REMEDIATION OF EMERGING MYCOTOXINS
USING A PREMIUM PRODUCT

Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites produced by fungal species in food and feed materials, mainly Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Penicillium sp.
Commonly, most people think of six main mycotoxins that contaminate feed:
Aflatoxins
Deoxinivalenol (DON)
T-2 toxin
Fumonisins
Ochratoxins
Zearalenone
The primary effects of these toxins on the performance and health of production animals are known and regulatory guidance on threshold levels for these toxins in food and feed materials exist.
Testing and reporting on the prevalence of mycotoxins in feed has increased in recent years, but many continue to go undetected.
Certainly, a topic of growing concern are EMERGING MYCOTOXINS.
Just as DON, T-2 toxin, and zearalenone, emerging mycotoxins are also commonly produced by various Fusarium species.

2
mycotoxins are likely to be frequent co-contaminants in feed with the major mycotoxins (Gruber-Dorninger, C.et al., 2017; Ekwomadu, T. I. et al., 2020).
Research indicates that emerging mycotoxins are rapidly becoming prevalent co-contaminants in feed grains (corn, wheat, barley, etc.) containing other Fusarium mycotoxins (Gruber-Dorninger, C.et al., 2017; Ekwomadu, T. I. et al., 2020; Jestoi, M., 2008).
For example, a recent study found that corn collected from across the U.S. averaged 7.5 mycotoxins with 90.3% and 97.1% of samples contained DON and emerging mycotoxins, respectively (Shike J, 2020a).
Recently corn survey conducted by PATENT CO DOO., Serbia in 2022 also demonstrated higher occurrence of emerging mycotoxins in corn
For more information read
Emerging Mycotoxins - The usual suspects

Fusaric acid

Fusaric acid (FA) is a mycotoxin produced by Fusarium species that has been shown to cause synergistic effects (increased toxicity and potential impact on livestock) in combination with:
Trichothecenes (Fusarium toxins including DON, T2/HT2 toxins, etc.)
Fumonisins
Zearalenone
Aflatoxins
3
Figure 1. Chemical structure of Fusaric acid.
Higher prevalence of Fumonisins and Fusaric acid in 2022 harvested corn
Enniatins
Enniatins (ENNs) are produced by multiple Fusarium molds, including F. avenaceum, F. oxysporum, and F. tricinctum.
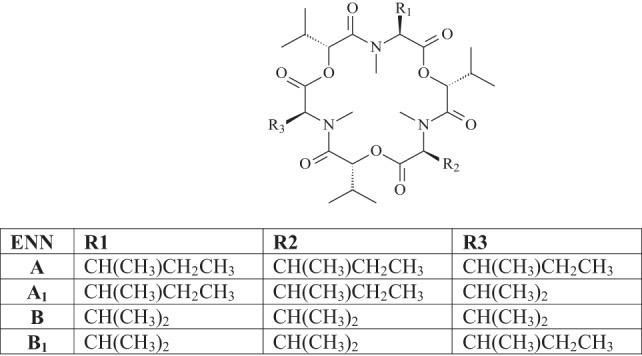

To date, 29 different ENNs have been identified in cereal grains, of which ENN A, A1, B, and B1 are the most frequently detected.

The toxicity of ENNs is based on their ionophoric properties which allow them to transport cations across membranes, thereby disrupting physiological ion levels (Gruber-Dorninger, C. et al., 2017).
Although ENNs are toxic in vitro, research suggests they are rapidly metabolized in vivo, thereby limiting their toxicity (Jestoi,M.,2008).
4
ENN R1 R2 R3 A CH(CH3)CH2CH3 CH(CH3)CH2CH3 CH(CH3)CH2CH3 A1 CH(CH3)CH2CH3 CH(CH3)CH2CH3 CH(CH3)2 B CH(CH3)2 CH(CH3)2 CH(CH3)2 B1 CH(CH3)2 CH(CH3)2 CH(CH3)CH2CH3
Figure 2. Chemical structure of enniatins.
Beauvericin

Like ENNs, the toxicity of Beauvericin (BEA) stems from its ionophoric nature.
Produced by F. proliferatum and F. verticillioides BEA has been found to co-occur with:
ENNs in wheat
Fumonisin B1 in corn
DON, zearalenone, and T-2 toxin in barley (Jestoi, M., 2008)
Although BEA has been observed to accumulate in egg yolks and broilers fed diets containing 2.5 ppm, it did not show a significant decline in performance (Gruber-Dorninger, C. et al., 2017; Ramos et al., 1996).
5
Figure 3. Chemical structure of Beauvericin.
Moniliformin
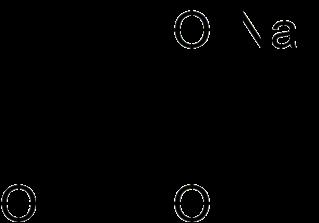
Moniliformin is a highly polar mycotoxin produced by many Fusarium species as well as by Penicillium melanoconidium that inhibits enzymes in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), thereby altering cellular metabolism.
The heart muscle is the primary target of MON in vivo, with poultry exposed to MON showing heart damage, impaired immune function, and decreased performance.
Overall, compared to other emerging mycotoxins, MON is expected to have higher acute toxicity (Jestoi, M., 2008).

6
Figure 4 Chemical structure of Moniliformin.
MycoRaid - An effective ally against emerging mycotoxins

MycoRaid is a premium mycotoxin remediation product developed by PATENT CO for bioremediation of polar and non-polar mycotoxins.
The following report shows the adsorption (pH 3.0) and desorption (pH 6.5) esults of MycoRaid for emerging mycotoxins.
Methodology
Adsorption analysis
In order to test the efficacy of MycoRaid against emerging mycotoxins, 100 mg of the mycotoxin remediation product was added to 15 ml Falcon tubes (test tubes) with:
10 ml of 0.1 M phosphate buffer adjusted to pH 3.0.
2 ppm of the tested emerging mycotoxins: MON, FA, ENN A, ENN A1, ENN B, ENN B1, or BEA.
To measure losses due to non-specific binding and to eliminate exogenous peaks, a control was prepared by adding 10 ml of 0.1 M phosphate buffer at pH 3 and the mycotoxin remediation product to a separate Falcon tube.
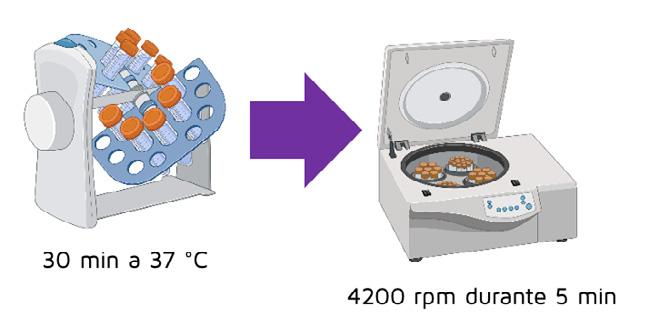
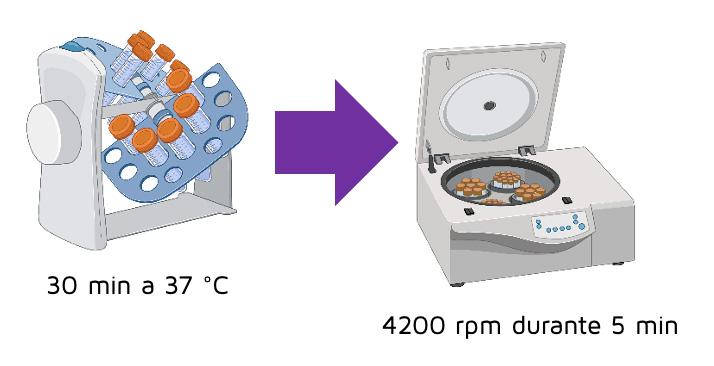
The tubes were placed on a rotator shaker for 30 or 60 minutes at 37 °C. After incubation, the samples were centrifuged (test and control samples) at 4200 rpm for 5 minutes.
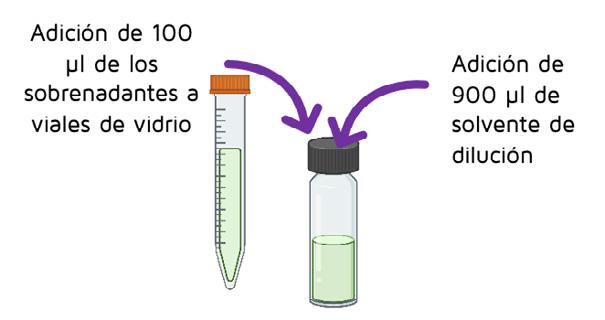
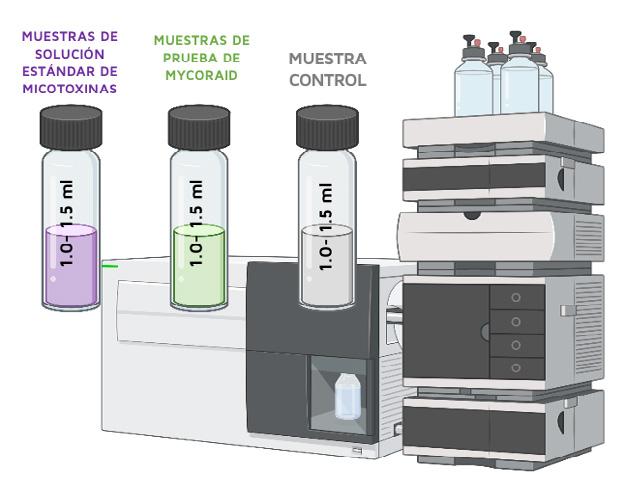
Samples and controls were analysed by LC-MS/MS using an aliquot of the original pH 3 buffered mycotoxin test solution as standard for each mycotoxin.
100 µl of the supernatant was taken to a glass vial where 900 µl of dilution solvent (50% acetonitrile:50% water, and 0,1% formic acid) was added.
7
ADSORPTION ANALYSIS
• 10 ml 0.1 M phosphate buffer
(pH 3)
• 2 ppm MON
TEST TUBES WITH
10 ml 0.1 M phosphate
0 mg MycoRaid
• 10 ml 0,1 M phosphate buffer (pH 3)
100 mg MycoRaid
• 10 ml 0.1 M phosphate buffer
(pH 3)
• 2 ppm FA
• 10 ml 0.1 M phosphate buffer
(pH 3)
• 2 ppm ENN A
l 0.1 M phosphate
0 mg MycoRaid
l 0.1 M phosphate
0 mg MycoRaid
CENTRIFUGATION OF TEST AND CONTROL TUBES
30
• 10 ml 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 3)
• 2 ppm ENN A1
• 10 ml 0.1 M phosphate buffer
(pH 3)
• 2 ppm ENN B
l 0.1 M phosphate
100 mg MycoRaid
l 0.1 M phosphate
0 mg MycoRaid
-60 min at 37 °C Addition of 100 µl supernatants to glass vials
3.PREPARATION FOR LC-MS/MS ANALYSIS















• 10 ml 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 3)
2 ppm ENN B1
• 10 ml 0.1 M phosphate buffer
(pH 3)
• 2 ppm BEA
l 0.1 M phosphate

100 mg MycoRaid
• 10 ml 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 3)
• 2 ppm BEA
100 mg MycoRaid
8
STANDARD MYCOTOXIN SAMPLES MYCORAID TEST SAMPLES CONTROL SAMPLE Addition
4.DETECTION OF MYCOTOXINS IN TEST, CONTROL, AND STANDARD SAMPLES VIA LC-MS/MS 4200 rpm for 5 min
of 900 µl dilution solvent
Desorption analysis
In order to determine the desorption rate of the samples, the supernatant was removed from the remaining sample and control Falcon tubes, and the mycotoxin remediation product pellets were resuspended in 4 ml of pH 6.5 buffer solution.
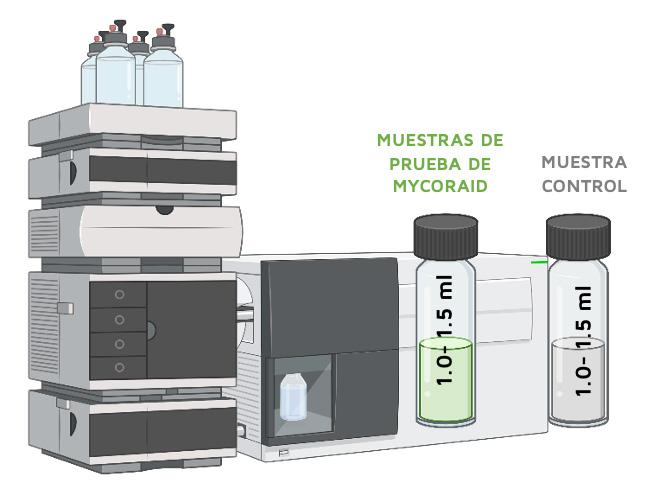

The tubes were placed on a rotator shaker for 30 minutes at 37 °C and, after incubation, the (test and control samples were centrifuged at 4200 rpm for 5 minutes.
500 µl of the supernatant was taken to a glass vial and where 500 µl of dilution solvent (0.2% formic acid in acetonitrile) was added.

Next, approximately 1 ml of the supernatants were pipetted into auto sample vials for LC-MS/MS analysis, and the samples and controls were analysed by LC-MS/MS.
DESORPTION ANALYSIS

1.SAMPLE PREPARATION
4.DETECTION OF MYCOTOXINS IN TEST, CONTROL, AND STANDARD TEST SOLUTION SAMPLES VIA LC-MS/MS
3.PREPARATION FOR LC-MS/ MS ANALYSIS
9
2. INCUBATION AND CENTRIFUGATION OF STANDARD, TEST, AND CONTROL TUBES
30 min at 37 °C 4200 rpm for 5 min Resuspension of pellets with 4 ml of pH 6.5 buffer solution TEST TUBES WITH MYCORAID MYCORAID TEST SAMPLES CONTROL TUBE CONTROL SAMPLE Addition
Addition of 500 µl dilution solvent
of 500 µl supernatants to glass vials
Calculations
The binding efficiency of the mycotoxin remediation product was determined by measuring the concentration of each mycotoxin in the solution and calculating the percentage (%) of mycotoxin bound.
Determination of mycotoxin ADSORPTION rate (%)
The binding efficiency of the mycotoxin remediation product was determined by measuring the mycotoxin concentration in solution and calculating the percentage (%) of mycotoxin bound.
Adsorption (%) = (control HPLC value-sample HPLC value)x100 (control HPLC value)
Determination of mycotoxin DESORPTION rate (%)
In order to calculate the mycotoxin desorption rate:
1. First, the amount of each mycotoxin bounded to the clay (µg) was determined by calculating the difference between the starting mycotoxin concentration at pH 3.0 (m pH 3.0 start) and the ending mycotoxin concentration at pH 3.0 (m pH 3.0 end):
Mycotoxin amount bound to clay (µg) =m pH 3.0 start- m pH 3.0 end where:
• m pH 3.0 start: amount of each mycotoxin in the Falcon tubes with a starting concentration of 20 µg (2ppm)
• m pH 3.0 end: amount of each mycotoxin amount in the Falcon tubes at pH 3.0 after 60 minutes of incubation (µg)
2.Secondly, the final mycotoxin desorption rate was calculated based on the following formula:
Mycotoxin desorbed (%) = ((m DES pH 6.5-m DES pH 6.5 CONTROL) x100) (Mycotoxin amount bound to clay )
Results
The overall efficacy of MycoRaid against emerging mycotoxins is shown in Figure 1.
It was calculated using adsorption and desorption data and the results demonstrate its effective mycotoxin binding capacity.

10
The results in Figure 1 show that MycoRaid can effectively remove 56% of MON, 89% of BEA and more than 95 % of fusaric acid and enniatins.
CONCLUSIONS
Due to lack of information on the toxicity and prevalence of emerging mycotoxins, it is difficult to assess their role on animal health and performance.
However, emerging toxins are likely to co-occur with the major mycotoxins that contaminate grains used in livestock production and, therefore, a remediation strategy should be implemented to reduce the carryover of mycotoxins from animals to humans.

11
% Efficacy Monilformin
100 Mycotoxins tested 80 60 40 56 97 97 97 99 99 89 20 10 0
Figure 1. Efficacy of MycoRaid against emerging mycotoxins.
Fusaricacid EnniatinB Beauvericin EnniatinB1 EnniatinA EnniatinA1
REFERENCES
Gruber-Dorninger, C. et al. (2017). Emerging mycotoxins: beyond traditionally determined food contaminants. J Agri Food chem, 65: 7052-7070.
Ekwomadu, T. I. et al. (2020). Variation of Fusarium free, masked, and emerging mycotoxin metabolites in maize form agriculture regions of south Africa, Toxins, 12(149); doi:10.3390/ toxins12030149.
Jestoi, M. (2008). Emerging Fusarium-mycotoxins fusaproliferin, beauvericin, enniatins, and moniliformin – a review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 48:1, 21-49.
Shike, J. (2020a) Continue testing for Mycotoxins, Pork Business. Available at: https://www. porkbusiness.com/news/hog-production/continue-testing-mycotoxins
Raj, J. et al. (2023). Higher prevalence of Fumonisins and Fusaric acid in 2022 harvested corn, Mycotoxinsite. Available at: https://mycotoxinsite.com/higher-prevalence-fumonisins-fusaric-acid-2022-harvested-corn/?lang=en
Ramos, A.J., Fink-Gremmels, J., and Hernández E. (1996). Prevention of toxic effects of mycotoxins by means of nonnutritive mycotoxin remediation product compounds. J. Food Protection, 59(6):631-641.
12






























