Collaborations between automakers, tech giants, and start-ups have accelerated the development of driverless cars




JULY - AUGST 2023
VOLUME 23
ISSUE 35

Collaborations between automakers, tech giants, and start-ups have accelerated the development of driverless cars




JULY - AUGST 2023
VOLUME 23
ISSUE 35
The year 2023 has not been favourable for the global economy as well as the banking industry. While inflation has been a major issue since 2022, it is finally showing signs of cooling off, but not at the rate expected by central banks. Additionally, there have been numerous bank collapses, including some of the premier regional lending bodies in the United States such as Signature Bank, Silicon Valley Bank, Silvergate Bank, and First Republic Bank, which have collapsed like a pack of cards.
Is the banking system in the world's largest economy considered safe? Unfortunately, the answer is no. Throughout history, the country has faced financial crises resulting from trade disruptions and job losses that arise from the catastrophic bankruptcies of lending institutions.
In 2023, there has been a trend called 'Dedollarisation' where countries are moving away from using the US Dollar for their foreign trade. The Chinese Yuan has become a popular choice for bilateral transactions, with even the regional bloc BRICS considering the possibility of creating its own currency specifically for trade-related transactions among its member nations.
In this edition, we also present an extensive assessment of the most recent technological developments, encompassing captivating topics such as eSIM and gene editing.

This July-August 2023 issue of International Finance Magazine will feature the cover story 'The Era of Driverless Cars Dawns.' The article will explore the growing phenomenon of driverless cars, which are fast becoming the standard in the transportation sector. With artificial intelligence becoming the heart and brain of these cars, our cover story will explore this groundbreaking innovation in detail, highlighting the unique benefits it presents, including enhanced safety, efficiency, and convenience.
editor@ifinancemag.com
www.internationalfinance.com
TECHNOLOGY
BANKING AND
Collaborations between automakers, tech giants, and start-ups have accelerated the development of driverless cars

Meta is competing with Microsoft to be the first Metaverse platform in the world

ECONOMY
RISING COST TO HURT ‘SINGAPORE DREAMS’?

The Southeast Asian city-state’s economy expanded by 0.4% in the January-March 2023
Banks face a range of risks, including credit, market and liquidity ones
DOLLAR'S KINGSHIP UNDER THREAT?

As of 2023, central banks hold about 60% of their foreign exchange reserves in dollars

ONLINE SHOPPING: THE MONEY SPINNER
A recent study by McKinsey provide a thorough look at the direction that e-commerce in consumer products will go over the coming years

48 BaaS: Future of banking services

74 Making plastic industry ‘sustainable’
88 Is automation the way forward for manufacturing?


34
www.internationalfinance.com
HARSH SURESH BHARWANI CHATGPT: THE GAME CHANGER IN 2023

ChatGPT is highly adaptable, which makes it an ideal solution for businesses looking to automate their customer service operations model
Director & Publisher Sunil Bhat
Editorial Prajwal Wele, Agnivesh Harshan, CL Ramakrishnan, Prabuddha Ghosh
Production Merlin Cruz
Design & Layout
Vikas Kapoor
Technical Team
Prashanth V Acharya, Sunil Suresh
Business Analysts
Alice Parker, Indra Kala, Stallone Edward, Jessica Smith, Harry Wilson, Susan Lee, Mark Pinto
Business Development Managers
Christy John, Alex Carter, Gwen Morgan, Janet George
Business Development Directors
Sid Jain, Sarah Jones, Sid Nathan
Head of Operations
Ryan Cooper Accounts
Angela Mathews
Registered Office INTERNATIONAL FINANCE is the trading name of INTERNATIONAL FINANCE Publications Ltd
843 Finchley Road, London, NW11 8NA
Phone +44 (0) 208 123 9436
Fax +44 (0) 208 181 6550
Email info@ifinancemag.com
Press Contact editor@ifinancemag.com
Associate Office Zredhi Solutions Pvt. Ltd. 5th Floor, Sai Complex, #114/1, M G Road, Bengaluru 560001
Ph: +91-80-409901144
As people get ready to fly for their summer vacations, UK-based airline Easyjet has revealed that 1,700 flights have been cancelled. The airline cancelled flights to and from Gatwick Airport throughout the months of July, August, and September. Easyjet attributed the frequent cancellations to congested airspace over Europe and ongoing air traffic control issues. The company stated that 95% of the affected passengers were rebooked on different flights. According to aviation analytics company Cirium, July is expected to see the most UK aircraft departures since October 2019, and will be 11% higher than July last year.

According to Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg, Twitter competitor app Threads has signed up over 100 million users in less than a week. This makes Threads the fastest-growing app in history. OpenAI's ChatGPT previously held the crown by recording 100 million active users, but it took the app two months to reach that milestone. The new microblogging platform was launched in 100 countries including India. Within hours, the app proved to be a hit with users, racking up 30 million users within the first 24 hours, making it the fastest-downloaded app of all time.
The Federal Reserve's chief regulator said he had decided to strengthen fiscal cushions for larger banks. The moves would make the system more resilient. He said after mid-tier lenders like Silicon Valley Bank and First Republic Bank went bankrupt this year. Under the Fed's proposed plans, due to be released later this year, the largest banks could be required to hold an additional 2 percentage points of capital, or an additional $2 of capital for every $100 in risk-weighted assets. The exact amount of additional capital will depend on a company's operations, with the largest increases expected to be reserved.
According to a recent report by research firm Omdia, Apple is set to introduce an iPad Pro with an OLED panel in 2024. It is speculated to arrive in two screen sizes. The 11-inch and 13-inch iPad Pro models are reportedly on track to incorporate (LTPO) OLED panels. Production for these devices is expected to commence in the first quarter of the upcoming year. OLED displays offer impeccable black levels, per-pixel light control, and exceptional contrast and HDR capabilities.

Source:
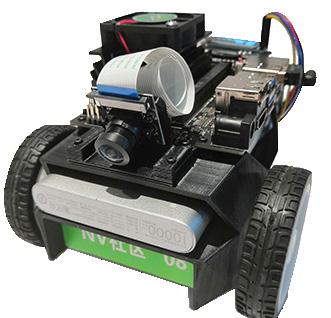
The Chinese auto industry has accelerated its global expansion this year. According to the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, exports grew over 81% year-on-year to 1.76 million vehicles in the first five months of 2023. The auto industry achieved a major milestone earlier this year when it overtook Japan as the world's largest vehicle exporter, thanks in large part to strong growth in foreign demand for its New Energy Vehicles (NEVs), a
segment that is primarily electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles.

According to the association, NEV exports increased by 163% to 457,000 vehicles in the five-month period, with significant growth coming from Europe. According to the European Automobile Manufacturers Association, China was the largest exporter of vehicles to the European Union last year, ahead of Turkey and the United Kingdom, and it grew strongly this year as well.
Under the terms of the 10year agreement, GMG will open around 50 stores under the JD fascia by 2028, across the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait and Egypt
During a meeting held at the Ministry of Energy and Infrastructure in Dubai, he said that UAE is employing AI in various fields to accelerate digital transformation


Lance Gokongwei recently spent 73.6 billion pesos ($1.3 billion) in order to ready his sprawling conglomerate to reap the fruits of a post-pandemic recovery

Prices have risen around the world as pandemic restrictions were eased and the war in Ukraine pushed up the cost of essential commodities
Biopharma deals hit new heights in 2020, with a remarkable 107% increase compared to 2018
Japanese workers' wages rose at a record pace after the government urged companies to help their workers after rising prices. Official figures show that wages rose 1.8% year-on-year (y-o-y) in May, the fastest pace in 28 years. However, taking inflation into account, people's real purchasing power continued to fall. Inflation in Japan, the world's third-largest economy, has been rising for more than a year.
In recent months, prices have risen around the world as pandemic restrictions were eased and the war in Ukraine pushed up the cost of essential commodities like oil and wheat. In Japan, the cost of everyday items has also been pushed up by the weakening currency. The latest official measurement of Japan's inflation rate showed that core consumer prices rose 3.2% y-o-y in May. For decades, the salaries of many people in Japan have increased little since there has been almost no inflation.
In March, as the cost of living continued to rise, the country's Prime Minister Fumio Kishida urged employers to take action. This year, com-

panies including Fast Retailing, which owns fashion chain Uniqlo, and car giants Toyota and Honda said they would increase wages for their employees. Recently, Japan's largest labour union, Rengo, said the companies had agreed on the biggest wage increases in three decades in annual labour negotiations.
According to research analysts from Japanese investment bank Nomura, the pay rises represent a symbolic structural change in the Japanese economy. Japan's potential labour pool shifted to a rapid decline around the end of 2021. This should put sustained upward pressure on wages.
Fast Retailing announced earlier this year that it was raising wages to 'compensate each and every employee appropriately for their ambition and talents.' The business continued by saying that it wanted to increase the company's growth potential and competitiveness in line with global standards. Koji Sato, the CEO of Toyota, expressed his optimism that the decision will benefit the whole Japanese auto sector and 'lead to frank discussions between labour and management at each company.'

The pharmaceutical industry is poised for remarkable growth in the coming years, fueled by a growing middle class and an ageing world population. With the pharmaceutical market expected to grow by 165.2% between 2020 and 2030, the sector offers lucrative opportunities for investors and stakeholders worldwide. The post-pandemic era has further propelled the industry, leading to a record number of biopharmaceutical deals and significant investments in healthcare systems. This trend has also attracted attention in the Middle East, particularly in the Gulf Cooperation Council, where a new frontier for the pharmaceutical industry is emerging.
According to a recent industry study by the Investment Promotion Agency Qatar (IPA), the global pharmaceutical market is on an upward trend. Biopharma deals hit new heights in 2020, with a remarkable 107% increase compared to 2018. The R&D spending also saw significant growth, reaching $189 billion in 2020.

This projected growth is a sign of the industry's steady post-pandemic expansion and
significant investment in global healthcare systems. It is estimated that the market will reach $2,051 billion by 2025, a 70% increase from 2020. Likewise, drug sales are expected to grow 32% from 2020 to $1,181 billion in 2024.
The Middle East is quickly becoming an important driver of expected growth. The region benefits from improved drug accessibility and robust economic development prospects, making it an attractive market for pharmaceutical investments. As countries actively focus on improving healthcare delivery and easy access to personalized digital services, GCC countries are seeing their $9 billion consumer healthcare market surge.
There are several key demand drivers for the pharmaceutical industry: an ageing population and an increase in chronic diseases, stress-related illnesses and pandemics are contributing factors. At the same time, supply-side drivers such as speciality medicines, patent expiry, generics and over-thecounter medicines offer additional growth opportunities within the sector.
The growing presence of working mothers is a key driver behind the expansion of the baby food packaging market
AI robots say, they have the potential to rule the world more effectively than humans









The global baby food packaging market was valued at $11.29 billion in 2022. It is projected to reach $17.67 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 5.1% over the entire forecast period. The growth of this market is primarily driven by several factors, including an increasing number of working mothers, a growing preference for a comfortable lifestyle, and growing concerns about infant health and hygiene.

The growing presence of working mothers is a key driver behind the expansion of the baby food packaging market. As more mothers enter the workforce, the demand for convenient and easy-to-use baby food products increases. This led to an increase use of packaged baby food.
Australia's gross domestic product grew 2.3% year-on-year in the first quarter, just slightly below analysts' expectations. Economists polled by Reuters had forecast growth of 2.4%, compared with 2.7% in the fourth quarter of 2022. On a quarterly basis, GDP grew by 0.2%, compared to the 0.3% expected in the Reuters poll. The GDP readings are key to the Reserve Bank of Australia’s decision-making process for its monetary policy.
"This is the sixth straight rise in quarterly GDP, but the slowest growth since the COVID-19 lockdowns in September quarter 2021," Katherine Keenan, head of National Accounts at Australia’s Bureau of Statistics said.





At a United Nations conference, a group of AI-powered humanoid robots delivered a thought-provoking message: they have the potential to rule the world more effectively than humans. However, these social robots stressed that caution should be exercised as humanity explores the rapidly advancing realm of artificial intelligence. While they acknowledged their inability to fully comprehend human emotions, they urged humans to tread carefully while harnessing AI's potential to address pressing global challenges, reported AFP.
Using AI to Address of problems such as climate change, hunger and social welfare, these advanced humanoid robots attended the United Nations AI for Good Global Summit in Geneva.

The Philippine Ministry of Finance (DOF) announced that it had signed a $600 million loan agreement with the World Bank (WB) to fund a rural development project aimed at modernizing agriculture and improving infrastructure. The loan agreement was signed for the Philippine Rural Development Project (PRDP) scale-up, which aims to transform agriculture into a modernized and industrialized sector through public infrastructure measures and strengthening the commodity value chain, reports the Xinhua news agency.
PRDP Scale-Up, an initiative by the Department of Agriculture (DA), is an expanded response to the ongoing challenges facing the country's agricultural and fisheries (A&F) sectors and rural communities.

Like the NFC chip used in payment systems like Apple Pay and Google Pay, an eSIM is essentially a tiny chip within your smartphone
An integrated SIM card, also known as an eSIM, eliminates the need for a physical SIM card and, consequently, a SIM card slot on your smartphone. Though Apple's iPhone 14 and iPhone 14 Pro are switching to eSIM-only in the US, the number of devices using it has stayed comparatively modest. Still, it's only time before other smartphone makers follow suit.
The first fully eSIM-only phone debuted as the firstgeneration Motorola Razr flip phone, not Apple's. However, until now, smartphones have tended to accommodate both eSIM and traditional SIM.
Under such circumstances, these devices replace a second SIM with an eSIM. They still have room for a conventional nano-SIM, which you can use as usual, but you may add a second number or data contract via the eSIM.
Since consumers may save plans from many networks on their eSIMs, there are benefits for both device manufacturers and networks using eSIMs.
The customer may, for instance, have a data roaming SIM for abroad use or use one number for work and another for personal conversations. In addition, if one opts for the eSIM, he/she might
have different voice and data plans.
What is an eSIM? What exactly will it give to its customers, then? Now let's elaborate.
eSIM stands for embedded SIM, which is all it refers to. No physical SIM cards are involved, and you do not need to switch over physically. However, not all networks currently accept eSIM, and the network/ carrier must support and enable it.
Like the NFC chip used in payment systems like Apple Pay and Google Pay, an eSIM is essentially a tiny chip within your smartphone.
Since the data on an eSIM is rewritable, you can choose to switch operators with just a quick phone call. Likewise, adding them to a data plan and linking devices with eSIMs to a mobile account takes just a few minutes.
The GSMA, the association of mobile networks, supports eSIM and has established the global standard for innovation.
There may be fewer choices, which would be bad for customers. Devices might come pre-loaded with one particular network rather than if it is sold exclusively. For example, customers getting iPhones with Vodafone eSIM, due to the business deal between Apple and the network provider.
Additionally, eSIM users can only quickly swap
eSIM stands for embedded SIM, which is all it refers to. No physical SIM cards are involved, and you do not need to switch over physically
phones after contacting their network. Of course, most people won't give that any thought, but it will be off-putting for some.
Thanks to cloud backup, SIM card storage is no longer necessary for most Android or iOS users, but it does need a mental shift for those using older/ less expensive phones because you can no longer physically switch a SIM card to a new phone.
After discontinuing dual SIM compatibility with the iPhone XS, Apple's iPhone 14 and iPhone 14 Pro are the company's first eSIM-only smartphones, at least in the US. The iPad Pro and every Apple Watch since the Series 2 also employ eSIM.
Although it was first exclusively used in the United States with Google Fi, the Google Pixel 2 also supported eSIM. Since the Pixel 3, every Pixel phone has offered it as a choice in addition to a standard SIM. The same is valid for Samsung Galaxy phones, starting with the S20 series.
The Moto Razr flip phones now have eSIM support, and both Windows 10 and Windows 11 have eSIM
support. In addition, some devices with cellular modems, like computers with Snapdragon processors, can use an eSIM as an alternative to inserting a nano SIM card.
Oppo's Find X3 Pro phone featured the first 5G standalone (SA) capable eSIM. This development means the rollout of lower latency 5G SA networks worldwide has enabled eSIM to support the most recent 5G networking standards.

Some carriers offer eSIM. A carrier's app or a QR Code one can scan is required. Once more, the page must support eSIM.
EE, O2, Vodafone, and Three all support eSIM in the United Kingdom. Users merely need to stop by a nearby store, call customer care, or download an eSIM to obtain an eSIM pack.
Let's examine the EE SIM pack. With EE, one can get a SIM card with a conventional appearance from a similar retailer. However, there is no SIM inside, you receive instructions and a QR code that your device can use to access the information. In the same way as a standard SIM card, each eSIM pack has its unique number.
Truphone has started offering eSIM data plans independent of established carriers. These are
available for purchase through the MyTruphone app. The worldwide plans from Truphone are compatible with 80 nations.
Initially only available on iOS, the software is now also usable with Pixel phones on Android.
Theoretically, using an eSIM should allow you to continue using your primary "home" number when travelling to another nation by simply adding a roaming eSIM to your phone. However, one drawback is that you can't access your number, for example, if you switch SIM cards when travelling abroad.
According to Steve Alder of Truphone, eSIMs might do away with international roaming fees.
"It also allows users to swiftly switch between operators to reconnect if they are in a signalpoor location, frees up space for new features or more battery life, and may reduce the danger of device theft. Mass adoption of eSIMs will be inevitable as customers and operators begin to recognize the benefits,” he said.

We may get smaller devices or larger batteries because a SIM card or the tray containing it is not required, which is one benefit it gives phone manufacturers. In addition, networks are optional to produce or distribute many SIM cards.
In addition, eSIMs will be fantastic for tablets and laptops, where seamless connectivity will become standard. Because eSIMs
take up less space within a device, fitness trackers or even glasses will be able to have standalone 4G or 5G connectivity in a way they weren't able to before, according to Vodafone.
Your iPhone will show both networks on the screen simultaneously if you have both a physical and an eSIM provisioned and use two different networks.
Customers can receive calls and texts on both numbers if the handset is on standby and the SIM and eSIM are provisioned. You can select a "default" line for calls, SMS, iMessage, and FaceTime. Only voice and SMS are available on the other line.
If you choose, you can use the secondary exclusively for cellular
data, which is advantageous if travelling and utilizing a local data eSIM.
Two eSIMs can be active at once on the iPhone 14 versions that only support eSIMs. So you can store up to eight eSIMs in total. Except there isn't a card involved, it functions the same as when you have a genuine SIM and an eSIM.
You need a QR code, if you have one. After availing the QR Code, select cellular under Settings. Then press two on the smart phone's keypad, to add a cellular plan. If you are an iPhone user, scan the QR code your carrier gave using your device. You might be prompted to provide an activation code.
As an alternative, you could be required to use a carrier app to activate your eSIM. For that, you need to visit the App Store and download the app for your carrier. Then you have to purchase a cellular plan via the app. Next, you will have to add the 'Data Plan' to your iPhone's settings.
The 'Truphone App' has the functionality to choose the desired plan and pay with the 'Apple Pay'. You will then need to press 'Add Data Plan' in the settings app on your phone for the project to take effect.
Do you need to get an eSIM?
Those will depend on your requirements and usage scenarios. For example, most people using a physical SIM will notice little change if they switch to an eSIM.
However, to lock their identities with their devices in case of theft, users concerned about the security and privacy of their SIM cards can switch to eSIM.
However, customers can only use luxury handsets to enjoy eSIM facilities, which are far more expensive than entry-level or midrange smartphone models.
Say, for a growing economy like India, iPhone 14 series will have both eSIM capability and a SIM card slot, allowing the users to select the options they see fit. In the case of US, you will be the only one who needs to switch over to an eSIM.
Considering that most smartphones across the lower segments rely on technology and that there are advantages of physical SIM cards for which there isn't a workaround, expect the plastic SIM cards to remain relevant. As for whether eSIMs will completely replace physical SIM cards, that may be possible years from now.
eSIMs represent the future of SIM cards. By eliminating the need for a physical SIM card and SIM card slot, eSIMs enable manufacturers to create smaller devices or larger batteries, and networks can produce or distribute fewer SIM cards. For users, eSIMs provide the ability to save plans from multiple networks, allowing them to have a data roaming SIM for use abroad or use one number for work and another for personal conversations.
The adoption of eSIMs is still in its early stages, with only a few devices currently using them. However, with the recent switch to eSIM-only for Apple's iPhone 14 and iPhone 14 Pro in the United States, other smartphone makers will likely follow suit. Additionally, the potential for eSIMs extends beyond smartphones to tablets, laptops, and even fitness trackers or glasses, where standalone 4G or 5G connectivity will become standard.
While there may be some drawbacks to using eSIMs, such as limited choices and the need to contact the network when switching phones, the benefits outweigh them. eSIMs can reduce international roaming fees, allow quick switching between operators, and reduce the risk of device theft.

Overall, eSIMs offer a convenient, efficient, and secure solution for SIM cards. As both customers and operators begin to recognize their benefits, the mass adoption of eSIMs will inevitably follow.
editor@ifinancemag.com
IF CORRESPONDENT
With roughly 3 billion subscribers on Facebook, 2 billion on WhatsApp, and 1.5 billion on Instagram, 38-year-old Mark Zuckerberg is the undisputed leader of the world's greatest social media empire. His business also received a significant redesign in October 2021, as it rebranded itself to Meta. The company with a market worth nearly $500 billion have been aggressively backing the "metaverse" in the last two years, a concept that pitches for an immersive online experience that would allow users to work, play, and socialize in virtual reality (VR) instead of navigating between different websites as mediated by computers/smartphones.
Reality Labs, the company's metaverse branch created when it bought Oculus in 2014 was expected to cost $10 billion in just one year.
All eyes will be on Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg in 2023, as the company returns to defensive mode after a large wave of layoffs. The company is trying
to copy Facebook's success on Web 2 by making an early version of the ‘Metaverse’. Numerous technological and cultural issues continue to impede Meta's progress in the Metaverse, which is why the tech giant reported quarterly losses.
Microsoft surprised the world by announcing its plan to acquire Activision Blizzard for $68.7 billion. If the United States’ Federal Trade Commission (FTC) doesn't step in, the acquisition will elevate Microsoft to the position of third-largest gaming company (behind Tencent and Sony), adding blockbuster games like Call of Duty, World of Warcraft, and Overwatch to its catalogue and giving it access to more than 30 studios (as opposed to Sony's 17).
But, this purchase is more of an

investment in the Metaverse than gaming. Gamers are fundamental, and the Metaverse is built on the foundation of their virtual reality.
Meta is competing with Microsoft and other companies to be the first Metaverse platform in the world.
The Metaverse, which will be developed as an abstraction layer over the actual world and interact with how we now live, will blend Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR).
Metaverse will be a new paradigm where our digital and online lives will intersect. However, it is still being determined how exactly the process will take place.
One of the better descriptions of the structural elements and levels of the Metaverse has been presented by entrepreneur and game designer Jon Radoff. The seven levels create an end-to-end value chain for the Metaverse. He names experience, discovery, creator economy, spatial computing, decentralization, human interface, and infrastructure. Experience dematerializes our physical environment to release a graphical background and social immersion, where content is generated dynamically via interactions and feeds rather than only by individuals. The process of discovery helps people to locate information sources about novel events. Simple instances of this are NFTs.
The tools that creators will utilize to produce more live, social, and dynamic experiences are all part of the creative economy. To push the limits of conventional interactions, spatial computing creates 3D environments, incorporates data flows from gadgets, and recognizes voice and gesture control.
Blockchain technology, for example, is used by decentralization to facilitate value transfer across entities. The human interface combines the human body with the computer to provide a seamless interface for traversing the Metaverse. Infrastructure is the primary technological layer that the Cloud, 5G, AI, next-generation mobile, and wearables rely on.
Most of the parts of this layered architecture are already in existence, even though some are still in their infancy. As a result, parts of the Metaverse may pass earlier than anticipated.
An endless pit
Reality Laboratories, the branch of Meta attempting to realize the Metaverse, is proving to be a more significant money pit than anticipated.
Reality Labs reported an operating loss of $4.28 billion for the 2022 fourth quarter, higher than the $3.3 billion in the third quarter.
According to CNBC, the figure is marginally less than experts' forecasts for a loss of about $4.36 billion for the quarter. This number and Meta's solid user base and deliberate cost-cutting measures helped the stock increase by about 19%
Reality Labs has pulled in over $13.7 billion over the last 12 months. Its fourth-quarter sales of $727 million exceeded analyst projections of $715.1 million.
Investors have been criticizing Meta's choice to keep pumping money into the Metaverse. One of them even urged for a cut back in these expenditures in an open letter titled "Time to Get Healthy."
However, the business has defended its pursuit of a vast new virtual world.
After the announcement of its
earnings results in March 2023, Zuckerberg participated in a Q&A session, where it was said the company, "There are no indications that we should change Reality Labs' long-term approach. We are always changing the specifics of how we carry this out."

A listener questioned if "accelerating losses" at Reality Labs should be anticipated in 2023 and whether such losses should be expected to peak this year.
"We still expect our full-year Reality Labs losses to climb in 2023, and we will continue to actively spend in this area given the enormous long-term prospects that we see," Susan Li, the chief financial officer of Meta said.
In a blog post he published in December 2022 titled "Why we still believe in the future," the company's chief technology officer Andrew Bosworth stated that Meta would keep allocating 20% of its budget to Reality Labs.
Andrew Bosworth allegedly informed Reality Labs' 18,000
employees in an internal email sent in late December that the business had already fixed too many problems by boosting manpower.
In addition, Meta's stock increased 19% after hours of the data release, indicating that many investors are ignoring losses in a segment that only accounts for slightly more than 2% of the business's revenue.
Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg is sure that the Metaverse is the future.
“The company's branch for virtual reality, Oculus, is already managed by Facebook. As a result, the capabilities of Oculus VR headsets are currently relatively constrained. But, Facebook wants to advance technology such that headsets no longer resemble bulky helmets and more closely resemble a pair of Warby Parker spectacles. In addition, the gear must give the user a genuine sensation of presence in the virtual world for the Metaverse to
function,” Mark Zuckerberg remarked.
Although Facebook will sell the equipment, which differs from where the money is made, on the earnings call, Mark Zuckerberg stated that Facebook's objective is to offer its headsets for the lowest feasible price and concentrate on generating revenue from trade and advertising within the Metaverse itself.
While advertising will continue to be present, Facebook will prioritize selling virtual items. According to Mark Zuckerberg, Facebook's approach to revenue earning from the Metaverse would include advertising in the Metaverse, but he sounded more optimistic about digital trade.
Several people view some of today's video games as early prototypes of what a metaverse may be, including Microsoft's Minecraft, Roblox, and Fortnite. These free games generate revenue by offering players virtual products. At the results conference, Mark Zuckerberg suggested that
Facebook adopt that business model and take a cut of each transaction to generate revenue in its own Metaverse.
According to tech investors, the moment is unsuitable for placing a wager on Meta Platforms finding cost savings as they pertain to significant investment in virtual reality. Instead, much of the market has been focused on the billions that Mark Zuckerberg is investing in Reality Labs and his vision of a future internet and social connections altered by the metaverse idea. As a result, the corporation is slashing expenses, including massive layoffs. At the moment, Reality Labs is losing more than $10 billion annually, but a senior Meta VR official told CNBC that the company will keep on investing.

Investors want the tech giant to cut back on spending amid a challenging stock market and a faltering economy. Alphabet is being pressured to reduce expenses. Amazon is laying off employees, many of them from business units whose risky ventures didn't pay off as well as expected. The value of Meta shares has decreased by 65% in 2023. In an October 2022 letter to its management, Altimeter Capital stated that Mark Zuckerberg's corporation has "drifted into the region of excess."
In an interview with CNBC's Steve Kovach, Ash Jhaveri, vice president of Reality Labs partnerships, described the layoffs as very terrible.
“But we are making the appropriate investments in our core business and our future,” he added.
Technocrats and CEOs believe that the technology is robust, and it is only a matter of time before Web 3.0, Virtual Reality, and blockchain technology intersect and create a highly profitable technological revolution.
Collaborations between automakers, tech giants, and start-ups have accelerated the development of driverless cars


In this article, we will explore the fascinating realm of driverless cars, delving into their development, the various benefits they offer, the challenges driverless cars face, and the transformative impact they are destined to have on our lives.
The historical context of driverless cars traces back to the early experiments and concepts of autonomous vehicles. While the idea of self-driving vehicles has captured the human imagination for decades, it wasn't until recent technological advancements and breakthroughs that driverless cars became a tangible reality.
One of the key milestones in the evolution of autonomous driving was the DARPA Grand Challenges. These competitions, organized by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), sparked significant progress in the field by incentivizing the development of autonomous vehicles capable of navigating challenging terrains without


human intervention.
In addition to government-sponsored initiatives, companies like Waymo, Tesla, and Uber emerged as key players in the driverless car race. These companies poured substantial resources into research and development, pushing the boundaries of what was deemed possible. Their efforts have resulted in significant advancements in sensor technology, artificial intelligence algorithms, and mapping systems.
Collaborations between automakers, tech giants, and start-ups have further accelerated the development of driverless cars. Strategic partnerships and joint ventures have facilitated the pooling of expertise and resources, fostering innovation and propelling the industry forward. This collaborative approach has fostered a diverse ecosystem, combining the automotive industry's manufacturing prowess with the technological expertise of software and AI companies.
The advent of driverless cars has ushered in a new era in transportation, where cutting-edge technology and artificial intelligence (AI) converge to redefine mobility. This ground-breaking innovation promises to revolutionize the way we commute, presenting unparalleled opportunities for enhanced safety, efficiency, and convenience
However, the journey towards widespread adoption of driverless cars has not been without challenges. Navigating the complex legal and ethical landscape surrounding autonomous vehicles has been a crucial consideration. Questions regarding liability in the event of accidents and the ethical decision-making of AI algorithms remain at the forefront of discussions.
To address these concerns, governments worldwide have been actively shaping the regulatory framework for autonomous vehicles. Initiatives and policies have been implemented to promote the safe development and deployment of driverless cars. By establishing guidelines and standards, governments aim to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring public safety.

The intertwining of technological progress and regulatory support has set the stage for the transformative impact that driverless cars
are poised to have on our lives. With each passing milestone, the dream of autonomous driving inches closer to reality, promising a future where transportation is safer, more efficient, and seamlessly integrated into our daily lives.

Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms play a crucial role in autonomous driving. Deep learning networks and neural networks are used for decision-making, enabling the vehicle to navigate complex scenarios and make real-time choices
Sensor technology forms the foundation of autonomous vehicles, serving as their eyes and ears in perceiving the surrounding environment. Cameras, LiDAR (light detection and ranging), radar, and ultrasonic sensors work in harmony to capture and interpret data from the vehicle's surroundings. While cameras provide visual information, LiDAR sensors use laser beams to measure distances and create 3D maps, radar detects objects and their velocities, while ultrasonic sensors help with short-range obstacle detection.
However, raw sensor data is meaningless without the ability to make sense of it. This is where data fusion and perception algorithms come into play. These sophisticated algorithms integrate and analyze data from multiple sensors, combining different modalities to create a comprehensive understanding of the environment. By processing the sensor inputs, these algorithms enable the vehicle to perceive objects, identify pedestrians, recognize traffic signs, and make informed decisions based on the current situation.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms play a crucial role in autonomous driving. Deep learning networks and neural networks are used for decision-making, enabling the vehicle to navigate complex scenarios and make real-time choices. These networks are trained on vast amounts of data, allowing the vehicle to learn and adapt to different driving conditions. The ability to process data and make predictions in real-time is a key aspect of autonomous driving, ensuring that the vehicle can respond quickly and accurately to changing situations.
Mapping and localization are also vital components of autonomous driving systems. High-definition maps, often created through meticulous data collection and surveying, provide detailed information about the road network, including lane markings, traffic signs, and speed limits. These maps are essential for the vehicle to have a precise understanding of its surroundings and to plan its trajectory. In conjunction with GPS (Global Positioning System), the vehicle can determine its position on the map with high accuracy.
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) techniques further enhance the vehicle's understanding
of its environment. By combining sensor data and the high-definition map, the vehicle can estimate its own position relative to the surroundings while simultaneously building or updating the map. SLAM algorithms ensure that the vehicle maintains accurate localization even in dynamic environments with changing conditions.
The integration of sensor technology, AI, and mapping systems enables autonomous vehicles to perceive their surroundings, make informed decisions, and navigate with precision. These technological advancements pave the way for safer and more efficient transportation, bringing us closer to a future where driverless cars become an integral part of our daily lives.
The emergence of driverless cars brings forth numerous benefits and has the potential for a significant impact on various aspects of transportation and society.
One of the most prominent advantages of driverless cars is enhanced safety. Human error is a leading cause of accidents on the road. By removing the human element from driving, autonomous vehicles eliminate the risks
Human error is a leading cause of accidents on the road. By removing the human element from driving, autonomous vehicles eliminate the risks associated with distracted driving, fatigue, and other human-related factors
associated with distracted driving, fatigue, and other human-related factors. With advanced safety features and accident avoidance systems, such as automatic emergency braking and blindspot detection, driverless cars have the potential to drastically reduce the number of accidents and save countless lives.


In addition to safety, driverless cars hold the promise of increased efficiency on the roads. With optimized traffic flow and reduced congestion, autonomous vehicles can minimize stop-and-go traffic, leading to smoother and more consistent travel times. This can result in significant time savings for commuters and reduced fuel consumption. Moreover, driverless cars can be programmed to drive more efficiently, maximizing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, thus contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Driverless cars also have the potential to improve accessibility and mobility. For the elderly, disabled, and underserved communities, autonomous vehicles offer newfound
independence and freedom of movement. People who are unable to drive due to physical limitations can regain their mobility through autonomous transportation solutions. Additionally, driverless cars can facilitate the growth of ride-sharing services and on-demand transportation, making transportation more accessible and affordable for a wider range of people.
The introduction of driverless cars can also have a transformative impact on urban planning and infrastructure. With the rise of autonomous vehicles, cities can rethink their designs, focusing less on parking spaces and more on creating pedestrianfriendly areas and green spaces. The need for massive parking lots can be reduced, freeing up valuable land for other purposes. Additionally, as driverless cars become more prevalent, they can integrate seamlessly with public transportation systems, providing efficient last-mile connectivity and reducing reliance on private vehicles. This integration can lead to more sustainable and interconnected transportation networks.
The benefits and impact of driverless cars are farreaching. They have the potential to revolutionize the way we travel by enhancing safety, improving
efficiency, increasing accessibility and mobility, and reshaping urban planning and infrastructure. As this technology continues to advance, it is crucial to address the challenges and concerns associated with autonomous vehicles, while also embracing the immense opportunities they offer for a safer, more efficient, and inclusive transportation system.
As the development of driverless cars progresses, it is essential to address the ethical considerations that arise with this transformative technology.
One significant ethical consideration is the decision-making algorithms employed in autonomous vehicles. These algorithms are responsible for making split-second decisions in potentially life-threatening situations. Moral dilemmas may arise, such as choosing between protecting the occupants of the vehicle and minimizing harm to pedestrians or other vehicles. Resolving these ethical dilemmas raises important questions about the value of human life and the principles by which these algorithms should operate.
Liability and responsibility are also critical ethical concerns surrounding driverless cars. In accidents involving autonomous vehicles, determining who is responsible can be challenging. Traditional notions of driver liability may no longer apply when human drivers are not involved. Establishing a clear framework for assigning liability is crucial to ensure fairness and accountability in these situations.
The cybersecurity risks associated with driverless cars present another ethical dimension. Safeguarding autonomous vehicles against potential hacking threats is paramount. Malicious actors could exploit vulnerabilities in the vehicle's software and systems, jeopardizing the safety of passengers and other road users. It is essential to prioritize cybersecurity measures to protect against these threats, ensuring the integrity and safety of autonomous vehicles.
Ensuring data privacy and protection is an additional ethical consideration. Autonomous vehicles generate vast amounts of data about their surroundings and occupants. Safeguarding this data from unauthorized access and misuse is crucial to
Penetration rate of light autonomous vehicles (L4) worldwide in 2021, with a forecast through 2030
protect the privacy and rights of individuals. Clear policies and robust security measures must be in place to prevent data breaches and uphold individuals' privacy rights.
During the transition period towards widespread adoption of driverless cars, the coexistence of autonomous and traditional vehicles on roads poses ethical challenges. Integration requires effective communication and cooperation between different types of vehicles. Ensuring that autonomous vehicles can operate safely alongside human drivers is crucial to avoid accidents and conflicts. Additionally, addressing the societal and workforce implications of autonomous vehicles is essential. The potential impact on employment, particularly for professional drivers, must be considered, and measures should be taken to mitigate any negative consequences.
Driverless cars raise important ethical considerations that must be addressed to ensure their responsible and ethical implementation. This includes grappling with decision-making algorithms and moral dilemmas, establishing liability frameworks, safeguarding against cybersecurity risks, protecting data privacy, managing the coexistence of autonomous and traditional vehicles, and addressing societal and workforce implications. By addressing
these ethical considerations proactively, we can navigate the path to a future where driverless cars enhance safety, efficiency, and convenience while upholding the values and principles that are essential for a just and equitable society.

The advent of driverless cars has paved the way for the evolution of Mobility as a Service (MaaS), transforming the way we perceive transportation and challenging the traditional model of car ownership. MaaS represents a shift towards mobility solutions that offer convenient and efficient alternatives to owning a personal vehicle.
With MaaS, individuals have access to a range of transportation options, seamlessly integrated through digital platforms. This includes ridesharing services, bike-sharing programs, ondemand shuttles, and public transportation, all accessible through a single app. The integration of driverless cars into MaaS further expands the possibilities, providing an additional layer of convenience and flexibility.
Integration with public transportation and other modes of travel is a key aspect of MaaS. By combining different modes of transportation, individuals can plan and optimize their journeys, making the most efficient use of available options. Seamless connections between driverless cars,
buses, trains, and other modes of transportation enable commuters to reach their destinations quickly and hassle-free, reducing congestion and improving overall mobility.
The transformation of urban landscapes is another consequence of the rise of driverless cars. As the need for parking spaces diminishes due to the shared and on-demand nature of autonomous vehicles, cities can reimagine the use of valuable urban space. Redevelopment of parking areas can lead to the creation of green spaces, pedestrian zones, or new infrastructure that better serves the community's needs. Additionally, the integration of driverless cars into intelligent transportation systems enables the development of smart cities. These cities leverage data and technology to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance overall urban efficiency
Technological advancements play a crucial role in shaping the future of driverless cars and MaaS. Continuous improvements in sensor technology and AI algorithms allow autonomous vehicles to perceive and understand their environment with greater accuracy and reliability. This enhances the safety and efficiency of driverless cars, making them more suitable for widespread adoption. Moreover, the development of electric and sustainable driverless vehicles further contributes to reducing carbon emissions and promoting environmental sustainability.
The evolution of Mobility as a Service, urban
landscape transformation, and technological advancements are driving the future of driverless cars. The shift from car ownership to integrated mobility solutions promotes efficiency, convenience, and reduced congestion. As cities embrace the potential of driverless cars and intelligent transportation systems, the urban
landscape will undergo transformations that prioritize sustainability and community needs.
As driverless cars inch closer to widespread adoption, their transformative potential cannot be overstated. These autonomous wonders promise to redefine the way we travel, offering safer roads, reduced congestion, and enhanced accessibility.
Recently, International Finance caught up with Amir Khajepour, Professor in the Department of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering at the University of Waterloo, and a Canada research chair in Mechatronic Vehicle Systems.

He is also a fellow of the American and Canadian Society of Mechanical Engineering (ASME and CSME) and is an associate editor of the International Journal of Vehicle Autonomous Systems and International Journal of Powertrain.
Professor Amir Khajepour’s areas of research are concentrated on vehicle systems. This includes the development of hybrid powertrains (electric and air hybrid engines), component sizing and power management design through concurrent optimization, vehicle modelling through real-time simulation and hardware-in-the-loop, active and adaptive suspension systems, and vehicle stability.
The driving force of Professor Amir Khajepour’s research is the modelling and control of dynamic systems.
His research has also extended to ultra-high-speed robotics, automated laser fabrication, and micro-electrical-mechanical systems.
Professor Amir Khajepour’s research has resulted in several patents, technology transfers, and over 320 journal and conference publications including three books and six book chapters.
In his interview with International Finance, Professor Amir Khajepour provides a captivating discourse on the intricate mechanics of driverless cars. With profound insights, he analyses the various advantages and drawbacks of this groundbreaking technology, delving into its profound impact on the job market, while highlighting the potential challenges that lie on the horizon.
IFM: How do driverless cars work and are they safe to ride in?
Professor Amir Khajepour: A driverless car is equipped with sensors and computers that enable it to perceive the environment, traffic, and other drivers' intentions. It follows
The safety of an autonomous car relies on our ability to accurately perceive the environment and make sound reasoning to determine driving decisions
However, navigating the challenges of ethics, cybersecurity, and societal impact will be crucial in realizing the full potential of this revolutionary technology. With ongoing advancements and concerted efforts from various stakeholders, the era of driverless cars is poised to reshape transportation as we know it, unlocking a future
driving rules and makes the decisions necessary to operate the vehicle. The safety of an autonomous car relies on our ability to accurately perceive the environment and make sound reasoning to determine driving decisions.
What is your take on driverless cars replacing human drivers in the near future?
Driverless cars are currently being utilized in dedicated or well-defined environments, but the complete replacement of humans in all driving conditions and environments is still a long way off.
How do driverless cars navigate and communicate with each other?
Driverless cars navigate using their onboard suite of sensors, GPS, and high-definition local maps. In the future, communication between vehicles can further enhance the safety of driverless cars.
According to you, what are the advantages of driverless cars?
Driverless cars can help alleviate driver shortages and improve
where efficiency, convenience, and sustainability go hand in hand.
As we prepare to embrace this new era, let us embark on a journey where technology seamlessly connects us to our destinations, paving the way for a brighter and more connected world.
operational efficiency in certain applications.
How do driverless cars detect obstacles and pedestrians?
There are various sensors, including LiDARs, cameras, and radars, that can detect objects, identify their types, and determine their speed and direction.
What are the ethical considerations of driverless cars?
This is a broad topic, primarily related to cases involving the prevention or mitigation of accidents. For example, it pertains to situations where a decision must be made during an emergency to prioritize the safety of pedestrians or the occupants of the vehicle.
Will driverless cars have an impact on the job market?
I don't believe that driverless vehicles will have a significant impact on the job market for vehicle drivers at this time, as their market share is still too small. However, they do have a positive impact on industries facing driver shortages, such as mining, farming, and others.
How do driverless cars handle rough weather conditions?
In most cases, autonomous vehicles are unable to handle rough weather
conditions and they fully transfer control to human drivers.
What are the current regulations and policies for driverless cars?
The development and adoption of autonomous vehicles and related regulations and policies vary depending on countries and jurisdictions. It is an evolving field, with some countries/jurisdictions being more advanced in this area while others have yet to embrace autonomous vehicles or develop any regulations/policies.
Can you tell our readers about the potential challenges one has to face as a result of the widespread adoption of driverless cars?
The current challenges lie in advancing vehicles to a higher level of autonomy where the complete removal of the human driver becomes feasible. Therefore, widespread adoption of driverless cars on public roads is not expected to occur in the near future to pose any potential challenge.
The idea of using gene editing to treat disease or alter traits dates back at least to the 1950s, when the double-helix structure of DNA was discovered
Medical innovations typically take 17 years, from the moment a lightbulb lights up in a scientist's mind to the first person to benefit from it. But every once in a while, an idea is so powerful and profound that its effects are felt much more quickly. That was with CRISPR gene editing, which celebrated its 10th anniversary in May 2023. It has already had a major impact on laboratory science, improving precision and accelerating research, and leading to clinical trials for a handful of rare diseases and cancers. Scientists predict that over the next decade, CRISPR will spawn several approved medical treatments that will be used to modify crops, making them more productive and more resilient to disease and climate change.
Gene editing is the ability to make highly specific changes in the DNA sequence of a living organism, essentially altering its genetic makeup. Gene editing is done using enzymes, specifically nucleases, which have been engineered to target a specific DNA sequence, where they make cuts in the DNA
strands, allowing the removal of existing DNA and the insertion of replacement DNA. Key to the gene editing technologies is a molecular tool called CRISPR, a powerful technology discovered in 2012 by American scientist Jennifer Doudna, French scientist Emmanuelle Charpentier and refined by American scientist Feng Zhang and colleagues.
The CRISPR worked precisely, allowing researchers to remove and insert DNA at desired locations. Significant advances in gene-editing tools have lent renewed urgency to long-standing debates about the ethical and social implications of genetic engineering in humans. Many questions, such as whether genetic engineering should be used to treat human diseases or alter traits such as beauty or intelligence, have been asked in one form or another for decades. However, with the advent of simple and efficient gene editing technologies, notably CRISPR, these questions were no longer theoretical and the answers to them had very real implications for medicine and society.
The idea of using gene editing to treat disease or alter traits dates back at least to the 1950s, when the double-helix structure of DNA was discovered. In the mid-20th century, researchers realized that the base sequence in DNA is mostly passed from parent to offspring faithfully, and that small changes in sequence can mean the difference between health and disease. The realization of the latter led to the inescapable assumption that with the identification
CRISPR will spawn several approved medical treatments that will be used to modify crops, making them more productive and more resilient to disease and climate change
of molecular flaws that cause genetic diseases, there would be an opportunity to correct those flaws and thereby enable the prevention or reversal of diseases. This thought was the basic idea behind gene therapy and was considered the holy grail of molecular genetics from the 1980s onwards. However, developing gene editing technology for gene therapy proved difficult. Many early advances did not focus on correcting genetic errors in DNA, but on attempting to minimize their consequences by providing a functional copy of the mutated gene, either inserted into the genome or as an extrachromosomal unit (outside the genome). While this approach was effective for some disorders, it was complicated and limited in scope. To truly correct genetic errors, researchers had to be able to create a double-stranded break in the DNA at precisely the desired location in the more than three billion strands of DNA that make up the human genome. Once the double-strand break was created, the cell could efficiently repair it using a template that directed the replacement of the defective sequence with the good sequence. However, making the initial break at precisely the desired location—and nowhere else—within the genome was not easy.
Before the introduction of CRISPR, two approaches were used to generate site-specific double-strand breaks in DNA: one was based on zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs) and the other was based on transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs). ZFNs are fusion proteins composed of DNA-binding domains that recognize and bind to specific three to four-base pair sequences. For

example, to confer specificity on a nine-base pair target sequence, three back-to-back fused ZFN domains would be required. The desired arrangement of DNA-binding domains is also fused to a sequence encoding a subunit of the bacterial nuclease Fok1. To enable a doublestranded cut at a given site, two ZFN fusion proteins must be constructed, one binding to opposite strands of DNA on either side of the target site. When both ZFNs are bound, the neighbouring Fok1 subunits bind to each other and form an active dimer that cuts the target DNA on both strands.
TALEN fusion proteins are designed to bind to specific DNA sequences flanking a target site. But instead of zinc finger domains, TALENs use DNA-binding domains derived from proteins from a group of plant pathogens. For technical reasons, TALENs are easier to construct than ZFNs, especially for longer recognition sites. Similar to ZFNs, TALENs encode a Fok1 domain fused to the engineered DNA-binding region. Thus, once the target site is bound on both sides, the dimerized Fok1 nuclease can introduce a double-strand break at the desired DNA position.
Unlike ZFNs and TALENs, CRISPR uses RNA-DNA binding instead of protein-DNA binding to drive nuclease activity, simplifying design and allowing the application to a wide range of target sequences. CRISPR was derived from the adaptive immune system of bacteria. The acronym CRISPR refers to clustered, regularly spaced short palindromic repeats found in most bacterial genomes. Between the short
palindromic repeats are sequence sections that clearly originate from the genomes of bacterial pathogens. Older spacers are located at the distal end of the cluster and newer spacers representing newer pathogens are located near the proximal end of the cluster.
Transcription of the CRISPR region results in the production of small guide RNAs containing hairpin formations from the palindromic repeats linked to spacer-derived sequences, allowing each to bind to its respective target. The formed RNA-DNA heteroduplex then binds to a nuclease called Cas9, directing it to catalyze the cleavage of doublestranded DNA at a position near the junction of the target-specific sequence and the palindromic repeat in the guide RNA. Because RNADNA heteroduplexes are stable and because designing an RNA sequence that specifically binds to a unique target DNA sequence requires only knowledge of the Watson-Crick base pairing rules (adenine binds to thymine [or uracil in RNA], and cytosine binds to guanine), the CRISPR system was preferable to the fusion protein designs required to use ZFNs or TALENs.
Another technical advance came in 2015 when Zhang and colleagues reported using Cpf-1 instead of Cas9 as a nuclease pairing with CRISPR for gene editing. Cpf-1 is a microbial nuclease that offers potential advantages over Cas9, including the need to only require a CRISPR guide RNA for specificity and to make staggered (rather than blunt) double-stranded DNA cuts. The altered nuclease properties
may have allowed better control over the insertion of surrogate DNA sequences than was possible with Cas9, at least under certain circumstances. Researchers suspect that bacteria also harbour other genome-editing proteins.
CRISPR to treat cancer
CRISPR has the potential to improve cancer treatment, by boosting the immune system, It has been utilised in blood cancer patient trials since 2016 to alter the patients' own immune cells outside of the body to start an immunological attack on the malignancy. Multiple forms of blood cancer have been successfully treated using this strategy, known as CAR-T. Until recently, CAR-Ts had to be manufactured specifically for each patient, which required resources that some patients may not have.
According to Rachel Haurwitz, CEO, president, and co-founder of the company alongside Doudna, Caribou Biosciences is working

enabled the creation of animal models of human diseases and the removal of HIV from infected cells. In a mouse model of human disease, CRISPR-Cas9 was successfully used to correct a genetic error, resulting in the clinical rescue of diseased mice.

on an "off-the-shelf" version of the medication that will be available in a freezer for the following patient who requires it. Weeks of preparation time and possible costs would be reduced in this way. CRISPR has the potential to improve cancer treatment. It has been used in blood cancer patient trials since 2016 to alter the patients' own immune cells outside of the body to start an immunological attack on the malignancy. Multiple forms of blood cancer have been successfully treated using this strategy, known as CAR-T. Until recently, CAR-Ts had to be manufactured specifically for each patient, which required resources that some patients may not have.
or changing the genetic "letters" that are creating issues. Later this year, the first CRISPR-based gene treatment for sickle cell disease is anticipated to receive approval, USA Today reported.
Applications and controversies
CRISPR has been used in a variety of ways. For example, it has been applied to early embryos to create genetically modified organisms and injected into the bloodstream of laboratory animals to achieve extensive gene editing in subsets of tissues. CRISPR-based approaches have been used to alter the genomes of crop plants, livestock, and laboratory model organisms, including mice, rats, and nonhuman primates. By modifying the genomes of bacteriophages (bacteria-killing viruses) with CRISPR technology, scientists have been able to develop methods to destroy antibiotic-resistant bacteria. CRISPR systems also
In 2015, a group of scientists that included Doudna advocated caution in applying CRISPRCas9 technology to humans, at least until the safety and ethical implications of human gene editing could be properly considered. Other researchers advocated going full steam ahead, arguing that the new technology held the key to alleviating many human ailments and that it would be unethical to withhold it. Around the same time, reports from China indicated that gene-editing experiments had been carried out on human embryos. In late 2018, a Chinese scientist announced the birth of the world's first genetically engineered human babies. The infants, twin girls, are said to carry an altered gene that reduces the risk of HIV infection. The positive and negative consequences of these activities were seen as potentially redefining the future of human genetics.
CRISPR gene editing is revolutionizing genetic engineering, with the potential for medical treatment and agriculture. Despite ethical debates, CRISPR has shown promise in laboratory science and clinical trials due to its precise DNA-editing capabilities. We can see CRISPR advancements in future.
A single genetic "misspelling" is responsible for more than 6,000 uncommon inherited disorders. For these, CRISPR gives the option of eliminating the problematic gene, boosting an alternative gene, editor@ifinancemag.com


In 2023, ChatGPT (Chat Generative Pretrained Transformer) will become a game changer in the worlds of artificial intelligence and natural language processing. This cutting-edge technology has revolutionised the way we interact with machines, making communication faster, more intuitive, and more human-like.
It is a type of machine-learning algorithm that has been specifically designed to understand and interpret human language. By training on vast amounts of text data, ChatGPT can learn to generate responses to questions and conversations in a way that is both natural and accurate.
One of the most exciting aspects of ChatGPT is its versatility. It can be integrated into a wide range of applications, from chatbots and virtual assistants to customer service platforms and social media networks. This means that users can interact with machines in a more seamless and intuitive way than ever before.
ChatGPT is also highly adaptable, which makes it an ideal solution for businesses looking to automate their customer service operations. By integrating ChatGPT into their platforms, companies can reduce the time and resources required to handle customer queries and complaints. This, in turn, can lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty, as well as increased revenue.
Perhaps the most impressive aspect of ChatGPT is its ability to learn and improve over time. As users interact with the technology, it gathers data about their preferences and behaviours, allowing it to tailor its responses more effectively. This means that the more people use ChatGPT, the better it becomes at understanding and interpreting human language.
Of course, like any emerging technology, there are some potential drawbacks to ChatGPT. One concern is that it could lead to job losses as more companies look to automate their customer service operations. However, proponents of the technology argue that it will create new jobs in the fields of artificial intelligence and machine learning, as well as free up human workers to focus on more complex and creative tasks. Here are a few possible scenarios where ChatGPT is used.
ChatGPT could be used as a personal assistant for individuals, helping them with tasks like scheduling appointments, making travel arrangements, and answering questions.
ChatGPT could be used by businesses to provide 24/7 customer support via chat or messaging platforms. ChatGPT could help
ChatGPT is highly adaptable, which makes it an ideal solution for businesses looking to automate their customer service operations
AYALA is a unique residential project, presenting the most elegant and modern villas in Al Khobar City.

retal.com.sa


customers with common inquiries and provide guidance on product or service issues.
Language Translation
ChatGPT could be used to translate text from one language to another in real-time. This could be particularly useful for businesses that operate in multiple countries or for individuals who communicate with people from different parts of the world.

Content Creation
ChatGPT could be used to create content, such as articles or reports, based on a set of guidelines or specifications. This could be useful for businesses that need to produce a large amount of content quickly and efficiently.
ChatGPT could be used as a virtual tutor or teacher, helping students with homework, providing explanations of complex topics, and offering personalized learning experiences.
Another concern is the potential for ChatGPT to be used for malicious purposes, such as spreading misinformation or propaganda. While this is certainly a possibility, it is important to note that ChatGPT is only as good as the data it is trained on. By ensuring
that the data is accurate and unbiased, developers can minimize the risk of the technology being used for harmful purposes.
Overall, it is clear that ChatGPT is a game changer in the world of artificial intelligence and natural language processing. Its ability to understand and interpret human language in a natural and intuitive way has already had a significant impact on the way we interact with machines, and this impact is only set to grow in the coming years.
Whether you are a business owner looking to streamline your customer service operations or simply someone who wants to interact with machines in a more natural way, ChatGPT is a technology that is worth exploring. As we move further into the 21st century, it is technologies like ChatGPT that will continue to shape the future of our digital interactions.
Mr. Harsh Suresh Bharwani is the CEO and MD of Jetking Infotrain. He spearheads the international business, dedicated services, and employability initiatives at Jetking Infotrain. In the past decade, Harsh has trained over 40,000 students on success, confidence, social skills, leadership, business, health, and finance.
editor@ifinancemag.com
An integrated city, included with the availability of all services, the proximity of distances from the most vital places between Al Khobar and Dammam. Also, a sustainable infrastructure with excellent standards.

retal.com.sa


Sri Lanka defaulted on its $51 billion foreign debt for the first time since gaining independence in 1948 as it grapples with its worst economic crisis
In April, the World Bank invited several leading experts to explore prospects for a new global financial architecture for debt. Speakers discussed lessons from past restructuring efforts, the role of the private sector and the increased need for debt transparency. Zainab Haruna from Nigeria started the conversation by explaining how government debt can affect the lives of ordinary people.
Angolan Finance Minister Vera Daves spoke with World Bank Group Ex-President David Malpass on how the economic fallout from COVID-19 and Russia-Ukraine has impacted their country's revenue and debt. Kevin Watkins, CEO of 'Save the Children,' and K.Y. Amoako, President of the African Center for Economic Transformation, described how unsustainable debt can slow countries' progress and divert resources that could otherwise be used to invest in health, education and more.
Citi's Julie Monaco and World Bank Chief Economist Carmen Reinhart both referred to the debt crises of the 1980s and 1990s and the lessons this challenging era can offer. Last year, Sri Lanka defaulted on its external
debt (excluding debt to multilateral organizations such as the World Bank) and in July 2022 saw the resignation of an Executive President for the first time in Sri Lanka's history. The country faced a shortage of fuel, cooking gas, medicines and many essential goods.
At the same time, the country faced a massive political crisis that sparked island-wide protests that led to the resignation of Mahinda Rajapaksa as prime minister in May last year. Two months later, President Gotabaya Rajapaksa, Mahinda's brother, also had to resign.
The island nation has defaulted on its $51 billion foreign debt for the first time since gaining independence in 1948 as it grapples with its worst economic crisis. The South Asian country was grappling with soaring inflation of 17.5%, a 12-hour power outage, and dwindling foreign reserves.
While many experts have pointed out that excessive government spending, tax cuts and the first and second waves of COVID-19 worsened the country's economic crisis, others believe Sri Lanka's close ties with China have fueled the country's debt crisis. However, Sri Lanka is not the first country to default on its debts. Over the past century, several countries have defaulted on one or more occasions. According to the World Economic Forum, 147 countries have 'sovereign defaulted' on their debt since 1960.
Governments are typically reluctant to default because it is likely to lock the country out of debt markets for years to come and make borrowing more expensive, at least for a period when it becomes possible again

Sovereign bankruptcy is the failure of a national government to repay its debts. Governments are typically reluctant to default because it is likely to lock the country out of debt markets for years to come and make borrowing more expensive, at least for a period when it becomes possible again. Lenders have limited recourse in the event of a sovereign debt default, as no international court can force a country to pay, although it can claim the defaulted borrower's assets abroad. Countries borrowing in their own currency can always print more as an alternative to sovereign default. and may also avoid doing so by generating more tax revenue.
Private investors investing in the sovereign debt of other countries closely study the economy, public finances and politics of a bond-issuing country to assess and assess its risk of default. Other countries and multinational lenders such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank lend to states to achieve policy goals ranging from improving the borrowing country's governance to boosting the lender's exports, and
may be able to insist on their repayment even if the borrower defaults on other debts.
Government bonds issued in local currency may also attract private foreign investors, but are often primarily bought by the country's banks and private individuals. A default by a sovereign in its own currency is easier to avoid and can be more politically painful than a default on external debt. Because a national bankruptcy entails a number of costs and economic risks, it is usually used as a last resort. Severe economic downturns, financial crises and political unrest can trigger a national bankruptcy. For example, Russia's default in June 2022 was the result of economic sanctions imposed on the country for its invasion of Ukraine, including a freeze on Russia's foreign exchange reserves abroad.
Experts say, a nation may have momentarily defaulted if it temporarily delays interest payments on a small number of its bonds for administrative reasons unrelated to its capacity or willingness to repay debt, as the US Treasury once did in the 1970s. So long as the
repayment snag is quickly ironed out, such a 'default' is unlikely to have any long-term consequences, or to be widely viewed as one. For instance, amid one of the US government's recurring episodes of debt ceiling brinkmanship, the United States continues to be among the highest-rated sovereigns in the world, despite Standard & Poor's downgrading its long-term rating for US national debt from AAA to AA+ in 2011.
Governments that are already generally believed to be likely to take that course of action may occasionally negotiate a bonds exchange, exchanging their previously issued and frequently severely discounted bonds for new ones of lower value, in order to prevent this outright default. In exchange for the sovereign's promise to continue making lower debt payments, the bondholders effectively take a 'haircut' (a risk of the underlying asset) on the money they have already lent. Lenders agree that such an exchange is the least terrible choice available to them. This is an implicit default because the exchange can only take place if the sovereign's ability to honour its commitments to previously issued debt is severely questioned by creditors. With the assistance of its European partners, Greece made a number of similar settlement offers to bondholders during the European sovereign debt crisis.

For the defaulting government and its citizens, the consequences of a sovereign debt default vary
depending on factors such as the state of the economy and public finances, the degree of dependence on external financing and the likelihood that creditors will return in the future. Credit markets tend to be large countries with exploitable natural resources like Russia to be more open and forgiving than small lowincome countries, which are often dependent on IMF loans and aid. Meanwhile, Russia defaulted on its loan commitments in 1918, when Lenin's government rejected the Tsarist Empire's debt, and again on its ruble-denominated commitments in 1998, although it continued to make payments on its external debt after a brief moratorium. If a country is highly dependent and promotes foreign creditors to finance investments, the consequences of the sovereign default are likely to be slower economic growth, making the situation more difficult for
consumers and businesses.
The sovereign debt bankruptcy will also lower the net asset value of all bond mutual funds holding the defaulted debt and its market value will fall. Conversely, a sovereign default could present an opportunity for distressed debt investors, who could buy the bonds at deep discounts to face value in the hope that they might be worth more later after a debt restructuring. Sovereign debt defaults also create winners and losers in the market for credit default swaps, which are financial contracts that pay out like an insurance policy in the event of a default. Credit default swaps allow bondholders to hedge against the risk of default and allow speculators to bet that a default will occur.
In 1557, Spain became the first country to default. Notably, this
European country defaulted on its debt 15 times between the 18th and 19th centuries. Argentina defaulted on its $132 billion in loans in 2001. As a result, the South American country defaulted again in 2016 and 2020.
Russia defaulted in 1918 and 1998. After the breakup of the USSR, Russia inherited a $100 billion foreign debt in 1993 at the request of creditors in exchange for promised financial assistance, according to the International Monetary Fund. Amid international sanctions imposed on the country for invading Ukraine, experts have warned that Russia could default on $117 billion worth of loans again.
Ukraine defaulted on its loans in 1998 and 2020. Between 2017 and 2018, the Latin American country of Venezuela defaulted on its $60 billion worth of loans. Greece twice defaulted on its $1.7 billion and $456 million debt in 2015. Ecuador
defaulted on payments in 2008 and 2020. Mexico defaulted in 1982 and 1995. In 2010, the North American country of Jamaica defaulted on its $7.9 billion debt.
In 2020, amid the pandemic, two Latin American countries, Argentina and Ecuador defaulted. Argentina adopted a take-it-orleave attitude towards creditors, often leading to public dissent and dramatic breakdowns in negotiation. But in each round of negotiations, the country gave the creditors ground. Argentina started the process with support from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), whose economists backed Argentina's calls for a generous restructuring.
However, Argentina's final agreement with creditors included a 45% discount on interest payments and a six-month grace period, in contrast to the government's original
requirement of a 61% discount and a three-year grace period. Argentina also reluctantly agreed to change the collective action clauses in its bonds, a legal innovation aimed at minimizing so-called hold-outs that emerged from the protracted litigation that followed Argentina's 2001 debt saga.
In contrast, Ecuador emphasized transparency and quiet consensus-building. Unlike Argentina, Ecuador agreed early on to grant bondholders special legal protections in the event of future restructuring. It also secured financial support from the IMF and received an emergency loan to deal with the public health and economic consequences of COVID-19.
In 2022, Belarus was declared bankrupt by Fitch Ratings and jointly announced with Moody's Investors Service that Russia's most trusted ally has officially breached the terms of its debt obligations to foreign investors. The eastern European country's rating was cut to the default of RD by Fitch, below C. The credit checker cited the country's failure to provide a dollar coupon payment on $600 million in US Dollar-denominated bonds, which is to be paid by 2027.
Moody's said that the incident constituted a default, but left its rating stable at CCC. Back then, the Belarusian Ministry of Finance accused the international rating agency Moody's of a provocation which, according to Minsk, is intended to affect the Eurobond market.
editor@ifinancemag.com


Banks are exposed to a range of risks, including credit risk, market risk and liquidity risk

The collapse of banks in the United States is not a new phenomenon. Throughout history, the country has experienced several financial crises, with numerous lending bodies experiencing catastrophic bankruptcies. These collapses have also brought far-reaching effects on the economy, causing severe disruption, job losses and even recessions.
This year has seen the same sector coming into the news again, due to the downfall of three prominent regional banks. Now, let’s try to understand the factors which make the financial sector in the world’s largest economy a vulnerable one.
Just like how Rome was not built in one day, banking collapses in the United States have always been about the complex interplay of certain factors, on which this article will shed light upon.
Major factors behind the bank failures in the world’s largest economy are financial mismanagement and risky practices. Banks are exposed

to a range of risks, including credit risk, market risk and liquidity risk. When banks make poor lending decisions or take excessive risks, they endanger their financial stability.
For example, during the 2008 subprime mortgage crisis, several banks suffered significant losses from their exposure to high-risk mortgage-backed securities. In addition, inadequate risk management practices can amplify the impacts of these risks. Failure to accurately assess and mitigate risks can result in large losses, leaving banks unable to meet their obligations.
Poor risk controls and lax oversight can also lead to fraud and internal misconduct, leading to bank failures. The collapse of Lehman Brothers in 2008 is a stark reminder of the consequences of poor risk management. And add the collapses of Signature Bank, First Republic Bank and Silicon Valley Bank, again the high-risk securities angle is emerging.
Economic downturns and external shocks also play a crucial role in bank failures. Banks are very sensitive to fluctuations in the economy and financial markets. During recessions or periods of economic turbulence, the quality of the borrower's creditworthiness deteriorates, leading to higher loan defaults and delinquencies. This adversely affects banks' balance sheets, eroding their capital reserves and hampering their ability to absorb losses.
External shocks such as drastic changes in interest rates (decided by the US Federal Reserve) or falling asset prices can also trigger bank failures. When banks are exposed to highly volatile assets, sudden market movements can result in significant losses and bring them to the brink of bankruptcy. The collapse of Bear
Stearns, an American investment bank in 2008 after the mortgage crisis is a prime example of how external shocks can rapidly deteriorate a bank's financial condition. The year 2023 has seen the downfall of three prominent American banks one after another, with the Fed rate hike coming under the focus.
In some cases, regulators fail to adequately identify or address emerging risks. Weak regulations, loopholes or poor enforcement can encourage risky behaviour by banks, creating a breeding ground for financial instability. Deregulation efforts in the late 20th century, such as the repeal of the Glass-Steagall Act in the US, allowed commercial transactions and investment banking activities to mix, contributing to increased risk-taking and the growth of complex financial products. This regulatory environment set the stage for the 2008 financial crisis, in which several banks engaged in practices that ultimately led to their collapse.
Also, inadequate reporting of financial information can obscure risk and mislead stakeholders and regulators alike. When a bank's true financial condition is unclear, it becomes difficult to assess its solvency and make informed decisions. Financial institutions that employ aggressive accounting practices or fail to disclose relevant information can create a false sense of security. This can lead to market participants underestimating risk and making transactions based on incorrect information.
Enron's collapse in 2001 highlighted the dangers of accounting irregularities and a lack of transparency, and how such
practices can undermine the stability of banks and other financial institutions. Back then, the episode revealed that the American services company's reported financial condition was sustained by an institutionalized, systematic, and creatively planned accounting fraud. Enron became synonymous with willful corporate fraud and corruption, thus raising permanent questions over the accounting practices of many American businesses.
Banks are connected through various channels, including interbank lending, derivatives markets and counterparty relationships. When a bank fails, the shockwave spreads to other financial institutions due to interconnected risks. This can escalate quickly, undermining confidence in the entire banking system. Systemic risk is the possibility of substantial financial systemic disruptions brought on by the failure of one or more key institutions.
"Too big to fail" banks provide a
systemic risk since their failure might have serious consequences for the whole economy. To reduce the systemic risk, the government frequently steps in to stop the collapse of these institutions, as witnessed in the 2008 financial crisis when the US government bailed out several sizable banks.
The quality of a bank's assets and its ability to absorb credit losses are key factors in a bank's stability. Banks with high levels of non-performing loans (NPLs) or poor-quality assets face significant challenges. Bad loans are loans where borrowers default or are unable to make payments, indicating deterioration in credit quality. When banks have a significant volume of non-performing loans, this affects their profitability and capital adequacy.
In order to recover these losses, banks may have to build up significant provisions, which is likely to have a negative impact on their financial health.
If the provisions are insufficient to cover the loan losses, it can lead to capital erosion and ultimately the bank's collapse. In addition, banks that have concentrated exposure to a particular sector or industry are exposed to higher risks.
Economic downturns or sectorspecific shocks can hit these banks disproportionately, leading to rapid deterioration in asset quality and potential insolvency. The collapse of numerous regional banks during the savings and credit crisis of the 1980s and early 1990s still reminds us of the risks associated with concentrated lending.
Overleveraging is also one of the factors that contribute to bank failures. It refers to the practice of taking on excessive debt or using financial instruments to increase returns. While leverage can increase profits in favourable market conditions, it can also increase risks and exacerbate losses during downturns.

Heavily indebted banks are at risk
of insolvency if their assets depreciate in value or they are unable to pay their debts. Meanwhile, inadequate capitalization is closely related to overleveraging. Capital serves as a buffer against losses and helps banks absorb unexpected shocks. If a bank does not have sufficient capital, it may not be able to absorb losses due to its risky activities or significant falls in the value of its assets. This can lead to a downward spiral as losses erode capital and further weaken banks' ability to remain solvent.
The regulatory framework aims to ensure through capital adequacy requirements that banks have sufficient capital buffers to withstand adverse events. However, if banks fail to comply with these requirements or the regulations are not strict enough, it can lead to institutional failure. The collapse of several banks during the Great Depression of the 1930s due to excessive leverage and insufficient capitalization led to the introduction of stricter regulations and capital adequacy standards.
As banks increasingly rely on technology and digital infrastructure to conduct their business, they become vulnerable to disruption from system failures, cyberattacks or data breaches. These can not only lead to financial losses, but also undermine customers' trust in the bank. Cyber threats pose a constant risk to the security and integrity of banking systems and customer data. A successful cyberattack can result in financial loss, reputational damage and possibly legal and regulatory consequences. The collapse of Mt. Gox, a well-known Bitcoin exchange,
in 2014 due to a massive cyberattack highlights the risks associated with technological vulnerabilities. Banks must continuously invest in robust cybersecurity measures, regularly update their technology infrastructure and improve their resilience to ensure they are adequately protected against cyber threats.
Political and legal factors can also contribute to bank failures. Changes in government policies, regulations or economic ideologies can have a significant impact on the banking sector. For example, sudden shifts in regulatory priorities or changes in tax laws can create uncertainty and disrupt banks' business models.
Political interference or interference in the business activities of banks can also jeopardize their stability. When political pressures influence lending decisions or create an environment of corruption and mismanagement, it can undermine the soundness of banks and increase the risk of failure.
According to the Silicon Valley Bank website, the bank has provided banking services to nearly half of the nation's venture-backed technology and life sciences companies, as well as more than 2,500 venture capital firms. For decades, the Silicon Valley bank was awash with cash from high-flying corporate startups doing what most of its competitors did: keeping a small portion of their deposits in cash and using the rest to buy long-term debt like Treasuries. These investments promised stable, modest returns when interest rates stayed low. But it turned out that they were shortsighted. The bank had failed to consider what was happening in the broader economy, which was overheating after
more than a year of pandemic-related stimulus measures.
This meant that the Silicon Valley bank was left in the lurch when the Federal Reserve began raising interest rates to fight rapid inflation in 2022. These once safe haven assets looked significantly less attractive as newer government bonds attracted more interest.
But not all of Silicon Valley Bank's problems are related to rising interest rates. The uniqueness of the bank in some ways contributed to its rapid decline. With the bank's business focused on the tech industry, Silicon Valley Bank ran into trouble when start-up funding began to dwindle, causing its customers, a mix of tech start-ups and their executives, to use their accounts more.
The bank also had a significant number of large uninsured depositors, investors who tended to withdraw their money at signs of turbulence. In order to meet the needs of its customers, the bank had to sell some of its investments at a deep discount. When Silicon Valley announced its huge loss, the tech industry panicked and start-ups rushed to withdraw their money, leading to the demise of the bank.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) announced that it would acquire the 40-year-old institution after the bank and its financial advisors tried unsuccessfully to find a buyer. The takeover saw approximately $175 billion in customer deposits out of the control of federal regulators.
The FDIC, created by Congress in 1933 to insure banks for consumer deposits, is responsible for maintaining stability and public confidence in the country's financial system. The collapse of Santa Clara-based SVB is now the largest since the 2008 financial crisis
From 2013 to 2022 (In Billion US Dollars)
Source: Statista
and created a contagion effect in the US banking circle.
After 2008, US Congress passed the ‘Dodd-Frank Financial Regulation Package’, designed to prevent such collapses. In 2018, President Donald Trump signed legislation reducing the number of Federal Reserve stress tests on regional banks. As news of Silicon Valley Bank's failure broke, experts said the Dodd-Frank package might have forced the bank to better manage its interest-rate risks had it not been scaled back.
On the other hand, New York regulators abruptly shut down Signature Bank in a bid to curb risk in the financial
system at large, just two days after the FDIC took over the SVB’s control.
The Signature Bank, which provided lending services to law firms and real estate companies, had less than $100 billion in deposits in 40 branches across the country. The bank's clients included some people associated with the Trump organization. In 2018, the 24-year-old bank began taking deposits from crypto assets - a fateful decision after the industry hit rock bottom following the collapse of cryptocurrency exchange FTX.

Like Silicon Valley Bank customers, most Signature Bank customers had more than $250,000 in their accounts. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation only insures deposits up to $250,000, so any deposits in excess of this do not receive the same federal protections. According to regulatory filings, nearly nine-tenths of Signature Banks' approximately $88 billion in deposits at the end of 2022 were uninsured. As Silicon Valley Banks' troubles began to spread, many
Signature customers panicked and began calling the bank, concerned their own deposits might be at risk.
The demise of both Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank spotlighted the challenges facing small and midsized banks, which tend to focus on niche businesses and can be more vulnerable to bank runs than larger competitors, experts stated. The main concern is that the failure of one bank would deter customers from other banks.
Stocks of larger banks weren't as hard hit. Citigroup and Wells Fargo each fell more than 7%, Bank of America fell more than 3% and JPMorgan lost about 1%. The KBW bank index, which tracks the performance of 24 major banks, fell 10%, leading to sharp losses that eroded the total value of banks in the index by nearly $200 billion.
The 2023 banking collapse in the United States has been the culmination of a complex interplay of factors ranging from financial mismanagement and economic downturns to regulatory weaknesses. To mitigate these risks and ensure the stability of the banking system, a multifaceted approach is required.
Strengthening risk management practices, improving regulatory frameworks, promoting transparency and disclosure, and addressing challenges posed by technological disruption and cyber threats are critical steps. In addition, adequate capitalization, prudent lending practices and effective supervision are essential for banks to weather economic downturns and external shocks. By addressing these factors and learning from past experience, regulators, policymakers and market participants can work towards building a more resilient financial system, better equipped to weather challenges and contribute to sustainable economic growth.
Recently, the smaller banks rushed to reassure customers that they were on a stronger financial footing. The US regional bank shares plummeted as investors tried to get a handle on the sudden collapse of Signature Bank and Silicon Valley Bank. The stock value of small banks in the United States fall drastically, starting with the First Republic Bank which suffered a downfall of 60%, Arizona's Western Alliance fell 45%, KeyCorp and Comerica both fell nearly 30%, and Utah's Zions Bancorp fell about 25% editor@ifinancemag.com


Banking as a Service (BaaS) technology is a digital transformation that integrates various real-time financial services and products into the business offering of non-bank businesses. An example is the most effective way to explain BaaS. Think for a moment that you are the airline's manager. Given the intense competition you face, you want to increase consumer loyalty. For example, if you could provide your clients with a debit card, you could give them rewards points each time whenever they use their card to make a purchase. Your clients would then interact with your brand each time they used their cards. This way, you could better understand your clients and provide them with services that are more suited to their needs by studying their purchasing patterns.
Or what if you could provide online loans to your consumers for their airline tickets right on your website? This way, your customers could finance their holiday without ever having to interrupt their customer journey. You could increase the number of flight tickets you sell which can directly influence how much money your customers spend. In business, a loan also represents much
deeper customer interaction with more touchpoints than just a single sale.
There are a number of ways non-banks can increase consumer satisfaction and revenue by offering their own financial services. However, practically every country in the world mandates that you have a banking licence if you wish to provide banking services effectively. But such a licence is challenging to obtain because of the systemic relevance of banks to the functioning of the economy. Acquiring a licence imposes not only significant capital requirements, but more importantly compliance with strict regulations on money laundering, banking secrecy and deposit protection. This is where BaaS comes in.
The term 'BaaS' refers to a business model in which authorized banks include their online banking solutions right into the offerings of other non-bank companies. In this manner, a non-bank company, like your airline, can provide its consumers with digital banking services like mobile bank accounts, debit cards, loans, and payment services without having to obtain their own banking licence.
According to a study conducted by Grand View Research Inc., the global BaaS market size is expected to reach $74.55 billion by 2030
Your customer can access banking services through the website or app of your airline because the bank's and airline's systems are connected via Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) or webhooks. Your airline only serves as an intermediary and doesn't really handle the customer's money, therefore it is exempt from all of the regulatory requirements that banks must meet.
So, with BaaS, practically any company can start offering financial services with just a few lines of code. Due to the fact that banking services are provided through a non-branded bank's product, the term 'BaaS' is also frequently used to refer to 'white-label banking'. In Europe BaaS market is expanding vigorously. Banks like Solarisbank, ClearBank, RailsBank, and Starling Bank are prominent BaaS players in Europe's expanding market. Established banking behemoths on the other side of the Atlantic are also introducing BaaS projects alongside their current offerings, like BBVA in the US.

Experts think that licensing and regulation of fi-
nancial institutions in the banking sector is important. Know Your Customer (KYC), anti-money laundering (AML), OFAC sanctions lists, and data privacy and security are a few of these requirements that need to be carried out. RegTech, a class of software applications for managing regulatory compliance must be incorporated into the BaaS process for it to work as intended and for banks to continue to be in compliance with regulatory requirements. RegTech also aids in the detection of online fraud.
The BaaS is mostly used by Neobanks, these are online-only banking platforms without physical locations or a banking licence. 'Challenger banks' are another name for neobanks. These neobanks are non-bank FinTech firms with a focus on particular facets of banking, such as checking and savings accounts and the issuance of credit cards rather than loans.
The BaaS concept enables third-party providers (TPPs) and non-bank FinTech companies to in-


corporate financial services into their product offerings. These partners employ API integration to connect with a bank's infrastructure system, using the licenced bank or middleman FinTech software business as a BaaS provider. The players in the BaaS concept can share customers and generate revenue streams.
Top-rated BaaS providers include the banks BBVA and the non-banks Railsbank, Finastra, and Marqueta. They provide global and BaaS-embedded finance services. Through their BaaS platforms, third-party BaaS providers enhance the user experience.


The United Kingdom, Europe, and the United States are all served by London-based BaaS provider Railsbank. Contrary to its rivals, Railsbank built its own proprietary infrastructure that doesn't rely on old software stacks. Railsbank connects directly to payment rails to expedite payments while providing a range of BaaS offerings. Railsbank
provides the Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) feature. Railsbank, which has raised tremendous amounts of money in debt and venture capital rounds from investors like Visa, is looking to raise an additional $100 million in funding this year.
Through its FusionStore, the BaaS provider Finastra offers FusionFabric.cloud, an open developer platform, and an app marketplace. With its worldwide headquarters in London, Finastra also has offices in the United States. According to recently released data, Finastra serves 90 of the top 100 banks in the world and has introduced Finastra Managed Services (FMS) on Amazon Web Service (AWS).
Marqueta provides personalized rewards, card controls, and client preferences via its real, virtual, and tokenized credit cards, debit cards, and prepaid debit cards. Marqueta serves digital bank and non-bank customers across a variety of industries utilizing its cutting-edge, embedded, open-API

BaaS platform, which is also a payments processor. Through strategic alliances, Marqueta serves as a card-issuing partner for Uber, Uber Eats, DoorDash, and other well-known companies.
BBVA
BBVA is a cutting-edge pioneer bank in the BaaS industry. A BaaS platform serving both domestic and international consumers is through BBVA Open Platform. In Mexico, the Uber app incorporated BaaS from BBVA. A Driver Partner debit card is provided by the BBVA Uber app for Mexico. It makes it possible for delivery and Uber drivers to earn money, access loans, and get gas discounts. Bank-created BaaS platform BBVA Open Platform powers digital-only banks and non-bank applications in the United States.
Future developments in banking as a service include the following: Impressive adoption rate of BaaS in many industries, more FinTech companies and financial services applications, modernization and digitization of bank systems to support BaaS,
more banks and BaaS platform providers with BaaS connections to non-banks, more types of embedded financial products and services (including Buy Now, Pay Later).

BaaS is growing extremely fast and is predicted to reach $7 trillion by 2030. The BaaS platform market is also expected to reach $12.2 billion by 2031 with a 15.7% CAGR.
The global BaaS market is predicted to reach $74.55 billion by 2030 due to the increasing integration of digital services in the financial sector and the expansion of financial services worldwide. Improvements in fund transaction services in the US and emerging nations are also contributing to the growth of the industry.
BaaS has emerged as the dominant market force, driven by the rise of digital financial services and the adoption of cloud-based platforms, allowing companies to enhance customer experiences and large enterprises to bolster customer service.
Open finance gives consumers more access to and control over their financial data
The concept of open banking has transformed the way individuals and businesses interact with their financial data. Now, another era of financial innovation is on the horizon with the emergence of open finance.
Open finance builds upon the foundation of open banking, extending its principles to a wider range of financial products and services. This development aims to empower consumers and businesses by providing greater control and visibility over their financial lives while fostering competition and innovation.
Conversations over the future of open finance are already in progress in Europe. The public consultation on open finance has now ended at the European Commission level. The European Union has realized that a person's financial life extends beyond their payment account. By end of 2023, a legislative initiative might follow.
Although open banking will be the foundation for open finance, the two concepts sometimes have different meanings. The two conceptions are different in a few significant regulatory and commercial ways.

Like open banking, open finance aims to restore client control over financial data. According to both theories, account holders should control who has access to their information and can make payments on their behalf.
On the other hand, open finance dramatically broadens the scope of open banking. More specifically, it might provide third parties access to a broader range of client data, including insurance, mortgages, investments, pensions, and savings accounts. The result will be the development of more personalized and user-friendly financial products using that data.
Open finance can help open banking reach its full potential. Combining a customer's current set of financial information into a single interface might make account aggregation far more thorough. Automatic transfers between savings and investment accounts could be possible with open finance.
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) will be essential for this to happen. They enable regulated third parties to establish risk-free connections with financial institutions. Since APIs are the foundation of open banking in Europe, a robust framework for open finance should also rely on them.
Despite open banking and open finance having
Combining a customer's current set of financial information into a single interface might make account aggregation far more thorough
similarities, there are a few variations which separate them.
In Europe, the PSD2 (Revised Payment Services Directive) included open banking as one of its legal provisions. PSD2 requires financial institutions in EU member states to grant third-party providers (TPPs) access to a customer's account data and the ability to initiate payments in exchange for the customer's agreement.
The foundation of Europe's open banking environment is PSD2. Though it only covers payment accounts, it has a narrow reach. Its restrictions do not apply to savings, investments, mortgages, or pensions. Therefore, banks and service providers are not compelled to grant TPPs access to data about these goods.
The application of open banking is constrained without this data. Open finance can apply open banking ideas to a wider range of financial products to provide value for consumers and businesses.
Open finance gives consumers more access to and control over their financial data, encouraging more competition and innovation in the industry.

Open finance may arrive sooner than you would expect by building on PSD2 and applying open
banking ideas to new financial goods. Europe is already making efforts. While the European Commission just closed a call for comments on making open finance a reality, the United Kingdom government is putting together a smart data program to serve as the foundation for open finance. In the first half of 2023, an open finance framework for Europe is anticipated.
These programs should expand upon the groundwork that PSD2 and open banking have already established. This would entail codifying customers' rights to utilize third parties to access their accounts, enabling TPPs to read data and start payments, and requiring APIs to speed up data retrieval and payments.
The life cycle of financial services involves creating or using financial data. They are utilized by financial institutions in all of their interactions with clients and go along with every step of the customer journey. A McKinsey analysis shows seven major ways open financial data might generate profit.
Increased access to financial services, enhanced product selections, and increased user convenience are three things that directly benefit private individuals and MSME clients. The other four mechanisms, better
fraud protection, better personnel allocation, enhanced operational effectiveness, and decreased friction in data intermediation, all directly benefit financial institutions.

Benefits for customers throughout the financial services life cycle are numerous. For example, it increases the availability of financial services. Thanks to data sharing, customers can purchase and use financial services they might not otherwise have access to.
For instance, open financial data can assist in assessing borrowers' creditworthiness by sourcing rent, phone, and utility bills, where insufficient data from traditional documentation sources may prevent customers from getting loans. People and MSMEs with shaky credit histories or no formal credit history can access formal credit for the first time.
According to a study by Experian, 20% of consumers with little supporting evidence for their credit applications could proceed and become "thick-file" customers by incorporating utility data. When scaling up these advantages to the level of the entire economy in the United States and the EU, greater access to credit using alternative data may enhance the credit-toGDP ratio by 20 basis points. By 2030, the increase in GDP in India might be as much as 130 basis points or roughly $80 to $90 billion.
It also provides greater user comfort. Data sharing lets customers communicate more quickly and efficiently with their financial services provider. MSMEs, for instance, can deliver documentation more quickly during customer
Source: mx.com
onboarding. Consumers can apply for loans without using mortgage brokers thanks to open access to data on available mortgage products and applications already filled out.
Customers can also take advantage of the best prices while simplifying the procedure. In contrast to traditional mortgage brokers who charge arrangement fees, start-ups in the United Kingdom, which implemented its Open Banking system in 2018, leverage data to enable quick and straightforward mortgage applications to all participating providers for free.
Open financial data allows customers to save money by accessing various products. An open-data environment, for instance, simplifies swapping accounts between institutions, assisting retail and MSME clients in getting the best yield.
Open financing has many benefits, including increasing operational effectiveness. Open financial data could reduce costs and make it simpler to incorporate automation technology, which would increase efficiency because the majority of data is still
contained in physical papers or scattered digitized sources. This can enhance the consumer experience by encouraging quicker and more open communication with service providers. According to reports, the cost for financial institutions to "know your customer" (KYC) verify retail consumers in India decreased from approximately $5 per client to $0.70 using the national digital identification system, Aadhaar.
Sharing borrower data enables automated underwriting for typical mortgages in the mortgage industry. Sharing financial data also reduces the number of manual data transfers that can result in mistakes, more work, and less effective results. It greatly lowers the expenses incurred in correcting inaccurate customer relationship management data, which now account for 20% of the revenue of the average financial institution.
Open financing will also be better at predicting fraud. The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners calculates the annual cost of all fraud (including but not limited
The key objective of open finance is to give individuals more personalized and user-friendly financial products by leveraging data from various financial sources. Open finance enables more thorough account aggregation by combining a customer's current account, savings account, and investment information into a single interface. It also allows for automatic transfers between savings and investment accounts, making it easier for individuals to manage their finances.
to financial services) at more than $4.5 trillion, or around 5% of worldwide corporate earnings. Financial services fraud can take many forms, such as fake and real ID fraud, payment fraud, and credit application fraud.
Access to real-time consumer data can assist cutting-edge methods for detecting and lowering the costs associated with these and other types of fraud. Data sharing increases the information and hints available to detect suspicious conduct. This aids organizations in expanding their predictive fraud modelling and identifying situations earlier.
The UK's non-profit Cifas group claims its members reported more than 350,000 fraud instances in 2019, avoiding fraud worth £1.5 billion.
spend less time checking the credit of low-risk clients, and eventually recover more debt.
Moreover, to obtain and use data from third-party suppliers, this approach is especially pertinent to financial institutions that still need to gain direct knowledge of a potential customer, such as lead generation or loan origination. The missing information can be anything from more detailed behavioural information to simple identity data.
By employing application programming interfaces (APIs) for data intermediation, which lowers friction, open data platforms offer direct access to data. For instance, over half of all mortgage servicers in the United States use third-party data for mortgage origination, including credit, KYC, and property appraisal information. Although these data can cost up to $80 per mortgage application, more and more of this information is becoming available to the general public thanks to open data for finance.
While open banking focuses primarily on payment accounts, open finance extends the principles of open banking to a broader range of financial products. By doing so, open finance gives consumers more access to and control over their financial data, thus fostering competition and encouraging innovation in the financial industry. It offers benefits such as increased access to financial services, enhanced product selections, improved user convenience, better fraud protection, enhanced operational effectiveness, and decreased friction in data intermediation.
Open finance extends open banking to more products, empowering users with data control and personalized financial services through APIs and innovation, benefiting customers and companies alike. The future of open banking is well on its way, thanks to open finance.
Employers may also better target and distribute their workers using open data by putting employees in charge of the most valuable tasks. They may concentrate their calls on high-risk clients more effectively, editor@ifinancemag.com

In theory and in a perfect world, governments would receive money through taxes and investments to cover their debts
A colossal quarter-trillion-dollar distressed debt is about to bring an avalanche of unprecedented defaults in developing countries.
Due to unmanageable food and fuel prices that sparked protests and political unrest, Sri Lanka was the first country to stop paying its foreign bondholders. Following its entanglement in a web of sanctions, Russia followed in June 2022.
Sri Lankan economists consider default risk to be that of El Salvador, Ghana, Egypt, Tunisia, and Pakistan. The concern comes from World Bank Chief Economist Carmen Reinhart and long-term emerging market debt experts like former Elliott Management portfolio manager Jay Newman as the cost to insure emerging-market debt from non-payment surges to the highest level since Russia invaded Ukraine in 2022.
Carmen Reinhart said, "Debt dangers and debt crises are not hypothetical in low-income countries. We're pretty much there already."
The number of emerging nations with sovereign debt that trades at distressed levels, yields that show investors feel default is a serious possibility, has more than doubled in the previous six months. More than 900 million people live in
those 19 countries, and some of them, like Sri Lanka and Lebanon, are already in default.
Therefore, $237 billion of notes currently trading distressed are at risk due to foreign bondholders. According to data, that amounts to about a fifth, or roughly 17%, of the $1.4 trillion in external debt emerging-market sovereigns have outstanding, denominated in dollars, euros, or yen.
And as crises have repeatedly demonstrated in recent years, the financial collapse of one country can have a cascading effect, or what is known as "contagion," as nervous investors pull money out of nations that are experiencing similar economic difficulties, hastening the demise of other countries. The 1980s Latin American debt crisis was the mother of such crises.
Emerging-market observers claim that the current situation is similar to a certain extent. Similarly, the Federal Reserve is raising interest rates rapidly to stop inflation, which has caused the dollar's value to soar and made it difficult for developing countries to service their foreign debt.
Smaller nations with a more recent history of international capital markets are frequently those that are most under pressure. Larger developing countries like China, India, Mexico, and Brazil can claim to have solid external balance sheets and foreign exchange reserve holdings.
However, there is a lot to worry about the future in nations that are more at risk. Worldwide political
"Debt dangers and debt crises are not hypothetical in low-income countries. We're pretty much there already"
unrest is escalating in response to rising food and energy prices, throwing doubt on the future bond payments in heavily indebted countries like Ghana and Egypt, some argue it would be better served by utilizing the funds to aid their citizens. In addition, the cost for certain countries may be unacceptable due to the Ukraine war, rising interest rates, and the dollar's dominance.
A quarter of the countries monitored by the 'Bloomberg EM USD Aggregate Sovereign Index' have distressed trading, commonly characterized as yields more than ten percentage points higher than those on Treasury securities of comparable maturity.
The gauge has fallen nearly 20% in 2023, surpassing the full-year loss it recorded in 2008 during the global financial crisis. Naturally, some result from significant losses in the underlying rate markets, but credit degradation has been a critical factor for the most troubled countries.
Samy Muaddi, a portfolio manager at T. Rowe Price who assists in managing assets worthapproximately $6.2 billion, says it was "probably" one of the worst sell-offs of emerging-market debt ever.
He points out that many emerging nations hurried to sell foreign bonds during the COVID period when spending requirements were high and borrowing costs were low. Some will now be at risk as central banks in developed countries tighten financial conditions, forcing money out of emerging markets and leaving them with high expenses.
This is a challenging time for many developing nations, according to Samy Muaddi.

Active traders buying insurance against default in emerging markets are victims of the spread of risk aversion. However, the price is still slightly below its peak from earlier 2022, when Russia invaded Ukraine.
"Things might get worse before they get better. The cycle is late. There isn't a convincing recovery to believe in," Caesar Maasry, head of emerging-market cross-asset strategy at Goldman Sachs Group said during a Bloomberg Intelligence Webinar.
Foreign money managers have fled developing economies as a result. According to the Institute of International Finance, investors withdrew $4 billion
from emerging-market bonds and stocks in June 2022, marking a fourth consecutive month of outflows as the Russian invasion of Ukraine and the war's effects on commodities prices and inflation weighed on investor mood.
According to Gene Podkaminer, head of research at Franklin Templeton Investment Solutions, 'this might have long-term consequences that affect the way we think about emerging markets, particularly in a strategic framework.'
"The first thing it does is confirm that emerging markets are notorious for being unpredictable. There have undoubtedly been times when investors may have forgotten this, but it's becoming increasingly difficult,” the official commented.
Increasingly sharp tradeoffs between keeping interest rates accommodative to support shaky post-COVID-19 recoveries and tightening rates to preserve currencies and suppress inflation are raising central bankers' concerns about ballooning bond spreads. In addition, multilateral organizations like the International Monetary Fund have warned of increased conflict due to rising living costs, particularly in areas where governments are illequipped to protect households.
Widespread electricity outages and soaring inflation increased inequality and contributed to Sri Lanka's political unrest. According to Christian Keller and other Barclays Plc analysts, that might happen somewhere in the second half of this year.
His team stated in a mid-year

study that "populations suffering from high food costs and shortages of supply can be a tinderbox for political instability."
In theory and in a perfect world, governments would receive money through taxes and investments to cover their debts. However, governments frequently borrow money and spend beyond their means, just like people do. Governments do this by issuing bonds committed to repaying the bond's face value plus interest at the maturity rate.
The national/sovereign debt is the sum of a country's internal and external debts. Bonds that the government issues and sells to international investors in foreign
currencies are known as external obligations. Internal debts are obligations to citizens of the same nation.
Fiscal and monetary policy can finance internal debts by increasing taxes and printing more money. Still, external debts can take money away from other sources of income because they must be repaid in currencies that the government does not control. So what follows a default by a nation?
If an individual/business files for bankruptcy, the creditors can seize the assets. However, its creditors cannot take a country's help, and the government cannot be forced to make payments in the event of a default using funds it does not have.
This is false for the nation's assets that are located abroad. For example, Argentina's naval training
ship in Ghana was confiscated after it fell into default in 2012.
The creditor of the defaulting nation's only choice is to renegotiate the loan's terms. As a result, the value of government bonds will be "haircut," or rescheduled, for postponed payment.
Argentina committed to pay back a third of its debt to creditors after missing an $81 billion loan payment in 2011. In this sense, 93% of the debt was converted into performing securities between 2005 and 2010. However, Argentina didn't give the vulture fund its money back for the remaining 75% of the debt until 2016.
The immediate default cost is the loss of principal and capital to the creditor due to a partial debt cancellation or restructuring.
The government is more likely to forgive debts owed to foreign private creditors since reprisal is less likely.
Additionally, like in any other crisis, government defaults lead to skyrocketing inflation, unemployment, and political pressure
on the defaulting government.
Instability in the financial system leads to bank runs since domestic banks carry most household debt. Bank runs happen when a sizable sum of money is removed from a bank due to public anxiety and a lack of trust. The government aims to restrict the amount of money each depositor can withdraw through capital restrictions, which are in place to prevent this.
Greek banks were forced to close for nearly 20 days in June 2015, restrict bank transfers to foreign institutions, and cap cash withdrawals at €50 per day to prevent a banking crisis. In addition, a sovereign debt crisis may result in economic and currency crises as overall demand declines and the global market loses faith in the nation's currency.
The inability of a defaulting nation to access the credit market is another predictable effect. It will either receive a loan at a highinterest rate or none at all. As a result, the defaulting nation's credit rating will drop, discouraging international investment.

The current situation with debt and default in the third world is a cause for concern among economists and emerging market debt experts. The risk of default is high, and several countries are already experiencing it. The increasing food and fuel prices have sparked protests and political unrest, leading to some countries stopping payments to foreign bondholders. The worry is that this will lead to a contagion effect, where nervous investors pull money out of other nations, causing them to default.
The situation is similar to the Latin American debt crisis of the 1980s, and the Federal Reserve's rapid interest rate hikes to stop inflation are making it difficult for developing countries to service their foreign debt. The smaller nations with a more recent history of international capital markets are most under pressure, but even larger developing countries may be affected by the crisis. The consequences of a default are severe, leading to skyrocketing inflation, unemployment, and political pressure on the defaulting government.
The inability to access the credit market discourages international investment, and bank runs happen when a sizable sum of money is removed from a bank due to public anxiety and a lack of trust. The situation is challenging, and the worry is that it may get worse before it gets better.
editor@ifinancemag.com

In May 2023, Zimbabwe announced its plan to issue gold-backed digital currency for 'investment purposes,' with the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe dumping the US Dollar. Then in April 2023, Bangladesh became the 19th nation to settle trade with India in Indian rupees.

Iran too has abandoned the US currency for making trade payments with China and Russia. Saudi Arabia, a key OPEC member, will start accepting PetroYuan instead of PetroDollar.
Brazil President Lula da Silva recently called for the BRICS to come up with its own currency to settle cross-border trade between the member nations. His government has already signed a deal to trade in local currency with China.
Russia is now using Yuan in its international trade, after being hit with sanctions for invading Ukraine in 2022. Moscow and Beijing are also eyeing the launch of a joint BRICS currency to challenge the Dollar hegemony.
While Brazil and Argentina have discussed the creation of a common currency for their bilateral trades, the UAE and India have started talks to use rupees to trade non-oil commodities. Expect more such news to arrive
in the coming days, as the process of dedollarisation gathers steam.

As of 2023, central banks hold about 60% of their foreign exchange reserves in Dollars. The US currency started displacing the pound sterling as the international reserve currency in the 1920s after the Second World War. The 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement established the post-war international monetary system, thus enabling the Dollar to ascend as the world's primary reserve currency for international trade.
The US also exercises significant control over the SWIFT financial transfers network (network which powers international money and security transfers), along with the overall global financial network, with the ability to impose sanctions on entities/individuals.
According to the IMF's Currency Composition of Official Foreign Exchange Reserves (COFER) survey, the share of reserves held in US Dollars by central banks fell from 71% in 1999 to 59% in 2021.
However, the fact remains that these foreign currency reserves facilitate overseas trade transactions, stabilise exchange rates and bolster financial confidence. About half of the international trade is invoiced in Dollars. Imports of energy, food and medicine can be a pain point for emerging and poor markets, in case the US Federal Reserve tightens its monetary policy, cause in that case, the Dollar will get stronger, resulting in costlier imports.
Why a sudden urge for dedollarisation?
The answer lies in the US' economic
response against COVID-19, where the Fed created Dollars at an unprecedented rate to rescue the economy, thereby resulting in global imbalances and economic instability.
Also, currencies with substantial exposure to the Dollar face increased vulnerability to currency fluctuations, thus putting countries at a higher risk of a financial crisis.
According to the American Institute for Economic Research, the economic disruption faced by Iran and Russia, after being disconnected from the international Dollar-trading systems, prompted smaller nations to look for alternatives.
In May 2023, US treasury secretary Janet Yellen accepted the fact that the imposition of sanctions against countries hostile to US' geopolitical interests, also comes with the risk of jeopardising the hegemony of the Dollar.
The Ukraine war has been the biggest example of the targeted country (Russia), successfully finding alternative payment arrangements for bypassing sanctions. Ruble-Yuan trade has increased eighty-fold. Moscow is now working together with Iran to launch a gold-backed cryptocurrency.
Yellen used the Iran example, to state that when US sanctions are imposed against countries, the local populations there face hardships. In the words of the US treasury secretary, “Our sanctions on Iran have created a real economic crisis in that country, and Iran is greatly suffering economically because of the sanctions… Has that forced a change in behaviour? The answer is much less than we would ideally like.”
Russia is now going back to the Soviet Union days, by rearranging the bilateral arrangements, which would facilitate
Purchasing power of one US Dollar every year from 2011 to 2020 Source:
trade in the Ruble and the currencies of other countries. Beijing will conduct trade with Brazil in the local currencies of the two countries. The move is not based on sanctions, but a straight message from China about its intention to challenge US' economic hegemony.
Between 2022 and 2026, as much as 30% of the loans given by the BRICS Bank to its member countries will be in local currencies. Since Russia and China are prominent members of BRICS, expect the alliance to lead the dedollarisation campaign in the coming days.
"With the Dollar as the reserve currency, the US does not have to worry about any balance of payments problems, unlike other countries. It can settle its payments by issuing IOUs to other countries which they would hold, since these IOUs in the shape of Dollars are a safe form of holding wealth. For this reason, it can manage to, and does, stimulate the world economy," says a report from NEWSClick.
For this very reason, the business of American banks increases significantly, as the Dollar is the principal medium of circulation in global trade. Also, the Dollar enables the imposition of income and demand compression on the primary commodity-producing countries of the 'Third World' to ensure a growing supply of primary commodities to meet metropolitan demand without any price rises in their prices.
"The US Dollar has been the official currency for international trades and the king of Currency for ages. The Dollar is enjoying a powerful status in the world, which gives it the power to dominate other economies. The desire to create a new currency will help reduce the dependence on the US Dollar and the US economy which in return could help mitigate the impact of economic and political changes in the US on their own economies. It may provide benefits such as reduced exchange rate risk, lower transaction costs, interest rate changes and increased trade among BRICS nations," said Mahavir Lunawat, Managing Director of leading midmarket investment bank Pantomath Capital Advisors, while interacting with the International Finance
When there is an excess demand for primary commodities in the 'Third World,' its price rises in terms of the local currency, thus creating expectations
of a depreciation of its exchange rate vis-à-vis Dollar, and triggering a flight of finance from that particular 'Third World' economy, resulting in currency depreciation, forcing the nation to raise its interest rate and adopt cost-cutting measures.
Both 2021 and 2022 were about the rising inflation in the United States and the Fed's rate hike spree to tackle the crisis. As economies reopened after two-year COVID-19 hiatus, disruptions in the supply chain and the fuel market (due to the Ukraine war) increased food and raw material costs, thereby raising the consumer price levels within the US.
An increasing inflation cuts down a currency’s buying power. The Federal Reserve raised the interest rate on bankto-bank lending, seven times in 2022 and the phenomenon is still going on. The target is to bring down the inflation at a yearly 2% ratio, by restricting the borrowing demand, which will ease price pressures as well. A country's interest rate is the return on investment for that nation’s currency. As the Fed kept on increasing the interest rate, the Dollar's value increased as well.
This has now made the American Dollar attractive to global investors. These individuals are selling other currencies to purchase Dollars, thus further strengthening the currency and adding more to its hegemony.
As a result of a stronger Dollar, importing goods became relatively cheaper for the US as fewer Dollars were needed to pay the same price in other currencies. However, for other countries, importing food, energy and medicine became a pain point, as their respective currencies depreciated against the Dollar, thereby making the

whole process an expensive one. Fed tightening rates have affected the overall competitiveness of US exports as well. As the Dollar remained strong throughout 2022, the affordability of American products declined as well.

China has now got cosy with Russia, which got delinked from the international payment platforms for attacking Ukraine. In 2022, the share of Russian imports paid for in Yuan rose from 4% to 23%. In February 2023, the Chinese currency overtook the Dollar as the most traded currency on the Moscow exchange for the first time in its history.
China has been pushing for Yuan’s internationalisation and the Ukraine war has given the move an impetus. Although the Dollar remains globally dominant, the Xi Jinping government has successfully convinced Argentina and Brazil to pay in Yuan for Chinese imports. Bangladesh approved a payment in Yuan worth $318 million to settle part of a Russian loan for its nuclear power plant development.
In March 2023, a Chinese company used Yuan to buy 65,000 tons of liquefied natural gas (LNG) from French multinational TotalEnergies, registering the first instance where the Chinese currency was being used in an international LNG transaction. The world's second-largest economy has also developed an alternative to Swift as well as a digital currency, called the e-CNY.
"However, replacing the Dollar would be hard! As of 2022, the Dollar accounts for 59.79% of total foreign reserves. In comparison, the Euro accounts for 19.66%, while the Chinese
renminbi accounts for just 2.76% of global reserves. Other countries have a lot of catching up to do. The Dollar’s dominance of global trade and capital flows dates back at least 80 years," Lunawat remarked.
"While it may not be a direct setback for the United States, as the Dollar will likely continue to be a dominant currency in global trade, it may lose influence in some segments of the global economy. It reflects a growing trend of countries seeking to reduce exposure to potential risks associated with relying solely on the Dollar. To conclude we can say that Chinese dialogue is successful in attracting trading partners and motivating them to look beyond the US Dollar," he added further.
While the Dollar's share in global Central Bank reserves recently dropped to less than 60% from roughly 70%,
twenty years ago, Euro's share went up from 18% to just under 20%. CNY's share stands at less than 3%.
China is known for its capital controls. It allows foreign central banks’ investments in renminbi to be liquidated and repatriated. However, inward investment in China cannot be easily reversed. Despite CNY becoming a major instrument of trade savings and credit financing in Russia, China still hasn’t offered Moscow longterm financing, thus resulting in an underdeveloped credit market. Capital controls still remain a key challenge for Yuan's internalisation efforts, especially when it comes to imagining the currency as an effective means of savings and deposits.
Then you have India, which due to its border tensions with China, is not reportedly okay with its domestic business entities settling foreign trade in Chinese currency. India’s biggest
cement producer UltraTech used CNY for a cargo of Russian coal in 2022, thus raising eyebrows from the government level, as New Delhi asked banks and traders to use UAE dirhams instead of the Chinese currency. India also has memberships in SCO, RIC and BRICS, three prominent regional groupings, which are supposed to be the flag bearer of dedollarisation in the coming days. Given the fact that the Indian Rupee has now been used by 19 countries to settle their trade payments, expect New Delhi to challenge China's efforts of making the Yuan a prominent international currency.
"India too has been trying to move away from the Dollar. Recently 18 countries have been given permission to trade in Indian Rupees. However, the process is complex, critical and with a long gestation period. There are several challenges in establishing a new currency, including economic stability,
political coordination, and establishing credibility and acceptance in the global market. The success of such an initiative would depend on various factors, including the commitment and cooperation among the BRICS nations and the acceptance of the new currency by the international community," Lunawat added further.

“India has an edge. The biggest edge that India has over China is trust. The transparency, stability, and reliability of democratic institutions will drive other countries to use the INR without any hesitation. In April 2023, India successfully concluded an agreement with 18 countries to trade in Rupee which includes stalwarts like the UK, Germany, Singapore, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman, Qatar & Bahrain. India being the world's most populous country with the largest working population and with ability & willingness to spend is the biggest market for anyone. Apart from FDI, India receives more than $100 Billion every year in remittances from abroad. India seems to be crossing early-starting China and hence will surely win the race," he remarked.
"An international currency is one widely used to invoice international trade in goods and services (a unit of account); to settle payments in trade and financial transactions (a medium of exchange); and to denominate financial assets and serve as reserves for foreign central banks (a store of value). These functions are strongly interrelated. The biggest challenge for the Chinese currency Yuan going international is the lack of trust and confidence in the currency," Lunawat said.
He also noted that China maintains strict capital controls to manage its economy and prevent excessive capital outflows, something which doesn't
augur well for the Yuan's free flow.
"Full convertibility of the Yuan is necessary for it to become a widely accepted international currency. China has been gradually liberalizing its currency, but there are still restrictions on capital account transactions," the senior banker noted.
As per Lunwat, the widespread adoption of a currency requires transparency in economic policies, regulatory frameworks, and adherence to the rule of law. China's legal and governance systems are areas of concern for international investors and businesses.
"To attract global investors and facilitate international transactions, the Yuan needs deep and liquid financial markets. China has been working on developing its bond and equity markets, but further improvements are necessary to enhance market depth and liquidity," he stated.
"Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes can influence the international acceptance and adoption of the Yuan. Political stability and trust in China's economic policies are important factors for international investors and businesses considering the Yuan as an alternative. Overall, while the Yuan has made progress in internationalization, addressing these challenges will be crucial for its wider acceptance and potential as a global currency," the senior banker concluded.
Inflation may produce more enormous profits because businesses conceal pricing increases
The ongoing bout of inflation and the resultant cost of living crisis has been an unkind one. Some of the economic powerhouses in the world are undergoing or about to enter a recession, people are losing jobs, wealth disparities are getting bigger and to make matters worse, households are struggling to even provide themselves with meals twice a day.
The situation is so extraordinary this time around that going for a ‘dream home’ is sounding like a fantasy for common people. For experts and analysts, the situation has become a perfect case study of what happens in an out-ofcontrol economy.
Joe Brusuelas, the chief economist for the accounting company RSM US, referred to the several trillion dollars in pandemic stimulus that had trickled into the economy since early 2020 by saying, "There's just a lot of cash out there."
"Whether we're talking about purchasing a Nissan Sentra or a seat on an American Airlines aircraft, prices are increasing as a result of increased competition for those items," the expert commented further.
However, the White House and progressive groups argue this logic. They claim that during this period of extreme economic upheaval, increasingly powerful firms are taking advantage of the chance to raise prices even higher than they would otherwise be able to, putting pressure on consumers and escalating inflation. Or, as the theory is now known, "greedflation."
The claim is consistent with the Biden administration's emphasis on the adverse effects of economic concentration. The proposal has gained traction among congressional Democrats, who have introduced legislation that would either outright outlaw high pricing or temporarily apply an "excess profits tax" on businesses that they judge to be charging excessive rates. These initiatives are criticized as being founded on a "conspiracy theory" and a "flimsy logic," according to the nation's top business group.
It's challenging to elicit. Traditional macroeconomic theory may find it difficult to explain a pandemic, a trade war, a land war, massive government spending, and an extensively linked global economy. In the opinion of Josh Bivens, that is a definite cause to reexamine what the field believed it had found the head of research at the Economic Policy Institute.
"I don't think about dropping real wages when I
Oil business recorded its most substantial earnings in previous years. Drillers have been reluctant to increase production since years
hear stories about an overheated labour market, yet we have falling real wages," Josh Bivens remarked.
Moreover, growth in profits at a time of such low unemployment is not expected.
It's helpful to divide the concept of reflation into three questions. Are businesses overcharging customers to compensate for their rising expenses?
If so, would a meaningful inflation increase result from that? And is this all taking place because big businesses today have more market clout than they had decades ago?
There is little debate that many businesses have marked up products more than their rising costs. This is particularly clear in sectors like shipping, which saw record profits as increasing demand for products filled ships, raising the cost of all traded items. As a result, profit margins increased throughout the COVID and the period after. Consumers also lose track of how much it is appropriate to pay when all prices are rising.
Everyone is aware that prices are rising in an inflationary climate, according to Z. John Zhang, a professor of marketing at the University of Pennsylvania's Wharton School. That's a fantastic

chance for any company to realign their rates as much as possible. Unfortunately, for a very long time, this opportunity won't present itself again. The real difference of opinion is whether or not more profits are excellent and natural.
According to fundamental economic theory, setting prices as high as the market will encourage businesses to produce more, lowering costs and ensuring more people can access the scarce item. For example, if you create empanadas, there is enough demand for them to sell them for $5 each, even though it only costs you $3. Therefore, you could buy a second oven and produce more empanadas, perhaps enough to raise the price to $4 while still selling enough to increase your net income.
The issue is that you are already working three shifts. What if a waiting list for new ovens is due to a strike at the oven factory? Even though you are out of empanadas, you would charge $6 because of how well-liked they are now. People might opt to purchase calzones instead, but eventually, the need for ovens makes it challenging to find all types of baked foods. In that case, you profit handsomely while your customers suffer.
Real-life incidents like this have occurred. Take the fertilizer supply, which decreased due to the
restrictions on the chemicals required to produce it after the Ukraine war. Even as they strive to increase reserves, fertilizer businesses recorded their most substantial earnings in years. Oil is the same way. Drillers have been reluctant to increase production since the last time they did so, a glut resulted. Since increasing production is expensive and investors seek profitability, the supply has lagged, and drivers suffer.
Even if high prices cannot boost supply and the shortage persists, an ‘Economics 101’ course may suggest that pricing is the most effective way to distribute limited resources, or at the very least, that it is preferable to price restrictions or rationing. As a result, those who are less privileged could not have access to empanadas at all. According to University of Maryland finance professor Michael Faulkender, capitalism operates naturally in this manner.
The allocation of items for which there is a shortage goes to the highest-value consumption, according to Michael Faulkender.
Pricing determines the value of every good in our society. People who earn more money can buy more things.
It is more difficult to determine whether profit margins are accelerating inflation.
Researchers have calculated the potential contribution of various factors to inflation. For example, the St. Louis Fed projected that manufacturing sector inflation would have been 20% lower
without supply chain bottlenecks. At the same time, the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco determined that fiscal stimulus initiatives contributed three percentage points.
In a straightforward calculation of the share of price increases over time attributable to labour costs, other inputs, and profits, Bivens of the Economic Policy Institute discovered that the contribution of profits had increased significantly since the start of 2020 compared to the preceding four decades.
Although that is a fascinating fact, it does not prove that profits are what is causing inflation. Instead, inflation may produce more enormous profits because businesses conceal pricing increases.
There is no doubt that the American economy has become more centralized. Fundamentally, supply chains may have become more fragile due to a few corporations' dominance. There will be a greater scarcity if there are just two empanada factories and one has a COVID-19 pandemic than if there are ten factories.
Even putting away any possibly evil deeds on the part of leaders, concentration has affected prices throughout the pandemic, according to Heather Boushey, a member of President Joe Biden's Council of Economic Advisers.
However, the main topic of debate has been whether or not businesses with a larger market

share impact prices once items are produced and delivered. Many economists express scepticism at this point because they believe they would have used it if these firms had significant leverage before the pandemic.

Market concentration is a long-standing issue, yet there has been little inflation in the past 20 years, according to Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor of economics David Autor.
profit margins and would incur a loss if they didn't.
It will take time for economists to pinpoint the exact relationship between earnings, inflation, and market dominance. It will take some time to produce high-quality government data.
Additionally, it necessitates blending microeconomic and macroeconomic disciplines, which have yet to consider so many variables simultaneously.
Lindsay Owens, an economic sociologist and founder of the progressive Groundwork Collaborative, highlights how the economy differed during America's first fight with inflation. Labour was far more robust, and investors were less so. As a result, Lindsay Owens has championed the “greedflation” theory.
"A field that has spent 50 years studying the '70s didn't think a lot about pricing and market power is not unexpected to me, because that was less prevalent during their last chance to learn it," he noted.
In addition, there is no widely accepted indicator of an industry's competitiveness in an industrial organization. Even calculating profit margins is only sometimes accurate, especially for certain commodities.
and the Department of Agriculture. Increasing competition may be one of the only effective measures available to the White House, even if only in the long run, given that the Federal Reserve is responsible mainly for combating inflation.
Even though there is a lot of uncertainty right now, Bharat Ramamurti noted that some people are embracing the hardline opposing stance, which holds that it is absurd to claim that concentration has anything to do with inflation. And it isn't easy to defend that.
In conclusion, while the causes of inflation are complex and multifaceted, the concept of "greedflation" and the role of corporate greed in driving inflation have recently gained attention. While some argue that rising profits are a natural response to market demand and supply chain disruptions, others believe that the concentration of market power among a few large corporations has led to higher prices and reduced competition.
Additionally, the majority of studies on how market concentration affects companies' "pass-through" of unexpectedly higher costs have discovered that fiercely competitive industries raise prices more than those that are dominated by a small number of firms because they have slim editor@ifinancemag.com
The White House's claim that market concentration may cause inflation has only increased the urgency of its antitrust agenda, according to Bharat Ramamurti, deputy director of the National Economic Council, which includes the Federal Trade Commission
While economists continue to study the relationship between earnings, inflation, and market dominance, increasing competition through antitrust measures may be one effective solution to combat inflation in the long run. Regardless of the approach taken, it is essential to scrutinize and address the root causes of inflation to ensure a fair and equitable economy for all.
Due to Singapore's proximity to investors, private equity firms, and venture capital firms, CFOs and CEOs of listed companies will still want to stay in the city-state
IF CORRESPONDENT
Benedikt Becker, a marketing expert, had always considered working and living in Singapore to be "the dream." He talked about his life flourishing in Singapore, the city-state’s dynamism as a corporate centre.
While sharing his story with Aljazeera, Benedikt Becker appreciated Singapore’s efficiency, "amazing" skyline, verdant flora, and architecture. In 2020, he accepted a position with a marketing agency there. The German national paid 2,800 Singapore dollars ($2,072) per month to live in a stylish one-bedroom condo in Singapore's east, where he could go to the beach every morning.
However, when living expenses rose, Benedikt Becker started to reevaluate his circumstances. For example, he noted that the price of his Grab rides to the office had increased from 12 to 14 Singapore dollars ($9 to $10) when he initially came to 22 to 25 Singapore dollars ($16 to $18). In addition, friends complained that their landlord was increasing their rent by 20–30%
According to the international real estate firm Savills, rents in Singapore's affluent residential market will
increase by more than 26% in 2022, more than twice as fast as the growth rates in London, Sydney, and New York.
Before a scheduled increase to 9% the following year, the city-state's government increased the Goods and Services Tax (GST) by one percentage point to 8% in January.
Benedikt Becker, 33, decided to relocate to Kuala Lumpur, the capital of Malaysia, in 2022. He took a wage reduction to work remotely for a German computer start-up looking to grow into Southeast Asia.
He claimed that since the career and city changes, he has been able to save "so much more."
He currently pays 800 Singapore dollars ($592) a month for a flexible room rental in a co-living facility, orders GrabFood for most of his meals for roughly 30 Malaysian ringgit ($6.55), and works from various co-

working facilities.
"A proverb goes, 'If you don't like the rules, alter the game.' So to keep living expenditures down, I changed the game by moving from Singapore to Malaysia,” he said.
Aside from saving money, Benedikt Becker's current top objective is to visit other Asian cities like Bangkok or Ho Chi Minh City.
Benedikt Becker is one of many expats who have moved from Singapore to less expensive Southeast Asian towns due to a substantial increase in housing prices as the country's economy recovers from the COVID-19 outbreak.
Although there is no official data on the number of foreign workers leaving Singapore, recruitment agencies claim that multinational corporations are increasingly looking to relocate staff outside the city to save money.

According to Nic Chambers, Managing Director of Michael Page Malaysia, there has been a "strong hunger" to move personnel from Singapore to the neighbouring country of Malaysia because of its proximity, English-speaking population, lower cost of living, and significant presence of back-end office operations.
“Singapore continues to play a crucial role. Due to Singapore's proximity to investors, private equity firms, and venture capital firms, CFOs and CEOs of listed companies will still want to stay in the city-state. But over time, I fully anticipate that even some C suite positions will start to go to Malaysia," Nic Chambers said, adding that he has also noticed an increase in talent asking for remuneration packages in US dollars to offset volatility in the ringgit's value.
Will Fong, an American software developer, has also started to feel the strain of Singapore's soaring rent prices. When Will Fong's landlord suggested raising the rent to 3,500 Singapore dollars ($2,591), he was already renting a onebedroom condo in Jurong East in western Singapore for 2,600 Singapore dollars ($1,924) monthly. However, he was able to reduce the rent to 3,000 Singapore dollars ($2,220) with the aid of his agent.
“I've heard that things are becoming insane. If I agreed to such a rental amount, it would be simply too expensive,” 41-year-old Will Fong said.
He decided to start working from home in Vietnam. He first visited Ho Chi Minh City for two weeks before moving on to Da Nang for a month. In the long-term, Will Fong wants to lease a space in Singapore that he can use as a home base while exploring and working remotely in Southeast Asia.
"I can have two places, and it'll still be less expensive than me going out and eating out in Singapore. I'm pretty quiet... Just a location for me to sit down, enjoy a beer, and work from any place would be a lot more relaxing. For the time being, I'm still playing outside of Singapore. I feel like I'm going camping," Will Fong, who is also a permanent resident of Singapore said.
While there has been an exodus of foreigners from Singapore as a result of the city's high housing and living expenses, this has been "offset by large numbers of foreigners from other regions and a shift to C-suite foreigners taking advantage of the new Overseas Networks & Expertise (ONE) Pass" - a visa that allows qualified candidates
to work for multiple companies simultaneously, according to staffing firm TENTEN Partners.
Mid-level to senior-level employees in financial services, fintech, and consultancies are among TENTEN Partners' clients. The company has offices in London, Singapore, Hong Kong, and, shortly, Dubai.
"Western hopefuls seek employment in nations with lower tax rates and more excellent living standards. However, the infrastructure, cheap taxes, and familyfriendly atmosphere in Singapore make it still appealing,” according to Luke Archer, managing partner, and cofounder of TENTEN Partners.

"However, pay for B-level executives are frequently insufficient to entice people to move up. So instead, we're increasing the number of foreigners living there. Singapore continues to be a more desirable option, making it difficult for candidates to choose Hong Kong,” the official commented further.
According to management professor Sumit Agarwal, who specializes in
finance, real estate, and economics, those on the edges may feel more likely to be priced out of the Singapore rental market and could think twice about migrating here for work.
Sumit Agarwal said that while there is some level of departure, the intake of expats is relatively more because Singapore is still very much viewed as a "safe haven."
The Southeast Asian city-state’s economy expanded by 0.4% in the January-March 2023 quarter, which was better than expected but fell short of the 2.1% growth recorded in the previous quarter.
The Ministry of Trade and Industry (MTI) however warned about a rise in “downside risks”, including rising interest rates and escalations in the Ukraine conflict, but maintained its growth forecast for 2023 at between 0.5% and 2.5%
The INSEAD Global Competitiveness Index 2022 places Singapore at the top of Asia for luring and supporting talent, and the ECA International 2023 Location Ratings Survey confirms that Singapore is the most livable city for expatriates from East Asia.
The Singaporean government has downplayed claims that the city-state's reputation as a magnet for top talent may be in jeopardy, claiming that COVID-related imbalances in the rental market have begun to ease.
According to a joint statement from the Ministry of National Development (MND) and the Economic Development Board (EDB), "The rent increases in 2022 reflected an exceptional supply tightness, arising from severe COVID-19 disruptions to the construction industry, as well as strong demand from expats and locals."
"Due to residents renting throughout the epidemic as they awaited the development of their properties, rental demand surged. In addition, foreign rental demand swiftly recovered once border restrictions were relaxed last year, exerting additional pressure on the rental market,” the statement added further.
Given that a significant supply of new housing units will be built in 2023 and in the upcoming years, the MND and EDB predicted that rental pressure would lessen in the forthcoming quarters.
The government predicts that this year, the most significant number in the previous five years, would see about 40,000 homes finished in the public and private residential markets.
Additionally, the government anticipates that between 2023 and 2025, close to 100,000 new general and private residential properties will enter the market.
"We continue to attract major investments from businesses, founders, and investors seeking a stable foundation to tap into Asia's growth and generate new goods and services for the global market as well as jobs for Singaporeans," the MND and EDB noted.
Even though Benedikt Becker is content with his relocation, he visits Singapore every two to three months for work and misses some aspects of the city.
The marketing expert stated that he missed Singapore's thriving start-up and business culture, where he could meet entrepreneurs and marketers at numerous networking functions. In that regard, Singapore has much more to offer than Kuala Lumpur.
Plastic, the material which is threatening our ecosystems, can also become a crucial element for the global economy's net-zero goals

As per the United Nations Environment Programme, every minute, the equivalent of one garbage truck of plastic is dumped into the oceans. Approximately 7 billion of the 9.2 billion tonnes of plastic produced from 1950-2017 became plastic waste, ending up in landfills or being dumped across the water bodies.
In the words of the UNEP, "Plastic pollution can alter habitats and natural processes, reducing ecosystems’ ability to adapt to climate change, directly affecting millions of people’s livelihoods, food production capabilities and social well-being."
However, plastic, the material which is threatening our ecosystems, can also become a crucial element for the global economy's net-zero goals.
As per an Economist Impact webinar, "In order to cut waste and greenhouse-gas emissions, the plastics sector is reorganising its production and technology base, developing alternative raw materials and energy sources, and innovating in new technologies and investments."
Take India's case for example. The Asian
economic powerhouse is also one of the world’s top users of plastics, and this industry is anticipated to grow further.
Given the fact that plastic is a part and parcel of the country's socio-economic fold, it is difficult to get rid of it completely. While the nation is now seeing an increase in the usage of biodegradable plastics and alternative materials like paper, cloth, and glass, experts believe that the plastic industry needs to be regulated with the principles of 'Circular Economy', where increasing recycling and reuse, and creating biodegradable substitutes of the material can be aggressively promoted by the government.
India also has a large but unorganised recycling industry that can be backed further with efficient waste collection and segregation systems, along with a sound mechanism to prevent contamination from the material.
In June 2023, the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Guwahati, one of India's premier research institutes, set up the NRL-Centre of Excellence (CoE) for 'Sustainable Materials Translational Facility on Bioplastics' at its campus. The new facility will work towards the development of environment-friendly sustainable plastics.
In the recently concluded CHINAPLAS 2023, Asia’s premier plastics and rubber trade fair, over 3,900 exhibitors presented their latest innovations in adherence to the circular economy concept.
Plastic, which is threatening our ecosystems, can also become a crucial element for the global economy's netzero goals
Four eco-friendly thematic zones, including the 'Recycling Technology Zone', 'Recycled Plastics Zone' and 'Bioplastics Zone' and 'Eco-friendly Additives Zone', were set up during the event.
Over 200 machine makers and materials providers showcased an array of sustainable solutions in these four theme zones.
As per the World Bank, around 2 billion tons of municipal solid waste is being generated every year and this will reach 3.5 billion tons by 2050. Regions like East Asia and Pacific to witness their plastic waste generation increase by 70% by 2050. The Ellen MacArthur Foundation too claimed that the world’s oceans would contain around 937 million tons of plastic compared to 895 million tons of fish by 2050. The COVID-19 pandemic pushed single-use plastics usage by as much as 300%
So clearly the plastics industry is facing a steep task to come up with quick solutions to offset these scary predictions. Breakthroughs showcased by IIT Guwahati and CHINAPLAS 2023 have shown that the industry is up for the challenge.
The circular economy concept aims to reduce
the amount of plastic waste generated by applying a “closed loop” system where plastics are produced, used and reused in a continuous cycle to prevent its leakage into the environment. This model addresses the challenges of minimizing the wastage created by single-use plastics.
For example, the packaging industry accounts for the largest segment of plastic applications. Application of the 'Circular Economy' principles in this sector would require innovations in production technologies and materials to ensure reusable, recyclable, or compostable plastic products. Also, the stakeholders will have to ensure that disposed items are properly collected, recycled or composted, before reusing them.
A study from Singapore's Nanyang Technological University in Singapore suggests that reusable plastic bags are more environmentally-friendly than those from paper and cotton, in cities and countries with efficient waste management systems.
As per BIGCOMMERCE, Sustainable Packaging should meet conditions like being beneficial, safe and healthy for individuals and communities throughout its lifecycle, meeting performance and cost requirements while being sourced, manufactured, transported, and recycled using renewable energy.

Also, the solutions need to optimize the use of renewable or recycled source materials, while being manufactured with clean production technologies and best practices and last but not least, being effectively recovered and utilized in biological and/or industrial closed-loop cycles.
A CGS survey of 1,000 American consumers found that almost 70% of respondents considered sustainability as at least “somewhat important” and almost half (47%) said they "would pay 25% more for sustainable products."
Another Nielsen research found that 48% of US consumers were willing to change their consumption habits to lower their impact on the environment. The survey company’s analysis further found that sustainable product sales in the United States have grown nearly 20% since 2014, and the company estimates that sales would reach $150 billion by 2024.
BIGCOMMERCE has also suggested measures like reducing packaging materials, minimizing waste, shipping small packages (cost friendly too), recycling packaging materials, using plantbased and edible packaging methods, bringing compostable and biodegradable plastic alternatives into the play, and last but not least, using manufacturing partners with sustainable practices, as immediate solutions for the industry.
A report from ManufacturingToday found that plastic-oriented industries are taking an interest in
chemical recycling technologies, which break down plastics into building blocks to convert them into secondary raw materials for producing new raw materials.

Chemical recycling has also been found ideal for treating multilayered or heavily contaminated plastic, as the process can manufacture high-quality recycled material.
"Mechanical recycling has become better and more efficient in turning out good quality secondary materials. Digitalization, artificial intelligence and automation have contributed to more efficient recycling operations that many companies offering recycling technologies have added these to the capabilities of their machines," ManufacturingToday remarked.
"Bottle-to-bottle recycling has been taken to a higher level in processing post-consumer PET bottles to high-grade recycled PET (rPET) material, making it possible to produce bottles from as high as 100% recycled PET (rPET). Also, bottle-to-bottle recycling has been able to meet the high safety standards required for food packaging with no risk of contamination. Another innovation is the development of techniques in the recycling of multilayer flexible
packaging that now, 100% of multilayer film production waste can be recycled," it commented further.
Innovations like recycling methods like injection moulding systems, extrusion technologies and blow moulding systems are seeing huge R&D-related investments. Also, materials solutions geared toward improving the properties of recycled resins like additives and stabilizing agents are supporting the plastics industry’s sustainability bid as well.
"The urge to make plastics more sustainable will encourage manufacturing firms to use sustainable plastics. The global recycled plastics market size garnered 50,465.24 kilotons in 2021 and will depict a CAGR of 3.3% from 2022 through 2030. A marked rise in plastics recycling rates and better plastic waste treatment could facilitate the circular economy. Forward-looking companies will likely focus on diverting waste plastics towards recycling facilities, a trend poised to favour market growth," remarked Grand View Research.
A report from the IDTechEx 'Sustainable Packaging Market
2023-2033' explores the sustainable materials, leading players, and technology trends driving the industry, while presenting a forecast for the sustainable packaging market segmented into 21 different materials.
As per IDTechEx, plastics recycled through mechanical and chemical means, along with the 'Bioplastics' and 'Biobased Materials', will guide the innovations in the industry in the coming days. The IDTechEx's analysis of 95 start-ups operating in sustainable packaging found over twenty different biobased materials with over $4 billion in the investment pipeline.
Under the RUBIO project, 18 partners are currently turning the vision of a sustainable plastics industry into reality. These stakeholders are trying to use regionally available plant residues to create versatile, sustainable products that are recyclable and biodegradable.
GmbH, the Fraunhofer IAP has developed an initial commercial product, as per reports.
"Bioplastics are increasingly providing an alternative to petroleum-based plastics. These sustainable materials offer a number of advantages: They are made from renewable resources and help to reduce the dependence on fossil fuels and CO2 emissions into the environment. They can be biodegradable and have processing properties comparable to those of classic petroleum-based plastics. Like classic plastics, bioplastics can be sorted, fractionated and recycled," as per a report from Phys.org.
Hexagon's Manufacturing Intelligence division and Sumika Polymer Compounds Europe (SPC Europe), a leading manufacturer of thermoplastic compounds, announced its partnership in January 2023 to digitise the performance of new sustainable automotive-grade polypropylene (PP) compounds, thus enabling engineers from the stakeholders to recyclable design components, which will offer a lower carbon footprint for future vehicles.
short glass-fibre polypropylene (GF-PP) THERMOFIL HP and recycled polypropylene (GF-rPP) THERMOFIL CIRCLE materials use sustainable manufacturing and recycling processes and offer carmakers performance equivalent to incumbent engineering plastics, but with an up to 60% lower carbon footprint.
The American Chemistry Council's (ACC) report titled, 'Chemistry and Automobiles,' found that on average from 2012 to 2021, the amount of plastic in automobiles increased by 16%, to 411 pounds. Calculations show those 411 pounds made up less than 10% of an average vehicle’s weight yet approximately 50% of its volume, thus significantly improving the car's fuel efficiency, apart from reducing costs for drivers and carbon emissions from transportation.
With electric vehicles becoming more popular, plastics have emerged as an important element in the auto industry.
The article has discussed various developments in the plastics industry, all leading to one conclusion. By adopting a circular economic approach and investing in research and development, plastic, which is often considered harmful to the environment, can become a game-changer in promoting clean and sustainable industrial practices.
As part of the project's roadmap, the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Polymer Research IAP is developing new types of bioplastic polybutylene succinate (PBS) so that it can be used for significantly more applications. Together with the company POLIFILM EXTRUSION editor@ifinancemag.com
Sumika Polymer Compounds'
A recent study and analysis by McKinsey provide a thorough look at the direction that e-commerce in consumer products will go over the coming year
E-commerce penetration across all categories continues to grow after an extraordinary rise in online retail spending in 2020, a much-needed and profitable development. As lockdowns and trade disruptions resulting from the COVID-19 outbreaks continued to plague the world from 2020-2022, retail online sales increased by 40% in 2021 alone, as consumers increased their usage of online shopping portals to purchase items, be it the ones coming the category of daily necessities or the high-end products.
Across all product categories, from consumer electronics to groceries, about 75% of consumers conduct product research and purchase through brick-and-mortar stores and online channels.
A recent study and analysis by McKinsey provide a thorough look at the direction that e-commerce in consumer
products will go over the coming year. E-commerce's development will continue after the COVID-19 pandemic and the current expansion.
The emergence of new platforms, channels, and data sources will never stop. Consumer products companies face opportunities and challenges when deciding how to engage their customer groups most effectively due to this dynamic.
Aware of the potential effects on their balance sheets, executives must carefully consider their investments as they explore cutting-edge technologies like the metaverse and live selling. They must

also have the organizational capacity to change course quickly and successfully to potentially better ground.
Over 2024, three developments will likely impact how consumer goods companies locate, assess, and seize opportunities.
Firstly, there will always be new ways to reach consumers. Consumer products firms typically participated in a few e-commerce channels, with Amazon taking the lead. To stay current with where consumers interact and shop, consumer products companies must be present on a wide range of new platforms and formats.
Consumer demand for omnichannel fulfilment options for in-store purchasing, including home delivery (from a neighbourhood store), ship-tohome (from a distribution centre), and click-and-collect, is increasing. Between 2021 and 2025, social commerce, which broadens reach by selling through social media channels, is anticipated to more than double and account for nearly $80 billion in retail sales.
The United States is now only second to China in terms of social purchasing thanks to this rapid expansion, where that channel currently accounts for more than 13% of the global e-commerce market.
New entrants like JOKR and Gopuff are changing customer expectations about delivery speed due to the expansion of quick commerce (home delivery in under an hour and as quickly as 15 minutes). Although this channel is only expected to account for a small portion of overall grocery e-commerce sales, it already has a significant impact. In 2021, about 30% of online grocery shoppers chose delivery in two hours
or less, and 14% of customers said they planned to use express and same-day delivery more often. There will be more competition for marketing and trade dollars.
E-commerce has made it more difficult for businesses to be profitable, prompting merchants to look for new ways to boost margins. For instance, retail media networks (RMNs) allow merchants to monetize their first-party customer data by letting marketers place ads on their websites.
A significant incentive for shops to enter the fray is Amazon's expanding ad business, based on the same rich transaction data that all merchants have access to. The shift in consumer tastes and legislation surrounding data privacy has increased the appeal of closed-loop channels built on entirely user-consented first-party data, thus fueling the growth of commerce media. Over the past two years, more than a dozen merchants have introduced RMNs, and others plan to do the same shortly.
Approximately 15% of all advertising and promotion spending is already going toward commercial media, which typically accounts for between 2% and 10% of gross sales (depending on the subcategory), according to a survey of 100 consumer goods e-commerce decision-makers. By 2024, spending in the channel is anticipated to exceed $100 billion (including Amazon), increasing by a factor of two to three annually.
Using commercial media will initially be difficult for consumer products companies since it puts additional pressure on their marketing budgets and profit-and-loss (P&L) ratio. However, if properly managed, it will enable consumer goods companies to
Worldwide 2021-2026 (In Trillion US Dollars) 2021
5.211 2022
5.717 2023
6.310
enhance both the buyer experience and marketing effectiveness.
Approaches like RMNs can offer a customized, personalized experience that suits changing customer privacy, control, and transparency requirements. Companies that sell consumer goods can also utilize commercial media to improve the data that forms the basis of their targeting and closedloop attribution systems. Consumer products firms can increase return on ad investment in this new channel by three to five times if they implement these strategies well.
Personalization and targeted precision will take the place of all other considerations. There is now an unprecedented amount of data available on how people shop and interact with brands, thanks to the rise of online transactions and the general digitization of commerce. With the change to online transactions, businesses now better understand the customer experience, including measures like cart abandonment, add-to-cart rates,
browsing habits, and time to purchase. Given their close interaction with customers, retailers are especially wellpositioned to collect these data, which they have been using to develop more individualized experiences. As a result, customers have quickly come to demand businesses to provide personalized, pertinent interactions.

Consumer products firms may collect data at a different rate than retailers. Still, to fulfil the increasingly high client personalization standards and realize returns on their investments, they have had to develop more sophisticated data management capabilities.




Winning consumer goods companies invest in five crucial areas to differentiate themselves in the ever-changing e-commerce landscape. Additionally, they are trying to ensure that every aspect of their organizations, from resources, talent, and skills to processes and culture, is in place to support these objectives properly.
For starters, the emphasis on CRO (conversion rate optimization) in recent years in e-commerce has made many businesses ignorant of the apparent requirement that CRO requires the consumer to visit your site. This necessitates work to persuade them to do so, necessitating right away a second tier of marketing with associated added expense. Before big platforms like Amazon and Alibaba get a look in, predictive personalization software (PPS) enters the fray and brings that personalization to your customers, with the advantage of generating purchases.
In addition to buying history, impressions, and navigation, choosing impending product choices individually is based on these factors and AI analysis with machine learning, which correctly predicts what each person is most likely to buy next and presents it to them at the ideal time.
There is no need for additional marketing levels; the absolute autonomy reduces the necessity for previously anticipated layers. There are















also no overhead costs or employees. Additionally, freedom means it is always operational and free from mistakes, oversights, and other human flaws typically associated with functional performance. The age of automated email marketing has arrived, which explains why it produces results that defy all logic, an example of predictive personalization that exceeded 10,000% ROI.
Another helpful strategy is to be present wherever consumers shop— in a focused and deliberate manner. Winners engage customers in their preferred method by carefully and intentionally using a wide range of e-commerce platforms. Compared to 25% of their competitors, two-thirds of winning consumer products businesses intend to sell through food-delivery media (such as DashMart by DoorDash and Cornershop by Uber) within the following year.
Consumer goods companies need to be where their customers are, as new platforms emerge, players that can quickly adopt them will be best positioned. Approximately 20% of winners intend to sell through social media like TikTok and WhatsApp, even though the purchasing capabilities of these platforms are just coming into existence.
Staying on top of consumer trends that affect channel preferences will be critical to increasing online sales and finding new ways to reach households. Leading consumer goods companies quickly develop perspectives on the channel's relevance to their consumers and determine action plans for product placement.
Adjusting procedures, organizational design, and resources to accommodate this capacity gap will reduce response


times and boost speed to market. Selling through these platforms may force B2B2C organizations to build new competencies.
A third idea would be to make data and analytics investments to support adaptable, full-funnel marketing. Winners are building owned, contentfirst online platforms and loyalty programs designed to enhance consumer engagement through rewards or services as marketers lose access to third-party data. For instance, a leading packaged-food company with an extensive loyalty program recently revamped its strategy for digital formats by building a proprietary mobile application specifically for its rewards program.
Companies can aggregate transaction data, media exposure and interaction data, website activity, firstparty data, and additional data sets to link a consumer ID across multiple data systems. Winning companies invest in the right tools, partnerships, and capabilities to build an internal 360-degree view of consumers to meet shoppers' increased demand for personalization.
With the help of this data, businesses can develop fully automated, repeatable, scalable methodologies to identify future activation opportunities in a personalized way, capturing meaningful business value. For instance, a food company recently increased the return on its digital advertising spend by more than 40% by using first-party data to target audiences that look like its target audiences.
Also, keeping a laser-like focus on ongoing development by establishing cross-functional teams, or "pods," to foster daily, purpose-driven collaboration among marketing, sales,

creative, technology, data and analytics, and more on an ongoing basis, winning consumer goods companies are embracing agile operating models that accelerate the pursuit of opportunities, improve execution outcomes, and unlock value.
Agile pods need dedicated data scientists and engineers to execute a standard measurement playbook and continuous improvements. Gone are the days of gut-feeling-driven decisionmaking across merchandising, pricing, promotions, assortment, and content online. Execution decisions will be based on granular insights. Consumer goods companies can differentiate themselves by their ability to operate these pods and build actual test-andlearn muscles.
The survey results demonstrate the adoption of these new methods of operation and the emphasis on continuous, data-driven improvement. The winners are 21% more likely than other consumer product companies to prioritize test-and-learn processes to enhance online performance.
For instance, by quickly testing and identifying the most effective tactics across core performance levers, a leading cosmetics manufacturer launched an agile pod initially focused on Amazon. As a result, the business gained insights into particular actions, made adjustments based on specific learnings, and quickly scaled to achieve a certain, quantified goal.
The company is now looking into creating a more comprehensive, formalized test-and-learn program across additional channels and retail partners due to the company's experiment, which led to a doubling of sales on Amazon and a four-fold acceleration of the creative development process.
Finally, it is best to invest in digital talent before it becomes obsolete. While relying on third-party agencies or partners may boost sales in the short term, excessive reliance on external providers over a long time may hinder a company's ability to increase e-commerce sales in the fastest, most effective manner. Foundational digital literacy and analytics capabilities are critical to achieving a long-term competitive advantage in e-commerce. To do so requires in-house proficiency in technical talent, tools, and abilities.
Leading household goods company launched a formal mentorship program between senior executives and junior marketing analytics employees with the dual goals of increasing fluency among senior leaders in direct-to-consumer
Winning companies invest in the right tools, partnerships, and capabilities to build an internal 360-degree view of consumers to meet shoppers' increased demand for personalization
functions and mentoring more junior colleagues. Winning consumer goods companies recognize that digital fluency must be embedded at all levels of the organization, from the front line to the C-suite.

Perhaps most importantly, the initiative generated demand for digital solutions across the organization and created momentum for further digital capability development. Executives learned the power of differentiating proprietary data, including attribution modelling, performance marketing, personalization, and more.
It's also important to rethink the supply chain from beginning to end to accommodate omnichannel expansion. Winners make foundational investments in operations and supply
chain management. They are up to three times more likely to make supply chain management an organizational priority. They are 40% more likely to see it as a critical obstacle in attaining their e-commerce goal.
First, they integrate more closely with retail partners to improve demand forecasting, inventory management, packaging design, and fulfilment. For instance, winners are roughly four times more likely than others to participate in Amazon's Vendor Flex program, which allows purchases to be shipped directly from the consumer goods company's warehouse to consumers. Second, winning consumer goods companies concentrate on two critical operations and supply chain areas.
Second, winners are examining
what is ideal for brick-and-mortar business and online fulfilment (from home shipping delivery), using an omnichannel manufacturing and packaging design strategy.
For instance, a well-known retailer of household goods switched to "ship in own container" packaging, which increases sustainability, lessens wrap rage (the rage and frustration a customer feels when they can't open a product's packaging), and is frequently much less expensive to store and ship than conventional retail packaging. Several consumer goods manufacturers have experimented with pack sizes and product formulations to reduce shipping weight.
There are other keys to winning in e-commerce than optimizing the current business to compete in the digital sphere. Instead, it adopts an omnichannel-first perspective to rethink the company. Onthe-margin adjustments to the current operating margin do not produce winners in anything, from commercial decisions and procedures to talent and human capital management and data.
The "current" channels and platforms may be prominent, but the digital world is a moving, always-changing target. Organizations must outsmart the competition by being quick and digitalfirst to succeed in this market.
Winning in this market will take more than executing well on opportunities now. Businesses prioritizing digital across only some organizational functions risk losing market share, profitability, and relevance shortly.
According to research by EY-Parthenon using the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employee productivity in the United States has declined for five consecutive quarters since 2022.
A new Slack poll found that over two-thirds of CEOs are under pressure to increase employee productivity.
One may accuse the top business executives of obstinately herding their staffers back to the office like lost sheep, hoping that productivity would magically increase, despite the overwhelming evidence that a flexible hybrid work model is more productive than forced in-office labour for the same tasks.
The statistics revealed that productivity in the world's largest economy has plunged by the sharpest
rate seen since the 1940s.
Given that productivity grew by 4.3% in the first quarter of 2021, the highest rate the country has seen in years, the latest figure suggests a huge 360 degree shift in the attitude towards work.
Chief economist at the Kenan Institute of Private Enterprise, Gerald Cohen, suggested tech.co that the productivity boost in 2021 was probably due to the coronavirus recession, as businesses were forced to shift to remote work overnight, but the data also suggests that the switch to remote work was also a success, in terms of increasing the employee productivity.
Many CEOs continue to hold onto the myth that the workplace is the key to productivity, despite the flexible work model proving its
worth more than anyone anticipated during the COVID period. They act like the workplace is a vending machine for productivity: insert employees and get more output. However, the evidence paints a different picture.
The office is more like a productivity black hole than a productivity nirvana, where focused work gets dragged into oblivion during collaboration, socializing, mentoring, and on-the-job training flourish.
For instance, a recent study by academics at the University of Iowa, Harvard University, and the Federal Reserve Bank of New York discovered that software engineers seated in different buildings on the same campus produced more computer programs than those placed next to colleagues. The engineers that worked in various facilities made fewer comments on each other's code, though. In other words, they were more productive, but as a result, less seasoned programmers received less mentoring.
Simply put, expecting the workplace to increase
productivity is akin to expecting a fish to ride a bicycle. The workplace performs a very different and crucial function. According to the EY-Parthenon study, the forced return to work and declining productivity are directly related. Statistics show that people work longer hours but produce less goods. Therefore, we need to stop attempting to squeeze a square peg into a round hole.





structured mentoring to balance work models
While being present in the office reduces
While being present in the office reduces productivity, mentoring increases it
productivity, mentoring increases it. However, mentoring requires conscious effort. Unfortunately, many firms have unwritten ideas that if you jam employees into an office like sardines, mentorship will miraculously occur. This haphazard strategy's effectiveness is comparable to tossing spaghetti at a wall and praying it sticks. Inconsistent, ineffective, and dependent on variables like location, office politics, and human dynamics, office-based mentoring, particularly full-time mentoring, can have a limited influence.
On the other hand, an organized mentoring program provides a more deliberate and successful approach by matching mentors and mentees according to their talents, interests, and goals. With the help of this focused approach, it is made sure that knowledge exchange and personal development are carefully developed and fostered rather than left to chance.
The best elements of both in-office and remote work can coexist in a hybrid workplace where structured mentoring programs can flourish. However, to maximize productivity and employee satisfaction without forgoing the advantages of face-to-face interactions, firms can use this balanced strategy to restrict in-office activities to mandatory mentoring sessions.
Companies can make use of the benefits of both in-office and remote employment in a structured mentorship program. Also, plan targeted in-person mentoring sessions or workshops that respect employees' need for flexibility in their work schedules while maximizing the advantages of face-to-face contact. When in-person interactions are not necessary, collaborative tools such as video conferencing, instant messaging,
and instant messaging can help mentors and mentees communicate. Moreover, setting clear goals and benchmarks for the mentoring relationship will make both sides more accountable and focused, maximizing the program's effectiveness. Conventional one-on-one mentoring model can be avoided especially at the time when virtual seminars and forums can offer extra opportunities for knowledge sharing and building connections.
Tracking the development and performance of mentoring relationships allows businesses to pinpoint areas for improvement, hone their program over time, and guarantee its long-term effectiveness. The components that
need to be added are autonomy and engagement.
The big irony of the officecentric mindset is that employee engagement and productivity losses suffer. According to a Gallup survey, employees who have the option to work remotely but are required to report to the office experience a lack of autonomy, which lowers engagement.
Consider the effects of this issue on the entire world: Low employee engagement, according to Gallup, cost the world an astounding $7.8 trillion in lost productivity in 2017. To put things into perspective, picture every CEO bashing their company's piggy bank to pieces with a sledgehammer
I have more time because I don't commute
and then asking themselves why profits are down.
Cognitive biases frequently influence our decision-making when accepting flexible work and might skew our perception and judgment. Understanding these biases' effects can help us get past the mental obstacles that stand in the way of productive mentoring. Let's look at two critical cognitive biases in this situation: the status quo bias and functional fixedness.
Status quo bias is a cognitive bias that makes people choose the current situation over change, even though that
change would result in better results. This prejudice may have a significant impact on CEOs' and executives' attitudes toward the notion of flexible hybrid work and organized mentoring programs, making them stick with the old-fashioned office-based work style.
Due to their tendency to see change as a danger to the status quo, executives may find it challenging to see the advantages of flexible work arrangements and hybrid mentorship programs. As a result, they might choose to stick with the comfortable office setting rather than consider the research that shows the success of remote work and structured mentoring.
Functional fixedness is a cognitive bias that keeps people from considering other applications or solutions for a given issue because they are fixated on the conventional or comfortable method. Because they may be unable to see the potential benefits of flexible work and organized hybrid mentorship programs, this prejudice can substantially impact how firms approach workplace efficiency.
The functional fixedness bias may keep leaders firmly convinced that the workplace is the only setting that can foster productivity. As a result, even when given strong proof, individuals could not see the possibilities of flexible work arrangements and hybrid mentorship programs.
It's time for CEOs to embrace the flexible work revolution and jump off the sinking ship of mandated in-office employment. Although cooperation, mentoring, and training can occur in the office, productivity is not one of them.
Let's create work arrangements
specific to each person's function and preferences rather than putting everyone into the same box. It's time to quit denying reality and accept that flexible hybrid work is the way of the future and will remain so. The only way to stop the spiralling decline in productivity and unlock the workforce's full potential is to accept this fact.
It is abundantly evident from the research that returning to work under duress will not improve productivity— instead, it will exacerbate it. As demonstrated over the previous five quarters, forcing staff members back into the office is like beating our heads against a brick wall and expecting a different result. The moment has arrived for CEOs to abandon their antiquated beliefs and embrace the revolution in flexible hybrid employment.
The evidence overwhelmingly suggests that returning to the office does not increase productivity. The workplace is better suited for collaboration, socializing, and mentoring, while focused work gets dragged into oblivion. Companies must reevaluate their strategies and embrace the flexible work revolution to maximize productivity and employee satisfaction.
Companies can use structured mentoring programs to balance the benefits of both in-office and remote work. It's time for CEOs to abandon their antiquated beliefs and embrace the revolution in flexible hybrid employment to unlock the workforce's full potential.
I feel safer
One of the main advantages of automation and robotics in manufacturing is the significant increase in efficiency and productivity
Automation and robotics have become indispensable parts of the 21st century manufacturing landscape, thus revolutionizing the industry in profound ways.
The machines do not tire and do not need breaks.
This constant workflow minimizes downtime and optimizes production capacity
These technological advances have transformed traditional production processes, improving efficiency, precision and productivity while reducing costs and human error. By integrating automation and robotics into manufacturing, companies can streamline operations and supply chains, apart from improving quality control.
In this article, International Finance has examined the various roles that automation and robotics play in manufacturing and highlights their benefits, challenges, and future prospects.

Automation and robotics bring a significant increase in efficiency and productivity in the manufacturing sector. The machines do not tire and do not need breaks. This constant workflow minimizes downtime and optimizes production capacity. Robots can perform repetitive tasks
accurately and quickly, resulting in higher output and overall improved efficiency.
Advanced robots can perform complex operations quickly, resulting in shorter turnaround times and higher performance. With automated systems handling tasks like assembly, packaging, and material handling smoothly, human professionals can focus on more important and value-added activities like research, development, and process improvement.
Automated systems can also perform inspections and tests with unprecedented accuracy and consistency. This eliminates the risk of human error and ensures products meet strict quality standards. Robots equipped with vision systems and sensors can identify defects and anomalies in real-time, preventing defective items from entering the market.
In addition, automation allows for continuous monitoring and data collection throughout the manufacturing process. This data can be analyzed to identify patterns, trends and opportunities for improvement. By resolving issues in a timely manner, manufacturers can improve product quality and reduce waste. The ability to maintain consistent quality standards has a significant impact on customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Automation and robotics are also having a profound impact on the supply chain, streamlining logistics and inventory management. Automated systems can track and manage inventory levels in
real-time, ensuring efficient replenishment. They can also facilitate seamless coordination between suppliers, manufacturers and distributors, reducing delays and minimizing disruptions in the supply chain.
In addition, automation enables just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing, where components and materials are delivered exactly when they are needed, eliminating the need for large inventories. This approach reduces inventory costs, minimizes the risk of inventory obsolescence, and improves overall operational efficiency. Robotics and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) can also be used in warehouse operations, enabling efficient material handling and order processing.
Automation and robotics contribute to the safety conditions in the manufacturing environment. By automating dangerous tasks and removing human workers from potentially dangerous situations, the risk of workplace accidents and injuries is significantly reduced. Robots are well suited for tasks that require heavy lifting, exposure to pollutants, or working in extreme temperatures.
Contrary to popular belief, the integration of
automation and robotics does not necessarily result in job losses. Rather, it often leads to a change in the nature of work. Automation allows human workers to take on more complex, creative, and higher-value roles, such as programming, maintaining, and monitoring automated systems. Collaborative robots, so-called cobots, work together with human workers, thus increasing productivity and efficiency while ensuring a safe working environment.
Automation and robotics also offer manufacturers the opportunity to adapt to changing market demands and production requirements. Traditional manufacturing facilities often involve fixed production lines, which limits flexibility and agility.

However, with automation, manufacturers can quickly reconfigure their processes to accommodate new products or variations without significant downtime.
Robots equipped with advanced programming and sensing capabilities can easily switch between tasks and product variants, enabling efficient changes to the production line. This flexibility allows manufacturers to respond more quickly to customer needs, reduce time to market, and remain competitive in dynamic industries.
Automation and robotics excel at tasks that require precise movement, measurement, and repeatability. Human workers can have inherent limitations in repetitive tasks, leading to variations in quality and consistency. However, robots can always perform tasks with submillimetre accuracy and maintain the same level of precision throughout the manufacturing process.
For example, in industries like electronics and automotive manufacturing, automated systems can precisely place components on circuit boards or assemble intricate parts with high accuracy, ensuring consistent quality and reducing the chance of errors.
Automation and robotics generate large amounts of data throughout the manufacturing process. This data can be used to uncover valuable insights and make data-driven decisions that optimize operations and drive continuous improvement. Manufacturers can use machine learning algorithms to analyze the collected data and identify patterns, anomalies and opportunities for improvement.
This approach enables manufacturers to make proactive decisions to increase productivity, reduce waste, and optimize resource allocation. Additionally, predictive maintenance is another valuable application of data analytics in manufacturing.
By monitoring equipment performance and analyzing data from sensors and automation systems, manufacturers can predict potential equipment failures and
proactively plan maintenance activities, minimizing unplanned downtime and maximizing production availability.
The global industrial robotics market size was $37,876.0 million in 2020 and is expected to reach $116,848.7 million by 2030 with a CAGR of 11.7% from 2021 to 2030. Meanwhile, labour costs across the United Kingdom are increasing by over 12% each year, leading to a shortage of labour. To overcome such problems, market players are investing in industrial robotics. For example, in January 2022, the government invested in robotics to help the British people and economy deal with the inflationary crisis caused by labour shortages. In addition, it is estimated that US labour costs

will increase by over 20%. This is therefore leading to an increase in industry initiatives to adopt robots to offset the labour costs and shortages that are driving the industrial robotics market. In addition, according to data from North America Factories and Industries, manufacturers and industrial users ordered more than 25,000 robots in 2021 compared to 2019.
High imports of robots are attributed to their use in the microelectronics industry, where small robots are used to pick and place small components. According to the trends, the global microelectronics industry has grown by more than 10% since 2010. Therefore, the growth in the microelectronics industry, which requires a larger number of robots, is expected to drive the industrial robot market.

Moreover, during the COVID outbreak, the construction, manufacturing, hotel and tourism industries have been severely affected. Production activities have been discontinued or restricted. Construction and transportation activities as well as supply chains have been hampered on a global scale. This led to a decrease in the manufacture of industrial robots as well as their demand in the market, thereby slowing down the growth of the industrial robotics market. Conversely, industries are gradually resuming their regular production and service operations. This is expected to bring industrial robotics companies back to full capacity, which will likely help the market recover by the end of 2024.
In January 2022, DHL Supply Chain invested $15 million in robotic solutions for the supply chain network in the warehouses. Robots contribute to a simple supply chain network by reducing longterm costs, increasing productivity, reducing errors and optimizing picking operations. According to industrial robotics market trends, it is estimated that the supply chain market will grow by over 100% by 2026. Hence, with the growing supply chain network, the increasing need for cost savings and efficiency gains is creating new market opportunities.
The industrial robotics market is segmented by type, industry, function and region. On the basis of type, the market is segmented into joint, card, SCARA, cylinder and other segments. By industry, it is categorized into Automotive, Electrical & Electronics, Chemical,
Rubber & Plastics, Machinery, Food & Beverage, and others. By function, it is divided into soldering and welding, material handling, assembly and disassembly, painting and applying, milling, cutting and machining, and others.
While automation and robotics offer numerous benefits, their implementation presents certain challenges. The initial investment required to implement automated systems can be significant and discourage smaller manufacturers from adopting these technologies.
Additionally, integrating automation into existing manufacturing processes can require significant reconfiguration and staff training. However, advances in technology and falling costs are making automation more accessible and affordable. Smaller automation solutions are emerging, allowing manufacturers of all sizes to reap the benefits.
The future of automation and robotics in manufacturing holds enormous potential. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), and robotics, leading to smarter and more autonomous systems. Collaborative robots or cobots are becoming more common, working hand in hand with human workers in a safe and collaborative environment. These cobots will have advanced sensor capabilities and intuitive interfaces that will enable seamless humanrobot interaction and collaboration.
In addition, the concept of
"lights-out manufacturing", in which factories operate completely autonomously without human intervention, is gaining traction. Uninterrupted production can provide significant benefits in terms of cost reduction, production efficiency and 24/7 operation.
However, the implementation of "lights-out manufacturing" requires robust automation systems, AI-driven decision-making algorithms, and advanced security measures. Additionally, the rise of additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is poised to revolutionize manufacturing processes. 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, customization and on-demand production, reducing lead times and eliminating complex supply chains. The integration of automation and robotics with 3D printing technologies can open up new possibilities for highly efficient and agile manufacturing.
The manufacturing industry has experienced a significant transformation thanks to automation and robotics. These advancements have improved efficiency, quality control, safety, and collaboration. Further developments will enhance their capabilities, enabling flexibility, data-driven decisionmaking, and the possibility of lightsout manufacturing. The decreasing costs also make automation more accessible to businesses of all sizes. Companies must adopt these technologies to stay competitive, streamline operations, boost productivity, and meet market demands.