3 minute read
Bamboo-bam
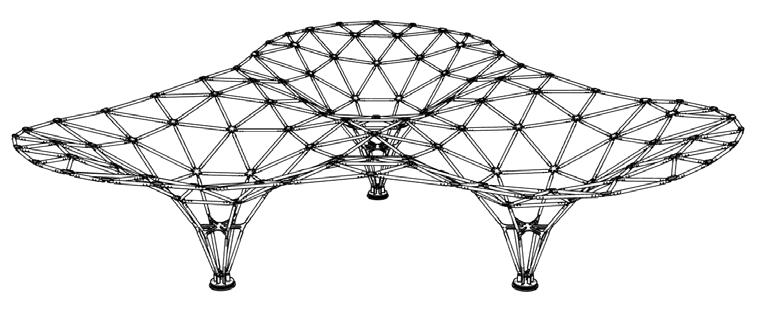
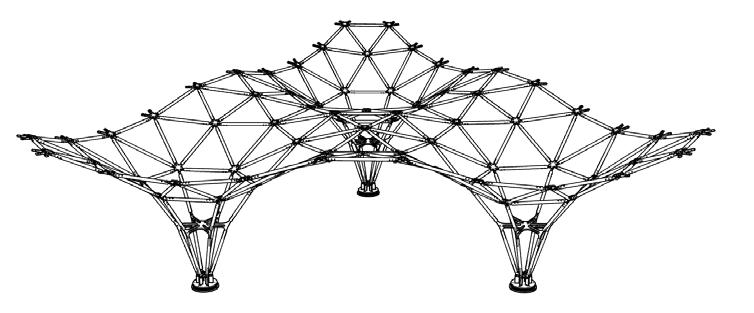
-a free form space structure-
Type: Workshop - Pavion
Advertisement
Year: May 2021 - November 2021
Location: Tehran, Iran
Area: 73 m²
Status: Completed
Held By: Digital Craft House, University of Art in Association with Bamboo Research Group, School of Architecture & Design, Virginia Tech

Supervisor & Tutor: Dr. Ramtin Haghnazar, Seyyed Ali Derazgisoo, Mehran Masoudi, Danial Keramat & Jonas Hauptman
Brief:
This 3 month-long workshop was related to designing a free-form spatial structure using non-standard bio-materials with the concerns of sustainability. During the workshop, we were divided into small groups and the process included material study, sustainability, computational and structural design, form-finding, and digital fabrication. The whole workshop was done by a group of about 40 people. Our team was mainly supposed to detect appropriate bamboos in the market and test them in terms of material properties and other tests like CNC and laser cut. Furthermore, we were supposed to study different form-finding methods using various tools like Karamba, Kangaroo, Peregrine, and etc.
Contributation to the project:
Idea Development, Construction
Modeling: Rhinoceros 7.0, Grasshopper
Rendering: Rhino Render
Presentation: Photoshop 2021, Premiere Pro
Material Study
4 types of bamboo were found and preliminary studying, assessing their quality, geometrical and mechanical studying and workability was done on them. Recommendations of BS ISO for grading bamboos were followed as well. In the end, a native species of bamboo was preferred over the others.




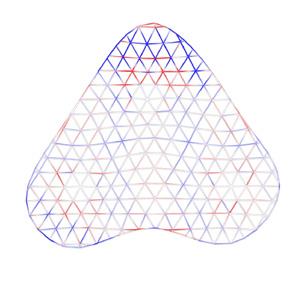
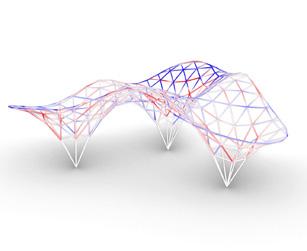
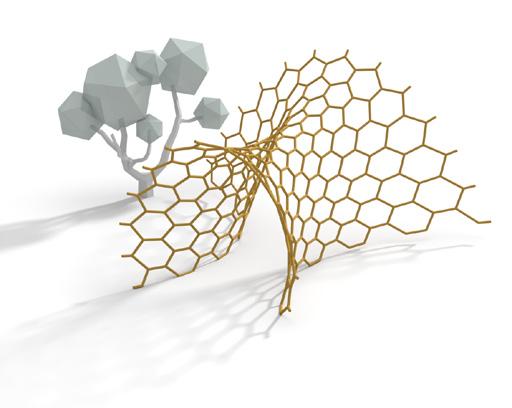
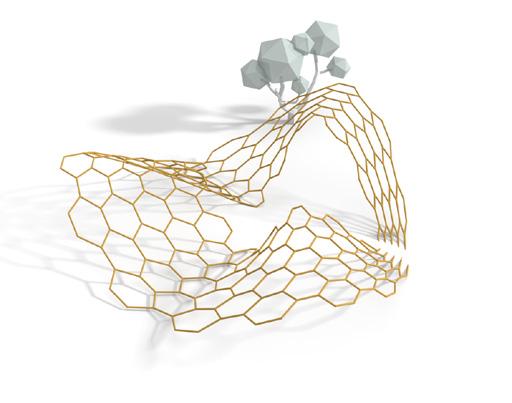
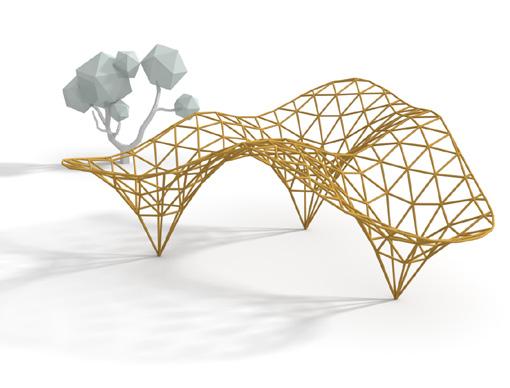
Form Finding
The study of different form-finding methods was assigned to two groups and our group was one of them. We studied available tools and plugins for each of method and alternatives. One code for each method was prepared to let students easily use and play around with those tools. Methods studied included force density, dynamic relaxation, graphic statics, and layout optimization. Our group was in charge of studying and working with tools like “Bats”, “Kangaroo”, “Karamba”, and “Peregrine”.
System Development
In a series of brainstorming sessions, various systems were proposed until a handful of them were chosen as final candidates. The candidates were then prototyped to experience the fabrication process for each. Some prototypes had undergone little changes compared to the suggested ideas while fabricating. Finally, an evaluation process was done based on various criteria to come to conclusion what are the pros and cons of each system. This part was done by another group.
Reconfigurable geometric shape based on the extrusion of each surface of a polyhedron along the normal direction.
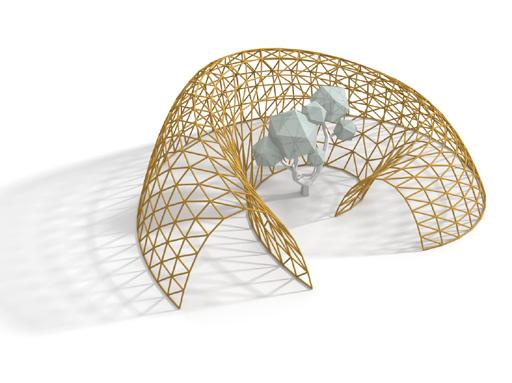
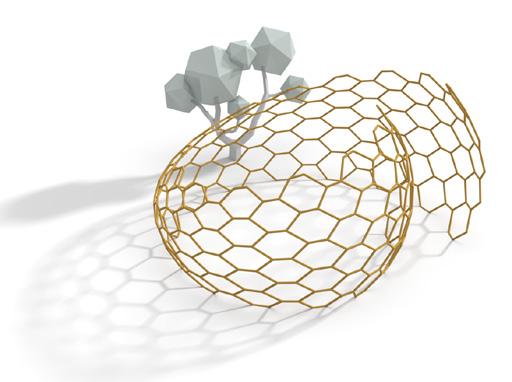
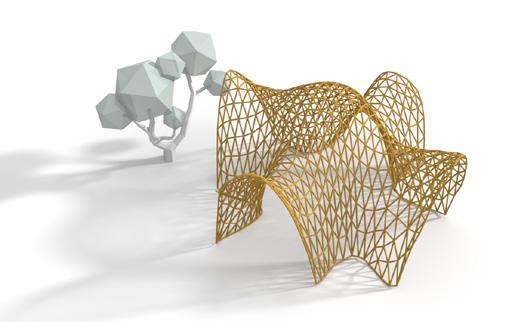
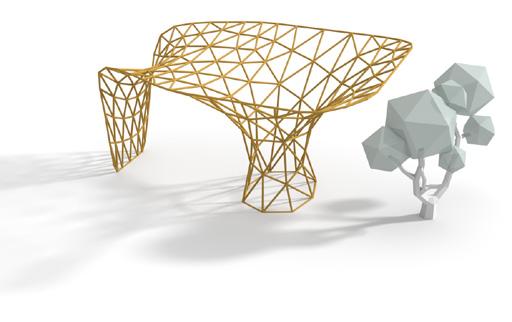
Material Testing:




Different types of mechanical tests and other methods have been done on bamboos so the result would help with the final output of structure’s system and form.






Evaluation & Design Workflow



Finally, suggested systems were evaluated based on visual elegance, the possibility of fabrication and assembly, structural performance, durability, and cost. Other considered factors were the usage of systems for 3 layer or 2 layer structures, needing to construct a CNC rotary system, and facilities provided in DC House Fab Lab. Considering these criteria, alternative RAdial was chosen. we developed a “digital design workflow” in a parametric modeling platform known as “grasshopper”. This digital workflow fully automates the modeling process and delivers the required outputs in a timely manner.


The workflow starts with getting two general inputs from the user: first, the wire mesh generated during the form design phase, and second, some numerical inputs about bamboo, CNC machine, Bolts and nuts, and node design preferences.


BIM Model & Prototyping

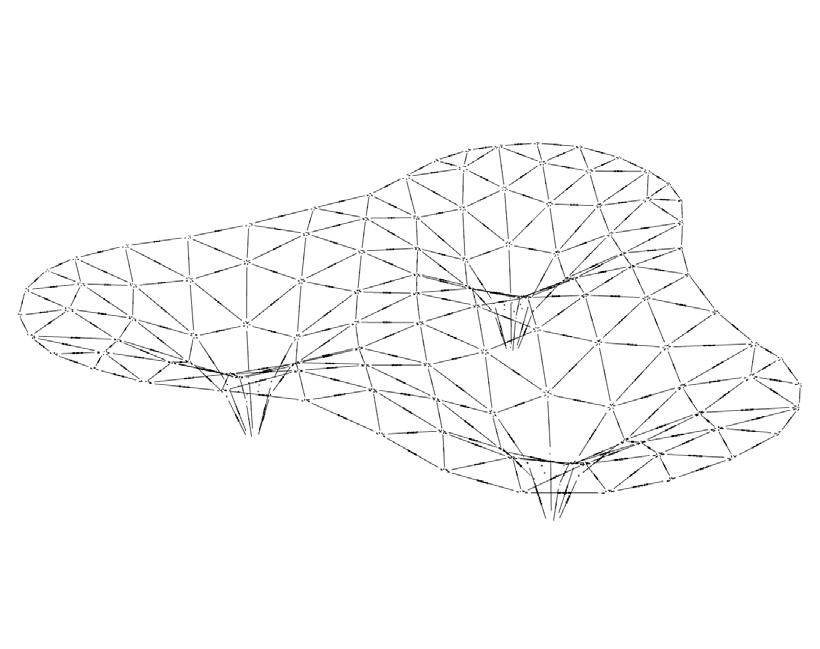
Finally, The second output is the shop drawing of the nodes and handles. These parts will be milled from plywood sheets with a 3 Axis CNC machine. Also, the shop data of bamboos is delivered. This data is used to saw and drill bamboo with a rotary CNC machine. The final output is the numerical statistics about the BIM model, such as element count and length. After all these, Prototyping starts on which some parts were constructed and tested to see if everything is working properly.
final step
After collecting and interpreting these data, it generates a completely comprehensive 3D model with labels for each element. As a result, it can be utilized as a coordination model during the assembly process.
Custom Digital Fabrication Tools


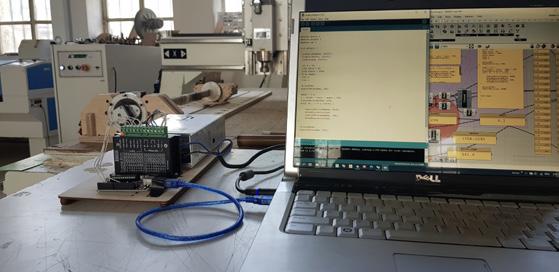
For the bamboo poles, we understood they would need four bolts at each end and not alighned to one another to connect to their respective joints. Three-axis CNC milling machines already existed that could drill vertically through the bamboo poles. Our poles couldn’t be rolled due to the fact that the drilling was only going one way. A rotary axis that was not affordable and might not fit our CNC bed had to be purchased or we had to design a custom one. We decided to go for the latter solution.



Fabrication Process And Assembly


The fabrication started with placing the three base elements in a proper position on the ground of University of Art in Tehran. Bamboos that had thicker mantle and were larger in diameter were placed on the basement structure using screw. Middle structures of basements which were similar to six-winged stars were then added and fixed to the bamboos of basements at the top. The three basements of the structure started to be constructed at the same time until they met each other in the middle. Bamboos and nodes which were located in the perimeter of the structure were assembled in the end in order to prevent the overthrow of the structure.