SCIENCE

GLO BAL THINKERS 3
DIGITAL PROjEcT
PRIMARY sample
2










TERM REVIEW 1 PAGE LEARNING EXPERIENCE TAKE ACTION SDG INTERDISCIPLINARY 1 14 Design a school garden to help people understand why plants are important. Life on land lIvInG bEInGs 8 We present all the tools used by people involved in science that will be used throughout the learning experiences. My STEAM TOoLbOx 26 Find out about animals with ‘superpowers’. Teach people to respect and protect them. Make a poster about them. Life below water 2 WE ARE ALl ANImAlS! 44 Create a wall display about a real ecosystem and how to protect it. Life on land 3 LoOkInG AfTEr nATurE! 70 Investigate one of your favourite toys to find out what it’s made from and how it works. Sustainable cities and communities 4 MATTEr ANd ENERgy! 90 Making a map identifying and locating local health centres. Good health and well-being 5 HoW To fInD A pLACE 110 Preparing proposals to enjoy landscapes in a sustainable way, without damaging them. Life on land 6 LANdScApE guARdIANs 138 Preparing proposals to defend and support the creation of safer and more sustainable cities. Sustainable cities and communities 7 CAN wE rEdEsIgN A cITy? Presenting environmentally friendly alternatives to reduce the consumption of natural resources, replacing the materials we use. Quality education 172 200 9 LoOkInG AT hIsToRy Drafting regulations or laws that protect everyone that forms part of our society. 156 8 Do wE wAnT TO cHANgE our lIfE? Reduced inequalities what are we goIng to learn? TERM REVIEW 2 TERM REVIEW 3
• The scientific method
• The project-based method
• Computational thinking
• Characteristics of living things
• Classifying living things
• Characteristics of plants
• General characteristics of animals
• Classifying animals
• Describing and classifying invertebrates
• Ecosystems
• Relationships in ecosystems
• Rocks
• Relief
KNOW HOW TO: LEARN, APPLy AND RESEARCH
• Programming by blocks
• ICT Plan
• Classifying plants
• Nutrition in plants
• Interaction and reproduction in plants
• Describing and classifying vertebrates
• Characteristics of human beings
• Vital functions: nutrition
• Vital functions: interaction
• Types of ecosystems in Andalucía
• Using ecosystems
• Changing ecosystems
• Protecting ecosystems
Competence-based activities
• Vital functions: reproduction
• Healthy habits
Competence-based activities
Competence-based activities
• Steam: Stephanie Kwolek and Maria Sibylla Merian
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · D o you waste food? : Store well, eat we
• Matter
• Physical and chemical changes
• Materials
• Planet Earth
• Seasons
• The globe
• Landscapes
• Inland landscapes
• Coastal landscapes
• Inland Spain
• Machines
• Inventions
• Projects
• World maps
• Using maps
• Types of maps
• Coastal Spain
• Spain’s islands
• Climate and landscape
• Relief in Andalucía
• Video game
Competence-based activities
• Steam: Beulah Louise Henry
• Plans
• Other types of orientation
Competence-based activities
• Taking care of landscapes
Competence-based activities
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · P rotecting marine life : A journey under the sea
• Localities
• Neighbourhoods and streets
• Citizen norms
• Population
• Population changes
• Population in Spain
• The passing of time
• Periods of history
• Prehistory and Ancient times
• The Middle Ages
• Organisation of a locality
• Organisation of a territory
• Andalucía
• Population and employment
• Population in Andalucía
• The Modern Age and the Contemporary Age
• Learning about the past through its remains
Competence-based activities
Competence-based activities
• Cultural heritage
• The history of Andalucía
Competence-based activities
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT · Time flies : The past is important
ANNEX
living THingS 1
I love animals! Some animals are endangered. It is very sad. I don’t like plants. They don’t do anything. They are so boring!

WHAT DO YOU THINK?
whaT Is goINg On arOUND you?

Why are plants important?
Why does Jorge need to learn more about plants? Our planet is in danger. Plants can help stop climate change!

WHAT cAN you do To HElp?

Design your school garden! Help people understand why plants are important.

14
TAKE
ACTIon
14
hoW CAn WE CLASSIFY LIVIng ThIngS?

Characteristics of living things
WHAT do you NEeD To knOW To TaKe aCTIOn? ES hIng’ MEAn?
1
2 Classifying living things
hoW CAn WE CLASSIFY pLAnTS?
Characteristics of plants

3
WhAT ArE pArTS LIKE?
hoW Do pLAnTS InTErACT AnD rEproDUCE?

Nutrition in plants
4 Classifying plants
5
hoW Do pLAnTS gET nUTrIEnTS AnD EnErgY?
6 Interaction and reproduction in plants


15
THINK WhAT DoES ‘LIVIng ThIng’ MEAn?
1 Look, listen and read. Living things perform three vital functions:
Nutrition
Living things eat and transform food into nutrients. Plants make their own food.
Interaction
Living things react and adapt to the world around them.

2 Match each vital function to a sentence in your notebook.

a) We come from other living things.
b) We react to things that happen.
c) We need food to live.
Your turn!
T h E ro B oTIC I n SECTS CASE
1. The brown beetles eat plant waste.
2. The silver beetles don’t eat!

3.The silver beetles stop when they have no energy.





















4.The brown beetles lay eggs.
reproduction
nutrition
Reproduction
Living things can produce similar living things.
interaction
1. They perform the nutrition function!

They are living things!
5.The silver beetles don’t lay eggs. WhAT YoU
LEArnED
All living things perform three vital functions.

16
How many living things can you name? What do all of them have in common? Characteristics of living things 1
ChECK
NOW I KNOW…
How many types of living things do you know?
Where do they live?
1 Look, listen and read. We can classify living things into animals, plants or other living things, like fungi or bacteria.


Living organisms



Other Plants


bacteria
protozoans






2 Classify these into plants, animals or other living things.

daisy pine tree



jellyfish mushroom


Animals
leopard algae

3 In pairs, choose a living thing. Then, ask yes or no questions and guess.
algae fungi ChECK
Yes, it is.
Is it an animal? Has it got legs?



Yes, it has!
4 Make a list of ten living things. In pairs, compare your lists and classify them into plants, animals or other living things.

NOW I KNOW…
Many plants, animals and other living things share our planet.
17
hoW
2
Classifying living things
CAn WE CLASSIFY LIVIng ThIngS?
THINK
WhAT YoU LEArnED
THINK
Have all plants got the same parts?
1 Look, listen and read.
Usually plants are green, they don’t move, they perform photosynthesis and some have got flowers.




Parts of a plant
Leaves
They perform photosynthesis. They can have different shapes.
Stem
It supports the leaves and keeps the plant straight.
strong, hard stem (trunk)
thin, flexible stem

Roots
They fix the plant in the ground and absorb water and mineral salts.
2 Explore. Look for a plant you like. Then, draw it and label its parts.
3 In pairs, compare your drawings. Share your ideas with your classmates.
a) Have all plants got the same parts?
b) How are they similar? How are they different?
c) Do you often see this plant?
d) Which plants do you want to grow in your school?
NOW I KNOW…
Different parts of a plant perform different functions. All of them are important!
Flowers
Flowers help plants to reproduce.
My plant has got stems.
It hasn’t got flowers.
18
WhAT ArE pArTS LIKE? Characteristics of plants 3
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
Calyx. Made of sepals. Pistil
Corolla. Made of petals.
Stamens. They produce pollen.
Classifying plants
hoW CAn WE CLASSIFY pLAnTS?
THINK
How many different plants do you know?
1 Look, listen and read.
Plants with flowers and seeds
Types of plants
Plants without flowers or seeds
2 Look at these plants and classify them.
ivy grapevine orange tree ficus




3 Choose a plant and guess with a classmate.
Has it got seeds/flowers? Yes, it has!
4 In pairs, write a riddle about a plant, like in the example.

I have got a long stem. I have got yellow petals. People eat my seeds. What am I?
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
NOW I KNOW…
Classifying plants can help us protect them.








19
4
Oak trees make seeds inside a fruit.
Fir trees produce seeds that aren’t inside a fruit.
Ferns make spores under their leaves.
Mosses produce spores on thin stems.
Fir tree Ferns Mosses Oak tree
Can plants eat or breathe?
1 Look, listen and read. Plants make their own food. They use light, minerals and carbon dioxide.
Nutrition in plants
1. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
3 The leaves use sunlight to transform substances into nutrients. This process is called photosynthesis.

p LA n T, MAKE Yo U r F oo D!
2. The leaves absorb carbon dioxide.
4. Plants produce and release oxygen it during photosynthesis.
5. Plants respire. They take oxygen and release carbon dioxide.

1 Help this plant make its own food. Put the steps in order.
ROOTS: absorb water and minerals from the soil.
LEAVES: release carbon dioxide from photosynthesis.
STEM: transports water and minerals to the leaves.
LEAVES: use light to turn everything into food.
LEAVES: absorb carbon dioxide from the air.
Go to ‘I'll tell you in a moment’ at anayaeducacion.es to learn about the importance of plants.


2 Discuss with your partner:
a) Have you got any plants at home?
b) How do you take care of them?
c) Do all plants need the same things?
I have got two plants at home.
NOW I KNOW…
Plants perform the nutrition function.
20 5 3 2 4 1
hoW Do pLAnTS
5 Nutrition in plants
THINK
gET nUTrIEnTS AnD EnErgY?
respiration carbon dioxide photosynthesis nutrients carbon dioxide minerals oxygen water oxygen solar energy ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
Computational thinking
THINK
Do plants move? Can they have baby plants?
2
Plants react to the changes around them.
The plant grows and forms flowers.

The pollen reaches the pistil
of a flower.
The seed falls to the graund. Each seed becomes a new plant.




Match the type of interaction in the pictures to the right sentence.
The pistil changes into a fruit. Seeds form inside.





a) They have got spikes for protection.
b) They turn to the sun for more light.

c) They close their leaves when an insect touches them.
3 Write sentences about reproduction in plants. Read them to a classmate. They have to say ‘True’ or ‘False’.

ChECK WhAT

YoU LEArnED

21
1 2 3
hoW
1 Look, listen and read. 6
Do pLAnTS InTErACT AnD rEproDUCE? Interaction and reproduction in plants
Interaction in plants Reproduction in plants
1 2 3 4 5 3 ºC 20 ºC
The pistil changes shape.
Plants also perform the interaction and reproduction functions.
NOW I KNOW…
MY ViSUAL SUMMARY
Living things
We can classify them into
They perform the three vital functions: nutrition, interaction and reproduction
I’m an animal. I eat other living things.
plants animals other living things

They are green and fixed in the ground.
Plants
They make their own food. They have got roots, a stem and leaves.
Parts of a plant

Flowers
This is the reproductive system of many plants.

Leaves
They perform photosynthesis.
Stem

It supports the leaves and keeps the plant straight.
Roots
They fix the plant in the ground and absorb water and minerals.
corolla
My senses detect the grasshopper. I react by sticking out my tongue out.

pistil

stamens calyx
Classifying plants
Plants with flowers and seeds
Plants without flowers or seeds

The seeds aren’t inside a fruit. The seeds are inside a fruit.

22
Mosses
Ferns
Nutrition in plants
The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil. These substances travel up the stem to the leaves.

The leaves absorb carbon dioxide. The leaves use sunlight to transform substances into nutrients. This is called photosynthesis. Plants produce and release oxygen during photosynthesis.


Plants respire . They take oxygen and expel carbon dioxide.
Interaction in plants
Plants detect what is happening and react to changes
You´re trapped!
Reproduction in plants

The pollen reaches the pistil of a flower.
The pistil changes shape.
The seeds fall to the ground. Each seed becomes a new plant. The plant grows and forms flowers.
The pistil changes into a fruit. Seeds form inside.





23
solar energy carbon dioxide carbon dioxide oxygen oxygen minerals water
PHOTOSYNTHESIS nutrients RESPIRATION
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 3 2 1
WhAT hAVE I LEArnED?
1 How do scientists classify new living things? Choose and explain.
a) They compare them with other living things and group them with similar living things.
b) They put them into smaller groups.
c) They make a new group.
d) They classify them without any criteria.
2 Say how these things are similar or different.
a) A fir tree and ferns.
b) A fir tree and an oak tree.
3 Match the function with the words from nutrition in plants.
a) The roots absorb it from the soil.
b) They absorb carbon dioxide.

c) Plants produce it when they perform photosynthesis.

d) The leaves use it to transform substances into nutrients. leaves light oxygen water

4 Complete the sentences:
a) Apple trees produce delicious ••• with ••• inside.
b) Ferns and ••• don’t produce seeds or ••• .

c) Some plants, like pine trees, don’t produce attractive •••. Their ••• are shaped like needles.



5 Make sentences with these words.
a) Senses, react, fixed, movement.
b) Oxygen, respire, living things, photosynthesis, life.
6 What do plants use light for?
7 Classify these living things.

8 Imagine one flower of a plant has got 1 pistil, 4 stamens and 8 petals. Calculate.

a) How many petals are there in 13 flowers?
b) How many stamens are there?
c) All the flowers become fruits, apart from one. How many fruits are there?
9 Draw two plants reacting to changes in the environment. Explain.
10 Investigate three types of fruit. What are their seeds like? Draw them in your notebook.
Don’t forget to complete your photo album at anayaeducacion.es.

Traffic lights. Apply this colour code to each activity in your notebook.
I knew the answer.
I needed help.
I couldn’t answer the question.
24
PORTFOLiO
bacteria fungi plants algae 1 2 3 4 8 7 9 5 6
Design your school garden! Help people understand why plants are important.
1 Think of three to five plants near you. Look for information and photos of each plant. Use these questions as a guide.
a) Where does it live in nature?
b) What does it look like?
c) How does it reproduce?
d) Has it got any special characteristics?
e) Does it provide food, materials or medicines?
Some ideas
• Plants give us oxygen, filter the air and improve the environment.
• Plants provide food, materials and medicines.

2 Draw a map of the school. Design your garden to help protect the plants on your list. Use pictures and bright colours.
3
Do you think plants are boring now? Copy and complete the ‘Before, I thought…’, ‘Now, I think…’ organiser with your thoughts.

Before, I thought… Now, I think… Reasons
What did I think about plants before?
hoW hAVE I LEArnED?
What do I think now? Why did my opinion change?
1 Some things in this learning experience are easy to learn and some things are difficult. Write the three most difficult things to learn and explain why in your notebook.
2 You know more about living things now. What living things from the learning experience do you find interesting or strange? Explain. Say what other things you want to learn about them.
Most difficult to learn Reasons
25
WE ARE ALL ANIMALS!
I love animals! They are part of ecosystems. It is important to respect and take care of them.

WHAT DO YOU THINK?
Why do you think animals have got wings, gills and claws?

Imagine an animal’s habitat disappears. Do you think it can live in a different place?
whaT Is goINg On arOUND you?
More than 5 000 animal species are in danger of extinction. Their habitat is disappearing or changing.
WHAT cAN you do To HElp?
Find out about animals with ‘superpowers’. Teach people to respect and protect them. Make a poster about them. TAKE ACTIon


26
2
14
WhAT TYpES oF AnIMALS ArE ThErE?
WHAT do you NEeD To knOW To TaKe aCTIOn?
1 General characteristics of animals

2 Classifying animals
3 Describing and classifying invertebrates
WhAT AnIMALS ArE LIKE US?
4 Describing and classifying vertebrates
5 Characteristics of human beings
hoW Do WE pErForM ThE nUTrITIon FUnCTIon?
6 Vital functions: nutrition
7 Vital functions: interaction
hoW Do WE pErForM ThE rEproDUCTIon FUnCTIon?



hoW ArE AnIMALS?
InVErTEBrATES: onLY InSECTS?

ArE WE A SpECIAL TYpE oF AnIMAL?

hoW Do WE pErForM ThE InTErACTIon FUnCTIon?
8 Vital functions: reproduction


9 Healthy habits
WhY IS hEALTh IMporTAnT?

27
How are animals and plants different?
1 Look, listen and read.
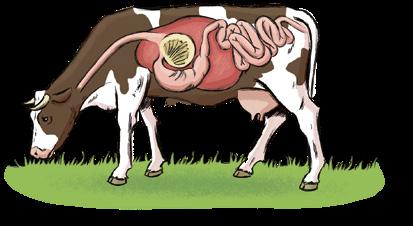
Animals are living things. They feed on other living things. They have got special body parts to perform the vital functions.
Nutrition function
Animals feed on living things. Their digestive system processes the food.
Animals use their respiratory system to breathe.

Animals use their senses to detect changes around them.

Interaction function
Their nervous system makes them react.
They use their muscles to react.
The respiratory system distributes substances around the body.
system under water
Reproduction function
Animals use their reproductive system to have babies.
They lay eggs.
2 Which of these animals breathe air? Which ones breathe under water? Copy and complete the table in your notebook.
sardine Breathe air Breathe under water

dolphin

3
fly human being
Mime three animals. Your classmate says the name. They also say gives birth or lays eggs.
NOW I KNOW…
Animals use different body parts to perform the vital functions.





They give birth.
It’s a dog! It gives birth to puppies.
28
hoW ArE AnIMALS? General characteristics of animals 1
t HINK
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
air
Classifying animals
WhAT TYpES oF AnIMALS ArE ThErE?
t HINK
Have you got bones in your body?
1 Look, listen and read.

We use the presence of a skeleton to classify animals into two large groups:

Vertebrate animals

They have got an internal skeleton with a backbone.
2
Invertebrate animals


They haven’t got an internal skeleton or a backbone.
Are these animals vertebrates or invertebrates? Tell a classmate.
bird kangaroo butterfly snail


1 Use these things to classify the animals in the drawings. Make a table.
a) Number of legs.
b) Colour.
c) How scary they are.
d) Their size.
e) Skeleton or no skeleton.
f) How they move.
ladybird lizard
ant bee
2 Which things are similar? Which things are very different?
3 Which classifications are useful? Which ones are scientific?
Go to ‘I'll tell you in a moment’ at anayaeducacion.es to learn how animals adapt to their environment.

dogs
bird duck
fish

NOW I KNOW…
Vertebrates have got a backbone.
Invertebrates haven’t got a backbone.
29 Your turn! CLASSIFYI ng T h E A n IMALS I n T h
2
ECK AT YoU rnED
onLY InSECTS?
t HINK
Can you name five invertebrate animals?



1 Look, listen and read.
Invertebrates have got soft bodies. Many have got hard, external structures for support and protection called exoskeletons. Most animals on Earth are invertebrates. These are some of the groups of invertebrates:

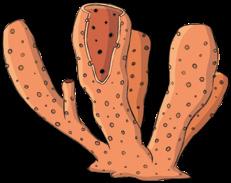
Sponges
They are aquatic. Their bodies have got holes called pores.
Jellyfish and polyps (cnidarians)
They are aquatic. They have got poisonous tentacles.
jellyfish

Arthropods

They are aquatic or terrestrial. Articulated exoskeletons cover their bodies. They have got a head, and some have got wings.

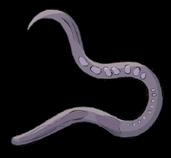
Worms
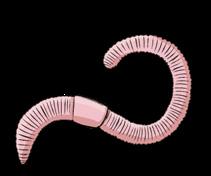
They are aquatic or terrestrial. They long, thin


Echinoderms

polyp

They are aquatic or terrestrial. Many have got shells.
They are aquatic. They have got different shapes: discs, cylinders, spheres and stars. Hard plates or spines cover their bodies.




30
Describing and classifying invertebrates 3
InVErTEBrATES:
millipede beetle spider wasp crab
sea urchin
Molluscs snail sea slug slug mussel
Write the invertebrate group for each animal.



3
What are the similarities and differences between jellyfish and crabs?





Crabs have got legs.

I n VE rTEB r ATES on T h E FIS h Co U n TE r
Imagine you are at the fish counter. There are many aquatic invertebrates. But, there are no labels with their names.
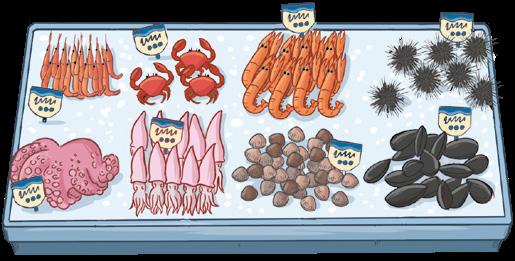

1 Use the key to classify them into groups and name them.
NOW I KNOW…
There are different types of invertebrates. Some have got shells, others have got spikes, but none of them have got a backbone!
31 2
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
wasp
earthworm crab starfish
mussel ladybird cuttlefish
crab
1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 Legs and an articulated exoskeleton ARTHROPODS SHRIMP CRAB LOBSTER Long body No legs Ball-shaped shell with spines ECHINODERMS SEA URCHIN MOLLUSCS Shell No shell Large head Eight arms Long body with arms Smooth and black COCKLE OCTOPUS SQUID MUSSEL No spines Light and rough No claws Two large claws Oval body Your turn!
jellyfish
WhAT AnIMALS ArE LIKE US?
t HINK
Can you name five vertebrate animals?



1 Look, listen and read.
The skeleton of most vertebrates has got bones. All vertebrates have got a backbone.

They have got a head, a trunk and limbs.
These are some of the groups of vertebrates:
Fish
They are aquatic. They breathe under water. They lay eggs.
scales
Reptiles

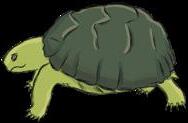
Amphibians

They are aquatic and terrestrial. They breathe air and under water. Most lay eggs.

Newt. Has got a tail.
They are aquatic or terrestrial. They breathe air. They lay eggs.
tortoise
scales four legs
Snake. No legs.
Birds
They are terrestrial. They breathe air. They lay eggs.
Penguins swim.
feathers
wings
Mammals

Ostriches don’t fly.

Frog. No tail.
thin, wet skin
fur
They are aquatic or terrestrial. They breathe air. Most give birth. They drink


mother’s milk.
Bats fly. Platypuses lays eggs.

32
Describing and classifying vertebrates 4
fox
fins
Choose a vertebrate animal. Describe its characteristics. Your classmate says the animal and the vertebrate group.


It has got two legs.
Is it an ostrich?
No, it isn’t!
3 Correct these sentences in your notebook. In your notebook, match each sentence to a picture.
a) All mammals have got fur.
b) Amphibians live in water.

c) Fish breathe air.
d) All birds can fly.
e) Reptiles give birth.

penguin dolphin frog

Dédalo is studying the backbone to build a bridge.

1 Do you want to work in biomimetics? Do this experiment and answer the questions.
a) Which model can hold more weight? A or B?
b) What is the function of the backbone in vertebrates?

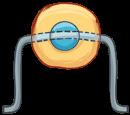

c) Imagine you want to make objects with artificial backbones. What can you make?
NOW I KNOW…
33 2
EX p E rTS I n BI o MIMETICS!
There are different types of vertebrates. Most of them have got bones. They all have a backbone. ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
A B
fish snake
Your turn!
Hi! My name is Dédalo. I am an expert in biomimetics. Aeroplane wings are a copy of bird wings. That’s an example of biomimetics!
How are we similar to other animals?
1 Look, listen and read. Human beings are vertebrates and mammals. We are part of a group of mammals called primates.

I’m a primate because I have got…
A face with eyes in the front.
A big and complex brain.
I’m different from primates because…
I’m more intelligent.
I have got less body hair.

I have got hands that can manipulate objects.
I walk on two legs.
2 Why are human beings mammals? Why are human beings primates? Explain.
3 Why are humans more intelligent than other primates? Tell a classmate five things we can do but other primates cannot.
What can we do that primates can’t?
ro
B oTS or A n D ro IDS?
We can read!
Automatic machines called robots are a human invention. An android is a robot that looks like a human being.
1 What type of robot is an android?
2 Can it do things that other robots can’t?
Hello! I’m a very advanced android.
Wow! Cool!
NOW I KNOW…
Human beings are vertebrates and mammals. We are a special type of primate.

34
HINK ArE WE
SpECIAL TYpE oF
5
t
A
AnIMAL? Characteristics of human beings
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
Your turn!
What happens when you eat an apple?
1 Look, listen and read.
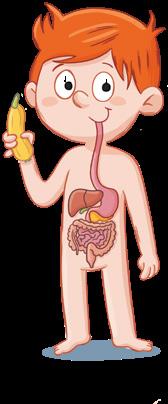
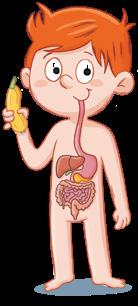
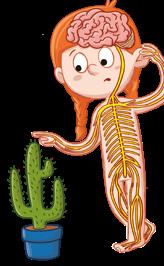
Like all living things, humans perform the nutrition, interaction and reproduction functions. We have got special body parts to perform these. Systems in the nutrition function
Digestive system
mouth
oesophagus
stomach
intestines
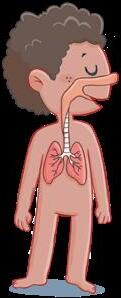
Respiratory system
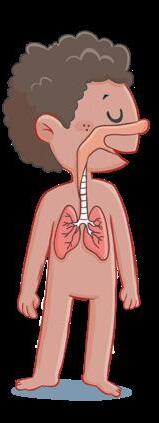
2
We use it to breathe. We inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide.
nasal passages
larynx
trachea
lungs
We use it to eat and drink.
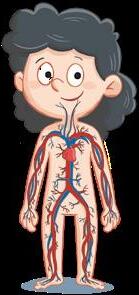
Heart.
Circulatory system
It moves substances around the body.
The heart pumps the blood.
Blood circulates along the blood vessels.
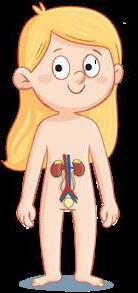
Excretory system
The kidneys produce urine.
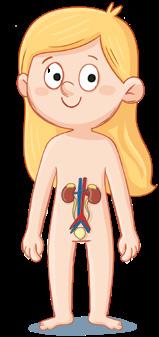
It expels waste.
What are the body parts of the systems involved in the nutrition function? Ask a classmate.
What have you got in your circulatory system?
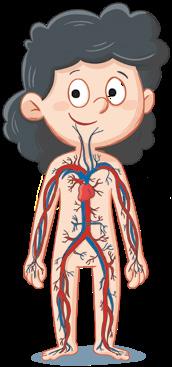
I have got a heart, blood vessels and blood.
The skin produces sweat.
3 Think about what you eat. Which animals are similar to us? Animals that eat plants, that eat meat, or both?
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
NOW I KNOW…
Human beings perform the three basic functions. There are four systems in the nutrition function.
35
t HINK hoW Do WE pErForM ThE nUTrITIon FUnCTIon? Vital functions: nutrition 6
Vital functions: interaction
t HINK
What do you use the five senses for?
1 Look, listen and read.
Systems in the interaction function
Send information.
Sends instructions.
They detect changes around us. It processes the information from the senses and interprets it. It receives the information and reacts with movements.
2 What performs these functions? Tell a classmate.
a) It processes information and sends instructions to the body.

b) It reacts to information with movements.
c) They detect changes in the environment.
A DIA gr AM o F T h E I n TE r ACTI on FU n CTI on
1 Look at this example of a diagram. Now, draw one to show the interaction function of a person eating.
Go to ‘I'll tell you in a moment’ at anayaeducacion.es

NOW I KNOW…
The senses as well as the nervous and locomotor systems are part of the interaction function.
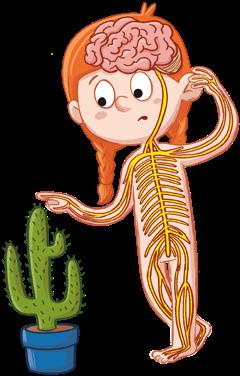
36 hoW Do WE pErForM ThE InTErACTIon FUnCTIon?
7
Locomotor
Senses
system
sight smell taste hearing touch
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
brain skeleton muscles nerves Computational thinking I choose a store I BUY IT Yes Yes No Is it in my budget? Have they got the shirt I want? No
Nervous system
t HINK
What is your date of birth?
1 Look, listen and read. Human beings give birth to babies. We call them children.
Stages of life
Human babies develop in the mother’s reproductive system. Then, they are born.

old age
2 Match these descriptions to the ‘Stages of life’ pictures.
We don’t walk. We drink milk and grow quickly. We get our first teeth.
Our body changes a lot. We become independent.
Our body doesn’t change a lot. We have got experience and can start to have children.
3
Our body changes again. We do things more slowly. We have got a lot of experience.
We grow a lot and learn from our family. Our adult teeth appear.
Ask members of your family their age. In what stage of life are they? Tell a classmate.




NOW I KNOW…
Our mother gives birth to us. The stages of life are infancy, childhood, adolescence, adulthood and old age.

37 Vital functions: reproduction hoW Do WE pErForM ThE rEproDUCTIon FUnCTIon? 8
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
function
system 1 5 4 3 2 childhood adulthood infancy
Reproduction
Reproductive
adolescence
Pregnancy
t HINK
Have you got a healthy diet?
1 Look, listen and read.

Eat well, drink water and breathe clean air


What can we do to stay healthy?

Be happy

38
Healthy habits 9
WhY IS hEALTh IMporTAnT?
Do exercise
and surroundings clean Sleep 8 to 10 hours a day
Keep your body
BEI ng h EALT h Y IS noT DIFFICULT!
Read the things this girl does to stay healthy.
I don’t eat many sweets.
I brush my teeth.
1 Think of three more things you do to have a good hygiene and eat healthy. Make flashcards. Add a drawing or a picture.

2 Show your flashcards to your classmates. Explain what you do to stay healthy.
3 Read the tips this doctor gives to the girl and answer.

I drink four to five glasses of water a day. I don’t go to smoky or dusty places. Have regular health checks.

I eat five pieces of fruit every day. My favourite fruit is watermelon.

Don’t do things that are dangerous for your health.
Have vaccines to fight illnesses.
What things can be dangerous for your health?
What parts of your body does the doctor examine in health checks?
Ask which vaccines you have got. Have all your classmates got the same ones?
NOW I KNOW…
There are many things we can do to keep our body healthy.
39
ChECK WhAT YoU LEArnED
Your turn!
MY VISUAL SUMMARY
Animals
They perform the vital functions


We classify them into invertebrates (no backbone) vertebrates (with a backbone)













Some types of invertebrates

Sponges Jellyfish and polyps


Some types of vertebrates




Molluscs


Worms



Reptiles

Birds


Mammals

40
vertebrates
Human beings
are
mammals
The nutrition function
The digestive system
The respiratory system
primates
The circulatory system
The excretory system
The interaction function
Senses
The reproduction function
The reproductive system performs this function. We give birth to babies.

Nervous system

Locomotor system
Health is important
For your body to work correctly:
Eat well Keep your body and surroundings clean
Sleep 8 to 10 hours a day
Be happy
Do exercise

41
PORTFOLIO
WHAT HAVE I LEARNED?
1 Imagine you meet aliens. How can you explain what an animal is? Write a simple explanation.
2 What do these animals eat? Put them into groups: wolf, grasshopper, mouse, eagle, chimpanzee, sheep.
3 Are there more vertebrates or invertebrates in the world?
4 Compare an ant, a crab and a tarantula.
9 Classify these vertebrates into the correct group.


a) How many legs has each one got?
b) How are they different?
c) How are they similar?
5 Say the name of these insects:
a) It has got four big, colourful wings. It drinks nectar from flowers.
b) It has got a round body. Hard, red wings with black spots protect its body.




6 Make a table with the five groups of vertebrates. Write two characteristics and two examples for each group.
7 Some animals can fly. In which groups of invertebrates and vertebrates can we find them? Give examples.


8 Think of two vertebrate and two invertebrate animals. What food or materials do we get from them?

10 Human beings are mammals.
a) Why are we mammals?
b) Write the names of four mammals in your notebook.
11 Match in your notebook. Systems: excretory, respiratory, digestive, circulatory.
Functions:
a) Moves substances around the body.
b) Expels waste.
c) Processes food and water.
d) Obtains oxygen and expels carbon dioxide.
12 Choose one health tip. Explain why you think it is important.
Don’t forget to complete your photo album at anayaeducacion.es.

Traffic lights. Apply this colour code to each activity in your notebook.
I knew the answer.
I needed help.
I couldn’t answer the question.
42
A F D B
tarantula
ant
crab
Find out about animals with ‘superpowers’. Teach people to respect and protect them. Make a poster about them.

Some animals have got the ‘superpower’ to regenerate parts of their bodies. For example, starfish can regenerate their arms.

1 Investigate. What other animals have the ‘superpower’ of regeneration? Copy this table in your notebook. Complete it with information about your animal.
I see I think I ask
What body part can it regenerate? Why do you think it can regenerate that body part? What questions have you got that you can’t answer?
2 Is your animal or its habitat endangered? Investigate.
3 Make a poster of your animal. Include pictures, information about its regeneration and its habitat. Is it endangered? Explain why. Tell your classmates about it.
hoW hAVE I LEArnED?
1 Think about what you learned. Copy and complete these sentences in your notebook.
a) I like learning…
b) I don’t like…
c) It is difficult to…
d) It is fun and easy to…

2 Tell your classmates what you think.
a) Are there ‘good’ and ‘bad’ animals?
b) Do we respect the animals around us?
c) How do I act with animals now?
43
LOOKING AFTER NATURE!
When one part of an ecosystem disappears, the entire ecosystem suffers the consequences.


WHAT DO YOU THINK?
What living and non-living thigs are there in the picture?

How can humans damage
WHAT Is GOING On arOUND you?
All living things depend on other living things. Squirrels need trees to live in and humans use many natural resources.

WHAT cAN you do To HElp?
Create a wall display about a real ecosystem and how to protect it.

44 3 15
TAKE ACTIon
wHaT do you NEeD To knOW To TAkE aCTIOn?
Ecosystems
1
HoW Do LIVInG THInGS InTErACT WITH THE ECoSYSTEM?
2
Relationships in ecosystems
WHErE Do LIVInG THInGS LIVE?
Rocks
3
WHAT roCKS SHApE THE rELIEF?

4 Relief
5 Types of ecosystems in Andalucía


HoW Do HUMAnS InTErACT WITH ECoSYSTEMS?


6
Using ecosystems
WHAT ArE THE non-LIVInG THInGS In An ECoSYSTEM LIKE?


Changing ecosystems
7


HoW CAn WE TAKE CArE oF ECoSYSTEMS?
8 Protecting ecosystems
WHAT ArE THE MAIn ECoSYSTEMS In AnDALUCÍA?
HoW Do WE DAMAGE ECoSYSTEMS?
45
WHErE Do LIVInG THInGS LIVE?
Can living things exist without their environment?
1 Look, listen and read.
An ecosystem is all the living things in a place, and the environment where they live.


Living things interact with the environment and with each other.
An ecosystem consists of living things

the relationships between all these elements
2 Look at the pictures above and answer.

a) Name the living things in the ecosystem.
b) Name the elements in the environment.
c) What non-living things do these living things need?

In pairs, choose a living or a non-living thing. Then, ask yes or no questions and guess.

zebra water air

snake tree sun


grass eagle rock
NOW I KNOW…
Have you got fur/legs/wings/ beak/leaves?
Are you big/ small/green/hot/ cold/hard/soft?

Animals, plants and other living things cannot live alone. They all depend on other living things.

Yes, I have. / No, I haven’t.
Yes, I am. / No, I’m not.
CHECK WHAT YoU LEArnED
3
1 Ecosystems 46
THINK
wildebeest grasses gazelle acacia zebra air soil sun water
non-living things
Relationships in ecosystems
HoW Do LIVInG THInGS InTErACT WITH THE ECoSYSTEM? 2
How do living things interact with other living things?
1 Look, listen and read. There are different types of relationships between the living things in an ecosystem. The most important ones are feeding relationships.
Food chains represent who eats who in an ecosystem.
Plants are food for the grasshopper.
The grasshopper is food for the lizard.



The lizard is food for the eagle.

1 Look and do the activities.
Squirrels live in trees.
Materials
• A ball of yarn • Cards with living and non-living things
Ants build anthills in the soil. Bees take pollen from one flower to another.


Squirrels eat fruit from trees.
Squirrels and birds drink water from the pond.
Plants use light to make food.
a) Copy and colour the pictures in your notebook. Read the clues and draw lines to connect them.
b) Classify them into living and non-living things.
c) Show the relationships in this ecosystem. You need a ball of yarn and cards. Go to ‘We are all connected’ at anayaeducacion.es





Go to ‘I'll tell you in a moment’ at anayaeducacion.es to learn more about the relationships between the living things in an ecosystem.
Birds eat insects (ants and bees).

Plants get water and mineral substances from the soil.
Squirrels are living things.

CHECK WHAT YoU LEArnED
NOW I KNOW…
All the living things in an ecosystem interact.
47
rYTHI
THINK EVE
n G IS Conn ECTED
squirrel ant pond tree soil bee sun bird
Your turn!
WHAT ArE THE non-LIVInG THInGS In An ECoSYSTEM LIKE?
What non-living things can you find in nature? THINK
1 Look, listen and read. Some of the non-living things in an ecosystem are the air, the sun, climate and rocks. Rocks form the ground we live on. Rocks have got different shapes, colours and sizes. They appear in different ways in nature.
Types of rocks
It is very hard. Its components are black, white and pink.
It is hard. It is usually grey or black. It has got layers.
It is a volcanic rock. It is very hard. It can be grey or black.
2 Read the definitions and match them to the correct rock.
a) It is usually grey or black. It has got layers.
b) It is very hard. It has got three different components.
c) It can contain fossils.
d) It is a volcanic rock and it is very hard.

What are the differences between marble and obsidian? Look at the pictures and describe them.



What is marble like?
Marble is white/black. It is hard/medium-hard/soft.

It is medium-hard. It can be white, grey or brown. It can contain fossils.

3 Rocks 48
3
Granite
Slate Basalt Limestone
marble obsidian
basalt
slate
limestone granite
Rocks contain minerals. There are many different types of minerals. They can have different shapes, brightness, hardness and colours.










1 Look and match the properties to the correct mineral.

a) It is very hard.
b) It has got geometric shapes.
c) It is shiny.
d) It is soft.
e) It is yellow.
2 We can make objects using rocks and minerals. Look at the pictures and complete the sentences with the correct words.
a) We can use ••• for ••• .
b) We can use ••• for •••
c) We can use ••• for ••• .
d) We can use ••• for ••• .
Minerals


Uses
Choose a mineral or a rock. Then, ask questions and guess.
Is it smooth/rough?
It’s green/yellow/black.
Is it hard/soft?
It shines. / It doesn’t shine. CHECK
We can find different types of rocks and minerals in nature.
49 ro CKS A n D MI
E
n
r ALS
4
WHAT
LEArnED
YoU
pyrite diamond sulphur talc quartz furniture sculpting jewellery building slate limestone diamond granite Your turn!
NOW I KNOW…
WHAT roCKS SHApE THE rELIEF?

THINK
Why are rocks so important?
1 Look, listen and read. The different types of rocks in an ecosystem determine the landforms in the area. Relief is all the landforms in an area.
Different rocks form different types of relief


We can find granite in mountains. It usually forms big round blocks.



We can also find smaller blocks of granite. They’re formed by the action of cold.
volcanoes.
4 Relief 50
Granite
Basalt
Slate
The rocks above the water come from
Basalt can form columns.
Slate forms landscapes of thin layers of dark rock.
Slate can form layers with other rocks, like limestone.
Paste or draw three pictures of granite, basalt, slate and limestone reliefs in your notebook. Write a brief description of the landscapes.

• Now, choose one and say why you like it.
Basalt landscapes are my favourite ones.
Why do you like them?
Because they are beautiful.
NOW I KNOW…
Rocks shape the relief and determine the type of ecosystem.




CHECK WHAT YoU LEArnED

51 2
Match the rock with the type of landform.
Limestone forms thick layers. Water erodes them, forming landscapes.
Limestone
3
1 3 2 4
Limestone can create huge vertical cliffs.
basalt
slate limestone
granite
5 Types of ecosystems in Andalucía


WHAT ArE THE MAIn ECoSYSTEMS In AnDALUCÍA?
THINK
How many different ecosystems can you identify near you?
1 Look, listen and read.
Ecosystems can be terrestrial or aquatic. In natural ecosystems, there is no human intervention. In artificial ecosystems, humans change the environment.
Types of ecosystems in Andalucía
2
Plants: holm oaks, cork oaks, rockrose and rosemary.
Animals: insects, dormice, rabbits, deer, wild boars, birds and lynx.

Marsh
Plants: rushes and reeds.
Animals: aquatic birds (ducks and cranes), fish and invertebrates.

Plants: glasswort, houseleek and sandwort.
Animals: aquatic birds, fish, jellyfish, crabs, starfish, sea urchins and octopuses.

Plants: holm oaks and pasture.


Animals: birds of prey, reptiles, amphibians, and farm animals, such as pigs.

Choose a forest, a marsh, a beach or a dehesa near you and draw it. Name the animals and plants you can see. Draw a food chain. Then, describe it to a classmate.
The animals/plants in this ecosystem are rabbits/ crabs/rushes/pastures...

52
Dehesa
Beach Mediterranean forest
TY p ES o F ECo SYSTEMS
We classify ecosystems by the type of environment. Ecosystems can be terrestrial or aquatic.

1 Look at the pictures and answer the questions.
A terrestrial ecosystem: a forest.
An aquatic ecosystem: a pond.
a) Draw a food chain for each ecosystem. Include at least one plant and two animals.

b) Why are those ecosystems terrestrial and aquatic? Explain your answer and describe them to a classmate.
c) Look at the pictures below. Do the animals live in terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems?

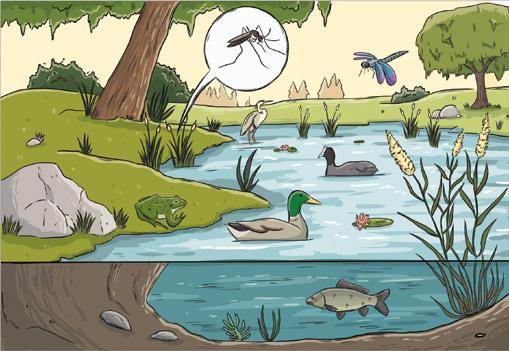
The animals in aquatic ecosystems live in water.


turkey

spider

squirrel

lobster
seal

lynx

squid
Go to ‘Terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems’ at anayaeducacion.es

CHECK WHAT YoU LEArnED
NOW I KNOW…
There are many different ecosystems, like rivers, ponds and forests.
53
wild boar jellyfish
Your turn!
HoW Do HUMAnS InTErACT WITH ECoSYSTEMS?
THINK
What things can you get from nature?
1 Look, listen and read.
Natural resources are the things that we use from nature.

What do ecosystems give us?
2
Food

We get food from farming and fishing.
Water Land

We need water to drink and for sailing, irrigation, washing and energy.


Raw materials
We use rocks, wood, wool, cotton and other materials to make things, and for medicine and energy.

What do we use these resources for?
sunlight
cotton
sheep
We use land for building houses and roads, and for farming.

Well-being
We use ecosystems for exercise. We admire their beauty, and we do activities in them.
What do we use cotton for?
We use cotton for making clothes.
oil
lettuce
trees gardens
Ecosystems can be urban, like cities. Name five living things you can find in an urban ecosystem.
3
6 Using ecosystems 54
MY SUSTAI n ABLE CITY Co M p ETITI on !
I take care of forests!
Hi! I’m Esther. I’m a forest engineer. I make plans for using natural resources without damaging the environment. I plan how to prevent fires, collect and use wood, etc.

I build sustainable cities!

Hi! I’m Roberto. I’m a town planner. I make the urban ecosystem a nice place for living things. I plan where to put houses, roads, parks, offices, etc.


Step 1
Imagine you are Esther or Roberto.
What can you do to improve your city?
Step 2
What natural resources do you need to make the changes?
Represent your ideas. You can use modelling clay, drawings, videos, anything you want!
Step 3
Present your sustainable city to your classmates. Vote for your favourite. Build the best project!
CHECK WHAT YoU LEArnED
NOW I KNOW…
55
We get food, water, land, raw materials and well-being from nature. Your turn!
HoW Do WE DAMAGE ECoSYSTEMS?
THINK
Are there any damaged ecosystems near you?
1 Look, listen and read.
When we take natural resources from the environment and use them, we change ecosystems.
We damage ecosystems when we…
… use all the resources. … cause pollution. … occupy lots of space.
When we consume resources too fast, they can’t recover. This is called over-exploitation.

Human activities pollute ecosystems with smoke, plastic, noise and light.

2 Match the sentences to the pictures in your notebook.
Cities, roads, industries and farms use lots of space. We don’t leave a lot for other living things.

a) We consume coal too quickly. Ecosystems take millions of years to produce more.
b) We hunt animals and catch fish that are endangered.

c) We cut down too many trees. Trees take many years to grow.
d) We destroy the habitats of plants and animals when we build roads.


e) Toxic emissions from industry pollute the environment.

f) The light and noise from campsites disturb animals.


7 Changing ecosystems 56
1 4 5 2 3 6
Our ecosystems are in danger!
Air pollution is a big problem! The Earth’s atmosphere and the seas are also getting warmer. This is called global warming. All these things are causing climate change.
Some species of living things are extinct. Other species, like the Greek tortoise in Almería and Murcia, are endangered. Fires, uncontrolled urbanisation and unsustainable farming methods are some of the causes.

1 Look at these endangered animals. Match each description to the correct animal and the correct question.
I
Humans take my horn and use it for medicine.
I
What animal is it?
Where does it live? Why is it endangered?


2 Make cards with the pictures of the animals and the information about them. Then, tell your classmates about them.

3 Brainstorm ideas and make a poster with five tips for reducing damage to the environment.
See worksheet 2 from the ICT Plan at anayaeducacion.es to learn how to create digital content.

NOW I KNOW…
Human activities cause problems in many ecosystems, and some are disappearing.
TIPS!
1) Stop polluting!
2) …
3) …
CHECK WHAT YoU LEArnED
57 I D on ’T WA n T To DISA pp EA r !
Pacific Ocean Polar bear Arctic
suffocate from eating plastic in the sea.
can’t hunt for food because the ice is melting.
Javan rhinoceros Indonesia
1 2 3
Leatherback turtle
Your turn!
THINK
What do you do to protect ecosystems?
1 Look, listen and read. We need to protect resources and ecosystems. We should use natural resources carefully. Everyone can help by living more sustainably.
Tips for living more sustainably
Recycle
Separate plastic, glass, paper and cardboard for recycling.
Save water

Have a shower, not a bath. Turn off taps when you aren’t using them.
Reuse
Objects made from plastic and other materials.
Save energy


Turn off lights and appliances when you aren’t using them.

Respect nature
Respect animals and plants when you visit the countryside. Don’t leave rubbish and never start a fire.
2 Choose the correct action for a sustainable lifestyle.
1) When I want some water in a restaurant, I…
a) ask for tap water in a jug.
2) In the toilet, I…
a) throw tissues in the bin.
3) During my break, I…
a) leave my banana peel on the bench.
3
b) ask for bottled water.
b) flush tissues down the toilet.
b) throw my banana peel in the bin.


In pairs, make suggestions to take care of the environment.
Do you want to go to school by car?

No, I don’t. It isn’t good for the environment.
Then let’s go by bike!
Yes, that sounds great!
CAn WE TAKE CArE oF ECoSYSTEMS? 8 Protecting ecosystems 58
HoW
THE SUSTAI n ABILITY Co DE
Do you know this symbol? Gary Anderson designed it in 1971. It’s the international symbol for recycling. The three arrows represent the three steps of recycling: reduce, reuse and recycle.

1 Find objects in your home with this symbol or look for objects on the Internet. Make a list of the objects you find.





2 There are different logos for different sustainable actions. Look at the pictures and match them to their meaning.
3 Work in groups. It’s time to take action!
a) Brainstorm sustainable actions that you can take in class or around your school. For example:
• Recycle paper, cardboard and packaging.
• Collect toys and give them to charity.
• Turn off taps when you aren’t using them.
• Turn off lights when you aren’t using them.
b) Design a logo for each action. Keep them simple. People need to understand their meaning.
c) Put your logos around your classroom or school to help people be sustainable.

For help using ICT sustainably, see worksheet 5 from the ICT Plan at anayaeducacion.es.
NOW I KNOW…
We can do many things to live sustainably: recycle, reuse objects, save water, save energy and respect nature.
59
CHECK WHAT YoU LEArnED
Put rubbish in the right place. Use plasticrecycled bags.
bottles.plastic Use solar
1 3 2 4 A C B D
Reuse
energy.
Computational thinking
MY VISUAL SUMMARY
Ecosystems
An ecosystem consists of: non-living things, living things and the relationships between all these elements.




Non-living things: the air, the sun, climate, water and rocks.
Relationships: the main relationships are feeding relationships.
There are different types of rocks: granite, basalt, slate and limestone.




The rocks in an ecosystem determine the landforms.

60
Humans and ecosystems
food


land
Natural resources are things that we use from nature.



water

raw materials
We sometimes damage ecosystems when we use natural resources
Using all the resources
Pollution from smoke, plastic, noise and light.
Occupying space
Separate waste for recycling
Save water
well-being
Extinction of species

Global warming
Looking after ecosystems
Save energy




Give toys and clothes to charity

Reuse objects
Respect nature
61
PORTFOLIO
WHAT HAVE I LEArnED?
1 What is in the school ecosystem? Choose one answer.
a) The building, the playground, and the school’s furniture and objects.
b) The building, the playground, the school’s furniture and objects, and the people.
c) The building, the playground, the school’s furniture and objects, the people, animals and plants, the sun, the air, and the interactions between all these things.
2 Look at the pictures and describe two feeding relationships.
5 Describe three human activities that use these natural resources.
a) Water b) Rocks
c) Trees d) Land
6 Look at the picture and answer the questions.
a) Which things do not belong in this environment?
b) How do these things harm living things?



c) How can we remove pollution from this environment?
7 Match each type of damage to its causes. Suggest actions to prevent each type.
a) Air pollution.
b) Extinction of living things.
c) A lot of waste.
3 Guess the rock in the picture. What type of relief can this rock form?

1) We occupy space and destroy habitats.


2) We use many resources and don’t recycle.

3) Cars cause toxic emissions.
Don’t forget to complete your photo album at anayaeducacion.es

4 Imagine all the plants on Earth disappear. How does this affect the ecosystems? Answer the questions. Explain your answers.

a) What happens immediately?
b) What happens months later?
c) What happens years later?
Traffic lights. Apply this colour code to each activity in your notebook.
I knew the answer.
I needed help.
I couldn’t answer the question.
62
Research a real ecosystem and make a wall display about how to protect it.
In groups, follow these steps. Step 1. Choose an ecosystem like the ones in the pictures.
Step 2. Look for pictures and information about it.
• Which countries have this ecosystem?


• What living things live there? Include animals and other living things.

• Is this ecosystem in danger?
• How can we protect it?
Step 3. Use the pictures and information to make a colourful wall display.
2 Copy and complete the ‘Before, I thought…’, ‘Now, I think…’, organiser in your notebook.


Before, I thought…
What did I think about ecosystems before?
HoW HAVE I LEArnED?
1 Copy the diagram. Evaluate yourself for each category. Connect the dots to make a pentagon. A big pentagon means you are learning a lot!
Now, I think… Reasons
What do I think now? Why did my opinion change?
2 Which things did you find surprising or interesting? Explain. How do these things improve people’s lives?
63
1
1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 Attention Group work
problems
of
Solving
Studying Quality
my work
Match each vital function to a sentence.
We need food to live.
4

Which group does each animal belong to? Write it in your notebook.
We react to things around us.
Nutrition
2 MIPONDECOTIOS RIGOMALTH CATCODFINIOI RATNIOBSACT


Find five non-living things.
3
Which substances do plants produce?
Which substances do they use? Classify them into two groups.

D R H R O C K S H L K I M R F P O F D V M L J T F N I O R D X V R E L I E F S C F P Y F R F J N L Y Z A I R J B V R Y R P J W A T E R R E T K Y T R D V N K R E G C L I M A T E I B U Y L O G R V B N W 5 Minerals Oxygen Water Food Carbon dioxide A C D E F B


REVIEW TERM 1 64
These words refer to computational thinking. Order the letters in your notebook. KECHICNG TAPTNER LANOITATUPMOC
1 Reproduction Interaction
We come from other living things.
With a classmate, name the healthy habits in the pictures.





Find the odd one out in each group. Explain your answers.
Look at this piece of news.
The forest fire in the nature park is affecting a lot of land. Many plants and animals are dying.
In your notebook, say which sentence you think is true.
a) We can plant new trees and introduce new animals to repopulate the park.
b) Parks can’t recover after a fire.
65
6
8
A B D C E
7 Senses Nervous system Muscles Nutrition A Egg Viviparous Reproduction Dog B Oxygen Lungs Gills Trout C Vertebrate Backbone Gills Hen D Heart Blood vessels Circulation Oesophagus E
Match these living things with the correct descriptions in your notebook.

I am a herbivore. I eat plants.
Many frogs, dragonflies, plants and herons live in a lake. In your notebook, complete the food chain.




I am a vertebrate. I have got fins and I breathe through gills.

I am an arthropod. I have got articulated legs.
I am a carnivore. I eat other animals.
What happens if all the plants disappear?
I am a cnidarian. I have got poisonous tentacles.

I am a vertebrate. I have got a shell and I breathe through lungs.

I am an omnivore. I eat plants and animals.


11
Look at these pictures. Choose one word for each one.
Pollution Vegetation Ecosystems
Grass Waste Farming


Natural resources Recycling


66 REVIEW TERM 1
9
10
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
A
B C
GREAT SCIENTISTS
Stephanie Kwolek was a scientist. She discovered the material Kevlar. It is stronger than steel. We use it to make bullet-proof vests.
Stephanie Kwolek
Wow! It looks like another experiment’s gone wrong. But what is Stephanie doing?
Instead of throwing the sample away, she takes it to the spinning machine.
The machine attendant looks at the mixture and gets angry.
‘What are you bringing this to me for? It doesn’t meet the conditions. I’m not going to put it in my machine, it might break down.’


‘What if it turns out that we’re wrong?
Scan the code for the complete story.
What if cloudy samples can also be used to obtain fibres? We are scientists, we have to experiment!’
Maria Sibylla Merian was a naturalist, an explorer and a painter. She painted pretty pictures of insects and plants, bringing art and science together.
Maria Sibylla Merian
Maria is very observant and very curious.
She loves butterflies and wonders if they all come from ugly, hairy caterpillars. The only way to find out is to observe.
For years she studies and draws the caterpillars, the cocoons they form, and the butterflies that emerge from them. It looks like a magical transformation!

Scan the code for the complete story.




67
STEAM
THATPROJECTSIMPRINT LEAVEAN

DISCOVER THE INTERDISCIPLINARY PROJECT

Do you waste food?
STORE WELL,EAT WELL
Organising food in the fridge helps preserve it. Get organising!
Create a wall display on how to organise a fridge!
2 DESIGN
Do you forget about food in the fridge? Does it go bad? How do you organise your fridge? Discuss your ideas in groups.
Look for information about where to store different foods: in the fridge, freezer or cupboard.
Cut out pictures of different foods from magazines or do drawings. Think about the temperature they need. Then decide where they should go. Now you can help put the shopping away at home!

68 1 P i ensa THINK
D iseña
PRESENT
What do you know about storing food now?
How can you use this information?
BUILD
3 C ONSTRUYE C onstruy e
Create your wall display on how to organise a fridge:
You can draw the outline of a fridge. Put what you know about organising food into practice.



Use products that your family normally buys.
CHECK 5
C omprue b a
Prepare a presentation about an organised fridge. Explain how to preserve and not waste food.
69
4 PRESENTA P resent a t ERM 1
©
GRUPO ANAYA, S.A., 2023 - C/ Valentín Beato, 21 - 28037 Madrid.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior permission of the publishers.
GLO BAL THINKERS
SCIENCE www.anayaeducacion.es CERTIFIED FIBER PAPER 9229570





































































































































































































































































































































































































































































