Art











Business Studiesprovides transferable skills allowingstudentsa smoothtransitionfrom an educationalenvironmentto a work environment, by providing an insight to a multitude of business sectorsand departments.The GCSE Business specification will give studentsthe opportunity to explore real business issues and how businesses work. A relevant and diverse specification, students will consider the practical application of business concepts
The units provide opportunitiesto explore theories and conceptsin the mostrelevant way, throughthe contextof events in the business and economicworld. In Year 10 studentswill study and investigatethe purpose of business activity,the role of business enterprise and entrepreneurship, and the dynamic nature of business.Students will study the importance of external influences on business and how businesses change in response to these influences. Students will study the interdependent nature of business operations.
There will be three units of approx. 12 weeks each. Each lessonwill include at least one LORIC skill.
Homeworkwill be set on Seneca learning and quizizz: both are automatedmarkingto track individual studentprogress and identify gaps in learning,
Developan in-depth knowledge of the subject area
Developthe skills of application, analysis and evaluation
Enable studentsto have a wider understandingof issues in the world they live
Enable students to make progress regardless of ability, disability, gender, race or sexuality
Developconfidence in our studentsso that they are able to live safe, healthy and fulfilling lives
Equip studentswith the 21st century knowledge and skills needed beyond Shrewsbury Academy
Encouragestudentsto develop the knowledge and skills needed for employmentor training
Offer studentsthe chance to achieve and have high aspirationsand ambition
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take place at the end of each unit.
Homework will be set on online platforms and results will be used in lesson to address misconceptions and learning gaps.
Teachers will live mark/ sample mark non formal assessments.
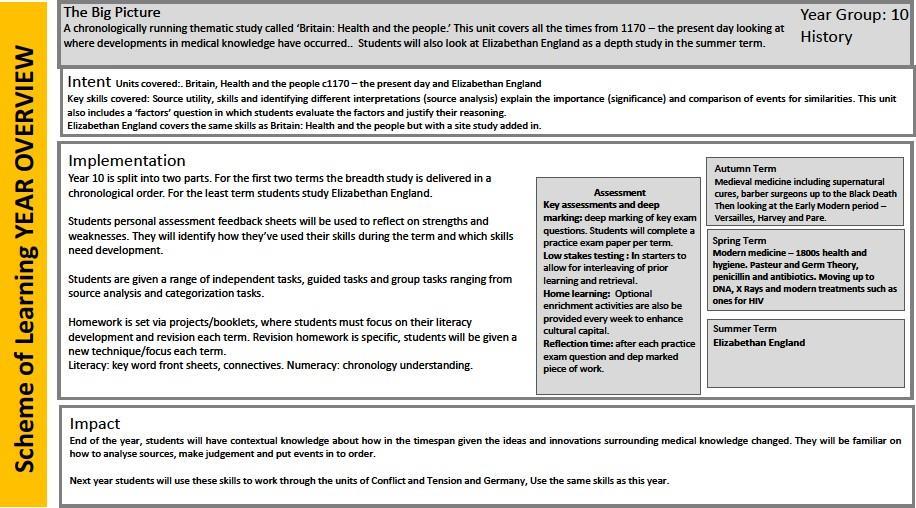
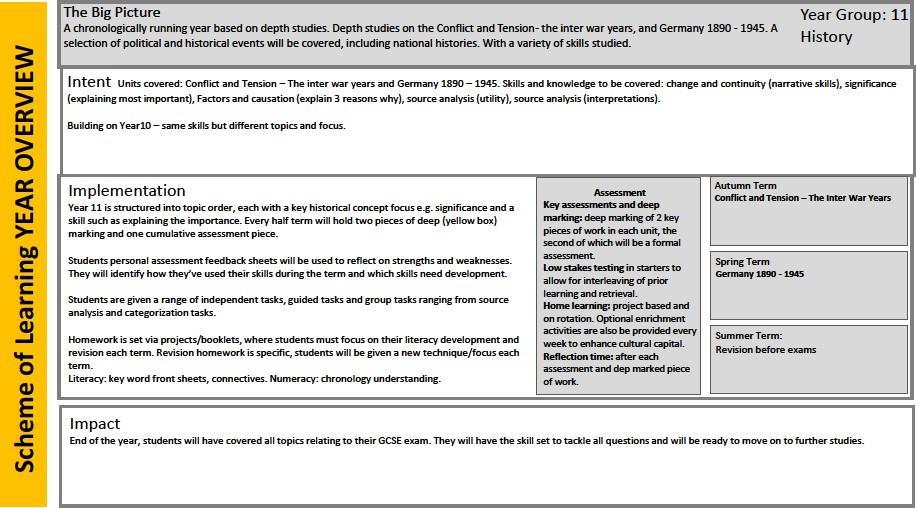
Autumn Term -Business in the real world -The purpose and nature of businesses -Business ownership -Setting business aimsand objectivesBusiness in the real world Business StakeholdersBusiness location -Business Planning -Expanding a business
Spring Term - Influences on businessTechnical influences -Ethical and environmental considerations -The economic climate on businesses - GlobalisationLegislation -Competitive environment
Summer Term - Business operationsProductionprocesses -The role of procurement -The concept of qualityBusiness operations- Good customer services –Marketing- Identifying and understanding
Initially the aim will be for learners to engage and start to develop confidence in this new subject. Not only is thisan opportunity to build their knowledge of business it is also a chance to experience a number of sectorsthat could ultimately shape their own transitionfrom our school.
In KS4, booksare marked in line with Shrewsbury Academy’smarking policy.Studentsare then given feedback and time to improvetheir work. As well as this, data is collectedusing multiplechoice quizzes on every sub-topicand the student’scompleteformal assessmentsat the end of each unit. This allows the teacher to assessthe knowledge and skills developed and identify misconceptions.
Business Studies provides transferable skills allowingstudents a smoothtransitionfrom an educationalenvironment to a work environment, by providing an insight to a multitude of business sectorsand departments. The GCSE Business specification will give studentsthe opportunity to explore real business issues and how businesses work. A relevant and diverse specification, students will consider the practical application of business concepts
Intent ’Learning Programme’units to be covered:3.4 Human resources (3.4.1-3.4.4)- 3.5
The units provide opportunitiesto explore theories and conceptsin the mostrelevant way, through the contextof events in the business and economicworld. In Year 11 studentswill study and investigatethe purpose of business activity,the role of business enterprise and entrepreneurship, and the dynamic nature of business.Studentswill study the importance of external influences on business and how businesses change in response to these influences. Students will study, human resources, marketing and finance.
There will be three units of approx. 13 weeks each. Each lessonwill include at least one LORIC skill.
Homeworkwill be set on Seneca learning and quizizz: both are automatedmarkingto track individual studentprogress and identify gaps in learning,
Developan in-depth knowledge of the subject area
Developthe skills of application, analysis and evaluation
Enable studentsto have a wider understandingof issues in the world they live
Enable students to make progress regardless of ability, disability, gender, race or sexuality
Developconfidence in our studentsso that they are able to live safe, healthy and fulfilling lives
Equip studentswith the 21st century knowledge and skills needed beyond Shrewsbury Academy
Encourage studentsto develop the knowledge and skills needed for employmentor training
Offer studentsthe chance to achieve and have high aspirationsand ambition
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take place at the end of each unit.
Homework will be set on online platforms and results will be used in lesson to address misconceptions and learning gaps.
Teachers will live mark/ sample mark non formal assessments.
Autumn Term- Human ResourcesRecruitment and selection of employeesMotivating employees -Motivating employees -Training
Spring Term- Marketing-The purpose and methodsof market research -The elements of the marketing mix: price, product, promotion and place -Finance -Sources of finance Cash Flow- Financial terms and calculations
Summer Term –Finance- Analysing the financial performance of a business Revision
In KS4, booksare marked in line with Shrewsbury Academy’smarking policy.Studentsare then given feedback and time to improve their work. As well as this, data is collectedusing multiplechoice quizzes on every sub-topicand the student’scompleteformal assessmentsat the end of each unit. This allows the teacher to assessthe knowledge and skills developed and identify misconceptions.
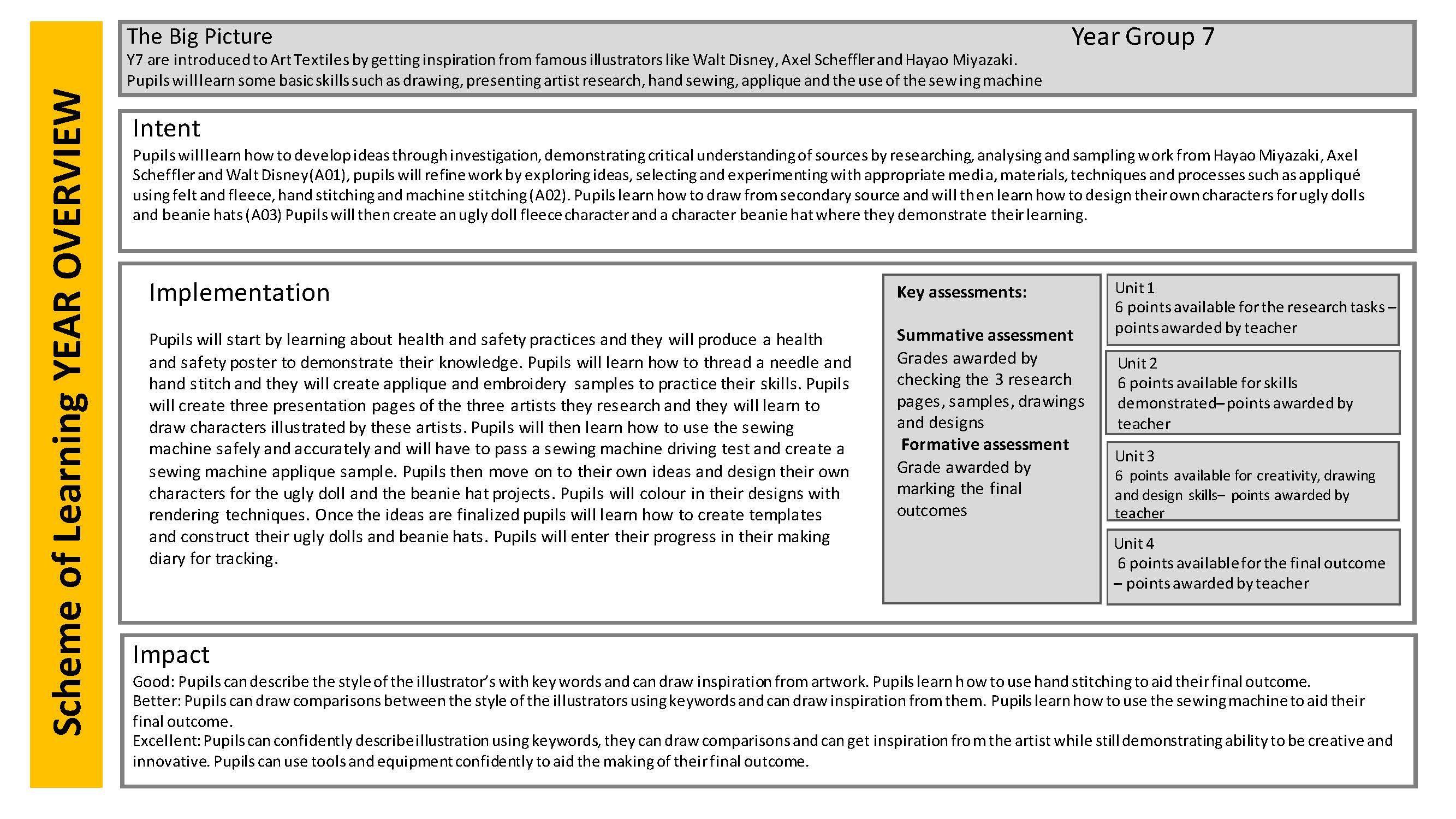
The Big Picture: To begin the process of buildinga skills base. To develop an understandingof the design process throughboth practical and theorywork. Studentswill feel safe in the DT area; be able to follow simple Health & Safety guidelines and demonstrate to others how to use tools and machinery correctly. They will become increasingly confident and accurate in their use of technique.
IntentYear 7 offers studentsthe opportunityto become acquaintedwith the DT room,, its tools, machinery and materials. It is a year of exploration and discovery. Studentswill work to develop a deep understandingof the risks associated with this room. They will be able to work in safety and look out for other studentssafety –using emergency procedures correctly if required.They will develop their knowledge of materials – being able to identifydifferenttypes of wood, nails, screws and pins. The will be able to use a limited numberof tools, safely and with increased levels of accuracy. They will develop a deeper understandingof the design process – being able to draw using specific techniques; writing clear design briefs and specifications; liaising with clients and evaluating their work by highlightingareas of success and areas for improvement.
1 hour lessons per week. The year 7 creative curriculum will run over one full term. (Autumn, Spring, Summer)
Students will complete a set of themed tasks – H/S posters; drawing styles; writing tasks and practical study
Students will work independently,listening to instructions and following demonstrations
The more confident students within the groups will have the ability to show leadership by supporting their peers
Students will be provided with their materials but will be encouraged to bring in additionalmaterials from home – especially if a student wishes to work on a larger scale practical piece.
Students will reflect on previouslessons via verbaland written response. Use of key wordsand correct phraseology will be encouraged throughout – building up a skill vital in any future GCSE exam
The aim in Year7 is to create a WOW! Students will be genuinely excited aboutworking in such a dynamic atmosphere;take a real interestin their work and enjoy all elements of the design process. The use of literacy will be developed throughout lessons by use of key word and communication as students follow instructions and demonstrations. Numeracy is a key element, expressed in measurement of lengths, widths, depth and volume.
Key assessments:
Each practical lesson students will be given a red dot sticker to denote an area for development. Other assessments will be verbal and written. This will be recorded on data, pillar drops and Arbor. Theory and knowledge will be self and peer assessed. Homework (evaluation skills) will be marked fortnightly and feedback provided.
Testing / end of unit test
Autumn Term End of unit drawing test
Spring Term End of unit drawing test
SummerTerm End of unit drawing test
Students will be able to successfully produce two high quality products to take home. Their confidence levels will have developed and they will feel encouraged to expand and refine their skills. Both their practical and theory skills will develop. A clear knowledge of the design process will develop over KS3; building a skills base ready for the start of a GCSE course. Students knowledge of materials, tools,machinery and techniques will allow them the opportunity to design and manufacture increasingly complex prototypes. This first year will prepare them for the next stage and to ultimately gain top level GCSE grades. It also allows them to build a separate and vital life skills base in planning, organisation, IT, literacy / numeracy and meeting deadlines.
Intent A scheme of work addresses both theory and practical tasks. It will emphasise the importance of hygiene and safety in the kitchen. Recognise kitchen equipment. Students will carry out practical taks to develop confidence and independent learning in the kitchen. Dishes to include fruit salad (knife skills), Multi-cultural pizza, using the hob –spaghetti Bolognese/ curry, small cakes (weighing and measuring). Muffins (textures and flavours). This will prepare students for increase in skills levels during Year 8 and 9
1 hour lessonsper week. The year 7 creative curriculum will run over one full term.(Autumn, spring, Summer)
Theory lessonsbased on hygiene and safety, kitchen equipmentweighing and measuring Demonstrations–to reinforce practical skills (visual learning)
Practicaltasks– Kinesthetic learning. The dishes that are produced become more complexed throughoutthe term. Studentswill work independently reading the methodand listening to instructions.The more confident students within the groups will have the ability to show leadership by supporting their peers.
Purchasingingredients will be a weekly home learning task and we encourage studentsto weigh their own ingredients
Evaluations(homework).Students revisit the practical tasks and review ‘what went well’, ‘what can be improved’
Literacy is challenged throughout, mainly through starter activities and plenaries. Key words and communicationas students follow recipe instructions incorrect spellings are highlighted when marking.
Numeracy will be used through weighing and measuring tasks, timingsand temperature
Key assessments:
Practical tasks
Classwork to be peer and self assessed
Homework marked and feedback provided End of unit / topic assessment
Tastetesting – reviewing ‘what went well’ and ‘even better if ‘
Autumn Term End of unit test
Spring Term End of unit test
SummerTerm End of unit test
Students can successfully produce high quality finished products that they are proud of. Their confidence levels will have improved and they will be trying these recipes over and over again at home. They will learn a range of basic skills that they will develop over the next few years. This will prepare them for gaining good grades if they were to select the subject at GCSE leval and will equip them with general life skills for future (organisation, costings,weighing, cooking,and washing up)
Subject knowledge of all students will be developed through practical experiences of cooking and tasting sessions as well as building knowledge of theory
The Big Picture: To furtherdevelop a skills base. To furtherdevelop an understandingof the design process throughboth practical and theory work. Students will feel safe in the DT area. Studentswill be able to use a wider range of tools, machinery and techniques in their practical work. Their drawing skills will develop to encompass isometric and orthographictechniques.Their knowledge of material capabilities will increase.
IntentYear 8 offers studentsthe opportunityto develop their skills and understandingof the design process. They will be able to write a detailed brief and specification. Studentswill be able to expand on these documents by writing a client profile, a client questionnaire and a piece of market research. They will be able to complete a series of three initial ideas in an isomeric drawing style and one final design in an orthographic style. Their design work will be complete with two full evaluations – self and client. Their practical skills and techniques will develop with investigations into differenthand tools, machinery, materials and construction techniques – measuring, cutting(basic joints), fixing and finishing.Research into the capabilities of tools, machinery and materials will form a key part of this process.
1 hour lessons per week. The year 8 creative curriculum will run over one full term. (Autumn, Spring, Summer)
Students will complete a set of themed tasks – set stages in design process (to incorporatedrawing techniques); writing tasks and practical study
Students will work independently,listening to instructions and following demonstrations
The more confident students within the groups will have the ability to show leadership by supporting their peers
Students will be provided with their materialsbut will be encouraged to bring in additional materialsfrom home – especially if a student wishes to work on a larger scale practical piece. Students will reflect on previouslessons via verbaland written response. Use of key wordsand correct phraseology will be encouraged throughout – building up a skill vital in any future GCSE exam
The aim in Year 8 is to continuing WOW’ing! Students will be genuinely excited about workingin such a dynamicatmosphere;take a realinterest in their workand enjoy all elements of the design process. The use of literacy will be developed throughout lessons by use of key word and communication as students follow instructions and demonstrations. Numeracy is a key element, expressed in measurement of lengths, widths, depth and volume.
Key assessments: Each practical lesson students will be given a red dot sticker to denote an area for development. Other assessments will be verbal and written. This will be recorded on data, pillar drops and Arbor. Theory and knowledge will be self and peer assessed. Homework (evaluation skills) will be marked fortnightly and feedback provided. Testing / end of unit test
Autumn Term End of unit drawing test
Spring Term End of unit drawing test
SummerTerm End of unit drawing test
Studentswill be able to successfully produce one woodenproduct to take home. Their confidence levels will be continuallyrising and they will feel encouraged to expand and refine their skills.Both their practical and theory skills will develop. A clear knowledge of the design processwill develop throughout KS3; building a skills base ready for the start of a GCSE course. Studentsknowledge of materials,tools,machinery and techniques will allow them the opportunity to design and manufacture increasingly complexand advanced prototypes. This secondyear will prepare them for the next stage and to ultimatelygain top level GCSE grades. It also allowsthem to build a separate and vital life skills base in planning, organisation, IT, working independently & as part of a team, literacy / numeracy and meetingdeadlines.
Intent A scheme of workaddresses both theory and practical tasks. It will involve a research task to explore staple dishes / ingredients froma range of countries. Recipes include Banana Bread (Caribbean), Chili con Carne (Mexico), Brownies and Chocolate chip Cookies (America). Stir fry (China), Flapjacks (Scotland) and lastly Shrewsbury Biscuits to complete the journey / toic
1 hour lessons per week. The year 8 creative curriculumwill run over one full term. (Autumn,spring, Summer)
Students will complete a set of skills that follow on fromYear 7. The dishes that are produced again become more complexed throughout the term
Students will work independentlyreading the methods and listening to instructions
The more confident students within the groups will have the ability to show leadership by supporting their peers
Purchasing ingredients will be a weekly home learning task and we are encouraging students to weigh their own ingredients. The Year 8 focus is based on staple foods / ingredients from other countries which links to various target groups / nutritional needs
Students will reflect on previous lessons by answering mini exam style questions throughout the term. This willhelp to develop and recall knowledge as part of revisionfor exams
The aim within Food is to create as many ‘WOW’ moments as possible. To get students excited about trying new foods as well as new skills and techniques. Postcards sent home for recognizing excellent work
The use of literacy will be developed throughout lessons by use of key word and communication as students follow their recipes. Numeracy will be used through weighing and measuring tasks, timings and temperature.
Key assessments:
Each practical lesson students will be given an overall assessment for their skill level, independence, hygiene, safety and final outcome
This will be recorded on data, pillar drops and Arbor. Marks will include absences and no ingredients. Theory and knowledge will be self and peer assessed. Homework (evaluation skills) will be marked fortnightly and feedback provided.
Testing / end of unit test
Autumn Term End of unit test
Spring Term End of unit test
SummerTerm End of unit test
Studentscan successfully produce high quality finished products that they are proud of. Their confidence levels will have improvedand they will be trying these recipes over and over again at home. Their skills level and confidence within cookingwill develop and they will be able to take the dishes and know and understand how to adapt them to suit a range of needs (coeliac,LactoseIntolerant and Vegetarian). They will experience new foods along with new preparation and cookingmethods. This will prepare them for gaining goodgrades, if they were to select the subject at GCSE level and will equip them with general life skillsfor future ( planning, organisation,timing, costings,weighing, cookingand washing up)
students
progression by continuing to prepare and cook dishes that followthe topic ‘Dishes fromaround the World’
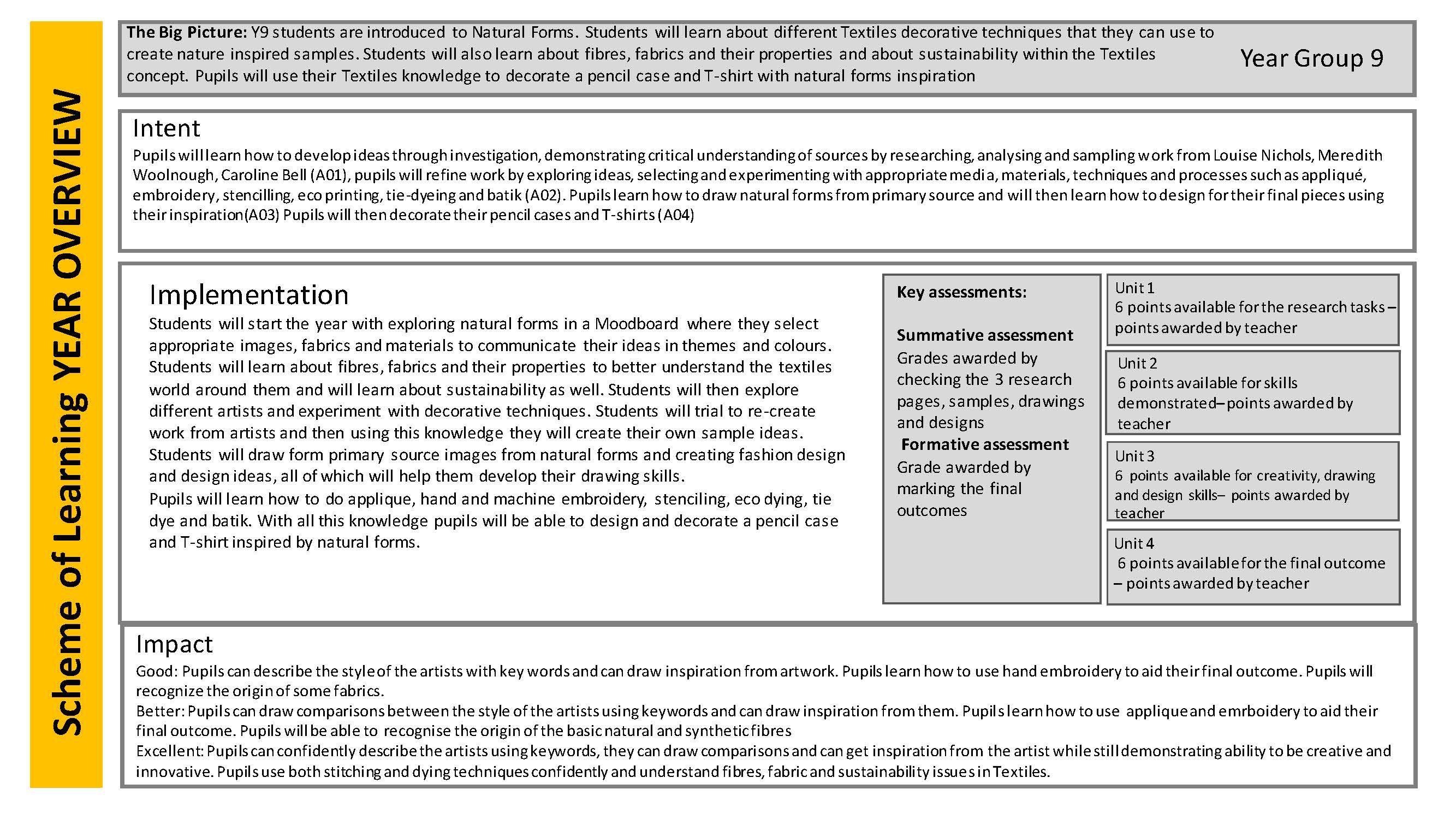
The Big Picture: To secure a confident and competent skills base. To furtherdevelop an understandingof the design process throughboth practical and theorywork. Students will be able to use a full range of hand tools, electric tools, machinery and techniques in theirpractical work. Their isometric and orthographic drawing techniques will be developed and secure. Their knowledge of material capabilities will be comprehensive.
IntentYear 9 offers studentsthe opportunityto develop their skills fully and understandthe full design process. They will be able to write a detailed brief and specification. Students will be able to expand on these documents by writing a client profile, a client questionnaire and a piece of market research. A mood bard will be completed .They will be able to complete a series of three initial ideas in an isomeric drawing style and one final design in an orthographic style. Their design work will be complete with two full evaluations – self and client. Their practical skills and techniques will develop with investigations into differenthand tools, machinery, materials and construction techniques– measuring, cutting(basic joints), fixing and finishing.Research into the capabilities of tools, machinery and materials will form a key part of this process. A manufacturingdiary will form an ongoing project – recording he manufacture of the prototype from start to finish.
1 hour lessons per week. The year 9 creative curriculum will run over one full term. (Autumn, Spring, Summer)
Students will complete a set of themed tasks – set stages in design process (to incorporatedrawing techniques);writing tasks and practical study. CAD and CAM will be introducedand utilisied. Students will work independently,listening to instructions and following demonstrations
The more confident students within the groups will have the ability to show leadership by supporting their peers
Students will be provided with their materialsbut will be encouraged to bring in additional materialsfrom home – especially if a student wishes to work on a larger scale practical piece. Students will reflect on previouslessons via verbaland written response. Use of key wordsand correct phraseology will be encouraged throughout – building up a skill vital in any future GCSE exam
The aim in Year 9 is to continuing WOW’ing! Students will be genuinely excited aboutworkingin such a dynamicatmosphere;take a realinterest in their workand enjoy all elements of the design process. The use of literacy will be developed throughout by use of key wordand phraseology as students follow instructionsand demonstrations. Numeracyis a key element, expressed in measurement of lengths, widths, depth, weight and volume.
Key assessments: Each practical lesson students will be given a red dot sticker to denote an area for development. Other assessments will be verbal and written. This will be recorded on data, pillar drops and Arbor. Theory and knowledge will be self and peer assessed. Homework (evaluation skills) will be marked fortnightly and feedback provided.
Testing / end of unit test
Autumn Term
End of unit drawing test
Spring Term
End of unit drawing test
SummerTerm
End of unit drawing test
Studentswill be able to successfully produce a series of woodenproductsto take home.Their confidence levels will be continually rising and they will feel encouraged to expand and refine their skills. Both their practical and theory skills will develop. A clear knowledge of the full design processwill develop throughout; building a comprehensive skills base ready for the start of a GCSE course. Students knowledge of materials, hand tools,electric tolls, machinery and techniques will allow them the opportunity to design and manufacture increasingly complexand advanced prototypes.This third and final KS3 year will prepare them for the next stage and to ultimatelygain a top level GCSE result. It also allowsthem to build a separate and vital life skills base in planning, organisation,IT, working independently & as part of a team, literacy / numeracy and meetingdeadlines.
The Big Picture To furtherdevelop the knowledge and skills of preparing,cooking and presentinga wide range of cooking food. Subject knowledge of all studentswill be developedthrough practical experiences of cooking and tasting sessions as well as buildingknowledge of theory from year 7 and 8. the new skills now become more advanced in preparationfor GCSE
IntentYear 9 aims to increase the skill set even furtherby following the 'Eat Well Plate’. Each section will be explored and dishes created in line with each of the 5 sections. Fruit /Vegetables, Meat/ Fish/ Eggs. (Protein). Pasta, Potatoes, Bread , Rice (Carbohydrates). Dairy products (Minerals and Vitamins)
Studentswill carry out investigative tasks on the research of reducingFat and Sugar in the diet. To develop students knowledge and understandingas they increase their skills levels as the dishes become even more complexed and challenging.
The next steps from here are to encourage studentsto opt for the subject for GCSE. Year 9 will provide them with the skills levels they will need to begin the course
1 hour lessons per week. The year 9 creative curriculumwill run over one full term. (Autumn,Spring, Summer)
Students will complete a set of skills that follow on from Year 7 and 8. The dishes that are produced again become more complexed throughout the term challenging students abilities. Students will work independentlyreading the methods and listening to instructions
The more confident students within the groups will have the ability to show leadership by supporting their peers
Purchasing ingredients will be a weeklyhome learning task and we are encouraging students to weigh their own ingredients. The Year 9 focus is based on the ‘Eat Well Plate’ and to explore extensively each of the 5 sections
Students will reflect on previous lessons by answering mini exam style questions throughoutthe term. This willhelp to develop and recall knowledge as part of revisionfor exams
The aim within Food is to create as many ‘WOW’ moments as possible. To get students excited about trying new foods as well as new skills and techniques. Postcards sent home for recognizing excellent work
The use of literacy will be developed throughout lessons by use of key word and communication as students follow their recipes. Numeracy will be used through weighing and measuring tasks, timings and temperature.
Key assessments:
Each practical lesson students will be given an overall assessment for their skill level, independence, hygiene, safety and final outcome
This will be recorded on data, pillar drops and Arbor. Marks will include absences and no ingredients. Theory and knowledge will be self and peer assessed. Homework (evaluation skills) will be marked fortnightly and feedback provided.
Testing / end of unit test
Autumn Term End of unit test
Spring Term End of unit test
SummerTerm End of unit test
Studentswill be able to successfully produce high quality finished productsthat they are proud of. Their confidence levels will have improvedand they will be trying these recipes over and over again at home. Their skills level and confidence within cookingwill developand they will be able to take the dishes and know and understand how to adapt them to suit a range of needs. They will experience new foodsalong with new preparation and cookingmethods. This will prepare them for gaining goodgrades, if they were to select the subject at GCSE level and will equip them with general life skillsfor future ( planning, organisation,timing, costings,weighing, cookingand washing up)
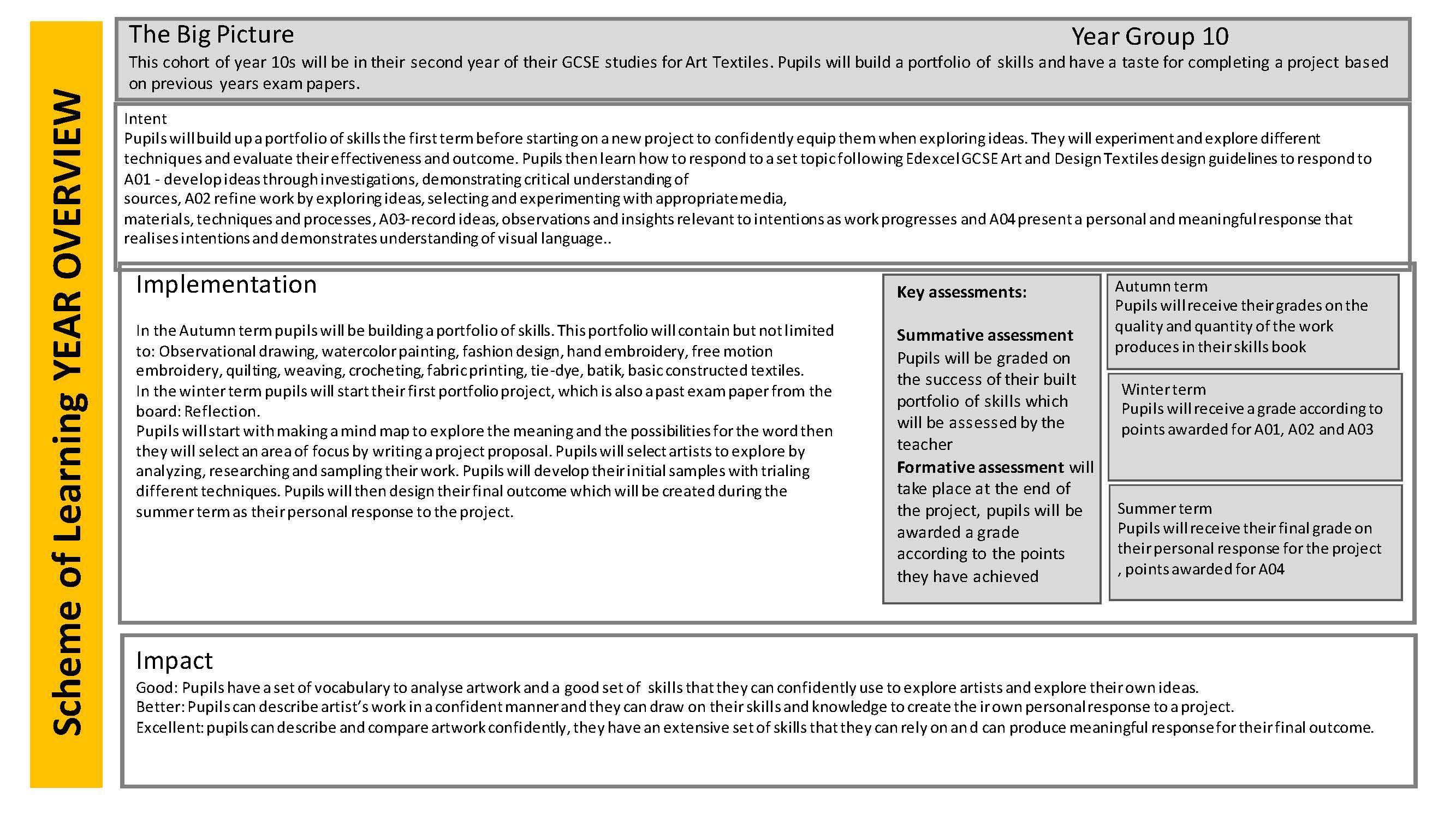
The Big Picture: To employ for the first time a confident and competent skills base. To complete a full GCSE style project bringingtogetherall sections of the design process. Students will be able to use writing, drawing, manufacturingand evaluating skills to create a mixed media prototype– a bedside table top tidy. The prototypewill be commissioned and evaluated by a client. Theory lessons (exam prep) will begin.
IntentYear 10 offers students the opportunityto demonstrate their skills fully and understandof the full design process. They will be able to write a detailed brief and specification. Students will be able to expand on these documents by writing a client profile, a client questionnaire and a piece of market research. A mood bard will be completed .They will be able to complete a series of three initial ideas in an isomeric drawing style and one final design in an orthographic style. Their design work will be complete with two full evaluations– self and client. Their practical and technical skills base will allow them the opportunityto demonstrate a wide range of construction techniques, in a range of materials and using a range of tools and machinery. A manufacturingdiary (with photographic evidence) will form an integral part of the completed project – recording the manufacture of the prototype from start to finish. A client evaluationwill complete the process.
Two lessons per week. The year 10 creative curriculum will run over three full terms. (Autumn, Spring, Summer)
Students will complete a set of themed tasks – set stages in design process (to incorporate drawing techniques); writing tasks, theory and practical study. CAD and CAM will be introduced and utilisied. Students will work independently,listening to instructions and following demonstrations
The more confident students within the groups will have the ability to show leadership by supporting their peers
Students will be provided with their materialsbut will be encouraged to bring in additional materialsfrom home – especially if a student wishes to work on a larger scale or more expensively costed practical piece. Students will reflect on previouslessons via verbaland written response. Use of key wordsand correct phraseologywill be encouraged throughout – building up a skill vital for future GCSE exams
The aim in Year 10 is to continuing WOW’ing! Students will be genuinely excited about workingin such a dynamicatmosphere;take a realinterest in their workand enjoy all elements of the design process. The use of literacy will be developed throughout by use of key wordand phraseology as students follow instructionsand demonstrations. Numeracyis a key element, expressed in measurement of lengths, widths, depth, weight and volume.
Key assessments: Each practical lesson students will be given a red dot sticker to denote an area for development. Other assessments will be verbal and written. This will be recorded on data, pillar drops and Arbor. Theory and knowledge will be self and peer assessed. Homework (evaluation skills) will be marked fortnightly and feedback provided. Testing / end of unit test
Autumn Term End of unit written test
Spring Term End of unit written test
SummerTerm First mock exam
Studentswill be able to successfully produce one final prototypeto take home.Their confidencelevels will be continuallyrising and they will feel encouragedto expand and refine their skills. Both their practical and theory skills will develop. A clear knowledge of the full design process will be embedded; a comprehensive skills base ready to utilise. Studentsknowledge of materials,hand tools, electric tolls, machinery and techniques will allow them the opportunity to design and manufacture increasingly complex and advanced prototypes.This first GCSE year will give studentsthe opportunityto showcasethe skills base they built throughoutKS3. It also allows them to continueto build a separate and vital life skills base in planning, organisation,IT, working independently & as part of a team, literacy / numeracy and meetingdeadlines.
Intent. Studentswill follow the AQA Food Preparation and NutritionSpecification. Five areas will be followed. Food Nutrition and Health, Food Science, Food safety, Food Choice, Food Provenance.
The full GCSE course builds on the knowledge of KS3 studentsprovidingthem with more opportunityto research and carry out a range of complex practical skills
The course leads into Btec Hospitality and Catering with the opportunityto furtherexplore the topics in greater depth
The course to be deliveredin sections looking at the above 5 key topics identifiedfrom the course specification
The majority of the specification will be delivered throughpreparation and making activities. Studentswill be able to make the connection between theory and practice to apply their understandingof food and nutritionto practical preparation. Food preparation skills will have a heavy influence, students will learn and carry out 12 skill groups. These will be integrated into schemes of work
The aim within GCSE Food is to create as many ‘WOW’ moments as possible. To get students excited about trying new foods as well as new complex skills and techniques. Postcards sent home for recognizingexcellent work
The use of literacy will be developedthroughoutlessons by use of key word and communication as students follow their recipes. Numeracy will be used throughweighing and measuring tasks, timings and temperature.
Key assessments:
Each practical lesson students will be given an overall assessment for their skill level, independence, hygiene, safety and final outcome This will be recorded on data, pillar drops and Arbor. Marks will include absences and no ingredients.
Theory and knowledge will be self and peer assessed. Homework (evaluation skills) will be marked fortnightly and feedback provided. Testing / end of unit test will involve past exam papers
Autumn Term
Ongoingpast exam questions related to topic
End of unit test
Spring Term
Ongoing past exam questionsrelated to topic
End of unit test
SummerTerm
End of unit test
Studentsto gain a strong knowledgebase for use in exams,both mock 1 (autumn term) and mock 2 (spring term) and the end of year 11 exams requirethe same knowledge.
Students gain important knowledgeand skills neededto complete high quality GCSE project work
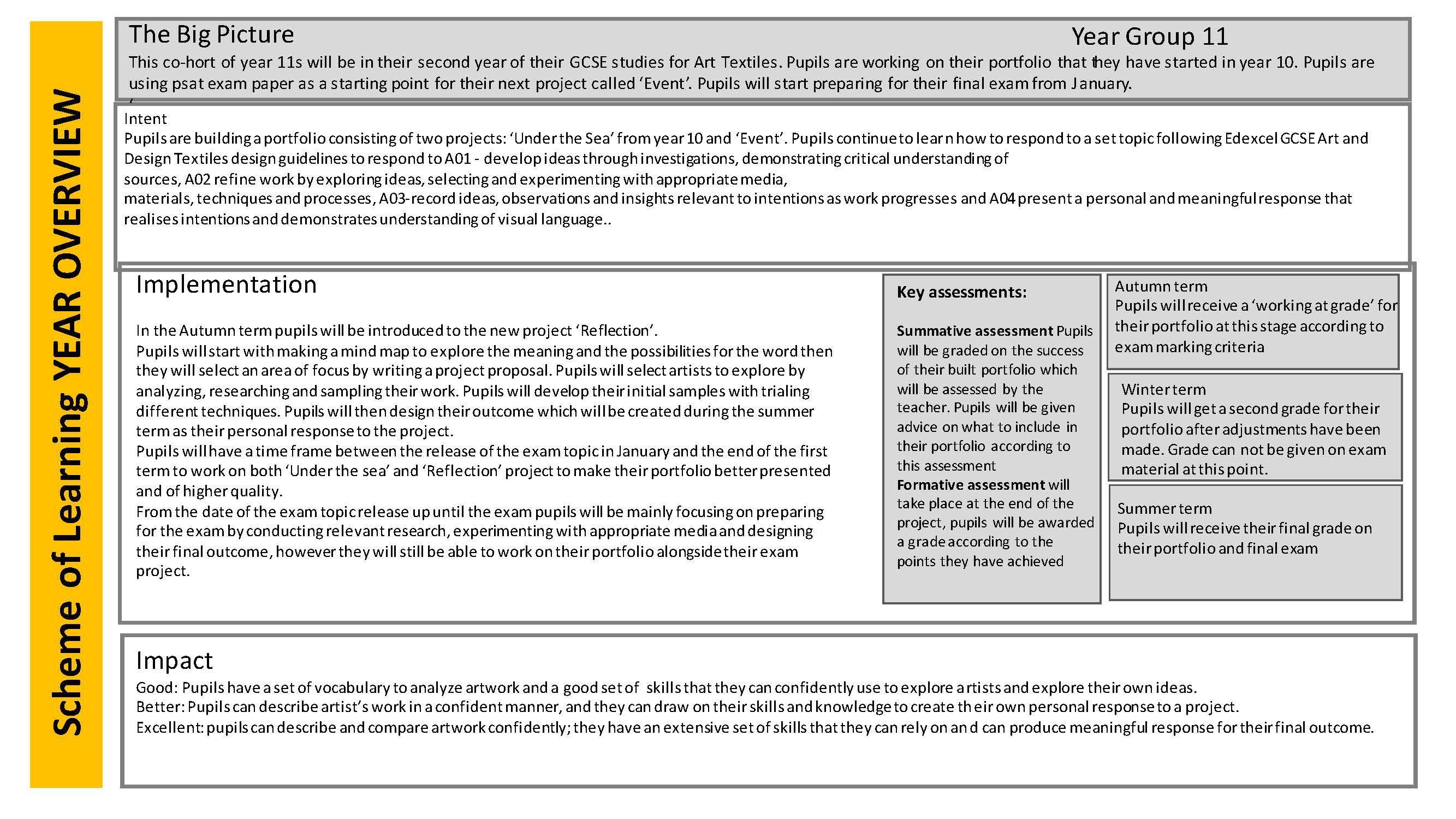
The Big Picture: To employ a confident and competent skills base. To complete a section of a final GCSE project / contextual challenge bringing togetherall sections of the design process. Students will be able to use writing, drawing, manufacturing and evaluating skills to create their final prototype.The prototype will be commissioned and evaluated by a client. Theory lessons in preparation for written exam will continue.
IntentYear 11 gives students the opportunityto demonstrate their full skills range and comprehensive understandof the design process. They will be able to write a detailedbrief and specification. Studentswill be able to expand on these documents by writing a client profile, a client questionnaireand a piece of market research. A mood bard will be completed .They will be able to complete a series of three initial ideas in an isomeric drawing style and one final design in an orthographic style. Their design work will be completed with two full evaluations – self and client. Their practical and technical skills base will allow them the opportunityto demonstrate a wide range of construction techniques, in a range of materials and using a range of tools and machinery. A manufacturingdiary (with photographic evidence) will form an integralpart of the completed project – recording the manufacture of the prototype from start to finish. A client evaluation will complete the process.
Two lessons per week. The year 11 creative curriculum will run over the academic year.(Autumn, Spring and part of Summer)
Students will complete one full project (contextualchallenge) – fully documented, with practical and photographic evidence
Students will work independently,listening to instructions and following demonstrations
The more confident students within the groups will have the ability to show leadership by supporting (verballyand through demonstration) their peers
Students will be provided with their materialsbut will be encouraged to bring in additional materialsfrom home – especially if a student wishes to work on a larger scale or more expensively costed practical piece. Students will reflect on previouslessons via verbaland written response. Use of key wordsand correct phraseology will be encouraged throughout – building up a skill vital for the future written exam
The aim in Year 11 is to continuing WOW’ing! Students will be genuinely excited about workingin such a dynamicatmosphere;take a realinterest in their workand enjoy all elements of the design process. The use of literacy will be developed throughout by use of key wordand phraseology as students follow instructionsand demonstrations. Numeracyis a key element, expressed in measurement of lengths, widths, depth, weight and volume.
Key assessments:
Each practical lesson students will be given a red dot sticker to denote an area for development. Other assessments will be verbal and written. This will be recorded on data, pillar drops and Arbor. Theory and knowledge will be self and peer assessed. Homework (evaluation skills) will be marked fortnightly and feedback provided. Testing / end of unit test
Autumn Term
Mockexam (2)– written paper
Spring Term Mockexam (3) –writtenpaper Prototype and paperwork completed
SummerTerm
Final writtenexam
Studentswill be able to successfully produce one final prototypefor assessment.Their confidence levels will be high and they will still feel encouragedto expand and refine their skills. Boththeir practical and theory skills will develop. A clear knowledge of the full design processwill be embedded; a comprehensive skills base to utilise fully. Studentsknowledge of materials,hand tools,electric tolls, machinery and techniques will allow them the opportunity to design and manufacture a prototypemodel that fully matchesthe contextualchallenge. This final GCSE year will give studentsthe opportunityto showcasethe skills base they built throughoutKS3 and Year 10. It also allowsthem to continueto build a separate and vital life skillsbase in planning, organisation,IT, working independently & as part of a team, literacy / numeracy and meeting deadlines.
Intent. Complete 50% coursework (100 marks total) March / April)
Revisit exam techniqueand exam topics after coursework is complete
All skills taughtin Year 10 have led to studentscompleting their major project in Year 11, students have been taught knowledge and skills to ensure they are able to work safely, competently and quickly without compromising quality.
Studentsto use the skills they have to complete a major project and exceed their minimum grade
Completion of Task 1 Food investigation ( 30 marks). Students’ understanding of the working characteristics, functional and chemical properties of ingredients.
Completion of Task 2. Foodpreparation assessment ( 70 marks).
Students’ knowledge, skills and understanding in relation to the Planning, preparation, Cooking, Presentation of foodand application of nutrition related to the chosen task.
Students will prepare, cook and present a final menu of three dishes within a single period of no more than 3 hours, planning in advance how this will be achieved.
Communication to students’ home to share short term success with student’s parents will be used to ensure positive caring mentality is always displayed
Key assessments:
Mock 1 and 2 for Year 11 in Autumn, Spring half terms
Deep marking at the end of each task (November), (March / April)for full coursework
Feedbackcannot be given specifically to each student so feedback contains a list of tasks that need to be completed for each area of coursework
Autumn Term
Tracking of progress through investigative task working towards PPG’s
Spring Term
Tracking of progress through Food Preparation Task working towards PPG’s
Impact Complete all coursework by the deadline of Easter
SummerTerm
Coursework is at least 1 grade over their minimum, but data shows that at least 2 grades over minimum is highlylikely to produce a least minimum grade overall so this is the aim for all students
Studentswill be introducedto the basic skillsrequired for dance and drama. Introductionto someof the main elementsof theatre including vocaland physical skills. In Dance studentswill be introduced to action, space, dynamicsand relationships.
Studentswill complete SOL on: Dance introduction, Drama introduction, Dance styles, Twisted fairytales, Music videos and DarkwoodManor.
Drama Skills Covered: Vocal Skills, Physical Skills, Still Image, Thought Cross Cutting, Improvisation, Mime,, Movement, Narration, Scripted Work, Multi-Role, Line learning & Props
Dance Skills covered: Expressive skills, Movement memory, Safe working practices, Choreography, Action, Space, Dynamics & Relationships, Unison, Canon, Mirror, Contact, Levels, Studentswill have limitedexperience of Dance and Drama, so we are introducingskills that are the foundationto both disciplines. Studentswill build on this foundationand repeat some elementsin Year 8 in order to embed understanding of key skills and techniques.
Students will rotate between Dance/Dramathroughout the year. They complete 3 schemes of dance and 3 of dramaoverthe course of the year and this will allow flexibility of a half term if teachers want to develop aspects of a scheme or spend more time showcasing work. Lessons are deliveredin the dance studio.
Students will be encouraged to give constructive peer feedback on a regular basis to form part of the assessment process. Independence will be nurtured during the rehearsalprocess.
Interleavingof the key skills in Drama/Dance will happen throughout all schemes and during every year of study.
When outstanding workis produced we will record these and showcase on our social medias. We will also encourage all students to attend our thriving extra curricular programme.
Students can rehearse and developperformanceskills for practical assessments in one to one sessions and group sessions by booking the dance studio at break/lunch..
Students will develop confidence with key Drama/Dance vocabulary.
Key assessments: Teacher assessments logged on Arbour and one peer assessment opportunityper sow. Teacher assessment will generate a PPG. Students respond to verbalteacher feedback every lesson during rehearsal time.
Autumn Term
Dance
Introduction to Dance skills
Drama
Introduction to Drama skills
Spring Term
Dance Dance styles
Drama
Twisted Fairy tales
SummerTerm
Dance Music videos
Drama
Darkwood Manor
Studentsshouldhave a good foundationin Dance/ Drama and understand what goodDance/Dramapiece lookslike. They should understand different genres and display performance confidence.
Knowledgeand skills will be repeated, built on and extended each year to create a strongfoundationfor GCSE and to developa confidence
Studentswill continue to develop the basic skills required for dance and drama. Studentswill be introduced to musical theatre through both disciplines. Students will develop characterization and expressive skills.
Studentswill completeSOL on: Theatre In Education, Musical theatre, Everybody’stalking about Jamie, Worlddance, Music videos and Girls like that.
DramaSkills Covered: Vocal Skills, Physical Skills, Evaluating, Stimuliselection, Rehearsal, Target audience, Freeze Frame, Cross Cutting, Improvisation,Script work, Characterisation
Dance Skills covered: Projection, Focus & Musicality, Movement memory, Safe working practises, Communicationof choreographic intent, Aural setting, Motif & choreographic devices. Studentswill build upon their Year 7 foundationof Drama/Dramaskills and build these in a more challengingway. Devising/Chorepgraphy skills will be introduced to consolidateand apply skills. Studentswill build upon these skills and techniquesin Year 9 so that they are ready and confident to do GCSE if they opt for it.
Students will rotate between Dance/Drama throughoutthe year. They complete 3 schemes of drama and 3 of dance over the course of the year and this will allow flexibilityof a half term if teachers want to developaspects of a scheme or spend more time showcasing work. Lessons are deliveredin the dance studio.
Students will be encouraged to give constructive peer feedback on a regular basis to form part of the assessment process. Independence will be nurtured during the rehearsalprocess.
Interleavingof the key skills in Drama/Dance will happen throughout all schemes and during every year of study.
When outstanding workis produced we will record these and showcase on our social medias. We will also encourage all students to attend our thriving extra curricular programme.
Students can rehearse and developperformanceskills for practical assessments in one to one sessions and group sessions by booking the dance studio at break/lunch..
Students will develop confidence with key Drama/Dance vocabulary.
Key assessments:
Teacher assessments logged on Arbour and one peer assessment opportunityper sow. Teacher assessment will generate a PPG. Students respond to verbalteacher feedback every lesson during rehearsal time.
Autumn Term
Dance Musical Theatre
Drama Theatre In Education
Spring Term
Dance World Dance
Drama
Girls Like That
SummerTerm
Dance Music Videos
Drama
Everybody’s Talking About Jamie
Studentswill have a greater understandingof how the mainskills in Dance/Dramacan be applied in performance. They shouldunderstand different genres and display performance confidence. The quality of work being produced should be showingmore depth. Knowledgeand skills will be repeated, built on and extended next year to create a strongfoundationfor GCSE and to develop a confidence.
Studentswill study schemesof work that directly feed into the GCSE Dance and GCSE Drama specifications.They will continue to develop all key skills that have been imbedded in year 7 and 8.
Studentswill completeSOL on: Street dance, I love you mum I promiseI wont die, Physicaltheatre, Gang culture, Swansongand Let him ‘ave it.
DramaSkills Covered: Body language, Gestures, Facial expression, Projection, accent, clarity, accent, Improvisation,Mime, Cross cutting,Freeze frame, Characterisation,Flash back/forward Dance Skills covered: Projection, Focus, Musicality, Strength, Control, Coordination, Movementmemory, Safe working practices, Communicationof choreographic intent, Transitions Students will build upon their Year 8 experience of Drama/Danceskills and build these in a more challengingway. Devisingand choreography skills will be developed for thosewho are optingfor GCSE. Studentswho are optingfor GCSE Drama/Dance will have built up a bank of key skills and techniques thatthey can developfurther in GCSE.
Students will rotate between Dance/Dramathroughout the year. They complete 3 schemes of dance and 3 of dramaoverthe course of the year and this will allow flexibility of a half term if teachers want to develop aspects of a scheme or spend more time showcasing work. Lessons are deliveredin the dance studio.
Students will be encouraged to give constructive peer feedback on a regular bases to form part of the assessment process. Independence will be nurtured during the rehearsalprocess.
Interleavingof the key skills in Drama/Dance will happen throughout all schemes and during every year of study.
When outstanding workis produced we will record these and showcase on our social medias. We will also encourage all students to attend our thriving extra curricular programme.
Students can rehearse and developperformanceskills for practical assessments in one to one sessions and group sessions by booking the dance studio at break/lunch..
Students will develop confidence with key Drama/Dance vocabulary.
Key assessments:
Teacher assessments logged on Arbour and one peer assessment opportunityper sow. Teacher assessment will generate a PPG.
Students respond to verbalteacher feedback every lesson during rehearsal time.
Autumn Term
Dance Street dance
Drama
I love you mum, I promise I wont die
Spring Term
Dance Physical Theatre
Drama
Gang culture
SummerTerm
Dance Swansong
Drama Let Him ‘Ave It
Studentswill have a greater understandingof how the mainskills in Dance/ Dramacan be applied in performance. They shouldunderstand different genres and display performance confidence. The quality of work being produced should be showingmore depth and thosecontinuingto GCSE will have a foundationin skills to extend their understandingin preparation for the demandsof the courses.
Knowledgeand skills will be repeated, built on and extended next year to create a strongfoundationfor GCSE and to develop a confidence.
Studentswill completethree componentsthat promoteinvolvement in and enjoymentof drama, as performers and/or designer. Studentswill attend live theatre performances to develop skills as informed and thoughtful audience members.
Studentswill complete EDUQAS GCSE Drama
Skills Covered: Performance Skills, Design Skills, Directing Skills, Stage Design, Character Interpretation, Evaluation of Live Theatre. Studentswill developall their Key Stage 3 knowledge and understandingof theatre to a higher level. They will study a full play in depth and attenda live theatre performance. Studyingthis course will allow studentsto go on to study A-Level Drama/Theatre Studies. This course forms part of the natural progressionwith an added level of challenge and intensity.
Studentswill complete 3 Componentsof the course over the 2 years. Studentshave two hours of lessons each week in the dance studio.Lessonsare a mixture of practical and theory.
Studentswill be encouraged to give constructivepeer feedback on a regular bases to form part of the assessmentprocess.Independence will be nurtured during the rehearsal process.
Interweavingof the key skills in Dramawill happen during teachingof set text so that studentsare confident in seeing the bigger picture of how theatre is constructedin order to convey the themes/playwrights intentions.
When outstandingwork is produced we will record these and showcaseon our socialmedias.
Studentscan rehearse and develop performance skills for practical assessmentsin one to one sessions and group sessionsby bookingthe dance studio at break/lunch. Weekly theory intervention sessionsrun before schooland studentsare invited on a weekly basis depending on weekly achievement/progress/effort.
Studentswill develop confidence with key Drama vocabulary so they can apply in written exam.
Key assessments: Comp 1 & 2 - Mocks and final assessment.
Comp 2 - Visiting Examiner
Mock Exams added to Arbourto inform PPG and current progress.
Students respond to verbal teacher feedback every lesson during rehearsal time.
Autumn Term
Y10: Comp 1 mock
Y11: Comp 1
Spring Term
Y10: Comp 2 mock & Comp 3
Y11: Comp 2 & Comp 3
SummerTerm
Y10: Comp 1 & Comp 3
Y11: Comp 3
Studentswill be able to apply all Drama skills and knowledge of Practitioner/Genre with confidence in performance. Studentswill developa greater understanding and awareness of how all elementsof theatre must blend togetherin order to create the final performance. Knowledge and skills will be repeated, built on and extended in a more challengingway if studentscontinue to study at A-Level at sixth form or college.
Studentswill completethree componentsthat promoteinvolvement in and enjoymentof drama, as performers and/or designer. Studentswill attend live theatre performances to develop skills as informed and thoughtful audience members.
Studentswill complete EDUQAS GCSE Drama
Skills Covered: Performance Skills, Design Skills, Directing Skills, Stage Design, Character Interpretation, Evaluation of Live Theatre. Studentswill developall their Key Stage 3 knowledge and understandingof theatre to a higher level. They will study a full play in depth and attenda live theatre performance. Studyingthis course will allow studentsto go on to study A-Level Drama/Theatre Studies. This course forms part of the natural progressionwith an added level of challenge and intensity.
Studentswill complete 3 Componentsof the course over the 2 years. Studentshave two hours of lessons each week in the dance studio.Lessonsare a mixture of practical and theory.
Studentswill be encouraged to give constructivepeer feedback on a regular bases to form part of the assessmentprocess.Independence will be nurtured during the rehearsal process.
Interweavingof the key skills in Dramawill happen during teachingof set text so that studentsare confident in seeing the bigger picture of how theatre is constructedin order to convey the themes/playwrights intentions.
When outstandingwork is produced we will record these and showcaseon our socialmedias.
Studentscan rehearse and develop performance skills for practical assessmentsin one to one sessions and group sessionsby bookingthe dance studio at break/lunch. Weekly theory intervention sessionsrun before schooland studentsare invited on a weekly basis depending on weekly achievement/progress/effort.
Studentswill develop confidence with key Drama vocabulary so they can apply in written exam.
Key assessments: Comp 1 & 2 - Mocks and final assessment.
Comp 2 - Visiting Examiner
Mock Exams added to Arbourto inform PPG and current progress.
Students respond to verbal teacher feedback every lesson during rehearsal time.
Autumn Term
Y10: Comp 1 mock
Y11: Comp 1
Spring Term
Y10: Comp 2 mock & Comp 3
Y11: Comp 2 & Comp 3
SummerTerm
Y10: Comp 1 & Comp 3
Y11: Comp 3
Studentswill be able to apply all Drama skills and knowledge of Practitioner/Genre with confidence in performance. Studentswill developa greater understanding and awareness of how all elementsof theatre must blend togetherin order to create the final performance. Knowledge and skills will be repeated, built on and extended in a more challengingway if studentscontinue to study at A-Level at sixth form or college.
Y7 English is a challenging yet welcomingintroductionto the study of secondary English. From The LochNess Monsterto the Oliver Twist, studentswill engage and respond to a wide range of fictionand non fiction texts,developingtheir reading and writing skills.
Intent ’Learning Programme’units to be covered: Monsters;Poetry; Thriller and Nasty Victorians. Studentsare baseline testedand then followschemeswhich develop reading and writing skills. The schemes bring in more non-fictionand real world English than KS2 but build on the creativitythat is encourages in Y5 and Y6. The schemesinclude textssimilar to thosestudied later in schoolto build confidence and resilience. Topics have been selectedto engage studentswhilstalso stretching and challenging them. Some legacy GCSE textshave been included to increase challenge. Literacy lessonswill form part of the scheme with studentsusing the building better sentences scheme to study grammar topicssuch as: word classes, punctuation and sentence structure.
There will be four LP units of approx. 10 weeks each. Each lessonwill include at least one LORIC skill.
Independence and study skills will be fostered through: challengingtexts and questions, group and pair work, modelling, homework and independent reading for pleasure.
Flipped learning, literacy tasks, comprehensiontasksand creative work will be set for homework. Students’revision skills will be developed by in class and homework assessmentpreparation.
WOW moments:learning about Yetis, Unicorns and the Loch Ness Monster, delivering speeches to the whole year group about Jurassic park, enjoying spookythriller texts,learning about gruesome Victorians,enjoying funny poems and exploring climate change, racism and conflictthrough poetry.
Literacy skills will be addressed through: dedicated literacy lessons using the building better sentences scheme,literacy homework,key words, words of the week, spelling tests,AR and reading for pleasure.
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will takeweeks 4 and week 8.
Mad time will take place weekly during literacy lessons.
Homework will be peer marked or used in lesson.
Teachers will live mark/ sample mark non formal assessments.
Autumn Term
Baseline testing – GCSE exam
Assessments: speech, persuasive letter
Spring Term
Poetry reading assessment
Thriller writing assessment
SummerTerm
Dickens reading assessment
End of year GCSE style exam
Good: Students can access KS3 work. They read with independence, understandingand resilience. They write with accuracy.
Better: Studentscan confidently engage with KS3 work: They read with independence, understandingand fluency. They write with accuracy, controland growing ambition.
Excellent: Students confidently engage with the most challengingKS3 texts.They demonstrate evaluative skills when reading and analysing texts. They write with ambition,creativity and fluency.
Y8 is a wonderful representationof the diversity and power of the study of English. The range and depth of literary units provide studentswith the skills they need for GCSE whilst exploring real-life issues such as racism and discrimination.
Intent ’Learning Programme’units: 19th Century Literature, Shakespeare, Poetry – character and voice and Of Mice and Men. These schemesinclude a range of textsfrom our literary heritage. Studentswill be engaged by the breadth of textsstudied in order to develop an enjoymentand appreciationof novels, poetry and plays. Studentswill begin to prepare for GCSE English literature through this diverse explorationof literature. Somelegacy GCSE textshave been included to increase challenge. Literacy lessonswill form part of the scheme with studentsusing the building better sentences scheme to study grammartopicssuch as: word classes, punctuation and sentence structure.
There will be four LP units of approx. 10 weekseach. Each lessonwill include at least one LORIC skill.
Autumn Term
Key assessments:
Baseline testing – GCSE exam
Writng on contemporary issues
Reading assessment – 19th century literature
Independence and study skills will be fosteredthrough: challenging textsand questions,group and pair
Formal assessment will take place week 5. work, modelling, homeworkand independent reading for pleasure.
Flipped learning, literacy tasks, comprehensiontasksand creative work will be set for homework.
Students’revision skills will be developed by in class assessmentpreparation.
Homework will be weekly spellings which will be peer marked.
Literacy skills will be addressed through: dedicated literacy starters, using the building better sentences scheme,spelling homework,key words, words of the week, spelling tests,AR and reading for pleasure.
Teachers will live mark/ sample mark non formal assessments.
Spring Term
Reading assessment – Shakespeare
Reading assessmentPoetry character and voice
SummerTerm
Creative writing - OMAM
End of year GCSE style exam
Good: Students understand some uses of language and structure of texts and they read with independence, understandingand resilience. They write with accuracy. Better: Studentshave a goodunderstanding of the language and structure of texts.They read with independence, understandingand fluency. They write with accuracy, controland growing ambition.
Excellent: Students show confidence evaluating the uses of language and structure within texts.Students confidently engage with the mostchallenging KS3 texts.They demonstrate evaluative skills when reading and analysing texts.They write with ambition,creativity and fluency.
Year 9 is the first year of GCSE where students will focus on Component1 and Component2 EDUQAS GCSE English Literature. Students will build on the analytical skills and knowledgedevelopedin previous years of study to explore the followingfour units: Shakespeare, Poetry Anthology, An Inspector Calls and An Inspector Calls.
EDUQAS GCSE English Literature set text preliminarystudying/reading for Component 1 and 2 – Working towards AO1, AO2 and AO3 skills for Close Analysis, Comparisonand Balloon Questions
• Students will cover initial GCSE content in year 9 Lessons, alongside annotating all relevantset texts, to develop the necessary skills to complete exam questions looking towards their end of year GCSE English Literature exams in Year 10.
• The skills gained and developed within the units of work include: applyingcritical skills in close reading; describing and analysing key features of language choice; using associated terminology accurately; analysing and evaluating contextual factors; exploring connections between the texts; supporting points with apt quotation;organising their response effectively using coherent written expression;critically evaluating how contextual factors affect form and structure; analysing how language features shape meaning. Students will also be given the opportunityto complete GCSE English Language style tasks in preparationfor the non – examassessed component:Spoken Language at the end of Year 10.
There will be four LP units of approximately 10 weeks each. Each lesson will include at least one LORIC skill.
Independence and study skills will be fostered through: challenging texts and questions, group and pair work, modelling, homework and independentreading for pleasure.
Flippedlearning,literacy tasks, comprehension tasks and creative work will be set for homework.
Students’revision skills will be developed in class and homework assessment preparation.
WOW moments: Theatre trips, cinematic experience, drama in the classroom, role-play, use of social media, discussion of real world issues, CSI Investigations.
Literacy skills will be addressed through:dedicated literacy lessons using the buildingbetter sentences scheme, literacy homework, key words, words of the week, vocabularytests and readingfor pleasure
Assessment Markers: Formal assessment will take place during week 5 and week 9 of each LP
MAD Time will take place weekly during literacy lessons.
Autumn Term
• Half Term 1 / Teacher 1: An Inspector Calls
• Half Term 2 / Teacher 2: A Christmas Carol
Spring Term
• Half Term 1 /Teacher 1: Macbeth
• Half Term 2 /Teacher 2: Macbeth
Homework will be peer marked or used in lesson. Summer Term
Teachers will live mark/ sample mark non formal assessments.
• Half Term 1 / Teacher 1: Anthology Poetry
• Half term 2/ Teacher 2: Anthology Poetry
Good:Students will be able to describe the plot of the play/novella/content of poems
Better: Students willbe able to understand the plot, characters, context and themes associated with the play/novella or poems
Excellent: Students will be able to apply this knowledge of the context to a transactional/narrative piece of writing.
Year 10 is the final year of the English Literature GCSE course where students will focus on Component 1 and Component2. Students will build on the analytical skills and knowledgedevelopedin previous years of study to explore the followingfive units: Shakespeare, Poetry Anthology, An Inspector Calls, Jekyll and Hyde and Unseen Poetry
AQA GCSE English Literature Revision Component 1 and 2 – Working towards AO1, AO2 and AO3 and AO4 skillsfor Close Analysis, Comparison and SPaG.
• Students will revisit content covered in Year 9 lessons, alongside using their annotated anthologies and set texts, to develop the necessary skillsto complete exam questionslookingtowards their end of year GCSE English Literature exams.
• The skillsgained and developed within the units of work include: applying critical skills in close reading; describing and analysing key features of language choice; using associatedterminology accurately; analysing and evaluating contextual factors; exploring connectionsbetween the texts; supporting points with apt quotation; organising their response effectively using coherent written expression; critically evaluating how contextualfactors affect form and structure; analysing how language features shape meaning. Students will also be given the opportunityto completeGCSE English Language style tasks in preparation for the non – exam assessedcomponent: Spoken Language at the end of Year 10.
• Units are structured into 3 key segments
1) Read and revise
2) Plan and write exam responses
3) Learn quotations connected to weekly themes
• LORIC promotion in this unit of study:
L – LORIC Leaders – assessing LORIC in each lesson
O – Creation of flashcards for revision – ensuring organization of key themes/characters
R – Learning key quotes for home learning alongside Audiopi
I – Using year 9 annotationsto support flashcard creation, planning for assessments and applying Audiopi at home to annotations
C – Discussion during read and revise sections – key themes and context
• Independent learner behaviours will come through in Revision Guides and Audiopi at home learning tasks and the applicationof this knowledge to assessments; creation of revision flash cards for assessment and final exams; learning quotes weekly to support assessments and end of year exams. Therefore home learning is imperative in order for students to develop their responses fullywith knowledge gained from GCSE Pod.
• Revision skillswill come through in WAGOLL tasks, home learning and the unit structure of read, revise, plan, write, learn.
• WOW moments – discovery of connectionsbetween poems, texts and contexts as a means ofengaging students with a deeper level of understanding. Celebration of students who are apply to apply contextual details in revision for and planning of assessments (context kings and queens)
• Literacy – weekly focus in each unit – designated in LPs
Assessment Markers:
Weekly Assessments: For example – AIC
1 – Eric – Close Analysis
2 – Goole – Close Analysis
3 – Shelia – Close Analysis
4 – Gerald– Close Analysis
5– Mrs Birling – Comparison
6– Eva – Close Analysis
Mock – Mr Birling/Class
HomeLearning –
Audiopi/Revision
Guides/Flashcards/Revision
Workshops
Peer Assessment – Exam Practice
Questions
Autumn Term
• Half Term 1:
• Powerand conflict and Unseen
• Half Term 2 :
• Inspector Calls
Spring Term
• Half Term 1: Jekyll and Hyde
• Half Term 2: Macbeth
Summer Term
• Half Term 1: Exam Texhnique
• Half term 2: Speech PreparationGCSE English Language
Student grades will show that they can analyse texts confidently and have a strong grasp of the knowledge and concepts taught, alongside a deeper knowledge of subject terminology. Students will demonstrate self confidence in lessons regarding tackling all types of exam responses with the skills and exam structures developed through revision and planning of text assessments
Year 11 is the final year of the English LanguageGCSE course where students will focus on Component 1 and Component2 revision. Students will build on the analytical skills and knowledgedeveloped in previous years of study to explore the following units: Narrative Writing, Transactional Writing and Reading in preparation for their final exams.
AQA GCSE English Language Revision Component 1 and 2 – Reading (AO1, AO2, AO3 and AO4), Writing (AO5 and AO6)
• Students willrevisit content covered throughout KS3.
• The skills gained and developed within the units of work include: Identifying and interpreting explicitand implicitinformationand ideas; selectingand synthesisingevidence from different texts;explaining, commentingon and analysing how writers use language and structure to achieve effects and influence readers; using relevant subject terminologyto support their views; comparingwriters' ideas and perspectives, as well as how these are conveyed,acrosstwo or more texts; evaluating textscritically and supporting this with appropriate textual references; communicatingclearly, effectively, and imaginatively,selecting and adaptingtone, style and register for different forms, purposes and audiences; organising information and ideas, using structural and grammaticalfeatures to support coherence and cohesionof texts; using a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate spelling and punctuation.
There will be four LP units of approximately 10 weeks each. Each lesson will include at least one LORIC skill.
Independence and study skills will be fostered through:challenging texts and questions, group and pair work, modelling,homework, practice exam questionsand independentreading,
Flippedlearning,literacy tasks, comprehension tasks, practice papers will be set for homework.
Students’revision skills will be developed in class and homework assessment preparation.
WAGOLL moments: Using students’ work as WAGOLLs and celebrating studentsuccess in assemblies.
Literacy skills will be addressed through:dedicated literacy lessons using the buildingbetter sentences scheme, literacy homework, key words, words of the week, vocabularytests and readingfor pleasure.
Assessment Markers:
Autumn Term
• Writing Assessment: Creative Prose
Formalassessmentwill take place weekly for each unit.
Homeworkwill be peer marked or used in lesson.
Teachers will live mark/ sample mark non formal assessment based work.
• Writing Assessment: Transactional Writing
Spring Term
• Reading: Component 1, SectionA; Component 2, Section A
Summer Term
• PracticePapers – Reading and Writing Assessments
By the end of Year 11, studentswill be able to analyse textsconfidently and have a stronggrasp of the knowledge and conceptstaught, alongside a deeper knowledge of subject terminology.They will be able to use a wide range of varied and appropriate vocabulary to express themselves.They will also be familiar with all stylesof exam questionsand know how to approach and structure each response. In Year 11, studentswill consolidatethe skills and knowledge acquired in previous years and completeweekly revision tasks linked to practice questions.


A chronologically runningyear which starts with the Roman transitionto Anglo Saxons and then onwards to the Battle of Hastings and life duringthe medieval period . A selection of political and social historic events will be covered, and the Tudorswill also be explored; investigating the breadth and depth of the monarchy.
Intent Unitscovered: Bridging unit, 1066 and the Battle of Hastings, How did the Normans keep control?,Medieval life and the Tudors. Key skills covered: inference skills and identifying different interpretations (source analysis), describe key features, explain why (causation), explain the importance(significance). Knowledge to be covered: what is chronology, How did William win Hastings? Domesday book, Motte and Bailey castles, influence of the church, the Tudors and how the monarchy changes over time.
Year 7 is structured in chronological order, each with a key historical concept focus e.g. significance and a skill such as explaining the importance. Every half term will hold two pieces of deep (yellow box) marking and one cumulative assessment piece.
Studentspersonal assessment feedback sheets will be used to reflect on strengths and weaknesses. They will identifyhow they’ve used their skills duringthe term and which skills need development.
Studentsare given a range of independenttasks, guided tasks and group tasks rangingfrom source analysis and categorization tasks.
Homework is set via projects/booklets, where students must focus on their literacy developmentand revision each term. Revision homework is specific, studentswill be given a new technique/focus each term.
Literacy: key word front sheets, connectives. Numeracy: chronology understanding.
Key assessments and deep marking: deep marking of 2 key pieces of work in each unit, the second of which will be a formal assessment. Low stakes testing : in starters to allow for interleaving of prior learning and retrieval. Homelearning: project based and on rotation. Optional enrichment activities are also be provided every week to enhance cultural capital. Reflection time: after each assessment and dep markedpiece of work.
Autumn Term
Bridging Unit and NormanConquest
Spring Term
Medieval England.
SummerTerm
The Tudors
End of the year, students will have contextual knowledgeabout how people in the medieval period organized society,what their lives were like, why key events were importantand what events led to other developments.They will be familiar on how to analyse sourcesand put events in to order.
Next year these skills will be developedby studentsexplaining not just what is important,but deciding which factors are more importantthat others.
A chronologically runningyear based on depthand breadthstudies. Breadth studies completed based on the power of the monarchy and World War
1. Depthstudies on the Stuarts, and duringVictorian time. A selection of political and historical events will be covered, includingboth local and nationalhistories. With a variety of skills studied.
Intent Unitscovered: The Stuarts, Slave trade and empire, Industrial revolution,civil rights and WW1. Skills and knowledge to be covered: change and continuity (narrative skills), significance (explaining most important factors), causation (explain 3 reasons why), source analysis (utility), source analysis (interpretations).
Buildingon Year 7: Year 7 ends in 1500’s and year 8 starts here. Students will consider how the monarchy and governmentchanges over time. The studentsdevelop further their skills on explaining importance by considering the mostimportantfactor and applying criteria.
Year 8 is structured in chronologicalorder, each with a key historical conceptfocus e.g. significance and a skill such as explaining the importance.Every half term will hold two pieces of deep (yellow box) marking and one cumulativeassessmentpiece.
Studentspersonal assessmentfeedback sheetswill be used to reflect on strengthsand weaknesses. They will identify how they’ve used their skillsduring the term and which skillsneed development.
Studentsare given a range of independent tasks,guided tasksand group tasksranging from source analysis and categorization tasks.
Homework is set via projects/booklets, where students must focus on their literacy development and revision each term. Revision homework is specific, students will be given a new technique/focus each term.
Literacy: key word front sheets, connectives. Numeracy: chronology understanding.
Key assessments and deep marking: deep marking of 2 key pieces of work in each unit, the second of which will be a formal assessment. Low stakes testing : in starters to allow for interleavingof prior learning and retrieval.
Homelearning: project based and on rotation. Optional enrichment activities are also be provided every week to enhance cultural capital. Reflection time: after each assessment and dep markedpiece of work.
Autumn Term
The Stuarts and Empire/Slave Trade
Spring Term Civil Rights and Industrial Revolution
SummerTerm World War 1
End of the year, students will have a strong overview to the key features of different historical periods. They will be able to identify long term and short term causes. They will be confidenton analyzing sources and lookingat historical interpretations.
Next year these skills will be developedby exploring source analysis skills on why historians hold different interpretations and using criteria further to come to well developed judgements on significance.
BigPicture: Preparationfor,andintroductionto, OCR Cambridge Nationals Level 1/2 Certificate in Creative imedia
StudentswillbeintroducedtoCambridgeNationalCertificateinCreativeimediathiscourse equipsstudentswithawiderangeof knowledgeandskillsneededto workinthecreativedigitalmediasector.Theystartatpre-productionanddeveloptheirskillsthroughpracticalassignmentsastheycreatefinalmultimedia products.
Intent:Thepupils will begin tocomplete R081 andR082 inYear10.
UnitR081 is apaper based exam whichis externally assessed.Theaim ofthisunit istoacquirealltheknowledgeandskills thatunderpintheimedia course.
UnitR082 is aninternallyassessedunit. Theaim ofthis unit is forlearnerstounderstandthebasics ofdigitalgraphicseditingforthe creativeand digitalmediasector.Theywill learnwhereandwhydigitalgraphicsareusedandwhattechniquesareinvolvedintheircreation.Theywill be able to planthecreationofdigitalgraphics,createnew digitalgraphicsusing a rangeofeditingtechniques andreviewacompleted graphicagainst a specific brief.
Implementation
Students will workthroughthecourseworkareas,reflectingregularlyontheir knowledge and understandingthroughout.Each unit providesopportunitiestobuild up skills throughpracticaland theoreticalactivities.
Thepreproductionskills unit will concludewith anexam whichis 25% ofthe course. Thereis anopportunitytoresitif requiredinyear 11toimprovegrade.
R082 assignment is 25% ofthecoursework.
Homeworkwill consistmostlyofaflipped learningactivity approachthathasproven throughresearchbased learning tobe effective in supportingdevelopmentofprior knowledgetoenhance inclass learning. Eachunit will havea number ofhomework activities planned tosupportknowledge skills requiredforthatparticularunit,.
Key assessments:
• Exam paper in January externally assessed
• Homework will be peer marked or used in lesson.
• Coursework R082 marked on completion ( summer term).
Externally moderated
Autumn Term
• Assessment: Exam R081
• Projectbased assessment
Spring Term
• Projectbased assessment
Summer Term
• Projectbased assessment R082
WImpact: Students will develop good knowledge, skills and understanding of: exam based unit which underpins the entire course. Learning by a hands on approach also enables the pupils to work at their own pace this also promotes learning through interaction and collaboration. Students will build up transferableskills througheach skills unit in preparationfortheimedia courseunits R084 andR085 inyear 11
TheBigPicture:InYear11. Thepupilswillbegintocompletethe2optionalunitswhichareR084andR085. Theseareinternallyassessedunits(coursework).Theaimoftheseunitsis forlearnerstocontinuetodeveloptheirskills intheplanning,creationandevaluation processesinvolvedinclient-leddigitalprojects.Itisvitalthatstudentsmeetdeadlinesasthiscanaffecttheiroverallgrade.
Intent:R084comic: throughthisunit, studentswill exploredifferentgenres ofcomicstripandthebasics ofcomicstripcreation.Thisunit builds on UnitsR081 andR082. Contentincludes: Understandingcomicstripsandtheircreation, Being able toplanandproduceamultipage comicstripand developtheknowledgetoreview thefinalmultipage comic.
Ro85web design: Multipage websites arethebasis ofinternetcontentandarethereforeusedextensively inthecreativedigitalmediasector,whether formobile phonesorcomputersinalltheirforms.Students will havetheopportunitytounderstandthebasics ofcreatingmultipage websites through thisunit. Theywill alsobe able todemonstratetheircreativitybycombiningcomponentstocreateafunctional,intuitive andaestheticallypleasing website. Gaining knowledge oftheproperties,purposesandfeaturesofmultipage websites , Being able toplanandcreatemultipage websites, using multimediacomponents andDevelopingtheknowledgetoreviewthefinalwebsite against aspecific brief.Thisunit buildsonUnits R081 andR082.
Autumn Term
Studentswill workthroughthecourseworkareas,reflectingregularlyontheir knowledge andunderstandingthroughout.Each unit providesopportunitiestobuild up skills through practicaland theoreticalactivities.
R084 assignment is 25% ofthecoursework. R085 assignment is 25% ofthecoursework.
Homeworkwill consistmostlyofaflipped learningactivityapproachthathasproven throughresearchbased learning tobe effective in supportingdevelopmentofprior knowledgetoenhance inclass learning. Eachunit will haveanumber ofhomework activities plannedtosupportknowledge skills requiredforthatparticularunit.
Key assessments:
• Assessment: R084
• Internalassessment
/externalmoderation
• Homework will be peer marked or used in lesson.
• Coursework
R084/R085 marked on completion ( summer term). Externally moderated
Spring Term
• Assessment: R085
• Internalassessment
/externalmoderation
Summer Term
• Courseworkcompleted May/June ( resitR081)
WImpact: Students will develop good knowledge, skills and understanding of: exam based unit which underpins the entire course. Learning by a hands on approach also enables the pupils to work at their own pace this also promotes learning through interaction and collaboration. Students will build up transferableskills througheachskills unit in preparationfortheimediacourseunits R084 andR085 inyear 11
StudentswillbeintroducedtoInformationCommunicationTechnologythey willdevelopanunderstandingand knowledgeof howcomputersworkthedifferenttypes ofhardwareand differentsoftwareapplications, howdatabaseswork,animationand programmingskills using visualprogrammingsoftware.
Intent:
TheUnitsthatwillbecoveredare:PowerPoint,E Safety, Digital leaners,Computational thinking,Programming,Databases,Animationand Graphics
Skills:studentswillbeintroducedtotheimportanceof filestructures,theywilldevelopa knowledgeandunderstandingofhowcomputerswork,exploring hardware,softwareand computercomponents.Studentswilldevelop an understandingof programmingusing visualbasedprogrammingsoftwareand willwork througharangeof activitiesdeveloping theirownprogrambasedon theirknowledgeandunderstanding.Theywillbuildafunctioningdatabaseusingarangeof softwaretools.Studentswillsortand searchinformationstoredusing filters.Studentswilluseanimationsoftwaretocreatea projectbasedassessmentaswell asusinggraphicsoftwaretocreatetheirgraphicsfortheanimation.
Implementation
Key assessments:
Autumn Term Studentswillworkthroughthetopicareas,reflectingregularlyontheirknowledgeand
• Assessment: baseline understandingthroughout.Each topicprovidesopportunitiestobuildup skills through Baseline assessment will
• Projectbased assessment practicaland theoreticalactivities. take place at start and end of each topic to Eachunitwillconcludewithatopicbasedassessmenthighlightingtheskillsdevelopedduring measure progress. theunit,pupilswillreflectandimprovethroughpeerandself assessment.
Deep marking points
Spring Term
• Assessment: baseline
LORICopportunitiesareprovidedthroughouteachmodule,theseincludegrouptasksthat
• Projectbased assessment providechancesforstudentstointeractwithother,demonstratelevelsof communicationand Homework will be peer leadership. marked or used in lesson.
Summer Term researchbasedlearningtobeeffectivein supportingdevelopment of priorknowledgeto Teachers will live mark/
Homeworkwillconsistmostlyofa flippedlearningactivityapproachthathas proventhrough
• Assessment: baseline enhanceinclasslearning. Eachprojectwillhaveanumberof homeworkactivitiesplanned. and mark each topic
• Projectbased assessment based assessment.
Impact: Students will haveanoverallgoodknowledge andunderstandingofhowcomputersystems work,howthe benefits ofusing ICTcanbe used topromoteLearningby a handsonapproachalsoenabling the pupils toworkattheirownpace, openingupa wide rangeofup-to-datelearningmaterials throughtheuse oftheinternet,enrichinglearningthroughtheuse of:audio,video,images, text andanimation.Thisinternenhances learningthrough interactionandcollaboration.Students will build up transferableskills throughthedatabase unit andwill developa goodknowledge andunderstanding ofprogrammingskills and terminologyin preparationforlearning textual based programmingin year 8 .
Studentswillbeintroducedtocomputing,computercrime,cybersecurityhowtoprotectdata,identifyscams,hacking andcopyrightimplications,howspreadsheets canbeusedeffectivelytocreateadatabase,graphicsoftwareandwebdesignsoftware.
Intent:
TheUnitsthatwillbecoveredare:Computing,Computercrimeand cybersecurity,Databases,Graphicsand introductiontowebdesign Skills:Studentswilldevelopanunderstandingof binaryanddenary,programmingusingvisualtextualbasedprogrammingsoftwareandwillworkthrougharangeof activitiesdeveloping their ownprogrambasedontheirknowledgeandunderstanding.Theywillbuildafunctioningdatabaseusinga rangeof softwaretools. Studentswilldeveloptheirskillsandunderstandingofusingagraphicssoftwaretoeditand creategraphicsusingallthetoolsavailablewithPhotoshop.Students willusewebdesignsoftwaretocreateawebsiteforagivenaudiencetoincludemasterpage,suitablenavigationsystem,linkedpages,hyperlinksanduseof multi mediathroughoutthewebsite.
Studentswillworkthroughthetopicareas,reflectingregularlyontheirknowledgeand understandingthroughout.Each topicprovidesopportunitiestobuildup skills through practicaland theoreticalactivities.
Eachunitwillconcludewithatopicbasedassessmenthighlighting theskillsdevelopedduring theunit,pupilswillreflectandimprovethroughpeerandself assessment.
LORICopportunitiesareprovidedthroughouteachmodule,theseincludegrouptasksthat providechancesforstudentstointeractwithother,demonstratelevelsof communication and leadership.
Homeworkwillconsistmostlyofa flippedlearningactivityapproachthathas proventhrough researchbasedlearningtobeeffectivein supportingdevelopment of priorknowledgeto enhanceinclasslearning. Eachprojectwillhaveanumberofhomeworkactivitiesplanned.
Key assessments:
• Baseline assessment will take place at start and end of each topic to measure progress.
• Deep marking points
• Homework will be peer marked or used in lesson.
• Teachers will live mark/ and mark each topic based assessment.
Autumn Term
• Assessment: baseline
• Projectbased assessment
Spring Term
• Assessment: baseline
• Projectbased assessment
Summer Term
• Assessment: baseline
• Projectbased assessment
Impact: Students will developgoodknowledge andunderstandingof:computing, computercrime, cybersecurity,designinggraphicsandweb design. Learning by a hands on approach also enables the pupils to work at their own pace this also promotes learning through interaction and collaboration. Students will build up transferable skills through the computer crime ,cyberbullying, graphics and web design units to develop a good knowledge and skills understandinginpreparationforimedia skills courseinyear 9 .
StudentswillbeintroducedtoCambridgeNationalCertificateinCreativeimediathiscourse equipsstudentswithawiderangeofknowledgeandskillsneeded to workinthecreativedigitalmediasector.Theystartatpre-productionanddeveloptheirskillsthroughpracticalassignmentsastheycreatefinalmultimedia products.
Intent:
Year9 is used as a skills building year,inpreparationforstudentsstartingtheir courseworkin Year10. Anumber of ‘mini projects’arecompleted withtheaim ofstudentsexploringdifferentwork-basedscenarioswheretheyarerequiredtodesign, createandevaluate digitalsolutionsanddevelop theirICTskills. Students'will developkeyskills inplanning andcreatingdigitalmedia,web programmingandmultimediasolutionsthatmeetbotha client’sandatargetaudience’srequirements.
Studentswillworkthroughthetopicareas,reflectingregularlyontheirknowledgeand understandingthroughout.Each topicprovidesopportunitiestobuildup skills through practicaland theoreticalactivities.
Eachunitwillconcludewithatopicbasedassessmenthighlighting theskillsdevelopedduring theunit,pupilswillreflectandimprovethroughpeerandself assessment.
LORICopportunitiesareprovidedthroughouteachmodule,theseincludegrouptasksthat providechancesforstudentstointeractwithother,demonstratelevelsof communication and leadership.
Homeworkwillconsistmostlyofa flippedlearningactivityapproachthathas proventhrough researchbasedlearningtobeeffectivein supportingdevelopment of priorknowledgeto enhanceinclasslearning. Eachprojectwillhaveanumberofhomeworkactivitiesplanned.
Key assessments:
• Baseline assessment will take place at start and end of each topic to measure progress.
• Homework will be peer marked or used in lesson.
• Teachers will live mark/ and mark each topic based assessment.
Autumn Term
• Assessment: exam paper
• Projectbased assessment
Spring Term
• Assessment: baseline
• Projectbased assessment
Summer Term
• Assessment: baseline
• Projectbased assessment
Impact: Students will develop good knowledge, skills and understanding of: exam based unit which underpins the entire course. Learning by a hands on approach also enables the pupils to work at their own pace this also promotes learning through interaction and collaboration. Students will build up transferableskills througheach skills unit in preparationfortheimedia courseyear 10/11
Y7 Mathematics is a challenging transition to the study of secondary Mathematics. They will experience “mastery” alongside more traditional teaching methods to gain a deeper understanding, more confidence and competence in their mathematics.
Intent ’Learning Programme’ blocks to be covered: Algebraic Thinking, Place Value and Proportion, Applications of Number, Directed Number, Fractional Thinking, Lines and Angles and Reasoning with Number.
Each term is split into two halves with a common theme, each half is split into further blocks that ensure students spend enough time to get a deep understanding of the topic covered. Blocks have been designed with interleaving as a key element enabling students to revisit previous work, develop knowledge and understanding and further extend their skills. Number work is emphasized throughout the blocks alongside estimation. Calculator skills have been incorporated throughout the curriculum, thus enabling all students to access the materials presented. Any student will be able to follow the main content of all lessons with higher levels being accessed as and when a class/student requires it.
There will be 6 LP blocks of approx. 6 weeks each. Each lesson will involve a WRM flashback task. Independence and study skills will be fostered through: challenging questions and problems, group and pair work, modelling, homework and PLC after each half termly assessment. Each block starts with a student self reflective log which is revisited after each objective has been taught (may be across a few lessons)
Lessons will be based around multiple representations; Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract to give a deeper understanding of concepts. Reasoning will be developed through the exploration of mathematical patterns and images with a variety of problem-solving methods for just one question.
Learning to move forward and uncover mathematical ideas from mistakes and misconceptions via true/false, spot the mistake and other reasoning tasks where students are required to make a judgement and justify their answers.
Knowledge organisers will be provided for each block to enable students to recall keywords, facts, formulas and/or formal methods.
WOW moments will occur when students solve complex problems, when the barrier wall disappears and they have a moment of satisfying clarity (no matter how brief) or spotting a relationship that was previously unseen.
Numeracy and calculator skills will be embedded.
Key assessments:
Minimum of 2 formal assessments will take place every half term. Key homeworks per unit will be issued along side additional supporting homework tasks. Low stake testing as required Live marking will occur during lessons as required
Students will have increased understanding and confidence in maths and be able to apply new skills to a variety of new and challenging mathematical problems. Students will know more and remember more. There will be an increase in attainment, evidenced in regular, formal and interleaved assessments.
Y8 Mathematics is the revisiting of topics within new contexts whilst extending and further developing mathematical thinking and skills. They will experience “mastery” alongside more traditional teaching methods to gain a deeper understanding, more confidence and competence in their mathematics.
Intent ’Learning Programme’ blocks to be covered: Proportional Reasoning, Representations, Algebraic Techniques, Developing Number, Developing Geometry and Reasoning with Data
Each term is split into two halves with a common theme, each half is split into further blocks that ensure students spend enough time to get a deep understanding of the topic covered. Blocks have been designed with interleaving as a key element enabling students to revisit previous work, develop knowledge and understanding and further extend their skills. Number work is emphasized throughout the blocks alongside estimation. Calculator skills have been incorporated throughout the curriculum, thus enabling all students to access the materials presented. Any student will be able to follow the main content of all lessons with higher levels being accessed as and when a class/student requires it.
There will be 6 LP blocks of approx. 6 weeks each. Each lesson will involve a WRM flashback task. Independence and study skills will be fostered through: challenging questions and problems, group and pair work, modelling, homework and PLC after each half termly assessment. Each block starts with a student self reflective log which is revisited after each objective has been taught (may be across a few lessons)
Lessons will be based around multiple representations; Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract to give a deeper understanding of concepts. Reasoning will be developed through the exploration of mathematical patterns and images with a variety of problem solving methods for just one question.
Learning to move forward and uncover mathematical ideas from mistakes and misconceptions via true/false, spot the mistake and other reasoning tasks where students are required to make a judgement and justify their answers.
Knowledge organiser will be provided for each block to enable students to recall keywords, facts, formulas and/or formal methods.
WOW moments will occur when students solve complex problems, when the barrier wall disappears and they have a moment of satisfying clarity (no matter how brief) or spotting a relationship that was previously unseen.
Numeracy and calculator skills will be embedded.
Key assessments:
Minimum 2 formal assessment will take place every half term. Key homeworks per unit will be issued along side additional supporting homework tasks. Low stake testing as required Live marking will occur during lessons as required
Autumn Term Summer Term
Developing number assessment
Developing Geometry assessment
Reasoning with data assessment End of year Exam
Students will have increased understanding and confidence in maths and be able to apply new skills to a variety of new and challenging mathematical problems. Students will know more and remember more. There will be an increase in attainment, evidenced in regular, formal and interleaved assessments.
Y9 Mathematics is the foundation blocks for the GCSE examination, students will be exposed to the crossover topics from the two tiers. They will experience “mastery” alongside more traditional teaching methods to gain a deeper understanding, more confidence and competence in their mathematics.
Intent ’Learning Programme’ blocks to be covered: Reasoning with Algebra, Constructing in 2 and 3 Dimensions, Reasoning with Number, Reasoning with Geometry, Reasoning with Proportion, and Representations.
Each term is split into two halves with a common theme, each half is split into further blocks that ensure students spend enough time to get a deep understanding of the topic covered. Blocks have been designed with interleaving as a key element enabling students to revisit previous work, develop knowledge and understanding and further extend their skills. Number work is emphasized throughout the blocks alongside estimation. Calculator skills have been incorporated throughout the curriculum, thus enabling all students to access the materials presented. Any student will be able to follow the main content of all lessons with higher levels being accesses as and when a class/student requires it.
There will be 6 LP blocks of approx. 6 weeks each. Each lesson will involve a WRM flashback task. Independence and study skills will be fostered through: challenging questions and problems, group and pair work, modelling, homework and PLC after each unit and past paper assessment. Each block starts with a student self reflective log which is revisited after each objective has been taught (may be across a few lessons)
Lessons will be based around multiple representations; Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract to give a deeper understanding of concepts. Reasoning will be developed through the exploration of mathematical patterns and images with a variety of problem solving methods for just one question. Formal structure to answering GCSE questions will be explored.
Learning to move forward and uncover mathematical ideas from mistakes and misconceptions via true/false, spot the mistake and other reasoning tasks where students are required to make a judgement and justify their answers.
Knowledge organiser will be provided for each block to enable students to recall keywords, facts, formulas and/or formal methods.
WOW moments will occur when students solve complex problems, when the barrier wall disappears and they have a moment of satisfying clarity (no matter how brief) or spotting a relationship that was previously unseen.
Numeracy and calculator skills will be embedded.
Key assessments:
Minimum 2 formal assessments will take place every half term. Key homeworks per unit will be issued along side additional supporting homework tasks. Low stake testing as required
Live marking will occur during lessons as required
Reasoning with Algebra
Constructing in 2 and 3 Dimensions
Reasoning with Number
Reasoning with Geometry
Reasoning with Proportion Representations End-of-Year Test
Students will have increased understanding and confidence in maths and be able to apply new skills to a variety of new and challenging mathematical problems. Students will know more and remember more. Students will have developed their AO2/3 skills enabling them to manipulate familiar and unfamiliar vocabulary and deduce mathematical content. They will have experience a variety of question types and be suitably prepared to answer examination style questions. There will be an increase in attainment, evidenced in regular, formal and interleaved assessments.
Y10 Mathematics (Foundation Tier) builds upon GCSE content initially taught in Year 9. In 2022/23, Key Stage 3 learning journeys have been updated and as a result, this continuity is not evident; however, the sequencing of learning has been carefully designed to ensure comprehensive coverage of the syllabus requirements.
Intent ‘Learning Programme’ blocks to be covered:
Angles, Statistics, Ratio and Proportion, Right-angled Trigonometry, Equations & Graphs, Congruence, Similarity & Vectors. Each term is split into units to ensure content is covered and students spend enough time to get a deep understanding of the topic covered. Units incorporate interleaving as a key element enabling students to revisit previous work, develop knowledge and understanding and further extend their skills. Number work is emphasized throughout the blocks alongside estimation. Calculator skills have been incorporated throughout the curriculum.
There will be 6 LP units of approx. 5/6 weeks each. Each unit will be assessed with a topic-specific assessment task – typically a written test.
Independence and study skills will be fostered through: challenging questions and problems, group and pair work, modelling, homework and PLC after each unit and past paper assessment.
Lessons will be based around multiple representations; Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract to give a deeper understanding of concepts. Reasoning will be developed through the exploration of mathematical patterns and images with a variety of problem solving methods for just one question. Formal structure to answering GCSE questions will be embedded.
Learning to move forward and uncover mathematical ideas from mistakes and misconceptions via true/false, spot the mistake and other reasoning tasks where students are required to make a judgement and justify their answers.
Knowledge organisers will be provided for each unit to enable students to recall keywords, facts, formulas and/or formal methods.
WOW moments will occur when students solve complex problems, when the barrier wall disappears and they have a moment of satisfying clarity (no matter how brief) or spotting a relationship that was previously unseen.
Numeracy and calculator skills will be embedded.
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take place every unit Key homework's per unit will be issued along side additional supporting homework tasks and past papers.
Low stake testing as required
Live marking will occur during lessons as required Past papers (one per term)
Autumn Term
Unit 1: Angles
Unit 2: Statistics
Unit 3: Ratio & Proportion
Spring Term
Unit 4: Right-angled Trigonometry
Unit 5: Equations & Graphs
Summer Term
Unit 6 : Congruence, Similarity and Vectors
REVIEW AND END-OF-YEAR ASSESSMENT
Students will have increased understanding and confidence in maths and be able to apply new skills to a variety of new and challenging mathematical problems. Students will know more and remember more. Students will have developed their AO2/3 skills enabling them to manipulate familiar and unfamiliar vocabulary and deduce mathematical content. They will be familiar with a variety of exam questions and be suitably prepared to answer examination style questions. There will be an increase in attainment, evidenced in regular, formal and interleaved assessments.
Y11 Mathematics is the final year of the GCSE where students will continue to develop and build mathematical skills and knowledge required for their final examination in the summer.
Intent ’Learning Programme’ blocks to be covered:
Multiplicative Reasoning, Fractions, Perimeter, Volume and Area, Algebra. (Significant time also allocated to revision for Mock and GCSE examinations during which time content from throughout the entire GCSE course will be revised and retaught)
Terms are split into units to ensure content is covered and students spend enough time to get a deep understanding of the topic covered. During the final half-term of the year students will follow bespoke revision timetables based on previous PLC’s and exam feed back. Units have an element of interleaving as a key element enabling students to revisit previous work, develop knowledge and understanding and further extend their skills.
There will be 3 LP units of approximately 6 weeks each. Each unit will be assessed with a topic-specific assessment task – typically a written test.
Independence and study skills will be fostered through: challenging questions and problems, group and pair work, modelling, homework and PLC after each unit and past paper assessment. Lessons will be based around multiple representations; Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract to give a deeper understanding of concepts. Reasoning will be developed through the exploration of mathematical patterns and images with a variety of problem solving methods for just one question. Formal structure to answering GCSE questions will be embedded.
Learning to move forward and uncover mathematical ideas from mistakes and misconceptions via true/false, spot the mistake and other reasoning tasks where students are required to make a judgement and justify their answers.
Knowledge organisers will be provided for each unit to enable students to recall keywords, facts, formulas and/or formal methods.
WOW moments will occur when students solve complex problems, when the barrier wall disappears and they have a moment of satisfying clarity (no matter how brief) or spotting a relationship that was previously unseen.
Numeracy and calculator skills will be embedded.
Autumn Term
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take place every unit. Key homework's per unit will be issued along side additional supporting homework tasks and past papers. Low stake testing as required
Live marking will occur during lessons as required
Unit 7: Multiplicative Reasoning
Unit 8: Perimeter, Area and Volume
REVISION AND MOCK 1
Spring Term
Unit 9: Algebra
REVISION AND MOCK 2
Summer Term
Exam preparations
GCSE Examinations
Students will have the desired understanding and confidence in maths and be able to apply skills to a variety of challenging mathematical problems. Students will know more and remember more. Students will have developed their AO1/2/3 skills enabling them to manipulate familiar and unfamiliar vocabulary and deduce mathematical content. They will be familiar with a variety of exam questions and be suitably prepared to answer all examination style questions. Students will achieve their maximum attainment level to progress to their next level of study.
Y10 Mathematics (Higher Tier) builds upon GCSE content initially taught in Year 9. In 2022/23, Key Stage 3 learning journeys have been updated and as a result, this continuity is not evident; however, the sequencing of learning has been carefully designed to ensure comprehensive coverage of the syllabus requirements.
Intent ‘Learning Programme’ blocks to be covered:
Angles & Trigonometry, Further Statistics, Multiplicative Reasoning, Trigonometry, Equations & Graphs, Similarity & Congruence. Each term is split into units to ensure content is covered and students spend enough time to get a deep understanding of the topic covered. Units incorporate interleaving as a key element enabling students to revisit previous work, develop knowledge and understanding and further extend their skills. Number work is emphasized throughout the blocks alongside estimation. Calculator skills have been incorporated throughout the curriculum.
There will be 6 LP units of approx. 5/6 weeks each. Each unit will be assessed with a topic-specific assessment task – typically a written test.
Independence and study skills will be fostered through: challenging questions and problems, group and pair work, modelling, homework and PLC after each unit and past paper assessment.
Lessons will be based around multiple representations; Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract to give a deeper understanding of concepts. Reasoning will be developed through the exploration of mathematical patterns and images with a variety of problem solving methods for just one question. Formal structure to answering GCSE questions will be embedded.
Learning to move forward and uncover mathematical ideas from mistakes and misconceptions via true/false, spot the mistake and other reasoning tasks where students are required to make a judgement and justify their answers.
Knowledge organisers will be provided for each unit to enable students to recall keywords, facts, formulas and/or formal methods.
WOW moments will occur when students solve complex problems, when the barrier wall disappears and they have a moment of satisfying clarity (no matter how brief) or spotting a relationship that was previously unseen.
Numeracy and calculator skills will be embedded.
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take place every unit Key homework's per unit will be issued along side additional supporting homework tasks and past papers.
Low stake testing as required
Live marking will occur during lessons as required Past papers (one per term)
Autumn Term
Unit 1: Angles and Trigonometry
Unit 2: Further Statistics
Unit 3: Multiplicative Reasoning
Spring Term
Unit 4: Trigonometry
Unit 5: Equations & Graphs
Summer Term
Unit 6 : Similarity and Congruence
REVIEW & END-OF-YEAR ASSESSMENT
Students will have increased understanding and confidence in maths and be able to apply new skills to a variety of new and challenging mathematical problems. Students will know more and remember more. Students will have developed their AO2/3 skills enabling them to manipulate familiar and unfamiliar vocabulary and deduce mathematical content. They will be familiar with a variety of exam questions and be suitably prepared to answer examination style questions. There will be an increase in attainment, evidenced in regular, formal and interleaved assessments.
Y11 Mathematics is the final year of the GCSE where students will continue to develop and build mathematical skills and knowledge required for their final examination in the summer.
Intent ’Learning Programme’ blocks to be covered:
Proportion and Graphs, Vectors, Circle Theorems (Significant time also allocated to revision for Mock and GCSE examinations during which time content from throughout the entire GCSE course will be revised and retaught)
Terms are split into units to ensure content is covered and students spend enough time to get a deep understanding of the topic covered. During the final half-term of the year students will follow bespoke revision timetables based on previous PLC’s and exam feed back. Units have an element of interleaving as a key element enabling students to revisit previous work, develop knowledge and understanding and further extend their skills.
3 LP units of approximately 6 weeks each. Each unit will be assessed with a topic-specific assessment task – typically a written test.
Independence and study skills will be fostered through: challenging questions and problems, group and pair work, modelling, homework and PLC after each unit and past paper assessment. Lessons will be based around multiple representations; Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract to give a deeper understanding of concepts. Reasoning will be developed through the exploration of mathematical patterns and images with a variety of problem solving methods for just one question. Formal structure to answering GCSE questions will be embedded.
Learning to move forward and uncover mathematical ideas from mistakes and misconceptions via true/false, spot the mistake and other reasoning tasks where students are required to make a judgement and justify their answers.
Knowledge organisers will be provided for each unit to enable students to recall keywords, facts, formulas and/or formal methods.
WOW moments will occur when students solve complex problems, when the barrier wall disappears and they have a moment of satisfying clarity (no matter how brief) or spotting a relationship that was previously unseen.
Numeracy and calculator skills will be embedded.
Autumn Term
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take place every unit. Key homework's per unit will be issued along side additional supporting homework tasks and past papers. Low stake testing as required
Live marking will occur during lessons as required
Unit 7: Proportion and Graphs
Unit 8: Vectors
REVISION AND MOCK 1
Spring Term
Unit 9: Circle Theorems
REVISION AND MOCK 2
Summer Term
EXAM PREPARATION
GCSE Examinations
Students will have the desired understanding and confidence in maths and be able to apply skills to a variety of challenging mathematical problems. Students will know more and remember more. Students will have developed their AO1/2/3 skills enabling them to manipulate familiar and unfamiliar vocabulary and deduce mathematical content. They will be familiar with a variety of exam questions and be suitably prepared to answer all examination style questions. Students will achieve their maximum attainment level to progress to their next level of study.
• Describing and identifying people, including oneself (greetings, providing personal data, describing appearance and personality ,asking questions about oneself and others)
• Expressing one’s feelings and opinions(expressing positiveand negative feelings, likes and dislikes and providing reasons)
• Describingdaily routine behavior in different contexts(talking about what routine one usually have at home and at school, indicating time, expressing a purpose)
• Comparingand contrasting(expressing likes and dislikes, supporting an opinion, explaining preferences, comparingpeople and things)
• Pupils will study four areas of communicativefunctions.
•A streamlined selection of key language patterns will be taught with emphasis on repetition, recycling and rehearsing with mostteaching and learning activitieslinked to sentence builders.
•Pupilswill learn phrases or chunks with a long term aim of internalizing the patternsin the TL. Listeningand reading activities(receptive skills) will be used to introduce and constantlymodelnew language patterns. Speaking and writing activitieswill consolidateand strengthen these new structures with a view to pupils being able to speak and write with greater spontaneityand confidence (productive skills).
•Interleaving (referring back to key language patterns and chunks on a regular basis) will be an essentialpart of teaching, giving pupils plenty opportunity to recycle language from parts of the term or year.
•Home learning will be heavily reliant on the sentence builders and will developautomatisationof chunks acquisitionand manipulation through adapted activities.
•MFL is heavily literacy focused and it is developed by using appropriate linguistic terms, functions, by comparinghow similar or dissimilar languagesare, and producingaccurate TL occurrences.
•MFL and LORIC: planning, executing, reviewing and implementingchanges in extended tasks, revival of the language leaders scheme, e-pals programme,
• WOW moment: Trivial Pursuits revision cards, plan and teach a lesson, plenary/starters competition,etc.
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take after each unit.
Mad time will take place weekly during literacy lessons.
Homework will be peer marked or used in lesson.
Teachers will live mark/ sample mark non formal assessments.
•By the end of the year pupils will be able to understand, ask questionsand talk about themselvesand othersin great details using chunks of language and linguisticsfeatures accurately and confidently.
•In Year 8 pupils will study further areas of communicativefunctionswhich build on thoseacquired in year 7. As such further tensesand patterns will be taught thus enhancingthe complexitywithwhich pupils can express themselvesin TL and embedding the four skills areas from an early stage so that they can better cope with the demands of the GCSE.
• Describing places, objectsand natural phenomena (describing location,size, appearance, weather etc.)
• Describingroutine behavior in the present (talking about what one usually does, indicating time, expressing a purpose, etc.)
• Comparingand contrasting(expressing likes and dislikes, supporting an opinion, explaining preferences, comparingpeople and things)
• Making arrangements (making suggestions, inviting, accepting, refusing, etc.)
• Making plans for the future (indicating time, making predictions, hypothesizing, discussingprobability, wishes, etc.)
• Pupils will study four areas of communicativefunctions.
•A streamlined selectionof key language patterns will be taught with emphasis on repetition,recycling and rehearsing with mostteaching and learning activitieslinked to sentence builders.
•Pupilswill learn phrases or chunks with a long term aim of internalizing the patternsin the TL. Listeningand reading activities(receptive skills) will be used to introduce and constantlymodelnew language patterns. Speaking and writing activitieswill consolidateand strengthen these new structures with a view to pupils being able to speak and write with greater spontaneityand confidence (productive skills).
•Interleaving (referring back to key language patterns and chunks on a regular basis) will be an essentialpart of teaching, giving pupils plenty opportunityto recycle language from parts of the term or year.
•Home learning will be heavily reliant on the sentence builders and will developautomatisationof chunks acquisitionand manipulation through adapted activities.
•MFL is heavily literacy focused and it is developed by using appropriate linguistic terms, functions, by comparinghow similar or dissimilar languagesare, and producingaccurate TL occurrences.
•MFL and LORIC: planning, executing, reviewingand implementing changes in extended tasks, revival of the language leaders scheme, e-pals programme,
• WOW moment: Trivial Pursuitsrevision cards, plan and teach a lesson, plenary/starters competition,etc.
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take after each unit.
Mad time will take place weekly during literacy lessons.
Homework will be peer marked or used in lesson.
Teachers will live mark/ sample mark non formal assessments.
Autumn Term
Baseline testing – per unit
Assessments: reading and listening
Spring Term
Writing and listening
SummerTerm
Reading and speaking and writing
•By the end of the year pupils will be able to understand,ask questionsand talk aboutwhere they live, what they do in their free time, includingsportsand other leisure activitiesand what they are going to do at a later date in great details using chunks of language and linguistics features accurately and confidently.
•In Year 9 pupils will study further areas of communicativefunctionswhich build on thoseacquired in year 7 and 8. As such further tenses and patterns will be taught thus enhancing the complexitywithwhich pupils can express themselvesin TL and embedding the four skills areas from an early stage so that they can better cope with the demands of the GCSE
• Describingplaces, objectsand natural phenomena in the present, future and past (describing how location,size, appearance, weather is, is going to be, and was etc. )
• Describingroutine behavior and activitiesin the present, future and past (talking about where and what one did, does and is goingto do indicating time, expressing a purpose etc.)
• Describing past events (setting the scene, sequencing, evaluating the consequences of actionsand events, etc.)
• Comparingand contrasting(expressing likes and dislikes, supporting an opinion, explaining preferences, comparingpeople and things)
• Solving problems (describing the problem, providing solutions, discussingpossible consequences, arguing for and against)
• Pupilswill study four areas of communicativefunctions.
•A streamlined selectionof key language patterns will be taught with emphasis on repetition,recycling and rehearsing with mostteaching and learning activitieslinked to sentence builders.
•Pupilswill learn phrases or chunks with a long term aim of internalizing the patternsin the TL. Listeningand reading activities(receptive skills) will be used to introduce and constantlymodelnew language patterns. Speaking and writing activitieswill consolidateand strengthen these new structures with a view to pupils being able to speak and write with greater spontaneityand confidence (productive skills).
•Interleaving(referring back to key language patterns and chunks on a regular basis) will be an essentialpart of teaching, giving pupils plenty opportunityto recycle language from parts of the term or year.
•Home learning will be heavily reliant on the sentence builders and will developautomatisationof chunks acquisitionand manipulation through adapted activities.
•MFL is heavily literacy focused and it is developed by using appropriate linguistic terms, functions, by comparinghow similar or dissimilar languagesare, and producingaccurate TL occurrences.
•MFL and LORIC: planning, executing, reviewing and implementingchanges in extended tasks, revival of the language leaders scheme, e-pals programme,
• WOW moment: Tavel brochure, evaluation of technology,planning a lesson, presenting
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take after each unit.
Autumn Term
Baseline testing – per unit
Assessments: reading and listening
Homework will be peer marked or used in lesson.
Teachers will live mark/ sample mark non formal assessments.
Spring Term
Writing and listening
SummerTerm
Reading and speaking and writing
•By the end of the year pupils will be able to understand, ask questionsand talk their holidays(where they normally go, where they went a previous holidaysand where they are going to go and what they did, usually do and are goingto do) as well as talk about the technologythey use, the advantagesand disadvantagesof it in great details using chunks of language and linguistics features accurately and confidently.
•In Year 10 pupils will study further areas of communicativefunctionswhich build on thoseacquired in year 7, 8 and 9. As such further tenses and patterns will be taught thus enhancing the complexitywith which pupils can express themselvesin TL and embeddingthe four skills areas from an early stageso that they can better cope with the demandsof the GCSE.
The Big Picture: Year 10 is the first year of GCSE where studentswill focus and completeYouthculture, holidaysand schoolof AQA GCSE. Studentswill build on the linguisticskills and knowledge developed in previous years of study to explore the 3 themes. Students will focus on practicing their grammaticalskills, includingpast, present and future time frames and the formatof the speaking and writing examsin preparation for GCSE
• Communicationand interact effectively, take part in short conversations, asking and answering questionsand exchanging opinions. Use accurate pronunciation and intonation
• followand understand clear speech across a range of contexts,identify key points, messagesand opinionsand deduce meaning from a variety of short and longer spoken texts
• understand and respond to different types of written language. Identify key points,details and opinionsin a variety of shortand longer written texts
• communicateeffectively in writing for a variety of purposes, write short texts,using familiar language, produce clear and coherent extended textsto present facts and express ideas and opinions
• Studentswill develop their ability to communicateand coherently in speech and writing, conveyingwhat they want to say with increasing accuracy.
• They will be increasingly able to express ideas and develop thoughtsand ideas spontaneouslyand fluently.
Studentswill develop an awareness and understandingof the culture and identity of the countries and cultures where French is spoken.
• Studentswill develop language learning skills for both immediateuse and to prepare them for further languagestudy and use in school,higher educationor employment.
•Interleaving(referring back to key language patterns and chunks on a regular basis) will be an essential part of teaching, giving pupils plenty opportunityto recycle language from parts of the term or year.
•Home learning will be heavily reliant on the sentence builders and will develop automatisationof chunks acquisitionand manipulationthrough adapted activities.
•MFL is heavily literacy focused and it is developed by using appropriate linguistic terms, functions, by comparinghow similar or dissimilar languages are, and producing accurate TL occurrences.
•MFL and LORIC: planning, executing, reviewing and implementingchanges in extended tasks, revival of the language leaders scheme, e-pals programme.
Autumn Term
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take after each unit.
Key vocabulary quizzes
Preparation of conversation questions
Role Play practice
GCSE Pod & E-Learning
reading for gist
Reading comprehension
Translation activities
Guided writing Extended
writing Exam style practice questions
Baseline testing –
Assessments:reading, listening and writing
Spring Term
All four skills
SummerTerm
All four skills - mocks
By the end of the year, studentswill be able to understand, ask questionsand talk abouttopicsfrom all three themesaccurately and with confidence. They will be able to manipulate familiar and unfamiliar vocabulary and grammaticalstructuresand deduce meaning. They will be familiar will all stylesof exam questionsand be suitably prepared to answer all questions. In Year 11, studentswill build on skills and knowledge acquired in previous years and completerevision activities.Tenses and grammaticalstructures will be revised, enabling studentsto themselvesexpress in French with increasing complexityand preparing them for the demands of the GCSE at the end of Year 11
The Big Picture: Year 10 is the first year of GCSE where studentswill focus and completeYouthculture, holidaysand schoolof AQA GCSE. Studentswill build on the linguisticskills and knowledge developed in previous years of study to explore the 3 themes. Students will focus on practicing their grammaticalskills, includingpast, present and future time frames and the formatof the speaking and writing examsin preparation for GCSE
• Communicationand interact effectively, take part in short conversations, asking and answering questionsand exchanging opinions. Use accurate pronunciation and intonation
• followand understand clear speech across a range of contexts,identify key points, messagesand opinionsand deduce meaning from a variety of short and longer spoken texts
• understand and respond to different types of written language. Identify key points,details and opinionsin a variety of shortand longer written texts
• communicateeffectively in writing for a variety of purposes, write short texts,using familiar language, produce clear and coherent extended textsto present facts and express ideas and opinions
• Studentswill develop their ability to communicateand coherently in speech and writing, conveyingwhat they want to say with increasing accuracy.
• They will be increasingly able to express ideas and develop thoughtsand ideas spontaneouslyand fluently.
Studentswill develop an awareness and understandingof the culture and identity of the countries and cultures where French is spoken.
• Studentswill develop language learning skills for both immediateuse and to prepare them for further languagestudy and use in school,higher educationor employment.
•Interleaving(referring back to key language patterns and chunks on a regular basis) will be an essential part of teaching, giving pupils plenty opportunityto recycle language from parts of the term or year.
•Home learning will be heavily reliant on the sentence builders and will develop automatisationof chunks acquisitionand manipulationthrough adapted activities.
•MFL is heavily literacy focused and it is developed by using appropriate linguistic terms, functions, by comparinghow similar or dissimilar languages are, and producing accurate TL occurrences.
•MFL and LORIC: planning, executing, reviewing and implementingchanges in extended tasks, revival of the language leaders scheme, e-pals programme.
Autumn Term
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take after each unit.
Key vocabulary quizzes
Preparation of conversation questions
Role Play practice
GCSE Pod & E-Learning
reading for gist
Reading comprehension
Translation activities
Guided writing Extended
writing Exam style practice questions
Baseline testing –
Assessments:reading, listening and writing
Spring Term
All four skills
SummerTerm
All four skills - mocks
By the end of the year, studentswill be able to understand, ask questionsand talk abouttopicsfrom all three themesaccurately and with confidence. They will be able to manipulate familiar and unfamiliar vocabulary and grammaticalstructuresand deduce meaning. They will be familiar will all stylesof exam questionsand be suitably prepared to answer allquestions. In Year 11, studentswill build on skills and knowledge acquired in previous years and completerevision activities. Tenses and grammaticalstructures will be revised, enabling studentsto themselvesexpressin Spanish with increasing complexityand preparing them for the demands of the GCSE at the end of Year 11
The Big Picture: Year 11 is the final year of GCSE where studentswill focus and completeWorldof Work and Localarea of AQA GCSE. Studentswill build on the linguisticskills and knowledge developed in previous years of study to explore the 3 themes. Students will focus on practicing their grammaticalskills, includingpast, present and future time frames and the formatof the speaking and writing examsin preparation for GCSE
• Communicationand interact effectively, take part in short conversations, asking and answering questionsand exchanging opinions. Use accurate pronunciation and intonation
• followand understand clear speech across a range of contexts,identify key points, messagesand opinionsand deduce meaning from a variety of short and longer spoken texts
• understand and respond to different types of written language. Identify key points,details and opinionsin a variety of shortand longer written texts
• communicateeffectively in writing for a variety of purposes, write short texts,using familiar language, produce clear and coherent extended textsto present facts and express ideas and opinions
• Studentswill develop their ability to communicateand coherently in speech and writing, conveyingwhat they want to say with increasing accuracy.
• They will be increasingly able to express ideas and develop thoughtsand ideas spontaneouslyand fluently.
Studentswill develop an awareness and understandingof the culture and identity of the countries and cultures where French is spoken.
• Studentswill develop language learning skills for both immediateuse and to prepare them for further languagestudy and use in school,higher educationor employment.
•Interleaving(referring back to key language patterns and chunks on a regular basis) will be an essential part of teaching, giving pupils plenty opportunityto recycle language from parts of the term or year.
•Home learning will be heavily reliant on the sentence builders and will develop automatisationof chunks acquisitionand manipulationthrough adapted activities.
•MFL is heavily literacy focused and it is developed by using appropriate linguistic terms, functions, by comparinghow similar or dissimilar languages are, and producing accurate TL occurrences.
•MFL and LORIC: planning, executing, reviewing and implementingchanges in extended tasks, revival of the language leaders scheme, e-pals programme.
Autumn Term
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take after each unit.
Key vocabulary quizzes
Preparation of conversation questions
Role Play practice
GCSE Pod & E-Learning
reading for gist
Reading comprehension
Translation activities
Guided writing Extended
writing Exam style practice questions
Baseline testing –
All four skills - mocks
Spring Term
All four skills
Mocks
SummerTerm
GCSE exam
By the end of the year, studentswill be able to understand, ask questionsand talk abouttopicsfrom all three themesaccurately and with confidence. They will be able to manipulate familiar and unfamiliar vocabulary and grammaticalstructuresand deduce meaning. They will be familiar will all stylesof exam questionsand be suitably prepared to answer allquestions. In Year 11, studentswill build on skills and knowledge acquired in previous years and completerevision activities. Tenses and grammaticalstructures will be revised, enabling studentsto themselvesexpressin French with increasing complexityand preparing them for the demands of the GCSE at the end of Year 11.
The Big Picture: Year 10 is the first year of GCSE where studentswill focus and completeYouthculture, holidaysand schoolof AQA GCSE. Studentswill build on the linguisticskills and knowledge developed in previous years of study to explore the 3 themes. Students will focus on practicing their grammaticalskills, includingpast, present and future time frames and the formatof the speaking and writing examsin preparation for GCSE
• Communicationand interact effectively, take part in short conversations, asking and answering questionsand exchanging opinions. Use accurate pronunciation and intonation
• followand understand clear speech across a range of contexts,identify key points, messagesand opinionsand deduce meaning from a variety of short and longer spoken texts
• understand and respond to different types of written language. Identify key points,details and opinionsin a variety of shortand longer written texts
• communicateeffectively in writing for a variety of purposes, write short texts,using familiar language, produce clear and coherent extended textsto present facts and express ideas and opinions
• Studentswill develop their ability to communicateand coherently in speech and writing, conveyingwhat they want to say with increasing accuracy.
• They will be increasingly able to express ideas and develop thoughtsand ideas spontaneouslyand fluently.
Studentswill develop an awareness and understandingof the culture and identity of the countries and cultures where French is spoken.
• Studentswill develop language learning skills for both immediateuse and to prepare them for further languagestudy and use in school,higher educationor employment.
•Interleaving(referring back to key language patterns and chunks on a regular basis) will be an essential part of teaching, giving pupils plenty opportunityto recycle language from parts of the term or year.
•Home learning will be heavily reliant on the sentence builders and will develop automatisationof chunks acquisitionand manipulationthrough adapted activities.
•MFL is heavily literacy focused and it is developed by using appropriate linguistic terms, functions, by comparinghow similar or dissimilar languages are, and producing accurate TL occurrences.
•MFL and LORIC: planning, executing, reviewing and implementingchanges in extended tasks, revival of the language leaders scheme, e-pals programme.
Autumn Term
Key assessments:
Formal assessment will take after each unit.
Key vocabulary quizzes
Preparation of conversation questions
Role Play practice
GCSE Pod & E-Learning
reading for gist
Reading comprehension
Translation activities
Guided writing Extended
writing Exam style practice questions
Baseline testing –
Assessments:reading, listening and writing
Spring Term
All four skills
SummerTerm
All four skills - mocks
By the end of the year, studentswill be able to understand, ask questionsand talk abouttopicsfrom all three themesaccurately and with confidence. They will be able to manipulate familiar and unfamiliar vocabulary and grammaticalstructuresand deduce meaning. They will be familiar will all stylesof exam questionsand be suitably prepared to answer all questions. In Year 11, studentswill build on skills and knowledge acquired in previous years and completerevision activities.Tenses and grammaticalstructures will be revised, enabling studentsto themselvesexpress in Spanish with increasing complexityand preparing them for the demands of the GCSE at the end of Year 11
Studentswill be introduced to the basic skills required for in music. Introductionto a musicalinstrument with specialist tutoringthrough Shropshire MusicService – Integrated Music Experience. They will begin to develop performance skills and knowledge of how music is put together
Studentswill complete SOL on: Musical Elements,Rhythm and Notation,Ensemble Performance all focused around the learning of one instrument and use of voice. Studentswill have limited experience of music Somewill have no knowledge of musical notationso we are introducingskills at a foundationlevel. Studentswill build on this foundationand repeat someelementsin Year 8 in order to embed understanding of key skills and techniques.
Students will rotate between Dance/Drama& Music throughout the year.They will complete 3 half terms of music throughout the year alternating between music and dance/drama.
Students will be introduced to an instrument in the first term. They will learnsome basic technique and focus on understandingthe musical elements. This will allowstudents to embed knowledge and skills at an early stage.
Students will be encouraged to give constructive peer feedback on a regular bases to form part of the assessment process. Independence will be nurturedduring the rehearsalprocess. Students will be baseline tested on musical elements and critical thinking skills in the Autumn term.
When outstanding workis produced we will record these and showcase on our social media platforms. We willalso encourage all students to attend our thriving extra curricular programme.
Students can rehearse and develop performanceskills for practical assessments in one to one sessions and group sessions by booking practice rooms at break/lunchtimeor in sessions 0/session 6.
Students will develop confidence with key vocabularyand musical literacy skills.
Key assessments: Teacher assessments logged on Arbor and one peer assessment opportunityper sow. Teacher assessment will generate a PPG. Students respond to verbalteacher feedback every lesson during rehearsal time.
Autumn Term
Introduction to Musical Elements
Spring Term Instrument Technique.
SummerTerm Performance Technique
Studentsshould have a goodfoundationin on their given instrument and have a basic understandingof the musicalelements. They should be able to demonstratea simple performance on their instrument showingconsistenttechnique, note reading skills and accurate rhythm. Studentswill show knowledge of practice routines, a basic understandingof how to maintainand look after their instrumentand critical thinking skills applied to listening to music. Knowledgeand skills will be repeated, built on and extended each year to create a strongfoundationfor GCSE and to developa confidence
Studentsreceive 1 music lesson a week on a carrousel with Performing Arts, rotatingMusic/Dance/Music/Drama/Music/Danceon a half termly basis. Developmentof musical skills, embedding the practices learnt in year 7 and developing upon those skill through a variety of musical settings.
Studentswill completeSOL on: Blues, MusicalTheatre and Reggae, all units will include tasks based around performing, composingand appraising skills. Studentswill have a baseline level of skills and knowledge focused on one instrument, they will continue developing this instrumentand begin incorporating others.
Studentswill be expected to show a more refined level of skill on their instruments, know the basic musicalelementsand be begin to discuss these conceptswith relationto a variety of musicalsettings.They will be able to identify a number of orchestral, contemporaryand world instruments and ensembles.More able studentswill be pushed to develop a deeper understanding of musical literacy, both written terms and notation,and begin performing and composingmore complexpassages.
Students will continue to workon instruments they began learningin year 7, they will also begin to develop performanceskills on a wider variety of instruments such as keyboardand percussion. They will begin to developensemble musicianship skills as well as a deeper focus on compositional techniques. The Blues unit will have a focus on individualperformanceon the students’ year 7 instrument. They will begin to broadentheir compositional knowledge by developing an understanding of some basic structures and improvisationtechniques. This will include some practical demonstration of harmony. In term two students will develop performance skills with other musicians and develop compositions in a musical theatre style.
Students will begin embed the musical element knowledge they began learning in year 7 through a composition project.
Student will be introduced to more worldmusic in the summer term exploringReggae and Caribbeanmusic. Students will exploremusical appraisal techniques in greater depth and begin to use more complex concepts to describe and explain what they are hearing.
When outstanding workis produced we will record these and showcase on our social media platforms. We will also encourage all students to attend our thriving extra curricular programme. Students can rehearse and develop performanceskills for practical assessments in one to one sessions and group sessions by booking practice rooms at break/lunchtimeor in sessions 0/session 6.
Key assessments:
Formative teacher assessments throughout each term in the three key areas.
Focused assessment of performance a specified piece each term
Appraisingassessment to Summative appraising assessment to take place in summer term. Students respond to verbal teacher feedback every lesson during rehearsal time.
AutumnTerm The Blues
Focus on performance, understanding structure, improvisation and basic harmony, appraisingfocus throughoutyear.
Spring Term Musical Theatre
Focus on ensemble performance, developingbasic composition skills
SummerTerm Reggae Technique
Focus on ensemble performance, composition throughsong writing,
At the end of the year, studentswill able to play and improvisearound a blues scales,some jazz chords. They wouldhave composedand performed a short piece for a musical theatre scene. They will have also begun developinga repertoire of songsto perform featuring songsin a Reggae style. Finally, after completingregular Listening and Appraising tests where studentslisten and analyse unfamiliar music using the musical elements,studentswill be able to demonstrate a performance on their instrument showing developmentof technique, note reading skills and accurate rhythm.
All of the above skills will create a stable foundationfor Year 9.
Studentsreceive 1 music lesson a week on a carrousel with Performing Arts, rotatingMusic/Dance/Music/Drama/Music/Danceon a half termly basis. Developmentof musical skills, embedding the practices learnt in year 7 and 8 developing upon those skill through a variety of musical settings.
Studentswill complete SOL on: Film Music, Minimalism and Ensemble Musicianship skills in a GCSE Pathway,all units are based on the three core componentsof GCSE Music. Studentswill cover skills from the three GCSE Components– Performing, Composingand Appraising.
Studentswill be expected to show a more refined level of skill on their instruments, know how to discus musicusing the musical elements.More able studentswill be pushed to develop a deeper understanding of musical literacy, both written terms and notation,and begin performing and composingmore complex passages.
Next Steps: Pupils will have a clear knowledge and understandingof the GCSE structure movinginto year 10.
Students will focus on implementing skills developed in year 7 and 8, they will further develop performance skills on a wider variety of instruments such as keyboardand percussion. They will be using ensemble musicianship skills developed in year 8 as well as a deeper focus on compositional techniques. The Film Music unit will have a focus on composing to a set brief and will embed elements of AoS3 – Film Music. In term two Students will be formally introduced to AoS1 – Musical Forms and Structures and will begin to embed this knowledge through Minimalist composition, using works such as Tubular Bells and Clapping Music andwill begin composing their own music with use of GarageBandand other music technology. Termthree will focus aroundAoS2 and introducing the GCSE Set Works – Bach’s Badinerie and Toto’s Africa. Students will be encouraged to work as ensembles to develop performances and show basic understandingof the GCSE set works.
When outstanding workis producedwe will recordthese and showcase on our social media platforms. We will also encourage all students to attend our thriving extra curricular programme. Students can rehearse and develop performanceskills for practical assessments in one to one sessions and group sessions by booking practice rooms at break/lunchtimeor in sessions 0/session 6.
Key assessments:
Formative teacher assessments throughout each term in the three key areas.
Focused assessment of performance a specified piece each term Appraisingassessment to Summative appraising assessment to take place in summer term. Students respond to verbal teacher feedback every lesson during rehearsal time.
AutumnTerm Film Music
Combiningof performance and composition. Beginningto incorporate musical elements into performances and compositions.
Spring Term Minimalism
Focus on composition, refining composition skills, use of musical elements whilst working to a set brief
SummerTerm Ensemble Musicianship Performing, Composing, Listening and Appraising,
At the end of the year, studentswill begin to show a portfolioof film musicand minimalistcompositionsas well as being able to demonstrateextractsfrom the two GCSE set works. Finally, after completingregular Listening and Appraising testswhere studentslisten and analyse unfamiliar music using the musical elements,students will be able to demonstratea performance on their instrument showing developmentof technique, note reading skills and accurate rhythm. All of the above skills will begin embed the foundationskills for GCSE Musicin Key Stage 4..
The Big Picture Appraisal: To developtheir listeningand appraising skills throughthe study of the 2 set works in four areas of study.
Composition:To develop their compositionskills through composingin a variety of styles to begin a portfolioof compositionslastingat least 3 minutes.
Performance: To develop performing skills by rehearsing and refining solo and ensemble performances. Performance portfolio shouldhave a combinedtime of at least 4 minutes.
Appraisal: To developtheir listening and appraising skills throughthe study of the musicalelementsacrossa variety of stylesand genres. Areas of Study: 1) Formsand Devices,2) Music for ensemble, 3) Film Music, 4) Popular Music.
Building on the skills developed throughout KS3, students will use their knowledge and understanding of musical elements,contextand language to make critical judgements about the repertoire and contextof music within the areas of study using specific music vocabulary associatedwith a particular style or genre.
Component 1 – Performance: 30%, Component 2 – Composition: 30%, Component 3 - Appraisal: 40% Lessons will follow the Eduqas GCSE course plan. Students will have complete a set of analysis notes, spider diagrams and score studies for both set works. Students will have 1 composition lesson per week and will refine performance skills during weekly instrumentallessons and termly mock performances.
Students will consolidate their learning through weekly listening diaries and working independentlyon their compositions and performances.
Essay questions prep to discuss and mark in class. Performance on-going rehearsaland practice. Revisiting set-works throughout the year. All exam material is covered in year 10 so that we revisit and build upon knowledge in year 11.
Literacy and numeracy are explored through extended exam questions and score studies. When outstanding workis produced we will record these and showcase on our social media platforms. We will also encourage all students to attend our thrivingextra curricularprogramme.
Students can rehearse and develop performanceskills for practical assessments in one to one sessions and group sessions by booking practice rooms at break/lunchtimeor in sessions 0/session 6.
Key assessments:
Score Studyon each set work.
Mock performance. Composition hand-in.
Low stakes testing
Set work key terms.
Deep marking points Set
work Essays
Home learning - Set work revision and performance
essays Examinations
Year 10 mock exams.
Conferencing/MAD time
Moderation March year 11
Autumn AoS1: Forms and Devices
Composing using structure and melody, class performance of Badinerie by Bach
AoS4: Popular music.
Rock and Pop terminology, primary & secondary chords, class performance of Africa by Toto.
Spring AoS2: Music for Ensemble
Composition, jazz, musical theatre,use of texture and sonority.
AoS3: Film Music
Composing to a brief,exploring relationship of story & music, effect of audience and use of musical elements to create a mood.
Summer
Consolidation of 4 Areas of Study
Appraisal:. All set works shouldbe coveredby the end of year 10. Studentswill have written a completeset of analysisnotes,spider diagram and score study.
Composition:Studentswill have begun composingin a variety of styles and have be toolsto completea set-brief compositionin year 11.
Performance: An soloand ensemble performance mockshould be recorded by the end of year 10.
Whatare the next steps.How can the knowledge/skillsfrom this year be extended next year?
Year 11 appraisal: exam technique, listening questions, unfamiliar comparisonessay questions. Composition:A high quality set-brief compositionwith all appropriate techniques.
Performance: A solo and ensemble performance of a suitable standard. Performancesshould reflect ABRSM/Trinity/RockSchool Grade 2 standard or above.
30% and 72 marks
What is the big picture?
Learners are required to complete 2 performances on their chosen instrument, demonstrating their knowledge and understanding music through performing. All learners are required to perform a minimumof two pieces, of which at least one must be as part of an ensemble performance lasting at least one minute. The other piece(s) may be performed either solo and/or as part of an ensemble.One piece must be linked to one of the four areas of study.
Studentswill completeall aspectsof the unit and will be marked using last years GCSE boundaries, and be graded to the same standard as year 11 Finale (Year 11) performance repertoire should be decided on by Summer Half term, in order to spend enough time in rehearsal to complete performances in the Autumnterm of year 11. Personalised summerrehearsal programswill be decided upon in Summer 2 half term. How does this link to and build on the previous year of learning?
Studentswill cover the fundamental performance skills needed in order to produce a repertoire of pieces suitable for their year 11 final performances. Students will have coveredseveral skills in key stage three and will have gained experience on a variety of different instruments.This experience shouldbe utilised in order to make choices of instrumentsand suitable repertoire to be carried forward into year 11.
Intent: What do you want the studentsto be able to know and do?
Knowledge Skills
Good Studentswill demonstrate a minimum of two performances, one of which must be an ensemble performance.
Studentswill perform for a combined minimum of 3 minutes. Repertoirewill be below grade 3 standard.
Students will demonstrate the ability to read basic notationappropriate to their instrument.
Students will demonstrate a minimum level of skill in the following areas:
• technical control
• expression and appropriate interpretation
• accuracy of rhythm and pitch
• appropriate pace and fluency
• effective use of dynamics
• stylistic awareness
• empathy(in ensembleplaying).
Ability level will reflect the ‘Easier than Standard’ repertoire
General features of an ‘Easier than standard’ piece are:
• A piece in an easy key for the instrument
Accuracy
• A less secure performance in terms of
• rhythm and/or pitch with frequent
• inaccuracies
• Irregularities in tempo,which compromise
• the fluency, occur more frequently
• Performance directions are followed inconsistently throughout the performance
Technical Control
• Inconsistent vocal/instrumental
• technique and intonation(where appropriate) throughout the performance
• Inconsistent control of sonority (tone) with some contrast where needed in the music
•The performance has inconsistent projection
Expression and Interpretation
An inconsistent performance which is
• Simple rhythmsand a narrow pitch range with simple
• intervals
• Few dynamic contrasts
• Simple or repetitive structure and phrase structure
• Steady tempo
• Single sonorityor tone quality required with limited
• changes in articulation
• Stylistically simple
Better Students will demonstrate at least two performances, one of which must be an ensembleperformance.
Studentswill perform for a combinedof 4 minutes. Repertoire will be of a grade 3 standard.
Students will demonstrate the ability to read basic notation appropriate to their instrumentand perform with a higher level of confidence to show a deeper level of understanding of their chosen instrument and repertoire.
Students will demonstrate an intermediate level of skill in the following areas:
• technical control
• expression and appropriate interpretation
• accuracy of rhythm and pitch
• appropriate pace and fluency
• effective use of dynamics
• stylistic awareness
• empathy(in ensembleplaying).
Ability level will reflect the ‘Standard level of difficulty’ repertoire
General features of a ‘Standard level of difficulty’ piece are:
• A piece in an easy or moderate key for the instrument
• The rhythmswill be varied, including dotted notes or triplets
• and the pitch range reasonably wide with wider intervals
• Dynamic contrasts including crescendo and diminuendo
• A contrastingsectionor a sectionwith different technical
• demands or different phrase lengths
• Possible contrast in tempo
• Some contrastsin sonorityor tone quality and articulation
• Some stylistic challenges
not always in keeping with the chosen style
Inconsistent communicationwith the audience
Some sense of rapport and balance between parts where other performers are present
Some effective balance between live and pre-recorded tracks, where appropriate
Accuracy
• The performance is generally accurate in
• terms of rhythm and/or pitch, however,
• there are occasional slips
• An appropriate tempo is generally
• maintained throughout, however the fluency of performance is compromised occasionally
• Most performance directions are followed appropriately in the performance
Technical Control
• Generally reliable vocal/ instrumental
• technique and intonation(where appropriate) throughout the performance
• Generally secure controlof sonority(tone) with the use of contrast mainlyappropriate to the music
•The performance is generally well- projected
Expression and Interpretation
• A generally expressive performance
• mainly in keeping with the chosen style
• Competent communication sustaining
• audience interest throughout most of
• the performance
• Generally effective rapport with other
• performers, where appropriate, resulting in a mostly balanced performance
• Generally effective balance between live and pre-recorded tracks, where appropriate
Excellent Students will demonstrate two performances, one of which must be an ensembleperformance.
Studentswill perform for a combined minimum of 3 minutes. Repertoire will be of a grade 3 standard or above. Students will demonstrate the ability to read basic notation appropriate to their instrumentand perform with a high level of confidence to show a deeper level of understanding of their chosen instrument and repertoire. They will show a higher level of proficiency on their chosen instrument and will demonstratethe ability to choose a repertoire that is sympatheticto their ability levels and perform their chosenrepertoire at a high standard.
Students will demonstratea high level of skill in the following areas:
• technical control
• expression and appropriate interpretation
• accuracy of rhythm and pitch
• appropriate pace and fluency
• effective use of dynamics
• stylistic awareness
• empathy(in ensembleplaying).
Ability level will reflect the ‘More Difficult Than Standard’ repertoire
General features of a ‘More difficult than standard’ piece are:
• A piece in any key appropriate for the instrument
• A piece displaying some intricate rhythms and a wide pitch
• range for the instrument
• The selected piece will allow for greater emphasis on
• interpretation
• Full range of dynamics
• Several contrastsin technical demands and phrase
• structure
• Contrastsin tempo or challenging tempo
• Contrastsin sonority or challenging tone quality with more
• complexarticulation
• Contrastsin style or greater stylistic challenges
• An accurate performance, secure in terms
• of rhythm and/or pitch
• An appropriate tempo is sustained
• throughout,resulting in a fluent
• performance
• All performance directions are followed
•appropriately throughout the performance
Technical Control
• Secure vocal/instrumental technique
• and intonation(where appropriate)
• throughoutthe whole performance
• Secure control of sonority(tone) with
• the use of contrast fully appropriate
• to the music
•The performance is well-projected
Expression and Interpretation
• An expressive performance in keeping
• with the chosen style
• Effective communication sustaining
• audience interest throughout the
• performance
• Effective rapport with other performers,
• where appropriate, resulting in a
• balanced performance
• Effective balance between live and
• pre-recorded tracks,where appropriate
What are the opportunities for “deeplearning”?
Questioning Rehearsals
Final performance
Peer assessmentof real Year 11 performances, peer modelling of performances and analysis of model performances moderated by exam board.
Use of different instrumentation– some students may be suited to performing on multiple instruments.
Different music roles –ensembleperformances requiring accompanists and harmony singing
Examples of Band 4 (top tier) performances shared and reviewed.
How do we ensure progress of SEND and PP students?
Mixed ability groups in initial lessons so more able can support SEND. SEND register checkedto support each student’s needs.
For final assessment students are grouped on ability. More one to one supportfor less able groups from teacher including peripatetic music staff.
Extra time given in rehearsals. Support given in writtenresources, such as notation shownin different forms, use of aural skills for learning pieces and use of video resources for learning repertoire.
What mightbe the pitfalls?
What home-learning tasksare planned?
What work will be “deep-marked”? What tracking data will be recorded?
Absence of student or othersin their group.
Inhibitions of performing.
Lack of rehearsal/practice time for students of lower abilities
Lack of access to instruments/rehearsal space.
Students may book the studio to rehearse for assessment. Students will complete portfolio at home.This will be broken down into three sections and students will have two weeks to complete each section. Students will also be required to carry out extensive research into their stimuluschoice in the early stages of the devising process.
Student performances will be videoed throughoutcourse, ‘mock’ performance assessment will be before end of Autumn 2 half term, pieces will be graded and reviewed, studentswill have the opportunity to review their own and peer review performances in order to see mistakes and limitations.
- Final assessmenton Arbor
- Audio recordings of performances must be taken before Easter Holidays, to give suitable time for marking and moderation of performances. Markswill be sent off to the exam board.
Engagement: What will be the “wow” moments?What are the “hooks” for student engagement?
Studentshave the opportunity to choosetheir own repertoire and decide which instrumentthey will be performing on for their final performances. They should have decided on the repertoire by the end of year 10 so will have the opportunity to work collaboratively with others (including other students not being assessed for music) to develop performances. Students will have the opportunity to perform in concerts and out-of-classroom performing opportunities to give them a ‘real-life’ performing opportunityto help build confidence and gain an understanding of dealing with nervous.
Impact:How will we know if outstanding learning has occurred?
Teachers will observe skills developing throughout the unit. Engagement, participation, applying knowledge, performance, understanding, confidence and verbal evaluation.Video and audio evidence of performances will be gathered in order to make coaching judgements and ultimately make final grade decisions. Performances will be reviewed regularly and high standard model performances will be analysed to gather experience of how to achieve top grades.
Next steps: How will this link to subsequent learning?
All skills used in performance can be adapted and related to in Component2 and 3, aural perception skills and musicalliteracy skills are required in all three components. Studentsmay perform their own compositionswhich will enable cross-use of coursework,should it be required.
30% and 72 marks
What is the big picture?
Learners must submit two compositionswith a total playing time of between 3-6 minutes.
Time frame: 1 term
1. A compositionwhich responds to a brief set by WJEC. The brief will be released during the first week of Septemberin the academicyear in which the assessment is to be taken.Learners select one from a choice of four briefs, each related to a different area of study:
Areaof study 1: Musical Forms and Devices
Areaof study 2: Music for Ensemble
Area of study 3: Film Music
Areaof study 4: Popular Music.
2. A free composition.Learners will composea piece of music in a style of their own choice.Learners will set their own brief for this composition.The brief itself is not assessed; however, learners are assessedon their musical response to the brief. Students will produce a portfolio of evidence, which can be developed into final compositionsduring Autumn term 1, final compositionswill be completedby the end of Autumn 2 half term.
Studentswill begin developing a portfolio of evidence so thatis can be built upon in year 11. Students should aim to further refine their compositionportfolio which will then be submittedfor final evidence in the Spring term of year 11. Studentswill completeall aspectsof the unit and will be marked using last years GCSE boundaries.
How does this link to and build on the previous year of learning?
Studentswill have developed basic compositionskills in a variety of areas in key stage three. Students will have a foundationof knowledge of a variety of different styles and be able to composesimple melodic ideas which can be applied in a variety of ways. Studentswill have begun developing a ‘musical stimuluslibrary’ of ideas that they will be able to build upon in their compositions.
Intent: What do you want the studentsto be able to know and do?
Good Learners will develop a minimum of two compositionswith a minimum combined length of 3 minutes.
Learners must completeone compositionto a brief set by the exam board and one free composition.Learners may use compositionalideas they have developed in previous academicyears.
All compositionsmustrelate to one of the four areas of study:
Area of study 1: Musical Formsand Devices
Area of study 2: Music for Ensemble
Area of study 3: Film Music
Area of study 4: Popular Music.
• Learners will be able to demonstrate a basic level of knowledge of the overarching elements of music.
Learners will develop music literacy skills including:
• Basic knowledge of treble and bass clef notation,
• Limiteduse of scales, applicationof different sonorities,
• Basic applicationof different musicaltextures,
• Some use of dynamics and tempo appropriate to chosen musical styles.
• A limited ability to develop musical ideas which are coherent and appropriate to a set brief.
• Application of compositionalstyles which are, on the whole, contextually appropriate.
Compositionswill generally show a Band 2 level of application of skills in the followingthree areas.
• Learners must show the knowledge of various compositionaltechniques and apply them in a relevant style. Applicationmay be limitedbut contextually appropriate.
• Learners must show knowledge of sonoritiesappropriate to different musical eras, styles and genre.
• Learners should be able to demonstratetheir knowledge both through practical applicationof their compositionskills and through a written compositionlog, which will document their compositional process and highlight the skills they have used.
• Compositionlogsmay have limited details but demonstrate an accurate commentaryon the individual compositionprocess. Learners must accurately documenthow their compositionrelates to their chosen area of study.
Creativity and Developmentof Musical Ideas
• Ideas are simple, offering some potentialfor development
• Some ideas are partially developed
• Somecontrastsof tone colour and mood
Technical Control of Musical Elements and Resources
• Some choicesof elements and resources are effective
• Somemusical elements are used inconsistently
• Inconsistent control of resources, including technology
Structure and StylisticCoherence
• Inconsistent organisation with some effective presentation of musical ideas
• The style and character is inconsistentin response to the chosen brief
• The outcome is inconsistent displaying some sense of coherence
Better Learners will complete two compositionswith a combined time of between 3-6 minutes.
Learners will completeone compositionto a brief set by the exam board and a free composition,both must relate to one of the four areas of study. Learners demonstrate mostly effective application of compositionaltechniques related to their chosen areas of study.
• Learners will be able to demonstratea good level of knowledge of the overarching elements of music.
• Learners must show the knowledge of various compositionaltechniques and apply them in a relevant style. Applicationwill be contextually appropriate and offer some potentialfor development.
• Learners must show good knowledge of sonorities appropriate to different musicaleras, styles and genre and be able to apply them to their compositions.
• Learners should be able to demonstratetheir knowledge both through practical applicationof their compositionskills and through a written compositionlog, which will document their compositional process and highlight the skills they have used.
• Compositionlogs will be detailed and demonstrate an accurate commentary on the individual compositionprocess. Learners must accurately document how
Learners will develop music literacy skills including:
• Good knowledgeof treble and bass clef notation,
• A wider use of scales, applicationof different sonorities,
• Appropriate application of different musical textures,
• Use of dynamics and tempo appropriate to chosen musical styles.
• Ability to develop musicalideas which are coherent and appropriate to a set brief.
• Application of compositional styles which are contextually appropriate. Compositionswill generally show a Band 3 level of application of skills in the followingthree areas.
• Ideas are generally effective, offering potential for further development
• The content is competently developed throughout the piece
• Generally effective contrastsof tone colourand mood
their compositionrelates to their chosen area of study. Compositionlogs will offer some potentialfor further development of compositions.
• Generally effective choice of elements and resources
• A variety of musicalelementsare used competently
• Resources, including technology, are generally well controlled
• A well-organised piece with effective presentation of musical ideas
• The style and character is generally effective in response to the chosen brief
• The outcomeis generally effective and coherent
Excellent Learners will complete two compositionswith a combined time of between 3-6 minutes.
Learners will completeone compositionto a brief set by the exam board and a free composition,both must relate to one of the four areas of study. Learners demonstrate highly effective application of compositionaltechniques related to their chosenareas of study.
• Learners will be able to demonstrate a strong level of knowledge of the overarching elements of music.
• Learners must show the knowledge of various compositionaltechniques and apply them in a relevant style. Applicationwill be contextually appropriate and demonstrate a degree of development through their compositionalprocess, resulting in two highly effective final compositions.
• Learners must show good knowledge of sonorities appropriate to different musicaleras, styles and genre and be able to apply them to their compositions.
• Learners should be able to demonstratetheir knowledge both through practical applicationof their compositionskills and through a written compositionlog, which will accurately document their compositionalprocess and highlight the skillsthey have used.
• Compositionlogs will be detailed and demonstrate an accurate commentary on the individual compositionprocess. Learners must accurately document how their compositionrelates to their chosen area of study and log the use of any ideas they have used from external sources. Compositionlogs will demonstrate that learners have identified areas within their compositionswith potentialfor further development.
Learners will developmusic literacy skills including:
• Strongknowledge of treble and bass clef notation,
• A wider use of scales, applicationof different sonorities which reflect the areas of study chosen for each composition,
• Strong application of different musical textures,
• Good use of dynamics and tempo appropriate to chosen musical styles.
• Ability to develop musicalideas which are coherent and appropriate to the set brief.
• Strong application of compositional styles which are contextually appropriate. Compositionswill generally show a Band 4 level of application of skills in the followingthree areas.
• Ideas are highly effective, offering much potential for creative development
• The content is skilfully developed throughoutthe piece
• Highly effective contrastsof tone colour and moods
• Highly effective choiceof elementsand resources
• A wide variety of musical elements are used skilfully
• Resources, including technology, are skilfully controlled
What are the opportunities for “deep-learning”?
Questioning
Rehearsals
Masterclasses on different musical styles to show appropriate compositions skills needed for each of the four areas of study. Use of flipped learning processes to ensure compositionalskills are embedded early and application of skills can then be developedat a higher level.
How do we ensure progress of SEND and PP students?
Mixed ability groups in initial lessonsso more able can support SEND. SEND register checkedto support each student’s needs.
Composition exercisescan be used for development with scaffolding to and skill ladders to demonstrate how students should approach their compositions. Stimulus libraries should be developed throughout year 10 showing appropriate phrases and musical ideas that can be built upon for final compositions.
Structure and StylisticCoherence
• A very well-organised piece with a highly effective presentation of musical ideas
• The style and character is highly effective in response to the chosenbrief
• The outcome is highly effective, musical and fully coherent
What mightbe the pitfalls? What home-learning tasks are planned? What work will be “deep-marked”? What trackingdata will be recorded?
Lack of ICT equipment for accessing cloud based learning platforms, Lack of home ICT equipment preventing work from being continued by students in their own time.
Lack of confidence in compositional ideas and limited ability to play a wider variety of instruments can lead to misconceptions and mis-application of compositional ideas which are not suited to the chosen instrumentation.
Studentsmay book the studio to practice their composition skills. Students will have accessto online learning platforms to facilitate flipped learning approaches and enable compositionsto be continued at home. Cloud based software so compositions can be shared between home and school,as well as ability for peer review and on-going student-teacher dialogue.
There will be a progress point one, commenton how to improve with a grade. There will be a teacher assessmentin the final lessonwith a commentand grade. All work will be given a GCSE grade based on last year’s boundaries of this unit.
On-going dialogue will be active on each compositionfor studentsusing cloud-based composition platform. Compositionswill be regularly downloadedand backed up in order for peer review and moderation.
Marking criteria is shared with students and compositionsare regularly reviewed against them. Model compositionsdemonstrating the different bands of marks are shared and analysed.
Final assessment entered on Arbor
Final submissionof compositionswill be fore Easter holiday of Year 11 to ensure time for marking and moderation before submission to exam board. Marks will be sent off to the exam board before early May deadline.
Engagement: What will be the “wow” moments?What are the “hooks” for student engagement?
Students have the opportunityto choosethe area of study in which they will be composing,for both the set brief and free composition.Studentshave the opportunity to build upon work they may have already completedin earlier years which may offer a higher level of refinement and show applicationof potentialfor improvements. They should have begun composingtheir free compositionin year 10 and will be expectedto build up on this. Studentswill have the opportunityto ‘deep-dive’ into their chosenmusicalstyles in order to analyse the techniques and devices they need to apply in order to create a highly effective composition.Studentswill have the opportunity to present their compositionsin concerts and out-of-classroom performing opportunities to give them a ‘real-life’ performing opportunity to help build confidence, to gain an understandingof dealing with nervous, and to hear their compositionsperformed by other musicians in order to understand further areas for improvement.
Impact: How will we know if outstanding learning has occurred?
Teachers will observe skills developing throughout the unit. Engagement, participation, applying knowledge, performance, understanding, confidence and verbal evaluation.Video and audio evidence of compositionswill be gathered in order to make coachingjudgements and ultimately make final grade decisions. Compositions will be reviewed regularly and high standard model compositionswill be analysed to gather experience of how to achieve top grades.
Next steps: How will this link to subsequent learning?
All skills used in compositioncan be adapted and related to in Component1 and 3, aural perception skills and musicalliteracy skills are required in all three components. Studentsmay perform their own compositionswhich will enable cross-use of coursework, should it be required.
40% and 96 marks.
What is the big picture?
Time frame: 1 term
This component requires Learners to develop knowledge and understanding of musical elements, musical contextsand musical language. Learners will develop a knowledge and understandingof music through the following four areas of study:
• Areaof study 1: Musical Forms and Devices
• Areaof study 2: Music for Ensemble
• Areaof study 3: Film Music
• Areaof study 4: Popular Music.
Component3 will be used as a mock exam in year 10 and 11, before sittinga final exam at the end of year 11. Studentswill completeall aspectsof the unit and will be marked using last years GCSE boundaries.
How does this link to and build on the previous year of learning?
Studentswill have had a foundation knowledge of the musical elements,musical language and have explored music in a variety of contextsthroughoutkey stage three.
Intent: What do you want the studentsto be able to know and do?
Knowledge Skills
Good Area of study 1: MusicalForms and Devices
• Students will demonstrate a basic knowledge of some of the commonmusicalforms and devices used in the Western Classical Tradition.
• Students will show reasonable knowledge of the Baroque, Classical and Romanticeras and how to identify music between them.
• Students will have reasonable knowledge of binary, ternary, minuet and trio rondo, variation and strophic forms.
Area of study 2: Music for Ensemble
• Studentswill demonstrate a basic knowledge of the use of texture and sonority.
• Studentswill show a reasonable knowledge of music composed for ensemble,such as jazz and blues, musicaltheatre and chamber music
• Students should be able to consider how music is composedfor small groups of instruments and voices.
Area of study 3: Film Music
Students should demonstrate a reasonable use of the following musical language, showing that they can discuss music in context, demonstrate a reasonable understanding of the purpose and intention in a composer’swork.
Musical Elements Words:
melody, harmony, tonality, form and structure, dynamics, sonority, texture, tempo, rhythm, metre
Studentswill demonstrate the ability to read, and write, simple musical notationusing treble and bass clef. Students may also demonstrate some use of graphic notationwhere traditional musical notationis not used. Students may also show a basic understandingof instrument specific notationsuch as TAB.
Students will show the ability to identify some musical patterns by ear, and recognise some chords.
Students shouldbe able to use roman numerals to identify chord I, IV and V. Studentsshould show a basic understandingof how to read some chord notation,such as identifying between major and minor chords. Studentsshould show a basic level of skill in appraising music through the explorationof a wide variety of music linked to the four areas of study.
Studentsshould show a basic ability to analyse a piece of music set out by the exam board as a ‘set work’ with regards to the musicalelements.
• Students should show a reasonable knowledge of how music contributesto the film industry and the varied areas in which music plays a part.
• Students should have a reasonable knowledge of music which is used for the purpose of dramatic underscore and thematicmusic, such as leitmotif.
• Students should show a reasonable knowledge of how music for film is created, developed and performed, and the impactthis has on the audience.
Area of study 4: Popular Music
• Studentsshould show a reasonable knowledge of popular music from several genres.
• Learners should demonstrate a reasonable knowledge of popular music practices through performance and compositionin component1 and 2.
• Students should demonstrate a reasonable knowledge of how the musicalelements explored in Area of study 1 are applied in the contextof popular music.
Area of study 1: MusicalForms and Devices
• Students will demonstrate a sound knowledge of some of the commonmusicalforms and devices used in the Western Classical Tradition.
• Students will show good, working knowledge of the Baroque, Classical and Romanticeras and how to accurately identify some differences between them.
• Students will have good knowledge of binary, ternary, minuet and trio rondo, variationand strophic forms and be able to use them in component 2.
Area of study 2: Music for Ensemble
• Students will demonstrate a sound knowledge of the use of texture and sonority.
• Students will show a good knowledge of music composedfor ensemble,such as jazz and blues, musicaltheatre and chamber music, and be able to perform examples for component1.
• Students should be able to consider how music is composedfor small groups of instruments and voices.
Area of study 3: Film Music
Studentswill identify the main features of binary, ternary, minuet and trio, rondo,variation and strophic forms, including how composersuse a variety of musicaldevices to create and developmusic
Through listening to and/or performing examples from chamber music, musicaltheatre, jazz and blues, learners will study texture, including how composerscombine musical lines in the following textures: Monophonic, homophonic, polyphonic, unison, chordal, layered, melody and accompaniment,round, canon, countermelody. Studentswill be able to consider how texture is used in a variety of instrumental and vocal groupings.
Students should demonstrate a reasonable use of the followingmusical language, showing that they can discuss music in context, demonstrate a reasonable understanding of the purpose and intention in a composer’swork.
Musical Elements Words:
melody, harmony, tonality, form and structure, dynamics, sonority, texture, tempo,rhythm, metre
Studentswill demonstrate the ability to read, and write, simple musical notationusing treble and bass clef. Students may also demonstrate some use of graphic notationwhere traditional musical notationis not used. Students may also show a basic understanding of instrument specific notationsuch as TAB.
Students will show the ability to identify some musical patterns by ear, and recognise some chords.
Students shouldbe able to use roman numerals to identify chord I, IV and V. Studentsshould show a basic understandingof how to read some chord notation,such as identifying between major and minor chords.
Studentsshould show a basic level of skill in appraising music through the explorationof a wide variety of music linked to the four areas of study.
• Students should show a sound knowledge of how music contributesto the film industry and the varied areas in which music plays a part.
• Studentsshould have a solid, working knowledge of music which is used for the purpose of dramatic underscore and thematic music, such as leitmotif.
• Students should show a reasonable knowledge of how music for film is created, developedand performed, and the impact this has on the audience and be able to demonstratethis knowledge in component 2.
Area of study 4: Popular Music
• Students should show a sound knowledge of popular music from several genres.
• Learners should demonstrate a good knowledge of popular music practices through performance and compositionin component 1 and 2.
• Students should demonstrate a good knowledge of how the musicalelements explored in Area of study 1 are applied in the contextof popular music.
Excellent Area of study 1: MusicalForms and Devices
• Students will demonstrate an excellent knowledge of some of the common musical forms and devices used in the Western Classical Tradition.
• Students will show excellent knowledge of the Baroque, Classical and Romanticeras and how to accurately identify some differences between them.
• Students will have excellent knowledge of binary, ternary, minuet and trio rondo, variationand strophicforms and be able to use them confidently in component 2.
Area of study 2: Music for Ensemble
• Students will demonstrate an excellent knowledge of the use of texture and sonority.
• Students will show a wide knowledge of music composedfor ensemble,such as jazz and blues, musicaltheatre and chamber music, and be able to perform several examples for component1.
• Students should be able to consider how music is composedfor small groups of instruments and voices.
Area of study 3: Film Music
Studentsshould show a basic ability to analyse a piece of music set out by the exam board as a ‘set work’ with regards to the musicalelements. Studentswill identify the main features of binary, ternary, minuet and trio, rondo,variation and strophic forms, including how composersuse a variety of musicaldevices to create and developmusic
Through listening to and/or performing examples from chamber music, musicaltheatre, jazz and blues, learners will study texture, including how composerscombine musical lines in the following textures: Monophonic, homophonic, polyphonic, unison, chordal, layered, melody and accompaniment,round, canon, countermelody. Studentswill be able to consider how texture is used in a variety of instrumental and vocal groupings.
Students should demonstrate a reasonable use of the following musical language, showing that they can discuss music in context, demonstrate a reasonable understanding of the purpose and intention in a composer’swork.
Musical Elements Words:
melody, harmony, tonality, form and structure, dynamics, sonority, texture, tempo, rhythm, metre Studentswill demonstrate the ability to read, and write, simple musical notationusing treble and bass clef. Students may also demonstrate some use of graphic notationwhere traditional musical notationis not used. Students may also show a basic understanding of instrument specific notationsuch as TAB.
Studentswill show the ability to identify some musicalpatterns by ear, and recognise some chords.
Students shouldbe able to use roman numerals to identify chord I, IV and V. Studentsshould show a basic understanding of how to read some chord notation,such as identifying between major and minor chords. Studentsshould show a basic level of skill in appraising music through the explorationof a wide variety of music linked to the four areas of study.
• Students should show an excellent knowledge of how music contributesto the film industry and the varied areas in which music plays a part.
• Students should have an excellent knowledge of music which is used for the purpose of dramatic underscore and thematicmusic, such as leitmotifand be able to accurately demonstrate these practices in component1 and 2.
• Students should show an excellent knowledge of how music for film is created, developedand performed, and the impact this has on the audience and be able to demonstratethis knowledge in component 2.
Area of study 4: Popular Music
• Students should show an excellent knowledge of popular music from several genres.
• Learners should demonstrate an excellent knowledge of popular music practices through performance and compositionin component1 and 2.
• Students should demonstrate an excellent knowledge of how the musicalelements explored in Area of study 1 are applied in the contextof popular music.
Studentsshould show a basic ability to analyse a piece of music set out by the exam board as a ‘set work’ with regards to the musicalelements. Studentswill identify the main features of binary, ternary, minuet and trio, rondo,variation and strophic forms, including how composersuse a variety of musicaldevices to create and developmusic
Through listening to and/or performing examples from chamber music, musicaltheatre, jazz and blues, learners will study texture, including how composerscombine musical lines in the following textures: Monophonic, homophonic, polyphonic, unison, chordal, layered, melody and accompaniment,round, canon, countermelody. Studentswill be able to consider how texture is used in a variety of instrumental and vocal groupings.
What are the opportunities for “deep-learning”?
Practical application of knowledge through performance and compositions
Regular ‘long-mark’ questions.
Final exam.
Peer assessment of class exam questions. Examples of full marks answers shared.
Practical exploration of each area of study, through performance,
How do we ensure progress of SEND and PP students?
What might be the pitfalls? What home-learning tasks are planned?
Whatwork will be “deepmarked”?
What tracking data will be recorded?
Mixed ability groups in initial lessonsso more able can support SEND.
SEND register checked to support each student’s needs.
More one to one support for less able students from teacher.
Extra time given in exams. Help sheetsand learning ladders to support theory knowledge for application in component1 and 2.
Studentswho struggle in English may find this challenging as they are required to answer a 10 mark long-answer question as part of the written paper.
Questionsrequire analytical and evaluative approaches to listeningto music which then must be transferred on to the page for the exam.
Students will have an exam style question to complete at home once every two weeks. This will comprise of a mixture of short/long answer questions from Section A/B.
Every fortnight the exam style questionwill be marked against last year’s GCSE music mark scheme and studentswill receive a grade based on last year’s boundaries.
- Final assessment on Arbor
- Final unit to be assessed in Year 11 via Externally assessed exam.
composition, group Musical dictionary to be work and independent compiled by learners work. Flipped learning throughout course. approaches for theory Session6 intervention concepts and learning programme. of musical vocabulary.
Engagement: What will be the “wow” moments?What are the “hooks” for student engagement?
Impact: How will we know if outstanding learning has occurred?
Teachers will observe skills developing throughout the unit. Engagement, participation, applying knowledge, performance, understanding, confidence and verbal evaluation, fortnightly exam style question written homework tasks.
Next steps: How will this link to subsequent learning?
All skills used in component3 shouldbe applied to in component1 and 2, aural perception skills and musicalliteracy skills are required in all three components. This is the final exam of their GCSE Music course.
30% and 72 marks
Time frame: 1 term
What is the big picture?
Learners are required to complete 2 performances on their chosen instrument, demonstrating their knowledge and understanding music through performing. All learners are required to perform a minimumof two pieces, of which at least one must be as part of an ensemble performance lasting at least one minute. The other piece(s) may be performed either solo and/or as part of an ensemble.One piece must be linked to one of the four areas of study.
This will be used as a mock before they completetheir final performance recording in year 11. Studentswill completeall aspectsof the unit and will be marked using last years GCSE boundaries.
Final Performance should be recorded before Spring Half Term. How does this link to and build on the previous year of learning?
Studentswill have begun rehearsing their final performance repertoire in year 10, they will have begun practising the instrumentalskills required to complete component1 in Key Stage 3 on various instruments.Students should have chosen their final repertoire by Summer Half Term of Year 10.
Intent: What do you want the studentsto be able to know and do?
Knowledge Skills
Good Students will demonstrate a minimum of two performances, one of which must be an ensemble performance.
Studentswill perform for a combined minimum of 3 minutes.
Repertoirewill be below grade 3 standard.
Students will demonstrate the ability to read basic notationappropriate to their instrument.
Students will demonstrate a minimum level of skill in the following areas:
• technical control
• expression and appropriate interpretation
• accuracy of rhythm and pitch
• appropriate pace and fluency
• effective use of dynamics
• stylistic awareness
• empathy(in ensembleplaying).
Ability level will reflect the ‘Easier than Standard’ repertoire
General features of an ‘Easier than standard’ piece are:
• A piece in an easy key for the instrument
• Simple rhythmsand a narrow pitch range with simple
• intervals
• A less secure performance in terms of
• rhythm and/or pitch with frequent
• inaccuracies
• Irregularities in tempo,which compromise
• the fluency, occur more frequently
• Performance directions are followed inconsistently throughout the performance
Technical Control
• Inconsistent vocal/instrumental
• technique and intonation(where appropriate) throughoutthe performance
• Inconsistent control of sonority (tone) with some contrast where needed in the music
•The performance has inconsistent projection
Expression and Interpretation
An inconsistent performance which is not always in keeping with the chosen style
• Few dynamic contrasts
• Simple or repetitive structure and phrase structure
• Steady tempo
• Single sonorityor tone quality required with limited
• changes in articulation
• Stylistically simple
Better Students will demonstrate at least two performances, one of which must be an ensembleperformance.
Studentswill perform for a combinedof 4 minutes. Repertoire will be of a grade 3 standard.
Students will demonstrate the ability to read basic notationappropriate to their instrumentand perform with a higher level of confidence to show a deeper level of understanding of their chosen instrument and repertoire.
Students will demonstrate an intermediate level of skill in the following areas:
• technical control
• expression and appropriate interpretation
• accuracy of rhythm and pitch
• appropriate pace and fluency
• effective use of dynamics
• stylistic awareness
• empathy(in ensembleplaying).
Ability level will reflect the ‘Standard level of difficulty’ repertoire
General features of a ‘Standard level of difficulty’ piece are:
• A piece in an easy or moderate key for the instrument
• The rhythmswill be varied, including dotted notes or triplets
• and the pitch range reasonably wide with wider intervals
• Dynamic contrasts including crescendo and diminuendo
• A contrastingsectionor a sectionwith different technical
• demands or different phrase lengths
• Possible contrast in tempo
• Some contrastsin sonorityor tone quality and articulation
• Some stylistic challenges
Excellent Students will demonstrate two performances, one of which must be an ensembleperformance.
Studentswill perform for a combined minimum of 3 minutes. Repertoire will be of a grade 3 standard or above.
Some sense of rapport and balance between parts where other performers are present
Some effective balance between live and pre-recorded tracks, where appropriate
Accuracy
• The performance is generally accurate in
• terms of rhythm and/or pitch, however,
• there are occasional slips
• An appropriate tempo is generally
• maintained throughout, however the fluency of performance is compromised occasionally
• Most performance directions are followed appropriately in the performance
Technical Control
• Generally reliable vocal/ instrumental
• technique and intonation(where appropriate) throughoutthe performance
• Generally secure controlof sonority(tone) with the use of contrast mainlyappropriate to the music
•The performance is generally well- projected
Expression and Interpretation
• A generally expressive performance
• mainly in keeping with the chosen style
• Competent communication sustaining
• audience interest throughout most of
• the performance
• Generally effective rapport with other
• performers, where appropriate, resulting in a mostly balanced performance
• Generally effective balance between live and pre-recorded tracks, where appropriate
Accuracy
• An accurate performance, secure in terms
• of rhythm and/or pitch
Students will demonstrate the ability to read basic notation appropriate to their instrumentand perform with a high level of confidence to show a deeper level of understanding of their chosen instrument and repertoire. They will show a higher level of proficiency on their chosen instrument and will demonstratethe ability to choose a repertoire that is sympatheticto their ability levels and perform their chosenrepertoire at a high standard. Studentswill demonstrate a high level of skill in the following areas:
• technical control
• expression and appropriate interpretation
• accuracy of rhythm and pitch
• appropriate pace and fluency
• effective use of dynamics
• stylistic awareness
• empathy (in ensemble playing).
Ability level will reflect the ‘More Difficult Than Standard’ repertoire
General features of a ‘More difficult than standard’ piece are:
• A piece in any key appropriate for the instrument
• A piece displaying some intricate rhythms and a wide pitch
• range for the instrument
• The selected piece will allow for greater emphasis on
• interpretation
• Full range of dynamics
• Several contrastsin technical demands and phrase
• structure
• Contrastsin tempo or challenging tempo
• Contrastsin sonority or challenging tone quality with more
• complexarticulation
• Contrastsin style or greater stylistic challenges
What are the opportunities for “deeplearning”?
Questioning
Rehearsals
Final performance
Peer assessmentof real Year 11 performances, peer modelling of
How do we ensure progress of SEND and PP students?
Mixed ability groups in initial lessons so more able can support SEND. SEND register checkedto support
What mightbe the pitfalls?
Absence of student or othersin their group.
Inhibitions of performing.
• An appropriate tempo is sustained
• throughout, resulting in a fluent
• performance
• All performance directions are followed
•appropriately throughout the performance
Technical Control
• Secure vocal/instrumental technique
• and intonation(where appropriate)
• throughoutthe whole performance
• Secure control of sonority(tone) with
• the use of contrastfully appropriate
• to the music
•The performance is well-projected
Expression and Interpretation
• An expressive performance in keeping
• with the chosen style
• Effective communication sustaining
• audience interest throughout the
• performance
• Effective rapport with other performers,
• where appropriate, resulting in a
• balanced performance
• Effective balance between live and
• pre-recorded tracks,where appropriate
What home-learning tasksare planned?
What work will be “deep-marked”? What tracking datawill be recorded?
Students may book the studio to rehearse for assessment. Students will complete portfolio
Student performances will be videoed throughoutcourse, ‘mock’ performance assessment will be before end of Autumn 2 half term, pieces will be graded and reviewed, studentswill have the
- Final assessmenton Arbor
- Audio recordings of performances must be taken before Easter Holidays, to
performances and analysis of model performances moderated by exam board.
Use of different instrumentation– some students may be suited to performing on multiple instruments.
Different music roles –ensembleperformances requiring accompanists and harmony singing
Examples of Band 4 (top tier) performances shared and reviewed.
each student’s needs. For final assessment students are grouped on ability. More one to one supportfor less able groups from teacher including peripatetic music staff. Extra time given in rehearsals. Support given in writtenresources, such as notation shownin different forms, use of aural skills for learning pieces and use of video resources for learning repertoire.
of rehearsal/practice time for students of lower abilities
Lack of access to instruments/rehearsal space.
at home.This will be broken down into three sections and students will have two weeks to complete each section. Students will also be required to carry out extensive research into their stimuluschoice in the early stages of the devising process.
opportunity to review their own and peer review performances in order to see mistakes and limitations.
give suitable time for marking and moderation of performances. Markswill be sent off to the exam board.
Engagement: What will be the “wow” moments?What are the “hooks” for student engagement?
Studentshave the opportunity to choosetheir own repertoire and decide which instrumentthey will be performing on for their final performances. They should have decided on the repertoire by the end of year 10 so will have the opportunity to work collaboratively with others (including other students not being assessed for music) to develop performances. Students will have the opportunity to perform in concerts and out-of-classroom performing opportunities to give them a ‘real-life’ performing opportunityto help build confidence and gain an understanding of dealing with nervous.
Impact: How will we know if outstanding learning has occurred?
Teachers will observe skills developing throughout the unit. Engagement, participation, applying knowledge, performance, understanding, confidence and verbal evaluation.Video and audio evidence of performances will be gathered in order to make coaching judgements and ultimatelymake final grade decisions. Performances will be reviewed regularly, and high standard model performances will be analysed to gather experience of how to achieve top grades.
Next steps: How will this link to subsequent learning?
All skills used in performance can be adapted and related to in Component2 and 3, aural perception skills and musicalliteracy skills are required in all three components. Studentsmay perform their own compositionswhich will enable cross-use of coursework, should it be required.
30% and 72 marks
What is the big picture?
Learners must submit two compositionswith a total playing time of between 3-6 minutes.
Time frame: 1 term
1. A compositionwhich responds to a brief set by WJEC. The brief will be released during the first week of Septemberin the academicyear in which the assessment is to be taken.Learners select one from a choice of four briefs, each related to a different area of study:
Areaof study 1: Musical Forms and Devices
Areaof study 2: Music for Ensemble
Area of study 3: Film Music
Areaof study 4: Popular Music.
2. A free composition.Learners will composea piece of music in a style of their own choice.Learners will set their own brief for this composition.The brief itself is not assessed; however, learners are assessedon their musical response to the brief. Students will produce a portfolio of evidence, which can be developed into final compositionsduring Autumn term 1, final compositionswill be completedby the end of Autumn 2 half term.
The portfolioof evidence will be used as part of their mock, before further developmentof compositionswhich will then be submittedfor final evidence in the Spring term of year 11. Studentswill completeall aspectsof the unit and will be marked using last years GCSE boundaries.
How does this link to and build on the previous year of learning?
Studentswill have developed basic compositionskills in a variety of areas in key stage three and begun developing compositionideas in year 10 suitable to be developed into full compositionsthat meet the final assessmentrequirements in year 11.
Intent: What do you want the studentsto be able to know and do?
Good Learners will develop a minimum of two compositionswith a minimum combined length of 3 minutes.
Learners must completeone compositionto a brief set by the exam board and one free composition.Learners may use compositionalideas they have developed in previous academicyears.
All compositionsmustrelate to one of the four areas of study:
Area of study 1: Musical Forms and Devices
Area of study 2: Music for Ensemble
Area of study 3: Film Music
Area of study 4: Popular Music.
• Learners will be able to demonstrate a basic level of knowledge of the overarching elements of music.
Learners will develop music literacy skills including:
• Basic knowledge of treble and bass clef notation,
• Limiteduse of scales, applicationof different sonorities,
• Basic applicationof different musicaltextures,
• Some use of dynamics and tempo appropriate to chosen musical styles.
• A limited ability to develop musical ideas which are coherent and appropriate to a set brief.
• Application of compositionalstyles which are, on the whole, contextually appropriate. Compositionswill generally show a Band 2 level of application of skills in the followingthree areas.
• Learners must show the knowledge of various compositionaltechniques and apply them in a relevant style. Applicationmay be limitedbut contextually appropriate.
• Learners must show knowledge of sonoritiesappropriate to different musical eras, styles and genre.
• Learners should be able to demonstratetheir knowledge both through practical applicationof their compositionskills and through a written compositionlog, which will document their compositional process and highlight the skills they have used.
• Compositionlogsmay have limited details but demonstrate an accurate commentaryon the individual compositionprocess. Learners must accurately documenthow their compositionrelates to their chosen area of study.
Creativity and Developmentof Musical Ideas
• Ideas are simple, offering some potentialfor development
• Some ideas are partially developed
• Somecontrastsof tone colour and mood
Technical Control of Musical Elements and Resources
• Some choicesof elements and resources are effective
• Somemusical elements are used inconsistently
• Inconsistent control of resources, including technology
Structure and StylisticCoherence
• Inconsistent organisation with some effective presentation of musical ideas
• The style and character is inconsistentin response to the chosen brief
• The outcome is inconsistent displaying some sense of coherence
Better Learners will complete two compositionswith a combined time of between 3-6 minutes.
Learners will completeone compositionto a brief set by the exam board and a free composition,both must relate to one of the four areas of study. Learners demonstrate mostly effective application of compositionaltechniques related to their chosen areas of study.
• Learners will be able to demonstratea good level of knowledge of the overarching elements of music.
• Learners must show the knowledge of various compositionaltechniques and apply them in a relevant style. Applicationwill be contextually appropriate and offer some potentialfor development.
• Learners must show good knowledge of sonorities appropriate to different musicaleras, styles and genre and be able to apply them to their compositions.
• Learners should be able to demonstratetheir knowledge both through practical applicationof their compositionskills and through a written compositionlog, which will document their compositionalprocess and highlight the skills they have used.
• Compositionlogs will be detailed and demonstrate an accurate commentary on the individual compositionprocess.Learners must accurately document how
Learners will develop music literacy skills including:
• Good knowledgeof treble and bass clef notation,
• A wider use of scales, applicationof different sonorities,
• Appropriate application of different musical textures,
• Use of dynamics and tempo appropriate to chosen musical styles.
• Ability to develop musicalideas which are coherent and appropriate to a set brief.
• Application of compositional styles which are contextually appropriate. Compositionswill generally show a Band 3 level of applicationof skills in the followingthree areas.
• Ideas are generally effective, offering potential for further development
• The content is competently developed throughout the piece
• Generally effective contrastsof tone colourand mood
their compositionrelates to their chosen area of study. Compositionlogs will offer some potentialfor further development of compositions.
• Generally effective choice of elements and resources
• A variety of musicalelementsare used competently
• Resources, including technology, are generally well controlled
• A well-organised piece with effective presentation of musical ideas
• The style and character is generally effective in response to the chosen brief
• The outcomeis generally effective and coherent
Excellent Learners will complete two compositionswith a combined time of between 3-6 minutes.
Learners will completeone compositionto a brief set by the exam board and a free composition,both must relate to one of the four areas of study. Learners demonstrate highly effective application of compositionaltechniques related to their chosenareas of study.
• Learners will be able to demonstrate a strong level of knowledge of the overarching elements of music.
• Learners must show the knowledge of various compositionaltechniques and apply them in a relevant style. Applicationwill be contextually appropriate and demonstrate a degree of development through their compositionalprocess, resulting in two highly effective final compositions.
• Learners must show good knowledge of sonorities appropriate to different musicaleras, styles and genre and be able to apply them to their compositions.
• Learners should be able to demonstratetheir knowledge both through practical applicationof their compositionskills and through a written compositionlog, which will accurately document their compositionalprocess and highlight the skillsthey have used.
• Compositionlogs will be detailed and demonstrate an accurate commentary on the individual compositionprocess. Learners must accurately document how their compositionrelates to their chosen area of study and log the use of any ideas they have used from external sources. Compositionlogs will demonstrate that learners have identified areas within their compositionswith potentialfor further development.
Learners will developmusic literacy skills including:
• Strongknowledge of treble and bass clef notation,
• A wider use of scales, applicationof different sonorities which reflect the areas of study chosen for each composition,
• Strong application of different musical textures,
• Good use of dynamics and tempo appropriate to chosen musical styles.
• Ability to develop musicalideas which are coherent and appropriate to the set brief.
• Strong application of compositional styles which are contextually appropriate. Compositionswill generally show a Band 4 level of application of skills in the followingthree areas.
• Ideas are highly effective, offering much potential for creative development
• The content is skilfully developed throughoutthe piece
• Highly effective contrastsof tone colour and moods
• Highly effective choiceof elementsand resources
• A wide variety of musical elements are used skilfully
• Resources, including technology, are skilfully controlled
What are the opportunities for “deep-learning”?
Questioning
Rehearsals
Masterclasses on different musical styles to show appropriate compositions skills needed for each of the four areas of study. Use of flipped learning processes to ensure compositionalskills are embedded early and application of skills can then be developedat a higher level.
How do we ensure progress of SEND and PP students?
Mixed ability groups in initial lessonsso more able can support SEND. SEND register checkedto support each student’s needs.
Composition exercisescan be used for development with scaffolding to and skill ladders to demonstrate how students should approach their compositions. Stimulus libraries should be developed throughout year 10 showing appropriate phrases and musical ideas that can be built upon for final compositions.
Structure and StylisticCoherence
• A very well-organised piece with a highly effective presentation of musical ideas
• The style and character is highly effective in response to the chosenbrief
• The outcome is highly effective, musical and fully coherent
What mightbe the pitfalls? What home-learning tasks are planned? What work will be “deep-marked”? What trackingdata will be recorded?
Lack of ICT equipment for accessing cloudbased learning platforms, Lack of home ICT equipment preventing work from being continued by students in their own time.
Lack of confidence in compositional ideas and limited ability to play a wider variety of instruments can lead to misconceptions and misapplication of compositional ideas which are not suited to the chosen instrumentation.
Studentsmay book the studio to practice their composition skills. Students will have accessto online learning platforms to facilitate flipped learning approaches and enable compositionsto be continued at home. Cloud based software so compositions can be shared between home and school,as well as ability for peer review and on-going student-teacher dialogue.
There will be a progress point one, commenton how to improve with a grade. There will be a teacher assessmentin the final lessonwith a commentand grade. All work will be given a GCSE grade based on last year’s boundaries of this unit.
On-going dialogue will be active on each compositionfor studentsusing cloud-based composition platform. Compositionswill be regularly downloadedand backed up in order for peer review and moderation.
Marking criteria is shared with students and compositionsare regularly reviewed against them. Model compositionsdemonstrating the different bands of marks are shared and analysed.
Final assessment entered on Arbor
Final submissionof compositionswill be before Easter holiday of Year 11 to ensure time for marking and moderation before submission to exam board. Marks will be sent off to the exam board before early May deadline.
Engagement: What will be the “wow” moments?What are the “hooks” for student engagement?
Students have the opportunity to choosethe area of study in which they will be composing,for both the set brief and free composition.Students have the opportunity to build upon work they may have already completedin earlier years which may offer a higher level of refinement and show applicationof potentialfor improvements. They should have begun composingtheir free compositionin year 10 and will be expected to build up on this. Studentswill have the opportunity to ‘deep-dive’ into their chosenmusicalstyles in order to analyse the techniques and devices they need to apply in order to create a highly effective composition.Studentswill have the opportunity to present their compositionsin concerts and out-of-classroomperforming opportunities to give them a ‘real-life’ performing opportunity to help build confidence, to gain an understanding of dealing with nervous, and to hear their compositionsperformed by other musicians in order to understand further areas for improvement.
Impact: How will we know if outstanding learning has occurred?
Teachers will observe skills developing throughout the unit. Engagement, participation, applying knowledge, performance, understanding, confidence and verbal evaluation.Video and audio evidence of compositionswill be gathered in order to make coachingjudgements and ultimately make final grade decisions. Compositions will be reviewed regularly and high standard model compositionswill be analysed to gather experience of how to achieve top grades.
Next steps: How will this link to subsequent learning?
All skills used in compositioncan be adapted and related to in Component1 and 3, aural perception skills and musicalliteracy skills are required in all three components. Studentsmay perform their own compositionswhich will enable cross-use of coursework, should it be required.
40% and 96 marks.
What is the big picture?
Time frame: 1 term
This componentrequires Learners to develop knowledge and understanding of musical elements, musical contexts and musical language. Learners will develop a knowledge and understandingof music through the following four areas of study:
• Areaof study 1: Musical Forms and Devices
• Areaof study 2: Music for Ensemble
• Areaof study 3: Film Music
• Areaof study 4: Popular Music.
Component3 will be used as a mockexam in year 10 and 11, before sittinga final exam at the end of year 11. Studentswill completeall aspectsof the unit and will be marked using last years GCSE boundaries.
Studentswill have had a foundation knowledge of the musical elements, musical language and have explored music in a variety of contextsthroughoutkey stage three. Studentswill have embedded this knowledge through performance and composition,demonstratingan applied knowledge of the key areas of study for component 3. The four areas of study will be examined, at length, in year 10 and explored for use in compositionand performance portfolios.
Intent: What do you want the studentsto be able to know and do?
Good Area of study 1: MusicalForms and Devices
• Students will demonstrate a basic knowledge of some of the commonmusicalforms and devices used in the Western Classical Tradition.
• Students will show reasonable knowledge of the Baroque, Classical and Romanticeras and how to identify music between them.
• Students will have reasonable knowledge of binary, ternary, minuet and trio rondo, variation and strophic forms.
Area of study 2: Music for Ensemble
• Studentswill demonstrate a basic knowledge of the use of texture and sonority.
• Students will show a reasonable knowledge of music composed for ensemble,such as jazz and blues, musicaltheatre and chamber music
• Students should be able to consider how music is composedfor small groups of instruments and voices.
Area of study 3: Film Music
Students should demonstrate a reasonable use of the following musical language, showing that they can discuss music in context, demonstrate a reasonable understanding of the purpose and intention in a composer’swork.
Musical Elements Words: melody, harmony, tonality, form and structure, dynamics, sonority, texture, tempo, rhythm, metre Studentswill demonstrate the ability to read, and write, simple musical notationusing treble and bass clef. Students may also demonstrate some use of graphic notationwhere traditional musical notationis not used. Students may also show a basic understandingof instrument specific notationsuch as TAB.
Students will show the ability to identify some musical patterns by ear, and recognise some chords.
Students shouldbe able to use roman numerals to identify chord I, IV and V. Studentsshould show a basic understandingof how to read some chord notation,such as identifying between major and minor chords. Studentsshould show a basic level of skill in appraising music through the explorationof a wide variety of music linked to the four areas of study.
• Students should show a reasonable knowledge of how music contributesto the film industry and the varied areas in which music plays a part.
• Students should have a reasonable knowledge of music which is used for the purpose of dramatic underscore and thematicmusic, such as leitmotif.
• Students should show a reasonable knowledge of how music for film is created, developed and performed, and the impactthis has on the audience.
Area of study 4: Popular Music
• Studentsshould show a reasonable knowledge of popular music from several genres.
• Learners should demonstrate a reasonable knowledge of popular music practices through performance and compositionin component1 and 2.
• Students should demonstrate a reasonable knowledge of how the musicalelements explored in Area of study 1 are applied in the contextof popular music.
Area of study 1: MusicalForms and Devices
• Students will demonstrate a sound knowledge of some of the commonmusicalforms and devices used in the Western Classical Tradition.
• Students will show good, working knowledge of the Baroque, Classical and Romanticeras and how to accurately identify some differences between them.
• Students will have good knowledge of binary, ternary, minuet and trio rondo, variationand strophic forms and be able to use them in component 2.
Area of study 2: Music for Ensemble
• Students will demonstrate a sound knowledge of the use of texture and sonority.
• Students will show a good knowledge of music composedfor ensemble,such as jazz and blues, musicaltheatre and chamber music, and be able to perform examples for component1.
• Students should be able to consider how music is composedfor small groups of instruments and voices.
Area of study 3: Film Music
Studentsshould show a basic ability to analyse a piece of music set out by the exam board as a ‘set work’ with regards to the musicalelements. Studentswill identify the main features of binary, ternary, minuet and trio, rondo,variation and strophic forms, including how composersuse a variety of musicaldevices to create and developmusic
Through listening to and/or performing examples from chamber music, musicaltheatre, jazz and blues, learners will study texture, including how composerscombine musical lines in the following textures: Monophonic, homophonic, polyphonic, unison, chordal, layered, melody and accompaniment,round, canon, countermelody. Studentswill be able to consider how texture is used in a variety of instrumental and vocal groupings.
Students should demonstrate a reasonable use of the followingmusical language, showing that they can discuss music in context, demonstrate a reasonable understanding of the purpose and intention in a composer’swork.
Musical Elements Words:
melody, harmony, tonality, form and structure, dynamics, sonority, texture, tempo,rhythm, metre
Studentswill demonstrate the ability to read, and write, simple musical notationusing treble and bass clef. Students may also demonstrate some use of graphic notationwhere traditional musical notationis not used. Students may also show a basic understanding of instrument specific notationsuch as TAB.
Students will show the ability to identify some musical patterns by ear, and recognise some chords.
Students shouldbe able to use roman numerals to identify chord I, IV and V. Studentsshould show a basic understandingof how to read some chord notation,such as identifying between major and minor chords.
Studentsshould show a basic level of skill in appraising music through the explorationof a wide variety of music linked to the four areas of study.
• Students should show a sound knowledge of how music contributesto the film industry and the varied areas in which music plays a part.
• Studentsshould have a solid, working knowledge of music which is used for the purpose of dramatic underscore and thematic music, such as leitmotif.
• Students should show a reasonable knowledge of how music for film is created, developedand performed, and the impact this has on the audience and be able to demonstratethis knowledge in component 2.
Area of study 4: Popular Music
• Students should show a sound knowledge of popular music from several genres.
• Learners should demonstrate a good knowledge of popular music practices through performance and compositionin component 1 and 2.
• Students should demonstrate a good knowledge of how the musicalelements explored in Area of study 1 are applied in the contextof popular music.
Excellent Area of study 1: MusicalForms and Devices
• Students will demonstrate an excellent knowledge of some of the common musical forms and devices used in the Western Classical Tradition.
• Students will show excellent knowledge of the Baroque, Classical and Romanticeras and how to accurately identify some differences between them.
• Students will have excellent knowledge of binary, ternary, minuet and trio rondo, variationand strophicforms and be able to use them confidently in component 2.
Area of study 2: Music for Ensemble
• Students will demonstrate an excellent knowledge of the use of texture and sonority.
• Students will show a wide knowledge of music composedfor ensemble,such as jazz and blues, musicaltheatre and chamber music, and be able to perform several examples for component1.
• Students should be able to consider how music is composedfor small groups of instruments and voices.
Area of study 3: Film Music
Studentsshould show a basic ability to analyse a piece of music set out by the exam board as a ‘set work’ with regards to the musicalelements. Studentswill identify the main features of binary, ternary, minuet and trio, rondo,variation and strophic forms, including how composersuse a variety of musicaldevices to create and developmusic
Through listening to and/or performing examples from chamber music, musicaltheatre, jazz and blues, learners will study texture, including how composerscombine musical lines in the following textures: Monophonic, homophonic, polyphonic, unison, chordal, layered, melody and accompaniment,round, canon, countermelody. Studentswill be able to consider how texture is used in a variety of instrumental and vocal groupings.
Students should demonstrate a reasonable use of the following musical language, showing that they can discuss music in context, demonstrate a reasonable understanding of the purpose and intention in a composer’swork.
Musical Elements Words:
melody, harmony, tonality, form and structure, dynamics, sonority, texture, tempo, rhythm, metre Studentswill demonstrate the ability to read, and write, simple musical notationusing treble and bass clef. Students may also demonstrate some use of graphic notationwhere traditional musical notationis not used. Students may also show a basic understanding of instrument specific notationsuch as TAB.
Studentswill show the ability to identify some musicalpatterns by ear, and recognise some chords.
Students shouldbe able to use roman numerals to identify chord I, IV and V. Studentsshould show a basic understanding of how to read some chord notation,such as identifying between major and minor chords. Studentsshould show a basic level of skill in appraising music through the explorationof a wide variety of music linked to the four areas of study.
• Students should show an excellent knowledge of how music contributesto the film industry and the varied areas in which music plays a part.
• Students should have an excellent knowledge of music which is used for the purpose of dramatic underscore and thematicmusic, such as leitmotifand be able to accurately demonstrate these practices in component1 and 2.
• Students should show an excellent knowledge of how music for film is created, developedand performed, and the impact this has on the audience and be able to demonstratethis knowledge in component 2.
Area of study 4: Popular Music
• Students should show an excellent knowledge of popular music from several genres.
• Learners should demonstrate an excellent knowledge of popular music practices through performance and compositionin component1 and 2.
• Students should demonstrate an excellent knowledge of how the musicalelements explored in Area of study 1 are applied in the contextof popular music.
Studentsshould show a basic ability to analyse a piece of music set out by the exam board as a ‘set work’ with regards to the musicalelements. Studentswill identify the main features of binary, ternary, minuet and trio, rondo,variation and strophic forms, including how composersuse a variety of musicaldevices to create and developmusic
Through listening to and/or performing examples from chamber music, musicaltheatre, jazz and blues, learners will study texture, including how composerscombine musical lines in the following textures: Monophonic, homophonic, polyphonic, unison, chordal, layered, melody and accompaniment,round, canon, countermelody. Studentswill be able to consider how texture is used in a variety of instrumental and vocal groupings.
What are the opportunities for “deep-learning”?
Practical application of knowledge through performance and compositions
Regular ‘long-mark’ questions.
Final exam.
Peer assessment of class exam questions. Examples of full marks answers shared.
Practical exploration of each area of study, through performance,
How do we ensure progress of SEND and PP students?
What might be the pitfalls? What home-learning tasks are planned?
Whatwork will be “deepmarked”?
What tracking data will be recorded?
Mixed ability groups in initial lessonsso more able can support SEND.
SEND register checked to support each student’s needs.
More one to one support for less able students from teacher.
Extra time given in exams. Help sheetsand learning ladders to support theory knowledge for application in component1 and 2.
Studentswho struggle in English may find this challenging as they are required to answer a 10 mark long-answer question as part of the written paper.
Questionsrequire analytical and evaluative approaches to listeningto music which then must be transferred on to the page for the exam.
Students will have an exam style question to complete at home once every two weeks. This will comprise of a mixture of short/long answer questions from Section A/B.
Every fortnight the exam style questionwill be marked against last year’s GCSE music mark scheme and studentswill receive a grade based on last year’s boundaries.
- Final assessment on Arbor
- Final unit to be assessed in Year 11 via Externally assessed exam.
composition, group Musical dictionary to be work and independent compiled by learners work. Flipped learning throughout course. approaches for theory Session6 intervention concepts and learning programme. of musical vocabulary.
Engagement: What will be the “wow” moments?What are the “hooks” for student engagement?
Impact: How will we know if outstanding learning has occurred?
Teachers will observe skills developing throughout the unit. Engagement, participation, applying knowledge, performance, understanding, confidence and verbal evaluation, fortnightly exam style question written homework tasks.
Next steps: How will this link to subsequent learning?
All skills used in component3 shouldbe applied to in component1 and 2, aural perception skills and musicalliteracy skills are required in all three components. This is the final exam of their GCSE Music course.
Students receive 3 lessons of Art per week. Year 10 Photography students begin their GCSE year working developing their knowledge and understanding of camera skills, they then learn how to build and set up a studio to develop images in a range of different settings. They then explore Photoshop to begin to create contemporary images thatfocus on the use of layering. Three very differentproject will be completed by Easter. Studentswill then start to develop more in-depthprojects based around the a set them, all work for year 10 will be completed before the summer break.
Units titles: Low and High Key Lighting, Sun Mi Ahn, Jasper James, illusion/Levitation,cut and paste.
Skills: Develop understanding of camera skills. A range of techniques appropriateto their coursework projects using photoshop as their primarycreative source.
GCSE Art structure 60% Coursework 40% Exam.
Year 10 100% course work
The GCSE in Photographyis a broad and flexible course that requires studentsto develop an appreciationof the creative processthrough a practical response, using a range of different processfrom traditionalcamera skills through to advance use of photoshoptechniques. Studentsshould explore critically how photographers, artists, craftspeople and designers from diverse cultures, times and societieshave arrived at solutionsand communicatedmeaning using the formal elements. Students should use this knowledge when developing new ideas, recording observationsand creating outcomeswhich fully realise their personal intentionsusing photography as a vehicle of expression.
Literacy: The ability to research and respond to other artists’ is expected in both a visual and written way. When evaluating their own work studentsexplain links with other Photographers’ ideas using keywords and vocabulary to clearly demonstrate critical understanding. Students will critically analyse and evaluate the work of othersexpressing their own views and opinions.
Numeracy: An understanding of scale and proportionis demonstratedthrough the use of scale whilst composing images.
Home learning: Individual research, analysis and investigations, both written and practical . Wow Moments:They will experience a wide range of exciting photography techniques, which they will developto create their own photography.
Consider your assessment Markers
Identify where the following will take place;
Key assessments
Continuous assessment
Low stakes testing
Deep marking points
Yellow Box marking every
3 weeks
Home learning
Weekly
Examinations – N/A
Conferencing/MAD time
Weekly
Moderation
Each half term –
Departmental standardisation
Autumn Term
Projectassessment– yellow box
Home learning once per week.
Peer and self reflection
Spring Term
Projectassessment– yellow box
Home learning once per week.
Peer and self reflection
SummerTerm
Projectassessment– yellow box
Home learning once per week.
Peer and self reflection.
Become proficient using the GCSE project structure to develop ideas. Become an independent photographer.
Studentsreceive 3 lessons of Photographyper week. Year 11 Art students begin their final GCSE year being presentedwith a range of personal projects. Pupils will be expected to complete two personal projects projects by the end of December. Januaryof year 11 pupilswill receive their exam topic from Edexcel which they will complete as a project over 20 hours. This culminates in a 10 hour exam whereby pupils complete a final outcome for their project. GCSE Photographyis completed by April.
Intent (including moving on from…)
Units: Coursework units/Examunit– students will focus on completing/extendingtheir coursework unit(S) and then completetheir exam unit after Christmas.
Skills: A range of techniques appropriate to their chosenproject using photoshopas their primary creative source.
60% Coursework 40% Exam.
The GCSE in Photographyis a broad and flexible course that requires studentsto develop an appreciationof the creative processthrougha practical response, using a range of different processfrom traditionalcamera skills through to advance use of photoshoptechniques. Studentsshould explore critically how photographers, artists,craftspeople and designers from diverse cultures, times and societieshave arrived at solutionsand communicatedmeaning using the formal elements. Students should use this knowledge when developing new ideas, recording observationsand creating outcomeswhich fully realise their personal intentions using photography as a vehicle of expression.
Literacy: The ability to research and respond to other artists’ is expected in both a visual and written way. When evaluating their own work students explain links with other Photographers’ ideas using keywords and vocabulary to clearly demonstrate critical understanding. Students will critically analyse and evaluate the work of othersexpressing their own views and opinions.
Numeracy: An understanding of scale and proportionis demonstratedthrough the use of scale whilst composing images.
Home learning: Individual research, analysis and investigations, both written and practical .
Wow Moments:They will experience a wide range of exciting photography techniques, which they will developto create their own photography.
Consider your assessment
Markers
Identify where the following will take place;
Key assessments
Continuous assessment
Low stakes testing
Deep marking points
Yellow Box marking every 3 weeks
Home learning
Weekly
Examinations – March/April
Conferencing/MAD time
Weekly
Moderation
Each half term –
Departmentalstandardisation
Autumn Term
Projectassessment– yellow box
Home learning once per week.
Peer and self reflection
Spring Term
Projectassessment– yellow box
Home learning once per week.
Peer and self reflection
Summer Term
Course Complete
Impact (including next steps…)
Become proficient using the GCSE project structure to develop ideas. Become an independent Photographer. Clearly demonstrate level of knowledge and understanding through completion of Exam Unit.
Studentswill be introduced to the basic skills required for PE and Sport. PhysicalEducation(PE) is studied by all studentsin year 7.
In year 7, the objective is to create a love for physical educationby experiencing a wide variety of different activities and developing respectful relationships, and not shying away from a challenge.
Students will complete SOL on: Physical Education.
PhysicalEducation skills Covered: Attack v Defense, Tactics, Passingand recieving, hand eye co-ordination, changing direction, teamwork,leadership, shooting, Control.Students will have 2 lessonsin Year 8. Lessonsare delivered in the Gym, FitnessSuite, Front Yard and Fields.
The physical education curriculum focuses on broadening knowledge, skills and understanding across a range of activity areas. Each year group has the opportunityto develop skill selection and application using tactics, strategies and compositional ideas that relate to specific activities. They will build on stamina, strength and flexibilityand be able to apply themselves in a range of competitive, creative and challenging activities.
Students will be encouraged to give constructive peer feedback on a regular basis to form part of the assessment process. Topic focus for activities include; Football, Rugby, Basketball, Basketball, Gymnastics, Badminton,Fitness, Netball, Athletics, Rounders, Cricket, Softball,
The physical education curriculum is broad and balanced and will guide all students to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to maintain and improve health-relatedfitness as part of their commitment to lifelong healthylifestyles. They will become educated with the relevantinformation and experiencesto be physically active outside school and throughoutlife.
We operate an extensive extra curricular programme that includes Football, Rugby, Basketball, Fitness, Rounders, Athletics, Cricket
Key assessments: Teacher assessments logged on Arbour and one peer assessment opportunityper sow. Teacher assessment will generate a PPG. Students respond to verbalteacher feedback every lesson.
Autumn Term
PE Games
OAA, Gymnastics, Fitness
Spring Term PE Games
OAA, Gymnastics, Fitness
SummerTerm PE Athletics, Cricket, Softball, Rounders
Studentsshould have a good foundation in PE and understand what a goodsportspersonneeds to be. They should have goodtacticalknowledge and understandingof tacticsand skills. Knowledgeand skills will be repeated, built on and extended each year to create a strongfoundationfor GCSE and to developa confidence. ThroughoutKey Stage 3 studentsgain confidence in applying more advanced skills, showing accurate technique and consistency within both isolateddrills and competitive situations.Students will further develop an ability to evaluate and assess movementsand sequences to produce refined outcomes.Leadership opportunities are facilitated to improve communicationskills, teamwork, organisational skills and confidence.Studentswill be expectedto lead warm-ups and somesportsrelated drills as well as score and officiate within a range of different activities.
Studentswill be introduced to the basic skills required for PE and Sport. PhysicalEducation(PE) is studied by all studentsin year 8.
In year 8, the objective is to create a love for physical educationby experiencing a wide variety of different activities and developing respectful relationships, and not shying away from a challenge.
Students will complete SOL on: Physical Education.
PhysicalEducation skills Covered: Attack v Defense, Tactics, Passingand recieving, hand eye co-ordination, changing direction, teamwork,leadership, shooting, Control.Students will have 2 lessonsin Year 8. Lessonsare delivered in the Gym, FitnessSuite, Front Yard and Fields.
The physical education curriculum focuses on broadening knowledge, skills and understanding across a range of activity areas. Each year group has the opportunityto develop skill selection and application using tactics, strategies and compositional ideas that relate to specific activities. They will build on stamina, strength and flexibilityand be able to apply themselves in a range of competitive, creative and challenging activities.
Students will be encouraged to give constructive peer feedback on a regular basis to form part of the assessment process. Topic focus for activities include; Football, Rugby, Basketball, Basketball, Gymnastics, Badminton,Fitness, Netball, Athletics, Rounders, Cricket, Softball,
The physical education curriculum is broad and balanced and will guide all students to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to maintain and improve health-relatedfitness as part of their commitment to lifelong healthylifestyles. They will become educated with the relevantinformation and experiencesto be physically active outside school and throughoutlife.
We operate an extensive extra curricular programme that includes Football, Rugby, Basketball, Fitness, Rounders, Athletics, Cricket
Key assessments: Teacher assessments logged on Arbour and one peer assessment opportunityper sow. Teacher assessment will generate a PPG. Students respond to verbalteacher feedback every lesson.
Autumn Term
PE Games
OAA, Gymnastics, Fitness
Spring Term PE Games
OAA, Gymnastics, Fitness
SummerTerm PE Athletics, Cricket, Softball, Rounders
Studentsshould have a good foundation in PE and understand what a goodsportspersonneeds to be. They should have goodtacticalknowledge and understandingof tacticsand skills. Knowledgeand skills will be repeated, built on and extended each year to create a strongfoundationfor GCSE and to developa confidence. ThroughoutKey Stage 3 studentsgain confidence in applying more advanced skills, showing accurate technique and consistency within both isolateddrills and competitive situations.Students will further develop an ability to evaluate and assess movementsand sequences to produce refined outcomes.Leadership opportunities are facilitated to improve communicationskills, teamwork, organisational skills and confidence.Studentswill be expectedto lead warm-ups and somesportsrelated drills as well as score and officiate within a range of different activities.
Studentswill be introduced to the basic skills required for PE and Sport. PhysicalEducation(PE) is studied by all studentsin year 9.
In year 9, the objective is to create a love for physical educationby experiencing a wide variety of different activitiesand developing respectful relationships, and not shying away from a challenge. Students will completeSOL on: PhysicalEducation.Physical Educationskills Covered: Attack v Defense, Tactics,Passing and recieving, hand eye co-ordination,changing direction,teamwork,leadership, shooting,Control.Students will have 2 lessonsin Year 8. Lessonsare delivered in the Gym, Fitness Suite, Front Yard and Fields.
The physical education curriculum focuses on broadeningknowledge, skills and understanding across a range of activity areas. Each year group has the opportunityto developskill selection and application using tactics, strategies and compositional ideas that relate to specific activities. They will build on stamina, strength and flexibilityand be able to apply themselves in a range of competitive, creative and challenging activities. Students will be encouraged to give constructive peer feedback on a regular basis to form part of the assessment process. Topic focus for activities include; Football, Rugby, Basketball, Basketball, Gymnastics, Badminton,Fitness, Netball, Athletics, Rounders, Cricket, Softball,
Throughoutthe PE learning journey, each student is exposed to information about the possible career paths that come under the umbrellaterm of sport. This is displayed in their changing rooms and a page has been integrated into the assessment document. Specific career links are referenced in lessons and within extracurricularactivities where they providethe scope to enable the student to clearly see the progression. This would entail writing up a match reportthat would link well to a career in sports journalismor leading a warm-up or skills session in a lesson which would link to a career as a sports coach or personal trainer. We operate an extensive extra curricular programme that includes Football, Rugby, Basketball, Fitness, Rounders, Athletics, Cricket
Key assessments: Teacher assessments logged on Arbour and one peer assessment opportunityper sow. Teacher assessment will generate a PPG. Students respond to verbalteacher feedback every lesson.
Autumn Term
PE Games
OAA, Gymnastics, Fitness
Spring Term
PE Games
OAA, Gymnastics, Fitness
SummerTerm
PE Athletics, Cricket, Softball, Rounders
Studentsshould have a good foundation in PE and understand what a goodsportspersonneeds to be. They should have goodtacticalknowledge and understandingof tacticsand skills. Knowledgeand skills will be repeated, built on and extended each year to create a strongfoundationfor GCSE and to developa confidence. ThroughoutKey Stage 3 studentsgain confidence in applying more advanced skills, showing accurate technique and consistency within both isolateddrills and competitive situations.Students will further develop an ability to evaluate and assess movementsand sequences to produce refined outcomes.Leadership opportunities are facilitated to improve communicationskills, teamwork, organisational skills and confidence.Studentswill be expectedto lead warm-ups and somesportsrelated drills as well as score and officiate within a range of different activities.
Studentswill be introduced to the advanced skills required for PE and Sport. PhysicalEducation(PE) is studied by all studentsin year 10. The aims of which are to encourage lifelong participation.
The Curriculum at Key Stage 4 focuses on the different physical and emotionalrequirementsneeded to competeat a goodlevel within a sport. Students will be encouraged to study a smallnumber of sportsin more detail, refining technical accuracy and executing skills with accurate precision, controland fluency. Positionspecific skills, set plays, strategies, tacticsand compositionalcreativitywill be embedded and developed within the practical content and will empower individuals to meet the challenges in formal and competitivesituations.
Throughoutthe PE learning journey, each student is exposed to information about the possible career paths that come under the umbrellaterm of sport. This is displayed in theirchanging rooms and a page has been integrated into the assessment document. Specific career links are referenced in lessons and within extracurricularactivities where they provide the scope to enable the student to clearly see the progression. This would entail writing up a match reportthat would link well to a career in sports journalismor leading a warm-up or skills session in a lesson which would link to a career as a sports coach or personal trainer. We operate an extensive extra curricular programme that includes Football, Rugby, Basketball, Fitness, Rounders, Athletics, Cricket .
The physical education curriculum focuses on broadening knowledge, skills and understandingacross a range of activity areas. Each year group has the opportunityto develop skill selection and application using tactics, strategies and compositional ideas that relate to specific activities. They will build on stamina, strength and flexibilityand be able to apply themselves in a range of competitive, creative and challenging activities. Students will be encouraged to give constructive peer feedback on a regular basis to form part of the assessment process. Topic focus for activities include; Football, Rugby, Basketball, Basketball, Badminton, Fitness, Netball, Athletics, Rounders, Cricket, Softball.
Autumn Term
Key assessments:
Teacher assessments in relation to effort
Students respond to verbalteacher feedback every lesson.
PE Games, Fitness
Spring Term PE Games Fitness
SummerTerm
PE Athletics, Cricket, Softball, Rounders
Studentsshould have a good foundationin PE and understand what a goodsportsperson needs to be. They should have goodtacticalknowledge and understanding of tacticsand skills. Knowledgeand skills will be repeated, built on and extended each year to create a strongcross curricular link. Throughout Key Stage 4 studentsgain confidence in applying moreadvanced skills, showingaccurate technique and consistencywithin both isolateddrills and competitivesituations.This will link with the OCR Cambridge Nationals.Each activity taught in the physical educationcurriculum embeds key skills that the studentslearn and develop. These skills include communication,resilience, problem solving and leadership. Studentsare made aware throughtheir lessonshow they have used these skills and how they wouldbe valued in the workplace. The studentsbank practical examplesthat can be referenced in personal statementsfor employers, colleges and universities.
Studentswill study a range of areas and activitieson the Cambridge National SportsStudiesCourse. Their will be 4 different assessment,and a mixtureof learning styles.
Studentswill complete OCR Cambridge Nationals in Sports Studies
Skills Covered: YEAR 10 -Developing Sports Skills (Assignment), Contemporary Issues in Sport (Exam)
YEAR 11 – Sports Leadership (Assignment) Developing Knowledge and skills in Outdoor activities (Assignment
Studentswill complete4 Componentsof the course over the 2 years. Studentshave three hours of lessons each week. 2 lessonsin ICT suite and 1 lessonpractically.
Developing sport skills
Students try out a range of sports-related skills and techniques, including different practice methods for improving both their own performance and that of others. They develop their knowledge of the use of tactics and strategies in both individual and team sporting activities as well as their understanding of the rules, enabling them to carry out a number of officiating roles within the activities.
Contemporary Issues in Sport
Studentsexplore a range of topicaland contemporary issues in sport, such as participation levels and barriers, promotingvalues and ethical behaviour, and how sport contributesto society as a whole beyond simply providing entertainment.
Sports leadership
Students learn about some of the knowledge, understanding and practical skills required to be an effective sport leader. They put their knowledge into practice by planning and delivering safe and effective sporting activity sessions.
Developing knowledge and skills in outdoor activities
Studentsfind out about a wide range of outdoorand adventure activitiesand the organisationsthat provide accessto them. Through planning and participatingin these type of activitiesthey will learn about the risks in involvedand gain an understanding of health and safety, risk assessmentsand the importanceof detailed planning for various scenarios and challenging environments. This will also help them develop their communication, decision-making and leadership skills
Key assessments:
1.DevelopingSports Skills (25%) (Assignment)
2.Contemporary Issues in Sport (25%) (Exam)
3.Sports Leadership (25%) (Asssignment)
4.DevelopingKnowledge and skills in Outdoor Activities
Autumn Term Year 10: Developing Sports Skills
Spring Term Year 10: Contemporary Issues
Summer Term Year 10: Developing Sports Skills
Autumn Term Year 11: Sports Leadership
Spring Term Year 11: Developing Knowledge of OAA Contemporary Issues Re-Take
Studentswill be able to apply all skills and Knowledge of all areas in relation to Contemporary, Sports Skills, Leadership, and OutdoorActivities. Studentswill develop a greater practical understanding across each practical area Opportunities for further education opportunities: Personaltrainer, teacher, psychologist,business leader, sports scientist, dietitian, armed forces, public services, sports coach, physiotherapist, journalist, events management, media and public relations.
Studentswill be introduced to the advanced skills required for PE and Sport. PhysicalEducation(PE) is studied by all studentsin year 11. The aims of which are to encourage lifelong participation.
The Curriculum at Key Stage 4 focuses on the different physical and emotionalrequirementsneeded to competeat a goodlevel within a sport. Students will be encouraged to study a smallnumber of sportsin more detail, refining technical accuracy and executing skills with accurate precision, controland fluency. Positionspecific skills, set plays, strategies, tacticsand compositionalcreativitywill be embedded and developed within the practical content and will empower individuals to meet the challenges in formal and competitivesituations.
Throughoutthe PE learning journey, each student is exposed to information about the possible career paths that come under the umbrellaterm of sport. This is displayed in theirchanging rooms and a page has been integrated into the assessment document. Specific career links are referenced in lessons and within extracurricularactivities where they provide the scope to enable the student to clearly see the progression. This would entail writing up a match reportthat would link well to a career in sports journalismor leading a warm-up or skills session in a lesson which would link to a career as a sports coach or personal trainer. We operate an extensive extra curricular programme that includes Football, Rugby, Basketball, Fitness, Rounders, Athletics, Cricket .
The physical education curriculum focuses on broadening knowledge, skills and understandingacross a range of activity areas. Each year group has the opportunityto develop skill selection and application using tactics, strategies and compositional ideas that relate to specific activities. They will build on stamina, strength and flexibilityand be able to apply themselves in a range of competitive, creative and challenging activities. Students will be encouraged to give constructive peer feedback on a regular basis to form part of the assessment process. Topic focus for activities include; Football, Rugby, Basketball, Basketball, Badminton, Fitness, Netball, Athletics, Rounders, Cricket, Softball.
Key
Studentsshould have a good foundationin PE and understand what a goodsportsperson needs to be. They should have goodtacticalknowledge and understanding of tacticsand skills. Knowledgeand skills will be repeated, built on and extended each year to create a strongcross curricular link. Throughout Key Stage 4 studentsgain confidence in applying moreadvanced skills, showingaccurate technique and consistencywithin both isolateddrills and competitivesituations.This will link with the OCR Cambridge Nationals.Each activity taught in the physical educationcurriculum embeds key skills that the studentslearn and develop. These skills include communication,resilience, problem solving and leadership. Studentsare made aware throughtheir lessonshow they have used these skills and how they wouldbe valued in the workplace. The studentsbank practical examplesthat can be referenced in personal statementsfor employers, colleges and universities.
Thefirst yearof the KS3 RE curriculum provides studentswith a broad and balanced overview of some key beliefs and teachingsacross and within world religions. It aims to promote love of learning in RE by focusing on engaging topics, from ideas about justice to Buddhistbeliefs about enlightenment. Studentsdevelop breadthof different beliefs but also depthof topics on a termly basis. Breadthof beliefs and teachingswill take place in the first half term and a deepdive into specific concept will be explored in the second half of the term. Students will develop their skills in description, explanation, analysis and evaluation. The content will be delivered over 55 minutes per week.
The Big Christian Story
of religion and beliefs including: • beliefs, practices Christianity and justice and sources of authority • influence on individuals, communities and societies • similarities and Islamic beliefs differences within and/or between religions and Hajj beliefs.
AO2: Analyse and evaluate aspects of religion and Buddhist beliefs belief, including their significance and influence.
AO1: Demonstrate knowledge and understanding Develop their knowledge and understanding of religions and non-religious beliefs, such as atheism. Develop their knowledge and understanding of religious beliefs, teachings and sources of wisdom and authority, including through their reading of key religious texts, other texts and scriptures of the religions they are studying Develop their ability to construct well-argued, well-informed, balanced and structured written arguments, demonstrating their depth and breadth of understanding of the subject • Reflect on and develop their own values, belief, meaning, purpose, truth and their influence on human life Reflect on and develop their own values, beliefs and attitudes in the light of what they have learnt and contribute to their preparation for adult life in a pluralistic society and global community.
Foundations laid in KS2 learning about the big six world religions.
To build on knowledge and understanding of the beliefs, teachings and practices of the big six.
Enlightenment
There will be a 55 minute lesson per week. The units will build on the A01and A02skills from the previous unit.
LORIC is developed through a range of tasks in lessons and as homework. A mix of individual, paired and grouped tasks are built into lessons to develop communication, leadership and resilience. These tasks range from discussion and debate to challenging academic written tasks and creative tasks, developing student’s interpersonal skills. Lessons and homework tasks also build initiative, organisation and resilience through a range of challenging activities.
Interleaving and retrieval practice are key elements of the KS3 curriculum and are built into schemes of work, with starter tasks often devoted to revision and retrieval. Specific revision skills are taught through revision lessons to start developing a base of revision skills that students can use independently in later years. The AO1 and AO2 skills sequentially builds literacy skills and numerical/statistical skills during the year, building on the foundation of skills from KS2 and revisiting these skills regularly in subsequent units.
Mastered Element tasks are embedded in each unit and are opportunities for students to demonstrate ‘wow moments’ showing thirst and love of learning.
Students are rewarded and celebrated through praise in lessons and contact with home as well as whole school rewards evenings.
Developing an understanding of individual identity.
Focusing on the beliefs of self and exploring the origins of these.
Studying of major world religions (such as; Christianity, Islam and Buddhism) to see how different people live, promoting tolerance and understanding.
Reflecting on responses to ‘ultimate questions’.
Studying different religious beliefs and justifying own views.
Working as part of a group or team, sometimes to create their own working teams.
Sharing of views and opinions with others and resolving any differences maturely.
Showing respect for people, living things, property and the environment.
Reflecting on one's contribution to society and how we can support other communities.
Learning about religious groups in the school and wider community and how they contribute towards the wider local community.
➢ Homework on a Humanities rotation, set in 2 cycles for RE.
➢ Skills embedded in lessons.
➢ Keyword and definition tests/quizzes.
➢ Completion of MAD time tasks following marking.
➢ Homework research tasks.
➢ Literacy focus embedded in lessons
➢ Keywords and definition
reviews/tests/quizzes
➢ Stats/data e.g. Hajj.
AutumnTerm
Deep marking/Yellow Box MAD Time are located in lessons half termly
End of unit assessment on ‘The Big Christian Story?’
Students will have started to develop their key A01and A02skills, skills of justification and debate, developing cultural capital and an understanding of the world around them and how they belong in 21st Century Britain. They will also have gained greater understanding of diversity and the importance of tolerance in society. They will be able to develop and make links synoptically, for instance, linking what a religious person believes may impact how they behave etc.
They will have deepened and broadened their understanding of diverse beliefs within and across religions moving beyond simple beliefs and teachings towards practices, building on their prior learning from KS2 so that they are able to tackle difficult issues and concepts confidently, justifying their own opinions and being able to participate in academic debate. They will have begun to develop their AO1 and AO2 RE skills meaning they are confident when starting the Year 8 curriculum next year.
The second year of the KS3 RE curriculum provides students with a broad and balanced overview of some key beliefs and teachings across and within world religions. It aims to continue to promote a love of learning RE by focusing on engaging topics, from ideas about life after death to the environment. Breadth of beliefs and teachings will take place in the first half term.
Skills: AO1 – demonstratesknowledge and understandingof religion and beliefs. AO2 – analyse and evaluate aspects of religion and belief, including their significance and influence. Knowledge: develop knowledge and understanding of religious and non-religious beliefs such as atheism. Knowledge of religious teachings and sources of wisdom including through reading religious textsand scriptures. Reflect and develop their own values, belief, meaning, purpose, truth and their influences on human life.
Prior: foundations laid in Year 7 learning aboutthe big 6 world religions.
Topics: Places of worship, celebrations, beliefs about life after death, cultural responses, beliefs about God and the environment.
There will be a 60 minute lessonper week. The units will build on the AO1 and AO2 skillsfrom the previous unit. LORIC is developed through a range of tasks in lessons and as homework. A mix of individual, paired and grouped tasks are built in to lessons to develop communication, leadership and resilience. These tasks range from discussion and debate to challenging academic written tasks and creative tasks, developing student’s interpersonal skills. Lessons and homework tasks also build initiative, organisationand resilience through a range of challenging activities.
Interleaving and retrieval practice are key elements of the KS3 curriculum and built in to schemes of work, with starter tasks often devoted to revision and retrieval. Specific revision skills are taught through revision lessonsto start developing a base of revision skills.
Masteredelementstasks are embedded in each unit and are opportunities for students to demonstrate “wow” momentsshowingthirst and love of learning.
Autumn Term
Deep marking/yellow box are evident in lessons half termly.
End of unit assessment:“Placesof worship”.
Spring Term
Deep marking/yellow box are evident in lessons half termly.
End of unit assessment:“Life after death?”
Autumn Term
Deep marking/yellow box are evident in lessons half termly.
End of unit assessment:The Environment
Studentswill have developed their key AO1 and AO2 skills, skills of justificationand debate, developing cultural capital and an understanding of the world around them and how they belong in 21st century Britain. They will also have gained even greater understandingof diversity and the importanceof tolerance in society.They will be able to developand make links synoptically,for instance, linking what a religious person believes may impact how they behave.
They will have deepened and broadened their understanding of diverse beliefs movingbeyondsimple beliefs and teachingstowards practises, building on their prior learning from year 7 so that they are able to tackle difficult issues and conceptsconfidently, justifying their own opinions and being able to participate in academic debate.
The final year of the KS3 RE curriculum builds on students’ knowledge of Islam and Christianity and developing skills in answering exam style questions,whilst also deepening the love of learning in RE by focusing on engaging and controversialtopicssuch as abortionand euthanasia. Students develop a more diverse understandingof moralissues whilst developing their skills in analysis and evaluation.
Skills: AO1 – demonstratesknowledge and understandingof religion and beliefs. AO2 – analyse and evaluate aspects of religion and belief, including their significance and influence. Knowledge: develop knowledge and understanding of religious and non-religious beliefs such as atheism. Knowledge of religious teachings and sources of wisdom including through reading religious textsand scriptures. Reflect and develop their own values, belief, meaning, purpose, truth and their influences on human life.
Prior: foundationslaid in Year 7 and 8 on beliefs, teachingsand practices in Islam and Christianity.
Topics: when does life begin? When does life end? Religion, crime and punishment; animal rights, religion and socialjustice and religion, peace an d conflict.
There will be a 60 minute lessonper week. The units will build on the AO1 and AO2 skillsfrom the previous unit. LORIC is developed through a range of tasks in lessons and as homework. A mix of individual, paired and grouped tasks are built in to lessons to develop communication, leadership and resilience. These tasks range from discussion and debate to challenging academic written tasks and creative tasks, developing student’s interpersonal skills. Lessons and homework tasks also build initiative, organisationand resilience through a range of challenging activities.
Interleaving and retrieval practice are key elements of the KS3 curriculum and built in to schemes of work, with starter tasks often devoted to revision and retrieval. Specific revision skills are taught through revision lessonsto start developing a base of revision skills.
Masteredelementstasks are embedded in each unit and are opportunities for students to demonstrate “wow” momentsshowingthirst and love of learning.
Autumn Term
Deep marking/yellow box are evident in lessons half termly.
End of unit assessment:“When does life begin?”
Spring Term
Deep marking/yellow box are evident in lessons half termly.
End of unit assessment:“When does life end?”
Autumn Term
Deep marking/yellow box are evident in lessons half termly.
End of unit assessment:Religion, crime and punishment.
Studentswill have developed their key AO1 and AO2 skills, skills of justificationand debate, developingcultural capital and an understandingof the world through grappling with moral issues.They will also have gained greater understandingof our world, including the law, society and legal changes.
They will have deepened and broadened their understanding of diverse beliefs within and across religions moving beyond simple beliefs and teachings towards practises; building on their prior learning so they are able to tackle difficulty issues and concepts confidently, justifying their own opinions and being able to participate in academic debate. They will have continued to sharpen their RE skills with a shift towardspreparationfor examsmeaning they are confidentwhen startingthe GCSSE course next year if they opt to do so.
This year will be a combinationof groundingpupils in the key conceptsthat underpin the three sciences and ensuring they have a firm grasp of these to then extend them into Year 8 along with developing their practical and investigative skills. Furthermore, their data handling, application and literacy skills will be developed and assessed throughout.
Unit 1: Not all scientists wear white coats – introduces safety in the lab and covers practical skills whilst learning about electricity (studied in Year 6) and acids and alkalis (Year5). Unit 2: 999 – looks at the fire triangle, types of energy, body systems (circulatorycovered in Year 6) and healthy lifestyles (also covered in Year 6). Unit 3: Titanic – pupils rediscoverthe particle model for solids, liquids and gases (coveredin Year 5) and then move onto forces (also Year 5) and density which is a new concept. Unit 4: Shipwrecked – pupils learnabouthealthy diets (Year6) and deficiency diseases, dissolving and separating mixtures (Year5) and properties of different materials (Year5). Unit 5: Earth in Danger – students learn about renewableand nonrenewableenergy sources, global warmingand then adaptationsin animals and food chains (Year6). Unit 6: Leaving Earth – the year ends with students learning about days, yearsand seasons (Year6) and space (Year6) whilst developingtheir calculations of speed. In every unit they will complete practicals to develop their skills with focuses on data handling, literacy, recall and learning to apply their knowledge.
The units are structured thematically to ensure students can holistically experience science and make connections betweenthe three disciplines rather than being taught separately. The theme of each unit then has a narrativeto help contextualize topics. Lessons are a combination of content-delivery with opportunities for learnersto consolidat and then apply their knowledge to new situations as well as explore new topics through practical investigations. This is where pupil’s LORIC skills will be reallydeveloped and reflected upon.
At times in each unit, pupils are expected to research new informationor apply their knowledge and work independently in this.
Homeworkswilleither look to be research-based or a consolidation/extension of what has been done in class to developkey skills or enhance retention. Revision homeworks will be set once per unit and guidance will be provided on how to do this as wellin-class revisionwhich will be more structured and model good revisiontechnique. WOW moments are interspersed throughout the course e.g. heartdissections, acids and alkalis, building their own rafts, shelters and rockets, learning about weird and wonderfuladaptations of animals. Achievements will be celebratedat both a class level with teacher praise and also a cohort level through the Alpha Centauri award. Thereare many opportunitiesto develop numeracy skills across most of the units and these are assessed and developed through data assessments and feedback. Graphsin particularare a real focus. For each unit students are providedwith a key wordlist and their literacy skills are assessed throughout the year along with a lot of practice of answeringapplication-style questions to ensure we are preparingthem for command words at GCSE.
Assessment
Within every unit pupils will complete an end of unit test comprised of recall and application questions that use command words similar to that of GCSE.
Across every 2 units, they will complete the following assessments which will be deep-marked:
Literacy Application Data Skills
AfL will take place throughout all lessons.
Autumn Term
Unit 1 – all 4 assessments
Unit 2 – Dataand skills
Spring Term Unit 3 – applicationand literacy Unit4 – Skills and data
SummerTerm Unit 5 – applicationand data
Unit 6 – literacy and data
End of Year test coveringall content.
We want to pupils to feel they are real scientistsby the end of Year 7; competentand comfortablein their practical skills e.g. handling glassware, using lab equipment, making accurate observationsas well as having a sound understanding of some of the key conceptsacross the sciences: forces, particle models, chemical reactions, body systems,animals within habitats and space. We need them to be able to take a piece of knowledgeand not just see this as a fact but understand it and be able to apply it to unknownsituations.As they head into Year 8 they will developboth their knowledge and skillsin all of these areas build upon these key conceptstohelp prepare for the step up to GCSE in Year 9. We don’t want them to see science as Biology,Chemistryand Physicsbut rather as a subject that explains the phenomenathey see in the world around them encouragingthem to want to find out more.
This year will be a continued combinationof grounding pupils in the key conceptsthat underpin the three sciences extend them based on their Y7 work, continuingto developing their practical and investigative skills, also their data handling, application and literacy skills will be developed and assessedthroughout.
Intent (including moving on from…)
Masterchef– Digestion (linking in to999 fromY7), microbes (links toShipwrecked Y7) and conduction of heat (linked toparticle model in Titanic Y7) Fireworks - Making, seeing & hearing fireworks(linking into Titanic and Leaving EarthfromY7).Down on theFarm - cells, inheritance, geneticsand evolution (linked into Earthin Danger Y7). Materials and Recycling - Material propertiesand reactions (linking into Titanic and Shipwrecked Y7).Going forGold - Joints,respiration and theeffectof drugs(links to 999and Shipwrecked fromY7) . TopGear- Forcesand motion(linked into Titanic and Leaving Earth).Inevery unit theywill completepracticals todevelop their skills with focuseson datahandling, literacy, recall and learning toapply their knowledge.
Implementation
The units are structured thematically as in Y7 to ensure students can holistically experience science and make connections between the three disciplines rather than being taught separately. The theme of each unit then has a narrativeto help contextualize topics. Lessons are a combination of content-delivery with opportunities for learnersto consolidate and then apply their knowledge to new situations as well as explorenew topics through practical investigations. This is where pupil’s LORIC skills will be really developed and reflected upon. At times in each unit, pupils are expected to research new information or apply their knowledge and work independently in this.
Homeworkswilleither look to be research-based or a consolidation/extension of what has been done in class to developkey skills or enhance retention. Revision homeworkswill be set once per unit and guidance will be providedon how to do this as well in-class revision which will be more structured and model good revision technique.
WOW moments are interspersed throughout the course e.g. model digestive systems, making sparklers, growing micro biotic cultures, remote controlled car racing. There are many opportunities to develop numeracy skills across most of the units and these are assessed and developed through data assessments and feedback. Graphsin particularremaina focus along with the developmentof skills with equations. For each unit students are provided with a key word list and their literacy skills are assessed throughout the year along with a lot of practice of answeringapplication-style questions to ensure we are preparing them for command words at GCSE.
Consider your assessment
Markers
Acrossevery 2 units, they will completethe following assessments which will be deep-marked: Literacy
Application Data Skills
AfL will take place throughoutall lessons.
Autumn Term
End of topictests
Application tasks
Datatasks
Literacy tasks
Spring Term
End of topic tests
Application tasks
Datatasks
Literacy tasks
SummerTerm
End of topictests
Application tasks
Datatasks
Literacy tasks
We want to pupils to feel they continue to be real scientistsby the end of Year 8; competentand comfortablein their practical skills e.g. handling glassware, using lab equipment, making accurate observationsas well as having a sound understanding of some of the key conceptsacross the sciences: body systemsand microbes; particle models; chemical reactions; sound and light travel; genetics and evolution;material properties; respiration; forces. We need them to be able to take a piece of knowledge and not just see this as a fact but understand it and be able to apply it to unknownsituations.As they head into Year 9 they will prepare for the step up to GCSE in Year 9. We don’t want them to see science as Biology,Chemistry and Physicsbut rather as a subject that explains the phenomenathey see in the world around them encouragingthem to want to find out more.
Studentsbegin to follow the GCSE specificationin Science, beginning with modulesthat underpin much of the specificationgoing on into Y10 and Y11. Practicalskills are built upon from KS3. Continue to engender a love of learning in science, and developingtheir thinking skills.
Unitscovered: PracticalSkills, B1 Cell Biology,C1 AtomicStructure, C5 Energy Changes, P1 Energy and B4 Bioenergetics. Skills and knowledge: In these units studentswill develop how to demonstrateand apply knowledge and understanding of scientific ideas, scientific enquiry, techniques and procedures. They will begin to analyse, evaluate, judge and draw conclusions from experimental procedures. Building on prior learning: All units build on the fundamentals that studentshave learned in the thematicKS3 units which have elementsof all three subjectspecialismsembedded within them. Next steps: All of the skills and many of the fundamentalideals learned in these moduleswill provide a firm base on which to build more complexscientific concepts and models.
The units taught begin with practical skills in order to maintain curiosity and enjoymentin science, but also building the foundations of thinking critically, working through problems and utilizing the mathematicalskills needed when analysis and interpreting experimentaldata. B1 and C1 are then taught as basic building blocks to the Biologyand Chemistry content– directly building on the conceptsof cells and atomsthat began at KS3. C5 is then taughtas a modulethat has easily derived applicationsto everyday life in exothermicand endothermicreactions.The P1 module on energy also provides a the basic fundamental conceptsneeded to the Physicscontentand builds upon the mathematicalskills that were nurtured in the Practicalskills unit. B4 is the final unit taught in Y9 which returns studentsto familiar topics of photosynthesisand respiration that were developed in KS3 modules.Home learning will be focused on flipped learning researching topicsand completingpast examinationquestions.Literacy and Numeracy skills are built in science, literacy through the use of 6 mark level of response questionsand numeracy thoughthe multiple equationsand mathematicalprocessesthat studentswill need to employ in all three sciences (10% of the Biology, 20% of the Chemistry and 30% of the PhysicsGCSE contentis L2 or equivalent mathematics).
Assessment:
All units include:
6 Mark LOR questions
Low stake testing
End of Unit Tests – using at least 2 practice tests prior to the actual test for all topics
Some units include:
Requiredpractical tasks set by the exam board
Autumn Term PracticalSkills, B1 and C1
Spring Term Graphing skills
C5 and P1
SummerTerm
Numeracy skills in Science
B4
By the end of the Year students will be confident with the fundamental principles, knowledge and application of this knowledge in all three subject areas. They will be able to understand what they need to do in response to certain exam style questions and LOR questions. Practical skills will have developed from KS3 and they will be confident in suggesting improvements and describing methods.All these skills will be further developed in Y10 and Y11 in preparation for their GCSE examinations.
Studentscontinue to follow the GCSE specificationin Science, building on the modulesthat underpin much of the specificationtaught in Y9 and KS3. Practical skills continue to be developed through class practical and required practical tasks
Unitscovered: B2 Organisation, B3 Infection and Response, B5 Homeostasis,C2 Bonding and Structure, C3 Quantitative Chemistry, C4 Chemical Changes, C9 Chemistry of the Atmosphere,C10 Using Resources, P2 Electricity, P3 Particle Model, P4 AtomicStructure. Skills and knowledge: In these units studentswill continue to develop how to demonstrate and apply knowledge and understandingof scientific ideas, scientific enquiry, techniques and procedures. They will continue to analyse, evaluate, judge and draw conclusionsfrom experimentalprocedures.Building on prior learning: All units build on the fundamentals that studentshave learned in the thematicKS3 units and Y9 units.Next steps: All of the skills and many of the fundamental ideals learned in these moduleswill provide a firm base on which to continuebuild more complex scientificconceptsand modelsin Y11.
The units taughtin Y10 are designed to cover all of the contentthat is covered in Paper one of each of the three science specialismsand more (contentthat appears and is assessedin Paper 2) in order to front load content.In all of these modules LORIC opportunitiespresent themselves naturally in practical lessons and also in lessonswhere past exam questionsare being tackled (communication,organisationand resilience in 6mark LOR questions). Home learning will be focused on flipped learning researching topicsand completing past examinationquestions.Some home learning will be specified interleaving homeworksto ensure the long term recall and long term embedding of knowledge of the units covered in Y9 and Y10. Literacy and Numeracy skills are built in science, literacy through the use of 6 mark level of response questionsand numeracy though the multiple equations and mathematicalprocesses that students will need to employ in all three sciences (10% of the Biology,20% of the Chemistry and 30% of the PhysicsGCSE contentis L2 or equivalent mathematics).
Assessment:
All units include:
6 Mark LOR questions
Low stake testing
End of Unit Tests
Some units include:
Requiredpractical tasks set by the exam board
Autumn Term
All assessmentsin each unit dependent on rotations B2, C2, C3, P2
Spring Term
All assessmentsin each unit dependent on rotations B3, P3, P4, C4
SummerTerm
All assessmentsin each unit dependent on rotations B5, C9, C10
By the end of the Year studentswill be confidentwith the fundamental and more complexprinciples, knowledge and application of this knowledge in all three subject areas. They will be able to understand what they need to do in response to all exam style questionsand LOR questions; they will be able to revise effectively as they head towardsYear 11. Their practical skills will have developed both in discussingvariables and describing methodsbut also analyzing data, interpreting results and suggesting improvements. It is also hoped that links can be made between other sciences as they develop as completescientists.
Studentscontinueto completethe GCSE specificationin Science, building on the modulesthat underpin much of the specification taught in Y9, Y10 and KS3. Practical skills continue to be developed through class practical and required practical tasks
Unitscovered: B6 Genetics, B7 Ecology,P5 Forces, P6 Waves, P7 Magnets,C6 Rates of Reaction, C7 Organic Chemistry, C8 Chemical Analysis. Skills and knowledge: In these units students will continue to develop how to demonstrateand apply knowledge and understanding of scientific ideas, scientific enquiry, techniques and procedures. They will continue to analyse, evaluate, judge and draw conclusionsfrom experimental procedures. Building on prior learning: All units build on the fundamentals that studentshave learned in the thematicKS3 units Y9 and Y10 units. Next steps: All of the skills and many of the fundamental ideals learned in these moduleswill provide a firm base on which to continue build more complexscientific conceptsand modelsin KS5 shouldthey choseto continuewith any science at Alevel.
The units taught in Y11 are designed to completelycover all of the remaining contentthat is covered in Paper two of each of the three science specialisms. In all of these modulesLORIC opportunities present themselvesnaturally in practical lessonsand also in lessonswhere past exam questionsare being tackled (communication,organisationand resilience in 6mark LOR questions).Home learning will be focused on flipped learning researching topics and completingpast examinationquestions, with added emphasis on exam style questionsand refining examinationtechnique in preparation for the examinations.Some home learning will be specified interleaving homeworksto ensure the long term recall and long term embedding of knowledge of the units coveredin Y9 and Y10. Literacy and Numeracy skills are built in science, literacy throughthe use of 6 mark level of response questionsand numeracy thoughthe multiple equations and mathematicalprocessesthat studentswill need to employ in all three sciences (10% of the Biology, 20% of the Chemistry and 30% of the PhysicsGCSE contentis L2 or equivalent mathematics).
Assessment:
All units include:
6 Mark LOR questions
Low stake testing
End of Unit Tests
Some units include:
Requiredpractical tasks set by the exam board
Autumn Term
All assessmentsin each unit dependent on rotations
B6, P5, C6
Spring Term
All assessmentsin each unit dependent on rotations
C7, C8, P6, P7
SummerTerm
All assessmentsin each unit dependent on rotations
B7 AND REVISION
By the end of the Year studentswill be confidentwith all of the fundamental and more complexprinciples, knowledge and application of this knowledge in all three subject areas. They will be able to understand what they need to do in response to all exam style questionsand LOR questions; they will be able to revise effectively as they head towardsthe final examinationsin the summerof Year 11.
Their practical skills will have developed both in discussingvariables and describing methodsbut also analyzing data, interpreting results and suggesting improvements. It is also hoped that links can be made between other sciences as they developas complete scientists.