HUAXU WANG
Major in Environmental Design, Jiangnan University
Application number: 23154191
Email: huaxuwang2001@outlook.com
Tel: +86 19850155919
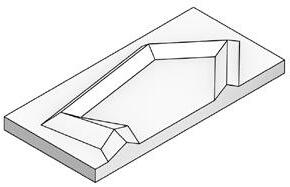
01 02 03 04 RESHAPE THE AXIS HEAL THE WOUNDS SOUNDPROOF, CONNECT, SETTLE UNSAID HISTORY
Wetland Planning, Yancheng, China Noise reduction habitat design, Chengdu, China
Plaza Design, Nanjing,
Historic Site Renewal Design, Athens,
PORTFOLIO
Purification
City
China
Greece
05 CATBLOCK CAFE
Applying for MLA Landscape Architecture, University College London
Interior design, Wuxi, China
HEAL THE WOUNDS
Purification Wetland Planning
Individual work
Duration: 05/2022-06/2022
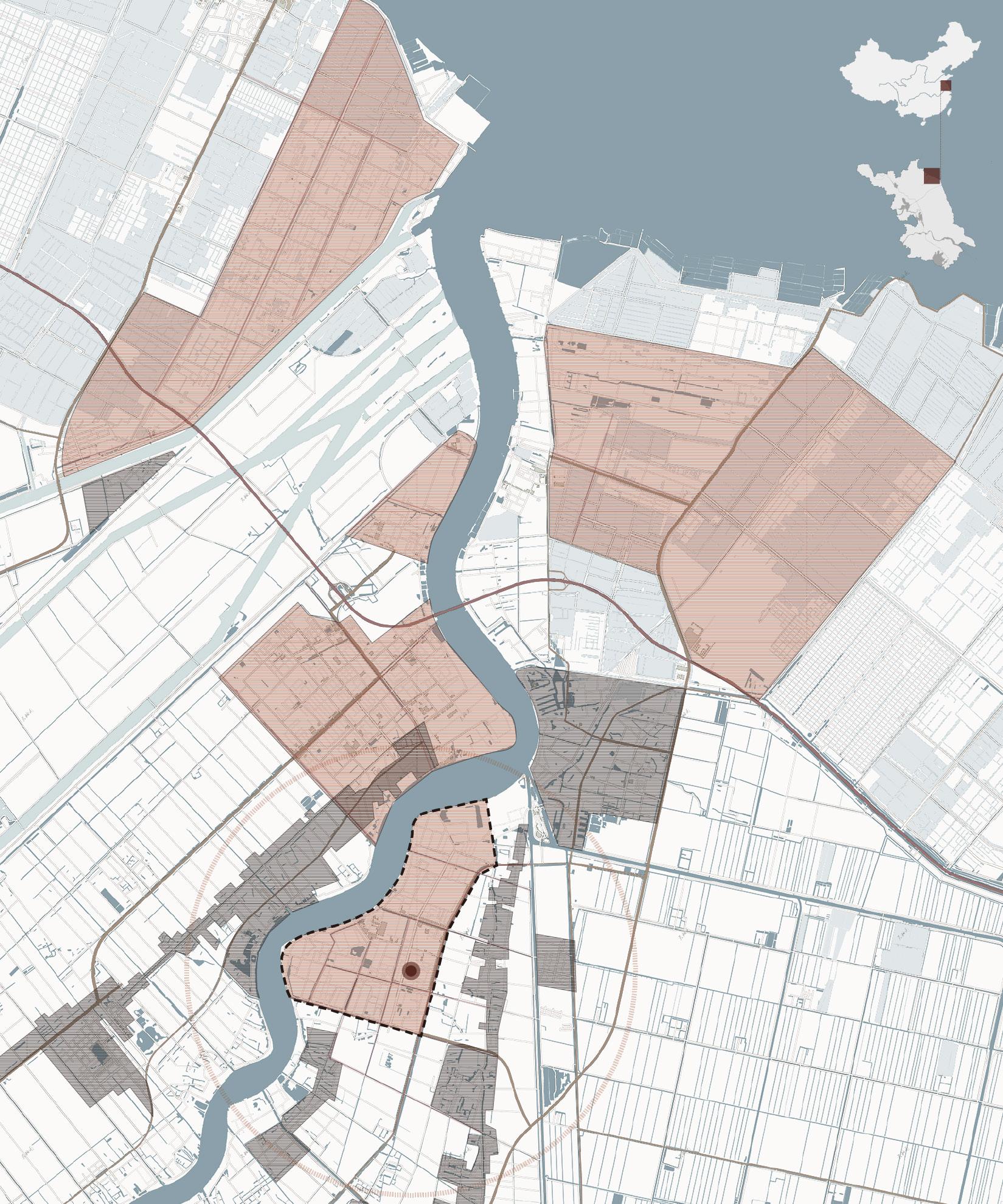
Site location: Yancheng, China
Area: 4 km²

Instructor: Liu Jia
The design tries to heal the wounds of the chemical park - severe water pollution and explosion accidents. Through the addition and arrangement of sewage plants, the design of protective belts and wetlands, and the adjustment of the layout of towns, farmland, and industrial areas; in order to achieve sustainable development of the local environment and economy, and to achieve the purpose of education and warning.
INDUSTRIALIZATION OF THE SITE

Excellent natural environment
Start of industrialization
Xiangshui Chenjiagang port Industrial Zone was established
INDUSTRIAL DISTRIBUTION ALONG GUAN RIVER
Xiangshui County is located in the northernmost part of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration in China, bordering the Yellow Sea in the east. The Guanhe River in the north of the county has a wide channel, a large flow rate, and convenient navigation. The chemical industry zone is distributed along the river and is large in scale, close to towns and agricultural areas.
Red-crowned cranes

Factory Emissions
Hazardous chemical wastes are landfilled, water pollution is serious, chlorine gas leaks from the plant.
False killer whales

Water pollution

The surface water next to the industrial zone is poor category 5 and no longer suitable for fish.
Illegal emissions from chemical plants
Huge casualty losses
The explosion killed 47 people, buildings were damaged and Chemical combustion caused the fire.

Air pollution
Carcinogenic pollutants in water
Explosion accident
On March 21, 2019 at 14:48 , a chemical plant in Chenjiagang Industrial Park exploded


Sewage pollution, Soil pollution
Serious pollution and ecological damage
Chemical leaks caused severe environmental contamination
01
C6H6 CH2Cl2
Farmland Salt field Residential area Water Irrigation Canal Industrial area Main Roads Explosion site C2H4Cl2 CHCl₃
Site boundary
2010 2005 2019 2002
China Jiangsu province
SITE
Yellow sea Duigou Industrial Park Port Industry Park Industry Park Chenjiagang Town Duigou Town Guan River Chengjiagang Industrial Park
WOUNDS OF INDUSTRY: WATER POLLUTION A NEW PLANNING SCENARIO

Long-term industrial management in Xiangshui County is not standardized, resulting in serious environmental pollution, which is the root cause of the explosion accident. The design intervenes from sewage treatment to seek strategies for local sustainable development.

Problems


Sewage Discharge



Hazards
Objectives
Polluted rivers Contaminated soil Contaminated undergroundwater Agro-industrial






Strategy
Damage to agriculture


Loss of wetlands and habitat Health problems
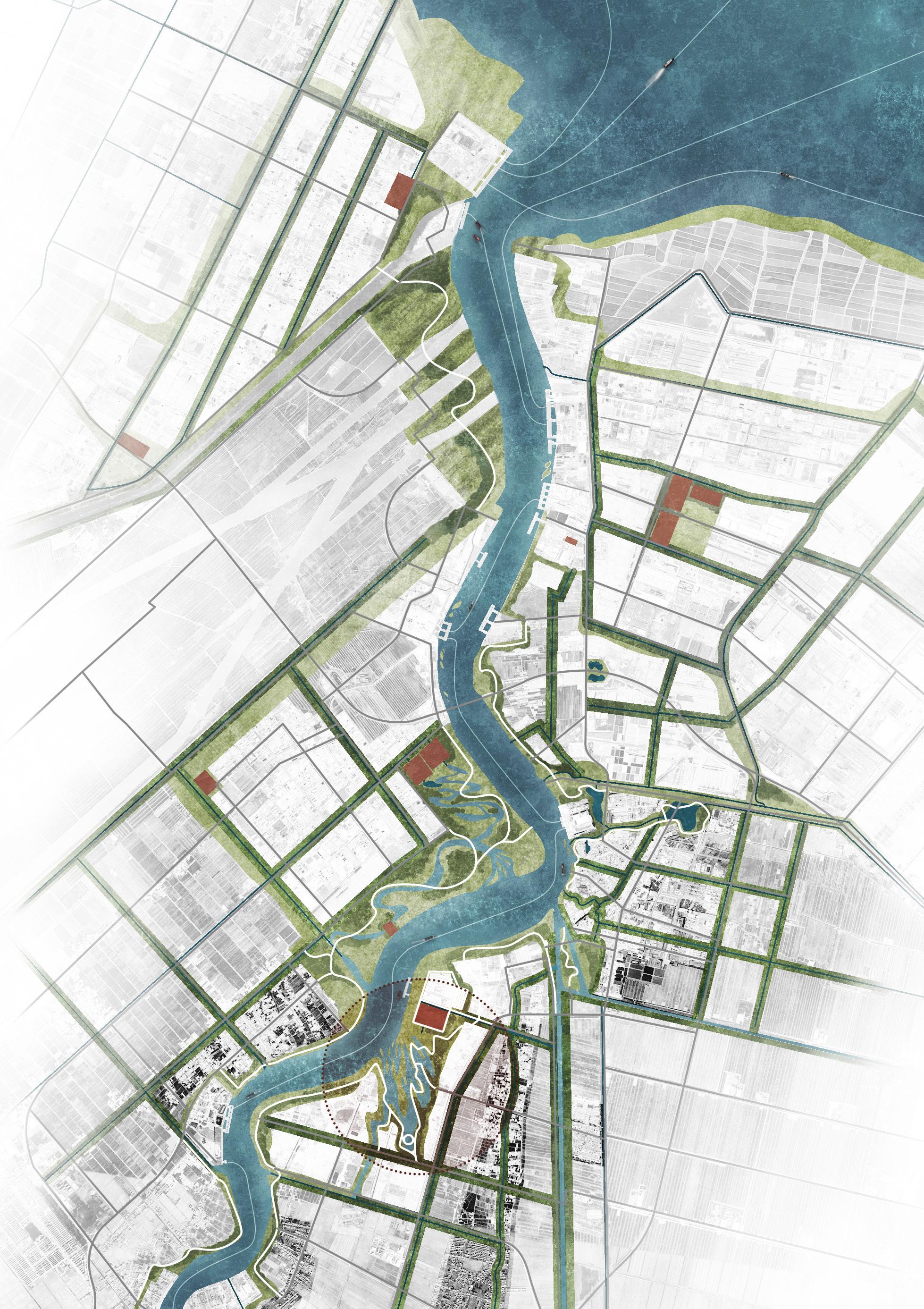
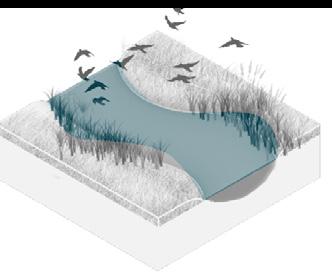 The project re-planned the Guan River watershed and adjusted the layout of urban farmland and industrial areas; installed wastewater treatment plants in each industrial park and designed purification wetlands downstream of the wastewater treatment plants.
The project re-planned the Guan River watershed and adjusted the layout of urban farmland and industrial areas; installed wastewater treatment plants in each industrial park and designed purification wetlands downstream of the wastewater treatment plants.
Domestic sewage
ecological habitats clean water for
awareness awaken
Agricultural wastewater Chemical wastewater
production system New
domestic use Environmental
Wise
planning of agriculture Natural purification wetlands Education and Warning
Sewage Treatment
Illegal
Farmland Residential area Industrial area Port Sewage plant Water wetlands Green belt Pedestrian route Main Roads Explosion site Yellow
pipeline discharge Direct sewage discharge
sea
Port
Duigou Industrial Park
Industry Park
Industry Park
Chenjiagang Town
Sigang Village
Duigou Town
Guan River
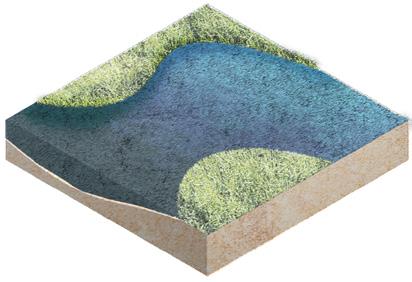
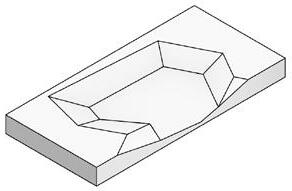
SEWAGE PURIFICATION WETLAND DESIGN Morphology and Fuction

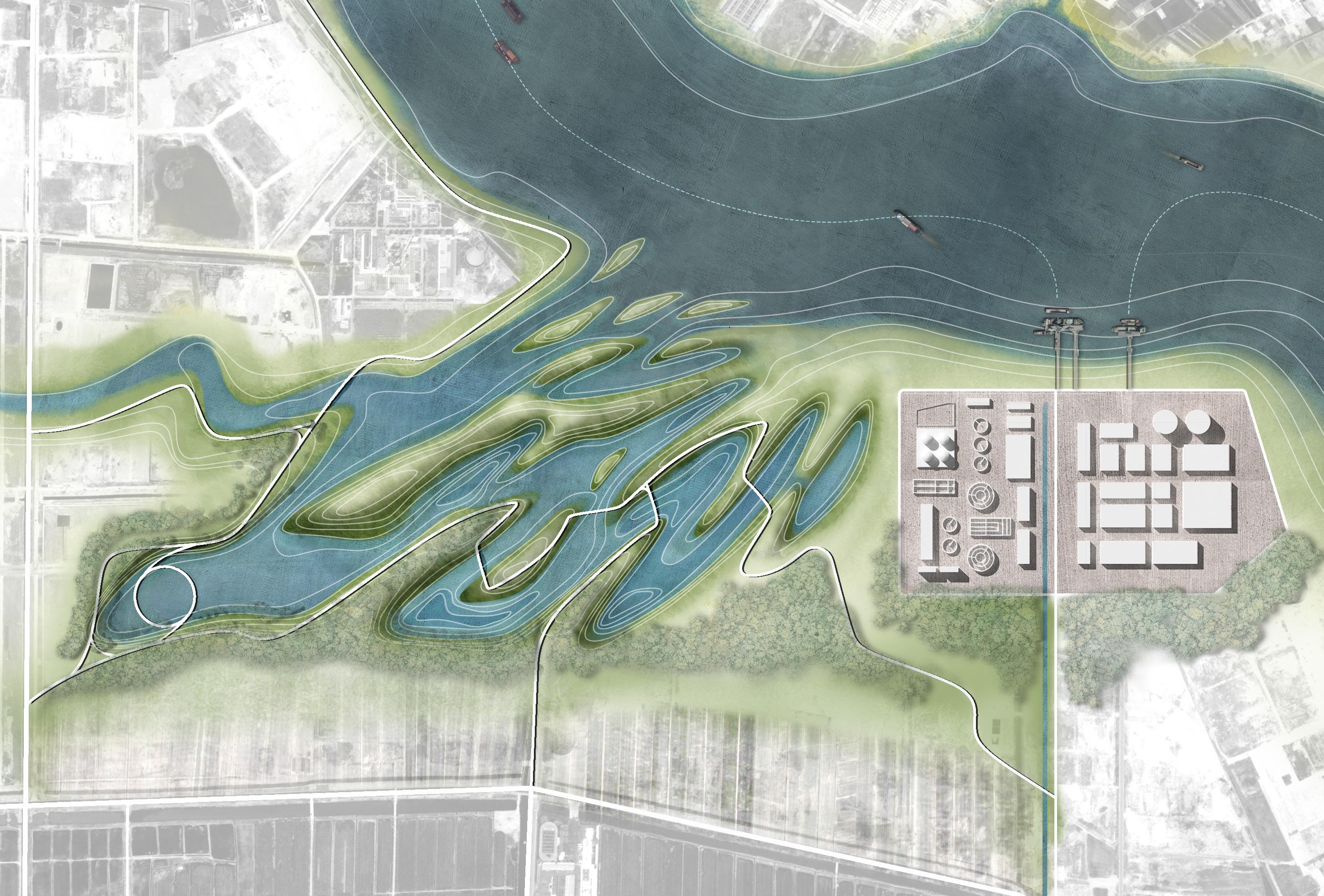
① Sewage plant
② Chemical plant
③ Sedimentation tank
④ Flow suppression inlet
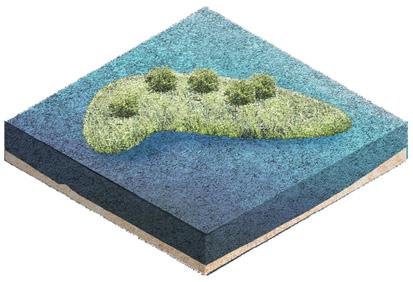
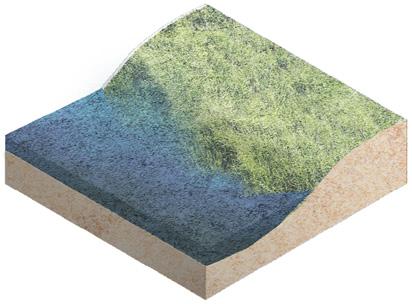
⑤ Surface flow wetland

⑥ Submerged flow wetland
⑦ Retention pond
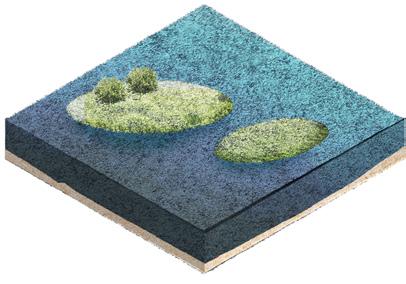
⑧ Open Water Area
⑨ Islands
⑩ Memorial spot
⑪ Beach Meadow
⑫ Ship port
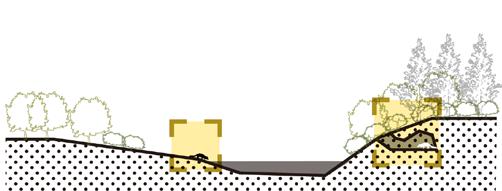
The wetland design starts from the process of natural purification of sewage and designs the landscape topography. The wastewater first flows out of the sewage treatment plant, enters a sedimentation tank for settling, filters through the flow suppression inlet, and then flows through surface flow wetlands and submerged wetlands, where it is purified by plants and soil. After that, it flows the monumental landscape of open water, and finally diverts through ecological islands to merge into the Guan river.
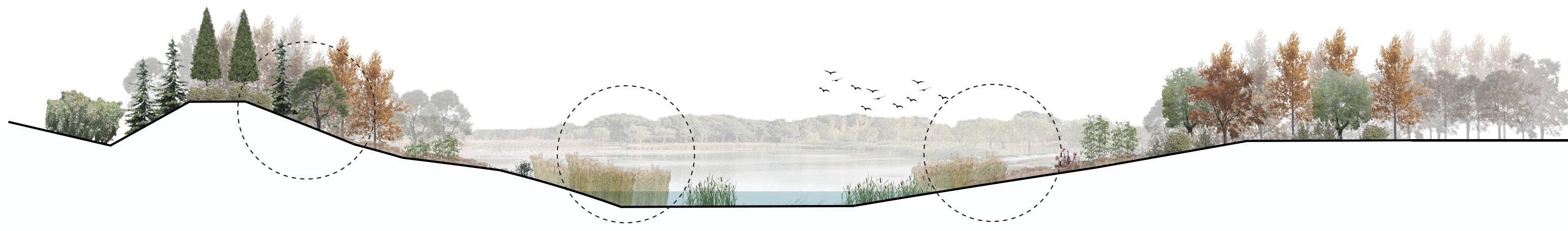
Section A-A'

Marsh Marsh Surface flow wetland
Open Water Area
Submerged flow wetland Retention pond
Flow
A A'
① ② ③ ④ ④ ④ ⑤ ⑦ ⑦ ⑨ ⑧ ⑩ ⑪ ⑫ ⑪ ⑥
Sedimentation tank
suppression inlet Islands
Water flow Form Functional wetlands Activity route 0 N 100 200 500M Sewage Treatment Original industry site Original sewage plant Explosion site Sewage treatment wetlands Memorial Ecological habitats Memorial and Warning Education
WETLAND NODE ANALYSIS PLANTING STRATEGY
Metasequoia glyptostroboides

Height: 35m
Wetland Index: FACU
Arundo donax

Height: 6m
Wetland Index: OBL
Phragmites australis




Stage1: Tank
Contains wastewater, reduces sediment, disperses stormwater








Stage2 : Wetland
Decontaminate, divert water flow, increase the flow time
Stage3 : Open Water Area
Stage 0
Sewage
Reduce flood peaks, improve water quality, wildlife sanctuary
Stage 1
Tank
Canna indica

Height: 1.5m
Wetland Index: FACW
Iris pseudacorus
Height: 0.6-0.7m
Wetland Index: OBL
Height: 1-3m
Wetland Index: OBL
Oenanthe javanica
Height: 0.15-0.8m
Wetland Index: OBL
Flow suppression inlet
Pinus elliottii

Height: 30m
Wetland Index: FACU
Cinnamomum camphora
Height: 30m
Wetland Index: FACU
Lythrum salicaria

Height: 0.3-1m
Wetland Index: OBL
Nelumbo nucifera
Height: 1-1.5m
Wetland Index: OBL
Nymphaea tetragona

Height: floating plant
Wetland Index: OBL
Trapa
Height: floating plant
Wetland Index: OBL
Marsh Floating wetland
Surface flow wetland Submerged flow wetland
Sedimentation tank Retention pond Island Memorial spot
Stage 2 Wetland
Salix babylonica

Height: 12-18m
Wetland Index: FAC
Ligustrum lucidum





Height: 25m
Wetland Index: FACU
Coix lacryma-jobi
Height: 1-2m
Wetland Index: OBL
Iris germanica

Height: 0.6-1m
Wetland Index: OBL
Pontederia cordata
Height: 0.2-0.8m
Wetland Index: OBL
Nymphoides peltata

Height: floating plant
Wetland Index: OBL
Stage 3
Open Water Area
NEW ECOLOGICAL HABITATS

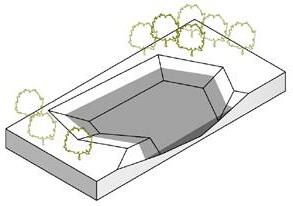
The new wetlands cleanse the effluent through the topography and also provide a diverse habitat for native flora and fauna. People visiting the wetlands can visualize the purifying power of nature and appreciate the beauty of life.
ENVIRONMENTAL AWARENESS AWAKEN
Signage
The chemical explosion created a circular crater 80m in diameter from which a large amount of contaminants leaked, deeply scarring nature. The design uses a circular walkway to enclose the original site of the explosion and a wedge-shaped monument to point to the center of the explosion. While being healed by the beautiful wetlands, the importance of controlling industrial pollution is remembered.
Memorial to the explosion made of concrete, wedge-shaped, point to the explosion site
 Round shallow pool
concrete pile
stainless steel grating pavement reinforced foundations
Stainless steel path
made of concrete, describtion of the accident
Wetland deep water
Black-capped Kingfisher protected wild animal
Metasequoia glyptostroboides remove TP, COD chemicals
Chinese sucker
Reed birds' nest Shrimp
Little Yellow Croaker
Surface flow wetland
Whooper Swan protected wild animal
Baer's Pochard protected wild animal
Red-crowned Crane protected wild animal
Arundo donax remove COD chemicals
Wetland Trail
Submerged flow wetland
Eurasian River Otter protected wild animal
Helical pile
Batter anchor with turnbuckle assembly
helix
Round shallow pool
concrete pile
stainless steel grating pavement reinforced foundations
Stainless steel path
made of concrete, describtion of the accident
Wetland deep water
Black-capped Kingfisher protected wild animal
Metasequoia glyptostroboides remove TP, COD chemicals
Chinese sucker
Reed birds' nest Shrimp
Little Yellow Croaker
Surface flow wetland
Whooper Swan protected wild animal
Baer's Pochard protected wild animal
Red-crowned Crane protected wild animal
Arundo donax remove COD chemicals
Wetland Trail
Submerged flow wetland
Eurasian River Otter protected wild animal
Helical pile
Batter anchor with turnbuckle assembly
helix
SOUNDPROOF, CONNECT, SETTLE
Noise reduction habitat design
Individual work
Duration: 06/2022-11/2022
Site location: Chengdu, China
Area: 65 ha
Instructor: Zhou Lin
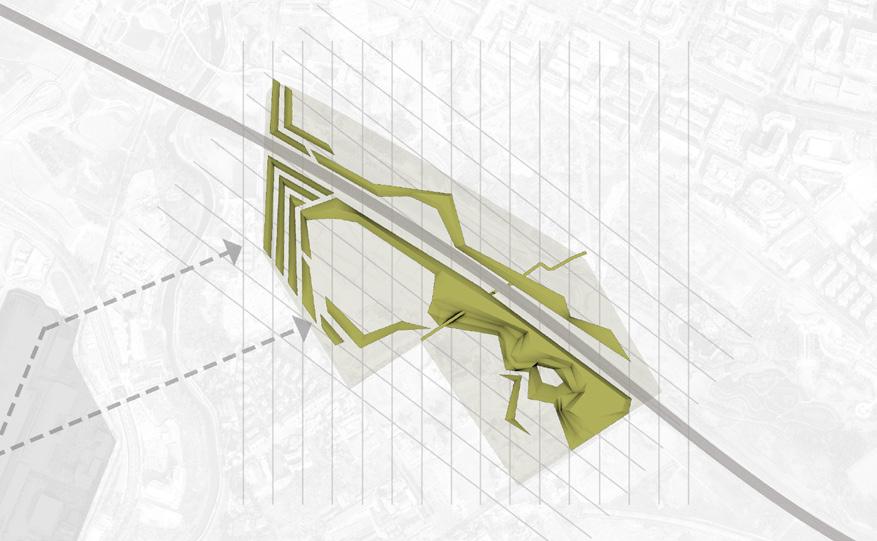
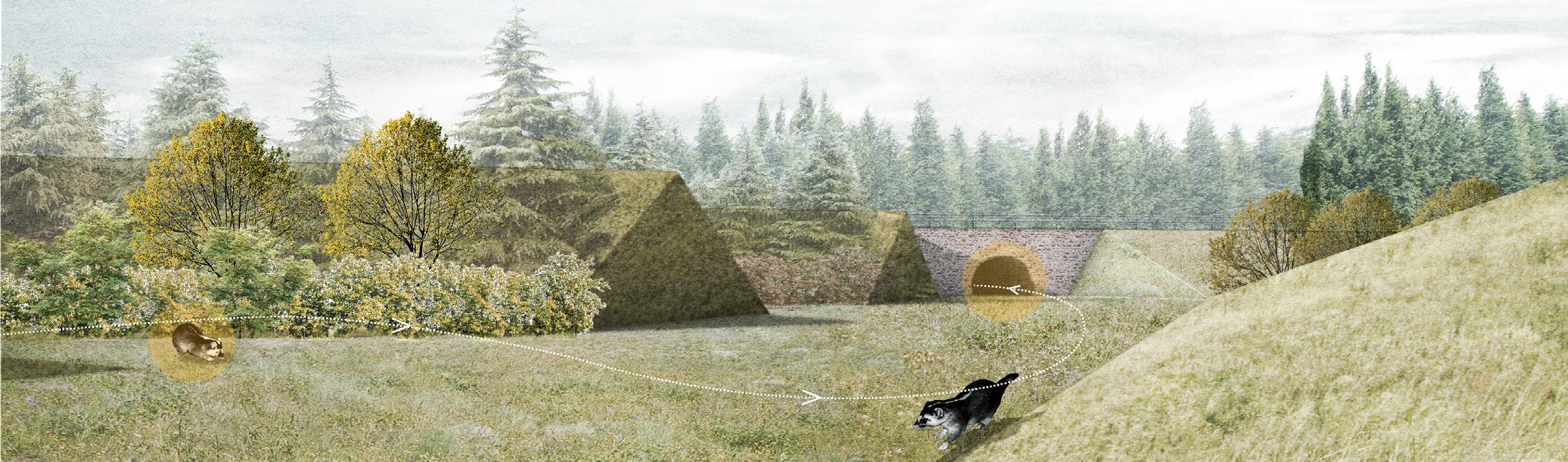
Based on the habits of Chinese ferret-badger, a native wild animal, the project uses topography and vegetation design to reduce the noise impact, connect the green space system cut off by the expressway, and create a habitat park.

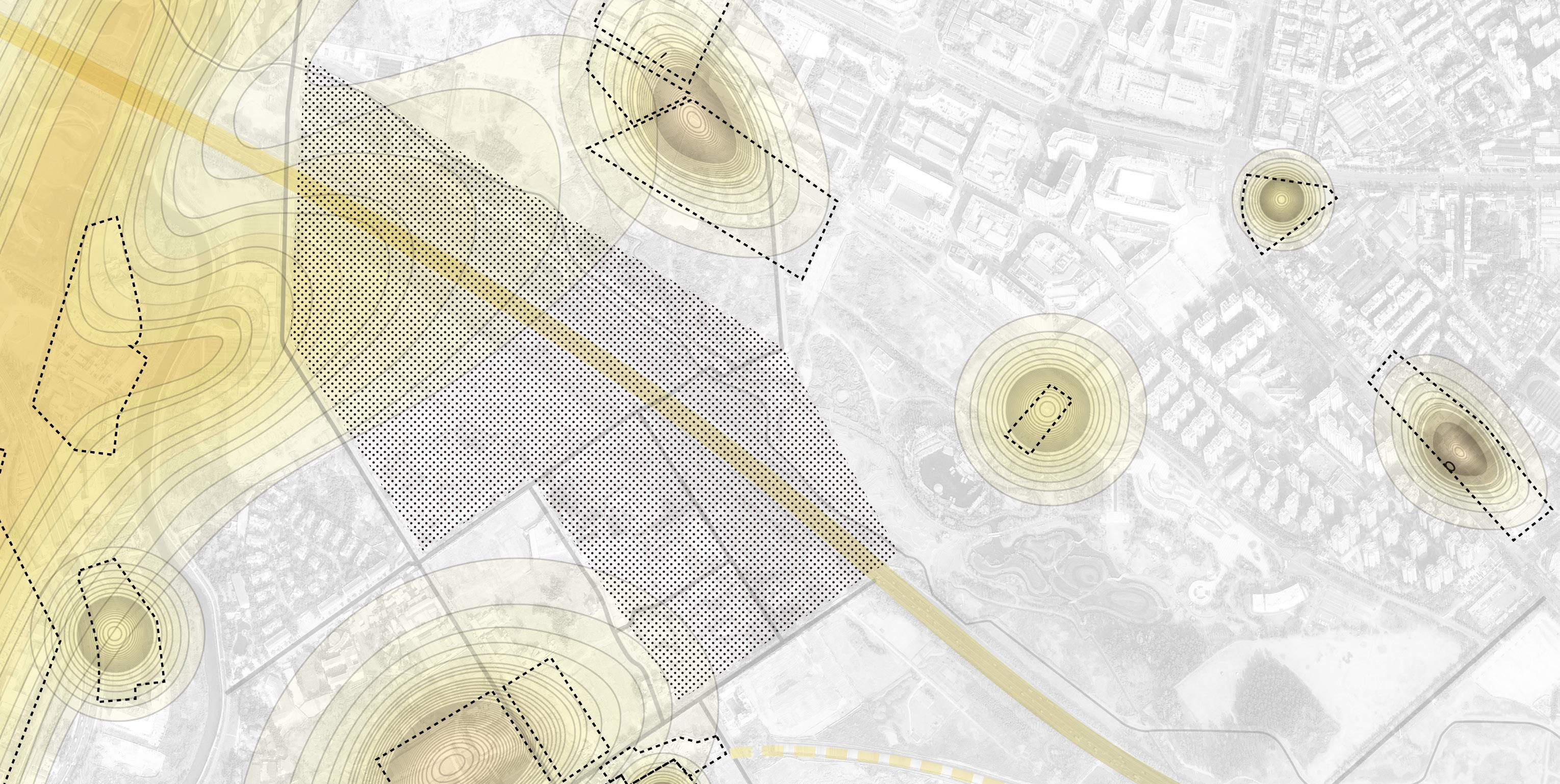
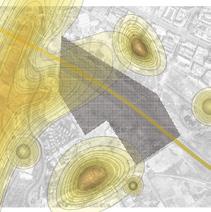
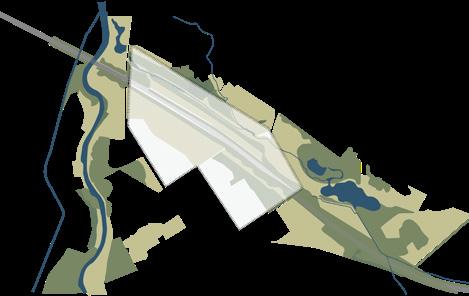
SITE ANALYSIS

The project is located next to the Chengdu Ring Expressway and the airport, which has serious noise pollution. Due to the construction of the greenway around the city, it offers the possibility to improve the habitat environment for local wildlife.
CITY GREENWAY AND NOISE CONDITION
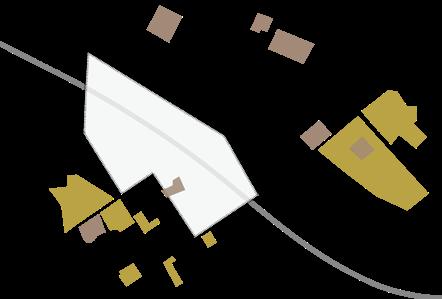
Potential umbrella species
Number of wildlives counted in 3 months
An area can support the stable life of two wild carnivorous mustelids, which means that this area has a relatively stable and complete food chain. Chinese ferret-badger is a representative urban wild animal, and protecting its habitat is beneficial to maintaining the stability of the urban ecology.

Melogale moschata
Mustela sibirica
Bambusicola thoracica
Chengdu cycling greenway and the site
Distribution of Melogale moschata in China
Diverse habitats in urban areas
THREATS AND STRATEGIES
Noise Strategy
Threats
● Noise interferes with badger's communication
● Hearing impairment, blurred vision and damage to organs
● Badgers abandon their habitats
Habitat Strategy

Threats
Zoothera dauma
● Blocked migrations
● Hit by car and killed
● Human interference
Schools and residential area Green spaces and habitats
Noise and highway threatens badgers' survival
The planes and cars are so noisy that my ears hurt
I want to have a safe and comfortable home without disturbance......
Help! my partner was knocked by a car!
ridges berms enclosure sink

airplane sound deflection
airplane noise buffer
road noise reflection
road noise barrier
noise reduction and absorption

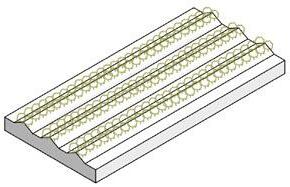
enclosure protection
noise reflection and absorption
wetland habitat
sound absorption green corridors
connect habitats nesting
green corridors foraging
foraging activity
Hit by car and killed Noise threat Separated habitats 70dB 20dB 30dB
02
merulacolchicusthoracica
sannio merulacolchicusthoracica Urocissa erythrorynchacolchicusthoracica 15 times 12 times 3 times 1 time 1 time 2 times 9 times 8 times
Phasianus colchicusthoracica Turdus
Garrulax
Cycling park Building site Qiming School Highway Parking lot Shuangliu Airport 80dB 80dB 70dB 70dB 70dB Design Site Noise Source Noise Range Highway
80dB Factory 0 200 400m 100
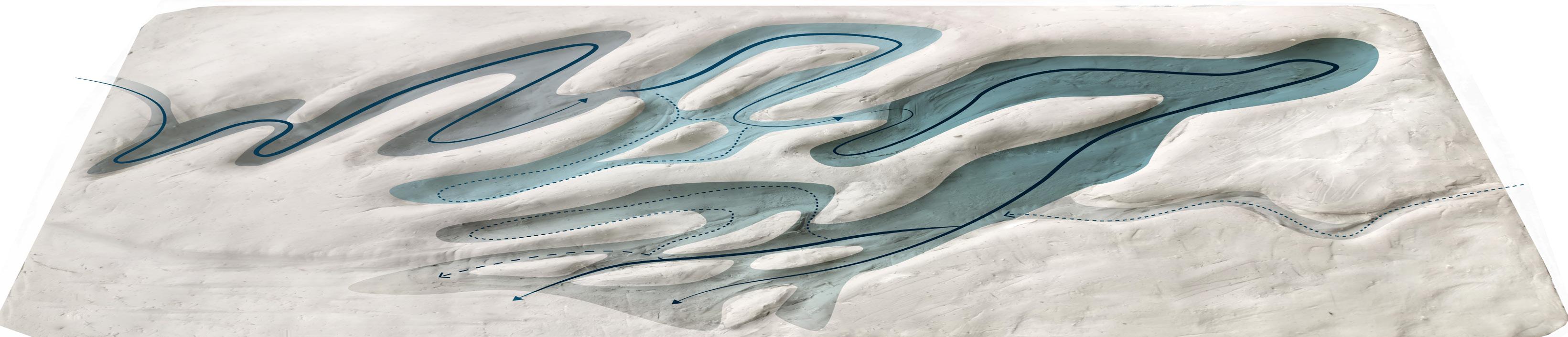
SOUND-GROUND DESIGN PROCESS
Landforms shaped from noise
Topography design




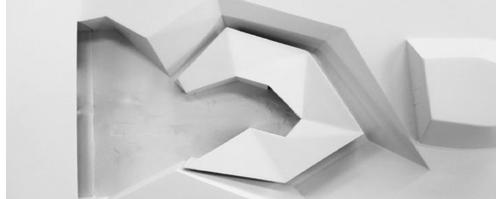
phase 1: ridges
phase 2: twist of ridges
phase 3: enclosure
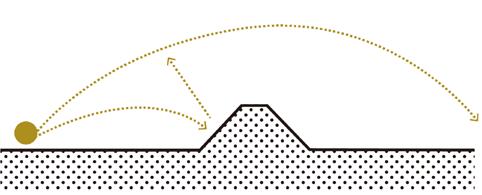
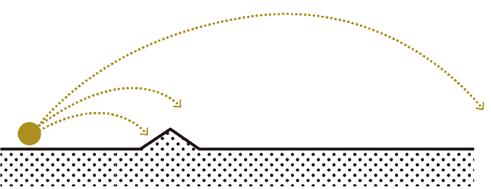
135°
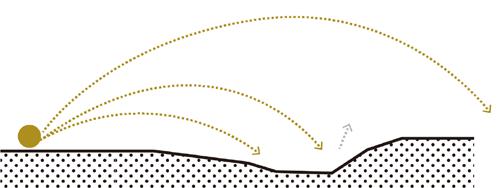
Step 1: the noise directions
Ground noise made by airplane moves in an angle of 135° and noise from the highway spreads to both sides of it.
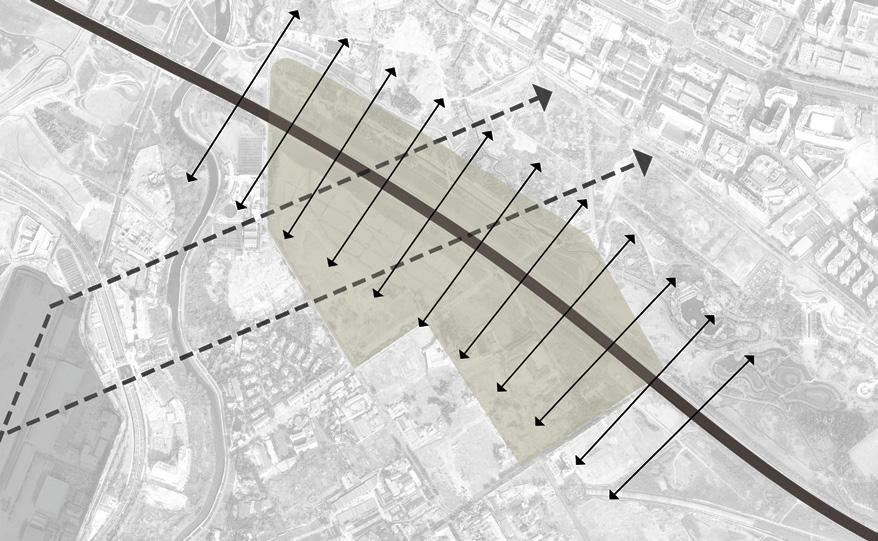
ridges to the direction of noise twisted berms

large size enclosure small size enclosure
combine different directions
berms along the road
open space
sink habitat

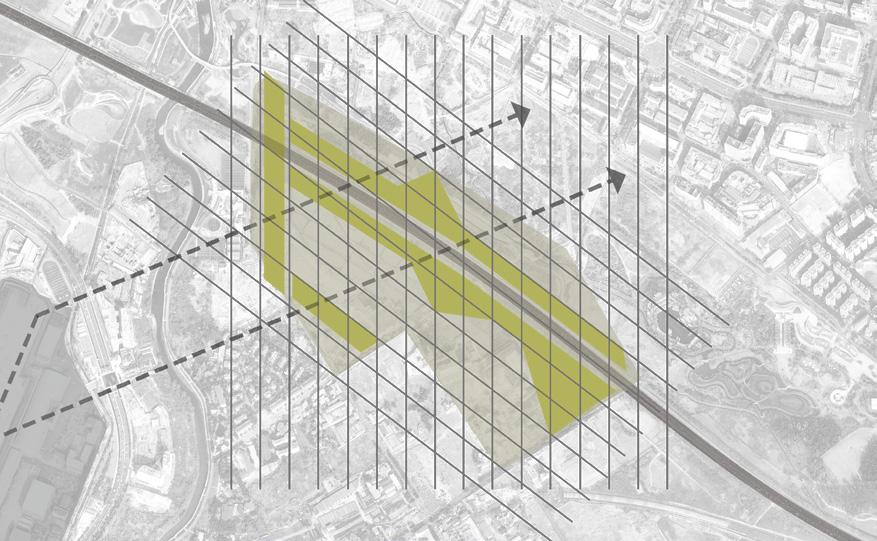
Step 2: frame to reduce the sound
Construct a grid system according to the direction of the noise to determine the position and shape of the noise buffer.





Step 3: ridges and slope to reduce the sound
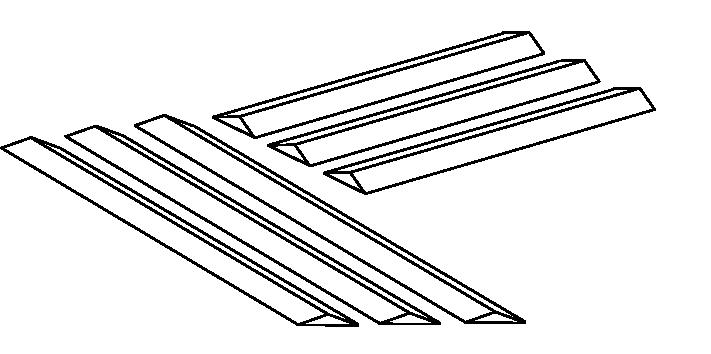
Various sheltered and open spaces are created by the grid, Increasing landform diversity.
ridges absorb and reflect low frequency of sound





berms and slope cut the loudness of traffic noise
provide farm area and food for Chinese ferret-badgers
provide water and shelter for Chinese ferret-badgers
original pattern extract forms apply forms to the site
low frequency sound buffer traffic noise barrier food resource field wetland habitat
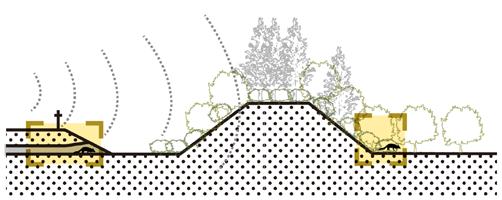
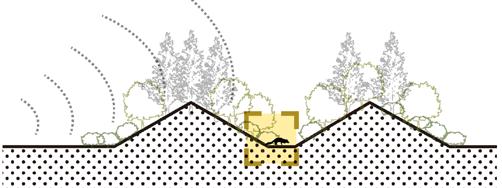
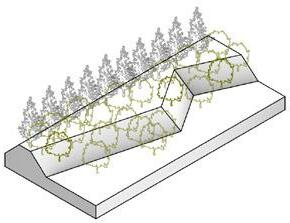
NOISE REDUCTION LANDSCAPE WITH HABITATS AND CORRIDORS
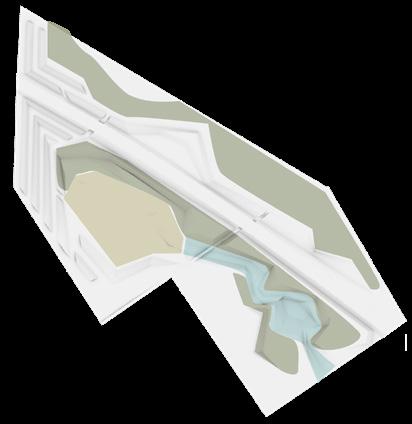

Low frequency sound buffer
Traffic noise barrier
Food resource field
Fruit trees
Open grassland
Underpass tunnel
Woodland
Wetland habitat
Pedestrian route
Bicycle trail
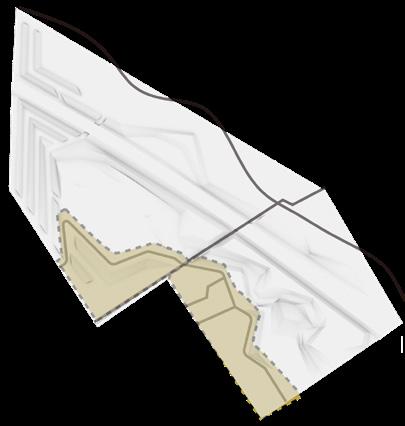
Connected Habitats
Badger Routes: 3.5 km added

Sound Buffer: 1.2 km² added
Habitats: 0.3 km² increased
Human area: 0.05 km²
0 100 200m 50 A A B B
1
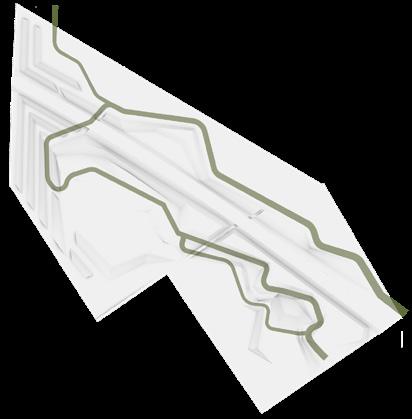
In the daytime, I rest in my burrow in the rock crevice. At dusk, I get out of my den and search for food along the river. I like eating fruit, insects and small Sometimes I go through the tunnel to look for companions.
This is my travel route. Don't get hit by car!
2 2 4 5 5 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 3
This is my forage route. Hide in the woods!
6 7 8 9 10
Badgers' corridor: Sound buffer, underpass
Traffic noise barrier and planting design reduce damage and disturbance to ferret badgers. Arbors, shrubs and grasslands serve as migration corridors for badgers to provide shelter, and fruit forests and fields provide food sources.
migrate corridor food sources
shaded corridor
road traffic noise barrier

Badgers' habitats: Slopes, woods, wetland

Gentle slope woodlands are suitable for badgers to make nests, and grasslands and shallow water are the areas where weasel badgers drink, prey and move.
PLANTS LIST
Metasequoia glyptostroboides
Ligustrum quihoui
Cedrus deodara Ginkgo biloba
Cinnamomum longipaniculatum
Sapindus saponaria
Linnaeus
Phragmites australis
Typha orientalis
Sagittaria trifolia
Prunus
Caulis Fici Tikouae
Medicago
Setaria viridis
drink forage nest
traffic noise
grasslands grasslands grove shallow water
barrier slope woods
field noise barrier berm slope woods wetland edible grass grove local fruit trees evergreen noise resistant trees
fruit trees food resource
DETAILDED PLANTING
0 6 12m 4 0 6 12m 4
The underpass tunnel is designed according to the size of the ferret badger. The topography and vegetation design act as ecological corridors to shelter its activities.
foraging by the water Nests in the woods
Section B
Section A
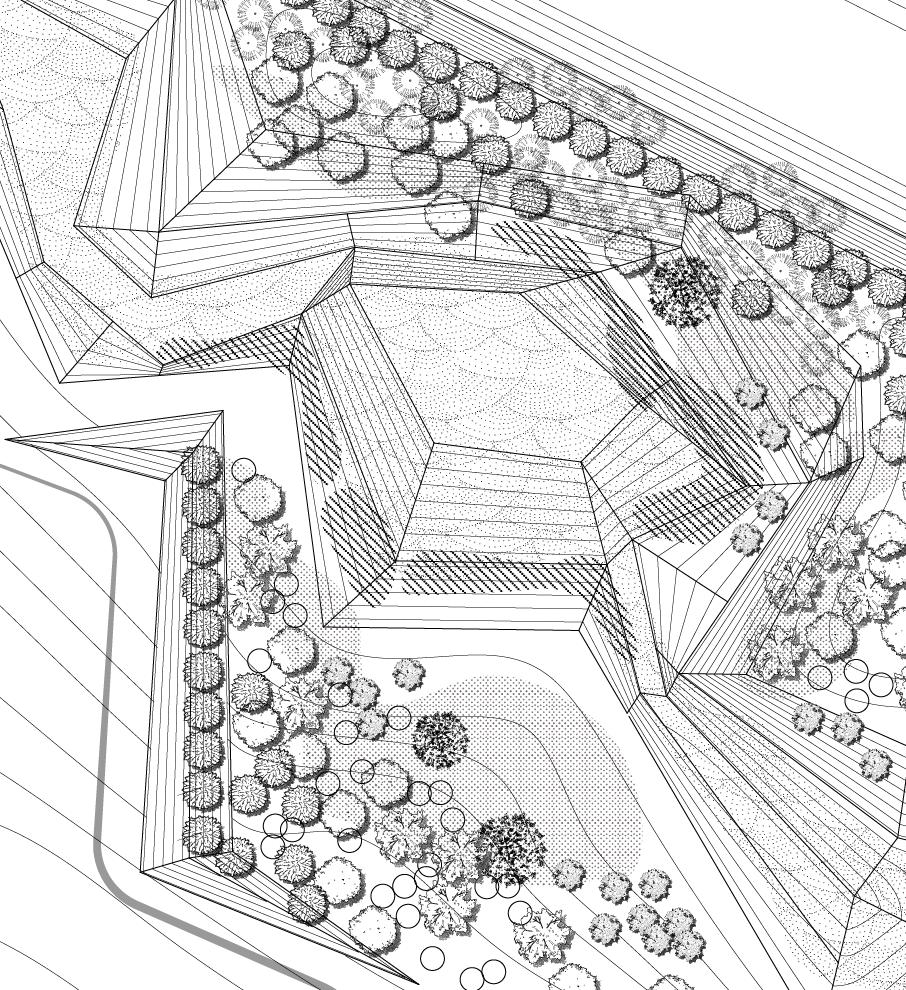
03 RESHAPE THE AXIS City Plaza Design
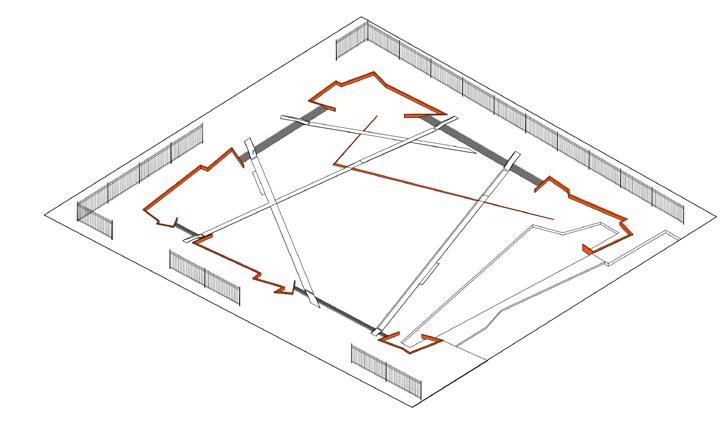
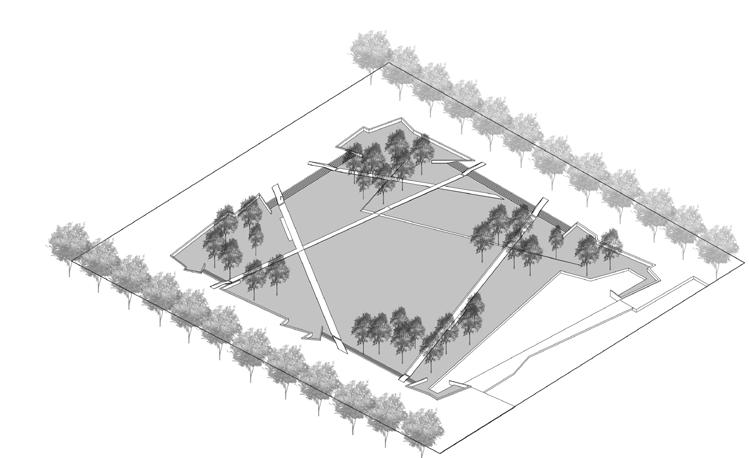
The design aims to "reshape the axis", using landscape topography and road pavement to create a rhythm of space, guide the spatial axis, and channel the traffic flow, in order to improve the chaotic site conditions and coordinate the conflict between the old and new buildings around.
Individual work
Duration: 03/2022-06/2022
Site location: Nanjing, China
Area: 6 ha
Instructor: Liu Jia
The clash of historic sites and modern architecture in the city center

The site is located in the middle of the old city of Nanjing with many historical sites. Due to urban development, the ancient buildings are surrounded by high-rise buildings and city arteries, and the appearance of the site is in a mess.
AIMS : REORDER THE SITE BY AXIS

Modern large volume buildings and wide road networks have broken the ancient city texture.From an urban perspective, the historic sites of Nanjing form a north-south axis; from the scale of the site, the Presidential Palace extends the north-south axis. The design will refer to this axis to shape a new space order.

N-S cultural axis
The site's new axis
Case study: Afrikaanderplein Plaza




The plaza divides the square site with axes, creating a new triangular spatial order, which is dynamic and streamlined for pedestrians.
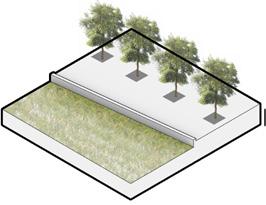
Strategy 1 wedges
Site Problems
The busy avenues, complicated city grid systems have created a strong sense of seperation, strong edges and boundaries hinder people from going in.





Bus line and station
Car lane
Heritage and tourists attraction
Use of wedges and retaining walls to create a sense of space
Strategy 2 roads
Highlight the axis by characteristic linear paving and benches.
Metro line and station
Broken public space
Circuitous tourist flow
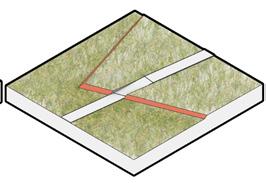
Strategy 3 trees
Rows of trees enclose the space, groves suggest the axis.
Axis
Xuanwu Lake
Jiming Temple
Presidential Palace
Xi'an Gate Xinjiekou
St.Paul's Church
Confucius Temple Tongji Gate
Beiji Temple
Gate of Presidential Palace, since 1870
Nanjing Library, built in 2006
Central Hotel, since 1927
Jiangsu Art Museum, built in 2008
Surrounding high-rise buildings
circulation inefficiency no hierarchy of constructions fragmentation of open space
1
PLAN VIEW Design Process
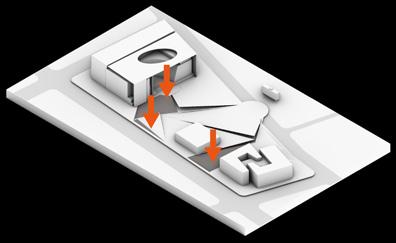
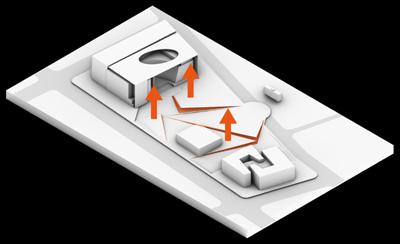
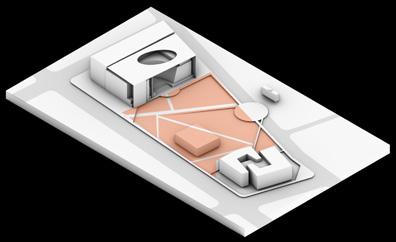
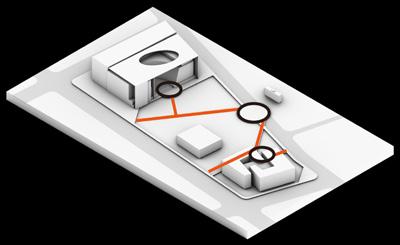
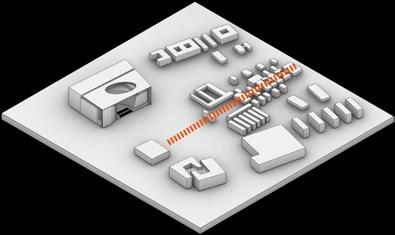
A. Park entrance
B. Subway entrance
C. Library square
D. Outdoor theater
E. Grassy slopes
F. Retaining wall
G. Water mirror
H. Benches
I. Gallery square
J. Grove
Strategies that emphasize the axis
Use bending retaining walls at the beginning and end of the axis, Set wedge-shaped retaining walls along the road
2 Linear elements
The trees planted in rows , the paving and benches directly guide the axis

3 Planting design
Trees planted in patches at both ends of the road suggest the axis, emphasizing the space at the beginning and end.

1 2
1'
2'
Vertical construction
1. Extend the north-south axis
2. Bifurcation of the axis
3. Axes guides the roads
4. Roads divide space
5. Sinking space
6. Lifting space
5 15 35m 0
A A A A C D E G F J H I B B
PROPOSED FINAL PERFORMANCE



The design reshaped the axial order of the site. The spatial axis is guided by landscape topography and road pavement, forming a clear and simple circulation network; the unified lawn and woods coordinate the conflicts between old and new buildings in the surrounding area, and carry various tourist activities.
The urban road passing underneath realizes the diversion of people and vehicles. The circular square echoes the curved enclosure of the Presidential Palace.
The Gallery square maintains a visual connection with the Presidential Palace, and at the same time provides space for gathering activities.
Central lawn, outdoor theatre, paths and shade trees provide spaces for rest and movement.



 Pedestrians follow the terrain uphill from the park entrance connected to the subway station, feeling the axis of the space.
Section 1-1'
Section 2-2'
Pedestrians follow the terrain uphill from the park entrance connected to the subway station, feeling the axis of the space.
Section 1-1'
Section 2-2'
5 15 35m 0
Kerameikos was the potters' quarter of the city, and was also the site of an important cemetery and numerous funerary sculptures erected along the Sacred Way.
04 UNSAID HISTORY
Historic Site Renewal Design

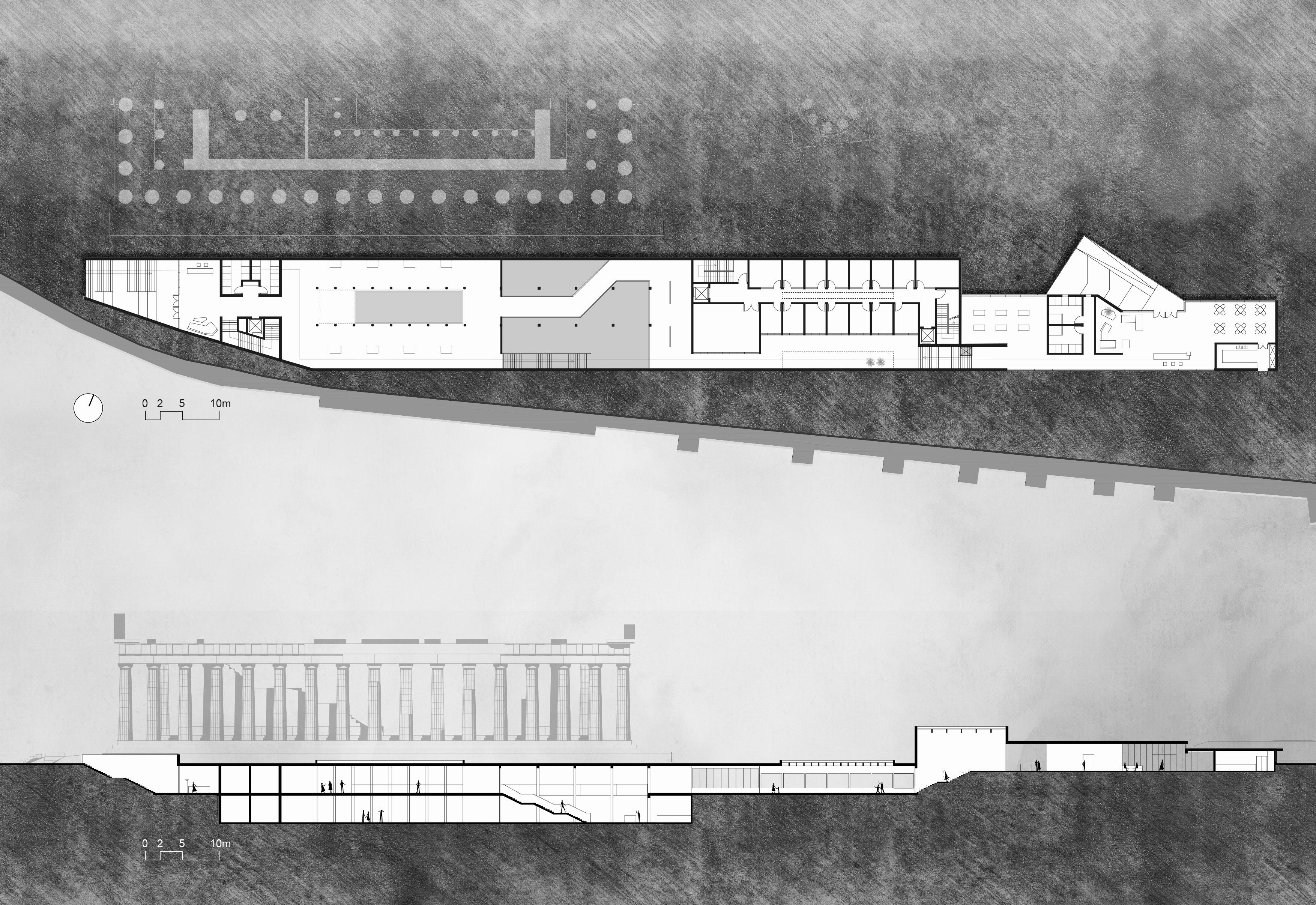
The Acropolis has a long history and has been built, destroyed and rebuilt many times since antiquity. Today we are able to enjoy our visit because of the diligent exploration and restoration by archaeologists since the recent past. Yet the archaeological process is like a silent story, attached to monuments and artifacts, unknown to the public. The project seeks to improve the Acropolis' infrastructure and landscape experience by incorporating a building that demonstrates the importance of archaeology to the Acropolis. The bulk of the building is located underground, while providing a visual connection to the site and offering visitors a new perspective on the Acropolis' history.

Archaeological sites Hills
ATHENS ARCHAEOLOGYCAL MAP
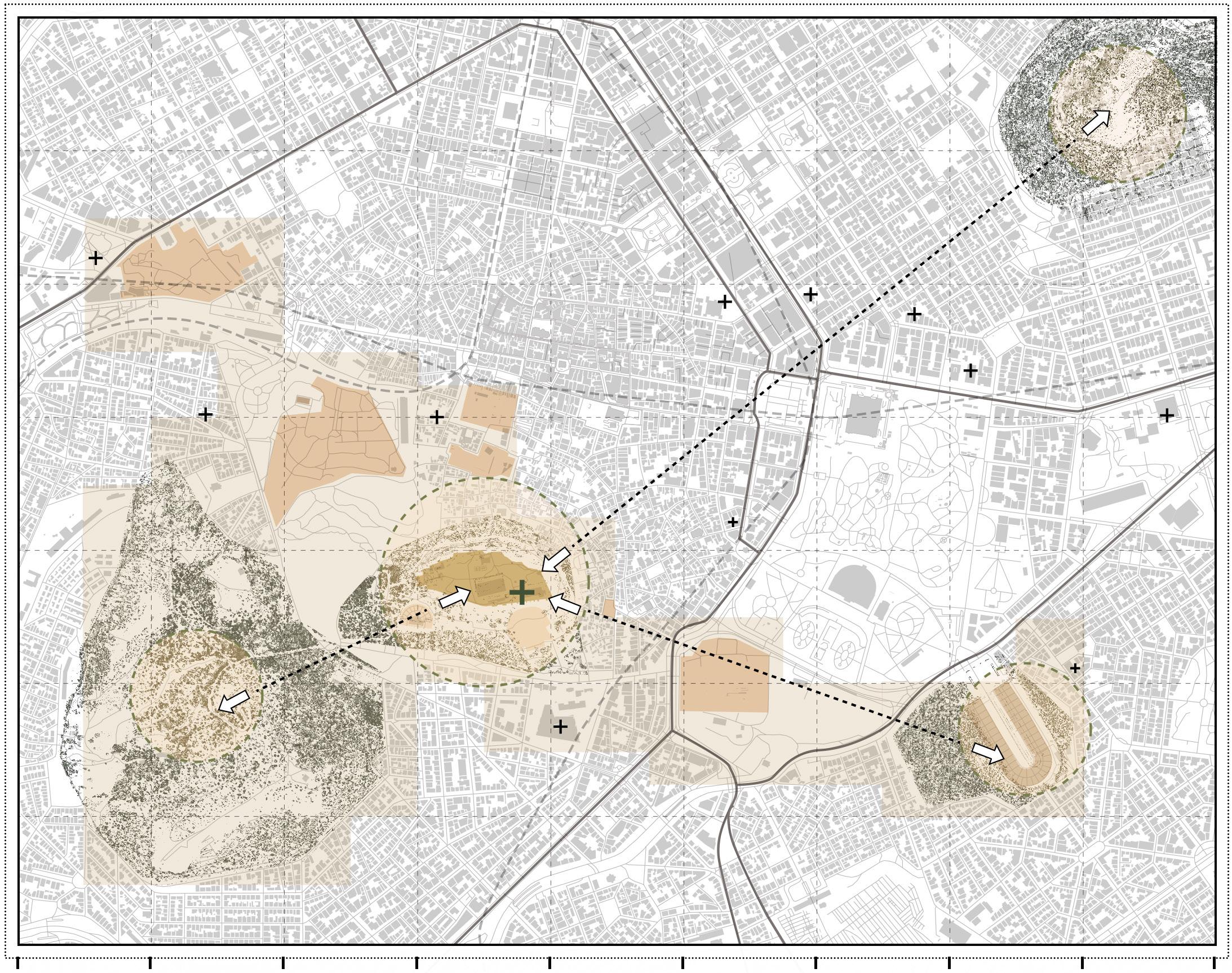
The surrounding area of the Acropolis is a world-renowned tourist attraction, where archaeological sites and museums gather. The site is on the hill of the Acropolis, not only has magnificent ancient Greek architectural relics, but also has a good landscape view.

Museums and galleries
Individual work
Duration: 10/202211/2022

Site location: Athens,Greece

Area: 2.7 ha
Instructor: Zhou Lin
The ancient Agora of Athens is the best-known example of an ancient Greek agora, whose initial use was for a commercial, assembly, or residential gathering place.



Thissio is a small settlement which is found south west of Monastiraki. It is famous for the plethora of trendy cafes and bars.
Pikionis’ paved pathways connects Propylaea to the Philopappou hill. It is designed by the architect Dimitris Pikionis.


Philopappos Hill is home to the Philopappos Monument, a square white-marble construction dedicated to Gaius Julius Antiochus Epiphanes Philopappos.
 Mount Lycabettus is a Cretaceous limestone hill in Athens. At 277 meters above sea level, its summit is the highest point in Central Athens and pine trees cover its base.
The Acropolis is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop and contains the remains of several ancient buildings.
The Arch of Hadrian is a monumental gateway resembling a Roman triumphal arch. It spanned an ancient road from the center of Athens.
The Temple of Olympian Zeus is a former colossal temple. During the Roman period the temple, it included 104 colossal columns, was renowned as the largest temple in Greece.
Mount Lycabettus is a Cretaceous limestone hill in Athens. At 277 meters above sea level, its summit is the highest point in Central Athens and pine trees cover its base.
The Acropolis is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop and contains the remains of several ancient buildings.
The Arch of Hadrian is a monumental gateway resembling a Roman triumphal arch. It spanned an ancient road from the center of Athens.
The Temple of Olympian Zeus is a former colossal temple. During the Roman period the temple, it included 104 colossal columns, was renowned as the largest temple in Greece.
300m 300m 300m 300m 300m 300m 300m 300m 300m Acropolis
Agora Olympian Stadium SITE Metro Line SiteVision SiteVision Highway
The Panathenaic Stadium is a multipurpose stadium in Athens, Greece. It is the only stadium in the world built entirely of marble.
Keramikos
ACROPOLIS'S HISTORY


SITE CONDITION PROBLEMS
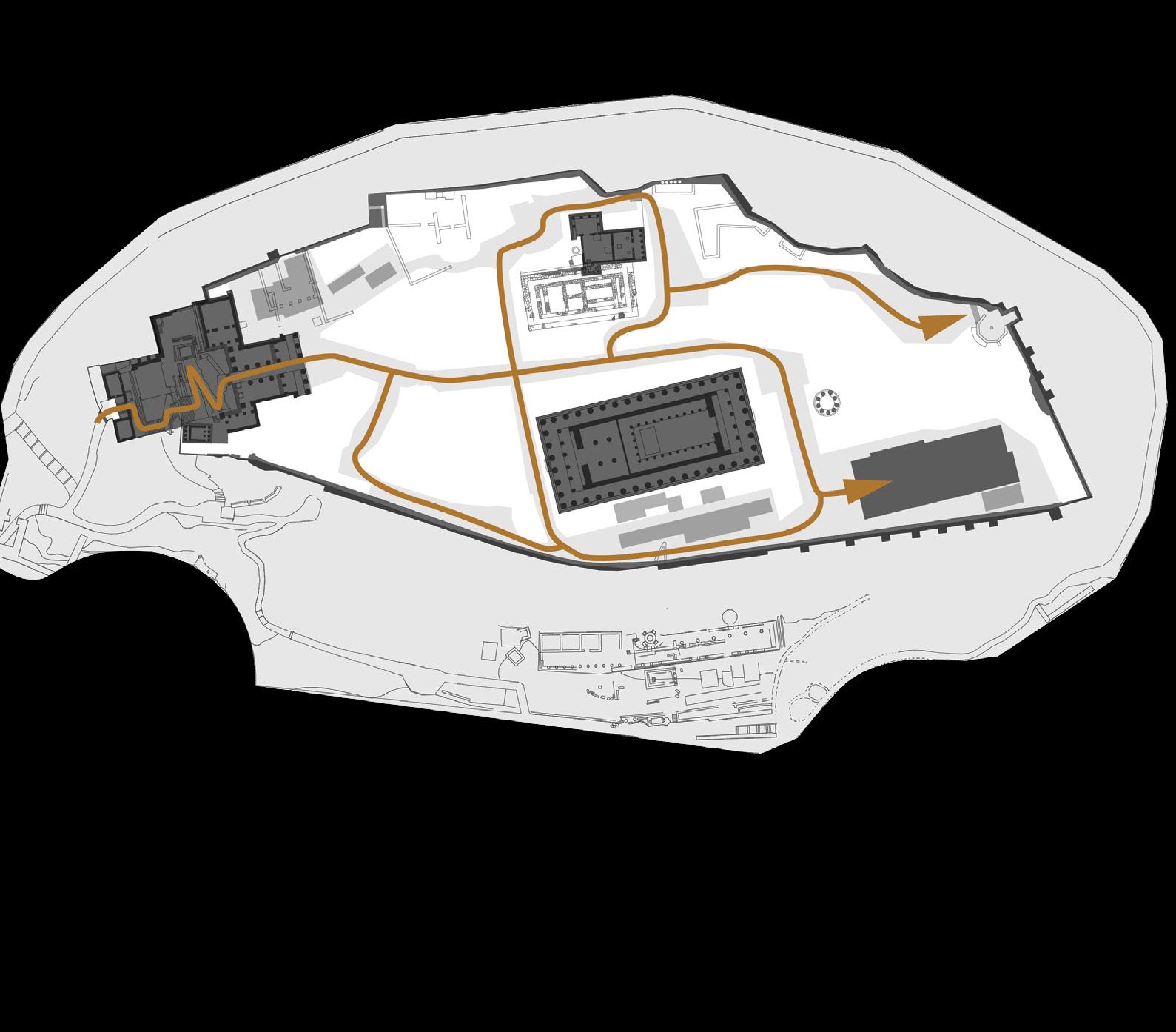
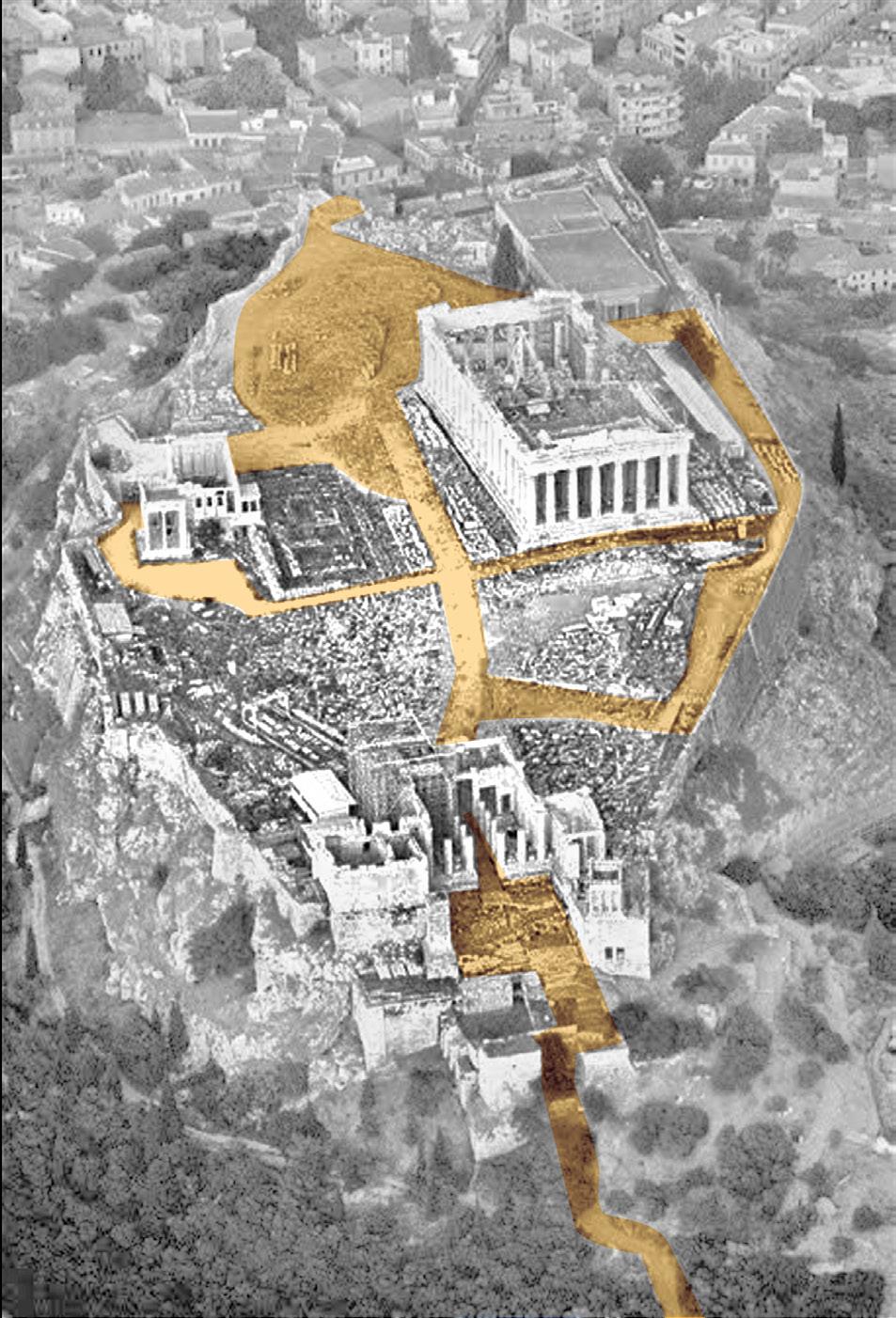
The Acropolis has a clear circulation, with three ancient buildings and the open space forming a strong sense of spatial sequence and ritual. The project adds a new building mass on the site of the old Acropolis Museum in the southeast corner of the site.

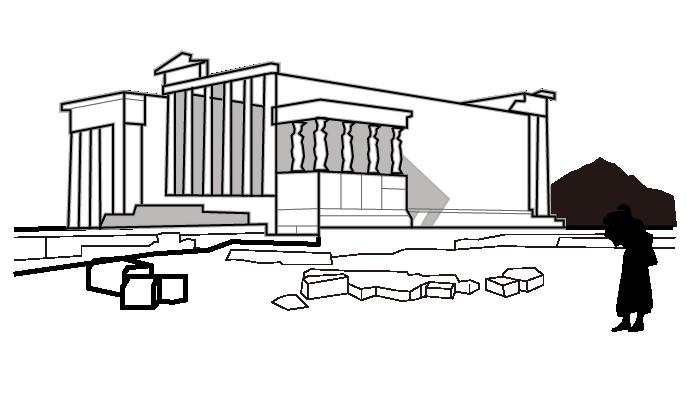


As the number of visitors grows, the landscape and services within the site are in urgent need of improvement.

Lack of spatial scene experience
ARCHITECTURE Acropolis
Propylaia
Roman Empire Turkish
Morean War, The Parthenon
Athens Charter Acropolis became a purely archaeological site Original site protection Acropolis restoration project starts Acropolis inscribed on World Heritage List New Acropolis Museum completed Venice Charter 1964 1975 2009 1985 Greek- Turkish War World War I World War II 1914-1918 1687 1821 1939-1945 1931 1834 1863-1874 338 BC 437-405 BC 146 BCE 1396 550 BC RESTORATION WARS
Erechtheion Lack of tourist services and rest facilities ? Cement road damages pristine surface 1 1 2 2 3 3
The Old Temple of Athena Battle of Chaeronea
era
exploded as an arsenal
Parthenon
The project began by sorting out the circulation network and designing road paving that has material continuity with the site. Landscape facilities such as seating, pergolas, and fountain were added to improve the visitor experience. A new museum building was placed in the southeast corner of the site, and the majority of its space is underground, echoing the nature of the archaeological work.









Vision spots Axis Architecture and facilities Landscape 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Propylaia Parthenon Erechtheion Old Temple of Athena (Remains) Roma and Agustus Temple (Remains) Acropolis Viewing Point Archeological Museum Fountain Observation Deck Meadow Staircase Accessible Elevaor Signage Shades and Bench
MASTER PLAN
Mediterranean pine Gravel pavement Athens Schist Surface A B C D E F Ruins of stones and grass Athens marble olive tree 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 9 10 11 12 13 A B C D 14 14 14 14 14 A D E F 0 5 15 30m
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Entrance hall Cafeteria Kitchen WC Exhibition room Restoration display hallway Heritage Exhibition Hall Exit hall Staircase Office area 1 2 ±0.000 -1.00 -4.00 -4.00 3 4 4 5 6 10 7 8 9 Entrance A Exit down down down -1F PLAN A-A' SECTION A'
SOUTH ELEVATION
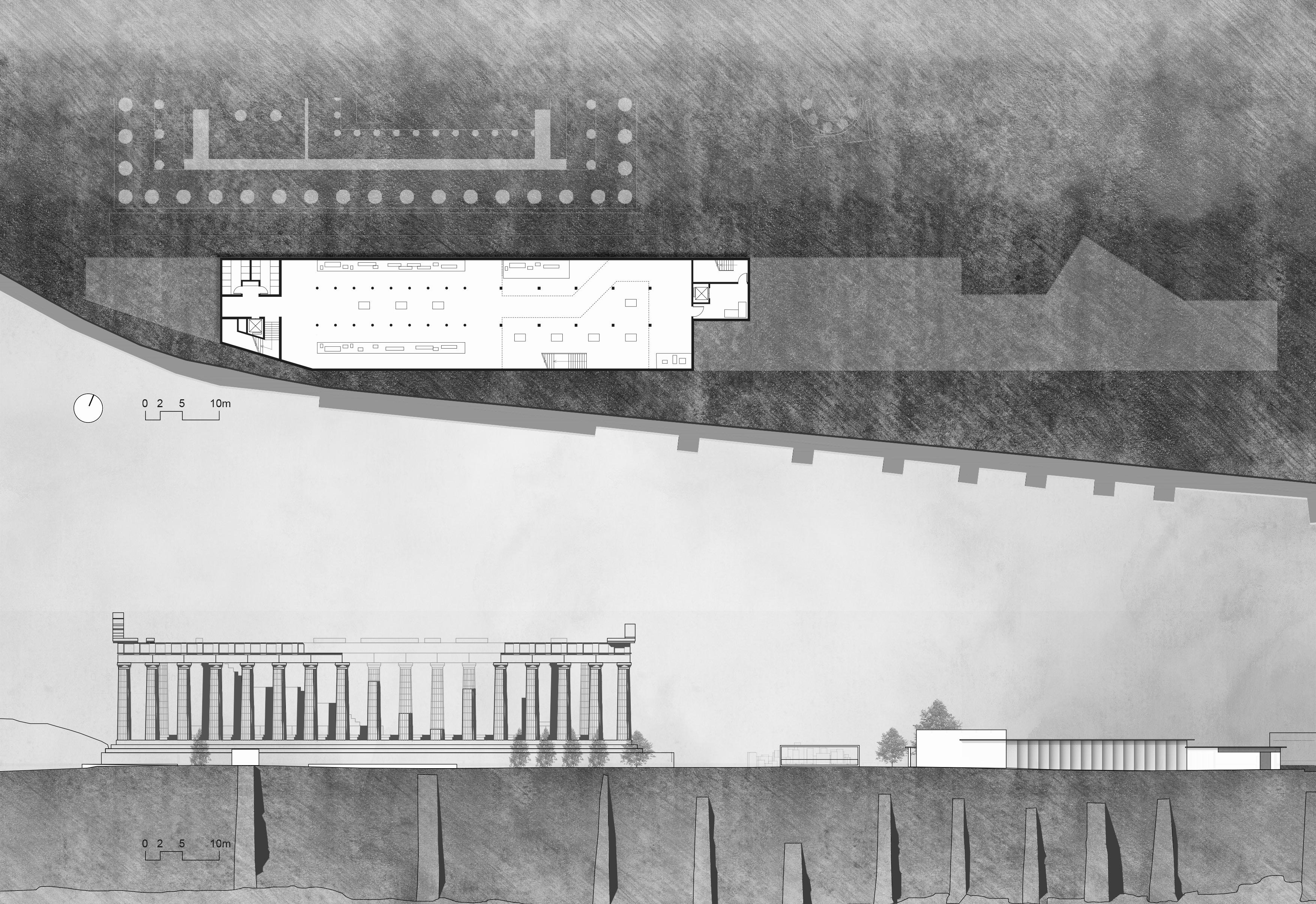
1 2 3 4 Archaeological Relics Exhibition Hall Heritage Exhibition Hall WC Staff lounge up up up -8.00 1 2 3 4 -2F PLAN
The building's skylight creates a visual connection to the landscape at the surface, providing a visual contrast between the past and present, and offering visitors a new perspective. The new building quietly blends into its environment, developing amidst the ancient traces buried to this day, revealing the archaeological history of the site.


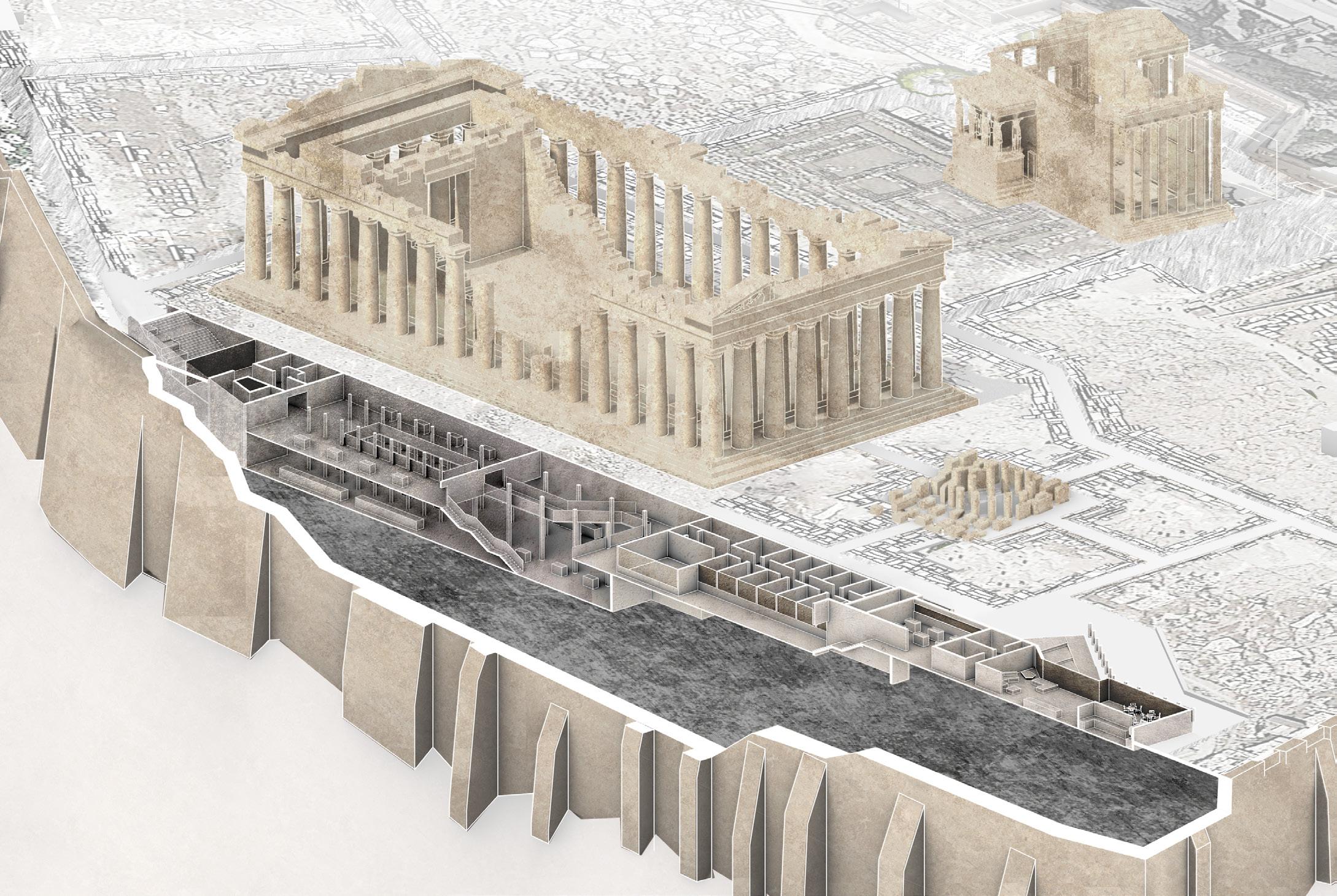

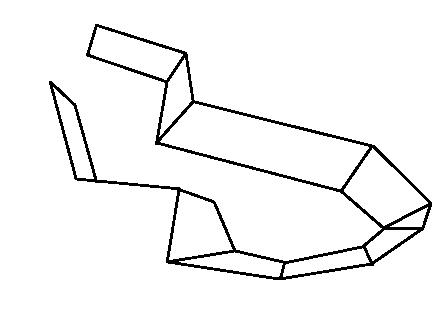
 AXONOMETRIC VIEW
Heritage exhibition hall
Entry ramp
Exit staircase
Restoration display hallway
AXONOMETRIC VIEW
Heritage exhibition hall
Entry ramp
Exit staircase
Restoration display hallway
Feeling and reflecting on history
Experience the process of archaeological work
The museum's entrance ramp hint at the archaeological theme
Back to reality from archaeological history
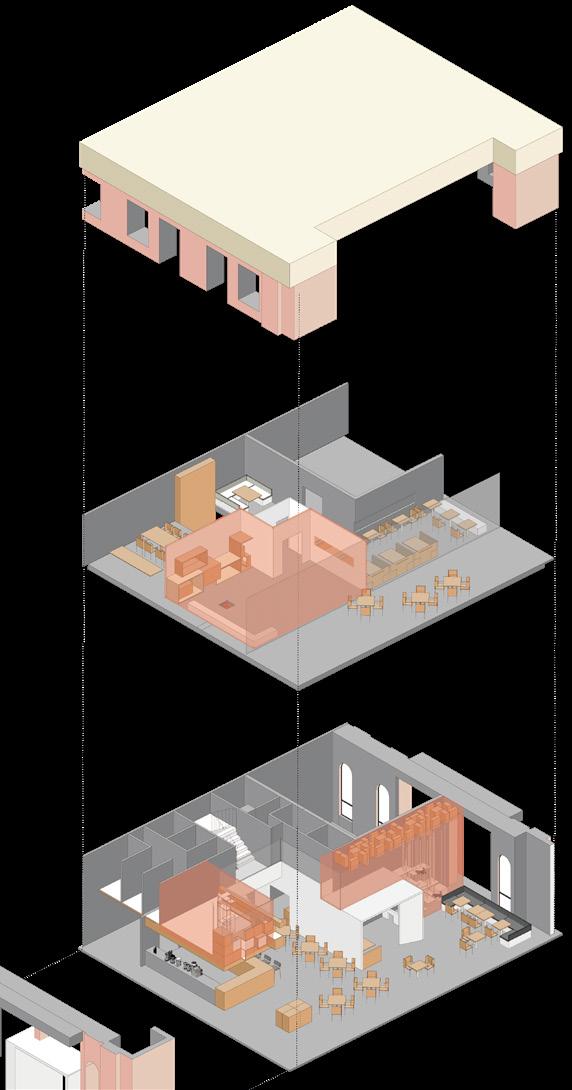
05 CATBLOCK CAFE
Cat Cafe Interior Design

Individual Work
Location: Wuxi, China
Duration: 11/2021-12/2021
Instructor: Ji Lin
EQUAL RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HUMAN AND CAT
In "Catblock Cafe", people are the objects and cats are the subjects.Through the combination of separation and intersection of human and cat activity area, the equal relationship between human and pet is explored.





In China, cat cafes are popular places where young office workers enjoy drinks and desserts, play with cats, and relieve stress at the same time. However, there are some problems with cat cafes, the core of which is that in cat cafes, the human customer is God and the cat serves the human. Sometimes the will of the human overrides the cat, and the relationship is not one of equality and mutual benefit.
STRATEGY: SEPARATION AND INTERACTION
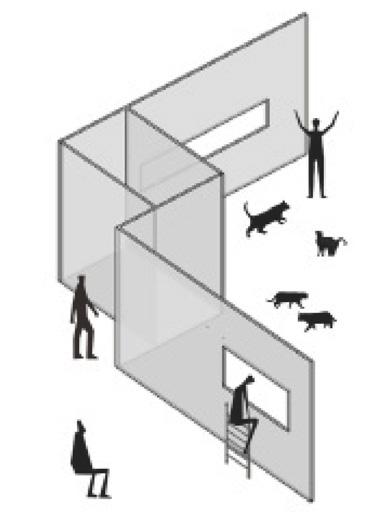
In a cat cafe, the encounter between a human and a cat is as brief as the encounters of passers on the street (low intensity contact). At "Catblock", in order to get close to cats quickly, people need to respect the perspective and habits of cats, and approach them with kindness and caution.
1 Cat watching people from high " blocks"
3 Cats have undisturbed space to move around
2 In the dining area, people can only spy on cats
5 Discreetly gaining the cat's trust and then interacting further
Interactive area
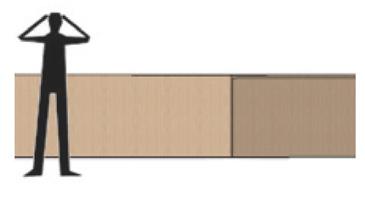
restaurant area
Cats' area
4 People in the window being observed by cats
Cats' area

restaurant area
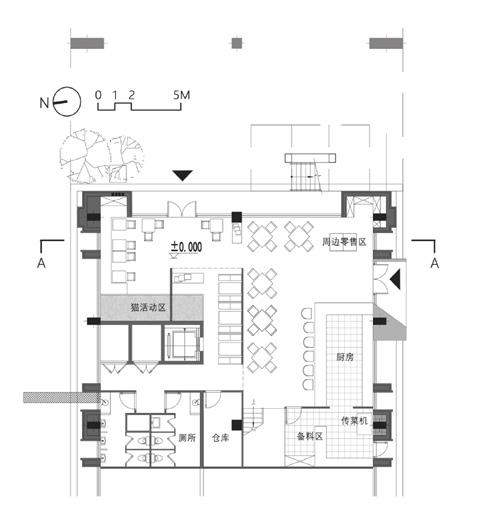
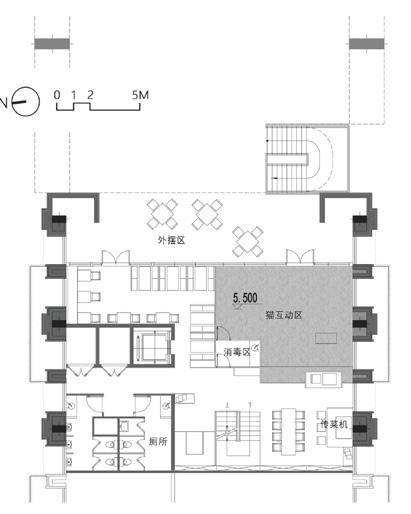 1st floor plan mezzanine floor plan 2nd floor plan
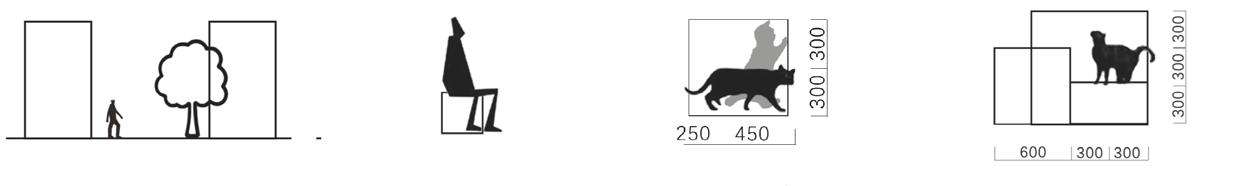
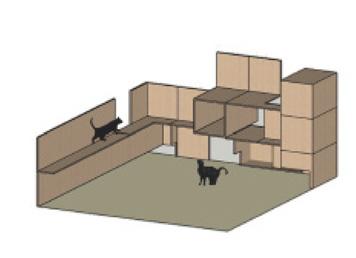
Block Scale Ergonomics
Cat Scale
Human and cat encounter "Cat Engineering"
1st floor plan mezzanine floor plan 2nd floor plan
Block Scale Ergonomics
Cat Scale
Human and cat encounter "Cat Engineering"




























 The project re-planned the Guan River watershed and adjusted the layout of urban farmland and industrial areas; installed wastewater treatment plants in each industrial park and designed purification wetlands downstream of the wastewater treatment plants.
The project re-planned the Guan River watershed and adjusted the layout of urban farmland and industrial areas; installed wastewater treatment plants in each industrial park and designed purification wetlands downstream of the wastewater treatment plants.






































 Round shallow pool
concrete pile
stainless steel grating pavement reinforced foundations
Stainless steel path
made of concrete, describtion of the accident
Wetland deep water
Black-capped Kingfisher protected wild animal
Metasequoia glyptostroboides remove TP, COD chemicals
Chinese sucker
Reed birds' nest Shrimp
Little Yellow Croaker
Surface flow wetland
Whooper Swan protected wild animal
Baer's Pochard protected wild animal
Red-crowned Crane protected wild animal
Arundo donax remove COD chemicals
Wetland Trail
Submerged flow wetland
Eurasian River Otter protected wild animal
Helical pile
Batter anchor with turnbuckle assembly
helix
Round shallow pool
concrete pile
stainless steel grating pavement reinforced foundations
Stainless steel path
made of concrete, describtion of the accident
Wetland deep water
Black-capped Kingfisher protected wild animal
Metasequoia glyptostroboides remove TP, COD chemicals
Chinese sucker
Reed birds' nest Shrimp
Little Yellow Croaker
Surface flow wetland
Whooper Swan protected wild animal
Baer's Pochard protected wild animal
Red-crowned Crane protected wild animal
Arundo donax remove COD chemicals
Wetland Trail
Submerged flow wetland
Eurasian River Otter protected wild animal
Helical pile
Batter anchor with turnbuckle assembly
helix

































































































 Pedestrians follow the terrain uphill from the park entrance connected to the subway station, feeling the axis of the space.
Section 1-1'
Section 2-2'
Pedestrians follow the terrain uphill from the park entrance connected to the subway station, feeling the axis of the space.
Section 1-1'
Section 2-2'










 Mount Lycabettus is a Cretaceous limestone hill in Athens. At 277 meters above sea level, its summit is the highest point in Central Athens and pine trees cover its base.
The Acropolis is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop and contains the remains of several ancient buildings.
The Arch of Hadrian is a monumental gateway resembling a Roman triumphal arch. It spanned an ancient road from the center of Athens.
The Temple of Olympian Zeus is a former colossal temple. During the Roman period the temple, it included 104 colossal columns, was renowned as the largest temple in Greece.
Mount Lycabettus is a Cretaceous limestone hill in Athens. At 277 meters above sea level, its summit is the highest point in Central Athens and pine trees cover its base.
The Acropolis is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop and contains the remains of several ancient buildings.
The Arch of Hadrian is a monumental gateway resembling a Roman triumphal arch. It spanned an ancient road from the center of Athens.
The Temple of Olympian Zeus is a former colossal temple. During the Roman period the temple, it included 104 colossal columns, was renowned as the largest temple in Greece.































 AXONOMETRIC VIEW
Heritage exhibition hall
Entry ramp
Exit staircase
Restoration display hallway
AXONOMETRIC VIEW
Heritage exhibition hall
Entry ramp
Exit staircase
Restoration display hallway














 1st floor plan mezzanine floor plan 2nd floor plan
Block Scale Ergonomics
Cat Scale
Human and cat encounter "Cat Engineering"
1st floor plan mezzanine floor plan 2nd floor plan
Block Scale Ergonomics
Cat Scale
Human and cat encounter "Cat Engineering"