
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Prajwal B M1 , Thippesh Babu L2 , Shreyas A Anju3
1 Bachelor of Engineering, Information Science and Engineering, Bapuji Institute of Engineering and technology, Karnataka, India
2 Bachelor of Engineering, Information Science and Engineering, Bapuji Institute of Engineering and technology, Karnataka, India
3 Bachelor of Engineering, Information Science and Engineering, Bapuji Institute of Engineering and technology, Karnataka, India ***
Abstract - 5G is referred to as the tactile internet; it is considered to be the next generation of mobile and wireless communication. It would be available in 2020, providing an experience of completely wireless communication known as WWWW (World Wide Wireless Web). This paper discusses mobile wireless communication evolution from 1G to the present 4G and future predictions for 5G. 5G technology is a user-centric mobileenvironmentwithseveraladvantagesover earlier networks. Users will experience drastic changes in speed,bandwidth,andcost,asthe5Goffershighspeeds,large bandwidth, and lower costs. The paper will discuss the evolution of "G" from zero to the fifth generation, including technologies such as TDMA, UMTS, and WWWW. It will also discuss the challenges faced in current technology and the expected advantages and applications of 5G. The paper will highlight the basic architecture and working concepts of 5G, explaining the role of software-defined radio and open wireless architectures. This research aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of 5G and its potential impact on future communication technology.
Key Words: 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, WWWW (World Wide Wireless Web), TDMA, UMTS.
5G, or fifth-generation mobile technology, represents a significantadvancementinwirelesscommunication,offering unprecedentedbandwidthandspeed.Thistechnologywill revolutionize mobile phone usage, offering features and capabilities exceeding anything witnessed before. Mobile usersareincreasinglyawareofthepotentialofmobilephone technology. 5G incorporates sophisticated features, positioning it as the most powerful and sought-after technology in the near future. 5G will change how users access their phones and bandwidth, opening up new possibilities. The development of 5G has seen significant progressfromearliergenerationsofwirelesstechnology(1G to 4G). 5G is set to impact the market value of traditional desktop computers and laptops, challenging their dominance. The affordability, reliability, and advanced featuresof5Gmakeitsuperiortoprevioustechnologies.
Theevolutionofmobilecommunicationnetworkshasbeen marked by significant advancements in technology and capabilities:
0G (Zero Generation Mobile System): This generation emerged in the late 1940s with the introductionofradiotelephoneservice,primarilyfor car users connected to the public telephone network12. Bell Laboratories' Improved Mobile Telephone Service (IMTS) in the 1960s brought enhancements like direct dialling and increased bandwidth12. Early analog systems, built upon IMTS, were developed in the late 60s and early 70s12.
1G (First Generation): 1G marked the first generation of analog cellular technology and primarily supported mobile telephony (voice) services231314.
2G (Second Generation): 2G introduced digital cellulartechnology,bringingimprovementssuchas digitalvoice,SMS,andhighercapacityforpacketized data231314.
3G (Third Generation): 3G technology utilizes Wide Band Wireless Networks to improve clarity andsupportsserviceswithaminimuminformation transfer rate of 2Mbps15. 3G networks facilitated high-volumedatamovement,thoughpackettransfer on the air-interface functioned similar to circuitswitched calls15. The need for a globally standardized network that provided services independent of technology platforms led to the developmentof3G15.3Gisn'tasinglestandardbut a collection of standards that operate together15. Organizationslikethe3rdGenerationPartnership Project (3GPP) played a crucial role in defining mobilesystemsmeetingtheIMT-2000standard15. 3Gbroughtintegratedhigh-qualityaudio,video,and dataservices314.
4G (Fourth Generation): 4G, or the All-IP generation, leverages IP-switched networks and offersdynamicinformationaccessandsupportfor

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
wearabledevices23131416.ItisbuiltuponOFDM (Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing) and CDMA technologies, enabling users to experience speeds up to 100 Mbps with a 1Gbps data bandwidth16.4GincorporatesfeatureslikeWiMAX, LTE, and Wi-Fi, providing dynamic information accessandsupportforwearabledevices1416.Italso supports advanced services like mobile TV, HDTV content,andDigitalVideoBroadcasting(DVB)1718.
5G (Fifth Generation): 5G, also known as LTE-E (LongTermEvolution-Enhanced),isexpectedtobea fully wireless communication system (WWWW)23419. The development of 5G aims to achieve ultra-densification, millimetre-wave technology, and massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output)19. 5G promises even faster communication, advanced security features (including SDR security), multiple data transfer paths, better cognitive radio capabilities, and a significantly larger bandwidth19. It will also introducedynamicinformationaccessandsupport forwearabledeviceswithAIcapabilities
1.2 Comparison of Mobile Technology Generations
Generation Deployment DataRate Technologies
0G 1940s–1970s Limited IMTS,AMTS
1G 1980s 2kbps Analog
2G 1990s 64kbps Digital
3G 2000s 2Mbps CDMA,UMTS
4G 2010s 1Gbps LTE,WiMAX
5G 2020s >1Gbps mmWave,MIMO
Despite the significant advancements of 4G, several issues necessitate the development and implementation of 5G technology:
High Densification of Traffic: Current mobile networks face capacity constraints due to the increasingvolumeofdatatraffic8.Apredicted1000fold increase in data traffic by 2020 and beyond posesasignificantchallenge21.
LatencyIssues:Usersexperiencelatencyproblems in applications like online gaming, video calling, videoconferencing,andinternettelephony22.
Security Concerns: With numerous users connected to 4G using various internet devices, securityconcernslikehacking,datatheft,andvirus attacksareheightened22.
Power Consumption:4Gtechnologyisknownfor its high power consumption, leading to reduced batterylifeofdevices22.
InfrastructureCosts:Thecostofcomponentsused in cell towers and the associated power consumptionaresubstantialconcerns22.
Operational Manpower: Operating and maintaining 4G systems requires a significant amountofmanpower22.
5G technology offers several advantages that address the limitationsofpreviousgenerationsandpavethewayfora moreefficientanduser-friendlycommunicationexperience:
High Speed and Bandwidth: 5G aims to deliver significantly higher data speeds and bandwidth compared to 4G2123. Users can expect download speedsexceeding1GbpsinLANsand500Mbpsin WANs, representing a substantial leap in performance23.
Low Latency: 5G will drastically reduce latency, enablingreal-timeapplicationslikeonlinegaming, videoconferencing,andcloudcomputing2425.\
ImprovedSecurity:Enhancedsecuritymeasuresin 5Gwilladdressconcernslikehacking,datatheft,and virusattacks,providingasaferuserexperience24
Reduced Power Consumption: 5G technology is designed for energy efficiency, leading to lower power consumption and longer battery life for devices23.
Network Convergence: 5G will facilitate the convergence of multimedia, voice, and data communication within a single network26. This means a seamless integration of services, eliminating the distinction between wireless and fixed-linecommunication26.
Global Mobility and Interoperability:5Gaimsto establishaunifiedglobalstandard,promotingglobal mobility and service portability27. This will allow users to subscribe to services from various providersusingasinglemobiledevice27.
All-IP Based Model: 5G relies on an All-IP model (AIPN)forseamlessinteroperabilityacrosswireless andmobilenetworks.Itprovidesaunifiedplatform for all radio access technologies using packet switching, ensuring optimized performance and cost-efficiency.
User Terminal: Central to 5G, the user terminal supports multiple independent and autonomous radioaccesstechnologies(RATs).
Radio Access Technologies (RATs): 5G ensures backwardcompatibilitybysupporting2G,3G,and 4G,enablingasmoothtransitionforusers.
Cloud Computing Resources (CCR): Cloud computing in 5G allows on-demand access to

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
configurable resources, enabling users to access apps and data remotely. CCR links the Reconfigurable Multi Technology Core (RMTC) to reconfiguration data for efficient resource management.
Reconfigurable Multi Technology Core (RMTC): Acting as the control unit, the RMTC manages diverse RATs using nanotechnology, cloud computing, and cognitive radio, dynamically adaptingtosystemanduserdemands.
Interoperability: 5Gensuresflexibilitybyenabling terminals and the RMTC to switch seamlessly betweenaccesssystems.
IP Addressing: Each device has a permanent "home"IPanda"careof"IPforitscurrentlocation, ensuring seamless communication by routing packetseffectively.
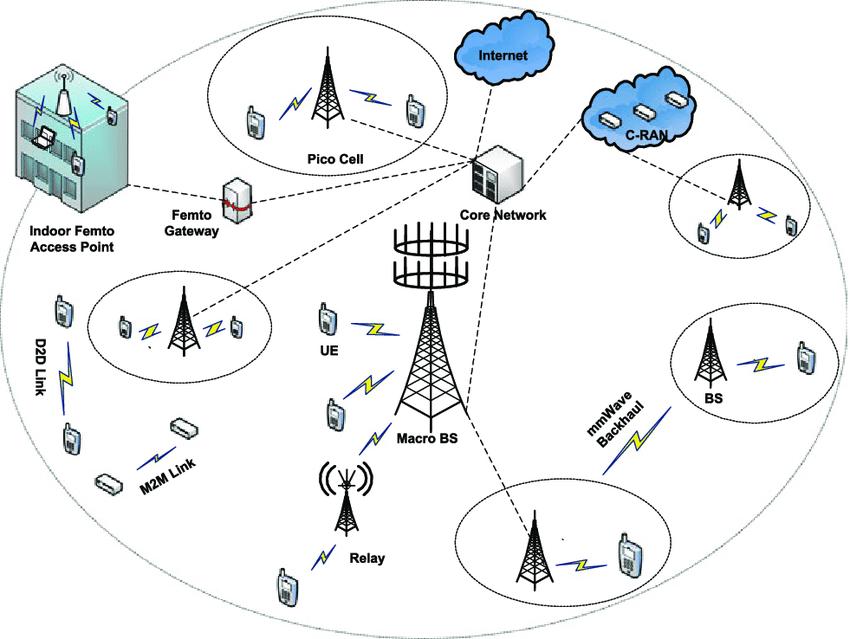
5Gnetworksoperateonseveralkeyconcepts:
User-Centric Design: 5G is fundamentally usercentric,meaningallfunctionalitiesandservicesare designedarounduserneedsandpreferences10
Error Avoidance: 5G will incorporate innovative erroravoidanceschemesthatcanbeupdatedviathe internet,enhancingreliability10.
Software-Defined Radios: The use of softwaredefined radios (SDRs) in 5G allows for greater flexibilityandadaptability10.
Open Wireless Architectures:5Gleveragesopen wireless architectures, encompassing the physical and data link layers of the OSI model, ensuring compatibilityandeaseofintegrationwithdifferent technologies1032
Thecapabilitiesof5Gwillenableawiderangeofapplications acrossvarioussectors:
Education: 5G will revolutionize education by providing cost-effective online learning opportunitiestoindividualsworldwide3334.
Security:5G'smulti-layeredsecurityarchitecture, incorporating features like authentication, authorization, encryption, and service policy agreements,willensuredataprotectionandsecure communication3436.
Tele-Medicine: 5G will empower tele-medicine applications, allowing patients to receive remote medical consultations and monitoring without visitinghospitals3334.
GPS:5GwillenhanceGPSaccuracyandreliability, enablingpreciselocationtrackingandnavigation37.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): 5G will provide the necessary bandwidth and speed to support AIpowered applications, creating intelligent and interconnectedenvironments3738.
Travelling:5Gwilltransformthetravelexperience through advanced mobile phone apps and the integration of Bluetooth and NFC technology, enabling seamless travel planning, information sharing,anddestinationexploration3738.
EconomicGrowth:Thewidespreadadoptionof5G will drive economic growth by creating new businessopportunities,promotinginnovation,and enabling access to high-value data and content services3637.
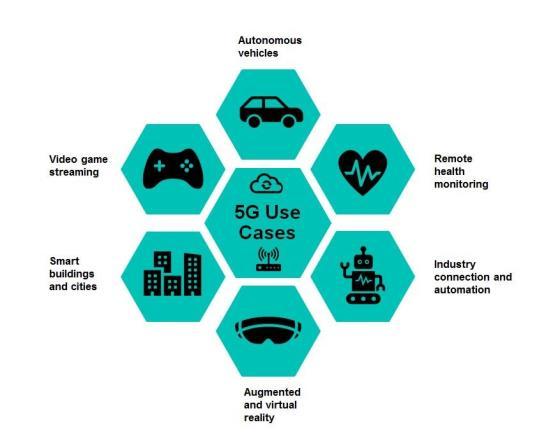
While5Gholdsimmensepromise,realizingitsfullpotential requiresovercomingseveralchallenges:
Data Rate and Network Capacity Expansion: Meeting the demand for higher data rates and network capacity while managing power

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
consumptionandcostsisasignificantchallenge17. The distribution of additional base stations, increased frequency band usage, and link developmentarecrucialforcapacityexpansion17.
Scalability and Flexibility:5G networks must be scalable and flexible to accommodate a growing number of users and devices with diverse requirements39.
Full-Duplex Communication: Implementing fullduplexwirelessradio,allowingsimultaneoussignal transmissionandreceptiononthesamefrequency, posestechnicalcomplexitiesintermsofinterference managementandsignalprocessing40.
Environmental Sustainability: Reducing the energyconsumptionof5Gnetworksandminimizing theirenvironmentalimpactisakeychallenge42.
LowLatencyandHighReliability:Achievingultralow latency and high reliability for real-time applications like remote surgery and industrial automation requires advancements in network protocolsandinfrastructure43.
SystemImplementationOptimization:Optimizing systemparameterslikedatarate,coverage,spectral efficiency, power efficiency, latency, and user equalityiscrucialforasuccessful5Grollout44.
EconomicImpacts:Ensuringtheaffordabilityof5G deployment, maintenance, and operation is importantforitswidespreadadoption45.
High Mobility and Handoff:Supportingseamless handoff and maintaining connectivity for users movingathighspeedsisachallenge46.
5G technology represents a paradigm shift in mobile communication, promising to revolutionize the way we connect and interact with the world. Its unprecedented speed, bandwidth, low latency, and enhanced security featureswillenableawiderangeofinnovativeapplications, transformingvarioussectors,includingeducation,healthcare, transportation,andentertainment.
While challenges remain in its development and implementation, ongoing research and technological advancementsarepavingthewayforasuccessful5Grollout. Therealizationof5G'sfullpotentialwillusherinaneweraof seamlessconnectivity,intelligentautomation,andimmersive experiences, shaping the future of communication and drivingsignificantsocietalandeconomicimpacts.
[1] Duda,A.andSreenan,C.J.(2003).ChallengesforQuality of Service in Next Generation Mobile Networks. Proceedings of Information Technology & Telecommunications Conference (IT&T).M. Young, The
TechnicalWriter’sHandbook.MillValley,CA:University Science,1989.
[2] ITU(2009).MeasuringtheInformationSociety;TheICT Development Index. [Online]. Available: http://www.itu.int/ITUD/ict/publications/idi/2009/material/IDI2009w5.pdf
[3] Mishra, A. (2004). Fundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation. JohnWiley&Sons,2004.
[4] Mousa, A. M. (2012). Prospective of Fifth Generation MobileCommunications. International Journal of NextGeneration Networks (IJNGN),4(3):1-30.
[5] Parikh, J., and Basu, A. (2011). LTE Advanced: The 4G MobileBroadbandTechnology. International Journal of Computer Applications,13(5):17-21.
[6] Akhilesh Kumar Pachauri and Ompal Singh. "5G Technology-Redefining wireless Communication in upcoming years," International Journal of Computer Science and Management Research,Vol1,Issue1, Aug 2012.
[7] Mohd.MaroofSiddiqui."Visionof5GCommunication,"A Mantri et al. (Eds.): HPAGC 2011, CCIS 169, SpringerVerlagBerlinHeidelberg,pp.252-256,2011.
[8] Sapana, S., and Pratap, S. "Key Concepts and Network Architecturefor5GMobile Technology," International Journal of Scientific Research Engineering & Technology (IJSRET),Volume1,Issue5,pp.165-170,August2012.
[9] Upadhyay, Niki. "5G WIRELESS TECHNOLOGY," GandhinagarInstituteofTechnology,Gujarat,India.
[10] Kumaravel, K. "Comparative Study of 3G and 4G in Mobile Technology." IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues,Vol.8,Issue5,No.3,Sep2011.
[11] Gupta, P. and Patil, P. "4G - A New Era in Wireless Telecommunication." Magister Program in Software Engineering,MalardalenUniversity.
[12] Patil, S., Patil, V., and Bhat, P. (2012). A Review on 5G Technology. International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT),1(1):26-30.
[13] UMTS World (2009). “UMTS/3G History and Future Milestones.” [Online]. Available: http://www.umtsworld.com/umts/history.htm
[14] Naik, G., Aigal, V., Sehgal, P., and Poojary, J. (2012). ChallengesintheImplementationofFourthGeneration WirelessSystems. International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA),2(2):1353-1355.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
[15] JayR.Churi,T.Sudish,Surendran,Shreyas,AjayTugdi. "Evolution of Network." International Conference in AdvanceinCommunicationandComputingTechnologies, 2012.
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page124