






mescreen™ decodes your cellular performance to unlock the peak potential for optimal living. This is more than guesswork, it's the first-of-itskind, precision pathway to discover your vitality
1. Precision data collection
Discover the root causes of your well-being by establishing your baseline
2. Performance validation
Validate the effectiveness of your health plan through data-tracking for continuous improvement.
3. Full health optimization
Periodic monitoring enablescontinual optimization, ensuring sustainable well-being and vitality.
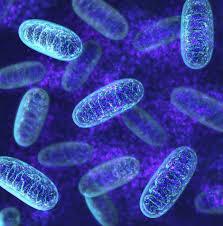
Mitochondria contribute to the synthesis of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and serotonin. These chemicals are essential for mood regulation, cognitive function, and communication between neurons.
Mitochondria are involved in the repair and regeneration of skin cells. They supply the energy needed for cellular repair processes and the production of new cells, which is crucial for wound healing and maintaining healthy skin.
The gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract, can influence mitochondrial function. Some microbial metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), can enhance mitochondrial activity and health.






Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA): Walnuts are an excellent source of ALA, a type of omega-3 fatty acid. Omega3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and help maintain mitochondrial membrane integrity, which is crucial for optimal mitochondrial function.
Magnesium and Copper: Walnuts are a good source of magnesium and copper. Magnesium is essential for ATP production and mitochondrial function, while copper plays a role in mitochondrial energy production and the function of antioxidant enzymes.
Regulation of
and Antioxidant
Walnuts contain melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep and has antioxidant properties. Melatonin helps protect mitochondria from oxidative damage and supports overall cellular health.
Magnesium and Manganese: Chia seeds are good sources of magnesium and manganese. Magnesium is essential for ATP production, which is critical for mitochondrial energy metabolism. Manganese is a cofactor for several antioxidant enzymes that help protect mitochondria from oxidative damage.
Amino Acids: Chia seeds provide a good amount of protein and essential amino acids. Protein is crucial for cellular repair and function, including that of mitochondria. Amino acids play a role in mitochondrial energy production and repair processes.

Support for Mitochondrial Membranes: ALA, an omega-3 fatty acid found in chia seeds, helps maintain the fluidity and integrity of mitochondrial membranes, which is important for efficient mitochondrial function and energy production.

Ellagitannins, a type of polyphenol found in pomegranates, are metabolized into ellagic acid. Ellagic acid has been shown to improve mitochondrial function by reducing oxidative stress and enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Pomegranates contain various polyphenols, including anthocyanins and tannins, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
Reducing inflammation helps protect mitochondria from damage and supports their overall health. Blood Sugar Regulation: Pomegranates can help regulate blood sugar levels. Stable blood sugar levels reduce the risk of metabolic disturbances and oxidative stress, which can impact mitochondrial health.

Blueberries have been shown to help regulate blood sugar levels. Stable blood sugar levels reduce the risk of metabolic disturbances and oxidative stress, both of which can affect mitochondrial health
Cellular Health: Blueberries contain vitamin K, which supports cellular health and mitochondrial function. Vitamin K is involved in various biological processes, including the regulation of inflammation and cellular repair.
Gut Health and Metabolism: Blueberries are rich in dietary fiber, which supports gut health and can influence mitochondrial function indirectly. A healthy gut microbiome can positively affect systemic inflammation and oxidative stress levels.

HIIT involves short bursts of intense activity followed by periods of rest or lowintensity exercise. This type of training stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, increasing the number and efficiency of mitochondria in muscle cells.
Examples: Sprinting, cycling at high intensity, or bodyweight exercises like burpees or jump squats.
Steady-state aerobic exercises improve mitochondrial function by increasing the number of mitochondria and their ability to produce energy. This type of exercise also improves cardiovascular health, supporting oxygen delivery to cells.
Examples: Running, swimming, cycling, or brisk walking.
Stimulates Mitochondrial Growth: Resistance or strength training helps to improve muscle mass and strength, which in turn can boost mitochondrial density. It also enhances metabolic function and insulin sensitivity.
Examples: Weight lifting, bodyweight exercises (e.g., squats, lunges), or resistance band workouts.
Consistency: Regular exercise is crucial for long-term mitochondrial health.

Variety: Combining different types of exercise can provide comprehensive benefits.
Intensity: Incorporating high-intensity intervals can significantly stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis.
Some research suggests that meditation may indirectly support mitochondrial biogenesis
Meditation helps balance the autonomic nervous system, shifting from the sympathetic (fight-orflight) to the parasympathetic (restand-digest) state.

Meditation has been shown to lower levels of oxidative stress by reducing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Reduced oxidative stress helps protect mitochondria from damage and supports their optimal function.
Meditation helps regulate stress hormones like cortisol.
Cold exposure activates brown adipose tissue (brown fat), which is rich in mitochondria. Brown fat helps generate heat through a process called non-shivering thermogenesis.

Regular cold exposure can enhance metabolic health by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Better metabolic health supports optimal mitochondrial function, as mitochondria are crucial for energy production and metabolic processes.
Cold exposure increases energy expenditure as the body works harder to maintain its core temperature. This increased caloric burn stimulates mitochondrial activity and energy production.

Regular sauna use is associated with improved cardiovascular health, including better blood pressure and reduced risk of heart disease. A healthy cardiovascular system supports adequate oxygen and nutrient delivery to cells, including mitochondria.
Saunas cause vasodilation, which improves blood flow circulation. Enhanced blood flow ensures that muscles a tissues receive more oxygen and nutrients, supporting overall mitochondrial health and function.

@discovermescreen

@mescreen
@Verseadiscovery