BIOLOGY WORKBOOK FOR
CSEC
Anne Tindaleii) What do you understand by the term ‘germination’?
iii) Complete the following table to give THREE conditions which seeds need to germinate and the role of EACH condition in the germination process.
ConditionRole in germination
b) To study germination in bean seeds, Jared soaked some seeds in water and lined a large glass jar with absorbent paper. He spaced the seeds around the jar, between its walls and the paper, and kept the paper moist.
i) What happened to the dry mass of Jared’s seeds during the first few days of germination?
ii) Outline the internal changes that occurred in his seeds as they began to germinate.
iii) What was the first observation Jared made which indicated that his seeds were germinating?
iv) Apart from his observation in iii), briefly describe the other observations that Jared made as his seeds germinated.
c) i) What are meristems?
ii) Identify TWO regions in plants where meristems are found.
1.
2.
iii) The diagram below shows a longitudinal section through the end of a root. Outline what is happening in each region, X, Y and Z , as the root grows in length.
iv) What is the function of the root cap?
a) i) Define reproduction.
ii) Give the TWO main differences between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction.
iii) Complete the following sentence. Asexual reproduction is described as being
iv) Complete the following table to give TWO advantages and TWO disadvantages of EACH type of reproduction.
a) i) What is the name given to the female gamete in humans?
ii) Label the diagram of the human female reproductive system.

iii) Draw lines to link the following structures and features. where fertilisation occurs contracts during birth where the embryo is implanted a ring of muscle has a rich blood supply produces female gametes a narrow tube lined with cilia secretes female sex hormones
b)
i) The human male gametes are called
ii) The figure below shows the human male reproductive system. Label parts G to

.
iii) Give the function or functions of EACH of the following structures.
reason
vi) A combination of factors makes HIV/AIDS difficult to control. Suggest TWO of these factors.
c) i) Suggest ONE reason why gonorrhea is much easier to treat than AIDS.
ii) Other than treating all cases of gonorrhea, suggest THREE ways in which gonorrhea can be controlled.
5 a) i) Of what importance are flowers to plants?
ii) Identify the parts of flowers Y and Z labelled P to W.
iii) What is the function of the part labelled T?
iv) To what does the term ‘pollination’ refer?
v) Distinguish between self pollination and cross pollination.
vi) Suggest how flowers Y and Z in ii) are pollinated. Y Z
vii) Discuss TWO characteristics of EACH flower that would aid in its pollination by the agent identified in vi).
b) i) Outline the events that follow pollination and lead to the formation of a zygote in a flowering plant.
ii) After its formation, the zygote divides by mitosis to form the embryo which develops into THREE parts. Identify these.
iii) Seeds can store food in one of two structures. Name these.
iv) State what happens to EACH of the following parts of a flower after fertilisation. the ovule
a) i) Why do flowering plants produce fruits?
ii) Fruits can be classified into TWO main types. Name these.
. 2.
iii) Label the fruit shown in the following diagram.
iv) Suggest TWO reasons why it is important that seeds are dispersed.
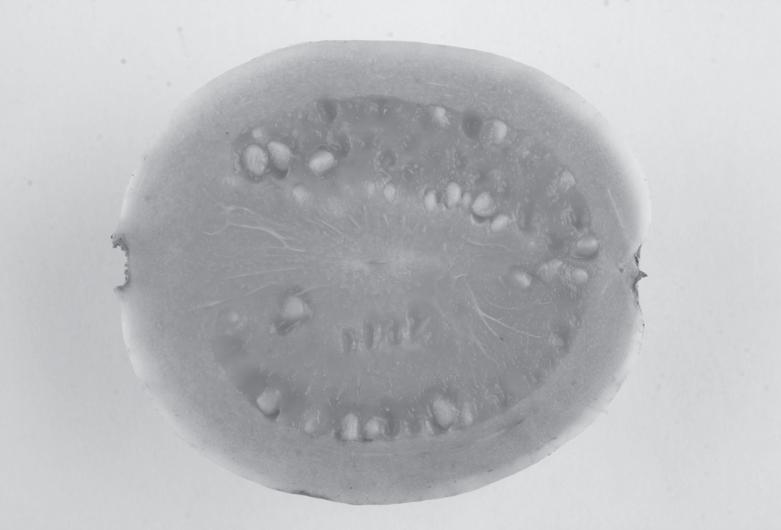


1.
2.
b) i) Identify the method of dispersal for the fruits Q to T shown in the following photographs.
ii) Suggest ONE characteristic of EACH fruit Q to T shown in i) that is useful in dispersing its seed or seeds by the method identified.

