Courtesy of Unsplashed
Courtesy of Unsplashed



























 Courtesy of Unsplashed
Courtesy of Unsplashed
Soumik Chemudupati, a 9th grader at the Liberal Arts and Science Academy (LASA), is the lead cybersecurity expert here at Bit By Bit. He covers how cybersecurity and the education system intertwine to “make sure the students are being safe,” the ethics of collecting that data, and how that impacts the students’ privacy. He’s been interested in technology from a young age, and is fascinated by how it can be used to solve real-world applications. He is very intrigued by puzzles and likes to experiment with different solving techniques. In his free time he likes to do origami and draw; it’s his creative outlet.



Hanxiang Mu is a 9th grader at the Liberal Arts and Science Academy (LASA), a large swimming enthusiast, and someone who is very interested in technology. After experiencing the COVID pandemic, he hopes to get back into swimming and enjoy one of his favorite activities. Having a lot of programming experience in numerous different languages from a young age, he aims to join an IT or physics company after college. Hanxiang plans to follow his father’s footsteps by exploring more about the technology at oil rigs, an industry his father worked in. As a proud member of Bit By Bit, his goal is to inspire people to learn about the real life application of technology and how they impact the daily lives of everyone around the world.

Reese Armstrong is a 9th grader at the Liberal Arts and Science Academy (LASA) and is a big Linux fan. As the Linux expert, he owns a server that runs Linux and uses a variant, Fedora, on his laptop. For his feature article, he will focus on informing readers about Linux. Reese has also been organizing hackathons where everybody’s welcome to join. Additionally, he enjoys tinkering and messing with computers to help him achieve his goals. As a member of Bit By Bit, his goal is to inspire readers to learn about Linux and how it impacts daily life.



Varik Choudary is a 9th grader at the Liberal Arts and Science Academy (LASA). As an avid reader, Varik even enjoys writing and drawing his own comics. This is his way of spending his free time on the weekends! He enjoys skateboarding and learning about hardware. Varik also has a very unique talent. He can ride a unicycle! Throughout this magazine Varik’s articles will be concentrating on the hardware aspect of technology. In his section of the magazine, Varik will expand on the ideas of how smartphones work and the differences between computers as well as virtual reality.

Alice Weber is a ninth grader at Liberal Arts and Science Academy (LASA). She enjoys rock climbing, as well as theater, and is very interested in technology. Alice first got interested in technology from her aunt, a computer science teacher, who gave her opportunities to learn about it. Her part of this magazine will explore AI (artificial intelligence). Alice will mainly focus on the misconceptions about AI, and why the basis in each system is the same. She will also create a timeline of the evolution of AI.


hacker, or the stolen data would be sold off. In a research effort, Jeremy Kirk, a technology reporter in Sydney, contacted the hacker to learn how he pulled off the attack. According to the hacker, they stole the data quite easily, saying, "No authenticate needed… All open to the internet for any one to use." It is this incident that serves as a perpetual reminder of how secure our data should be. Anyone at any time may try to steal this data, and without proper cybersecurity measures put in place, companies and clients may have to
An incident so extreme is not limited to major companies. In fact, cybersecurity issues can even occur to students and staff. Recently, the Austin Independent School District (AISD) sent out an announcement that


Security at Round Rock ISD, has thoughts on this idea. According to Apostolakos, COVID-19 did not affect as many school districts by making people more vulnerable. COVID-19 caused organizations to change their business processes. For example, when data is being collected, one still has to protect it one way or another. With COVID, many started building a relationship with their stakeholders, the people they are protecting, understanding how their business has changed, and changing their business model and processes to protect data, in those ways. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic forced organizations to rework and adjust their methods to protect students in a different environment.
as a planned attack, and many accounts had been compromised. Some of their data was lost, and part of it was related to many students and staff in AISD. Their access to these accounts was immediately suspended and they were not able to recov -



During the pandemic, some schools were targeted more while districts faced cyber attacks. For example, in May of 2020, a school district in Chicago was attacked, and 500,000 students’ records were compromised and stolen. Peter Aposotolakos, the Director of Information
Students must follow proper cybersecurity guidelines to stay safe on the internet. Although staff can help guide students in the right direction, they have to be knowledgeable about their activity online. According to Kyle Heaney, a cybersecurity professional at a globally leading bank State Street, students are most susceptible to phishing. Specifically, for students, there may be a scammer always trying to steal data by sending “phishy” links in their emails. Apostolakos agrees, saying, “It's also in the world of for a
the social media in and of itself, advertising in a process known as social engineering”. Apostolakos adds, “So when you see a trend of an app that says, I can make you look 20 years older, do you want to see what you look like when you're 50 or 80 on that app? If you don't read the policy, it may actually be stealing your data. It gives you a cool picture at the end or whatever. But at the end of it, the app could be a social engineering campaign from either, you know, a foreign entity or organized crime or, you know, a scamming ring or literally anything”.
Students must be careful how scammers are trying to get their information. Apostolakos wants students to keep one important thing in mind: “if an app is free, there's a very good chance that you're the product because they'll take your data and sell it”. For many companies, any data that is entered is considered to be theirs. They can easily take your data and sell it. For example, if you do a TikTok challenge, the rights do not stay with you. It almost, in a way, becomes property of TikTok. This is especially true with all of the ads you click and your activity. Therefore, student data is very valuable to a scammer because they cheaply get it from nefarious resources if students are not careful of their activity online.
tion. For example, Bruton says, “if someone sees that you're searching for a cruise, you know, you're wanting to get a ticket for a cruise ship. All of a sudden you'll start noticing that you're getting a lot more advertisements for cruise ships”. If you are on the internet, many companies out there have a very good idea of exactly what your interests are and what you do in your free time.
Digital footprint has a very large impact for students and young children in our modern society. Apostolakos defines digital footprint as all your activity on the internet stays on the internet forever.Apostolakos describes digital footprint through a splendid analogy: So when you walk, you create footprints. However, as you traverse the Internet, just understand that there is a foot. It's almost like walking in the sand. You leave a set of footprints behind you.” Apostolakos adds, “And some of them might be there forever. There's something you write or a picture you [take] that could be on the Internet for your entire life”.
Apostolakos Information Security Director

One’s activity online is also very important as it can make up their digital footprint. According to Mr. Donnie Bruton, Technology Manager at Round Rock ISD, there are many footprints and fingerprints you leave when you're using the Internet that you're not even aware of. There are many programs that are designed to track where you go on the internet and what you do on the internet. In our modern society, advertising has become a very large business. A lot of your searches online are used for marketing purposes, so that you can get personalized advertisements to captivate your atten-
With great powers comes great responsibility. Moreover, a large part of the digital footprint is being aware of what you're putting on the Internet. Because of digital footprint, it is very important to change your password, create a complex password, and enable multi-factor authentication as frequently as possible. One may believe that this is not that important. However, not changing your password can come back to haunt you due to your digital footprint. Let’s say that you decided to use one password for everything, and ended up getting compromised. If you came across

a website that you had not used in years, the credentials may still be valid. This is a huge security threat and is a result of digital footprint.
It is very important for students to manage their digital footprint and keep it clean. However, it might be hard for them to do that as they are not educated enough. This is one of the reasons many students are unable to develop good cybersecu-

protect their accounts,” says Heaney.
rity practices. According to Heaney, the biggest issue for cybersecurity is cyber awareness. If more people know about how to protect themselves online, they will be able to better protect their accounts from hackers and attackers. “As long as more people know how to protect themselves online, they'll be able to better

Young people and students often do not have the awareness or the experience to protect themselves online. Often, students will hear a notification on Instagram, a noise very soothing to them. When they unlock their phone, they will see a message from their friend, waiting for them to open. However, in many cases, their friend’s accounts have been hacked. As soon as they open the message from their friend, they are at high risk of getting hacked as well. This is just one example of how students get hacked. However, this is something that could happen to you at any time, especially if you are on multiple social media platforms. Because students are not aware of such hacks, they are very much susceptible to being hacked. So, to help students stay cyber aware, many companies and organizations have begun launching programs. For example, the United States Air Force launched a program called CyberPatriot, to encourage students to learn about cybersecurity through a fun competition. Additionally, colleges like CMU have introduced competitive CTFs, a cybersecurity
“game” that stands for “capture the flag”, like picoCTF. Through these “games”, students from all over the world are able to learn about internet safety and remain cyber aware.
You truly have to be prepared for anything. In cybersecurity, things are always changing. We must be able to adapt to these circumstances and continue developing new technologies.

Apostolakos adds, “You know,

there's a fundamental way to throw a baseball. There's a fundamental way to respond to an incident.” He also notes, “But things change, much like throwing a baseball. There's a curveball. You know, there's all kinds of different ways to throw pitches that a pitcher in baseball can throw.” Susceptible. Exposure. Caution. Uncertainty. Risk. Imminent. Threat. Youth. SECURITY. Cybersecurity is truly a game of cat and mouse: hackers and cybersecurity professionals competing to be the first one to make a move. As Heaney says, “Cyber security professionals have to be correct 100% of the time, but hackers only need to be correct 1% of the time.”
Cybersecurity professionals have to be correct 100% of the time, but hackers only need to be correct 1% of the time.
Kyle Heaney Security Professional at StateStreetCourtesy of Round Rock ISD, Large School District in TX
ofadultstryto hidetheirdigitalfootprint.







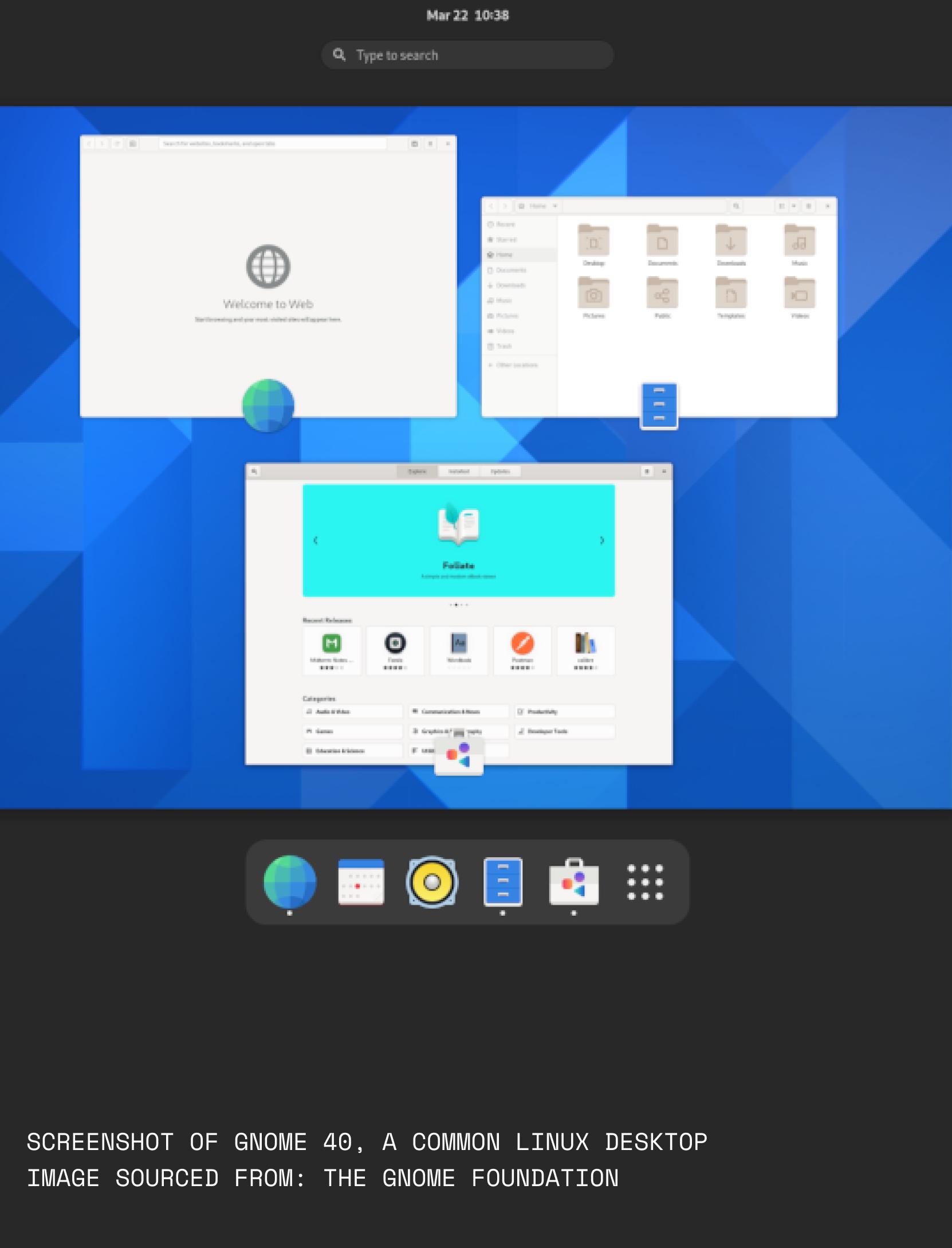


echnology is becoming more and more advanced as the years pass by. Computers run far faster, and are more higher powered than before. Moore’s Law is an observation, made by Gordon Moore, about how the number of transistors on microchips doubles roughly every two years. However, today’s microchip processors are reaching atomic scale and can’t physically get much smaller. What makes Moore’s law so significant is the fact that you can have over a billion transistors in a phone that you can fit into your pocket. I interviewed a Computer technician, under the alias of Mr. Robot. He thinks there is still some runway left for Moore’s Law. “State of the art is currently 3nm, even though that doesn’t sound like much, there’s still so much room to improve and TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) has a long track record of pioneering fabrication. It just keeps getting better and better with no inclination of slowing down. Until fabrication stagnates, I don’t see how Moore’s Law would cease to be accurate.”
Mr. Robot custom builds and fixes PCs. Custom-built PCs last longer than any store-bought PC. “This is because companies will intentionally build their computers to last for a couple of years so that customers can buy the new latest model.”

According to Mr. Robot, they will knowingly choose cases with no ventilation to purposefully hamstring longevity. The fans only have 30-to-50% of the airflow they should be getting. They intentionally manufacture them with CPU coolers with 120MM radiator size, which is insufficient for any unlocked Intel processor or Ryzen 7 CPU. The GPU is almost always overheating due to not enough airflow, leading it to its early death.
Companies will intentionally build their computers to last for a couple of years so that customers can buy the new latest model

GPU failure is the most common failure on store-bought prebuilt PCs.
Mr. Robot says, “Custom-built PCs leave the builder to dictate each component choice. With the proper research and education, you can select components of the highest quality that your budget will allow. It is typical to see a correctly built and configured custom computer last over 10 years, whereas store-bought PCs seldom see beyond 2 or 3 years. Arrhe -
nius’s Law of Chemical Reactivity states that for every 1C drop you experience a 2X increase in lifespan.” Well what happens when computers stop working after every 2 years?
Electronic waste is a term that describes non functioning electronic devices that have been discarded. Electronic waste makes up five percent of municipal solid waste, and it continues to increase as more electronics get sold. There are many impacts that go with elec -


tronic waste. It affects not only the environment, but human health as well. E-waste can expose people to toxic substances that are harmful. Electronic waste can decrease if devices were better built, to last a longer period of time.
Senthil Arasu, Senior Research CAD Engineer, talks about how much technology has changed over the past 20 years, and how it has made our lives easier. “If you look at the phones between what you have today to what, 20 years back when we had the phone, we’ve come a long way, I didn’t have that many pictures. 20 years back. But today, I take a lot more pictures, and I can keep them in
a very compact way in my pocket. I can see how technology has made it and it takes in all facets of life. That’s just one example. But technology is what is kind of breathing and making our lives a lot more livable.” Senthil works on the tools which chip designers use to design the latest processors at Apple.
Technology is continuously advancing, and making our lives easier and enjoyable. As consumers we should keep in mind the increasing issue of electronic waste and make our technology purchasing decisions mindfully.
“Electronic Waste | Britannica.” Encyclopædia Britannica, 2022, www.britannica.com/technology/electronic-waste. Semuels/Fresno, Alana. “The World Has an E-Waste Problem.” Time, Time, 23 May 2019, time.com/5594380/world-electronic-waste-problem/. “What Is E-Waste?” CalRecycle Home Page, 2022, calrecycle.ca.gov/electronics/whatisewaste/


It is typical to see a correctly build and configured custom computer last over 10 years, whereas store-bought PCs seldom see beyond 2 or 3 years
“







Throughout the years, Artcial intelligence, or AI, has been a mainstream topic that is often discussed, and yet there are still more misconceptions about AI than truths. While what we have learned from so many movies and games is fun to watch, it isn’t exactly accurate. AI isn’t smarter than the average person, nor is it able to suddenly gain sentience. So, what is AI, how does it work, and what are the real dangers of AI?

Most AI is no smarter than a young toddler. Although some AI is very specialized and can do one thing very well, it can’t do everything. For example there is a website called “This Person Does not Exist“ that creates human faces for fake people. Even though the program is very good at making faces, it is not very good at creating backgrounds. In every photo of a fake person the background is blurry. Although you may be able to get a general idea of what is behind them, like a brick wall, or a tree the background will never be in focus.

Despite there being many types of AI, from chatbots to parking tools, all AI have the same basis

that it works off of, a data set, requirements, and a goal. In terms of how AI learns, there are two main methods that can be used together with data sets and trials. Trials work by giving the AI several requirements and a goal. For example, if you were training a virtual car to park using AI, the goal would be to end up within the boundaries of a parking spot, and the requirements would be to not bump into anything along the way.
These goals need to be very specific when outlining the parameters of what the AI is supposed to do. It has to be given requirements and boundaries for the task. In one trial an AI was told to build a robot with a set of pieces that could run across terrain, jump over a gap, and cross a finish line. However, it was not given good enough parameters and instead of building a functioning robot, it simply used the parts to make a stack that it then tipped over until eventually, the head piece that needed to cross to get the point fell over the finish line.
Data sets can be almost anything from pictures of traffic lights to college essays. Data sets are used to train AI to find certain qualities making up something
and recognize them later. If you were trying to teach a self-driving car how to identify a traffic light, then you would show it different images of traffic lights, so that, in the future, the car would be able to point out and recognize traffic lights.
Unfortunately, using data sets to train an AI can have consequences. Because people are often biased, those biases can be reflected in the decisions we make. Giving an AI a daft set that a person created can often give the AI those same biases that the person had while creating the data set. If a person wants to create an AI that recognises the color blue but doesn’t like neon blue, then
that AI is less likely to recognise neon blue as blue. While this can be harmless, people have tried to pull the spotlight away from their own failure by saying that it’s just a fault in the robot, even though the robot is based on their own opinions and biases.
AI doesn’t know how to tell the difference between bias and fact. Most of the time AI is very specialized and can only do one or two things, so when people give it biased broad information, the AI just accepts everything as fact.

This has happened many times, the most infamous of which being ST. George’s Hospital Medical School.
The university decided to build an AI to help sort through the college admissions process in 1979. The problem was that many of the people who decided which applications were accepted only wanted to accept white men. When the AI was given good and bad examples of applications it
Even though this person does not exist is very well made it can’t do everything. For instance in all the photos, the person’s face may look real by the background is always blurry
“UT Computer Science Student
learned not to accept people who graduated from women’s colleges, or people with non european names. Originally the program was to make the process faster and more efficient, as well as creating fewer outliers in the student screening process which would help create a fair overall process for everyone. Unfortunately, it did the opposite. In 1986, the UK Commission for Racial Equality decided to investigate concerns about the school’s application rates and the algorithm was taken out of the process.


This is one of the most infoumas incidents involving the dangers of artificial intelegence in history. It is often used as an example
for classes when talking about the
ple’s behavior, and while AI is not dangerous by itself, human biases can make it unreliable and unstable.

The AI reflected a more long-standing problem within the university, however there is always the risk of the AI being used as an excuse for people’s behavior. While AI can be a helpful tool at times it can also be used to excuse and ignore peo-
The reason people often use Artificial intelligence as an excuse for their behavior is that even though the program can be blamed for the things that happen because of it, and they can be absolved of all blame even though they are the AI is based off of them.
This has also caused a problem with humanizing Artificial intelligence. When people start to think of the robots as people, they can be blamed in the same way people can be blamed for
problems while the people who made the program are absolved of all blame.
Huminization has not been the only problem in the past. AI art has also become a debate as of recently. This argument has been tied in with past arguments about computers taking people’s jobs.
Many artists, especially newer artists, are being affected by the rise of Artificial art. While currently AI art is not good enough to replace a real artist convincingly, it has also lowered many peoples spirits and there could be more potential issues with copywriting.



It will become much easier to steal art from people as many can just run another person’s art through a generator and come up with a new piece that can be passed off as their own. While it does add more opportunities for people to gain inspiration and
create their own things, it also keeps people from creating their own art, and as many artists
have referred to it as “soulless”.
The debate surrounding Artificial intelligence art has always been a problem however it has just been a part of different debates. Currently the debate is over AI generated art but in the past it has been around anything from referees to factory jobs.
Most AI isn’t dangerous in the same way it is in movies or tv shows. Your smart fridge is probably not going to take over the world, in fact most AI has about the intelligence level of a young toddler. The real danger of AI lies in how we use, and abuse it.
Artificial intelligence art is hurting young artists, it is soulless and all people have to do is type in a sentence to make something that would normally take hundreds of hours of work.
UT Computer Science Student
Through the years AI has developed, bringing along new challenges and concerns with it. From when the term was first coined, to present day AI has advanced a lot. In 1965 a man named John Mcar thy came up with the term “Ar tificial intelligence”. He and Alan Turring are considered the fathers of art ificial intelligence. He would later hold the first AI conference.
The first general purpose moving robot was made in 1968 and named “Shakey”. Made by SRI ( stanford research institute) international, Shaky could do things like short term planning, moving in paths, and arranging and rearranging small objects. Although Sha key was not originally designed to use ar tificial intelligence it was later adapted to run on AI and is considered by many ( but not all there is some debate over this) to be the first robot running on artificial intelligence. Shaky was retired to the computer histor y museum in 1972, aft er working for four years. Shak y has acted as template of sort s for future robots, especially those involved with Ai.
Deep blue is perhaps one of the most impor tant art ificial intelligence programs to ever be created, and cert ainly one of the most famous. Deep blue was a program developed by IBM (I nternational business machine) in 1997 and was made to play chess. Deep blue was made to beat any human chess play and on May 11 of 1977 it proved that it could. Deep blue played against the man widely considered be the best chess player in the world, Gar ry Kasparov. Over the course of several days it played several matches and eventually won with t wo wins, three ties , and a loss . Because of this match It was later renamed deep thought.
In 1965 John McCar thy created the term Ar tificial intelligence, and the first AI confrence


Deep Blue, a program that could beat any chess player was developed by IBM in 1997
In 1969 the first general purpose moving robot “Shakey” was built, soon af ter Shakey would run on AI
In 2011 computer questionsystem won
designed considcomputer as a

when y ifiand business ayer to severlater
In 2016 AlphaGo defeated world champion Go player Lee Sedol won 4/5 games and was later improved
Watson was a program that, in 2011 was able to win at the jeopardy game show against many top players using its abilit y to search through huge databases ver y fast . Watson is now generally accessible to the public to help people train AI quickly and has helped create thousands of programs around the world.

AlphaGo was a program with a team that set out to a more dif ficult challenge than the one the Deep blue designers had faced. They wanted to make an AI to win against top GO players . GO is a game with far more possibilities , and is much more dif ficult to predict. However in 2016 AlphaGo beat world champion Lee Sedol in 4 out of the 5 games it played.

AlphaGo continues to beat ever y GO champion who plays against it, and has even improved since the match against Lee Sedol. There is a very good documentar y about the program called AlphaGo.
2011, the computer question- answering system Watson won the quiz "Jeopardy!"
The possibilit y of AI taking people's jobs is start ing to become a more pressing issue

 Courtesy of New York Times
Courtesy of New York Times
nergy is considered a very critical thing to everyday life, including the world economy. Oil and gas have always been considered to be a major form of energy. Especially now, when the population is transitioning from this fuelpowered energy to clean energy. It’s critical to have affordable and safe energy like oil and gas. These fossil fuels formed millions of years ago from organic remains that went through extremely high pressure that eventually turned into liquid.
Luckily, Schlumberger exists, an oil/gas business that extracts fuel from the earth to allow many businesses and companies to power themselves. Schlumberger is the world’s largest oil service company. Thousands of oil drilling sites are placed around the world, especially in countries like the Middle East, Brazil, Mexico, and Russia.
When it comes to drilling, operators need to find the location of the oil reserves via exploration. One of the major exploration methods is called the seismic method, which utilizes a seismic source of energy to produce seismic waves. When these seismic waves travel into the earth, drillers place an array of receivers to receive the reflections of the waves and go through all kinds of calculations. From there, an image of what’s underground is formed, and following or afterwards the experts can use those images to find whether this place has oil or not. If oil is found, there’s a good chance that there are oil reserves in the area. Based on the results, they drill a well at the site to extract it. Unfortunately,
this process of finding oil is not very accurate. Oil drilling is a risky business. “Oil fields are usually involved with very high pressures and temperatures, creating many highly dangerous situations,” says Mi Bao, a Schlumberger project manager. “Any failures or mistakes could risk the operator’s welfare and/or damage expensive equipment.”

Among the most dangerous factors is the extremely high pressure from the downhole. If it is not controlled properly, the growing pressure can easily cause catastrophic consequences, effectively
and the operators have to follow the field-required procedures in the field operations to make sure these situations don’t occur,” Bao said.
destroying the well, damaging the equipment, and even injuring and killing people. This is caused by high pressure, piping fractures, or unstable structuring. Another cause could be chemical leaks or spills as those oil field operations involve a lot of chemicals, and when there is a chemical leak or spill, it can lead to environmental pollution. Procedures include wearing PPE (personal protective equipment), drilling with the guidance of software to detect risks, and more.
“It is very important to properly design every step of the process,

When the oil drilling sites are being built, the type of equipment transported to the oil site varies, depending on the kind of operations that will be used during the oil drill’s lifetime. Operations can be extremely different, but usually involve heavy equipment, like a lot of trucks, piping, and valves. It all starts with exploration. As mentioned before, exploration usually requires big vessels on the ocean or big trucks, depending on where the operation is and whether it’s on the ocean or land. They are usually equipped with sensors, electronics, and computers. Once you locate a field with a good oil reserve, you will have to drill the well. There are also pump jacks for extracting the oil to the surface by using pressure. The drilling itself normally involves huge drilling rigs, so it requires tons of pipes and casings.
One of the more popular operations used at drill sites is an operation called Hydraulic Fracturing. which involves
 An image of Mi Bao
An image of Mi Bao
It is very important to properly design every step of the process to make sure these situations don’tMi
Bao
Schlumberger Project Mananger
pumping sand and fluids to create artificial pressure.
pumping,” Bao states. “Lots of pumps. Lots of trucks. So, it’s very resource intensive.”
When the reservoir is found, it can be thousands of feet away, so it’s hard to find it with human eyes, but modern drilling operations are reliant on advanced sensing technologies to get the current operating conditions of the downhole/oil reservoir.
“So usually in the oil field industry, we will first use seismic devices to get a profile of the target region,” said Wendi Yu, a Schlumberger software architect.
of the drill at that moment. So all those directions are measured by using an array of accelerometers.



Yan He, a Schlumberger system project manager, explains: “Because we have different sensors in the drilling tools, it can tell us where we are at the ground so we always know how deep we are, what declination we have, and in what direction we are heading.”
“Together the huge amount of sand water keeps the pump
These conditions include the depth, temperatures, pressures, rock conditions, and the direction
Operators also use magnetometers, which are devices used to measure gravity and the magnetic field to try to determine the location and direction of the object, which is the drill bit (head) of the drill.

Lots of pumps. Lots of trucks. So, it’s very resource intensive.
Another way to find the location of the drill is to use mud logging. Mud logging is when the oil drilling
experts analyze the mud that is returned from the drill as the drill makes its way underground.
“When they make the decision [to change the direction of the drill bit], they will send the [trajectory change] command back to the borehole through the tool string so you can see where the command is from. The measured data will transmit back from the downhole to the surface. That’s how the operators can control the direction and they decide when [to edit the trajectory],” He said.

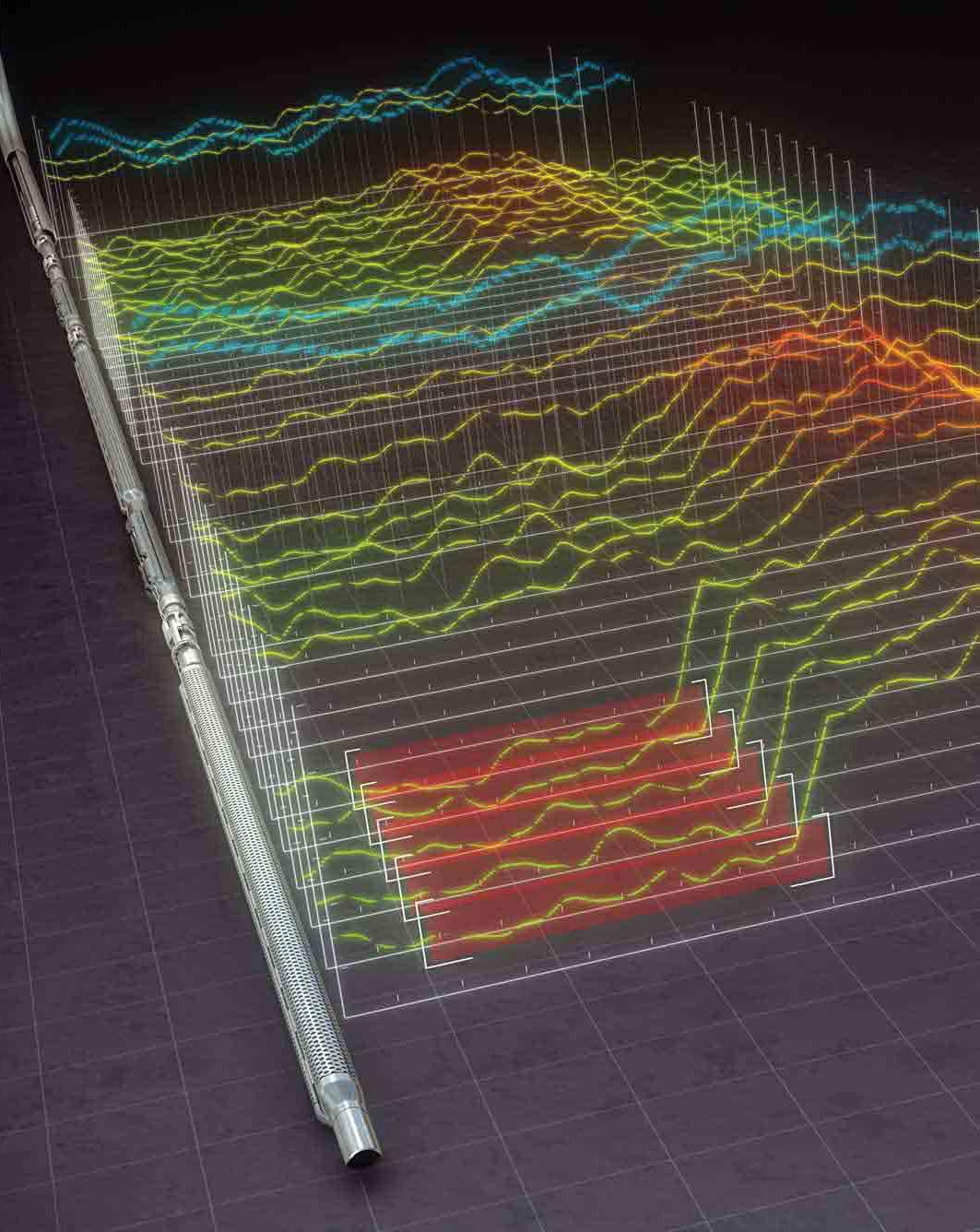
There are two main methods for receiving the conditions around the drill bit. The first method is mud logging (aka L. W. D.,
Logging While Drilling), which can get positional data while drilling to deliver real-time data to operators to save time and money. The other method is M. W. B. (Measurement While Drilling). The MWB method has drilling tools that are placed in the wellbore. These tools measure the inclination of the drill bit and the vertical depths of the well. This information is extremely useful for drilling.
“The drilling services at Schlumberger provide directional drilling services so that [the drill bit] can reach the production zone, which can produce the oil.” said He.



 An image visualizing the profile of the ground, created by Schlumberger sensors
Courtesy of Schlumberger
An image visualizing the profile of the ground, created by Schlumberger sensors
Courtesy of Schlumberger
than drilling multiple ver tical drilling wells. -
zontal formation.
Provides teams with better access to reserviors, increasing production rates. Allowing access to reserviors far from starting location.
Can avoid obstacles. Less soil disturbance. Reduces the risk of gas ruptures while developing new wells.

YOU Drill?
Ver y simple. degrees of depth, Analyzing these samples allows engineers to determine potential oil reserve locations. locations.
YOU Drill?
Larger environmental damage & footprint (cost more due to more source structures and causes more environmental damage (damaging underground formation).
Ex tremely capital-intensive. Requires large area to function
Will need multiple drill sites to cover wide reservoirs.