de noviembre 2024
MÁS INFORMACIÓN Y OFERTAS EN LA WEB DE LA BIBLIOTECA: http://bibliotecabiologia.usal.es/
BioNoticias. Resumen de prensa semanal
Elaborado por la Biblioteca de Biología. Universidad de Salamanca
Para leer el texto completo de los artículos pulse en el título
Para agrandar el texto pulse cualquier otra parte de la página
Puede enviarnos sus noticias a bibbiol@usal.es
Suscribirse a Bionotias + BioEmpleo: dirección de correo electrónico y su nombre a bibbiol@usal.es
Boletines anteriores en http://issuu.com/bibliotecabiologia

Biología

Crean una portería para vigilar las entradas y salidas de abejas en una colmena

Puede parecer un tanto extravagante incorporar este dispositivo artificial a una colmena, pero hay razones de peso para hacerlo.
La emergencia climática multiplicará por ocho el impacto en la infancia para 2050
El informe Estado Mundial de la Infancia 2024, presentado por UNICEF en el Día Mundial de la Infancia, describe un futuro complejo para niños y adolescentes.
La subida del nivel del mar amenaza la subsistencia de las poblaciones costeras del Mediterráneo
Un tercio de la población de la región mediterránea vive muy próxima al mar y depende de sus infraestructuras y actividades económicas circundantes para subsistir.
"Conocer mejor las plantas nos permite darnos un baño de humildad como seres humanos" Cuando nos referimos a la inteligencia o a las distintas inteligencias hay que determinar qué entendemos exactamente por este concepto y definir qué seres biológicos pueden mostrar signos de ella.
Descubren restos neandertales en la cueva de la Arbreda

Un equipo multidisciplinar ha identificado nuevos restos neandertales en el yacimiento de la cueva de l'Arbreda (Serinyà, Girona).
Advancements in genomic research reveal alternative transcription initiation sites in thousands of soybean genes
Rosalind Franklin, James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the structure of DNA that molecular blueprint for life over 70 years ago.
Secrets of horse genetics for conservation, breeding

Researchers are helping uncover new information about the Y chromosome in horses, which will help owners identify optimal lineages for breeding and help conservationists preserve breed diversity.
Vultures and artificial intelligence(s) as death detectors: High-tech approach for wildlife research and conservation
In order to use remote locations to record and assess the behavior of wildlife and environmental conditions, the GAIA Initiative developed an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm that reliably and automatically classifies behaviors of white-backed vultures using animal tag data.
Bioeconomy in Colombia: The race to save Colombia's vital shellfish Along Colombia's Pacific coast, a small shellfish called piangua has been a crucial part of local communities for generations.
How marine worms regenerate lost body parts
Many living organisms are able to regenerate damaged or lost tissue, but why some are particularly good at this and others are not fully understood.
New fossil reveals the evolution of flying reptiles

A newly discovered pterosaur fossil is shedding light on the evolutionary journey of these ancient flying reptiles.
New model can help understand coexistence in nature
Different species of seabirds can coexist on small, isolated islands despite eating the same kind of fish.
Living microbes discovered in Earth's driest desert
A new technique allows researchers to separate external and internal DNA to identify microbes colonizing the hostile environment of the Atacama Desert.
Tiny worm makes for big evolutionary discovery

The history of a major animal group, composed of millions of species of insects, arachnids, and nemotodes, has been elusive until now.
'Walk this Way': How ants create trails to multiple food sources
Researchers have discovered that in a foraging ant's search for food, it will leave pheromone trails connecting its colony to multiple food sources when they're available, successfully creating the first model that explains the phenomenon of trail formation to multiple food sources.
Mountain lions coexist with outdoor recreationists by taking the night shift
Mountain lions in greater Los Angeles are proactively shifting their activity to avoid interacting with cyclists, hikers, joggers and other recreationists, finds a new study.
One or many? Exploring the population groups of the largest animal on Earth
Hunted nearly to extinction during 20th century whaling, the Antarctic blue whale, the world's largest animal, went from a population size of roughly 200,000 to little more than 300.
Slow editing of protein blueprints leads to cell death
An international research team has uncovered a new mechanism crucial to the production of cellular proteins.
Scientific thought on emotions in animals

How do animal behavior researchers feel about the feelings of animals? A new survey helps to answer that question.
A single cell's siesta
Too much of a good thing is no good at all.
Biologists reveal the genetic 'switch' behind parrot color diversity
From the Carnival in Rio de Janeiro to the shoulders of pirates: parrots are synonymous with color for people across the world.
How conflicting memories of sex and starvation compete to drive behavior, study in worms shows

Two conflicting memories can both be activated in a worm's brain, even if only one memory actively drives the animal's behavior, finds a new study.
Generation of rat offspring from ovarian oocytes by cross-species transplantation
Attempts to obtain eggs and offspring using oocytes in ovary have been made for keeping desirable traits in livestock, preserving human fertility, etc.
Backyard birds learn from their new neighbors when moving house
Scientists have found a trigger for social learning in wild animals.
New species discovered with refined DNA technology

Sometimes plants are so similar to each other that the methods developed by 18th century scientist Carl Linnaeus for identifying species are not enough.
The blue-green sustainable proteins of seaweed may soon be on your plate
The protein in sea lettuce, a type of seaweed, is a promising complement to both meat and other current alternative protein sources.
Behavioral analysis in mice: More precise results despite fewer animals
Researchers are utilizing artificial intelligence to analyze the behavior of laboratory mice more efficiently and reduce the number of animals in experiments.

Biomedicina
Finger prick on track to become Alzheimer's test
A quick finger prick and a few drops of blood on a card that can be sent in regular mail.
A common heart failure medication may help prevent heart damage related to chemotherapy
A commonly prescribed medication for heart failure was linked to a lower risk of heart damage, or cardiotoxicity, among high-risk cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment using anthracyclines, according to recent research.
Brain-based visual impairment in children

Experts have identified five elements of a brain-based condition that has emerged as a leading cause of vision impairment starting in childhood in the United States and other industrialized nations.
Cardiovascular drugs may reduce dementia risk
Common cardiovascular drugs are linked to a lower risk of dementia in older age, according to a new study.
Avance del atlas de las células humanas con una resolución comparable a Google Maps

La segunda mitad del siglo XV se caracterizó por una expansión sin precedentes en el conocimiento del mundo, gracias a instrumentos como la brújula, y a los rudimentarios mapas existentes y cartas de navegación.
Changing the definition of cerebral palsy
Defining cerebral palsy only as a childhood condition fails to acknowledge the many adults living with the disease.
HIV
latency reversing properties in African plant
The Wistar Institute and the University of Buea in Cameroon has uncovered the mechanisms for a medicinal plant with anti-HIV potential in Croton oligandrus Pierre & Hutch, a species of African tree that has been used in traditional healing in Cameroon to treat a variety of diseases and conditions including cancers and diabetes.
The chilling sound of the Aztec death whistle

The Aztec skull whistle produces a shrill, screaming sound. A study shows that these whistles have a disturbing effect on the human brain.
High exposure to everyday chemicals during pregnancy linked to asthma risk in children
A new study sheds light on a potential link between exposure to certain everyday chemicals during pregnancy and the development of asthma in children.
Study identifies subtypes of fibroblasts in skin cancer
A study provides insights into the diversity of cancer-associated fibroblasts in white and black skin cancer and describes their different immunomodulatory roles in the tumor environment.
By exerting 'crowd control' over mouse cells, scientists make progress towards engineering tissues

Genes aren't the sole driver instructing cells to build multicellular structures, tissues, and organs.
Labeling cell particles with barcodes
Cell-to-cell communication through nanosized particles, working as messengers and carriers, can now be analyzed in a whole new way, thanks to a new method involving CRISPR gene-editing technology.
Neuroscientists discover how the brain slows anxious breathing

Scientists discovered a brain circuit that allows us to regulate voluntary breathing, which connects the brain's emotional and behavioral cortical area to its automatic breathing brainstem area.
Psychotic-like experiences in adolescents linked to depression and self-destructive behavior
Psychotic-like experiences, such as suspiciousness and unusual thoughts, are common among adolescents who are referred to adolescent psychiatric care.
How jetlag can disrupt our metabolism
Have you ever felt sluggish and out of sorts after a long-haul flight or a late-night shift?
How children learned for 99% of human history
Unlike kids in the United States, hunter-gatherer children in the Congo Basin have often learned how to hunt, identify edible plants and care for babies by the tender age of six or seven.
Earlier diabetes diagnosis linked to dementia risk
People diagnosed with type 2 diabetes at a younger age are at a higher risk for developing dementia than those diagnosed later in life, according to a new study.
¿Puede la contaminación del aire causar alzhéimer?

Diversos estudios han asociado la contaminación del aire con el aumento del riesgo de desarrollar la enfermedad de Alzheimer y otras demencias.
National Poll: Some parents need support managing children's anger Some parents may find it challenging to help their kids manage intense emotions.
Persisten los diagnósticos tardíos de VIH en España, pese al descenso de nuevos casos

España ha registrado un descenso en los nuevos diagnósticos de VIH durante la última década, con 3.196 casos reportados en 2023.
Study identifies potential new drug for Parkinson's-related cognitive decline, dementia
A recently published study found that a tiny protein called PNA5 appears to have a protective effect on brain cells, which could lead to treatments for the cognitive symptoms of Parkinson's disease and related disorders.
Developing an antibody to combat age-related muscle atrophy
As we age, our muscles atrophy. Earlier this year, researchers found that hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a protein critical in skeletal muscle development loses its functionality due to nitration as we age.
How cells habituate
Up until recently, habituation -- a simple form of learning was deemed the exclusive domain of complex organisms with brains and nervous systems, such as worms, insects, birds, and mammals.
Pregnant people might not be getting the nutrients they need New research reveals startling shortfalls in dietary nutrition during pregnancy.
New subtypes of common brain disorder

Researchers have used AI tools to describe three sub-types of Chiari type-1, which will help guide clinicians to make the most effective treatment decisions for their patients.
Researchers discover new cognitive blueprint for making and breaking habits
Cognitive neuroscientists have described a brand new approach to making habit change achievable and lasting.
Eradivir's EV25 therapeutic reduces advanced-stage influenza viral loads faster, more thoroughly in preclinical studies than current therapies
A research article shows that Eradivir's patent-pending antiviral therapeutic called EV25 reduces lung viral loads of advanced-stage influenza in preclinical studies quicker and more effectively than currently available therapies.
New nasal vaccine shows promise in curbing whooping cough spread

A new nasal whooping cough vaccine showed an ability to prevent both infection and transmission of the disease in mice.
Researchers use biophysics to design new vaccines against RSV and related respiratory viruses In most people, the lung-infecting pathogens known as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and human metapneumovirus (hMPV) trigger mild cold-like symptoms.
¿Pueden las células "aprender" como el cerebro?

Las células individuales son capaces de aprender, según un estudio dirigido por un equipo del Centro de Regulación Genómica (CRG) de Barcelona y la Harvard Medical School en Boston.
Creativity camp improves adolescent mental health, wellbeing
A research team found that Creativity Camp, a two-week arts intervention delivered as a day camp, had a positive impact on mental health and well-being in adolescents with depression.
Smarter blood tests deliver faster diagnoses, improved outcomes
New research now can identify more proteins, or biomarkers, in blood plasma, including those linked to specific diseases like cancer.
Nasal spray version of common diuretic has potential to help treat heart failure
A study testing a new nasal spray form of the medication bumetanide, a commonly prescribed diuretic, was found to be as safe and welltolerated (meaning with no significant nasal irritation) in healthy adults in comparison to the oral and intravenous forms of the medication.
Identifican un mecanismo clave en el desarrollo pulmonar humano

La IGFBP3 es una molécula ampliamente estudiada tanto en procesos patológicos como el cáncer—, como fisiológicos, y está implicada en la regulación de la proliferación, la diferenciación y la supervivencia celular.
Multiple sclerosis drug may help with poor working memory Fampridine is currently used to improve walking ability in multiple sclerosis.
Confinement may affect how we smell and feel about food

New research found confined and isolating environments changed the way people smelled and responded emotionally to certain food aromas.
A new discovery about pain signaling may contribute to better treatment of chronic pain When pain signals are passed along the nervous system, proteins called calcium channels play a key role.
Machine learning and supercomputer simulations help researchers to predict interactions between gold nanoparticles and blood proteins
Researchers have used machine learning and supercomputer simulations to investigate how tiny gold nanoparticles bind to blood proteins.
'Jekyll and Hyde' leaders do lasting damage, new research shows Employees struggle when supervisors swing between good and bad behaviour.
Inteligencia artificial que detecta en 10 segundos un tumor canceroso cerebral
En 10 segundos, una nueva inteligencia artificial detecta un tumor cerebral canceroso que a menudo pasa desapercibido durante la cirugía.
Cocoa or green tea could protect you from the negative effects of fatty foods during mental stress
New research has found that a flavanol-rich cocoa drink can protect the body's vasculature against stress even after eating high-fat food.
A new model to explore the epidermal renewal
The mechanisms underlying skin renewal are still poorly understood. Interleukin-38 (IL-38), a protein involved in regulating inflammatory responses, could be a game changer.
Promising daily tablet increases growth in children with dwarfism

A promising daily tablet is effective at increasing height and improving proportional limb growth in children with achondroplasia, the most common form of dwarfism, according to a new study.
Study identifies strategy for AI costefficiency in health care settings
A study has identified strategies for using large language models (LLMs), a type of artificial intelligence (AI), in health systems while maintaining cost efficiency and performance.
Diagnosing knee abnormalities like an experienced radiologist: A novel deep learning model
Multi-sequence knee magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an advanced non-invasive diagnostic method for knee pathology.
Scientists recreate mouse from gene older than animal life

An international team of researchers has achieved an unprecedented milestone: the creation of mouse stem cells capable of generating a fully developed mouse using genetic tools from a unicellular organism, with which we share a common ancestor that predates animals.
When hepatitis E viruses attack nerve cells

Hepatitis E viruses (HEV) typically cause liver infections. They can, however, also infect other organs and cause neurological disorders.
The women and stress behind rural farming in America
Recent research suggests the unique stresses from farm life may be taking a toll on one of the pillars of the families that make your dinners possible: the women who keep farming families running.
Neural mechanisms of sleepdependent motor learning revealed in new study on brain injury rehabilitation
Scientists reveal how sleep, especially naps, boosts motor learning after TBI, offering new insights into brain activity and rehabilitation strategies to enhance recovery outcomes.
New oral drug to calm abdominal pain
Researchers have developed a new class of oral painkillers to suppress chronic abdominal pain that is based on the peptide hormone oxytocin that drives childbirth contractions.
Protein in soy may reduce the risk of heart failure by affecting gut bacteria

Researchers have found a potential method to slow heart failure progression.
Alcohol-related deaths in the U.S. more than double from 1999 to 2020
Alcohol-related deaths in the U.S. nearly doubled from 1999 to 2020. The sharpest spike occurred among 25- to 34-year-olds (nearly fourfold), while individuals aged 55 to 64 had the highest rates.
How optogenetics can put the brakes on epilepsy seizures
In what could one day become a new treatment for epilepsy, researchers have used pulses of light to prevent seizure-like activity in neurons.
Study explores the pandemic's impact on breastfeeding practices in historically marginalized communities
A new study has found that 34 percent of mothers said stay-athome orders facilitated easier breastfeeding at home, stronger mother-child bonding, and extended breastfeeding duration for many women.
Dieting: Cause of the yo-yo effect deciphered

Researchers have discovered a mechanism behind the yo-yo effect: fat cells have a memory that is based on epigenetics.
High-dose IV vitamin C plus chemotherapy doubles survival in advanced pancreatic cancer
A randomized, phase 2 clinical trial shows that adding high-dose, intravenous (IV) vitamin C to chemotherapy doubles the overall survival of patients with late-stage metastatic pancreatic cancer from eight months to 16 months.
Gaming for the good!
It turns out gaming is good for you! New research indicates massive multiplayer online gamers learn by gaming and their skills in the workplace are enriched by those seemingly endless hours previously thought of as frittering away time.
¿Cómo frenar las resistencias antibacterianas sin crear nuevos antibióticos?

Más de 39 millones de personas morirán de infecciones resistentes a los antibióticos de aquí a 2050, según un análisis mundial de la resistencia a los antimicrobianos, que se publicó en The Lancet.
Climate change and eye maladies
Clinical visits by patients suffering ocular surface eye conditions more than doubled during times when ambient particulate matter from air pollution was in the atmosphere, signaling a possible association between climate change and ocular health, according to a new study.
Achilles heel of antibiotic-resistant bacteria

To stem the surging antibiotic resistance public health crisis, scientists seek solutions inside the mechanics of bacterial infection.
Traditional Mayan practices have long promoted unique levels of family harmony: But what effect is globalization having?
A new study shows that the past 30 years of globalization have brought fundamental shifts in some aspects of family interaction among Indigenous people in Guatemala.
New study shows how salmonella tricks gut defenses to cause infection
A study uncovered how Salmonella, a major cause of food poisoning, can invade the gut despite the presence of protective bacteria.
Rainforest protection reduces the number of respiratory diseases

Rainforest protection is not only good for biodiversity and the climate it also noticeably improves the health of humans who live in the corresponding regions.
Egyptians drank hallucinogenic cocktails in ancient rituals, study confirms
Scholars for the first time identified chemical signatures of the components of a liquid concoction contained in a Bes mug.
Stress makes mice's memories less specific
Stress is a double-edged sword when it comes to memory: stressful or otherwise emotional events are usually more memorable, but stress can also make it harder for us to retrieve memories.
Optical biosensor rapidly detects mpox virus
Researchers have developed an optical biosensor that detects the virus that causes mpox.
Time in nature benefits children with mental health difficulties
Researchers found that spending two hours a week of class time in a natural environment can reduce emotional distress among 10- to 12year-olds who had the most significant mental health problems before the program began.
Study uncovers first evidence of resistance to standard malaria treatment in African children with severe malaria

An international team of researchers has uncovered evidence of partial resistance to artemisinin derivatives- the primary treatment for malaria in young children with severe malaria.
New drug targets for Alzheimer's identified from cerebrospinal fluid Researchers have linked diseaserelated proteins and genes to identify specific cellular pathways responsible for Alzheimer's genesis and progression.
Neuro-oncology experts reveal how to use AI to improve brain cancer diagnosis, monitoring, treatment An international team of leading neuro-oncology researchers and clinicians has released new recommendations for good clinical practice regarding the use of artificial intelligence methods to more accurately diagnose, monitor and treat brain cancer.
Diabetes medication may be effective in helping people drink less alcohol
New research has found that certain types of medication used to treat diabetes may be effective in reducing alcohol use.
La elasticidad de los tejidos, clave en la respuesta celular

¿Qué tiene que ver un colchón viscoelástico con el correcto funcionamiento de las células?
How next-day responsibilities influence cannabis use
A study found that people are less likely to consume cannabis if they had an upcoming activity, which is consistent with other studies, and would reduce use the most for job interviews and caring for children.
How stress is fundamentally changing our memories

In a new study, researchers identify the biological processes behind stress-induced aversive memory generalization and highlight an intervention which could help restore appropriate memory specificity for people with PTSD.
Standardized autism screening during pediatric well visits identified more, younger children with high likelihood for autism diagnosis
New research found that the use of standardized autism screening during pediatric well-child visits identifies more children with high autism likelihood at a younger age, including those presenting with more subtle symptoms.
Exposure to marijuana in the womb may increase risk of addiction to opioids later in life, study finds

Evidence has been growing to suggest that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main psychoactive ingredient in cannabis, poses risks to the developing fetus by impacting brain development.
Scientists discover 'entirely unanticipated' role of protein netrin1 in spinal cord development
Researchers have uncovered a surprising new role for netrin1, a crucial protein in neural development, as a regulator that limits bone morphogenetic protein signaling in the developing spinal cord.
Zinc deficiency promotes Acinetobacter lung infection, study finds
Researchers discovered an unexpected link between zinc deficiency, the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-13 (IL-13), and Acinetobacter baumannii lung infection and demonstrated that blocking IL-13 prevented infectionassociated death in an animal model.
Long covid could cost the economy billions every year
Working days lost to long covid could be costing the economy billions of pounds every year as patients struggle to cope with symptoms and return to work, finds a new study.
New therapeutic approach for severe COVID-19: Faster recovery and reduction in mortality
Researchers have tested a novel therapeutic concept to treat virusinduced lung failure in patients with severe COVID-19 in a phase 2 clinical trial.
Children exposed to antiseizure meds during pregnancy face neurodevelopmental risks, study finds

Children born to mothers who take antiseizure medications to manage seizures and psychiatric conditions during pregnancy may face increased risks of neurodevelopmental conditions, according to new research.
Huntington's disease gene also enhances early brain development and intelligence, study finds

The Huntington's disease (HD) mutation eventually causes a fatal brain disease in adulthood, but a new study finds that early in life, children with the HD mutation have bigger brains and higher IQ than children without the mutation.
Scientists develop novel plug-andplay test to evaluate T cell immunotherapy effectiveness
A novel test enables real-time monitoring of T cells that have been engineered to fight cancer, after reintroduction into the body of a cancer patient.
Meta-analysis links high-risk Epstein-Barr virus lineage to nasopharyngeal cancer in southern China

Researchers have discovered a significant association between specific Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) variants and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Selenium carrier proteins: New starting point for cancer research
A recent study unveiled a key enzyme involved in producing selenoproteins, opening new strategies for treating certain types of cancer in children.
Scientists transform blood into regenerative materials, paving the way for personalized, blood-based, 3D-printed implants
Scientists have created a new 'biocooperative' material based on blood, which has shown to successfully repair bones, paving the way for personalised regenerative blood products that could be used as effective therapies to treat injury and disease.
Cash is King: The surprising truth about spending habits in a cashless world
Physical cash not only influences how much we spend but also fosters a profound sense of psychological ownership that digital payments cannot replicate, according to new research.
Researchers uncover potential treatment for rare genetic disorders

Researchers have identified a potential treatment for Sandhoff and Tay-Sachs diseases -- two rare, often fatal lysosomal storage disorders that cause progressive damage to nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
Sitting too long can harm heart health, even for active people
More time spent sitting, reclining or lying down during the day may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and death, according to a new study.
New insights into how we navigate space and store memories

Researchers have revealed how two neural circuits located in the brain's retrosplenial cortex are directly linked to spatial navigation and memory storage.
PTSD patients can benefit just as much from intensive outpatient programs as from inpatient clinics, new study shows Post-traumatic stress disorder comes in many forms and affects each person differently.
Social isolation, loneliness and frailty in older adults have a complex and sometimes mutually reinforcing relationship
A new article examines how social isolation, loneliness and frailty affect one another and the bidirectional relationship they exert as an individual gets older.
Potential single-dose smallpox and mpox vaccine moves forward
An FDA-approved vaccine for smallpox and mpox is effective but causes side effects.
Frequent emergency care during pregnancy could signal greater risk for severe maternal morbidity
A new study found that, among nearly 775,000 pregnant people in Massachusetts, 31 percent of these individuals had at least one unscheduled emergency visit to the hospital, and 3.3 percent had four or more unscheduled hospital visits.
New study sheds light on language development in children with hearing loss

Researchers find a link between early vocabulary composition and later language development in children with cochlear implants.
A new technology to isolate immunostimulatory members of the human gut microbiota: Nextgeneration IgA-seq
Scientists have developed a new technology to efficiently isolate a specific subset of gut bacteria from fecal samples that are recognized by IgA antibodies.
Clinical trial shows positive results for potential treatment to combat a challenging rare disease
Researchers have demonstrated that inebilizumab reduced the risk of symptoms by 87 percent in patients with the rare affliction known as immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD).
New roles in infectious process for molecule that inhibits flu

Researchers have identified new roles for a protein long known to protect against severe flu infection -among them, raising the minimum number of viral particles needed to cause sickness.
Drug combination prompts immune response in some resistant pancreatic cancers
A new drug strategy that regulates the tumor immune microenvironment may transform a tumor that resists immunotherapy into a susceptible one, according to a new study.
La EMA recomienda ahora aprobar el polémico fármaco lecanemab contra el alzhéimer

La EMA ha dado un giro en su evaluación del Leqembi (lecanemab), un fármaco diseñado para tratar el deterioro cognitivo leve o demencia temprana provocados por el alzhéimer.
New research shows relationship between heart shape and risk of cardiovascular disease
A new study has revealed that the shape of the heart is influenced in part by genetics and may help predict the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Treatment advances, predictive biomarkers stand to improve bladder cancer care
Recent advances in bladder cancer treatments may offer hope of curative care to more patients, including those with high-risk localized, muscle-invasive disease, according to a new editorial.
Remote telemedicine tool found highly accurate in diagnosing melanoma
Collecting images of suspiciouslooking skin growths and sending them off-site for specialists to analyze is as accurate in identifying skin cancers as having a dermatologist examine them in person, a new study shows.
Genetic legacy of Jomon huntergatherers linked to increased BMI in modern Japanese, study finds

New research exploring the roots of modern Japanese populations has linked the genetic signature of Jomon hunter-gatherers to a higher body mass index (BMI) among individuals, underlining that ancient human ancestors can leave a genetic legacy with impacts on health in modern day populations.
Children's gut bacteria may hold the key to diarrhea treatment Diarrhea claims the lives of 500,000 children each year in low- and middle-income countries.
New discovery enables gene therapy for muscular dystrophies, other disorders
StitchR, a new gene therapy technique, delivers large genes in two parts to treat muscular dystrophies by restoring critical proteins in animal models.
AI method can spot potential disease faster, better than humans, study finds
A 'deep learning' artificial intelligence model can identify pathology, or signs of disease, in images of animal and human tissue much faster, and often more accurately, than people.
The secrets of fossil teeth revealed by the synchrotron: A long childhood is the prelude to the evolution of a large brain

Could social bonds be the key to human big brains? A study of the fossil teeth of early Homo from Georgia dating back 1.77 million years reveals a prolonged childhood despite a small brain and an adulthood comparable to that of the great apes.
New study emphasizes the importance of arts and humanities in neurology training
Researchers have found teaching artistic observation to neurology residents contributed to the development of well-rounded physicians with the capacity to be both skilled clinicians and compassionate healers.
Texting abbreviations makes senders seem insincere, study finds If you want to seem sincere and receive more responses to your texts, spell out words instead of abbreviating them, according to new research.
NeuroMechFly v2: Simulating how fruit flies see, smell, and navigate
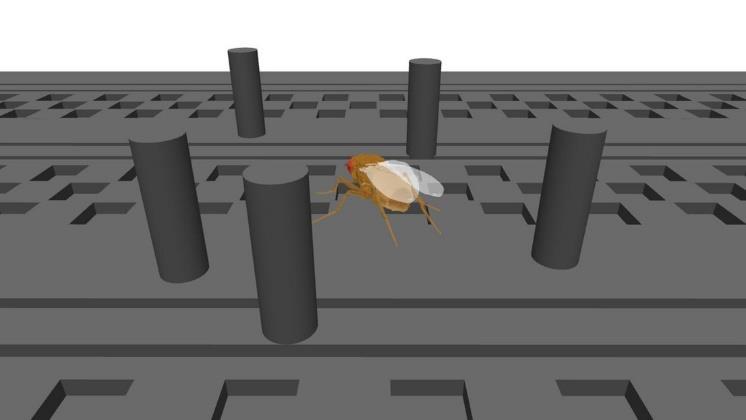
Scientists have advanced their NeuroMechFly model, simulating fruit fly movement in the real world.
Researchers reveal why a key tuberculosis drug works against resistant strains
A new study uncovers vulnerabilities in drug-resistant TB, offering hope for improved treatments.
Anti-anxiety and hallucination-like effects of psychedelics mediated by distinct neural circuits
New research suggests that it could be possible to separate treatment from hallucinations when developing new drugs based on psychedelics.
Los antidepresivos activan un receptor clave en la plasticidad neuronal

Un grupo de investigación internacional liderado por el Instituto de Biomedicina de Valencia (IBVCSIC) ha descubierto el mecanismo molecular por el que la fluoxetina, uno de los antidepresivos más usados en el mundol, activa un importante receptor que regula la supervivencia neuronal y la plasticidad de las conexiones neuronales en nuestro cerebro.
Researchers develop minimally invasive neural interface in revolutionary study
A team of researchers has developed a technique for diagnosing, managing and treating neurological disorders with minimal surgical risks.
'Achilles
heel' of drug-resistant pathogens
A new study has found highly vulnerable weakness in drugresistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis, offering a new way to kill them.
An advance toward inhalable mRNA medications, vaccines

Most people don't enjoy getting shots for treatments or vaccines. So, researchers are working to create more medicines, such as those made from messenger RNA (mRNA), that can be sprayed and inhaled.
Neuropathic pain drugs found to increase risk of hip fracture in older adults
A new study by medicine safety experts found the use of gabapentinoids medicines widely used to treat neuropathic pain increased the risk of hip fractures, especially in older patients who were frail or had kidney disease.
MRI-guided radiation therapy reduces long-term side effects for patients with prostate cancer
After a comprehensive two-year follow-up, researchers found that MRI-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for prostate cancer significantly reduced longterm side effects and improved quality of life, particularly in bowel and sexual health, compared to conventional CT-guided treatment.
Mathematical modelling leads to a better understanding of prostate cancer

Researchers have developed a threedimensional mathematical model of prostate cancer.
Robotic shorts support people when walking
Researchers have developed robotic trousers that enable people to walk more easily while expending measurably less energy.
Which risk factors are linked to having a severe stroke?
People with conditions or habits such as high blood pressure, an irregular heartbeat called atrial fibrillation, or smoking, not only have a higher risk of stroke, they may also have more severe strokes than people without these risk factors.
It's my brain's fault! Why teenagers make often unwise decisions
Adults exhibit a general tendency to make better decisions than adolescents, and this improvement drives an increase in specific and more sophisticated choice behaviors, according to a new study.
Human stem cell-derived heart cells are safe in monkeys, could treat congenital heart disease

A research team reported recently that heart muscle cells grown from induced pluripotent stem cells can integrate into the hearts of monkeys with a state of pressure overload.
How new therapies are revolutionizing the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis
The use of biologic and targeted therapies for children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) surpassed more typical therapies in recent years, according to researchers.
Cell aging in one organ can snowball into multi-organ failure

The aging and failure of cells that occurs when one part of the body is damaged can spread to other organs, a study suggests.
How studying fruit flies can help us understand congenital defects
Researchers elucidated the molecular details of how Drosophila larval epidermal cells (LECs) undergo cell death in a controlled manner to regulate epithelial tissue remodeling.
Recycling in middle age may be critical for brain health
New research highlights middle age as a pivotal period for brain health, with significant changes in how cells remove damaged mitochondria.
Metabolomic changes linked to psychotic-like experiences and cannabis use in adolescents
An exploratory study has examined metabolomic patterns associated with psychotic-like experiences in adolescents, highlighting the influence of cannabis use.
Las cremas con 10 % de urea mejoran la calidad de la piel de los pacientes con pie diabético

Las cremas específicas para pies que contienen un 10 % de urea, ya sean compradas en una farmacia o en un supermercado, mejoran de manera efectiva la calidad de la piel de los pacientes con pie diabético, según un estudio realizado por la Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM).
When sun protection begets malnutrition: Vitamin D deficiency in Japanese women
Researchers have developed a noninvasive, low-cost tool for assessing the risk of vitamin D deficiency in young women called ViDDPreS (Vitamin D Deficiency Predicting Scoring).
New model system for the development of potential active substances used in condensate modifying drugs
Researchers have developed a simple model system that can be used to break down fibrils -- the cause of numerous disorders including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease- into their constituent single units or liquid droplets.
Revolutionizing biology education: Scientists film 'giant' mimivirus in action
The COVID-19 pandemic has taught us all the importance of educating the public about viral infections.
Key influenza-severity risk factor found hiding in plain sight on our antibodies

Why do some people develop severe flu symptoms?
Air pollution exposure may be associated with eczema
People living in areas with higher levels of air pollution are more likely to have eczema, according to a new study.
Only certain paranormal beliefs may be linked with more stress and distress
In a new study, feelings of distress and reduced ability to cope with stress were associated with traditional paranormal beliefs, but not with new age philosophy.
Depression rates in LGBTQIA+ students are three times higher than their peers, new research suggests New findings uncover an alarming rise in depression rates among all higher education students in the United States, but especially among sexual and gender minorities.
Breaking every hour of sedentary time with 10 mins of light exercise significantly reduced blood pressure

Time spent sedentary beyond six hours per day during growth from childhood through young adulthood may cause an excess increase of 4 mmHg in systolic blood pressure, a new study shows.
Does AI improve doctors' diagnoses? Study puts it to the test Hospitals are already deploying artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance patient care.
Genetic variation enhances cancer drug sensitivity
By exploiting the genetic variation in cancer cells, an already approved cancer drug demonstrated enhanced effects against cancer cells in specific patient groups, according to a new study.
Early detection, intensive treatment critical for high-risk patients with Kawasaki Disease
A new scientific statement highlights new clinical data related to diagnosis, risk classification and treatment, emphasizing the need for tailored management strategies.
A step toward safer X-rays with new detector technology

Xrays are a common component of diagnostic testing and industrial monitoring, used for everything from monitoring your teeth to scanning your suitcase at the airport.
In 10 seconds, an AI model detects cancerous brain tumor often missed during surgery

Researchers have developed an AI powered model that in 10 seconds can determine during surgery if any part of a cancerous brain tumor that could be removed remains.
New genetic changes linked to testicular cancer offer fresh insights into the disease and its treatment
Scientists have identified new gene faults and evolutionary patterns contributing to testicular cancer.
New discovery may lead to more effective treatment for cardiovascular disease
Researchers have identified a new target to treat atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque clogs arteries and causes major cardiac issues, including stroke and heart attack.

Biotecnología
Investigadores desarrollan producto para controlar a fitopatógeno agresivo que daña los cultivos agrícolas

El Dr. Antonio Castillo lideró el desarrollo de un bactericida inocuo y eficaz, a partir del uso de bacteriófagos lícitos, para combatir al organismo fitopatógeno pseudomonas syringae, la cual causa graves daños a las plantaciones agrícolas.
Una bacteria multirresistente detectada en el nordeste de Brasil reviste riesgos para la salud global

Es una cepa de Klebsiella pneumoniae y su existencia había sido previamente registrada en Estados Unidos.
Identificado el mecanismo que controla la actividad de una hormona vegetal esencial en la respuesta a la sequía

Las respuestas a distintos tipos de estrés en plantas están reguladas de manera muy precisa por diferentes fitohormonas.

Medioambiente
Thermochemical tech shows promising path for building heat
Energy stored in thermochemical materials can effectively heat indoor spaces, particularly in humid regions, according to researchers.
Revitalizing neighborhoods in the wake of aging populations
Researchers examined the Senboku Hottokenai Network Project through a combination of case study and action research methodologies.
Researchers develop crystals to harvest water from air, inspired by desert life

Researchers have developed a new crystalline material that can harvest water from fog without any energy input.
Perovskite research boosts solar cell efficiency and product life
An international team has identified a strategy to improve both the performance and stability for solar cells made out of the 'miracle material' perovskite by mitigating a previously hidden degradation pathway.
New method of generating ecofriendly energy
Researchers have developed a new method of growing organic crystals that can be used for energyharvesting applications.
Study tracks PFAS, microplastics through landfills and wastewater treatment plants
Scientists find that most of the microplastics and the 'forever chemicals' known as PFAS cycle through landfills and wastewater treatment plants and end up back in the environment.
Building roots in glass, a bio-inspired approach to creating 3D microvascular networks using plants and fungi

Researchers have developed a new bio-inspired approach to building complex 3D microfluidic networks by utilizing plant roots and fungal hyphae as molds.
Will agricultural weeds finally claim the upper hand in a changing climate?

Afew years back, a group of weed scientists showed that soil-applied herbicides are less effective against agricultural weeds in the context of our changing climate.
Improving hurricane modeling with physics-informed machine learning
Researchers employ machine learning to more accurately model the boundary layer wind field of tropical cyclones.
Sliding seeds can provide insight into devastating landslides and rock avalanches
Researchers study how Champatis roll and bounce down inclines. The authors released a heap of the seeds down an inclined plane while a camera recorded their descent to analyze their speed and the dynamics of their movement.
Piden a la CE que intervenga ante el acuífero amenazado por la embotelladora de Bezoya en León Los socialistas españoles en el Parlamento Europeo han instado a la Comisión Europea a actuar para proteger el acuífero amenazado por el proyecto de Bezoya en Quintanilla de Flórez (León), Grupo Pascual.
El enfoque 'One Health', salud humana, animal y ambiental, es cada vez más importante
Desde la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) se demandaba hace unos días una integración conjunta de la salud en las negociaciones de la Cumbre del Clima COP29, que esta semana inician las reuniones al más alto nivel en Azerbaiyán.
El calor reduce la capacidad de la tierra de absorber carbono

Un nuevo estudio muestra que las olas de calor extremo de 2023, que provocaron enormes incendios forestales y graves sequías, también mermaron la capacidad de la tierra para absorber carbono atmosférico.
Modeling and analysis reveals technological, environmental challenges to increasing water recovery from desalination Using zero liquid discharge to increase water recovery from desalination is an emerging method to combat water scarcity, but is expensive, energy-intensive and comes with environmental risks.
España, liderazgo europeo en la reutilización de agua

España es líder en reutilización del agua residual tratada en la UE, agua que acaba en los ríos una vez reciclada, pero también es el país europeo con mayor desproporción entre los cauces fluviales ordinarios y los de crecida, por lo que el sector requiere más inversión.
American soil losing more nutrients for crops due to heavier rainstorms Phosphorus, a nutrient in soil essential for sustaining most forms of life, is increasingly disappearing from land as it is washed into waterways throughout the United States, according to a new study.
Revealing the hidden costs of what we eat
Shifting our diets to be more sustainable can be a powerful way for each of us to address both climate change and global food insecurity, however making such adjustments at the large scales necessary to make a difference globally can be a delicate matter.
Andalucía plantará 1,5 millones de árboles que absorberán 300.000 toneladas de CO2

El presidente andaluz y vicepresidente del Comité de las Regiones de la UE, Juanma Moreno, ha anunciado la plantación de 1,5 millones de árboles que absorberán 300.000 toneladas de CO2 en las próximas tres décadas, lo que supone el equivalente a las emisiones de 220.000 kilómetros diarios de coches de gasolina.
Novel electro-biodiesel a more efficient, cleaner alternative to existing alternatives
Scientists create biodiesel with electrocatalysis and bioconversion.
Ytterbium thin-disk lasers pave the way for sensitive detection of atmospheric pollutants
Alongside carbon dioxide, methane is a key driver of global warming. To detect and monitor the climate pollutants in the atmosphere precisely, scientists have developed an advanced laser technology.
How 70% of the Mediterranean Sea was lost 5.5 million years ago

A new study has highlighted just how significantly the level of the Mediterranean Sea dropped during the Messinian Salinity Crisis a major geological event that transformed the Mediterranean into a gigantic salt basin between 5.97 and 5.33 million years ago.
Diverse and diverging demands on forests in Germany
Forests provide biodiversity, ecosystem functions, income and much more.
Bee alert: Pesticides pose a real threat to over 70% of wild bees

A new study reveals alarming risks that pesticides pose to groundnesting bees, which are crucial for pollination and food production.
Tree islands restore nature in oil palm plantations
Southeast Asia's tropical forests are renowned for their biodiversity, but at the same time face significant threats from the expansion of oil palm plantations.
Redefining net zero will not stop global warming
An international group of authors who developed the science behind net zero demonstrate that relying on 'natural carbon sinks' like forests and oceans to offset ongoing CO2 emissions from fossil fuel use will not actually stop global warming.
Plastic bag bans have lingering impacts, even after repeals
A new study found that policies to curtail the use of single-use plastic bags in grocery stores and other retail outlets in Austin and Dallas, Texas, resulted in people buying more plastic bags, a behavior that continued after the rules were no longer in place.
Decline in West African coastal fish stocks threatens food security and livelihoods

Fish stocks along the West African coast have declined significantly over the past five decades, threatening food security and the livelihoods of the fishing communities that depend on them, according to a new study.
Caída abrupta de los niveles mundiales de agua dulce
La cantidad total de agua dulce de la Tierra disminuyó abruptamente a partir de mayo de 2014 y se ha mantenido baja desde entonces.
Aragón autoriza aumentar en un 53% las batidas en la Reserva de Caza de los Montes Universales No habrá cupo máximo por cazador y batida para hembras de ciervo de cualquier edad, machos de ciervo menores de dos años con cuerna sin ramificaciones y de menos de 25 cm de longitud, y machos y hembras de cualquier edad de gamo y jabalí, incluyendo la hembra guía.
Earliest evidence of humans using fire to shape the landscape of Tasmania

Some of the first human beings to arrive in Tasmania, over 41,000 years ago, used fire to shape and manage the landscape, about 2,000 years earlier than previously thought.
Biodiversity in the city: Designing urban spaces for humans and animals
Animals and plants also live and thrive on public squares. This creates opportunities for greater biodiversity and well-being for the human population.
Recycling batteries with citric acid
A simple, highly efficient, inexpensive, and environmentally friendly process could provide a viable pathway for the sustainable recycling of depleted lithium-ion batteries (LIBs): No chemicals beyond citric acid need to be added to leach out and separate over 99 % of the lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese metals contained in NCM batteries.
Four global policies could eliminate more than 90% of plastic waste and 30% of linked carbon emissions by 2050

A
new study determines that just four policies can reduce mismanaged plastic waste plastic that isn't recycled or properly disposed of and ends up as pollution -- by 91% and plastic-related greenhouse gasses by one-third.
Spectacular chimneys discovered in the Dead Sea
Researchers have discovered meterhigh chimneys on the floor of the Dead Sea.
Resilience index needed to keep us within planet's 'safe operating space'
Researchers are calling for a 'resilience index' to be used as an indicator of policy success instead of the current focus on GDP.
Study finds humidity diminishes daytime cooling gains in urban green spaces
During the day, green spaces are cooler than the surrounding built-up areas, but this effect is often counterbalanced by increased humidity.
Breakthrough in capturing 'hot' CO2 from industrial exhaust

Capturing carbon dioxide from the hot industrial exhaust of cement and steel plants requires cooling the exhaust from around 200 C to 60 C so that liquid amines can react with the CO2.
'Game changer' in lithium extraction: Researchers develop novel electrochemical reactor
Researchers have developed an innovative electrochemical reactor to extract lithium from natural brine solutions, offering a promising approach to address the growing demand for lithium used in rechargeable batteries.
Bluetooth technology unlocks urban animal secrets
Mobile phones could be the key to a cheaper and more reliable way of tracking animals for ecology and conservation research, according to a new study.
Linking data on genetics, traits and environment gives crop breeders a wider lens

The interplay between the genetic makeup of crops and the conditions in which they grow is difficult to untangle.
Climate change threatens key ocean plankton groups
Planktonic foraminifera are tiny marine organisms, which are essential to the ocean's carbon cycle.
'Cool' white car headlights more likely to dazzle moths

'Cool' white lights such as those in modern car headlights endanger moths by causing them to fly erratically, new research shows.
Faster flowing glaciers could help predict nearby volcanic activity
Glaciers that are within three miles of a volcano move nearly 50% quicker than average, a new study has found, which could help create early warning of future eruptions.
Wave-predicting robots could cut green energy costs
Underwater robots that can predict waves in real-time could reduce the cost of producing offshore renewable energy, a study suggests.
12,000-year-old stones may be very early evidence of wheel-like technology
A collection of perforated pebbles from an archaeological site in Israel may be spindle whorls, representing a key milestone in the development of rotational tools including wheels, according to a new study.
Scientists compile library for evaluating exoplanet water

By probing chemical processes observed in the Earth's hot mantle, scientists have started developing a library of basalt-based spectral signatures that not only will help reveal the composition of planets outside of our solar system but could demonstrate evidence of water on those exoplanets.
When it comes to corporate climate action, a single policy isn't enough
Climate-conscious investors should consider supporting companies with a wide range of climate policies, rather than companies that cherrypick specific individual policies, according to a new study.
Dispositivos de rastreo, tecnología para proteger a rinocerontes negros contra la extinción en Kenia

En un esfuerzo por aumentar el número de rinocerontes negros, especie en peligro de extinción, Kenia empezó un proyecto para identificar con dispositivos de rastreo a esos mamíferos, informó este jueves la ministra keniana de Turismo y Vida Silvestre, Rebeca Miano.
Engineers make converting CO2 into useful products more practical
A new electrode design developed at MIT boosts the efficiency of electrochemical reactions that turn carbon dioxide into ethylene and other products.
Extreme weather accelerates nitrate pollution in groundwater
Extreme weather from climate change, including droughts and heavy rains, may increase the risk of nitrates from fertilizers ending up in groundwater.
Pioneering research shows sea life will struggle to survive future global warming
A new study highlights how some marine life could face extinction over the next century, if human-induced global warming worsens.
Frog populations once decimated by disease mount a major comeback

Thanks to the consistent and focused efforts of researchers and conservationists to save, then reintroduce, mountain yellow-legged frogs to lakes in Yosemite National Park, their populations are again thriving.

Ciencia
Effortless robot movements
Humans and animals move with remarkable economy without consciously thinking about it by utilizing the natural oscillation patterns of their bodies.
New research explores volcanic caves, advancing the search for life on Mars

Through the intricate study of lava tubes caves formed following volcanic eruptions when lava cools down -- an international team of researchers has uncovered clues about Earth's ancient environments that could be significant in the search for life on Mars.
New idea may crack enigma of the Crab Nebula's 'zebra' pattern
A theoretical astrophysicist may have solved a nearly two-decade-old mystery over the origins of an unusual 'zebra' pattern seen in highfrequency radio pulses from the Crab Nebula.
Dos agujeros negros supermasivos en el espacio de un sistema solar

Una investigación reciente ha permitido conocer detalladamente uno de los exóticos fenómenos provocados en su entorno por dos agujeros negros con una masa conjunta de unos 40 millones de veces la del Sol (diez veces más que la del agujero negro supermasivo del centro de n ...
AI headphones create a 'sound bubble,' quieting all sounds more than a few feet away
Researchers have created a headphone prototype that allows listeners to hear people speaking within a bubble with a programmable radius of 3 to 6 feet.
Spinning fusion fuel for efficiency
A new method to increase fusionfuel efficiency would involve aligning the quantum spin of deuterium and tritium and changing the mix of the two fuels.
Scientists discover laser light can cast a shadow

Researchers have found that under certain conditions, a laser beam can act like an opaque object and cast a shadow, opening new possibilities for technologies that could use a laser beam to control another laser beam.
Robot identifies plants by 'touching' their leaves
Researchers have developed a robot that identifies different plant species at various stages of growth by 'touching' their leaves with an electrode.

Biblioteca. Facultad de Biología
Universidad de Salamanca. Campus Miguel de Unamuno c/Donantes de Sangre s/n 37007 Salamanca angelpoveda@usal.es
http://bibliotecabiologia.usal.es/
