Literacy Focus Skills™ based on the National Curriculum of England
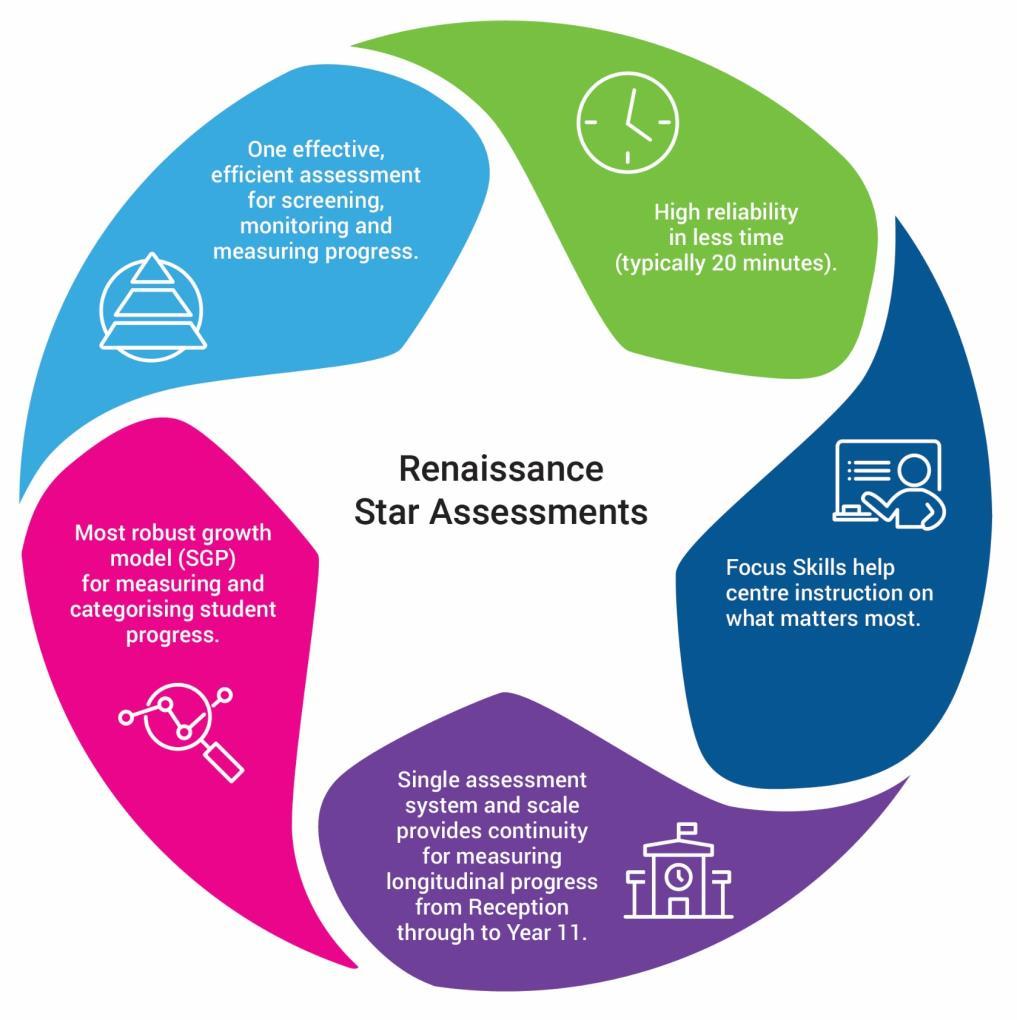
Focus Skills: The key building blocks for understanding


Focus Skills: The key building blocks for understanding

In 2014, the Department for Education adopted the current National Curriculum. The associated documents outlined the related programmes of study and attainment targets that detail what pupils should know and be able to do at any given year level. These are the “blueprints” that guide instruction, curriculum, and assessment. However, not all attainment targets are created equal. Some are foundational to that year level and required for learning skills yet to come; other targets may represent the introduction of ideas to be expanded in later years or extensions of existing skills that were taught earlier.
In this document, Renaissance present the Focus Skills™ of each year. They are the foundational skills that are essential to advancing learning (i.e., concepts learners must master along the way in order to move to the next step), supporting the development of future skills (i.e., serve as strong prerequisites for skills to come), and/or reflecting the emphasis of the National Curriculum at that year level.
Focus Skills stem from more than a decade of Renaissance’s work on developing and validating learning progressions. Learning progressions describe the incremental way students acquire knowledge–from lesser to more sophisticated understanding–within a subject area. Building new knowledge relies on developing understanding of prerequisite skills.
Focus Skills are key building blocks within the learning progressions
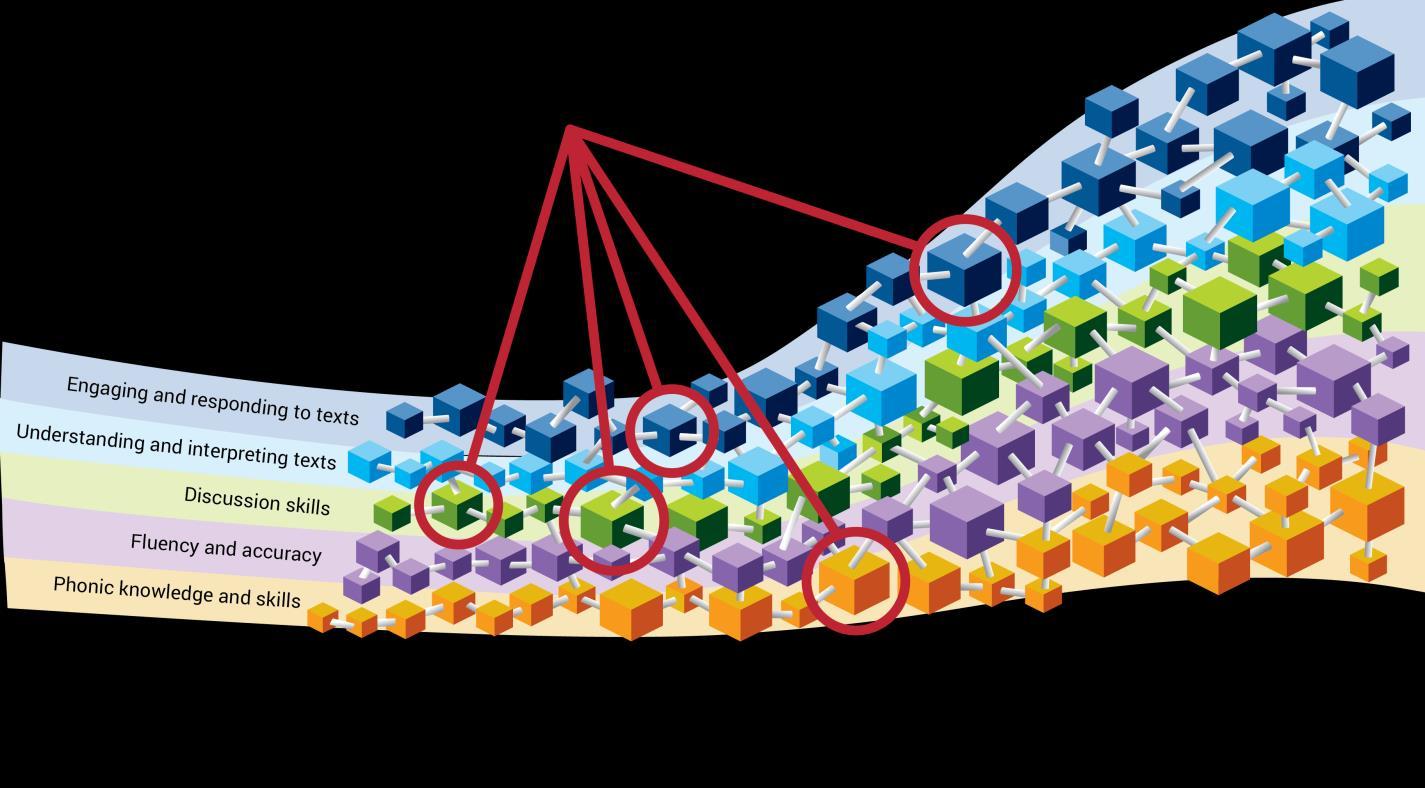
Renaissance contracted with the National Foundation for Educational Research (NFER) to develop a detailed learning progression based on the National Curriculum This began by developing an underlying framework or hierarchy of domains and sub-domains to accurately reflect the structure and organisation of the curriculum. Work then turned to identifying the discrete, teachable skill statements necessary to support each element of the curriculum Finally, specific attention was given to ordering the skills within and across year levels, based on how students would typically be expected to learn them (with successive complexity and sophistication). Not only was the order of skills in our learning progressions based on expert review and classroom experience, it was also validated by data from millions of student responses and more than 5,600 test questions.
Experts also identified a subset of the skills as Focus Skills, meaning those that represent the key building blocks of understanding. These skills require a specific level of competency and provide the foundation for the next levels of learning. The following are examples of Focus Skills from Year 2:
• Read, without having to blend first, familiar words containing grapheme-phoneme correspondences that have been taught
• Read familiar words quickly and accurately without having to blend explicitly as a first step
In contrast, a non-Focus skill from that same year is “Read unfamiliar words containing taught graphemes with accuracy and without hesitation, by sounding out the phonemes.” These three skills belong in the skill area Automatic Decoding, Independent Reading, which appears in the learning progression in Years 2 to 4. While students are practicing quickly sounding out and decoding unfamiliar words in the non-Focus skill, the broader emphasis is on automaticity with familiar words that does not require slowing down to blend. These are key steps in developing fluency.
It is not that other skills do not have value; rather, it is that some skills are more critical as building blocks and necessary foundations for future learning. Focus Skills are the most essential skills from each domain, and they are also ordered based on how most pupils would be expected to learn them.
Phonic knowledge and skills
Word recognition
Fluency and accuracy
Vocabulary
Discussion skills
Understanding and interpreting texts
Engaging and responding to texts
The Focus Skills are linked to the domains and headings associated with the year-level attainment targets as shown above (and colour coded as such throughout the document for easy reference).
For years, multiple authors have argued that teachers have been given many more educational objectives than could ever be addressed (Schmoker, 2018; Lemov, Woolway, and Yezzi, 2012; Stiggins, 2017; Kohn, 1999). Focus Skills are designed to help. In a word, they are about prioritisation. Within the massive cloud of all possible skills, they identify those that are “considered to be essential in underpinning future learning” (Kirkup et al., 2014). They resolve the dilemma that programmes of study often contain absolutely essential skills that are commingled with ones that are far more secondary in nature by clearly noting those that are non-negotiable skills.
This workbook contains a listing of all Focus Skills for reading based on the National Curriculum of England
Grain Size
We should note that all skills in Renaissance’s various learning progressions are at the discrete, teachable level. Attainment targets, in contrast, often comprise multiple skills. These skills, therefore, represent the unpacking or deconstructing of the targets that are advanced by many authors (Kirkup et al., 2014; Stiggins, 2005; Stiggins, 2017).
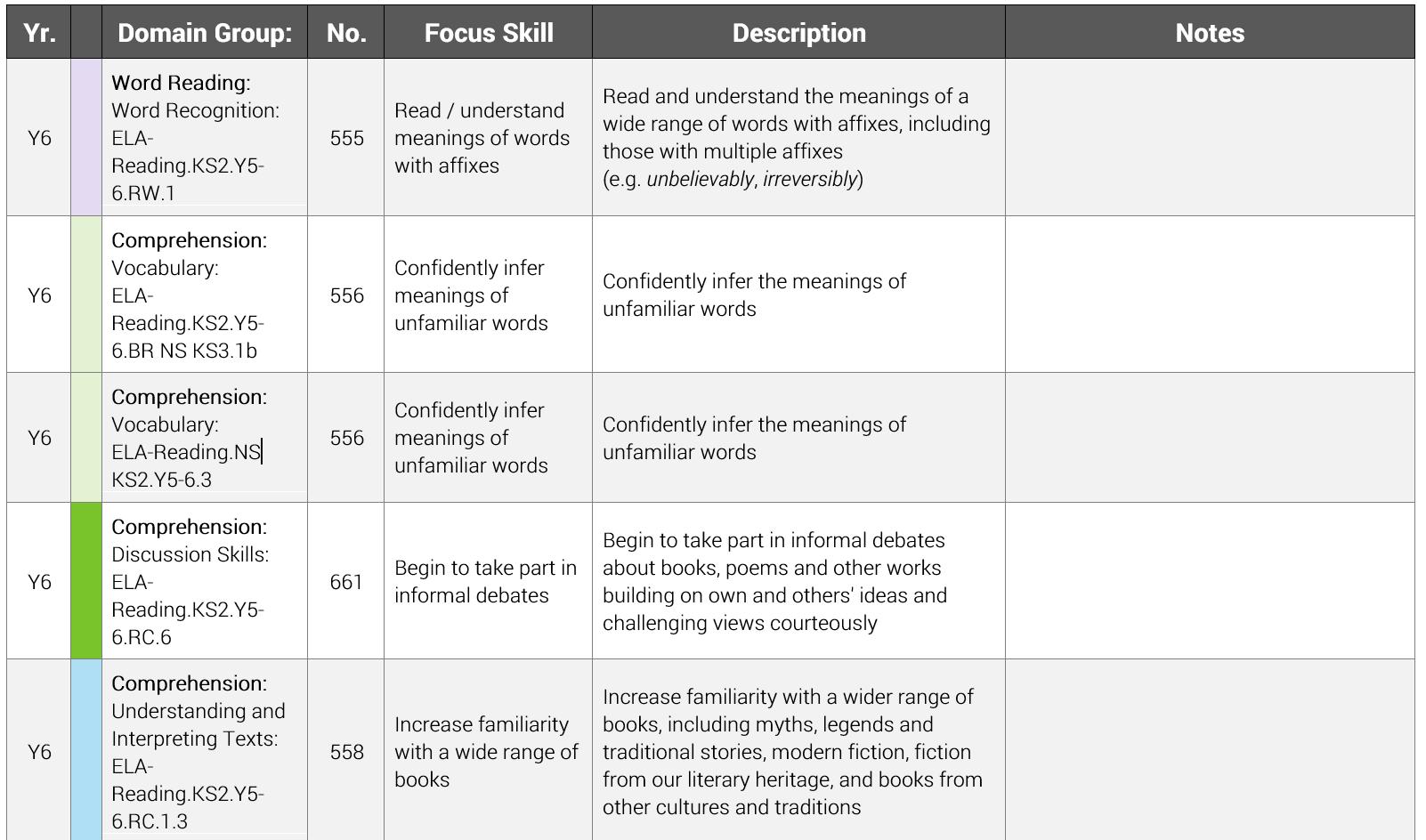
The “Yr.” heading indicates the year level (e.g. Year 6) associated with each skill. The “Domain Group” heading is drawn from the overall organisation of the National Curriculum and this field also includes coding referencing specific areas of and targets within the curriculum (e.g. ELA-Reading. KS2.Y5-6.RW.1) that documents the alignment between each Focus Skill and the National Curriculum This coding can also be used by Star customers to search for skills within the Skills and Resources area of the Reading Dashboard The “No ” heading stands for Number The value in that column represents the position of each individual skill within the overall learning progression and is generally suggestive of difficulty. Finally, the “Focus Skill” heading offers the name of the skill with the full skill description being available in the “Description” heading.
This information is organised based on feedback from multiple focus groups with teachers. Skills are sorted first by subdomain (e.g. Word Recognition) and then by overall order (No.). The sub-domain level was selected as the primary driver because teachers generally plan instruction focused on specific topics/skills sets In terms of the No. reference, a skill with 73 noted in the No. column is the 73rd skill in the overall progression.
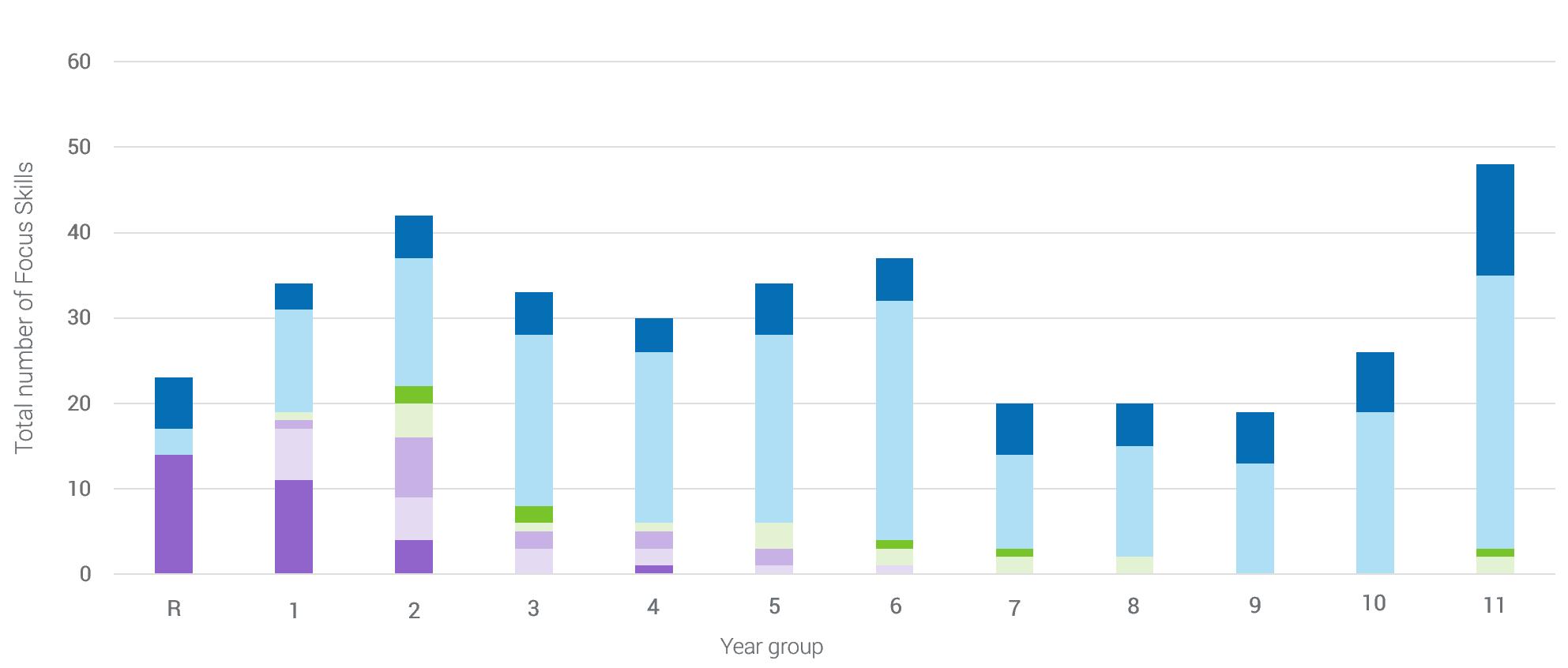
Focus Skills are a subset of an entire list of skills (usually 20-40%), and though they are ordered by domain, pupils need to integrate learning across domains to continue to make progress.
Also, readers will note that not all numbers appear within the “No.” heading. This is because Renaissance’s learning progressions include all skills, not just those that are noted as Focus Skills. These other skills are parts of the progressions built to reflect the National Curriculum, but they are not provided here. The complete skill list is available to Star customers within the software.
Use information from this workbook to do the following:
• Choose skills for targeted instruction and check for mastery during regular instruction
• Identify high leverage pre-requisites for review if students are struggling
• Prioritise instruction on the most important skills when trying to close performance gaps
We would note that in these current circumstances multiple authors (Hill and Loeb, 2020; Sawchuk, 2020) suggest that, rather than spend substantial time reviewing, teachers should focus on “moving students immediately into grade-level-appropriate content in the new school year, rather than repeating material from the end of the prior grade,” but also acknowledge that “where new lessons draw on concepts affected by the shutdown, schools can add extra review but in a ‘just in time’ fashion” (Hill and Loeb, 2020, n.p.).
While Focus Skills typically comprise anywhere from 20-40% of skills overall, depending on the subject, that does not mean we should allocate 20-40% of our time to them. We should allocate more. Fogarty, Kerns, and Pete (2018) call for essential skills to receive “disproportionate practice” (p. 95). Lemov, Woolway, and Yezzi note that “if you’re practicing one of those important skills one of the [ones that most drive] performance don’t stop when your [pupils] ‘know how to do it’” because “your goal with these . . . skills is excellence, not mere proficiency” (2012, p. 30). “Automaticity,” “and “fluency” are also terms that are relevant here. The goal, Lemov et al. note, “is to be great at the most important things” (p. 31).
R
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 9a
3 Know letters symbolise spoken sounds in words
Understand that letter(s) on the page symbolise spoken sounds in words
R
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 9a
Word Reading:
4 Know sounds for a set of single-letter graphemes
Recognise simple grapheme-phoneme correspondences for an initial set of singleletter graphemes consisting of consonants and vowels (e.g. the graphemes s, t, p, a,i) responding with one sound for each letter (e.g. the phonemes /s/,/t/,/p/,/a/,/i/)
R
Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 9a
Word Reading:
5 Know sounds for more single-letter graphemes
Recognise simple grapheme-phoneme correspondences for a wider set of singleletter graphemes consisting of consonants and vowels (e.g. d, g, m, k, o, e), responding with one sound for each letter (e.g. /d/,/g/,/m/, /k/,/o/,/e/)
R
Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 10
Word Reading:
6 Decode two-letter VC words with known phonemes
Decode by sounding and blending, phoneme by phoneme, two-letter VC words with known phonemes that are displayed (e.g. see the word on, blend out loud o-n, say out loud the word \"on\"; see the word it, blend out loud i-t, say out loud the word \"it\")
R
Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 10
Word Reading:
7 Decode CVC words with known phonemes
Decode by sounding and blending, phoneme by phoneme, a small number of three-letter CVC words with known phonemes (e.g. p-a-n, s-i-t)
R
Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 9a
Word Reading:
8 Choose correct phoneme for twoletter graphemes
Respond with the correct phoneme to a small set of graphemes where two letters represent one sound (e.g. respond with the phoneme /l/ to the grapheme ll as in the word fall; respond with the phoneme /k/ to the grapheme ck as in the word kick)
R
Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 10
Word Reading:
9 Decode a wider range of CVC words
Decode by blending, phoneme by phoneme, a wider range of three-letter CVC words made from grapheme-phoneme correspondences that have been taught (e.g. l-e-g, r-u-n, p-o-t)
R
Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 9a
Word Reading:
10 Use correct phonemes in simple exception words
Respond with the correct phoneme to unusual grapheme-phoneme correspondences in simple common exception words (e.g. respond with the phoneme /u:/ to the grapheme o in the word to; respond with the phoneme /ə/to the grapheme e in the word the)
R
Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 10
Word Reading:
11 Decode CVC words / graphemes of multiple letters
Decode by sounding and blending, phoneme by phoneme, CVC words where graphemes may be more than one letter, using grapheme-phoneme correspondences that have been taught, including consonant digraphs and vowel digraphs (e.g. sh-o-p, b-oa-t)
R
Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELA-Reading.R.EYFS
L ELG 9a
12 Decode / read aloud short sentences
Decode and read aloud, accurately, short sentences containing simple regular words with taught grapheme-phoneme correspondences
Y1
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RW .2
60 Recognise one grapheme for each of 40+ phonemes
Recognise at least one common graphemic representation for each of the 40+ phonemes
Y1
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELA-Reading.NS
KS1.Y1.1
61 Use correct phoneme for consonant digraphs
Respond with the correct phoneme to a wider range of graphemes where two letters represent one consonant sound (digraphs) (e.g. respond with the phoneme /ʃ/ to the grapheme sh in the word ship; respond with the phoneme /tʃ/ to the grapheme ch in the word chop; respond with the phoneme /θ/ to the grapheme th in the word thin)
Y1
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELA-Reading.NS
KS1.Y1.1
62 Respond with correct phoneme to vowel digraphs
Respond with the correct phoneme to a wider range of graphemes where two letters represent one vowel sound (digraphs) (e.g. respond with the phoneme /ɑ:/ to the grapheme ar in the word far; respond with the phoneme /ɜ:/ to the grapheme ir in the word bird)
Y1
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELA-Reading.NS
KS1.Y1.1
63 Respond with the correct phoneme to trigraphs
Respond with the correct phoneme to graphemes consisting of three letters (trigraphs) or more (e.g. respond with the phoneme /aı/ to the grapheme igh in the word high; respond with the phoneme /ıə/ to the grapheme ear in the word near)
Y1
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RW .2
64 Identify correspondences for all 40+ phonemes
Identify, at pace, correct correspondences for all 40+ phonemes, including alternative sounds for graphemes
Y1
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RW .3
65 Read unfamiliar words by blending
Read words that are not already familiar but that contain taught GPCs by blending, phoneme by phoneme, throughout the word (e.g. t-r-a-ck, th-r-u-sh)
Y1
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y1.2
65 Read unfamiliar words by blending
Read words that are not already familiar but that contain taught GPCs by blending, phoneme by phoneme, throughout the word (e.g. t-r-a-ck, th-r-u-sh)
Y1
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RW .5
73
Read words with taught words and simple suffixes
Read straightforward words with taught grapheme-phoneme correspondences that have simple suffixes, where application of the suffix does not involve changes to the root word (e.g. kick -ing, jump -ed, cold -est)
Y1
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RW .8
74 Read aloud, accurately, books with taught words
Read aloud, with accuracy, books that consist of words with taught graphemephoneme correspondences, including regular and common exception words
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RC.
1.3
95 Retell and reenact familiar key stories
Retell familiar key stories and fairy stories orally and re-enact in a variety of ways (e.g. using dolls or puppets)
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RC.
1.3
97
Become familiar with some key nonfiction types
Become familiar with some key non-fiction text types (e.g. simple, single-topic information books)
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.BR
KS2.Y3-4 RC.2.6
103 Understand presentation elements in literature
Identify and understand simple elements of text presentation in literary texts (e.g. cover, page, line)
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.BR
KS1.Y2 RC.1.2
111 Identify and understand basic story elements
Identify and understand basic story elements (e.g. stories have a beginning, ending and sequence of events)
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RC.
2.5
114 Make simple predictions with support
With prompting and support make simple predictions on the basis of what is read or heard (e.g. predict what a greedy character will do next)
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RC.
2.3
115 Discuss main story events and their causes
Discuss main story events and simple reasons for, or causes of, events (e.g. \"He slipped because the floor was wet.\")
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RC.
2.4
128 Make inferences about stories / picture books
With prompting and support, make inferences on the basis of what is being said and done in stories heard read aloud and from picture books (e.g. \"What do you think Baby Bear said? How did he feel?\")
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS1.Y1.6
134 Identify simple language patterns in non-fiction
Identify simple patterns of language and particular words and phrases used in nonfiction texts (e.g. first/next, Dear/From)
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.BR
KS1.Y2 RC.1.4
137 Identify and locate parts of non-fiction texts
Begin to identify and locate parts of nonfiction texts that give particular information (e.g. titles, contents page, index, pictures, labelled diagrams, charts)
Y1
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS1.Y1.6
142 Identify structures of informational text
Identify and understand the structural elements of texts that give information and how these differ from those that tell a story
Y1
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.RC.1 .1
Y1
84 Explain stories and poems heard read aloud
Explain understanding of a range of stories and poems heard read aloud, including those that are at a level beyond which can be read independently
Y1
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.BR
KS1.Y2 RC.2.4
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.BR
KS2.Y3-4 RC.1.7
129
Answer simple questions about information text
Answer 'who', 'what', 'where', 'when', 'why', and 'how' questions in response to prominent aspects of an appropriate information text, (e.g. \"Where do polar bears live?\")
134 Identify simple language patterns in non-fiction
Identify simple patterns of language and particular words and phrases used in nonfiction texts (e.g. first/next, Dear/From)
Y2
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELA-Reading.NS
KS1.Y2.1
150 Know all common graphemes for the 40+ phonemes
Recognise all common graphemes representing the 40+ phonemes when decoding words
Y2
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELA-Reading.NS
KS1.Y2.1
151
Note graphemephoneme relationships in all words
Recognise, with increased speed and accuracy, the grapheme-phoneme correspondences taught so far, including those in common exception words
Y2
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RW.2
160 Decode graphemes with multiple pronunciations
Decode, by blending phoneme by phoneme, throughout the word, a variety of words containing a common taught grapheme which may be pronounced differently in each word (e.g. the letter y maps to the phoneme /i:/in the word happy, the phoneme /aı/ in the word sky, the phoneme /j/ in the word yes)
Y2
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills:
ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RW.2
161 Decode different graphemes with the same phoneme
Decode, by blending phoneme by phoneme, throughout the word, a variety of words with common phonemes that are represented by different graphemes that have been taught (e.g. in some accents, pour, poor, pore; tie, high)
Y2
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RW.4
162 Read common exception words with ease
Read words that include common suffixes (-s, -es, -ing, -ed and -est), even when the application of the suffix involves changes to the root word (e.g. dropped, coming, biggest)
Y2
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.3
162 Read common exception words with ease
Read words that include common suffixes (-s, -es, -ing, -ed and -est), even when the application of the suffix involves changes to the root word (e.g. dropped, coming, biggest)
Y2
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.BR KS1.Y1 RW.7
165 Decode words with more complex contractions
In reading, decode words with a wider range of more complex contractions (e.g. you've, she'd, we're)
Y2
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RW.3
169
Decode words consisting of two or more syllables
Decode words consisting of two or more syllables that contain taught graphemes (e.g. container, pavement, supermarket)
Y2
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RW.5
170 Sound and blend words with unusual patterns
Use sounding and blending to decode a wider range of high-frequency words containing unusual grapheme-phoneme correspondences (e.g. s-t-r-aigh-t, though, c-al-m, r-ou-gh)
Y2
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RW.6
153 Read letter-sound correspondences automatically
Read, without having to blend first, familiar words containing grapheme-phoneme correspondences that have been taught
Y2
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.5
153 Read letter-sound correspondences automatically
Read, without having to blend first, familiar words containing grapheme-phoneme correspondences that have been taught
Y2
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RW.6
155
Read familiar words quickly and accurately
Read familiar words quickly and accurately without having to blend explicitly as a first step
Y2
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.5
155 Read familiar words quickly and accurately
Read familiar words quickly and accurately without having to blend explicitly as a first step
Y2
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RW.1
157 Sound out unfamiliar words automatically
Decode and read aloud sentences and passages consisting of words containing a widening set of taught graphemephoneme correspondences, sounding out unfamiliar words automatically
Y2
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RW.7
158 Read aloud with improved accuracy and fluency
Read aloud books that match the improved stage of phonic knowledge, automatically tackling unfamiliar words with accuracy and without hesitancy
Y2
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.5
158 Read aloud with improved accuracy and fluency
Read aloud books that match the improved stage of phonic knowledge, automatically tackling unfamiliar words with accuracy and without hesitancy
Y2
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.7
162 Read common exception words with ease
Read words that include common suffixes (-s, -es, -ing, -ed and -est), even when the application of the suffix involves changes to the root word (e.g. dropped, coming, biggest)
Y2
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.6
177 Discuss and clarify the meanings of new words
Discuss and clarify the meanings of new words
Y2
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.7
177 Discuss and clarify the meanings of new words
Discuss and clarify the meanings of new words
Y2
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.9
177 Discuss and clarify the meanings of new words
Discuss and clarify the meanings of new words
Y2
Comprehension: Discussion Skills: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.10
219 Discuss favourite words / phrases in literature
Identify and discuss favourite words and phrases in particular poems and fiction texts
Y2
Comprehension: Discussion Skills: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.10
220 Discuss favourite words / phrases in non-fiction
Identify and discuss favourite words and phrases in a particular non-fiction text
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.2.2
173 Correct inaccurate reading in fiction
Correct inaccurate reading in fiction texts by re-reading or using some other available phonological or contextual clues or grammatical and graphic knowledge (e.g. correcting 'he' to 'she' if the subject of the sentence was a female character)
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.6
177 Discuss and clarify the meanings of new words
Discuss and clarify the meanings of new words
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.1
179 Listen to poems / prose above one's reading level
Listen to a wide range of contemporary and classic poetry and stories that are at a level beyond which could be read independently (e.g. stories in chapter form)
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.1
180 Listen to nonfiction above one's reading level
Listen to a wider range of non-fiction that is at a level beyond which could be read independently (e.g. news reports, simple biographies)
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.5
184 Recognise recurring language in literature
Recognise simple recurring literary language across stories and poetry, including nursery rhymes (e.g. 'Once upon a time', 'and they all lived happily ever after')
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.BR
KS2.Y3-4 RC.1.2
188 Note why specific non-fiction texts are needed
Identify some reasons for needing, or choosing, specific non-fiction texts (e.g. to find out more about a topic, to be able to make something)
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.BR
KS2.Y3-4 RC.1.2
190 Read texts with varied structural features
Read literary texts with a wider range of structural and presentational features
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.1
191 Give likes/dislikes for challenging non-fiction
Give simple statements, sometimes with reasons, about likes and dislikes relating to a wide range of non-fiction that is at a level beyond which could be read independently
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.1
192 Give likes / dislikes for challenging literature
Give simple statements, sometimes with reasons, about likes and dislikes relating to a wide range of contemporary and classic poetry and stories that are at a level beyond which could be read independently
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.2.4
211 Answer questions about details in non-fiction
Answer 'who', 'what', 'where', 'when', 'why', and 'how' questions about key details of a non-fiction text (e.g. answering the question \"Why does the mother bird stay on the nest?\")
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.2.4
212 Answer basic questions about story's key details
Answer 'who', 'what', 'where', 'when', 'why', and 'how' questions about key details of a story (e.g. answering the question \"What made Red Riding Hood think there was something wrong with grandma?\")
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.BR
KS2.Y3-4 RC.2.6
224 Identify presentational features of literature
Identify presentational features of a range of literary texts (e.g. paragraphs and chapters in novels)
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.BR
KS2.Y3-4 RC.2.6
227 Identify presentational features in nonfiction
Identify common presentational features across a range of non-fiction texts (e.g. title, subheadings and charts)
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.4
228 Recognise various ways texts show information
Recognise that non-fiction books on similar themes can give different information in different ways (e.g. text vs. diagrams, charts)
Y2
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y1.BR
KS2.Y3-4 RC.2.6
237 Discuss the effect of words and phrases in texts
Talk about the effects of different words and phrases on the meaning of the nonfiction text (e.g. \"It shows how sharp its teeth are.\", \"It makes it sound dangerous.\")
Y2
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.BR
KS2.Y5-6 WC.1.3
206 Describe how characters respond to major events
Describe how characters respond to major events and challenges (e.g. \"The giraffe helps the others by using his long neck.\")
Y2
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.NS KS1.Y2.11
206 Describe how characters respond to major events
Describe how characters respond to major events and challenges (e.g. \"The giraffe helps the others by using his long neck.\")
Y2
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.7
219 Discuss favourite words / phrases in literature
Identify and discuss favourite words and phrases in particular poems and fiction texts
Y2
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.7
220 Discuss favourite words / phrases in non-fiction
Identify and discuss favourite words and phrases in a particular non-fiction text
Y2
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS1.Y2.RC.1.8
249 Recite poems from memory with proper intonation
Recite a growing range of poems from memory, with some understanding that intonation can affect meaning
Y3
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RW.2
254
Read words with unusual, infrequent patterns
Decode words with unusual graphemephoneme correspondences in a wider range of words, including words that are encountered less frequently (e.g. precious, wrung, concert)
Y3
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RW.1
256 Read and understand words with various prefixes
In reading, read and identify the meanings of words with a wider range of prefixes (e.g. dis-, mis-, in-)
Y3
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RW.1
257
Read / identify meanings of words with suffixes
In reading, read and identify the meanings of words with a wider range of suffixes (e.g. -ful, -less, -ly)
Y3
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.BR NS KS2.1a
258 Read at a speed allowing focus on understanding
With occasional support, read ageappropriate books, both silently and out loud, typically with accuracy and usually at a speed that allows a focus on understanding rather than decoding
Y3
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELA-Reading.NS KS2.Y3-4.1
258 Read at a speed allowing focus on understanding
With occasional support, read ageappropriate books, both silently and out loud, typically with accuracy and usually at a speed that allows a focus on understanding rather than decoding
Y3
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.3
259 Infer the meaning of unknown words from context
Begin to infer the meaning of unknown words from context and generate a range of possible meanings (e.g. for the word 'ochre' in a particular sentence, discuss which is the most likely meaning and why)
Y3
Comprehension: Discussion Skills: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.4
286 Participate in group discussions about books
Participate in discussion about books that are read independently, taking turns and listening to what others say; taking an active role in developing and agreeing on the rules for effective discussion (e.g. agreeing to include and respond to all members of the group)
Y3
Comprehension: Discussion Skills: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y3-4.10
286 Participate in group discussions about books
Participate in discussion about books that are read independently, taking turns and listening to what others say; taking an active role in developing and agreeing on the rules for effective discussion (e.g. agreeing to include and respond to all members of the group)
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.1
259 Infer the meaning of unknown words from context
Begin to infer the meaning of unknown words from context and generate a range of possible meanings (e.g. for the word 'ochre' in a particular sentence, discuss which is the most likely meaning and why)
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.1
262 Listen to nonfiction above one's reading level
Listen to a wide range of non-fiction, including reference books and textbooks, that is at a level beyond which could be read independently
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.4
264 Know a range of stories, myths, and legends
Become familiar with an increasing range of stories, fairy stories, myths and legends
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.3
275
Scan sections of nonfiction to find information
Scan sections of non-fiction texts in print or on screen, using contents pages, index, headings, subheadings, page numbers, hyperlinks, icons and drop-down menus, to locate information
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.6
276 Identify structure and organisation of text
Identify main features of structure and organisation (e.g. chronological and nonchronological organisation; use of alphabetical order) in a range of non-fiction texts (e.g. dictionaries, encyclopaedia)
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.7
280 Express views about stories and poems
Express views about stories and poems, with a focus on specific words and phrases that captured the reader's imagination
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.7
281 Express views about non-fiction texts
Express views about non-fiction texts, with a focus on specific words and phrases that captured the reader's interest
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.BR KS1.Y2 RC.2.2
294 Apply a variety of reading correction strategies
Correct inaccurate reading by re-reading, looking ahead, looking for marginal / diagrammatic explanation (if available), slowing pace, trying out different pronunciations or using other available clues
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.6
298 Identify main features of narrative structure
Identify main features of narrative structure (e.g. beginning, conflict/issue, resolution) in a range of literary texts
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.3
305 Use text and prior experience for reasoning
Deduce reasons for events based on mostly relevant evidence from the text and personal experiences (e.g. \"He hid the broken cup so he wouldn't get in trouble.\")
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.3
310 Draw simple inferences, based on textual details
Draw simple / local inferences such as inferring characters' predictable feelings and thoughts from their actions
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.3
311 Draw simple inferences from information in text
Draw simple / local inferences such as inferring predictable consequences from facts read in information texts
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.7
317 Identify the impact of language in nonfiction
Identify where the choice of language in a non-fiction text has helped to give a precise description or persuade the reader
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.5
320 Identify main ideas drawn from stories
Identify main ideas drawn from more than one paragraph of a story (e.g. \"Goldilocks finds lots of things that are too big, too small and just right.\")
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.5
322 Identify the major points of non-fiction texts
Talk about non-fiction texts, identifying major points and key themes
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.5
324 Summarise a story read independently
Summarise content from a sequence of paragraphs in a story that is read independently (e.g. events, aspects of characterisation and description)
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.BR NS KS2.Y5-6.6
329
Identify the main purpose of fiction texts
Begin to identify the main purpose of fiction texts (e.g. \"It shows that it's bad to be greedy.\")
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.BR NS KS2.Y5-6.6
330
Identify the main purpose of informational texts
Begin to identify the main purpose of informational texts (e.g. \"The author wants to show how special whales are.\")
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y3-4.5
338
Identify conventions used in non-fiction texts
Identify conventions used in different nonfiction texts (e.g. presentational devices such as numbering and headings in instructions; organisational features such as tables of contents, indexes, glossaries)
Y3
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.5
341
Identify conventions used in familiar stories
Identify conventions used in a range of familiar stories (e.g. magical events, heroic figures, pattern of three events)
Y3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.BR KS1.Y1 RC.2.3
304 Describe plot, justify opinions, refer to text
Describe events in stories and begin to justify opinions and preferences with reference to the relevant parts of the text (e.g. \"I think they should have stayed home because it said it was cloudy outside.\")
Y3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y3-4.8
309
Use drama techniques to extend understanding
Use drama techniques, including role-play and improvisation, to identify with and explore characters and to extend understanding of what is read
Y3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts:
ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y3-4.8
318 Identify the use / meaning of figurative language
Identify the use, and meaning, of figurative language in prose and poetry (e.g. 'as fast as lightning')
Y3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.1b
326
With aid, justify views about information read
With support, justify views about information that has been read (e.g. \"I think more people should use trains because it says they use less energy.\")
Y3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts:
ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.1b
327
With aid, justify views about stories and poems
With support, justify views about stories and poetry that have been read (e.g. \"I think she's the nastiest because of how she treats the children.\")
Y4
Word Reading: Phonic Knowledge and Skills: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y3-4.2
Word Reading:
350
Match decoded words to those heard but not seen
Attempt to match what has been decoded to words that may have already been heard but not seen in print
Y4
Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS2.Y3-
4.RW.2
348
Decode unusual sound-letter correspondences
Decode an increasingly wide range of words containing unusual graphemephoneme correspondences, including words that are encountered less frequently (e.g. pigeon, bawl, weapons)
Y4
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RW.1
349 Identify the meanings of words with affixes
In reading, identify the meanings of words with a wider range of prefixes and suffixes, including words with both a prefix and a suffix
Y4
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.1a
353 Read at a speed allowing focus on understanding
Read an increasing range of ageappropriate books, both silently and out loud, with accuracy and at a speed that allows a focus on understanding rather than the decoding of individual words
Y4
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y3-4.1
353 Read at a speed allowing focus on understanding
Read an increasing range of ageappropriate books, both silently and out loud, with accuracy and at a speed that allows a focus on understanding rather than the decoding of individual words
Y4
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.3
382
Use dictionaries with increasing confidence
Use dictionaries with increasing confidence, to check the meaning of unfamiliar vocabulary from reading
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.1
361 Listen to poetry / prose above one's reading level
Listen to an increasingly wide range of contemporary and classic poetry and stories that are at a level beyond which could be read independently (e.g. poetry in specific forms [haiku, limericks], novels in different genres [fantasy, science fiction])
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.4
Comprehension:
364 Use information gained from reading nonfiction
Read a range of non-fiction texts and be able to use the information gained from them (e.g. reading relevant parts of nonfiction texts in order to answer specific questions)
Y4
Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.2
Comprehension:
371 Identify purpose for reading selfselected texts
Identify the purpose for reading specific fiction texts which have been chosen independently (e.g. reading all the books in a particular series)
Y4
Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.3
Comprehension:
385 Annotate and make short notes from texts
Mark and annotate texts (e.g. underline key facts) and make short notes (e.g. listing, abbreviating) from printed text or on screen
Y4
Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.BR KS1.Y2 RC.2.2
387 Use a variety of strategies to correct reading
Correct inaccurate reading of fiction by speedily using available clues, looking back to confirm / deny inferences and / or adjust understanding to incorporate new information
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.3
392 Draw simple inferences / connect ideas in text
Draw simple / local inferences such as inferring predictable consequences from and making connections between facts read in a greater range of non-fiction texts, (e.g. newspaper articles, instructions)
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.4
397 Predict what might happen in a story
Make predictions about what might happen in a story drawing on what has been read so far and some details inferred (e.g. predict that two characters in conflict will end up as friends, drawing on evidence of their shifting attitudes)
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.3
398 Justify inferences from stories Justify inferences from stories with limited but mostly relevant evidence
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.6
400 Comment on an author's use of words in fiction
Comment on simple features of the author's use of language in fiction and poetry (e.g. \"All the words with 's' help to show how slippery it is.\")
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.BR KS1.Y2 RC.1.2
402 Identify and map the main stages of the story
Explore narrative order by identifying and mapping the main stages of the story: introduction, build-ups, climaxes or conflicts and resolutions
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.6
407 Identify structure / presentation of literary text
Identify the typical structural and presentational features of a range of literary texts including novels, poetry and plays (e.g. the use of scenes in plays, the use of stanzas in poetry)
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.6
408 Show how chapters / scenes / stanzas build ideas
Identify how chapters, scenes or stanzas can be used to order and build up ideas in literary texts
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.6
409 Identify how structural features affect texts
Identify how the author's use of specific structural and presentational features contributes to meaning in non-fiction texts (e.g. how headlines are used in newspapers to introduce the reader to the topic of articles)
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.7
410 Discuss how descriptive language creates effects
Discuss how expressive and descriptive language can create particular effects in fiction and poetry (e.g. create moods, arouse expectations, build tension, describe attitudes and emotions)
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.BR KS2.Y5-6 RC.2.5
419
Summarise a paragraph in a nonfiction text
Summarise a paragraph in a non-fiction text by identifying the most important elements / key ideas
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.2.5
421 Summarise main ideas from a nonfiction text
Summarise main ideas drawn from more than one paragraph of a non-fiction text
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.5
427 Identify themes in a range of fiction / poems
Identify themes in a wide range of fiction texts and poems (e.g. the triumph of good over evil or the use of magical devices in fairy stories and folk tales)
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y3-4.4
427 Identify themes in a range of fiction / poems
Identify themes in a wide range of fiction texts and poems (e.g. the triumph of good over evil or the use of magical devices in fairy stories and folk tales)
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.8
428 Discuss an increasing range of poetry types
Read, discuss and identify an increasing range of poetry types (e.g. free verse, narrative poetry)
Y4
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y34.BR KS2.Y5-6 RC.4
434 Distinguish between fact and opinion
Understand and use the terms fact and opinion, and begin to distinguish the two when reading
Y4
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y34.RC.1.6
Y4
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.1b
Y4
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.1b
Y4
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y3-4.8
356 Prepare poems and plays to be read aloud
367 Justify views and opinions of stories and poetry
368 Justify views and opinions of nonfiction texts
413 Explain figurative language's use in non-fiction
Prepare poems and plays to read aloud identifying how intonation, tone and volume can affect how meaning is conveyed
Justify views about stories and poetry that have been read with increasing independence, drawing on the text and considering alternative opinions
Justify views about non-fiction texts that have been read with increasing independence, drawing on the text and considering alternative opinions
Explain the use of expressive, descriptive and figurative language in a wide range of non-fiction texts (e.g. \"The author uses a lot of description to emphasise how beautiful the rainforest is.\")
Y5
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RW.1
442 Understand words with a variety of affixes
Read and understand the meanings of a wide range of words with prefixes and suffixes, including those with multiple suffixes (e.g. skilfully)
Y5
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.1
445 Read aloud with accuracy / fluency / expression
Read aloud and with accuracy, understanding and appropriate intonation, at a reasonable speaking pace, a progressively wider range of ageappropriate texts, including poetry
Y5
Word Reading: Fluency and Accuracy: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.2
445 Read aloud with accuracy / fluency / expression
Read aloud and with accuracy, understanding and appropriate intonation, at a reasonable speaking pace, a progressively wider range of ageappropriate texts, including poetry
Y5
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.3
443 Identify roots / derivations / spelling patterns
Identify word roots, derivations and spelling patterns in order to extend vocabulary (e.g. remit, permit, permission)
Y5
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.8
462
Use technical terms from literary texts
Learn and use technical terms related to the language of literary texts (e.g. style, effect, imagery)
Y5
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.8
463
Use technical terms from non-fiction texts
Learn and use technical terms related to the language of non-fiction texts (e.g. style, effect, imagery)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.1
443 Identify roots / derivations / spelling patterns
Identify word roots, derivations and spelling patterns in order to extend vocabulary (e.g. remit, permit, permission)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.1
448 Read a wide range of fiction / poetry / plays
Continue to read a wide range of fiction, poetry and plays
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.3
451 Increase familiarity with a range of nonfiction
Increase familiarity with a wide range of information and non-fiction texts, in order to support understanding (e.g. of science topics/processes)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.2
457 Adapt reading style based on purpose / text type
Adapt reading style depending on the purpose for reading, using knowledge of text organisation (e.g. use knowledge of the alphabetic organisation of dictionaries to efficiently search for a word)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.10
466 Use strategies to find / understand information
Use different techniques to aid understanding and to locate information in a text quickly and accurately (e.g. skimming, scanning and close reading)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.1
Comprehension:
476
Use text features to resolve inconsistencies
Know how to resolve inconsistencies in understanding (e.g., navigating straight back to the source of the inconsistency, looking at tables of contents / indices / headings to confirm / reject understanding)
Y5
Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.4
Comprehension:
477
Use text features to make detailed predictions
Make predictions about the content and themes of stories, drawing on a variety of features (e.g. title, cover, illustrations, blurb, author, genre)
Y5
Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.3
Comprehension:
485
Draw simple inferences from multiple sections
Draw simple inferences, such as inferring characters' feelings, thoughts and motives from their actions, by drawing on more than one section of text
Y5
Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.BR KS2.Y3-4 RC.2.3
488 Infer feelings / motives of characters
Infer feelings, thoughts and motives of characters from their actions and the actions of other characters (e.g. \"I think Jonny will be upset with his father's decision because he doesn't agree.\")
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.3
488 Infer feelings / motives of characters
Infer feelings, thoughts and motives of characters from their actions and the actions of other characters (e.g. \"I think Jonny will be upset with his father's decision because he doesn't agree.\")
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.BR KS2.Y3-4 RC.2.3
489
Justify inferences with relevant evidence
Justify inferences from information texts with relevant evidence (may include extraneous / irrelevant detail)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.3
489
Justify inferences with relevant evidence
Justify inferences from information texts with relevant evidence (may include extraneous / irrelevant detail)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.5
Comprehension:
491
Support a hypothesis in a fiction text
Summarise evidence from a fiction text to support a hypothesis (e.g. about what a character will do next, how a story will end)
Y5
Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.6
497
Identify how text structures present meaning
Identify how an author's use of different text structures presents meaning in nonfiction (e.g. how a cause and effect structure is used to present information in biographies of influential figures)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.2
500
Identify the purpose for reading nonfiction
Identify the purpose for reading non-fiction texts, describing how the text is structured to fulfil that purpose (e.g. understand that an instructional text may be presented in bullet points in order to efficiently convey information)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.5
504 Identify key themes / main ideas in fiction
Identify key themes and discuss reasons for events in fiction and poems
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.5
Comprehension:
505 Identify key themes / main ideas in nonfiction
Identify key themes and discuss main ideas in non-fiction texts
Y5
Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.BR NS KS2.Y5-6.6
514 Understand how fiction can be adapted
Understand how fiction can be adapted for different audiences and purposes (e.g. by changing vocabulary and sentence structures)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.6
515 Understand how informational texts are adapted
Understand how informational writing can be adapted for different audiences and purposes (e.g. by changing vocabulary and sentence structures)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.12
522 Compare information in nonfiction texts
Compare information in books on a topic or books on two similar topics to find out important details (e.g. life cycles of mammals vs. amphibians)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.6
539 Consider different accounts of the same event
Consider different accounts of the same event in non-fiction writing (e.g. eyewitness accounts)
Y5
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.11
549 Understand subject matter for literary response
Demonstrate awareness of some of the subject matter to be included in independent written response to a literary text (e.g. synopsis of plot, description of characters and own opinion)
Y5
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.7
Y5
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts:
ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.RC.8
Y5
447 Recite a wide range of poems from memory
460 Justify personal opinions of a literary text
Recite a wide range of poems from memory, spanning different forms and moods (e.g. narrative poems, nonsense verse)
Explain and justify personal opinions and views about literary texts, referring to some specific words and phrases from the text
Y5
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.RC.8
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.BR KS2.Y5-6 WC.1.3
461 Explain and justify opinions about nonfiction
Explain and justify personal opinions about non-fiction texts, referring to some specific words and phrases from the text
482 Describe settings in detail
Describe settings in detail, taking into account key characteristics (e.g. \"The most important thing about the castle is...\")
Y5
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.BR NS KS2.Y3-4.8
Y5
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.6
510 Use drama techniques to understand what is read
Continue to use drama techniques to explore characters, support understanding of the meaning of what is read and to explore themes and ideas
527 Compare story aspects within and between genres
Compare aspects of stories (e.g. plot, characters, settings, themes) within and between genres, with some awareness of purpose and effectiveness
Y6
Word Reading: Word Recognition: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RW.1
555
Read / understand meanings of words with affixes
Read and understand the meanings of a wide range of words with affixes, including those with multiple affixes (e.g. unbelievably, irreversibly)
Y6
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.BR NS KS3.1b
556 Confidently infer meanings of unfamiliar words
Confidently infer the meanings of unfamiliar words
Y6
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS KS2.Y5-6.3
556 Confidently infer meanings of unfamiliar words
Confidently infer the meanings of unfamiliar words
Y6
Comprehension: Discussion Skills: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.6
661 Begin to take part in informal debates
Begin to take part in informal debates about books, poems and other works building on own and others' ideas and challenging views courteously
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.3
558 Increase familiarity with a wide range of books
Increase familiarity with a wider range of books, including myths, legends and traditional stories, modern fiction, fiction from our literary heritage, and books from other cultures and traditions
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.1
561 Read an increasing wide range of nonfiction
Read an increasingly wide range of nonfiction (e.g. simple biographies, magazine articles)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.2
563 Read non-fiction with a range of structures
Confidently read non-fiction texts with a range of structural and presentational features (e.g. formal notices, text books)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.2
575 Read in different ways depending on the purpose
Read in different ways depending on the purpose for reading and set task (e.g. rereading relevant sections of text when completing comprehension questions)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.5
Comprehension:
576 Make /organise notes of relevant information
Make notes of relevant information, using simple abbreviations and organise notes (e.g. arranging note cards in order)
Y6
Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.BR KS1.Y2 RC.2.1
580 Synthesise prior knowledge / reading to predict
Synthesise previous knowledge (e.g. knowledge of story setting or topic) and prior reading experience (e.g. knowledge of common themes, story structure, genre conventions) and apply to what has been read so far in order to make a prediction
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.6
590 Discuss author's word choices in literary texts
Discuss the impact of the author's choices of expressive, descriptive and figurative language in literary texts on the reader
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.6
591 Discuss author's word choices in non-fiction
Discuss the impact of the author's choices of expressive, descriptive and figurative language in non-fiction texts on the reader (e.g. \"Readers will be more willing to donate to the charity because of the way the author has described the problems in developing countries.\")
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.3
594 Infer implicit meanings in nonnarrative texts
Make more complex inferences from nonnarrative texts by recognising implicit meanings at sentence and whole text level (e.g. deducing that a journalist is against foxes because of labelling them as 'pests')
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.3
595 Infer implicit meanings in fiction texts
Make more complex inferences, such as inferring characters' feelings, thoughts and motives from their actions, by recognising implicit meanings at sentence and whole text level
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.BR KS2.Y3-4 RC.2.3
600 Justify inferences from non-narrative text
Justify inferences from non-narrative texts with relevant evidence revealing reference (including quotation and / or paraphrase) to more than one section of text
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.3
600 Justify inferences from non-narrative text
Justify inferences from non-narrative texts with relevant evidence revealing reference (including quotation and / or paraphrase) to more than one section of text
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.5
603 Identify key details that support the main idea
Identify key details that support the main ideas in non-fiction texts
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.6
608 Note how organisation affects meaning of fiction
Identify how the organisational features of literary texts can contribute to their meaning (e.g. how the chronology of a novel contributes to its meaning)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.6
612
Identify how structural devices organise texts
Identify how authors use structural devices to organise non-fiction texts, with some awareness of impact and effect on the reader (e.g. how well a headline captures interest and summarises the article content)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.5
614 Identify key details that convey the theme
Identify key details that convey the theme in literary texts
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.5
615
Summarise several sections of story / poem
Summarise the main ideas drawn from several paragraphs of a story / several verses of a poem, identifying key details that support the main ideas (e.g. explain how a theme is developed, illustrating with textual reference)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.5
616
Summarise main ideas from multiple paragraphs
Summarise the main ideas drawn from more than one paragraph of a non-fiction text, identifying key details that support the main ideas
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.5
633 Discuss conventions of a range of non-fiction
Identify and discuss conventions in and across a wide range of non-fiction, and across authors from different periods (e.g. the use of first person in autobiographies, differing conventions in different styles of news reports - online vs. tabloid vs. broadsheet)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.7
633 Discuss conventions of a range of non-fiction
Identify and discuss conventions in and across a wide range of non-fiction, and across authors from different periods (e.g. the use of first person in autobiographies, differing conventions in different styles of news reports - online vs. tabloid vs. broadsheet)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.5
634 Discuss conventions of a range of literary texts
Identify and discuss conventions in and across a wide range of literary texts, and across authors from different periods (e.g. sonnets, war fiction)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.12
639 Explore techniques authors use to develop ideas
Explore how authors develop ideas and themes through the use of language and techniques (e.g. plot devices, changing narrators)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.6
640 Analyse structural features of literary texts
Analyse and compare the main structural features of a wide range of literary texts, using appropriate terminology in discussion (e.g. rhyme patterns, rhythm when discussing poetry; stage directions, scenes, when discussing plays)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS2.Y56.RC.2.6
641 Analyse structural features in nonfiction
Analyse the main structural and organisational features of a wide range of non-fiction texts, using appropriate terminology in discussion (e.g. comparison/contrast, cause/effect, problem/solution when discussing organisational structures)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.12
642 Compare literary texts Compare literary texts, identifying common themes and characters
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS2.Y5-6.12
644 Compare non-fiction texts Compare non-fiction texts, identifying common themes and ideas
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS KS2.Y5-6.6
648 Discuss author viewpoint within / across texts
Discuss author viewpoint within a nonfiction text and across more than one nonfiction text (e.g. compare how different authors treat the same issue)
Y6
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.R.BR NS KS2.Y5-6.6
651
Explain how author's experience affects writing
Explain how literary texts may be written differently by authors with different experiences (e.g. coming of age stories by authors of different cultures)
Y6
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.8
Y6
568
Modify intonation, tone and volume for audience
Modify intonation, tone and volume to communicate clearly to an audience (e.g. develop distinct voices or accents to delineate characters)
Y6
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.BR KS3 R.1.3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.BR KS3 R.1.2
Y6
571
Integrate information from several texts
Integrate information on a topic from several texts to develop a base of knowledge on a subject
578
Choose non-fiction considering purpose / context
Use awareness of purpose and context when choosing non-fiction texts (e.g. use an encyclopaedia/information text to gather factual information rather than a diary or article)
Y6
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.4
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS2.Y56.RC.1.4
625
Discuss personal reading of literary texts
Discuss personal reading of literary texts with others, recommending fiction books and offering reasons and evidence for personal views
626
Discuss reading of non-fiction / recommend books
Discuss personal reading of non-fiction with others, recommending books and offering reasons and evidence for personal views
Y7
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.1
669
Continue to learn and use new vocabulary
Continue to learn and use new vocabulary (e.g. from reading that occurs across the curriculum)
Y7
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS
KS3.4
669
Continue to learn and use new vocabulary
Continue to learn and use new vocabulary (e.g. from reading that occurs across the curriculum)
Y7
Comprehension: Discussion Skills: ELAReading.KS3.SE.1.3
680
Discuss literature; know some debate conventions
Continue to participate in discussion about books, poems and other works, with some awareness of the conventions for structured discussion and formal debate (e.g. taking roles for or against an argument, seconding the main speaker)
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS KS3.1
669
Continue to learn and use new vocabulary
Continue to learn and use new vocabulary (e.g. from reading that occurs across the curriculum)
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS KS3.1
679
Read non-fiction texts for a range of purposes
Read non-fiction texts for a range of purposes, including for interest and information, confidently adapting reading style depending on the purpose for reading
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.3
691
Use context of nonfiction to aid comprehension
Consider and understand the context of non-fiction texts and draw on this knowledge to support comprehension (e.g. relate content of text to the author's purposes and views)
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.BR NS
KS2.Y5-6.6
696 Explain how point of view influences the story
Explain how point of view influences the way the story is told and how the author develops the point of view of the narrator or the speaker (e.g. what the narrative descriptions reveal about the narrator)
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.1
702 Discuss effect of literary / grammar features
Identify and discuss the effect of authors' use of specific literary and grammatical features in literary texts
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.4
710 Understand staging / performing aspects of plays
Begin to be aware of how aspects of performance and staging help to communicate the dramatist's intentions effectively (e.g. by using a modern day setting for a Shakespeare play)
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.3
719 Identify viewpoints / purposes in literary text
Identify and understand the viewpoints and purposes in a literary text, often through overview, with some evidence from the text used to provide explanation (e.g. \"The author uses the characters' experiences to show the different ways that people can show courage.\")
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.3
720 Identify viewpoints / purposes in nonfiction
Identify and understand the viewpoints and purposes in a non-fiction text, often through overview, with some evidence from the text used to provide explanation (e.g. \"The author is strongly against war and uses facts and figures to persuade the reader to agree.\")
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.2
728
Cite multiple sections of literary works
Justify inferences from literary works with key pieces of evidence (by quotation and/or paraphrase) revealing reference to more than one section of the complete text
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.5
730
Compare idea development in texts on same topic
Compare similarities and differences in how facts and ideas are developed in different non-fiction texts on the same topic
Y7
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.2
745 Explore layers of meaning in nonfiction texts
Make more complex inferences, beginning to explore different layers of meaning in non-fiction texts, (e.g. looking at the implicit and explicit messages in advertorials or campaign literature)
Y7
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.6
Y7
673
Study a range of literary authors, some in depth
Study a range of literary authors, some in depth (e.g. Shakespeare)
Y7
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.NS KS3.5
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.1
Y7
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.1.3
Y7
673
Study a range of literary authors, some in depth
679 Read non-fiction texts for a range of purposes
684 Use information from previously read books
Study a range of literary authors, some in depth (e.g. Shakespeare)
Read non-fiction texts for a range of purposes, including for interest and information, confidently adapting reading style depending on the purpose for reading
Revisit books encountered previously in order to use information from texts for a variety of purposes
Y7
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.1
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.1
717
Evaluate literature relative to reading purpose
Identify the purposes for reading literary texts and begin to evaluate the text in relation to these purposes (e.g. comment on how engaging a book is when writing a review)
744
Evaluate the reliability of nonfiction sources
Evaluate the reliability of non-fiction sources (e.g. \"Is the author credible?\")
Y8
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.1
750 Understand vocabulary using context / resources
Use context, dictionaries and technical glossaries to aid in the understanding of new vocabulary (e.g. in subject specific textbooks)
Y8
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS KS3.4
750 Understand vocabulary using context / resources
Use context, dictionaries and technical glossaries to aid in the understanding of new vocabulary (e.g. in subject specific textbooks)
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.1.1.b
754 Read a wide range of fiction
Read a wide range of fiction, including in particular whole books (e.g. Lord of the Flies), short stories, poems and plays with a wide coverage of genres, historical periods, forms and authors, including highquality Shakespearian works
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.1.1.a
759
Study a range of non-narrative styles and topics
Study a greater range of non-narrative styles and topics (e.g. arguments, debates)
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.3
773 Investigate context of text to aid comprehension
Investigate the context of literary texts, and draw on this knowledge to support comprehension (e.g. the wider social context in An Inspector Calls, the context of WW2 in Goodnight Mr Tom)
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.3
782
Analyse how events influence story elements
Analyse how actions and events influence other story elements (e.g. an event: shapes characters, changes setting, delays resolution), using evidence from the text for support
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.1
785 Explain impact of language choice in literature
Explain the effectiveness and impact on the reader of the author's language choices in literary texts (e.g. \"The way the author describes the moor gives the reader a strong sense of fear and suspense.\")
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.1
788
Discuss rhetorical and grammatical features
Identify and discuss a range of literary, rhetorical and grammatical features used by authors in non-fiction texts, and their overall effects on readers
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.7
798 Explain intended effects of structure
Identify how the structure of a literary text creates specific effects and explain their effectiveness in line with the author's intended purpose and audience (e.g. how effective cliff-hangers, build-up and withholding of information are in the creation of suspense)
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.BR NS KS2.Y5-6.6
802 Analyse development / effect of point of view
Analyse how point of view influences the way the story is told, and how the author develops the point of view of the narrator or the speaker (e.g. \"How does the author gradually reveal the narrator's experience?\")
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.2
808 Justify inferences with key pieces of evidence
Justify inferences from non-narrative texts with key pieces of evidence (including quotation) revealing reference to the most relevant sections of text
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.7
818 Describe conventions in a range of literature
Identify, discuss and describe conventions in and across an increasingly wide range of literary texts (e.g. parody and satire)
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.7
819 Describe conventions of a range of non-fiction
Identify, discuss and describe conventions in and across an ever increasing range of non-fiction (e.g. the use of persuasive writing in advertisements and political writing)
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.2
820 Infer / explore layers of meaning in literature
Make more complex inferences, analysing and exploring the detail of different layers of meaning in literary texts (e.g. inferring and explaining the intended meaning of a poem about the endless nature of time)
Y8
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.3
824 Explain author's viewpoint in literary text
Clearly identify the author's viewpoint, with explanation developed through close reference to the literary text (e.g. \"You can tell that the author does not think Erik is a good person, because he describes all the terrible things he's done.\")
Y8
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.NS KS3.5
Y8
754 Read a wide range of fiction
Read a wide range of fiction, including in particular whole books (e.g. Lord of the Flies), short stories, poems and plays with a wide coverage of genres, historical periods, forms and authors, including highquality Shakespearian works
Y8
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.1
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS3.BR
NS KS4.1
Y8
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS3.BR
KS3 R.3.5
Y8
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.1
801 Evaluate texts in terms of their purposes
805 Understand conventions of literary criticism
812 Compare informational texts on the same topic
823 Appraise texts for value, quality or usefulness
Identify the purposes for reading nonfiction texts and confidently evaluate the text in terms of these purposes (e.g. comment on how successfully an article engages and informs its target readership)
Show greater familiarity with the conventions of literary criticism (e.g. by producing several pieces of textual evidence to support a single point with an explanation of their relevance)
Compare emphasis and interpretation in informational texts on the same topic
Begin to appraise non-fiction texts, deciding on value, quality or usefulness (e.g. looking for possible bias and comparing different sources on the same subject)
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.3
849 Analyse how setting affects other elements
Apply knowledge of settings (e.g. key characteristics, context) to analyse how aspects of setting affect plot, characters and theme (e.g. \"How does the setting influence Juliet's choices?\")
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.3
852 Analyse characters' effects on plot and theme
Analyse how authors explicitly and implicitly reveal characters and the effects of this on plot and theme (e.g. \"Explain fully how the author depicts the character's changing views of war.\")
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.BR KS4 R.2.7
867 Evaluate how structure creates effects / impact
Identify how a range of organisational features creates effects in non-fiction texts (e.g. how the author juxtaposes ideas in an argument to give emphasis to one particular view) and evaluate the effectiveness and impact of these choices
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.2
869 Use strongest evidence to justify inferences
Justify inferences from literary works with the strongest relevant evidence
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.4
876
Compare two texts' similar themes and concepts
Compare how two significant non-fiction texts address similar themes and concepts
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.3
877 Analyse choice of plot structures and effects
Analyse the plot structures in a variety of related literary texts and trace how they are developed through authors' choices and explore the effects of these choices (e.g. the effect of plot devices, foreshadowing)
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.4
878 Analyse elements in related literary texts
Analyse elements (e.g. plot, character, setting, theme) in a variety of related literary texts (e.g. texts from the same time period, texts based on a similar theme)
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.1
881
Analyse how literature's form conveys meaning
Analyse how meaning is conveyed differently in literary texts according to the form, layout and presentation selected by the author for specific purposes (e.g. the effect of having alternating chapters with different narrators compared to a text with a single narrator)
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.1
882
Analyse how form / layout convey meaning
Analyse how meaning is conveyed differently according to the form, layout and presentation selected by the author for specific purposes in non-fiction texts (e.g. compare formal biographies of historical figures which use headings and timelines with informal biographies of the same figures which use cartoons)
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.3
886
Analyse differing views / purposes in non-fiction
Analyse and respond to the range of ideas and differing viewpoints, purposes and themes in a variety of related information texts
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS KS3.1
890
Summarize from two or more nonfiction sources
Summarise and synthesise the information, main points and key themes from more than one non-fiction text (e.g. synthesising information about the childhood of a historical figure from two biographies)
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.3.2
893
Recognise / discuss / analyse poetic conventions
Recognise, discuss and analyse a wide range of poetic conventions
Y9
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.2.2
898
Analyse layers of meaning in nonfiction
Analyse, compare and respond to layers of meaning, subtlety and allusion in nonfiction texts (e.g. comparing the way a policy or story is reported in politically polarised newspapers)
Y9
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS3.R.1.3
837 Read a range of non-fiction topics and forms
Read a broad range of non-fiction, with an increasingly wide coverage of topics, historical periods, forms and authors, including high-quality works (e.g. reviews and critiques)
Y9
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts:
ELAReading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.1
840
Read literary texts for a range of purposes
Read literary texts for a range of purposes, applying understanding of these purposes in order to select the most effective reading style (e.g. paying close attention to stage directions when reading a playscript in preparation for a performance)
Y9
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts:
ELAReading.KS3.BR NS
KS2.Y5-6.9
842 Construct a research plan on a particular topic
Construct a plan for conducting research on a particular topic independently
Y9
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts:
ELAReading.KS3.R.1.3
875 Compare previously read literary texts
Make comparisons between literary texts that have been read previously
Y9
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS3.BR
KS4 R.2.1
890
Summarize from two or more nonfiction sources
Summarise and synthesise the information, main points and key themes from more than one non-fiction text (e.g. synthesising information about the childhood of a historical figure from two biographies)
Y9
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts:
ELAReading.KS3.BR NS
KS2.Y3-4.8
905
Use drama to analyse texts and themes
Use a range of dramatic approaches to analyse complex and challenging texts and themes (e.g. create tableaux to encapsulate key moments or themes)
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.1
918 Use appropriate reading style based on purpose
Read for a range of purposes using appropriate reading styles, including close reading of discursive texts, skimming and reading in a non-linear way when checking information in reference books
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.4
929 Analyse effects of character on plot or theme
Analyse the depth (e.g., static vs. dynamic; flat vs. round) of characters and how this affects the plot or theme
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
933 Analyse language choices in literary texts
Across a range of literary texts, analyse how the author's language choices contribute to the overall effect on the reader
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
934 Analyse language choices in information texts
Across a range of reading, analyse how the author's language choices contribute to the overall effect of the information text on the reader (e.g. where the language used suggests a level of unjustified expertise or authority)
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.3
935 Identify multiple themes in literary texts
Identify main and subsidiary themes in a wide range of literary texts
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.3
938 Explain themes in range of information texts
Identify and explain themes, ideas and information in a wide range of non-fiction texts
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.2
939 Interpret themes and ideas in texts
Interpret themes and ideas in texts, considering contexts and influences (e.g. origin of story, bias of author, cultural context)
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.3
939 Interpret themes and ideas in texts
Interpret themes and ideas in texts, considering contexts and influences (e.g. origin of story, bias of author, cultural context)
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.2
960 Evaluate text in cultural and historical context
Draw on knowledge of the context of nonfiction texts, including their social, historical and cultural context, in order to inform evaluation
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
961 Analyse distinguishing techniques of an author
Analyse distinguishing characteristics and techniques used by noted authors (e.g. comparing different works by the same author or different authors)
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
963 Compare and contrast themes in multiple texts
Identify and compare themes across literary texts, considering both similarities and differences between multiple texts
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
964 Compare and contrast multiple non-fiction texts
Identify and compare themes across nonfiction texts, considering both similarities and differences between multiple texts
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
972 Synthesise information from variety of sources
Summarise and synthesise information from a wide variety of non-fiction sources, recognising common threads and differences between them
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
973 Make critical comparisons of literary texts
Make critical comparisons referring to the contexts of literary texts (e.g. the presentation of women in Victorian short stories)
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
976 Compare non-fiction of different eras / traditions
Compare non-fiction texts and authors from different times, cultures and literary traditions, exploring their influence on each other and on culture
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
981 Analyse, compare / contrast literary viewpoints
Analyse, compare and contrast viewpoints and purposes, both within a literary text and between literary texts
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.2
982 Evaluate author's purpose in information text
Begin to analyse/evaluate the author's purpose and how the author's viewpoint is established/managed across an informational text (e.g. tracing how a persona is established in a weekly newspaper column)
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
984 Interpret and compare challenging literature
Analyse, compare and respond to and develop own interpretations of layers of meaning, subtlety and allusion in increasingly challenging literature (e.g. compare attitudes to war in two contrasting poems, inferring attitudes from language, theme, historical allusions or analyse and infer the complex messages and views presented in allegorical novels, such as Animal Farm)
Y10
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.BR NS
KS4.1
997 Show confidence at literary criticism
Show confidence with the conventions of literary criticism by supporting points with precise analysis and evidence and explanation, with deft selection of textual evidence to support the particular point of the essay / argument and referring to other sources to develop or clinch an argument
Y10
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.1.1.a
Y10
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.1.2
913
Re-read to appreciate English literary heritage
Read and appreciate the depth and power of the English literary heritage through rereading literature and other writing
913
Re-read to appreciate English literary heritage
Read and appreciate the depth and power of the English literary heritage through rereading literature and other writing
Y10
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.1.1.c
Y10
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS4.R.3
Y10
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS4.R.3
Y10
914 Appreciate nonnarrative and information texts
920 Acknowledge possible responses to literature
921 Acknowledge possible responses to non-fiction
Read and appreciate the depth and power of the English language through re-reading non-narrative and other information texts (e.g. journalism, biographies)
Identify and acknowledge different possible responses to literary texts
Identify and acknowledge different possible responses to non-fiction texts
Y10
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS4.BR KS3 R.2.3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.SE.1.6
981
Analyse, compare / contrast literary viewpoints
Analyse, compare and contrast viewpoints and purposes, both within a literary text and between literary texts
994 Perform plays and poetry with dramatic effects
Prepare and perform a range of plays and poetry, selecting appropriate dramatic effects and drawing on more sophisticated understandings of character and motive
Y11
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELAReading.KS4.BR NS
KS3.4
999 Use new vocabulary to read, write and speak Make confident use of new vocabulary in reading, writing and speech
Y11
Comprehension: Vocabulary: ELA-Reading.NS
KS4.5
999 Use new vocabulary to read, write and speak
Make confident use of new vocabulary in reading, writing and speech
Y11
Comprehension: Discussion Skills: ELA-Reading.NS
KS4.2
999 Use new vocabulary to read, write and speak
Make confident use of new vocabulary in reading, writing and speech
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELA-Reading.NS
KS4.6
1002 Read texts / poetry from English literary heritage
Read and appreciate the depth and power of the English literary heritage through reading a wide range of high-quality, challenging, classic literature, including whole texts and poetry since 1789, including representative Romantic poetry (e.g. Wordsworth)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.4
1014 Evaluate the impact and relevance of setting
Evaluate the impact and relevance of setting on a work of literature, taking critical knowledge of context and influences (e.g. other literary works, influential authors and thinkers) into account (e.g. \"How successful is Bronte's choice of setting in Jane Eyre in conveying Victorian social prejudices?\"), supporting points with detailed textual reference and analysis
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.4
1015 Interpret aspects of plot in literary texts
Evaluate and interpret aspects of plot (e.g. plot devices, crucial events) in literary texts and their relevance in advancing the plot or developing the theme (e.g. \"To what extent does the death of Tybalt proliferate violence in Romeo and Juliet?\")
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.3
1016 Critique plot choices, including sequence
Critique the significance and validity of the author's plot choices, including sequence of events (e.g. in giving insight to the meaning, theme or message), and evaluate these choices
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.4
1016 Critique plot choices, including sequence
Critique the significance and validity of the author's plot choices, including sequence of events (e.g. in giving insight to the meaning, theme or message), and evaluate these choices
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.4
1019 Evaluate development of characters
Evaluate the author's development of characters in light of genre and the author's intent (e.g. \"Is the author successful in realistically portraying the character's psychological depth?\")
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
1021 Evaluate effect of language in nonfiction
Evaluate how the language used in information texts supports the author's purpose and contributes to meaning
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
1022 Evaluate literary features and their impact
Analyse how specific literary, rhetorical and grammatical features in literary texts shape meaning in implicit and explicit ways to create impact, and evaluate the potential impact of these choices on different readers
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
1024 Evaluate figurative language in literary texts
Analyse and evaluate how language, including figurative language, contributes to quality and impact across a range of literary texts, using appropriate terminology (e.g. phrase, metaphor, irony, persona)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
1025 Analyse figurative language in information texts
Analyse and evaluate how language, including figurative language, contributes to quality and impact across a range of information texts, using appropriate terminology (e.g. phrase, metaphor, irony, persona)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.3
1026 Identify and interpret themes in literature
Confidently identify and interpret themes and ideas in a wide range of literary texts
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.3
1029 Explain purposes of themes in information texts
Explain the role and purpose of main and subsidiary themes in a variety of informational texts
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
1030 Evaluate development of themes in literature
Evaluate the development of themes and ideas in a literary work in light of genre and the author's intent
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
1032 Explain how structural features achieve effects
Explain, comment on and analyse an author's choice of structural features in literary texts, how these achieve specific effects (e.g. suspense or surprise) and evaluate their effectiveness and impact, using relevant subject terminology for this evaluation (e.g. the effect of the author subverting chronology, i.e. starting a story in medias res)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
1033 Explain structural features in nonfiction
Explain, comment on and analyse an author's choice of structural features, how these achieve specific effects and evaluate their effectiveness and impact in a range of non-fiction texts; using relevant subject terminology for this evaluation (e.g. how an argumentative text is structured to engage and convince the reader)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.2
1047 Use knowledge of context to inform evaluation
Draw on knowledge of the context of literary texts, including their social, historical and cultural context, and the literary tradition to which they belong, in order to inform evaluation
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.2
1053 Analyse content and context of literary texts
Analyse, compare and contrast literary texts with insight into their context as well as their content (e.g. the author's perspective on women in Victorian literature, considering the difference in women's rights then as opposed to today)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
1053
Analyse content and context of literary texts
Analyse, compare and contrast literary texts with insight into their context as well as their content (e.g. the author's perspective on women in Victorian literature, considering the difference in women's rights then as opposed to today)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
1054
Analyse content and context of information texts
Analyse, compare and contrast informational texts and sources with insight into their context as well as their content, evaluating their validity and relevance for a range of tasks and purposes
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
1055 Analyse features and impact on different readers
Analyse how specific rhetorical and grammatical features shape meaning in implicit and explicit ways to create impact, how techniques differ across a wide range of non-fiction texts and authors, and evaluate the potential impact of these choices on different readers
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.1
1061 Synthesise and redraft information from sources
Summarise and synthesise information from a range of sources, recognising common threads and differences and redrafting succinctly and appropriately relevant to the purpose
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.1
1062
Synthesise key ideas in order to compare texts
Summarise and synthesise the key ideas and themes from more than one literary text in order to support analysis or comparison (e.g. summarising the use of the theme of magic in A Midsummer Night's Dream and The Tempest to support a comparison between the two texts)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
1064 Critically compare works of literature
Make critical comparisons, referring to the contexts, themes, characterisation, style and literary quality of works of literature, and drawing on knowledge and skills from wider reading
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
1065
Critically compare contexts of nonfiction texts
Make critical comparisons referring to the contexts of non-fiction texts, and draw on knowledge and skills from wider reading
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
1067 Critically compare literary themes and ideas
Critically compare themes and main ideas across literary texts
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
1068 Compare themes / main ideas of informational texts
Critically compare themes and main ideas across informational texts
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.8
1069 Critically compare within and between texts
Make critical comparisons about contexts, themes, characterisation, style and literary quality within and between texts, drawing on critical understanding of the context (e.g. \"Compare the development of character foils in Jane Eyre. How does their development reflect differences in society at the time?\")
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
1072 Compare use of conventions in literary works
Evaluate and compare the use of conventions in and across a wide range of literary texts, including poetry, with critical discussion (e.g. the effect and purpose of various poetic conventions)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.7
1073
Analyse standard and unusual uses of conventions
Analyse, evaluate and compare conventions in and across a wide range of non-fiction texts, noting where texts differ from the standard conventions (e.g. autobiographies written in third person, speculative newspaper articles)
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.4
1074
Analyse narrator's vs. author's point of view
Analyse how the author develops the narrator's point of view, and explain how the author's viewpoint, or implied point of view, differs from the narrator's or speaker's (e.g. use of persona, unreliable narrator, multiple narrators)
Y11
Comprehension: ~ Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.3
1076 Develop interpretations of non-literary texts
Analyse, compare and respond to layers of meaning, subtlety and allusion in a range of increasingly challenging non-literary texts to develop subtle, original and inventive interpretations
Y11
Comprehension: Understanding and Interpreting Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.6
1077 Identify bias and misuse of evidence
Identify bias and misuse of evidence, including distinguishing between statements that are supported by evidence and those that are not
Y11
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.1.1.a
Y11
1002 Read texts / poetry from English literary heritage
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.1.1.c
Y11
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.1.1.b
Y11
1002 Read texts / poetry from English literary heritage
Read and appreciate the depth and power of the English literary heritage through reading a wide range of high-quality, challenging, classic literature, including whole texts and poetry since 1789, including representative Romantic poetry (e.g. Wordsworth)
Read and appreciate the depth and power of the English literary heritage through reading a wide range of high-quality, challenging, classic literature, including whole texts and poetry since 1789, including representative Romantic poetry (e.g. Wordsworth)
Y11
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS4.R.3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS4.BR KS3 R.3.4
Y11
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.1.1.a
1003 Appreciate the depth and power of English
1010 Read literary texts in-depth to discuss opinions
1036 Analyse effective techniques of stage drama
1036 Analyse effective techniques of stage drama
Read and appreciate the depth and power of the English language through reading a wide range of high-quality, challenging, extended literary non-fiction (e.g. essays)
Read literary texts in depth, critically and evaluatively, in order to discuss and explain opinions and points of view
Analyse the range of techniques that great dramatists use to make their work effective on stage (e.g. Shakespeare's use of soliloquy to communicate a character's true motivations to the audience)
Analyse the range of techniques that great dramatists use to make their work effective on stage (e.g. Shakespeare's use of soliloquy to communicate a character's true motivations to the audience)
Y11
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.5
Y11
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.2.5
Y11
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS4.R.3
Y11
1039 Select and cite support for literary analysis
1040 Select and cite evidence in nonfiction texts
1045
Select and cite appropriate evidence and pertinent quotations from literary texts in order to support own views
Select and cite appropriate evidence and pertinent quotations from non-fiction texts in order to support own views
Y11
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS4.R.3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELAReading.KS4.R.1.1.a
Y11
1046
Give an informed personal response to literature
Make informed personal responses to non-fiction
1047 Use knowledge of context to inform evaluation
Make an informed personal response that derives from analysis and evaluation of literary texts
Make an informed personal response that derives from analysis and evaluation of non-fiction texts
Draw on knowledge of the context of literary texts, including their social, historical and cultural context, and the literary tradition to which they belong, in order to inform evaluation
Y11
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS4.BR
KS3 R.2.3
Comprehension: Engaging and Responding to Texts: ELA-Reading.KS4.BR
KS3 R.2.3
1053 Analyse content and context of literary texts
Analyse, compare and contrast literary texts with insight into their context as well as their content (e.g. the author's perspective on women in Victorian literature, considering the difference in women's rights then as opposed to today)
1054 Analyse content and context of information texts
Analyse, compare and contrast informational texts and sources with insight into their context as well as their content, evaluating their validity and relevance for a range of tasks and purposes
Fogarty, R., Kerns, G. M., & Pete, B. M. (2018). Unlocking student talent: The new science of developing expertise. New York: Teachers College Press.
Kirkup, C., Jones, E., Everett, H., Stacey, O., and Pope, E. (2014). Developing National Curriculum-based learning progressions: Mathematics. Slough: National Foundation for Educational Research.
Kohn, A. (1999). The schools our children deserve: Moving beyond traditional classrooms and "tougher standards". Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Lemov, D., Woolway, E., & Yezzi, K. (2012). Practice perfect: 42 rules for getting better at getting better. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Marzano, R.J., Kendall, J. S., and Gaddy. B. B. (1999). “Deciding on ‘Essential Knowledge.’” Education Week, 21 April 1999: 68, 49.
Schmoker, M. J. (2018). Focus: Elevating the essentials to radically improve student learning. Alexandria, VA: ASCD.
Stiggins, R. J. (2005). Classroom assessment for student learning: Doing it right using it well. Portland, OR: Assessment Training Institute.
Stiggins, R. J. (2017). The perfect assessment system. Alexandria, VA: ASCD.
Sawchuk, S. (2020). 5 Tips for Measuring and Responding to COVID-19 Learning Loss. Education Week, 21 June 2020: online. https://www.edweek.org/ew/articles/2020/06/12/5-tips-for-measuring-and-responding-to.html