
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Niranjan Reddy Kotha
Sr.Cloud Infrastructure Security Engineer, Charter Communications/Cod Cores Inc., Colorado, USA
Abstract
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) refers to a network of medical devices and applications that communicate and exchange data to improve healthcare delivery. As IoMT technologies evolve, the healthcare sector increasingly relies on connected devices to monitor, diagnose, and treat patients. However, this reliance on interconnected devices introduces significant cybersecurity risks, especially the threat of malware attacks that can compromise patient data, device functionality, and overall healthcare operations. Malware attacks on medical devices can lead to severe consequences, including unauthorized access to sensitive patient information, disruptions in medical procedures, and even loss of life. This research investigates the vulnerabilities inherent in IoMT devices and explores strategies to mitigate the risk of malware infections. By examining the specific characteristics of IoMT devices, their communication protocols, and the evolving nature of cyber threats, this paper highlights the critical need for robust security measures. The study reviews existing security frameworks, outlines best practices, and provides recommendations for securing IoMT devices against malware,ensuringtheintegrityandconfidentialityofmedicaldata.
Keywords:IoMT,cybersecurity,malware,medicaldevices,healthcaresecurity
Introduction
The rise of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) has revolutionized the healthcare industry by enabling the seamless integration of medical devices with networks, data storage, and analytics tools. IoMT devices, ranging from wearable health monitors and diagnostic machines to infusion pumps and imaging systems, collect and transmit vast amounts of sensitive patient data, providing healthcare professionals with real-time insights for improved decision-making and patient outcomes. These devices offer unparalleled convenience, reduce the need for manual intervention, and facilitate theefficientmonitoringofpatienthealth,makingthemindispensabletomodernhealthcaresystems.
However, as IoMT devices become more ubiquitous, they also become attractive targets for cybercriminals. The interconnectednatureofIoMTsystemsmakesthemhighlysusceptibletoavarietyofcyberthreats,particularlymalware attacks. Malware, including viruses, ransomware, and Trojans, can compromise the functionality of medical devices, interfere with critical healthcare operations, and expose sensitive patient information to unauthorized entities. These security risks are exacerbated by several factors, including the increasing complexity of IoMT devices, the lack of standardized security protocols, and the often inadequate attention paid to cybersecurity in the development and deploymentofmedicaldevices.
The malware threat in healthcare is not just theoretical; several high-profile incidents have already demonstrated the devastating impact of cyberattacks on medical devices. The 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack, for example, affected thousands of healthcare systems worldwide, including medical devices, causing widespread disruption in hospitals and clinics.Morerecently,vulnerabilitiesininfusionpumpsand implantabledeviceshavebeenexploitedbymaliciousactors, highlightingtheneedforstrongercybersecuritymeasures.
This paper aims to address the growing threat of malware in IoMT devices and explore strategies for securing these critical healthcare technologies. By analyzing the unique vulnerabilities of medical devices, the paper identifies the main risksposedbymalwareanddiscussescurrenteffortsandbestpracticestomitigatethesethreats.Wealsoexaminetherole of regulations and standards in shaping the security landscape for IoMT devices and propose actionable solutions for strengtheningtheirdefenses. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
TherapidadoptionofIoMTdevicesinhealthcarehasintroducedsignificantsecurityrisks,primarilyrelatedtothethreat of malware attacks. These attacks can result in the unauthorized access, manipulation, or disruption of medical devices, compromising patient safety, confidentiality, and the integrity of healthcare systems. Despite the growing awareness of cybersecuritythreatsinhealthcare,manyIoMTdevicesareinadequatelyprotected,exposinghealthcareorganizationsand patients to malware risks. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a comprehensive approach to securing IoMT devices, ensuringthattheyareprotectedfrommalwareandothercyberthreats.Thisresearchaimstoexaminethenatureofthese threats, identify key vulnerabilities in IoMT devices, and explore the strategies needed to safeguard these critical technologies.
While this research provides a detailed overview of the threats and vulnerabilities associated with IoMT devices, it is important to acknowledge several limitations. First, the rapid pace of technological advancements means that the threat landscapeforIoMTdevicesisconstantlyevolving,andnewattackvectorsmayemergeafterthepublicationofthisstudy. Additionally,thediversityofIoMTdevices,eachwithuniquehardwareandsoftwareconfigurations,presentschallengesin providinguniversalsecuritysolutions.Thescopeofthisresearchisalsolimitedtomalware-relatedthreats,anditdoesnot exploreothercybersecurityissuessuchasdatabreachesorphysicaltamperingwithdevices.Lastly,duetotheproprietary natureofmanymedicaldevices,detailedcasestudiesandreal-worlddataonIoMTsecuritybreachesareoftenunavailable, limitingtheabilitytofullyanalyzethescopeoftheproblem.
SecuringIoMTdevicespresentsavarietyofchallenges.Someofthekeyobstaclesinclude:
1. Lack of Standardized Security Protocols: Many IoMT devices are developed by different manufacturers, each with its own security practices and protocols. This lack of standardization complicates efforts to secure these devicesandcreateuniformdefensesagainstmalwareattacks.
2. Legacy Systems:Manyhealthcareorganizationsstillrelyonlegacymedicaldevicesthatwerenotdesignedwith modern cybersecurity threats in mind. These devices are often not upgradable, making them vulnerable to malwareinfections.
3. Limited Resources for Security: Healthcare organizations, especially smaller hospitals and clinics, often face budgetconstraintsthatpreventthemfrominvestinginrobustcybersecuritymeasuresfortheirIoMTdevices.
4. Complexity and Diversity of Devices:ThesheervarietyofIoMT devices,from wearablestoimplantedmedical devices, each with different functions and communication protocols, makes it challenging to implement a onesize-fits-allsecuritysolution.
5. Vendor Dependency: Healthcare organizations often rely on device manufacturers and third-party vendors for softwareupdatesandsecuritypatches.Insomecases,thesevendorsmaybeslowtorespondtoemergingthreats orfailtoprovideadequateupdates.
This research utilizes a mixed-methods approach to thoroughly analyze the security challenges posed by malware in Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices. The methodology integrates both qualitative and quantitative data collection methodstocapturea comprehensiveunderstanding ofthetopic.Theaimistoexploretheunderlyingcausesofmalware vulnerabilities in IoMT devices and propose effective strategies for improving security. This methodology is divided into several key components: literature review, data collection, vulnerability assessment, security framework evaluation, and recommendations. Each component plays a crucial role in building a robust understanding of the issue and guiding the formulationofrecommendations.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The first component of the methodology is a comprehensive literature review, which aims to provide a thorough backgroundonthesecuritychallengesofIoMTdevices,particularlywithregardtomalwarerisks.Thisreviewsynthesizes existing research, industry reports, and case studies on the subject to identify key issues and vulnerabilities associated withIoMTdevices.Theliteraturereviewcoversseveralimportantaspects:
Malware Threats: It includes an examination of the types of malware that have been specifically targeted at medicaldevices.Thesemayincludeviruses,ransomware,Trojans,andwormsthathaveinfectedordisruptedthe functioning of medical devices in real-world scenarios. By reviewing published case studies and cybersecurity reports, the literature review helps identify patterns in malware infections and the tactics employed by cybercriminals.
Vulnerabilities in IoMT Devices:ThereviewfocusesonthecommonvulnerabilitiesfoundinIoMTdevices,such as insecure communication protocols, outdated software and firmware, lack of encryption, weak authentication mechanisms, and inadequate patch management. Understanding these vulnerabilities is essential for evaluating whymedicaldevicesareparticularlysusceptibletomalware.
Existing Security Solutions: The review also investigates the effectiveness of current security solutions and frameworks.Thisincludesevaluatingtheimpactofindustryregulations,suchasHIPAA,NISTguidelines,andFDA recommendations for cybersecurity in medical devices. It provides an overview of how these frameworks have addressedIoMTsecurityandidentifiesanygapsintheirapplicabilitytoemergingmalwarethreats.
Throughtheliteraturereview,theresearchestablishesthecontextforthestudy,highlightingthecriticalareasofconcern andprovidingafoundationforfurtheranalysis.
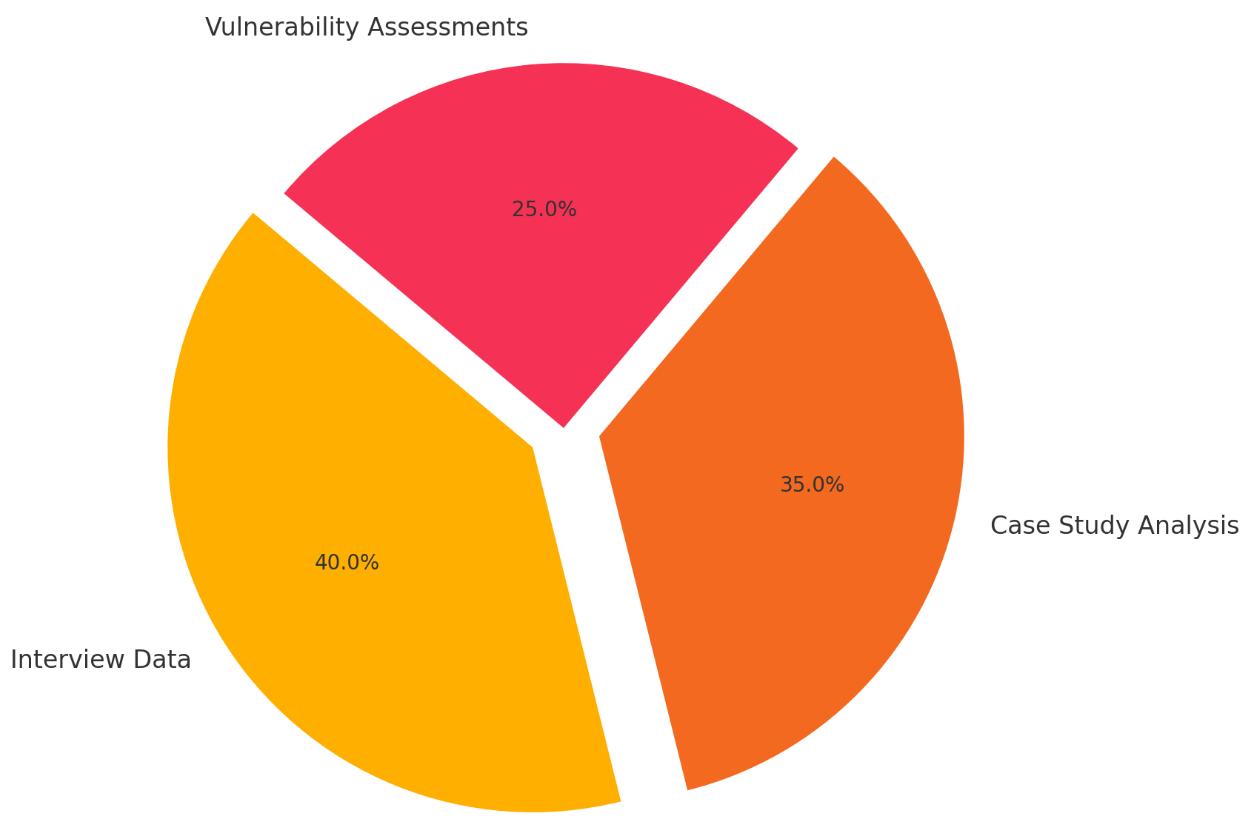
The next component of the methodology involves primary data collection, which seeks to gather real-world insights fromexpertsandpractitionersinthefieldsofcybersecurityandhealthcareIT.Thisdatacollectionprocessisdividedinto twomainapproaches:qualitativeinterviewsandreviewofincidentreports.
Interviews with Experts:Togainfirsthandknowledge ofthecurrentcybersecurity landscapeforIoMTdevices, semi-structured interviews are conducted with a range of professionals, including cybersecurity experts, healthcare IT managers, and device manufacturers. These interviews aim to provide insights into the following areas:

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The specific security challenges faced by healthcare organizations in securing IoMT devices against malwareattacks.
The current state of security practices for medical device manufacturers, including how they design, update,andsecuretheirdevices.
The perceived effectiveness of existing security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and networkisolation,inpreventingmalwareinfections.
Knowledgegapsorareaswhereorganizationsmaynotbetakingadequateprecautions.
These interviews provide rich qualitative data that offer a detailed understanding of the challenges and practices surroundingIoMTsecurity.Thefeedbackfromexpertshelpstoidentifycommonconcerns,emergingthreats,andareasin needofimprovement.
Incident Reports and Case Studies: A review of incident reports and case studies of malware attacks on IoMT devices is also conducted. These reports provide concrete examples of how malware has affected healthcare organizations, the types of malware involved, and the impact on both device functionality and patient safety. By analyzingreal-worldincidents,the researchcanidentifypatterns inattack methodsandcommon vulnerabilities exploited by cybercriminals. These case studies can highlight the weaknesses in existing security strategies and illustratethereal-worldconsequencesofmalwareinfections.
Thecombinationofexpertinterviewsandcasestudyanalysisenablesaholisticviewofthemalwarethreatlandscapeand itsimpactonIoMTdevices,offeringboththeoreticalandpracticalinsights.
Followingdatacollection,a technical vulnerability assessment iscarriedouttoevaluatethesusceptibilityofcommonly used IoMT devices to malware attacks. This assessment focuses on identifying specific vulnerabilities in the design, deployment,andoperationofthesedevicesthatmayexposethemtomalwarethreats.
Device Selection: A representative sample of IoMT devices is selected for analysis. These devices include wearablehealthmonitors, infusion pumps, diagnostic machines,and implantable medical devices. Thesampleis chosentocoverabroadrangeofdeviceswithvaryingfunctionalitiesandcommunicationprotocols.
Vulnerability Analysis:Eachdeviceisevaluatedforpotentialweaknessesinseveralkeyareas,including:
Firmware and Software: The research analyzes whether devices have outdated software, insecure communicationprotocols,orunpatchedsecurityvulnerabilitiesthatcouldallowmalwaretoinfectthem.
Authentication and Access Control: The study examines the effectiveness of user authentication and accesscontrolmechanisms,includingwhetherdevicesrelyonweakpasswordsordefaultcredentials.
Network Security:Thestudyevaluateshowdevicescommunicatewithhealthcaresystemsandexternal networks. Devices that use insecure networks or have open ports are more likely to be targeted by malware.
Physical Security:Insome cases,physical vulnerabilitiesare assessed,suchaswhethera devicecan be tamperedwithoraccessedbyunauthorizedindividuals.
Threat Simulation: In some cases, simulated malware attacks maybe performed in controlled environments to testhowdevicesrespondtodifferenttypesofmalware.Thesesimulationscanhighlightgapsinsecuritydefenses andofferinsightsintohowmalwareexploitsdevicevulnerabilities.
ThefindingsfromthisvulnerabilityassessmentarecrucialforunderstandingthetechnicalfactorsthatmakeIoMTdevices susceptibletomalwareandforidentifyingareasthatneedstrengthening.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Thenextcomponentinvolvesevaluatingexisting security frameworks andguidelinestodeterminetheireffectivenessin securingIoMTdevicesagainstmalwareattacks.Thisevaluationfocusesonframeworkssuchas:
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): HIPAA regulations provide guidelines for safeguarding patient information and ensuring the security of healthcare devices and systems. The evaluation assesseswhetherHIPAA’ssecuritycontrolsaresufficienttoaddresstherisksposedbymalwareinIoMTdevices.
NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology): NIST’s Cybersecurity Framework provides comprehensive guidance for securing critical infrastructure, including medical devices. This framework is analyzedforitsrelevanceandapplicabilitytoIoMTdevicesecurity,particularlyinaddressingmalwarethreats.
FDA (Food and Drug Administration) Guidelines: The FDA’s cybersecurity recommendations for medical devices, which include risk assessments, device testing, and vulnerability management, are evaluated to assess theiradequacyinmitigatingmalwarethreats.
TheresearchevaluateshowwelltheseframeworkssupportIoMTsecurity,highlightingstrengthsandweaknessesintheir implementation.Italsoexplorespotentialgapsinthesestandards,especiallyinrelationtomalwarethreats.
Based on the findings from the literature review, data collection, vulnerability assessment, and security framework evaluation, a set of recommendations is developed to improve the security of IoMT devices against malware attacks. Theserecommendationsarecategorizedinto:
Technical Measures: This includes suggestions for strengthening the design of IoMT devices, such as implementing robust encryption, secure communication protocols, and regular software updates. It may also involvetheadoptionofintrusiondetectionsystemsandmalwarescanningtoolstodetectandmitigatethreatsin real-time.
Organizational Practices: Recommendations for healthcare organizations include best practices for securing networks, ensuring proper device configuration, and implementing multi-layered access controls. Healthcare organizations should also train staff on cybersecurity awareness to prevent human error and mitigate insider threats.
Regulatory and Policy Recommendations: The research proposes improvements to existing regulatory frameworkstoensurethattheyaddressemergingmalwarethreats.Thismayinvolvecreatingnewguidelinesfor IoMTdevicemanufacturerstofollowduringthedesignanddeploymentphases toensurethatdevicesaresecure bydefault.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Discussion
TheIoMTecosystempresentssignificantcybersecuritychallenges,particularlyinrelationtomalwarethreats.Whilemany healthcareorganizationshaveadoptedsecuritybestpractices,suchasencryptionandaccesscontrols,therapidgrowthof IoMTdeviceshasoutpacedthedevelopmentofeffectivesecurity measures.Malwareattacksonmedicaldevicescanhave catastrophic consequences, including unauthorized access to patient data, device malfunctions, and even direct harm to patients.ThecomplexityanddiversityofIoMTdevices,combinedwithinconsistent securityprotocols,makeitdifficultto implementaunifieddefensestrategy.
Table 1: Vulnerabilities in IoMT Devices
Device
WearableHealthDevices
Lackofencryption,weakauthentication
InfusionPumps Insecuresoftware,outdatedfirmware
Datatheft,unauthorizedmonitoring
Disruptionofmedicationdelivery
ImagingSystems Pooraccesscontrols,networkexposure Imagemanipulation,databreaches
ImplantableDevices Insecurecommunicationprotocols Unauthorizedaccess,remotecontrol
Despite these challenges, advancements in IoMT security are ongoing. Regulatory frameworks, such as HIPAA and the FDA’s cybersecurity guidance for medical devices, are increasingly mandating stronger security measures. Additionally, the growing adoption of AI and machine learning in cybersecurity is providing new ways to detect and respond to malwarethreatsinreal-time.
Advantages
1. Comprehensive Insight:Thisstudyoffersadetailedexplorationofthespecificvulnerabilitiesandmalwarerisks faced by IoMT devices, providing actionable insights for healthcare organizations looking to enhance their securityposture.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
2. Practical Solutions: The research offers practical recommendations for securing IoMT devices, addressing both technicalandorganizationalchallenges.
3. Enhanced Awareness:Byidentifyingthekeythreatsandvulnerabilities,thisstudyhelpsraiseawarenessamong healthcare professionals and device manufacturers about the importance of cybersecurity in the medical device industry.
Conclusion
The threat of malware in the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is a growing concern for the healthcare sector. As more medical devices become connected, the attack surface for cybercriminals expands, leaving sensitive patient data and criticalhealthcarefunctionsvulnerable.The2024malwareattacksonhealthcaredeviceshavehighlightedtheurgentneed forstrongersecuritymeasurestoprotectthesedevices.ThispaperhasexaminedthevulnerabilitiesassociatedwithIoMT devices, analyzed the malware threats they face, and offered practical recommendations for securing these devices. By adopting multi-layered security approaches, developing standardized protocols, and incorporating regular updates and patches,healthcareorganizationscanmitigatetheriskofmalwareattacksandsafeguardpatientsafety.
References
[1] Smith, J., & Wang, A. (2021). "Cybersecurity in the Internet of Medical Things: Challenges and Solutions." IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,vol.68,no.6,pp.1-9.
[2] Brown,C.,&Zhao,H.(2020)."ASurveyofMalwareAttacksonMedicalDevices." IEEE Security & Privacy,vol.18, no.2,pp.23-31.
[3] Lee, S., & Gupta, R. (2022). "Medical Device Security: Addressing Malware Threats in IoMT." IEEE Internet of Things Journal,vol.9,no.3,pp.1045-1053.