5G Wireless Network Security and Privacy Dongfeng Fang
Visit to download the full and correct content document: https://ebookmass.com/product/5g-wireless-network-security-and-privacy-dongfeng-f ang/
More products digital (pdf, epub, mobi) instant download maybe you interests ...
Sustainable Wireless Network-On-chip Architectures 1st Edition Murray
https://ebookmass.com/product/sustainable-wireless-network-onchip-architectures-1st-edition-murray/
Security in Wireless Communication Networks Yi Qian
https://ebookmass.com/product/security-in-wireless-communicationnetworks-yi-qian/
The Wiley 5G REF: Security 1st Edition Rahim Tafazolli
https://ebookmass.com/product/the-wiley-5g-ref-security-1stedition-rahim-tafazolli/
Network security essentials: applications and standards
William Stallings
https://ebookmass.com/product/network-security-essentialsapplications-and-standards-william-stallings/
Computer Network Security 1st Edition Ali Sadiqui
https://ebookmass.com/product/computer-network-security-1stedition-ali-sadiqui/
Comptia Security+ Guide to Network Security Fundamentals 7th Edition Mark Ciampa
https://ebookmass.com/product/comptia-security-guide-to-networksecurity-fundamentals-7th-edition-mark-ciampa/
Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, Global Edition William Stallings
https://ebookmass.com/product/cryptography-and-network-securityprinciples-and-practice-global-edition-william-stallings/
Performance and Security for the Internet of Things: Emerging Wireless Technologies Haya Shajaiah
https://ebookmass.com/product/performance-and-security-for-theinternet-of-things-emerging-wireless-technologies-haya-shajaiah/
eTextbook 978-0134527338 Network Security Essentials: Applications and Standards (6th Edition)
https://ebookmass.com/product/etextbook-978-0134527338-networksecurity-essentials-applications-and-standards-6th-edition/
5GWirelessNetworkSecurityandPrivacy
Dongfeng(Phoenix)Fang
CaliforniaPolytechnicStateUniversity,SanLuisObispo SanLuisObispo
YiQian UniversityofNebraska–Lincoln Lincoln
RoseQingyangHu UtahStateUniversity Logan
Thiseditionfirstpublished2024 ©2024JohnWiley&SonsLtd
Allrightsreserved.Nopartofthispublicationmaybereproduced,storedinaretrievalsystem,or transmitted,inanyformorbyanymeans,electronic,mechanical,photocopying,recordingorotherwise, exceptaspermittedbylaw.Adviceonhowtoobtainpermissiontoreusematerialfromthistitleisavailable athttp://www.wiley.com/go/permissions.
TherightofDongfeng(Phoenix)Fang,YiQian,andRoseQingyangHutobeidentifiedastheauthorsof thisworkhasbeenassertedinaccordancewithlaw.
RegisteredOffices
JohnWiley&Sons,Inc.,111RiverStreet,Hoboken,NJ07030,USA
JohnWiley&SonsLtd,TheAtrium,SouthernGate,Chichester,WestSussex,PO198SQ,UK
Fordetailsofourglobaleditorialoffices,customerservices,andmoreinformationaboutWileyproducts visitusatwww.wiley.com.
Wileyalsopublishesitsbooksinavarietyofelectronicformatsandbyprint-on-demand.Somecontentthat appearsinstandardprintversionsofthisbookmaynotbeavailableinotherformats.
Trademarks:WileyandtheWileylogoaretrademarksorregisteredtrademarksofJohnWiley&Sons,Inc. and/oritsaffiliatesintheUnitedStatesandothercountriesandmaynotbeusedwithoutwritten permission.Allothertrademarksarethepropertyoftheirrespectiveowners.JohnWiley&Sons,Inc.isnot associatedwithanyproductorvendormentionedinthisbook.
LimitofLiability/DisclaimerofWarranty
Whilethepublisherandauthorshaveusedtheirbesteffortsinpreparingthiswork,theymakeno representationsorwarrantieswithrespecttotheaccuracyorcompletenessofthecontentsofthisworkand specificallydisclaimallwarranties,includingwithoutlimitationanyimpliedwarrantiesofmerchantability orfitnessforaparticularpurpose.Nowarrantymaybecreatedorextendedbysalesrepresentatives,written salesmaterialsorpromotionalstatementsforthiswork.Thisworkissoldwiththeunderstandingthatthe publisherisnotengagedinrenderingprofessionalservices.Theadviceandstrategiescontainedhereinmay notbesuitableforyoursituation.Youshouldconsultwithaspecialistwhereappropriate.Thefactthatan organization,website,orproductisreferredtointhisworkasacitationand/orpotentialsourceoffurther informationdoesnotmeanthatthepublisherandauthorsendorsetheinformationorservicesthe organization,website,orproductmayprovideorrecommendationsitmaymake.Further,readersshould beawarethatwebsiteslistedinthisworkmayhavechangedordisappearedbetweenwhenthisworkwas writtenandwhenitisread.Neitherthepublishernorauthorsshallbeliableforanylossofprofitorany othercommercialdamages,includingbutnotlimitedtospecial,incidental,consequential,orother damages.
LibraryofCongressCataloging-in-PublicationDataappliedfor: HardbackISBN:9781119784296
CoverDesign:Wiley
CoverImage:©ImmersionImagery/Shutterstock Setin9.5/12.5ptSTIXTwoTextbyStraive,Chennai,India
Contents
AbouttheAuthors ix
Preface xi
Acknowledgments xiii
Introduction xv
1Introductionto5GWirelessSystems 1
1.1MotivationsandObjectivesof5GWirelessNetworks 1
1.2SecurityDrivesandRequirements 2
1.35GWirelessNetworkArchitecture 4
1.3.1Overviewofthe5GWirelessNetworkArchitecture 4
1.3.2ComparisonBetweentheLegacyCellularNetworkandthe5GWireless Network 5
1.4Conclusion 6
2SecurityfromLegacyWirelessSystemsto5GNetworks 7
2.1NetworkSecurityforLegacySystems 7
2.2SecurityAttacksandSecurityServicesin5GWirelessNetworks 9
2.2.1SecurityAttacks 9
2.2.2SecurityServices 11
2.2.2.1Authentication 12
2.2.2.2Confidentiality 12
2.2.2.3Availability 13
2.2.2.4Integrity 14
2.3TheEvolutionofWirelessSecurityArchitecturesfrom3Gto5G 14
2.3.13GSecurityArchitecture 14
2.3.24GSecurityArchitecture 15
2.3.35GWirelessSecurityArchitecture 16
2.3.3.1OverviewoftheProposed5GWirelessSecurityArchitecture 16
2.3.3.2SecurityDomains 17
2.4Summary 18
3SecurityServicesandMechanismsin5GWirelessSystems 19
3.1CryptographicApproachesandPhysicalLayerSecurity 19
3.2Authentication 22
3.3Availability 27
3.4DataConfidentiality 29
3.5KeyManagement 33
3.6Privacy 35
3.7Conclusion 36
4AnEfficientSecuritySolutionBasedonPhysicalLayerSecurityin5G WirelessNetworks 37
4.1Enhancing5GSecurityThroughArtificialNoiseandInterference Utilization 37
4.2AHetNetSystemModelandSecurityAnalysis 38
4.2.1SystemModelandThreatModel 38
4.2.2SecurityAnalysis 40
4.3ProblemFormulationandAnalysis 42
4.3.1MaximumSecrecyRate 43
4.3.2TheProposedAlgorithm 43
4.4NumericalandSimulationResults 46
4.5Conclusion 49
5FlexibleandEfficientSecuritySchemesforIoTApplicationsin5G WirelessSystems 51
5.1IoTApplicationModelsandCurrentSecurityChallenges 51
5.2AGeneralSystemModelforIoTApplicationsOver5G 52
5.2.1SystemArchitecture 52
5.2.2TrustModels 54
5.2.3ThreatModelsandDesignObjectives 55
5.3The5GAuthenticationandSecureDataTransmissionScheme 56
5.3.1Overviewofthe5GAuthenticationandSecureDataTransmissionScheme 56
5.3.2TheDetailedScheme 57
5.3.2.1Phase1–SystemInitialization 57
5.3.2.2Phase2–AuthenticationandInitialSessionKeyAgreement 58
5.3.2.3Phase3–DataTransmission 58
5.3.2.4Phase4–DataReceiving 59
5.3.2.5Phase5–T2IoTDevicesAuthenticationandInitialSessionKeyAgreement 59
5.4SecurityAnalysis 60
5.4.1ProtocolVerification 61
5.4.2SecurityObjectives 61
5.4.2.1MutualAuthentication 61
5.4.2.2InitialSessionKeyAgreement 62
5.4.2.3DataConfidentialityandIntegrity 62
5.4.2.4ContextualPrivacy 62
5.4.2.5ForwardSecurity 62
5.4.2.6End-to-EndSecurity 63
5.4.2.7KeyEscrowResilience 63
5.5PerformanceEvaluation 63
5.5.1SecurityServices 63
5.5.2ComputationalOverhead 63
5.5.3CommunicationOverhead 66
5.6Conclusion 67
6SecureandEfficientMobilityManagementin5GWireless Networks 71
6.1HandoverIssuesandRequirementsOver5GWirelessNetworks 71
6.2A5GCNModelandHetNetSystemModel 72
6.35GHandoverScenariosandProcedures 75
6.3.1HandoverScenarios 75
6.3.2HandoverProcedures 76
6.4ANewAuthenticationProtocolfor5GNetworks 79
6.4.1Assumptions 80
6.4.2Pre-Authentication 80
6.4.3FullAuthentication 81
6.4.4FastAuthentication 83
6.4.4.1HandoverBetweenAPs 83
6.4.4.2HandoverBetweenBSs 84
6.5SecurityAnalysisoftheNew5GAuthenticationProtocols 84
6.6PerformanceEvaluations 85
6.6.1CommunicationOverhead 86
6.6.2ComputationOverhead 86
6.7Conclusion 87
7OpenIssuesandFutureResearchDirectionsforSecurityandPrivacy in5GNetworks 89
7.1NewTrustModels 89
7.2NewSecurityAttackModels 90
7.3PrivacyProtection 90
7.4UnifiedSecurityManagement 91 References 93 Index 103
AbouttheAuthors
Dongfeng(Phoenix)Fang isanassistantprofessorintheDepartmentofComputer ScienceandSoftwareEngineering,andDepartmentofComputerEngineeringatCalifornia PolytechnicStateUniversity,SanLuisObispo(CalPoly).Herresearchinterestsinclude networksecurity,wirelesssecurity,securityandprivacyofInternet-of-Things,andsecurity andprivacyinmachinelearning.
YiQian,PhD,isanIEEEFellowandisaProfessorintheDepartmentofElectricaland ComputerEngineeringattheUniversityofNebraska-Lincoln,USA.
RoseQingyangHu isaprofessorintheDepartmentofElectricalandComputerEngineeringandAssociateDeanforResearchofCollegeofEngineeringatUtahStateUniversity inLogan,USA.Herresearchinterestsincludenext-generationwirelesscommunications, wirelessnetworkdesignandoptimization.
Preface
5Gwirelesssystemisnotonlyanevolutionofthelegacy4Gnetworks,butalsoasystem withmanynewservicecapabilities,relatedtoourdailylife.Tosupportthesenewservice capabilities,5Gwirelesssystemsintegratemanynewtechnologies,whichcanpotentially bringnewsecurityvulnerabilities.Moreover,strictperformancerequirementsforcertain applicationscannotbesatisfiedwiththecurrentsecuritysolutions.Forinstance,vehicular communicationsover5GrequireextremelylowlatencyandIoTapplicationsdemandlow overhead.
Thenewdevelopmentsinnetworkarchitectureandalgorithmsbringthechallengesto theresearcherstofacenewsecurityvulnerabilitiesandhighperformancerequirementsof securitysolutions.Thisbookintendstosurveythecurrentchallengesinthefieldofsecurityandprivacyover5Gwirelesssystems,andtopresentflexibleandefficientsolutions forsecurityandprivacyover5Gwirelesssystems.Specifically,thebookfocusesonsecurity andprivacyimprovementsover5Gwirelesssystemsbasedonsecuritynetworkarchitecture,cryptographicsolutions,andphysicallayersecuritysolutionsforbetterflexibilityand efficiency.Therearesevenchaptersinthisbook.
Chapter1providesanintroductionto5Gwirelesssystems.Thechapterfirstintroduces themotivationsandobjectivesof5Gwirelessnetworks.Basedonthefeaturesof5Gwirelessnetworks,5Gsecuritydrivesandrequirementsarediscussed.Anoverviewofthe5G wirelessnetworkarchitectureispresented,andacomparisonbetweenthelegacycellular networkandthe5Gwirelessnetworkisdiscussedtobetterunderstandthesystems.
Chapter2discussescellularnetworksecurityfrom1Gto5G.Aoverviewofsecuritydevelopmentfrom1Gto4Gispresented.Securityattacksandsecurityservicesin5Gwireless networksarediscussed.Securityarchitecturesfrom3Gto5Gareillustrated.
Chapter3presentsthesecurityservicesandcurrentsolutionsforsecurityandprivacy over5Gsystems.Thefundamentalapproachesforprovidingsecurityin5Gwirelesssystems arefirstreviewed.Securitysolutionsareintroducedbasedonauthentication,availability, dataconfidentiality,keymanagement,andprivacy.
Chapter4discussesinterferencemanagementandsecurityinheterogeneousnetworks (HetNet)over5Gwirelesssystems.Currentstudiesandbackgroundofinterference managementandsecurityissuesonconfidentialityarefirstintroduced.AgeneralHetNet systemmodelandcorrespondingthreatmodelareproposed.Asecuritysolutionis proposedtoutilizetheexistinginterferencetoimproveconfidentialityinthe5Gnetwork.
xii Preface
Thischapterpresentsthedetailsoftheproposedmethod.Anexperimentalstudyand evaluationarethendemonstrated.
Chapter5dealswithimprovingflexibilityandefficiencyofsecurityschemesforheterogeneousIoTnetworksover5Gsystems.AfewsecurityandprivacyschemesforIoTapplicationsarefirstdiscussed.AgeneralIoTsystemarchitecture,trustmodels,threatmodels,and designobjectivesarepresented.Anauthenticationandsecuredatatransmissionschemeis proposed.Securityanalysisispresentedtoverifytheproposedscheme.Thischapteralso presentsanexperimentalstudyandevaluation.
Chapter6explorestheefficiencyofsecuremobilitymanagementover5Gnetworks basedonsoftware-definednetworking(SDN).AHetNetsystemmodelisproposedover aSDN-based5Gnetwork.Thehandoverscenariosandproceduresarediscussed.The proposedauthenticationprotocolsarepresentedwithsecurityanalysisandperformance analysisandevaluations.
Chapter7discussestheopenissuesandpossiblefutureresearchdirectionsover5G wirelessnetworks.
Wehopethatourreaderswillenjoythisbook.
California August2022
Dongfeng(Phoenix)Fang
CaliforniaPolytechnicStateUniversity,SanLuisObispo
YiQian
UniversityofNebraska-Lincoln
RoseQingyangHu
UtahStateUniversity
Acknowledgments
First,wewouldliketothankourfamiliesfortheirloveandsupport.
WewouldliketothankourcolleaguesandstudentsatCaliforniaPolytechnicState University,SanLuisObispo,UniversityofNebraska-Lincoln,andUtahStateUniversity fortheirsupportandenthusiasminthisbookprojectandtopic.
WeexpressourthankstothestaffatWileyfortheirsupportandtothebookreviewers fortheirgreatfeedback.WewouldliketothankSandraGrayson,JulietBooker,andBecky Cowanfortheirpatienceinhandlingpublicationissues.
ThisbookprojectwaspartiallysupportedbytheU.S.NationalScienceFoundationunder grantsCNS-2007995,CNS-2008145,CCCS-2139508,andCCCS-2139520.
Introduction
Theadvancedfeaturesoffifth-generation(5G)wirelessnetworksystemsyieldnew securityandprivacyrequirementsandchallenges.Thisbookaddressesthemotivationfor securityandprivacyof5Gwirelessnetworksystems,anoverviewof5Gwirelessnetwork systemssecurityandprivacyintermsofsecurityattacksandsolutions,andanewsecurity architecturefor5Gsystems.Theaimof5Gwirelessnetworksecurityistoensurethe provisionofrobustsecurityservicesto5Gwirelesssystems,withoutcompromisingthe high-performancecapabilitiesthatcharacterize5Gtechnology.Duetotheinadequacy of4Gsecurityarchitecturesfor5Gsystems,novelsecurityarchitecturesarerequiredto ensuretheeffectivenessandadaptabilityofsecurityin5Gwirelessnetworks.Thetopicsto beaddressedinthisbookinclude:
● Introductionandbackgroundof5Gwirelessnetworks,
● Attacksandsecurityservicesin5Gwirelessnetworks,
● Current5Gwirelesssecuritysolutions,
● Anew5Gwirelesssecurityarchitecture,
● Flexibleandefficientsecuritysolutions,e.g.,physicallayersecurity,authentication,and mobilitymanagement.
Introductionto5GWirelessSystems
Fifth-generationwirelessnetworks,or5G,arethefifth-generationmobilewireless telecommunicationsbeyondthecurrent4G/InternationalMobileTelecommunications (IMT)-AdvancedSystems[Panwaretal.,2016].5Gwirelessnetworkisnotonlyan evolutionofthelegacy4Gcellularnetworksbutalsoanewcommunicationsystemthat cansupportmanynewservicecapabilities[Fangetal.,2017a].Inthischapter,wewill introduceageneralbackgroundof5Gwirelessnetworksand5Gsecurity,including motivationsandobjectives,securitydrivesandrequirements,andageneral5Gwireless networkarchitecture.
1.1MotivationsandObjectivesof5GWirelessNetworks
Theresearchanddevelopmentof5Gtechnologyisfocusedonachievingadvancedfeatures suchasenhancedcapacitytosupportagreaternumberofusersatfasterspeedsthan4G, increaseddensityofmobilebroadbanduserstoimprovecoverage[Xuetal.,2021],andsupportingdevice-to-device(D2D)communicationsandmassivemachine-typecommunications[NGMNAlliance,2015].5Gplanningalsoaimstoprovidebetternetworkperformance atlowerlatencyandlowerenergyconsumptiontobettersupporttheimplementationofthe InternetofThings(IoT)[Andrewsetal.,2014].Morespecifically,thereareeightadvanced featuresof5Gwirelesssystemsasfollows[WarrenandDewar,2014]:
● Datarate:1–10Gbpsconnectionstoendpointsinthefield;
● Lowlatency:1-mslatency;
● Bandwidth:1000× bandwidthperunitarea;
● Connectivity:10–100× numberofconnecteddevices;
● Availability:99.999%availability;
● Coverage:100%coverage;
● Networkenergyefficiency:90%reductionofnetworkenergyusage;
● Deviceenergyefficiency:Upto10yearsofbatterylifeforlow-powerdevices.
Toachievetheseeightadvancednetworkperformancefeatures,varioustechnologies [Agiwaletal.,2016]areappliedto5Gsystems,suchasheterogeneousnetworks(HetNet), massivemultiple-inputmultiple-output(MIMO),millimeterwave(mmWave)[Qiaoetal., 2015],D2Dcommunications[Weietal.,2016],software-definednetwork(SDN)[Dabbagh 5GWirelessNetworkSecurityandPrivacy,FirstEdition.Dongfeng(Phoenix)Fang,YiQian,andRoseQingyangHu. ©2024JohnWiley&SonsLtd.Published2024byJohnWiley&SonsLtd.
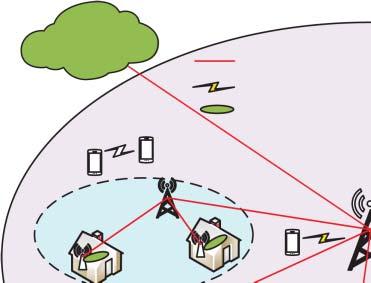
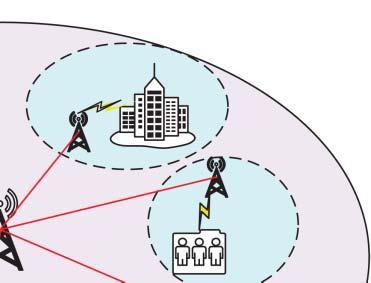
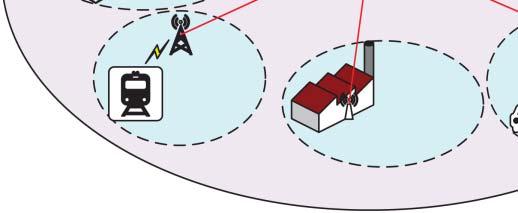
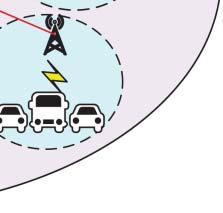
Figure1.1 Agenericarchitecturefor5Gwirelesssystems.
etal.,2015],networkfunctionsvirtualization(NFV)[Zhangetal.,2015],andnetworking slicing[NGMNAlliance,2016].Thestandardizationprocessfor5Gwirelesssystemshas beencarriedout.Figure1.1illustratesageneric5Gwirelesssystems.
5Gwirelesssystemscanprovidenotonlytraditionalvoiceanddatacommunicationsbut alsomanynewusecases[Xuetal.,2022,Wangetal.,2021b],newindustryapplications, andamultitudeofdevicesandapplicationstoconnectthesocietyatlarge[ABEricsson, 2018]asshowninFigure1.1.Different5Gusecasesarespecified,suchasvehicle-to-vehicle andvehicle-to-infrastructurecommunications[Fangetal.,2019b],industrialautomation, healthservices,smartcities,andsmarthomes[GlobalMobileSuppliersAssociation,2015]. Itisbelievedthat5Gwirelesssystemscanenhancemobilebroadbandwithcriticalservices andmassiveIoTapplications[Qualcomm,2016].Withthenewarchitecture,technologies, andusecasesin5Gwirelesssystems,itwillfacenewchallengestoprovidesecurityand privacyprotections[Huawei,2015].
1.2SecurityDrivesandRequirements
Toaccomplishtheobjectivesof5Gwirelessnetworks,severalfundamentalsecuritydrivers andrequirementsarenecessary.Figure1.2illustratesthemaindrivesfor5Gwirelesssecurityassupremebuilt-insecurity,flexiblesecuritymechanisms,andautomation.Supreme built-insecurityisneededsince,in5G,newusecases,newtechnologies,andnewnetworkingparadigmsareintroduced.Theotherusecasescanintroducespecificrequirements,suchasultra-lowlatencyinusercommunications,whichwillrequireimprovingthe
Figure1.2 Securitydrivesandrequirementsfor5Gwirelesssecurity.
performanceofthecurrentsecuritymechanisms.Newtechnologiesnotonlyyieldadvanced servicecapabilitiesbutalsoopenthedoortovulnerabilitiesandthusimposenewsecurity requirementsin5G[Liyanageetal.,2016].InHetNet,differentaccesstechnologiesmay havedifferentsecurityrequirements,andamulti-networkenvironmentmayneedhighly frequentauthenticationswithstringentdelayconstraints[Wangetal.,2016b].Massive MIMOhasbeendeemedacritical5Gtechniquetoachievehigherspectralefficiencyand energyefficiency.Itisalsoconsideredavaluabletechniqueagainstpassiveeavesdropping [Dengetal.,2015].Furthermore,SDNandNFVin5Gwillsupportnewservicedelivery modelsandthusrequirenewsecurityaspects[Chenetal.,2016b,Tianetal.,2017].With theadventof5Gnetworkingparadigms,anewsecurityarchitectureisneeded.Toaddress theseissues,securitymustbeconsideredanintegralpartoftheoverallarchitectureand shouldinitiallybeintegratedintothesystemdesign.
Tosupportvarioususecases,newtechnologies,newnetworkingparadigms,newthreats, newtrustmodelsinanoptimalway,andflexiblesecuritymechanismsareneededwith changingecosystemandgrowingneedfordependability.Basedonthecurrentresearchon 5Gwirelessnetworks,securityserviceson5Gwirelessnetworkshavemorespecificrequirementsduetotheadvancedfeaturesthat5Gwirelessnetworkshave,suchaslowlatency, andhighenergyefficiency.Withvariousapplicationson5Gwirelessnetworksandtheir networkperformances,flexiblesecuritymechanismsaredesiredwithbetterefficiencyperformance[Xuetal.,2019].
Thetrustmodelsofthelegacycellularnetworksand5Gwirelessnetworksarepresented inFigure1.3[Huawei,2015].Notonlyfulltrustbutalsosemi-trustornottrustareconsidered.Authenticationsarerequirednotonlybetweensubscribersandthetwooperators(the homeandservingnetworks)butalsoamongservicepartiesin5Gwirelessnetworks.Moreover,fortheusecaseofverticalindustries,thesecuritydemandsvarysignificantlyamong differentapplications.Forinstance,mobiledevicesrequirelightweightsecuritymechanismsastheirpowerresourceconstraint,whilehigh-speedservicesrequireefficientsecurityserviceswithlowlatency.Therefore,thegeneralflexibilityfor5Gsecuritymechanisms isanothercriticalrequirement[SchneiderandHorn,2015].Authenticationmanagementin 5Gismorecomplexduetovarioustypesofandamassivenumberofdevicesconnected.For differentapplications,differentauthenticationmodelscanbeimplemented.InFigure1.3, userauthenticationcanbedonebythenetworkprovider,serviceprovider,orboth.
Figure1.3 Trustmodelof4Gand5Gwirelessnetworks.
Besidesthesupremebuilt-insecurityandflexibilitysecuritymechanisms,security automationisalsoakeyelement.Itcombinesautomatedholisticsecuritymanagement withautomatedandintelligentsecuritycontrols[NOKIA,2017].Sincemorepersonal informationisusedinvariousapplications,suchassurveillanceappliedover5Gwireless networks,privacyconcernsescalate.Moreover,variousservicesin5Gcanbetiedcloser thanbefore.Forexample,thefixedtelephoneline,internetaccess,andTVservicecan beterminatedsimultaneouslyduetotheoutageofamajornetwork[Huawei,2015]. Therefore,securityautomationisneededtomakethe5Gsystemrobustagainstvarious securityattacks.
1.35GWirelessNetworkArchitecture
1.3.1Overviewofthe5GWirelessNetworkArchitecture
The5Gwirelessnetworkarchitectureisintroducedhere.AsshowninFigure1.4,theillustratedgeneral5Gwirelessnetworkarchitectureincludesauserinterface,acloud-based heterogeneousradioaccessnetwork,anext-generationcore,distributededgecloud,and acentralcloud.Thecloud-basedheterogeneousradioaccessnetworkcancombinevirtualization,centralization,andcoordinationtechniquesforefficientandflexibleresource allocation.Basedondifferentusecases,3GPPclassifiesmorethan70differentusecases intofourdifferentgroupssuchasmassiveIoT,criticalcommunications,networkoperation,andenhancedmobilebroadband.Inthecloud-basedheterogeneousaccessnetwork, besidesthe3GPPaccessandnon-3GPPaccess,othernewradiotechnologieswillbeadded formoreefficientspectrumutilization.Inthefirststageof5G,thelegacyevolvedpacket core(EPC)willstillbevalid.Networkslicingenablesdifferentparameterconfigurations forthenext-generationcoreaccordingtodifferentusecases.Newflexibleservice-oriented EPCbasedonnetworkslicing,SDN,andNFVwillbeusedinthenext-generationcoreas virtualevolvedpacketcore(VEPC)showninFigure1.4.TheVEPCiscomposedofmodularizednetworkfunctions.Basedondifferentusecases,thenetworkfunctionsappliedto eachVEPCcanbevarious.IntheVEPC,thecontrolplaneanduserplaneareseparated fortheflexibilityandscalabilityofthenext-generationcore.Edgecloudisdistributedto
improveservicequality.Thecentralcloudcanimplementglobaldatashareandcentralized control.
1.3.2ComparisonBetweentheLegacyCellularNetworkandthe5GWireless Network
Comparedwithlegacycellularnetworks,5Gwirelessnetworksintroducesomenew perspectivesandchanges.(i)Userequipmentandservicesarenotlimitedtoregular mobilephonesandregularvoiceanddataservices.Basedondifferentusecasesand requirements,userinterfacesareclassifiedintofourdifferentgroupssuchasmassiveIoT, criticalcommunications,networkoperation,andenhancedmobilebroadband.Everyuse casecanaffecttheradioaccessselectionandVEPCfunctions.(ii)Inadditionto3GPP accessandnon-3GPPaccessinthecloud-basedheterogeneousradioaccessnetwork,the 5Gaccessnetworkincludesothernewradios,whichbuildthefoundationofwireless standardsforthenext-generationmobilenetworksforhigherspectrumutilization.The newradioscansupporttheperformanceandconnectivityrequirementsofvarioususe casesin5Gwirelessnetworks.Moreover,therearemanytechnologiesappliedtotheaccess networktoimprovethenetworkperformance,suchasmassiveMIMO,HetNet,andD2D communications.(iii)Thenext-generationcorewillbebasedonthecloudusingnetwork slicing,SDN,andNFVtohandledifferentusecases.Theflexibleservice-orientedVEPC willbeapplied.Withnetworkslicing,SDN,andNFV,differentnetworkfunctionscanbe appliedtotheservice-orientedVEPCfordifferentusecases.Thenext-generationcoreis expectedtobeaccess-independent.Separationofcontrolanduserplaneisimportantto achieveanaccess-agnostic,flexible,andscalablearchitecture.(iv)Edgecloudisappliedto 5Gwirelessnetworkstoimprovetheperformanceofthenetwork,suchaslatency.
1.4Conclusion
Ageneralbackgroundof5Gwirelessnetworksisintroducedinthischapter.Themotivationsandobjectivesof5Gwirelessnetworksarepresented.Withtheexpectedimprovementsin5Gperformance,securitydrives,andrequirementsarediscussed.Ageneral5G wirelessnetworkarchitectureisillustratedinthischapter.Moreover,acomparisonofa 5Gwirelessnetworkarchitectureandlegacycellularnetworkarchitectureisanalyzed.Itis clearthatthe5Gwirelessnetworkintroducessignificantflexibilitytosupportnewusecases andcorrespondingdifferentservicerequirements.Newsecurityarchitectureandmechanismsareneededin5Gnetworks.
Thischapterprovidesanintroductiontotheevolutionofwirelessnetworksecurity,coveringthesecurityarchitectureandsecurityservicesofthesecondgeneration(2G)tothefifth generation(5G)ofwirelessnetworks.
2.1NetworkSecurityforLegacySystems
Basedonthetechnologiesandnetworkperformances,vulnerabilitiesandsecurityimplementationfrom2Gto4Garedifferent.
Securityservicesin2Gsystemsuchasglobalsystemformobilecommunications(GSM) includeuserauthentication,communicationencryption,useranonymity,anddetectionof stolen/compromisedequipment.
● Userauthentication:Theuserauthenticationisachallenge-responseschemebetweena userandthecellularnetwork(suchasvisitornetworkandhomenetwork).Toachieve userauthenticationrequiresarandomnumber(RAND)andakey,whichispre-storedin theSIMcardintheusermobiledevice.TheSIMcardalsostoresalgorithmsforachieving theuserauthentication.Theuserauthenticationisaone-wayauthentication,wherethe userisauthenticatedbythecellularnetworkbutthecellularnetworkcannotbeauthenticatedbytheuser.Whilethissecurityservicecaneffectivelypreventusersfrommisusing thenetworkservices,itcannotprovideprotectionagainstroguebasestations.
● Communicationencryption:Afteruserauthentication,asessionkeyisgeneratedto encrypttheuserdatabetweentheuserandthenetworkontheradiolink.Astream cipherisusedin2GGSMsystem.
● Anonymity:Anonymityisappliedtoprovideprivacyofinternationalmobilesubscriber identity(IMSI)ofeachuser,sinceIMSInotandisalsoassociatedwithuser’sidentity. Toachieveanonymity,insteadofusingIMSIallthetime,atemporarymobilesubscriber identity(TMSI)isusedandupdatedbetweentheuserandthenetworkbasedondifferent cases.
● Detectionofstolen/compromisedequipment:Eachmobiledevicehasaninternational mobileequipmentidentity,whichcanbeusedtoachievedetectionofstolenorcompromisedmobiledevice.
5GWirelessNetworkSecurityandPrivacy,FirstEdition.Dongfeng(Phoenix)Fang,YiQian,andRoseQingyangHu. ©2024JohnWiley&SonsLtd.Published2024byJohnWiley&SonsLtd.
While2Gtechnologyhasestablishedafoundationforsecurityincellularnetworks,it representsonlythebeginningofacontinuousefforttoenhanceandstrengthenthesecuritymeasuresinmobilecommunications.2Gnetworksarevulnerabletoattackstargeting securityalgorithms,signalingnetworks(throughexploitationofunencryptedmessages), securityprotocols(suchasroguebasestationattacks),anddenial-of-serviceattacks(includingjamming).Furthermore,2Gdoesnotprovidedataintegrity.
3Gsuchasuniversalmobiletelecommunicationsystem(UMTS)marksthebeginning ofamorecomprehensiveimplementationofsecuritymeasuresincellularnetworks.A securityarchitectureisdefinedby3GPPincludingfivegroupsofsecurityfeaturesinthe UMTS.Fromasecurityperspective,3Gnetworksintroducesignificantimprovementssuch asmutualauthentication,two-wayauthentication,andkeyagreementprotocols.Inadditiontothesemeasures,3Galsooffersenhanceddataintegritycomparedto2G.Theintroductionofstrongercryptographicalgorithmsfurtherbolstersthesecuritystrengthof3G networks.
● AKA:Theauthenticationandkeyagreement(AKA)mechanisminvolvesthreeentities asaUserServicesIdentityModule(USIM),theservingnetwork,andthehomenetwork.Alongtermkeyispre-sharedbetweentheUSIMandthenetwork.Basedona challenge–responsemechanism,thenetworkcanauthenticatetheUSIM,andtheUSIM canauthenticatethehomenetwork.Aftertheauthentication,twokeyswillbegenerated toachievedataconfidentialityanddataintegrityintheUSIMandthenetwork.
● Communicationencryption:Confidentialityisprovidedinthe3Gfordatatransmission overradiolinksbetweenusersandthebasestationsbyencryptingthedatawithacipher key,whichisgeneratedafterauthentication.Astreamcipherisusedwiththecipherkey, whichis128-bitlong.Therearealsootherinputswhichwillmakesurethatevenforthe samecipherkey,thestreamciphercangeneratedifferentkeystream.
● Dataintegrity:Besidesconfidentiality,dataintegrityisprovidedinthe3Gfordata transmissionoverradiolinksbetweenusersandthebasestationsbasedonamessage authenticationcode(MAC)withtheintegritykeyof128-bitlong,whichisgenerated afterauthentication.
● Useridentityconfidentiality:Asin2G,preservinguseridentityconfidentialityisacritical considerationin3Gnetworks.Toachievethis,3Gnetworksimplementtemporaryidentities,suchasTMSIinthecircuit-switcheddomainandP-TMSIinthepacket-switched domain.ThesetemporaryidentitiesareusedtolimitthefrequencyofIMSItransmission andenhanceuserprivacy.
● Detectionofstolen/compromisedequipment:Sameas2G.
● User-to-USIMauthentication:Apersonalidentificationnumber(PIN)isusedtoachieve user-to-USIMauthentication.ThisPINisonlyknownbytheuserandtheUSIM.
3Gnetworksbuilduponthesecuritymechanismsof2G,whileintroducingmodifications toenhanceoverallsecurity.Although3Gexpandsnetworkservicesandimprovesnetwork performance,italsointroducesnewvulnerabilities,suchasprivacyconcernsstemming fromtheintroductionoflocation-basedservices.Insummary,3Grepresentsasignificant improvementinsecuritycomparedto2G.
4Glong-termevolution(LTE)networksfeatureadifferentnetworkarchitecturecomparedto3G,designedtofurtherimprovenetworkperformance.Thisincludestheuseof
evolvedNodeBs(eNBs)amongotherenhancements.In4G,controlplane(CP)anduser plane(UP)areseparated.Thesecurityarchitectureof4Gnetworksdiffersslightlyfromthat of3Gnetworks.Inadditiontofurtherenhancingconfidentialityandintegrityalgorithms, 4Gnetworksintroducenewsecurityperspectivesduetotheirdifferentnetworkarchitecture.Forinstance,4Gprovidesmutualauthenticationbetweenuserequipment(UE)and theevolvedpacketcore(EPC),generatingacipherkeyandanintegritykeyaftermutual authentication.However,in4G,thesekeysareutilizeddifferently.Theuseofcomprehensivekeymanagementandhandoversecurityarealsocriticalcomponentsof4Gsecurityto ensuresecurityinmobilityscenarios.Thefollowingarethesecurityservicesprovidedin 4GLTEsystem.
● 4GAKA:4GAKAprotocolsbuildupon3GAKAtoprovidemutualauthentication betweenUEandEPC,ensuringtheauthenticationofentitieswhilealsofurnishing materialsforUPradioresourcecontrol(RRC)andnon-accessstratum(NAS)cipherkey andRRCandNASintegritykey.
● Keymanagement:4Ghasextendedkeyhierarchyof3Gwithmorekeysapplied.The twokeysgeneratedaftermutualauthenticationareusedtoderiveanintermediatekey KASME betweenUEandaccesssecuritymanagemententity(ASME). KASME canbeused togeneratemorekeys: KNASint , KNASenc ,and KeNB ,where KeNB canderive KUPenc , KRRCint ,and KRRCenc
● Confidentiality:Dataconfidentialityisprovidedin4Gbyencryptingcommunications. KNASenc isusedtoprovidedataconfidentialitybetweenUEandmobilitymanagement entity(MME). KUPenc and KRRCenc areusedtoensurecommunicationconfidentialityof userplanetrafficandradiospecificsignaling,respectively.
● Integrity:DataintegrityisensuredforcommunicationsbetweenUEandMMEby KNASint . Theintegrityofradiospecificsignalingisprotectedby KRRCint .Thereisnodataintegrity protectionforuserplanetraffic.
● Handoversecurity:ByintroducingeNBs,4GLTEalsoprovideshandoversecurity betweendifferenteNBstoensuretheauthenticationandkeymanagement.Moreover, handoversecuritybetween4Gandlegacysystemsisalsoprovided.Manyoftheresearch workfocusedonimprovethehandoverperformancewithrequiredsecurity.
4Gnetworksboaststrongersecurityimplementationscomparedtotheprevioussystems andcontinuetoplayacrucialroleinmoderncellularnetworks.Ongoingsecurityenhancementsareexpectedfor4Gnetworksaswell,furtherbolsteringtheirsecuritycapabilities. 2.2SecurityAttacksandSecurityServicesin5GWireless
2.2.1SecurityAttacks
Securityattackscanbecategorizedintotwomaintypesbasedontheirattackfeatures: passiveattacksandactiveattacks[Stallings,2017].Forapassiveattack,attackersaimto learnoruseinformationfromlegitimateuserswithoutinfluencingthecommunication itself.Twocommontypesofpassiveattackscanoccurinacellularnetwork:eavesdroppingandtrafficanalysis.Passiveattacksareintendedtoviolatedataconfidentialityand
Figure2.1 Attacksin5Gwirelessnetworks(a)eavesdropping,(b)jamming,(c)DDoS,and(d)MITM.
userprivacy.Unlikepassiveattacks,activeattackscanincludedatamodificationorinterruptionoflegitimatecommunications.Typicalactiveattacksareman-in-the-middleattacks (MITM),denial-of-service(DoS)attacks,anddistributeddenial-of-service(DDoS)attacks. Figure2.1illustratesbothpassiveandactiveattacksin5Gwirelessnetworks,eachofwhich isintroducedinthreekeyaspects:thetypeofattack(passiveoractive),thesecurityservicesimplementedtomitigatetheattack,andthecorrespondingmethodsutilizedtoavoid orpreventtheattack.
● Eavesdropping:Eavesdroppingisapassiveattackthatcanbelaunchedbyanunintended receivertointerceptamessagefromothers.Eavesdroppingdoesnotaffectnormal communication,asshowninFigure2.1a.Duetoitspassivenature,eavesdropping ishardtobedetected.Confidentialityisthesecurityserviceappliedtoprotectcommunicationfromthisattack.Encryptionofthesignalsovertheradiolinkisthemost commonmethodusedtomitigatetheeavesdroppingattack.Theeavesdroppercould notinterceptthereceivedsignaldirectlysincethedataisencrypted.Theencryption methodheavilydependsonthestrengthoftheencryptionalgorithm,thelengthof theencryptionkey,andthecomputingcapabilityoftheeavesdropper.Ascomputing powercontinuestorapidlyadvanceandadvanceddataanalysistechnologiesbecome increasinglyprevalent,eavesdropperscanexploitthesenewcapabilitiestolaunch theirattacks.Theeavesdroppingattackmodelsin5Garedistinctfromthoseinlegacy systems,primarilyduetothelimitedcomputingcapabilitiesoftheeavesdroppers inlegacysystem.Traditionalmechanismsdesignedtocombateavesdroppingare facingsignificantchallenges,asmanyofthemarepredicatedontheassumption
ofasmallnumberofsimultaneouseavesdropperswithlowcomputinganddata analysiscapabilities.Furthermore,advancedtechnologiessuchasHetNetdeployed in5Gwirelessnetworksmayexacerbatethedifficultyofthwartingeavesdropping attacks.
● Trafficanalysis:Trafficanalysisisatypeofpassiveattackwhereanunauthorizedrecipientinterceptsinformationbyanalyzingthetrafficofareceivedsignal,withoutdecipheringthecontentofthecommunication.Theinterceptedinformationcanincludedetails suchasthelocationandidentityofthecommunicationparties,andcanbeusedtodeduce sensitiveinformationaboutthecommunication.Evenifthesignalisencrypted,traffic analysiscanstillbeutilizedtorevealthepatternsofcommunicationparties.Trafficanalysisattackdoesnotimpactlegitimatecommunicationseither.Privacyprotectionisneeded againsttrafficanalysis.Currently,thereisasignificantamountofresearchfocusedon counteringtrafficanalysisattacks,suchasintroducingartificialnoisetodisrupttraffic patternsandpreventtheinterceptionofsensitiveinformation.
● Jamming:Unlikeeavesdroppingandtrafficanalysis,jammingcancompletelydisrupt communicationbetweenlegitimateusers.Figure2.1bisanexampleofthejamming attack.Themaliciousnodecangenerateintentionalinterferencethatcandisruptthe datacommunicationsbetweenlegitimateusers.Jammingcanalsopreventauthorized usersfromaccessingradioresources.Availabilityisasecurityserviceaimedatmitigating theimpactofjammingattacks.
● DoSandDDoS:DoSattacks,whichaimtoexhaustnetworkresources,areaviolationof networkavailabilityandcanbelaunchedbyadversaries.Jammingcanbeemployedas ameansofcarryingoutaDoSattack.Inthecasewheremultipledistributedadversaries areinvolved,aDDoSattackcanbeformed,asshowninFigure2.1c.Theseactiveattacks canoccuratdifferentnetworklayers,anddetectionmechanismsarecurrentlyemployed toidentifyandrecognizeDoSandDDoSattacks.
● MITM:InMITMattack,theattackersecretlytakescontrolofthecommunicationchannel betweentwolegitimateparties.TheMITMattackercanintercept,modify,andreplacethe communicationmessagesbetweenthetwolegitimateparties.Figure2.1dshowsaMITM attackmodel.MITMisanactiveattackthatcanbelaunchedindifferentlayers.Inparticular,MITMattacksaimtocompromisedataconfidentiality,integrity,andavailability. BasedonVerizon’sdatainvestigationreport[Bakeretal.,2011],MITMattackisoneof themostcommonsecurityattacks.Inalegacycellularnetwork,afalsebasestation-based MITMattackoccurswhenanattackercreatesafakebasetransceiverstationtointercept andmanipulatecommunicationsbetweenalegitimateuserandtheintendeddestination,resultinginacompromisedconnection[Contietal.,2016].Mutualauthentication betweenthemobiledeviceandthebasestationistypicallyusedtopreventfalsebase station-basedMITM.
2.2.2SecurityServices
Theemergenceof5Gwirelessnetworks,withtheirnovelarchitecture,technologies,and usecases,introducesnewsecuritychallengesanddemandsforsecurityservices.Thissubsectionintroducesfourtypesofsecurityservicesin5Gwirelesssystems:authentication
2SecurityfromLegacyWirelessSystemsto5GNetworks (entityauthentication,messageauthentication),confidentiality(dataconfidentiality,privacy),availability,andintegrity.
2.2.2.1Authentication
Entityauthenticationandmessageauthenticationarethetwotypesofauthentications. Totacklethepreviouslydiscussedattacks,entityauthenticationandmessageauthenticationareessentialin5Gwirelessnetworks.Entityauthenticationisusedtoensurethe communicatingentityistheonethatitclaimstobe.Inlegacycellularnetworks,mutual authenticationbetweenUEandMMEisimplementedbeforethetwopartiescommunicate.ThemutualauthenticationbetweenUEandMMEisthemostcriticalsecurityfeature inthetraditionalcellularsecurityframework.TheAKAin4GLTEcellularnetworksis symmetric-keybased.However,5GrequiresauthenticationnotonlybetweenUEandMME butalsobetweenotherthirdparties,suchasserviceproviders.Giventhedistincttrust modelof5Gnetworkscomparedtotraditionalcellularnetworks,ahybridandadaptable approachtoauthenticationmanagementbecomesnecessary.HybridandflexibleauthenticationofUEcanbeimplementedinthreedifferentways:authenticationbythenetwork only,authenticationbytheserviceprovideronly,andauthenticationbybothnetworkand serviceprovider[Huawei,2015].Duetotheveryhigh-speeddatarateandextremelylow latencyrequirementin5Gwirelessnetworks,authenticationin5Gisexpectedtobemuch fasterthanever.Moreover,themulti-tierarchitectureofthe5Gmayencounterveryfrequenthandoversandauthenticationsbetweendifferenttiersin5G.InDuanandWang [2016],toovercomethedifficultiesofkeymanagementinHetNetsandtoreducetheunnecessarylatencycausedbyfrequenthandovers,andauthenticationsbetweendifferenttiers, ansoftware-definednetworking(SDN)-enabledfastauthenticationschemeusingweighted secure-context-informationtransferisproposedtoimprovetheefficiencyofauthentication duringhandoversandtomeet5Glatencyrequirement.Apublic-key-basedAKAmechanismisproposedinEizaetal.[2016]andZhangetal.[2017a]asameansofenhancing securityservicesin5Gwirelessnetworks.
Messageauthenticationhasbecomeincreasinglyimportantwiththevariousnew applicationsin5Gwirelessnetworks.Moreover,messageauthenticationisfacingnew challengeswiththemorestrictrequirementsonlatency,spectrumefficiency(SE),and energyefficiency(EE)in5G.InDubrovaetal.[2015]anefficientCyclicRedundancy Check(CRC)-basedmessageauthenticationfor5Gisproposedasameansofdetecting bothrandomandmaliciouserrors,withouttheneedforincreasedbandwidth.
2.2.2.2Confidentiality
Confidentialityencompassestwodistinctdimensions,namely,dataconfidentialityandprivacy.Dataconfidentialityprotectsdatatransmissionfrompassiveattacksbylimitingthe dataaccesstointendedusersonlyandpreventingaccessfromordisclosuretounauthorized users.Privacysafeguardslegitimateusersagainstcontrolormanipulationoftheirinformation.Forexample,privacyprotectstrafficflowsfromanyanalysisofanattacker.Traffic patternsin5Gnetworkscanpotentiallyrevealsensitiveinformation,suchasthelocation ofsendersorreceivers.Witharangeofapplicationsin5G,includingvehicleroutingand healthmonitoring,userprivacycanbecompromisedbyvastamountsofdatagenerated.