- By end of the Spring term I can
Use fronted adverbials (Y4)
Use expanded noun phrases to convey complication information concisely Link ideas across paragraphs using adverbials commas after fronted adverbials (Y4) Use inverted commas and other punctuation to punctuate direct speech (Y4) Use expanded noun phrases to convey complication information concisely use modal verbs or adverbs to indicate degrees of possibility plan writing by identifying audience and purpose use brackets, dashes or commas to indicate parathesis
Use relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, when, whose, that or an omited relative pronoun Choose the appropriate register intergrate dialogue to convey character and advance the action use commas to clarify meaning of avoid ambiguity in writing Variety of verb forms used correctly and consistently including modal verbs and the present perfect form link ideas across paragraphs using adverbials link ideas using tense choices use brackets, dashes or commas to indicate parenthesis
- By end of the Spring term I can
Use expanded noun phrases to convey complication information concisely use passive verbs link ideas across paragraphs using a wider range of cohesive devices integrate dialogue to convey character and advance the action enhance meaning through selecting appropriate grammar and vocabulary use expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely use modal verbs and adverbs to indicate degrees of possibility use brackets, dashes or commas to indicate paranthesis
distinguish between the language of speech and writing recognise vocabulary and structures for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms use passive verbs use semi-colons to mark boundaries between independent clauses Use passive verbs variety of verb forms used correctly and consistently including the progressive and the present perfect forms use a wide range of devices to build cohesion use organisational and presentational devices to structure text use colons to mark boundaries between independent clauses
6 Green Forms recognisable lower-case letters, most of which are correctly formed. Uses the Tree Symbol to learn and practise letter formation, orientation and placement Understands which letters belong to which handwriting families (Jumper, Abracadabra, Window Cleaner, Special Squirter, Fisher and Slider)
7 Orange Forms recognisable lower-case letters, starting and finishing at the right place Forms capital letters correctly, Forms digits 0-9 correctly, Writing sits on the line.
8 Turquoise Forms lower-case letters and capital letters correctly, starting and finishing at the right place. Lower-case and capital letter sizing may not yet be consistent. Uses spaces between words that reflects the size of the letters
9 Purple Forms lower-case letters and capital letters of the correct size relative to one another All letters are written in the correct orientation, and relationship to one another, in preparation for joining. Uses adequate and consistent spaces between words
10 Gold Begins to use some of the diagonal and horizontal strokes needed to join letters Starts to understand which letters when adjacent to another are best left unjoined.
11 White More consistently uses the diagonal and horizontal strokes needed to join letters. More consistently leaves the appropriate adjacent letters unjoined Spaces between words continue to be consistent
12 Lime Writes with increasing legibility, consistency and quality. Ensures that the downstrokes of letters are parallel and equidistant. Ensures that ascenders and descenders of letters do not touch
13 Brown Writes legibly, fluently and in a consistently joined way (may show an individual style). Writes with increasing speed

- By end of the Spring term I can spell the following words:
according achieve aggressive attached available average awkward bruise category committee communicate community competition correspond criticise curiosity definite
develop excellent embarrass explanation familiar forty government harass identity interrupt lightning marvellous muscle necessary nuisance occupy occur
- By end of the Spring term I can spell the following words: accommodate accompany amateur ancient appreciate apparent bargain cemetery conscience conscious controversy convenience determined dictionary disastrous
environment equipment especially exaggerate existence foreign frequently guarantee immediately interfere individual language leisure mischievous neighbour
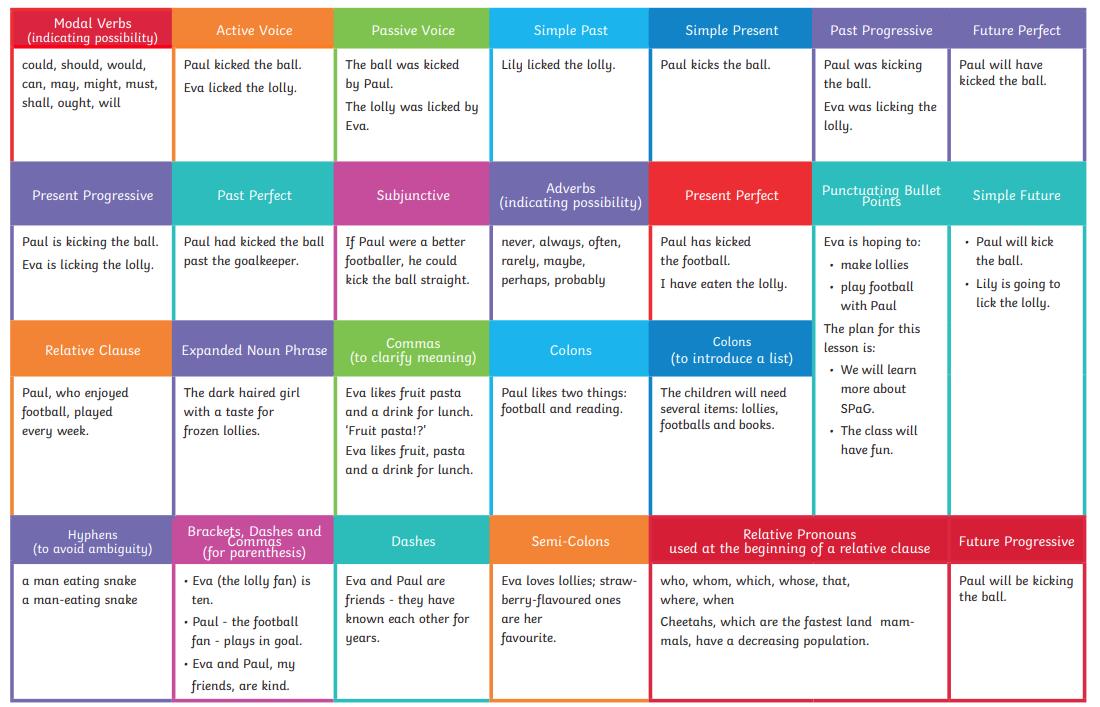
A relative clause is a special type of subordinate clause which adds extra information to another noun or clause. A relative clause uses a relative pronoun such as; ‘who’, ‘that’ or ‘which’. The extra information is embedded in a sentence with commas. James, who never does his homework, is very lazy. All the chocolate pudding was gone by the time I got to lunch, which really annoyed me.
Modal verbs change or affect other verbs in a sentence. They are used to show the level of possibility – certain, possible or impossible. My keys must be in the house.
Modal verbs also talk about ability, to ask permission, make requests or offers. May I ask a question? Could I have some Cohesive devices tea, please?
Relative Pronouns (who, which, where, that, when) introduce a relative clause. They refer back to a noun or clause what we already know.
The athlete, who won the race, trained hard. Where did you buy the jumper that you wore yesterday?
A letter or group of letters can be added to the beginning of a verb to make a new word with a slightly different meaning.
dis- (this reverses the verb meaning) disconnect de- (means ‘do the opposite’) deselect mis- (means ‘badly’) mislead over- (means ‘too much’) oversleep re- (means ‘again’ or ‘back’) revisit
To convert a noun or adjective, a letter or group of letters can be added to the end of a noun to make a verb.
-ate = assasinate -ise = authorise -ify = classify
Brackets are used to add extra information in a text. Curved brackets are most commonly used in a clause.
Mrs Jones (my teacher) works in Year 5.
We use parenthesis to add extra detail to a clause which is already grammatically correct. We may use brackets, dashes or commas to separate the information within the main clause.
Commas are used to embed a clause (a group of words that include a subject and verb) within a main clause. The comma is used before the embedded clause and immediately after. Michael, who sits next to me, is brilliant at Art.
A synonym is a word or phrase with the same or similar meaning to another. You can find synonyms in a thesaurus. Talk = speak = mention sleep = doze = kip
Bullet points can be used to break up complicated information, make the text easier to read or turn it into a list. A colon must be used before a list.
I need to buy:
• mushrooms
• toothpaste
• popcorn
Punctuation marks are important because they give writing flow. They also help to change how the reader understands the writing.
A semi-colon joins two independent clauses without using a conjunction such as ‘and’. We can go to the library in the morning; Mondays are usually quiet. A semi-colon may be used in a list to divide the items where commas are already used to avoid ambiguity. I have been to Birmingham, England; Paris, France; New York, USA; and Moscow, Russia.
The subject is the person, noun phrase, pronoun or thing which does the verb in a clause.
Wednesday is my favourite day. Sam’s mum is picking me up today. Are you coming to the sleepover?
An antonym is a word or phrase with the opposite meaning. young – old straight – bendy full – empty
A colon is used to tell the reader ‘this is what I mean’ or ‘as follows’ and indicates the information following it.
I ordered the following ingredients (and they are): eggs, butter and flour.
Would simply be written as,
I ordered the following ingredients: eggs, butter and flour.
A text which has cohesion fits logically together. A writer may use repetition of word or phrase, adverbials or ellipsis to build on writing. The day was fun, fun, fun.
Formal language uses unabbreviated words and an appropriate choice of vocabulary and grammar whereas informal language uses relative clauses with no relative pronouns and contractions. It is important to select the correct language for writing.
find out – discover ask for – request go in – enter
The object is the person, noun, pronoun or thing which usually comes directly after the verb. Wednesday is my favourite day. Sam’s mum is picking me up today. Are you coming to the sleepover?
● To interpret negative numbers in context, count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers through zero
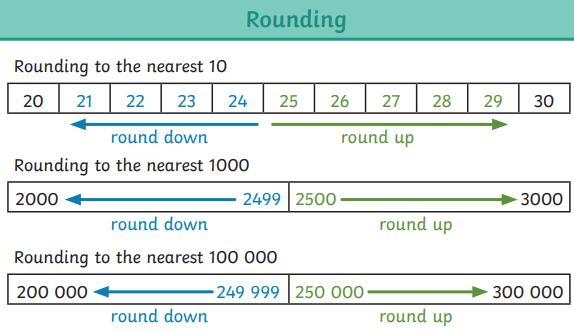
● To round any number up to 1,000,000 to the nearest 10, 100, 1000, 10,000 and 100,000
● To solve number problems and practical problems that involve all of the above.
Calculation ( Addition, subtraction, division, multiplication)
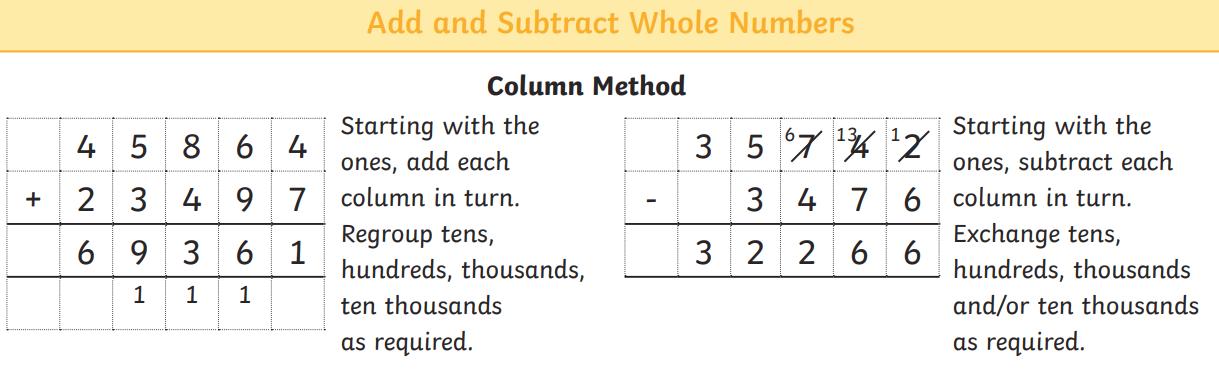
● To add and subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits, including using efficient written methods (columnar addition and subtraction)
● To solve addition and subtraction multi-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why.
● To use rounding to check answers to calculations and determine, in the context of a problem, levels of accuracy
● To solve problems involving numbers up to three decimal places
● To recognise and use square numbers and cube numbers, and the notation for squared (2) and cubed (3)
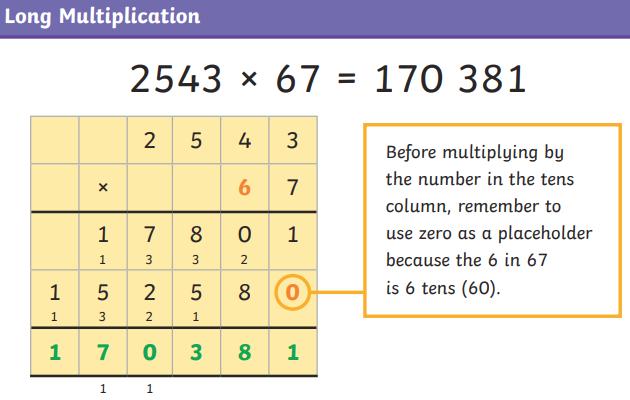
● To multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a one- or two-digit number using an efficient written method, including long multiplication for two-digit numbers.
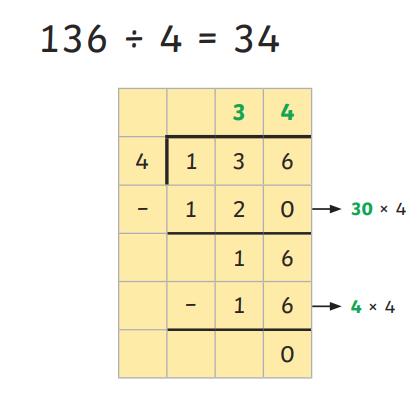
● To divide numbers up to 4 digits by a one-digit number using the efficient written method of short division and interpret remainders appropriately for the context
● To identify, describe and represent the position of a shape following a reflection or translation using the appropriate language, and know that the shape has not changed.
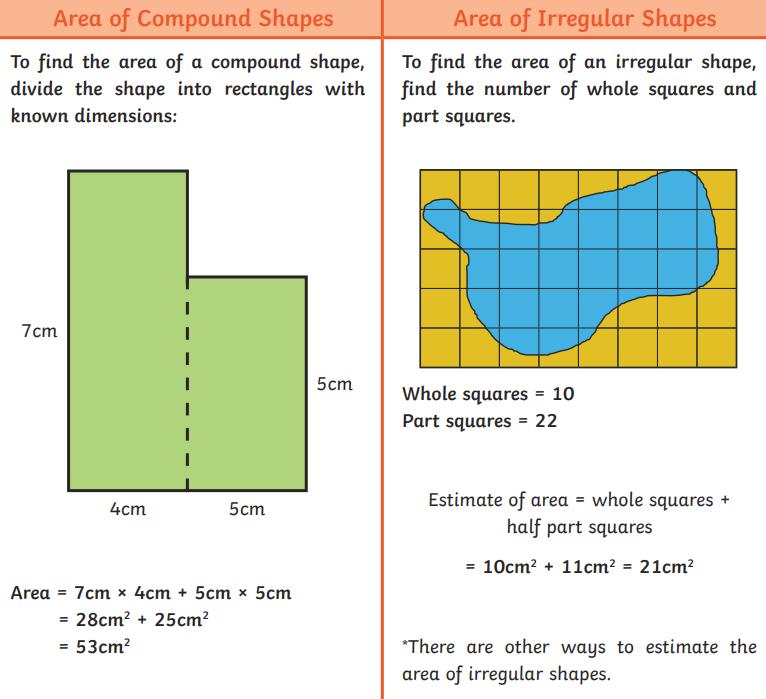
●To measure and calculate the perimeter of composite rectilinear shapes in centimetres and metres;
●To calculate and compare the area of rectangles (including squares), and including using standard units, square centimetres (cm2) and square metres (m2) and estimate the area of irregular shapes;
● To estimate volume [for example, using 1 cm3 blocks to build cuboids (including cubes)] and capacity [for example, using water]
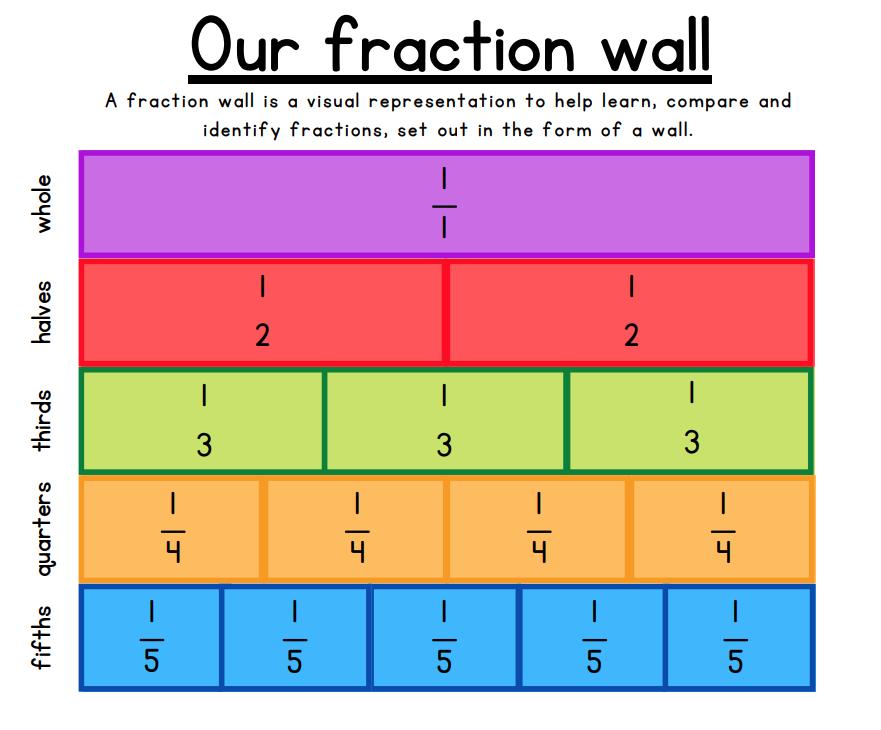
Fractions
● To recognise mixed numbers and improper fractions and convert from one form to the other; write mathematical statements > 1 as a mixed number
● To add and subtract fractions with the same denominator and multiples of the same number Decimals and Percentages
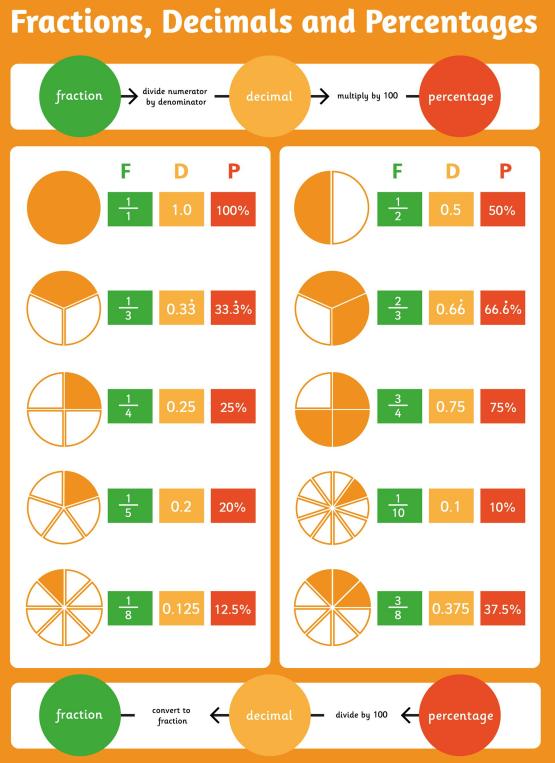
● To solve problems which require knowing percentage and decimal equivalents of and those fractions with a denominator of a multiple of 10 or 25
● To recognise the per cent symbol (%) and understand that per cent relates to ‘number of parts per hundred’, and write percentages as a fraction with denominator 100, and as a decimal
● To solve problems which require knowing percentage and decimal equivalents of and those fractions with a denominator of a multiple of 10 or 25.
To solve problems involving multiplication and division, including scaling by simple fractions and problems involving simple rates Algebra
● To find pairs of numbers that satisfy number sentences involving two unknowns. Data and statistics
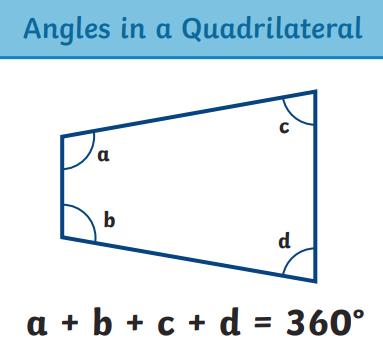
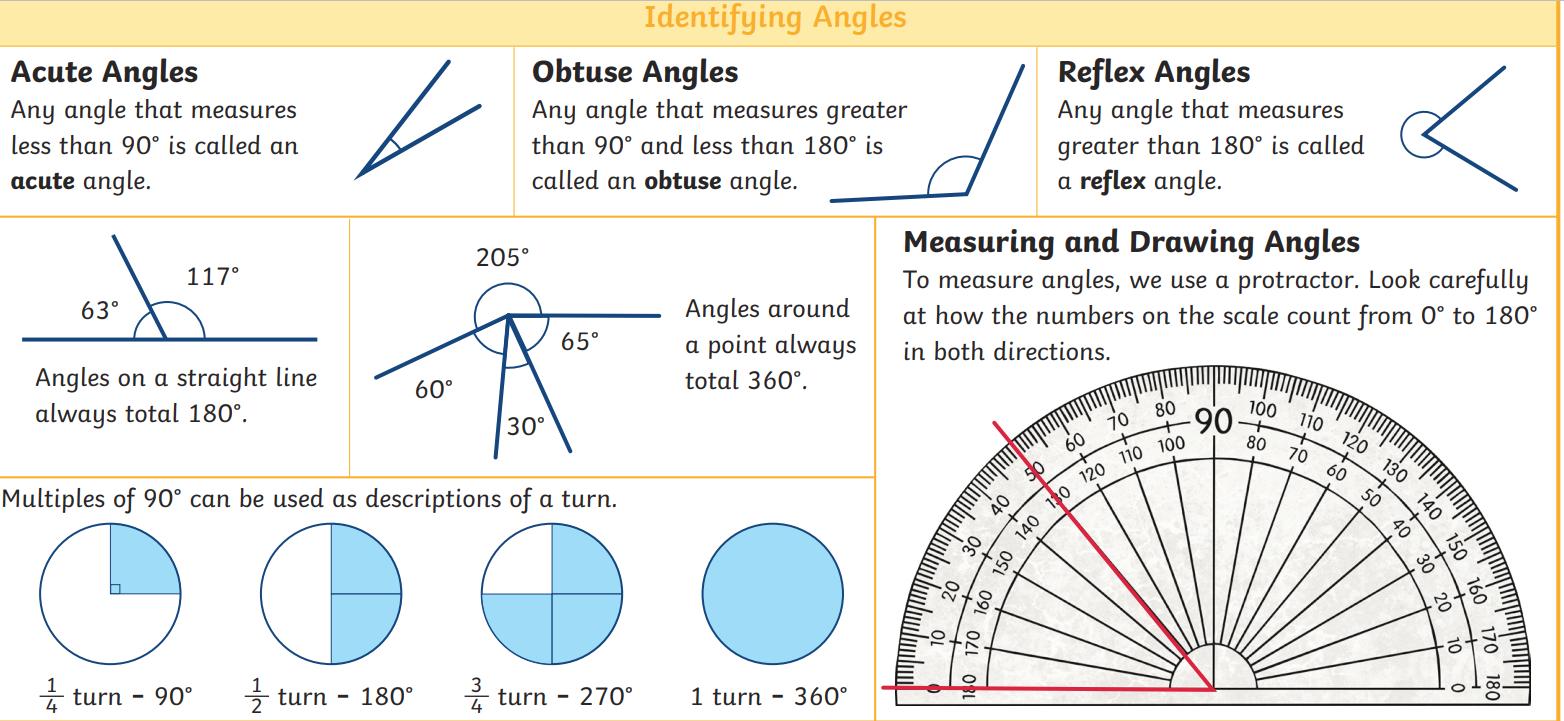
● To solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in a line graph Angles
● To use the properties of rectangles to deduce related facts and find missing lengths and angles.
● To read, write, order and compare numbers at least to 10,000,000 and determine the value of each digit
● To round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy.
● To use negative numbers in context and calculate intervals across zero
● To solve number problems and practical problems that involve all of the above Calculation ( Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division)
● To perform mental calculations, including with mixed operations and large numbers
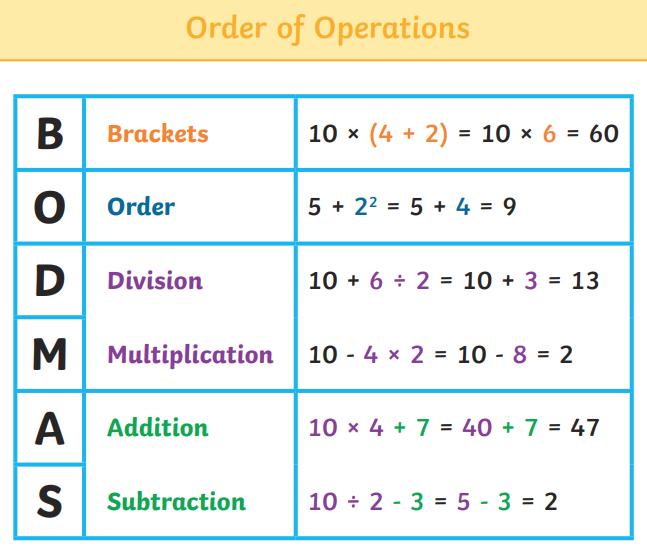
● To use their knowledge of the order of operations to carry out calculations involving the four operations
● To use estimation to check answers to calculations and determine, in the context of a problem, levels of accuracy
● To solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
● To use estimation to check answers to calculations and determine, in the context of a problem, levels of accuracy
●Add whole numbers and decimals using formal written methods (columnar addition)
●Subtract whole numbers and decimals using formal written methods (columnar subtraction).
● To identify common factors, common multiples and prime numbers
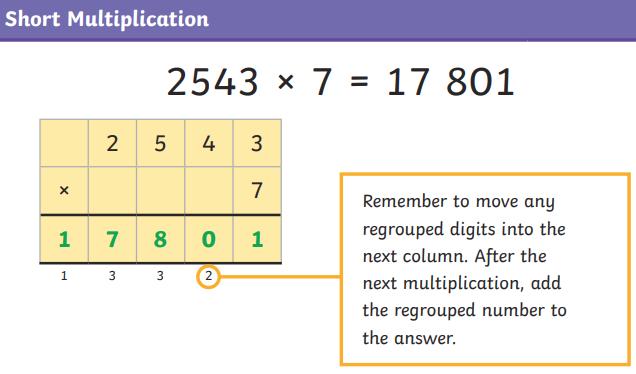
● To multiply multi-digit numbers up to 4 digits by a one-digit whole number using the efficient written method of short multiplication
● To divide numbers up to 4 digits by a one-digit whole number using the efficient written method of long division, and interpret remainders as whole number remainders,
● To solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
● To describe positions on the full co-ordinate grid (all four quadrants) Including on blank axis
● To draw and translate simple shapes on the co-ordinate plane and reflect them in the axes
● To recognise that shapes with the same area can have different perimeters and vice versa
● To calculate the area of parallelograms and triangles
● To recognise when it is necessary to use the formulae for area and volume of shapes
● To calculate, estimate and compare volume of cubes and cuboids using standard units, including centimetre cubed (cm3) and cubic metres (m3) and extending to other units such as mm3 and km3.
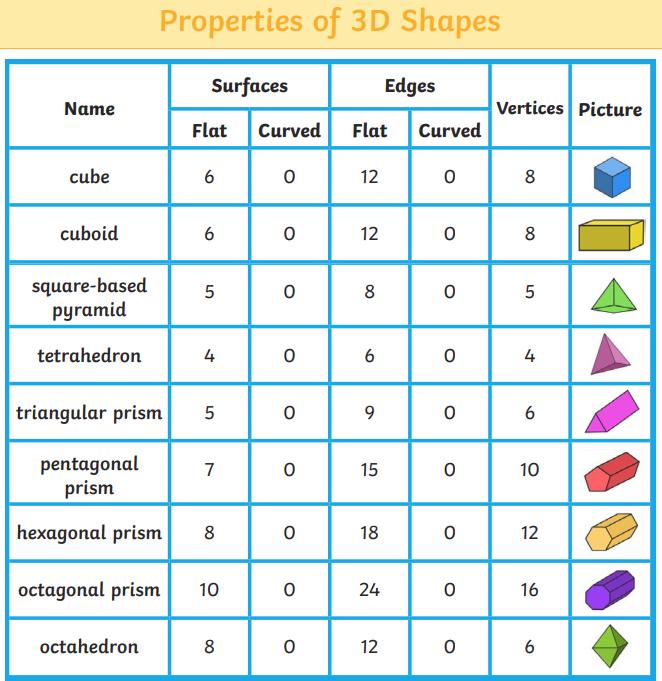
● To recognise, describe and build simple 3D shapes, including making nets
● To illustrate and name parts of circles, including radius, diameter and circumference and know that the diameter is twice the radius Fractions
● To add and subtract fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers, using the concept of equivalent fractions
● To multiply simple pairs of proper fractions, writing the answer in its simplest form.
● To divide proper fractions by whole numbers
Decimals and percentages
● To multiply one-digit numbers with up to two decimal places by whole numbers
● To use written division methods in cases where the answer has up to two decimal places
● To solve problems which require answers to be rounded to specified degrees of accuracy.
● To recall and use equivalences between simple fractions, decimals and percentages, including in different contexts
Recall and use equivalences between simple fractions, decimals and percentages, including in different contexts
Find percentages of amounts
Solve problems involving the calculation of percentages (for example, of measures, and such as 15% of 360) and the use of percentages for comparison.
● To solve problems involving the relative sizes of two quantities where missing values can be found by using integer multiplication and division facts
● To solve problems involving similar shapes where the scale factor is known or can be found
● To solve problems involving unequal sharing and grouping using knowledge of fractions and multiples.
Algebra
● To find pairs of numbers that satisfy number sentences involving two unknowns
● To enumerate all possibilities of combinations of two variables
Data and Statistics
● To calculate and interpret the mean as an average.
● To interpret and construct pie charts and line graphs and use these to solve problems;