Answers to the activities in the student’s book
Activities
1 Work in groups and discuss these questions before reading the unit.
a) The first two questions will be assessed for the correct use of the past tenses and the construction of sentences such as: I have never experienced an earthquake, but I visited Teide two years ago.
Spain is located between the Eurasian and African plates, which causes occasional earthquakes, especially in southern regions like Andalusia.
b) Some elements of relief that students study in this unit are: plain, plateau, mountain, basin, valley, beach, cape, gulf, island, continental shelf, continental slope, etc.
c) When a volcano erupts, it expels magna, a mixture of solid materials (rock fragments), liquids (lava) and gases from the earth’s crust and upper mantle.
d) Open answer. Example: I would prefer to spend my holidays along the Atlantic part of the Andalusian coastline rather than on the Mediterranean side. I think the Atlantic coast has nice sandy beaches. I like them better than the pebble beaches along the Mediterranean coastline.
2 What are the tectonic plates? What happens when they move? Discuss your answers with your classmates
The tectonic plates are the fragments or blocks into which the lithosphere is divided. The plates float on the asthenosphere. As they collide and break up, enormous quantities of energy are released, causing tremors and earthquakes or the formation of volcanoes. The movement of the tectonic plates is also responsible for the creation of different forms of relief.
Task:
3 Look at the picture about the propagation of an earthquake on the previous page. Write the difference between the hypocentre and the epicentre of an earthquake.
The hypocentre is the point within the Earth where the earthquake rupture starts. The epicentre is the point directly above it on the surface of the Earth.
4 Match each of these concepts with its definition.
a) 3.
b) 2.
c) 4.
d) 1.
5 2 Listen to the audio recording and complete the text with these words: lithosphere, Asia, Europe, continents, centimetres, today, asthenosphere, Pangaea. Then, answer the questions.
Millions of years ago, all of the continents that we know of were joined into just one: Pangaea. However, the lithosphere broke up into a dozen layers, which slipped into the asthenosphere, moving further apart or closer together, until the continents as we know them today were formed. Such movement continues to this day. Europe and North America continue to move 2.5 centimetres apart each year, while India and Asia move between 4 and 6 centimetres closer together each year.
a) In the beginning, Pangaea was the only continent on Earth.
b) No, the tectonic plates are constantly moving.
6 Match the erosive agents with their descriptions:
a) 4.
b) 2
c) 6.
preventing disasters
A Research what the Richter scale is. According to that scale, how serious was the earthquake recorded in Tokyo described in the article?
The purpose of the seismological Richter scale is to measure the energy released by an earthquake and, thus, its severity. The earthquake described in the article, with a 6.1 magnitude, is considered to be ‘strong’ according to the Richter scale.
B Summarise the human and material consequences from the earthquake. Why do you think this earthquake didn’t have any serious consequences?
The earthquake didn’t cause mortal victims. Regarding the material consequences, it caused damage to the rail network and some buildings. Japan sits along one of the world’s most active seismic zones, so its infrastructure and buildings are designed to withstand tremors.
d) 3. e) 5.
f) 1.
C Examine the map containing the tectonic plates and locate Japan, Indonesia and Pakistan. Why do you think earthquakes are frequent in these three countries?
All of these countries are located in the collision zones of two or more plates. In other words, they are located in regions with intense seismic activity, where earthquakes are frequent.
D Now locate Spain on the map. Are earthquakes frequent in Spain? Why or why not?
Spain is located between the Eurasian and African plates, which causes occasional earthquakes, especially in southern regions like Andalusia.
Teacher’sbook GEOGRAPHY & HISTORY 1 ESO The Earth’s relief algaida editores S. A. 6 2
Activities
7 Match the following coastal relief elements with their definition.
a) 4.
b) 6.
c) 1. d) 5. e) 3. f) 2.
8 Explain the difference between the following pairs of elements and discuss the answers with your classmates.
a) Both of them are flat but a plain is found in a lowlying area whereas a plateau is found on high ground.
b) An island is completely surrounded by water, whereas a peninsula is only partially surrounded by water and it is connected to the continent by a strip of land called an isthmus.
c) A gulf is a deep inlet of the sea into the land, whereas a cape is a piece of land that sticks out into the sea.
d) An ocean ridge is an underwater mountain range, whereas an ocean trench is a deep underwater depression.
9 Look at the world map included in the appendices and find the answers to the following questions. In pairs, use comparative and superlative structures to define each of the things that you have found. For example: The highest mountain in Europe is...; This continent is smaller than...
a)
• Europe, Africa, Asia and North America are found in the northern hemisphere.
• South America, Asia, Africa, Oceania and Antarctica are located in the southern hemisphere
b)
• In Asia, the highest peak is Mount Everest.
• In South America, Mount Aconcagua.
• In North America, Mount McKinley.
• In Africa, the Kibo volcano.
• In Europe, Mont Blanc.
• In Antarctica, Mount Vinson.
• In Oceania, the Puncak Jaya peak.
c)
The biggest continent in the world is Asia and the smallest is Oceania.
d)
• The biggest island in America is Greenland.
• The biggest island in Oceania is Papua New Guinea.
• The biggest island in Asia is Borneo.
• The biggest island in Africa is Madagascar.
• The biggest island in Europe is Great Britain.
• The biggest island in Antarctica is Alexander Island.
e)
• The longest river in America is the Amazon; the Nile in Africa; the Yangtze in Asia; the Volga in Europe; the Murray in Oceania; and the Onyx in Antarctica.
• The biggest lake in America is Lake Superior; Lake Victoria in Africa; Lake Baikal in Asia; Lake Ladoga in Europe; Lake Vostok in Antarctica; and Lake Eyre in Oceania.
10 2 Listen to the audio recording and complete the text. When Christopher Columbus reached the island of Guanahani in the Caribbean, he thought he had found the gateway to Asia. But he was wrong: the land he had discovered belonged to a continent that was unknown to Europeans. America is named after the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespuccio, who was the first person to reach the conclusion that the land they had found wasn’t Asia but part of a new continent.
11 With the help of an atlas, locate the following elements of relief and complete the table: Rocky Mountains, Canary Islands, Andes, Terranova, Appalachians, Baltic Coastal Plain, Pyrenees, Kamchatka Peninsula, Corsica, Great Rift Valley, Cyprus, Caucasus Mountains, Himalayas, British Isles, Madagascar, the Great Dividing Range, Scandinavian Mountains, Atlas Mountains, Korean Peninsula, Ethiopian massif, Japan, Drakensberg Mountains, Sri Lanka, New Zealand, Amazon Plain, Central Siberian Plateau, Labrador Peninsula.
Continent Elements
Africa
Canary Islands, Great Rift Valley, Madagascar, Atlas mountains, Ethiopian massif, Drakensberg mountains.
America Rocky Mountains, Andes, Terranova, Appalachians, Amazon Plain, Labrador Peninsula.
Asia
Europe
Korean Peninsula, Japan, Sri Lanka, Central Siberian Plateau, Kamchatka Peninsula, Himalayas.
Baltic Coastal Plain, Pyrenees, Corsica, Cyprus, Caucasus Mountains, British Isles, Scandinavian Mountains.
Oceania Great Dividing Range, New Zealand.
Teacher’sbook GEOGRAPHY & HISTORY 1 ESO The Earth’s relief algaida editores S. A. 7 2
Task: very deep knowledge
A Place in order, from shallowest to deepest, the spots in the oceans that appear in the text.
The deepest spots in the oceans that appear in the text are, from shallowest to deepest:
• Molloy Abyss (Arctic), 5,551 m.
• Factorian Abyss (Antarctic), 7,432 m.
• Brownson Abyss (Atlantic), 8,378 m.
• Challenger Abyss (Pacific), 10,924 m.
B Research what the highest spot on the planet is and what the highest spot in Spain is and calculate how many times each of the two would fit into the Challenger Abyss. The deepest spots in the 5 oceans are:
• Arctic Ocean: Molloy Abyss, 5,551 m.
• Atlantic Ocean: Brownson Abyss, 8,378 m.
• Antarctic Ocean: Factorian Abyss, 7,432 m.
• Indian Ocean: Unnamed Abyss, 7,187 m.
• Pacific Ocean: Challenger Abyss, 10,924 m.
C Use the physical world map in the annex and determine where such depths are located.
Mount Everest, with a height of 8,848 m, is the highest spot on Earth, and would fit 1.23 times into the Challenger Abyss. As for Teide, the highest peak in Spain at 3,715 m, it would fit 3 times over (2.94 times to be exact!)
D Work in groups: currently only 5 % of the planet’s ocean floor has been mapped. Why do you think we still don’t know enough about our seas and oceans?
The main issues are technical and economic. The pressure exerted by the ocean is 1,000 times greater than the atmospheric pressure at the Earth’s surface. Then you have to add the extremely poor visibility and extremely cold temperatures found at great depths. The technology required to explore such places is very expensive. However, knowing the ocean’s depths better would help us to better understand the underwater flora and fauna, which would make it possible to adequately protect them, something that is needed urgently since only 1.5 % of the world’s oceans are considered to be protected marine reserves. Research demonstrates that ocean trenches are carbon sinks, which could help us to combat climate change.
Activities
12 Look at the physical map of Europe included in the appendices. Complete the following table about European relief with at least two examples of each. Open answer. One possible answer could be as follows:
Great European Plain
Massifs, plateaus and ancient mountains
Young mountains in southern Europe
Peninsulas
Gulfs, capes and straits
Islands and archipelagos
Baltic Coastal Plain
East European Plain
Vosges Massif
Ural Mountains
The Alps
Caucasus Mountains
Iberian Peninsula Scandinavian
Peninsula
The English Channel
Gulf of Genoa
British Isles
Cyprus
13 Guess the names of these elements of Spanish relief and write the answers.
a) Canary Islands.
b) Central System.
c) Sierra Morena.
d) Sierra Nevada.
e) Guadalquivir Basin.
14 Complete this table including these elements of Spanish relief: Galician Massif; Canary Islands; Iberian Massif; Central Basin; Catalan Coastal Basin; Sierra Morena; Sierra de Toledo; Andalusian systems; Cantabrian Mountains; Pyrenees; Guadalquivir Basin; Basque Mountains.
Inside the Meseta Central System, Toledo Mountains.
Bordering the Meseta
Outside the Meseta
Galician Massif, Cantabrian Mountains, Sierra Morena, Iberian System.
Canary Islands, Catalan Coastal Range, Pyrenees, Basque Mountains, Baetic Systems, Guadalquivir Basin, Cantabrian Range.
15 Look at the map of Spain included in the appendices and answer the following questions:
a) El Hierro, La Gomera, La Palma, Tenerife, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria and Lanzarote make up the Canary Islands. Mallorca, Menorca, Ibiza and Formentera make up the Balearic Islands.
b) The Iberian Peninsula is surrounded by the Cantabrian Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Mediterranean Sea to the south and east.
c) The Pyrenees cross the Basque Country, Navarre, Aragón and Catalonia and form a border with France and Andorra.
d) Open answer: for example Ebro, Nalón, Narcea and Órbigo.
Teacher’sbook GEOGRAPHY & HISTORY 1 ESO The Earth’s relief algaida editores S. A. 8 2
16 2 Listen to the audio recording and complete the following text with the correct word.
Most of Spain’s territory is situated on the Iberian Peninsula, in south-west Europe. It also includes the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea, and Ceuta and Melilla on the coast of North Africa. It covers an area of 505,990 square kilometres. The peninsular boundaries are the Cantabrian Sea and the Pyrenees in the north, the Mediterranean Sea in the east, the Atlantic Ocean and Portugal in the west, and the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea in the south. The relief on the peninsula has an average height of 660 metres. This is partly because of a great plateau, called the Meseta, in the centre, formed by the erosion of ancient mountains.
18 Draw a map of Andalusia this in your notebook and mark the following elements of relief: Sub-Baetic Mountain Range; Penibaetic Mountain Range; Sierra Morena; Guadalquivir Basin; Atlantic Ocean; Mediterranean Sea; Sierra Nevada; Serranía de Ronda; Sierra de Cazorla; River
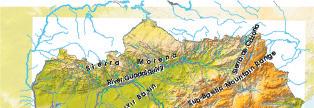
17 Order the following peaks from highest to lowest: Torre Cerredo, Puig Major, Las Villuercas, Mulhacén, Veleta, Teide, Teleno, Aneto, Moncayo. Then write sentences using the comparative and superlative.
Teide, Mulhacén, Aneto, Torre Cerredo, Moncayo, Teleno, Las Villuercas and Puig Major.
Open answer:
• Teide is higher than Teleno.
• Teide is the highest peak in Spain.
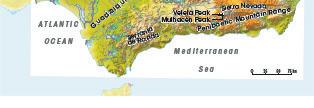

Mediterranean coasts of Andalusia? To which of the two Atlantic beaches are flat and sandy, while Mediterranean beaches are more rugged and rocky.
The picture A is the beach Punta Paloma (Tarifa, Cádiz), from the Atlantic coast.
The picture B is the beach Tropical (Granada), from the Mediterranean coast.
Grammar in geography and history
1 Read this text and identify the verbs in the present simple tense. Then, classify them by affirmative or negative:
The tectonic plates that make up the earth’s crust are in continuous movement, but we do not feel this movement, except when it occurs violently. An earthquake is a shaking or vibration at the surface of the earth, caused by tectonic plate movement. When two plates crash, they release a large amount of energy causing tremors that can be very severe. Most of the earthquakes that occur in the world are located in the Pacific Ring of Fire, a large area of the Pacific Ocean that connects America with Asia.
Earthquakes don’t only exist in the continents’ surface: vibrations can also occur on the ocean floor and are called ‘tsunamis’. A tsunami is a great sea wave caused by an underwater earthquake or underwater volcanic eruption.
Tsunamis are not frequent in Spain, but earthquakes are common in our country. Spain is situated between two tectonic plates and this produces about 2,500
earthquakes a year, although most of us do not notice them.
Affirmative present simple verbs Negative present simple verbs make up are occur, occurs is crash release causing connects produces do not feel don’t exist are not do not notice
2 Choose the correct option in the following sentences:
a) The Atlantic coastline of Andalusia have/has sandy beaches.
b) The Guadalquivir basin is/are in Andalusia
c) The Central System divide/divides the Meseta into the northern and southern sub-plateaus.
Teacher’sbook GEOGRAPHY & HISTORY 1 ESO The Earth’s relief algaida editores S. A. 9 2
d) The Canary Islands is/are of volcanic origin.
e) Young higher mountains predominate/predominates in the west of America
f) The continental surface represent/represents 29 % of our planet.
3 The following sentences contain information that is not correct. Rewrite the following sentences in the negative, so that the information they contain is correct. Then, write new affirmative sentences using the present simple and the correct information.
a) The core is not the outer layer of the Earth. The crust is the outer layer of the Earth.
b) Abyssal plains are not deep underwater depressions. Ocean trenches are deep underwater depressions.
c) Alpine mountain ranges do not predominate in the north of Europe. Alpine mountain ranges predominate in the south of Europe.
d) The Cantabrian mountains do not surround the Meseta in the south. Cantabrian mountains surround the Meseta in the north.
e) The Baetic mountain range does not separate Andalusia from the Meseta. The Sierra Morena separates Andalusia from the Meseta.
4 Use these words to write a question for the following answers:
a) What are the tectonic plates?
b) Where are the Himalayas?
c) Why are Earthquakes common in Spain?
d) How do we classify the units of relief of Spain?
e) Which is the biggest island of Africa?
5 Order the following words to make meaningful sentences:
a) The Andalusian coast is more than 1,000 km long.
b) The Baetic mountain ranges occupy the east and south of Andalusia.
c) The Great European Plain stretches from the Ural Mountains to the Pyrenees.
d) The European continent is part of the Eurasian landmass.
e) An island is a body of land completely surrounded by water.
Final Task: Fight the volcano
➊ Do some research and prepare a brief report on the latest eruption of the volcano on the island of La Palma, indicating when it began, when it ended and the main human and material damage it caused.
Open answer. The latest volcanic eruption on the Island of La Palma began on September 29, 2021, near the town of El Paso. At the present moment, the volcano continues to remain active/the volcano has ceased to erupt since… causing substantial economic damage. Students shall attempt to quantify the damage depending on the state of the eruption.
➋ The volcanic origin of the Canary Islands explains why volcanic eruptions occur frequently along the archipelago. Research when the previous volcanic eruption on the Canary Islands took place and determine how many eruptions occurred on the island of La Palma over the past one hundred years.
The previous volcanic eruption in the Canary Islands was the underwater eruption on the Island of Hierro in 2021. As for the island of La Palma, it underwent 3 volcanic eruptions since the middle of the past century: at San Juan in 1949, at Teneguía in 1971 and at Cumbre Vieja, which began in September of 2021.
➌ Make a list of the health risks posed by the ash and gases expelled by the eruption.
Among the health risks, we can include nasal, skin and eye irritation, sore throat, dry cough, stomach pain or pulmonary conditions (sense of a lack of air, shortness of breath, bronchitis).
➍ Although we cannot keep the lava from destroying towns and crops, we can mitigate the effects of a volcanic
eruption on humans. Work in groups and draft a series of recommendations for a population affected by a volcanic eruption, such as avoiding breathing the polluted air and if necessary, evacuating one’s home.
Open Answer. The idea is to get students to debate the measures in groups, then compare their answers and reach a consensus on a conclusion. The use of modal verbs and imperatives is key:
• Closing doors and windows
• Avoiding staying outdoors any longer than necessary
• Respecting restricted zones established by the authorities.
• Evacuation measures:
• In the event of seismic activity, stay calm.
• Stay abreast of the information provided by the authorities through the media.
• Prepare a small, lightweight emergency kit containing any necessary items: some clothing, food and water, a mobile phone with a charged battery, medicines and personal documents.
Teacher’sbook GEOGRAPHY & HISTORY 1 ESO The Earth’s relief algaida editores S. A. 10 2
3. Instrumentos de evaluación
Unidad 1 L a lengua y los hablantes (I ) C reación de un club de lec tur a Pr ogramación ............................................................................................................................................ 6
Unidad 2 L a lengua y los hablantes ( I I ) Dr amatización de regis tr os lingúís ticos
-
-
Exam
my portfolio - rúbrica
The Earth’s relief
Name:
Course: Group: Date:
1 Name the main characteristics of the layers of the Earth. What is the lithosphere?
2 Classify the following elements in the table: plain, continental slope, cape, abyssal plain, peninsula, ocean trench, plateau, mountain range, valley, isthmus.
3 Complete the table with the following elements of relief: Australia, Madagascar, Andes, Alaska, Tiber, The Alps, Japan, Great Rift Valley, Pyrenees, British Isles, Siberia, Greenland, Mount Kilimanjaro.
Continent Elements
Africa
America Asia Europa Oceania
4 Imagine you are planning a trip by car from Galicia to Almería. Name the main Spanish forms of relief you will see during your journey.
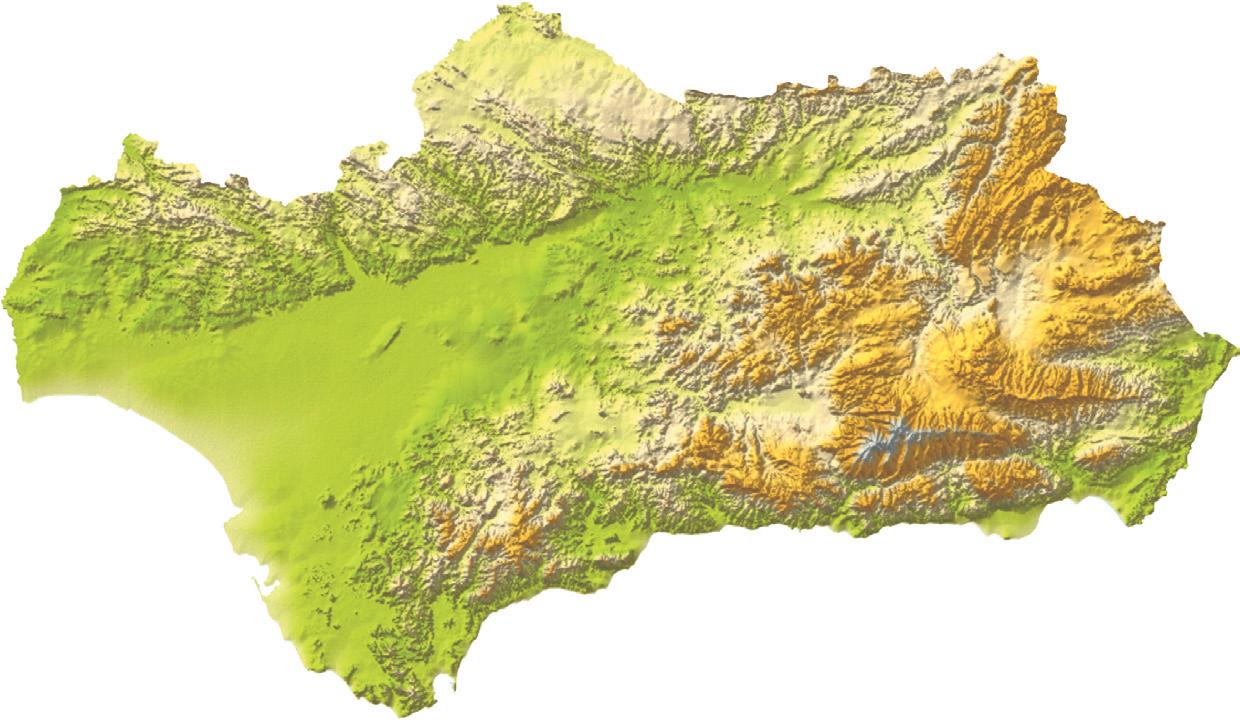
5 Locate on this map the following relief units: Sub-Baetic Mountain Range, Penibaetic Mountain Range, Sierra Morena, Guadalquivir Basin, Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, Sierra de Cazorla, Mulhacén Peak.


11 Pruebas y recusos de evaluación GEOGRAPHY & HISTORY 1 ESO algaida
editores, S.A. Material fotocopiable autorizado. Disponible en PDF.
Exam
2
Continental relief Costal relief Oceanic relief
ANSWERS TO THE EXAM
1
The crust is the thinnest layer of the Earth. It is the ground beneath our feet. The mantle is the largest layer. It is solid except at the top.
The core is the innermost layer of the Earth. It consists of an outer core and an inner core. They are both made up of iron and nickel, which are responsible for the Earth’s magnetic field.
The crust and the upper mantle form the lithosphere.
2
Continental relief Costal reliefOceanic relief
Plain Plateau Mountain range Valley Cape Peninsula Isthmus
3
Continental slope Abyssal plain Ocean trench
Continent Elements
Africa Great Rift Valley, Madagascar, Mount Kilimanjaro
America Andes, Greenland, Alaska
Asia Japan, Tibet, Siberia
Europa The Alps, Pyrenees, British Isles
Oceania Australia
4
The coherence of the student’s answers and the accuracy of the contents will be assessed. Throughout my journey from Galicia to Almería I will go through the Galician Massif, Mountains of León, Northern Sub-plateau, Central System, Southern Subplateau, Sub-Baetic Range and Penibaetic Range.
5



algaida editores S. A. 12 The Earth’s relief algaida editores S. A.
2
Skill
Listening
MY PORTFOLIO
I can…
When I listen, I can understand…
` The Continental Drift theor y.
` The origin of the name of America.
` My teacher’s explanations.
` Writing
I can write texts and express myself about…
` The layers of the Earth.
` Earthquakes and tectonic plates.
` Description of a picture.
` The main forms of relief in Spain.
` Reading
I can read and understand texts about…
` The different layers of the Earth.
` Continental and coastal relief: mountains, valley, plateau, cape, bay and gulf.
` The relief in the different continents.
` The Spanish continental and coastal relief.
` Speaking
When I speak, I can…
` Use correct sentences in different tenses.
` Explain the consequences of the movement of tectonic plates.
` Compare Mediterranean and Atlantic beaches of Andalusia.
` Conversation
When I have a conversation with my classmates, I can…
` Correct my answers with the help of my classmates.
` Use comparative and superlative sentences.
` Express my opinion and preferences.
` Use the vocabulary of the unit (tectonic plate, earthquake, cape, mountain and so on).
` …
I need to improve I need a little help I am doing well
Teacher’sbook GEOGRAPHY & HISTORY 1 ESO The Earth’s relief algaida editores S. A. 14 2
RÚBRICA PARA EVALUAR EL FINAL TASK: A VISUAL JOURNEY THROUGH THE EUROPEAN UNIT
ALUMNO/A_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
INDICADOR 4 EXCELENTE 3 SATISFACTORIO 2 MEJORABLE 1 INSUFICIENTE
Contenido
Originalidad
Uso del inglés
VideograGa/Interés
Cubre los temas en profundidad con detalles y ejemplos. El conocimiento del contenido es excelente.
El producto demuestra gran originalidad. Las ideas son creaEvas e ingeniosas.
Se expresa con soltura sin cometer errores gramaEcales, de expresión y pronunciación.
UEliza diferentes ángulos de cámara y/o tomas. Incluye efectos de sonido. Los efectos visuales y sonoros del vídeo son variados y correctos.
Incluye conocimiento básico sobre los temas. El conocimiento del contenido es correcto.
El producto demuestra cierta originalidad. El trabajo demuestra el uso de nuevas ideas.
Se expresa correctamente sin cometer muchos errores gramaEcales, de expresión y pronunciación.
UEliza diferentes ángulos de cámara y/o tomas. Incluye efectos de sonido. Pero estos efectos presentan fallos formales.
Incluye información esencial sobre los temas, pero Eene uno o dos errores en los hechos.
Usa ideas de otras personas, no hay casi evidencia de ideas originales.
Se expresa con dificultades, comeEendo algunos errores gramaEcales, de expresión y pronunciación.
Hay poca variedad en las tomas, ángulos y/o efectos de sonido.
El contenido es mínimo y Eene varios errores en los hechos.
Usa ideas de otras personas y no hay aspectos originales.
Se expresa con mucha dificultad, comeEendo numerosos errores en lengua inglesa.
El vídeo no presenta variedad de efectos.
VideograGa/Calidad
OBSERVACIONES:
La calidad del vídeo y del enfoque es excelente en todas sus partes, así como el sonido.
La calidad del vídeo, del enfoque y del sonido es buena en la mayor parte del vídeo. Presenta algunos fallos que perjudican la calidad: en el enfoque o en el sonido. Pero la calidad es suficiente.
El vídeo no presenta calidad suficiente.
4. audio scripts
Unidad 1 L a lengua y los hablantes (I ) C reación de un club de lec tur a Pr ogramación ............................................................................................................................................ 6
Unidad 2 L a lengua y los hablantes ( I I ) Dr amatización de regis tr os lingúís ticos
AUDIO SCRIPTS
2 Track 06. Unit 2, activity 5. Listen and complete the text.
Millions of years ago, all of the continents that we know of were joined into just one: Pangaea. However, the lithosphere broke up into a dozen layers which slipped onto the asthenosphere, moving further apart or closer together, until the continents as we know them today were formed. This is a continuous movement. Europe and North America continue to move 2.5 centimetres apart every year, while India and Asia move between 4 and 6 centimetres closer together every year.
2 Track 07. Unit 2, activity 10. Listen and complete the text.
When Christopher Columbus reached the island of Guanahani in the Caribbean, he thought he had found the gateway to Asia. But he was wrong: the land he had discovered belonged to a continent that was unknown to Europeans. America is named after the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespuccio, who was the first person to reach the conclusion that the land they had found wasn’t Asia but part of a new continent.
2 Track 07. Unit 2, activity 16. Listen and complete the text.
Most of Spain’s territory is situated on the Iberian Peninsula, in south-west Europe. It also includes the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea, and Ceuta and Melilla on the coast of North Africa. It covers an area of 505,990 square kilometres. The peninsular boundaries are the Cantabrian Sea and the Pyrenees in the north, the Mediterranean Sea in the east, the Atlantic Ocean and Portugal in the west, and the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea in the south. The relief on the peninsula has an average height of 660 metres. This is partly because of a great plateau, called the Meseta, in the centre, formed by the erosion of ancient mountains.
Teacher’sbook GEOGRAPHY & HISTORY 1 ESO The Earth’s relief algaida editores S. A. 13 2
5. atención a la
diversidad - adaptación curricular - adaptación del exam
Unidad 1 L a lengua y los hablantes (I ) C reación de un club de lec tur a Pr ogramación ............................................................................................................................................ 6
Unidad 2 L a lengua y los hablantes ( I I ) Dr amatización de regis tr os lingúís ticos
The Earth’s relief 2
➊ THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
The Earth is made up of three layers:
z The crust is the outer and the thinnest layer.
z The mantle is the middle and the thickest layer.
z The core is the innermost layer of the Earth.
The crust is broken up into blocks called tectonic plates, which float and move on the asthenosphere, the upper mantle , formed by semi-molten materials The collision and breaking up of the plates cause tremors and earthquakes.
➋ FORMATION AND DESTRUCTION OF THE EARTH’S RELIEF
Constant changes occur on the Earth’s surface. These changes are the result of creative forces (internal forces) and destructive forces (external forces) affecting the Earth’s relief.
CREATIVE FORCES THAT AFFECT RELIEF
Forces Effects
Movement of the tectonic plates
Volcanism (the action of volcanoes)
It causes the breaking up (faults) or folding (folds) of the Earth’s surface materials
It is is the result of the expulsion of magma from the mantle to the surface, produced by a crack in the Earth’s crust.
Activities
1 Match each of these concepts with its definition.
a) Mantle
b) Core
c) Asthenosphere
d) Crust
670 km
Internal structure of the Earth
Continental crust (25-70 km)
Oceanic crust (6-12 km)
Upper mantle Asthenosphere
Lower mantle
2900 km
5100 km
Geochemical model (chemical composition)
Outer core Mesosphere Endosphere
Inner core
Lithosphere (100 km)
300 km
2900 km
6370 km
Dynamic model (dynamic behaviour)
DESTRUCTIVE FORCES THAT AFFECT RELIEF Forces Effects
Erosion: the wearing away and fragmentation of the Earth’s surface
Geological processes
Transport: the transfer of eroded material to lower areas.
Sedimentation: the deposition of the eroded material, which forms layers or strata. Erosive agents Temperature, water, ice, wind, plants, trees and human beings.
1. It is the outermost layer of the Earth.
2. It is the deepest part of the Earth.
3. It is divided into the upper mantle and lower mantle.
4. The tectonic plates float on it.
2 Copy and complete this diagram about relief formation.
Relief formation
Creative forces affecting relief
Erosion
3 Complete these sentences with the following words: asthenosphere, erosive agents, sedimentation, tectonic plates, movement.
a) The are the blocks into which the crust is divided.
b) The tectonic plates float on
c) The of the tectonic plates is responsible for the creation of different forms of relief.
d) The is the deposition of the eroded material.
e) The agents are temperature, water, ice, wind, plants, trees, and human beings.
editores, S.A. Material fotocopiable autorizado. Disponible en PDF.
1 Geography & History 1.º ESO algaida
➌ THE MAIN ELEMENTS OF RELIEF
Continental relief
Coastal relief
Plains are flat areas of low altitude. Plateaus are high plains.
Mountains are grouped into ranges or ridges.
Basins, valleys, and depressions are areas of low relief.
It includes different relief forms: beaches, capes or outlets; gulfs or inlets.
Peninsulas are large areas of land surrounded by sea on all sides except for the isthmus, which joins it to the continent.
An archipelago is a group of islands near one another.
➍ THE RELIEF OF THE CONTINENTS
Continents are large land masses separated by oceans. Earth is made up of six continents: Europe, Asia, America, Africa, Oceania, and Antarctica. The main relief elements of the continents are:
ASIA
AMERICA
EUROPE
AFRICA
OCEANIA
In the center of the continent there are great mountain ranges (the Himalayas) and high plateaus (Tibet). The Siberian plains and plateaus are in the north. The south and east of the continent are formed by plains (Great China Plain), peninsulas (Arabia, Indochina) and archipelagos (Japan, the Philippines).
There are extensive plains (North American Great Plains, Amazon Plain) in the centre of the continent. Mountainous ranges predominate in the west (Rockies, Andes). There are lower mountains and plateaus (Appalachians, Brazilian Plateau) in the east.
The highest mountains are in the south of the continent (the Alps, the Caucasus, the Pyrenees). In the centre and in the north lower mountains predominate ( French Central Massif, the Scandinavian Mountains) and plains (Great Plain of Europe).
The Great Rift Valley is in the east. There are great mountain ranges in the north-west (Atlas) and south-east (Drakensberg Mountains) and plateaus and depressions in the centre (the Sahara plateau, the Chad basin).
It is made up of some islands and archipelagos: Australia, New Guinea, and New Zealand.
Activities
4 Find six elements of relief in this word search. Then, match them with the definitions below.
U G S T O Y A A K Q K Q
O P T I W Y F T G R H V
I A A W A V G K V A Q Z
C P H L P X G B H N U L
A R C H I P E L A G O T
A U O V S G T U E E G A
L P L A T E A U M Z H U
D L E C H O F R E K D U
P A N Y M N V A L L E Y
C I Q F U L K A V V F T
K N V K S T V N R B H E
T W V X V Y R G K S G I
a) A kind of elongated depression.
b) A line of mountains grouped together.
c) A group of islands near one another.
d) A strip of land connecting a peninsula to the continent.
e) A flat area of low altitude.
f) A high plain.
5 Are these statements true or false? Correct the false ones:
a) The Siberian plain is in northern Asia.
b) Oceania is made up of some islands and archipelagos, such as Australia, New Zealand or New Guinea.
c) The Great Rift Valley is located to the east of America.
d) The Alps ant the Pyrenees are mountain ranges in north Europe.
e) Tibet is an island located in Asia.
Adaptación 2. The Earth’s relief Geography & History 1.º ESO 2 algaida
editores, S.A. Material fotocopiable autorizado. Disponible en PDF.
Ridges
Valley Plateau Plain
Underwater ridge Ocean trench Continental shelf Continental slope Abyssal plain Bay Island Isthmus
Ranges
Cape
➎ THE RELIEF OF EUROPE
We can distinguish the following groups within the continental relief:
z The Great European Plain stretches from the Ural Mountains to the Pyrenees.
z Massifs, plateaus and ancient mountains: the Ural Mountains in Russia, the Scandinavian mountains in the Scandinavian peninsula, or the Vosges massif in France.
z Young mountains in Southern Europe: the Alps, the Pyrenees in Spain, the Apennine Mountains in Italy, or the Caucasus Mountains.
The European coastal relief presents a very extensive strip with an important variety of coastal landforms:
Peninsulas Iberian, Jutland, Scandinavian.
Capes Finisterre, San Mateo, San Vicente.
Gulfs Vizcaya, Finland, Genoa.
Straits Gibraltar, the English Channel. Islands and archipelagos British, Balearic, Icelandic.
➏ THE RELIEF OF SPAIN
The relief of mainland Spain is structured around a large plateau known as the Central Meseta. The Central System and Toledo Mountains are inside the Meseta. The Meseta is surrounded by the Galician-Leonese Massif, the Cantabrian Mountains, the Iberian System and the Sierra Morena. Other important relief forms outside the Meseta include the Basque Mountains, the Pyrenees, the Catalan-Coastal Range, the Baetic ranges, the Ebro basin, and the Guadalquivir basin.


There are two archipelagos: Canary Islands and Balearic Islands. The Spanish coastline is rectilinear except in the north-west.
THE RELIEF OF ANDALUSIA
The main elements of Andalusian relief are Sierra Morena, which separates Andalusia from the Meseta, the Baetic ranges, which occupy the east and south of Andalusia, and the Guadalquivir basin, in the centre of Andalusia.

Adaptación 2. The Earth’s relief Geography & History 1.º ESO 3
editores, S.A. Material fotocopiable autorizado. Disponible en PDF.
algaida
Landscape of the Great European Plain in Ukraine.
Torre Cerredo (2,650 m), the highest altitude in Picos de Europa (Cantabrian Mountains). Intrabaetic depression (Guadix-Baza).
Activities
6 Classify the following elements of the European relief in the table below: Caucasus Mountains, Ural Mountains, the Great European Plain, Gibraltar Strait, British Isles, the Iberian Peninsula, Jutland Peninsula, The Scandinavian Mountains, Iceland, Gulf of Genoa, and the Alps.
Plains
Massifs, plateaus and ancient mountains
Young mountains in southern Europe
Peninsulas
Gulfs, capes and straits Islands and archipelagos
7 Find on the map included in the appendices of the book these elements of relief. Then, locate them correctly on the map: Pyrenees, Iberian System, Sierra Morena, Cantabrian Range, Galician Massif, Southern Sub-Plateau,
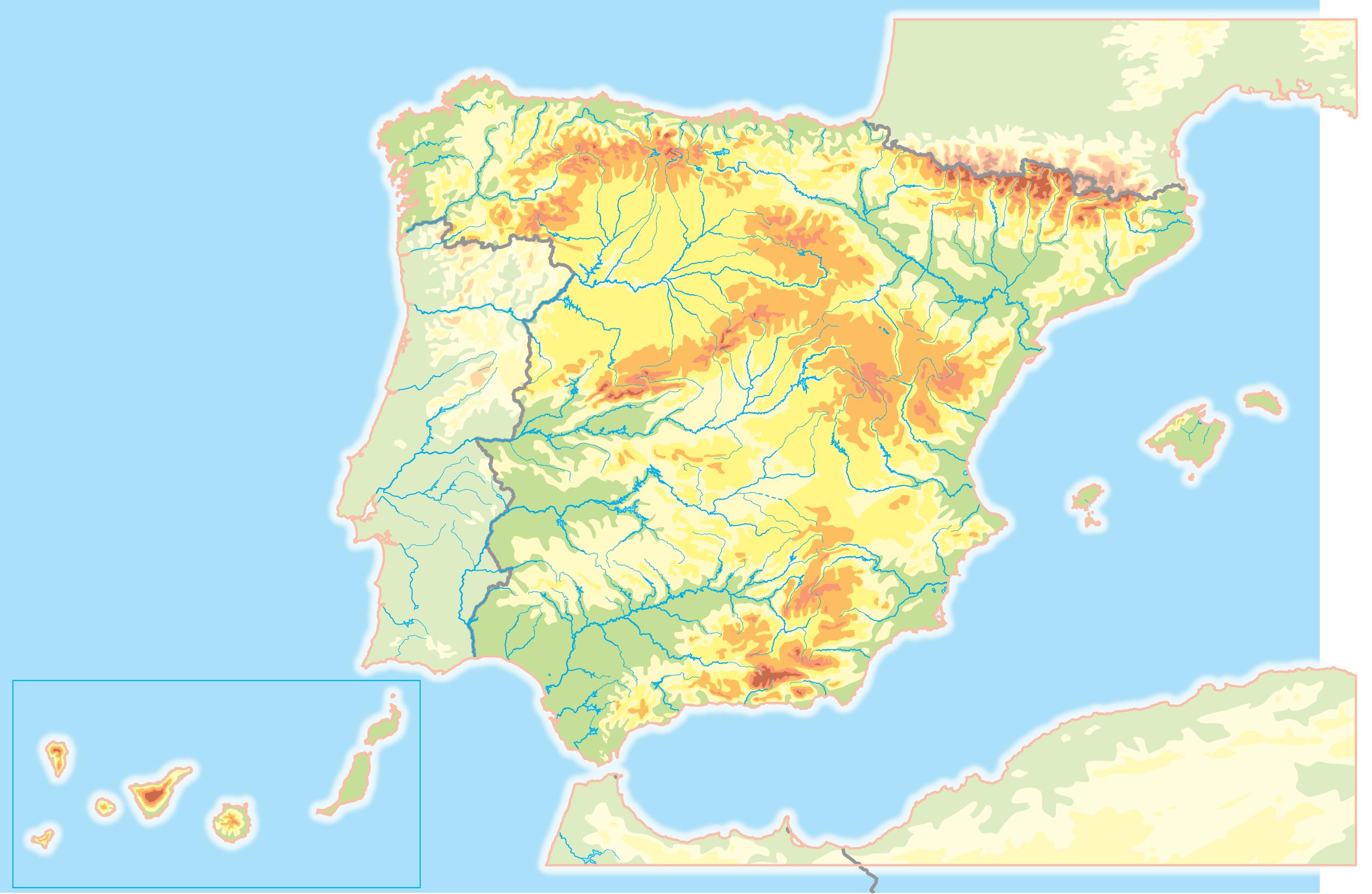
8 Complete the following sentences with the correct element of Andalusia relief:
a) is in the centre of Andalusia.
b) separates Andalusia from the Meseta.
c) are in the east and south of Andalusia.
Adaptación 2. The Earth’s relief Geography & History 1.º ESO 4 algaida editores, S.A. Material fotocopiable autorizado. Disponible en PDF.













