ENDEAVOUR ENERGY
IMPROVES PUBLIC SAFETY WITH ITS DIGITAL TWIN
SYDNEY WATER INSTALLS NEW IOT SENSORS IN MAJOR ROLLOUT
THE

FUTURE OF WATER MANAGEMENT WITH URBAN UTILITIES’ NEW CEO

WATER SEWER ELECTRICITY GAS www.utilitymagazine.com.au Issue #38, May 2023


























































































































Published by Monkey Media Enterprises
ABN: 36 426 734 954
C/- The Commons
36–38 Gipps St, Collingwood VIC 3066
P: (03) 9988 4950 monkeymedia.com.au info@monkeymedia.com.au utilitymagazine.com.au info@utilitymagazine.com.au
ISSN: 2203-2797
Editor
Katie Livingston
Journalists
Stephanie Nestor, Tayla Oates, Tess Macallan, Steph Barker
Design Manager
Alejandro Molano
Senior Designer
Luke Martin
Designers
Danielle Harris, Ozlem Munur, Jacqueline Buckmaster
National Media and Events Executives
Rima Munafo, Brett Thompson
Marketing Manager
Radhika Sud
Marketing Associates
James Holgate, Jackson Barnes
Digital Marketing Assistants
Natalie Ta, Bella Predika, Rhys Dawes
Publisher
Chris Bland
GM Growth and Strategy
Laura Harvey
Managing Editor
Jessica Dickers
FROM THE EDITOR
It is with great excitement that I am writing this letter as the new editor of Utility Magazine, and I am delighted to be joining the exceptional team at Monkey Media.
My predecessors worked tirelessly to maintain Utility’s reputation as a respected industry platform for Australia’s utilities to share and learn alongside each other, and this is a legacy I hope to both preserve and build on. I am excited to immerse myself in the industry and I’d love to hear from you with any story ideas or industry insights.
Utility is and always has been a publication by the industry, for the industry, and our goal is to reflect the challenges and concerns facing Australia’s utilities, as well as celebrate their exceptional work and achievements and share the latest innovations. On this note, my contact details are below and I encourage you to get in touch if you’d like to discuss any potential articles, collaborations or news that you would like to see in future issues.
In this edition, we’ve collaborated with some of the industry’s key figures to bring you exciting contributions that cover the most important issues affecting Australia's utilities. Climate change, and subsequently the advancements in renewable technology are constantly shaping the way in which both the water sector and energy networks operate.
In this issue, we explore how water utilities are managing the challenges posed by unprecedented weather conditions, and how they are keeping services going amid devastating floods. While swift action in an emergency is essential, we’re seeing a lot of preventative measures being implemented across the country and Sydney Water is already underway on the large-scale deployment of IoT wastewater monitoring sensors.
Over in the energy sector, we’re also seeing new technology making exciting improvements to Australia’s energy networks. This issue covers Endeavour Energy’s new digital twin technology, and how it has allowed the utility to identify clearances between rising floodwaters and power lines remotely. We also take a deep dive into the major funding for trial sensors that will increase utilities' capacity to support renewable energy and improve the efficiency of existing transmission lines.
We’re honored to be partnering with some big industry events, with this issue of the magazine being distributed at WIOA Queensland, OzWater, Locate23 and Australia Wind Energy 2023, and I look forward to meeting some of you in person at these events over the next few months.
The team and I are working hard to deliver the insightful content that Utility is renowned for, and I can’t wait to learn more about the industry and bring my very best to each and every issue.
We hope you enjoy this edition.
Katie Livingston Editor

welcome May 2023 ISSUE 38 1
Katie a line at katie.livingston@monkeymedia.net.au or feel free to call them on 03 9988 4950 to let them know what you think. Don't forget to follow Utility Magazine on social media
find us on LinkedIn, Twitter and YouTube.
Drop
–
Utility Magazine acknowledges Aboriginal Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and pays respect to their cultures and Elders past, present and emerging.
Scan to subscribe to Utility magazine’s weekly newsletter – delivered to your inbox every Thursday morning.
This document has been produced to international environmental management standard ISO14001 by a certified green printing company.






UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 2 CONTENTS SMART METERS Toowoomba Council turns the tap on for smart water meters .......... 96 Smart Water Metering: business transformational, not just remote meter reading 98 ENERGY STORAGE The next generation of energy storage 100 FUTURE FUELS How research is creating new knowledge for the energy transition 102 How to get Australia back in the global hydrogen race ........... 106 MICROTUNNELLING Yarra Valley Water’s trenchless technology innovator explores critical innovations ..................... 108 88 96 102 WATER MANAGEMENT Procuring innovative water asset management technology 52 Sydney Water installs new IoT sensors in major rollout 54 Sydney Water is undertaking the first wastewater monitoring Internet of Things (IoT) deployment of its scale in Australia, which is saving hundreds of thousands of dollars per month in potential blockages. Everything you need to know about sodium hypochlorite in water treatment 56 Building trust, driving innovation, and delivering value in the water sector 58 Remote automation infrastructure transforms distributed water scheme ............ 62
MANAGEMENT New high-voltage transmission line powering SA’s Eyre Peninsula 42 Homes, businesses and communities across South Australia’s Eyre Peninsula now have a more secure power supply following the completion of Eyre Peninsula Link. Achieving renewable-first controls 44 WATER MANAGEMENT Keeping water services flowing amid rare river flood ................... 46 Water management: are utilities security guards or stewards? 50 VEGETATION MANAGEMENT Vegetation management that's ahead of the pack 88 The power of vegetation management in the Red Centre ............................. 90 Augment vegetation management with satellite imagery 94 INDUSTRY INSIGHTS The future of water management with Urban Utilities’ new CEO 26 Creating innovative solutions to mitigate flood damage ............. 30 Mitigating cybersecurity threats in water and wastewater 32 Coliban Water uses laser-guided tunnel bore for sewer installation 34 Think you know how to work near gas pipelines? Think again .................................... 36 The role of digital connectivity in Industry 4.0 38 Four practical ways to implement effective compliance programs .................. 40 46 42 26
DEMAND
Benefits and challenges of
The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) is providing major funding to help New South Wales Transgrid and Infravision trial sensors that will increase capacity to support renewable energy and improve the efficiency of existing transmission lines.

SUSTAINABILITY
Unitywater
With a growing population, a changing climate and the desire to improve the liveability of South East Queensland front of mind, Unitywater has harnessed the power of science, technology and Mother Nature to implement key infrastructure projects that will help reduce the utility’s operating footprint. Unitywater Executive Manager Sustainable Infrastructure Solutions, Daniel Lambert, expands on some of the projects and key milestones that the water utility is delivering.
INSPECTION, CCTV & CONDITION ASSESSMENT
How QLD’s largest sewer was upgraded while the city slept 80

82 Aging infrastructure and rising sewerage temperatures pose increasing risks for corrosion of concrete sewerage pipes around the world. Failing pipes are a significant threat to utility operations, public health and the environment. However, there could soon be a solution. Professor in Structural Engineering at the University of South Australia STEM, Yan Zhuge, is leading a project focused on a self-healing concrete that could help prevent future pipelines from corroding.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 3 May 2023 ISSUE 38 In each issue Welcome from the Editor ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 1 A word from Energy Networks Australia ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 4 A word from WSAA ����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 6 News briefs ������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ 8 Advertisers’ index ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 112 Editorial schedule ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� 112 64 80 72 ENERGY NETWORKS
renewable
line sensors 64
Virtual asset assessment: digital intelligence solving network challenges 66 Endeavour Energy pioneers innovation with its digital twin 68 Overcoming challenges in Port Melbourne network augmentation project 70
transmission
Concrete solutions for Australia’s future pipelines
Boosting security for telecommunication assets .......... 84 Spacers assisting with corrosion management 86
on a green path to achieve sustainability goals 72
The equipment making vegetation management sustainable 74 Gippsland Water powers towards a 100 per cent renewable future 76 Increasing Australia’s digital capabilities and sustainability 78
THE IMPORTANCE OF TRANSMISSION DEVELOPMENT ACROSS AUSTRALIA’S STATES
 By Dominic Adams, GM Networks, Energy Networks Australia
By Dominic Adams, GM Networks, Energy Networks Australia
Firstly, we need to talk about the problems with the old national framework, which will help us understand what the state frameworks have to do better.
Secondly, it’s important to talk about Australia’s constitutional history to understand why state governments care about transmission development. Then we will turn to the things to keep an eye out for as we develop new transmission frameworks.
THE OLD NATIONAL FRAMEWORK
In mid-2018 the energy industry collectively realised, with the release of AEMO’s first Integrated System Plan, that transmission was needed yesterday. The image shows the huge amount of transmission infrastructure, including interconnectors, that needs to be built to reach our decarbonisation objectives.
AEMO’s 2022 Integrated System Plan identifies an additional 10,000km of transmission lines are needed to support 120GW of large scale renewable energy and storage on the national interconnected energy system. The focus on transmission delivery was subsequently dialled up. It soon became clear that the national framework just wasn’t up to the job. There were three main issues:
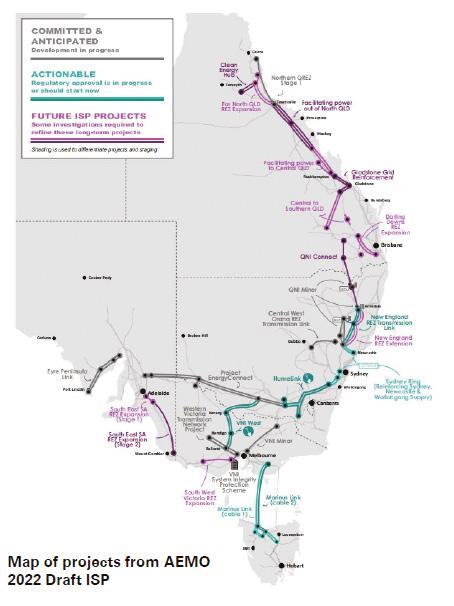
1. It wasn’t designed to connect renewables – it could connect a big generator like a Snowy 2.0 but it couldn’t handle that coordination task with adding lots of smaller generators
2. It wasn’t designed for scale – it didn’t have wriggle room or financial pressure valves to allow a bit more cash-flow here or to accommodate a higher risk there. You need these mechanisms if you’re going to put in 10,000km of new transmission within a decade
3. It wasn’t designed for speed –projects were held up because the critical path was to go through all the regulatory approvals and then pick up the tools Project EnergyConnect was a real-time case study. It needed the Clean Energy Finance Corporation support to deal with issue (2) and it needed government underwriting to deal with issue (3).
WHY STATE GOVERNMENTS CARE
Given the pace of the transition, the existing framework wasn’t going to deliver good outcomes for customers. The task ahead was, and still is, looking scary. So why is it state governments who seem to be leading the charge to deal with this? To answer this, we need
to go back to 1900 when the Australian Constitution was written. Back then:
• Sydney was four years away from electric streetlights
• Generators would shut down for Sundays
• The first high voltage transmission was 16 years away – for hydro in Tasmania
We can’t really blame them. In a federation like Australia, the buck stops with the states – as does the political and social imperative to keep the lights on. While the National Electricity Market formally commenced in 1998, interconnecting five east coast market jurisdictions, the more recent imperative to decarbonise our energy system, different state emissions reduction targets and system needs has led to a more bespoke state-bystate approach.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 4 A WORD FROM ENERGY NETWORKS AUSTRALIA
If you follow the media’s updates of Australia’s energy sector, it would appear state governments all seem to be building their own transmission frameworks. Well, you’d be right. Each state has its own framework for getting transmission built in its jurisdiction. As they get on with delivering projects, there are a few important things to keep an eye out for. To understand how we got here, we need to go back.
Consequently, all jurisdictions are moving with some urgency to bring the energy transition within their control. They are each going about it in different ways because their starting points are different – different market and ownership structures and in Victoria, different planning and investment rules. We often say of the transmission framework – both the physical system and the rules-based frameworks – that if you wanted to design what we need for the future you simply wouldn’t start where we are today.
NOTES FOR STATE FRAMEWORK DEVELOPERS
While each state is building its own framework to deliver much-needed new transmission, there are a few common issues and challenges that are worth keeping in mind:



Customers
There is only one reason we are on this journey. The challenge of managing the energy transition is a fine balance between environment, cost, and speed and it all comes back to the customer.
There is a big difference between working for customers and working with them. Building that trust and social licence requires transparency and genuine engagement. While transparency can sometimes meet its nemesis – confidentiality – it can pay significant dividends.
Risk allocation is critical
In the good old days when everything moved slowly, transmission businesses could arrive at a number through a regulatory process and back-to-back with a fixed price contract. It is not that simple anymore. Contractors should bear risks they can control, but they cannot control global supply chain costs and have limited ability to foresee all risks arising from greenfield projects. There are two options, to increase upfront prices or to share risks. How to solve this issue? See the first point.
This is a repeat game
There will be some mistakes, but the transition is not happening overnight, so we get to learn together. It is the mindset of listening to,
empathising, and partnering with your counterparties, whoever they are, that will get us through.
Workforce constraints need addressing
We have the capacity across the country to deliver about 700km of new transmission a year, which is not nearly enough. The silver lining is that we have an emerging talent pool of young apprentices, engineers and other skilled workers all keen to play their part in Australia’s energy transition. This is a once-in-a-lifetime transformation and we need to make this an attractive industry that looks after these future employees.
There are plenty more challenges to work through together and not all of them are known to us, given the rapid pace of the transition and the new technical and technological ground that is being broken. It is critical we continue to work together to share learnings and ensure the focus is always on the long-term interests of our customers.
UTILITY • MAY 2 023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 5 Unit 2 / 85 Heatherdale Road, Ringwood Vic 3134 PO Box 2500, North Ringwood Vic 3134 P: (03) 9872 4596 | F: (03) 9872 3293 | E: info@pezztrenchless.com.au | W: pezztrenchless.com.au Still the market leaders in laser guided microtunnelling Bore diameters from 325mm up to 2800mm Used for gravity sewers, water mains, storm water, gas and electrical conduits. Specialists in “free bore”, sleeve boring and pipe jacking in all sizes The
Trenchless
Next Generation in
Technology
RESEARCH, DEVELOPMENT AND INNOVATION IN THE WATER SECTOR
The urban water industry is currently facing significant challenges, driven by the external factors of increased climate variability, aging infrastructure and constraints on our supply chain, human resources and capital availability, coupled with increasing customer expectations and upward pressures on interest rates and affordability.

In a post-COVID environment, communities have focused on creating resilient, well-functioning, digitallyconnected and liveable cities. Research, development and innovation (RD&I) provide a clear avenue to help address these challenges in ways that are lower cost, while delivering enhanced customer and community value.
To assist the sector, WSAA – alongside a focused leadership team – has formulated an integrated, national RD&I strategic approach. Called the RD&I Ecosystem, it is designed to streamline and enhance the delivery and uptake of RD&I offerings for the sector and position the sector well for the future.
In March 2023, WSAA released a strategy outlining the key elements for the RD&I Ecosystem and the five-year implementation plan for coordination and collaboration in RD&I across the water sector. The Strategy builds on the national research priorities agenda and is a core component of WSAA's national strategic program for the sector.
The purpose of the RD&I Strategy is to help the urban water industry develop, support and harness the RD&I potential from both within the sector and across other industries for value creation that supports thriving communities, optimises customer value, enhances the natural environment and delivers business resilience.
The RD&I ecosystem framework consists of seven elements:
• Leadership to drive an RD&I culture
• Knowledge to find what’s gone before and what’s happening now
• Opportunities to bring ideas, people and technology together
• Collaboration to work more easily with others and produce better results
• Pathways to explain clearly what happens next
• Application to provide guidance on implementation
• Communications and engagement to create awareness and drive participation
Each element includes an objective, key actions to take us there, and ways to measure improvement.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU SECTION 6 A WORD FROM WSAA
To read WSAA’s Strategy online, visit: www.wsaa.asn.au/publication/urban-water-industryresearch-development-and-innovation-strategy.






IT DOESN’T JUST MEASURE VALUES. IT HAS VALUES. THE 6X ®. AVAILABLE NOW! The VEGAPULS 6X: A radar level sensor that is not only technically perfect, it also takes the user into account. It’s easy to set up and at home in virtually any process or industrial environment. Made by a company that bases its decisions on values that are good for everybody. VEGA. HOME OF VALUES. www.vega.com/radar
$120M ALLOCATED FOR COMMUNITY BATTERIES
The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) has announced $120 million in funding for the first round of the Community Batteries Funding Program.
The program aims to support the deployment of 342 community batteries across Australia to lower energy bills, cut emissions and reduce pressure on the electricity grid.
ARENA Chief Executive, Darren Miller, said community batteries represent the next step in optimising distributed energy resources in the electricity grid.
“Not everyone is able to install rooftop solar, but by storing electricity close to the point of consumer demand, we can reduce network costs and alleviate constraints in areas with high solar penetration. This will
ultimately reduce electricity costs for all consumers.” Mr Miller said.

ARENA is now seeking applications for up to $20 million in funding to deploy a minimum of five community batteries.



To be eligible for ARENA funding, each community battery must be between 50kW and 5MW in size and connected to the distribution network.
ARENA has allocated $120 million in funding for round one, split equally across two streams:
• Stream A: Distributed Network Service Providers (DNSP)

• Stream B: Applicants that are not DNSPs
Community batteries provide energy storage in the distribution network that can store excess solar energy for later use, putting downward pressure on

household electricity costs and easing pressure on the local electricity grid.
As part of the 2022/23 Federal Budget, the Government allocated $200 million for the Household Solar budget measure to deploy 400 community batteries across Australia.
ARENA was allocated $171 million of this funding to deliver at least 342 batteries, $120 million allocated to round one and the remaining funding allocated to a future round, based on learnings from this tranche.
The Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water (DCCEEW) will deliver an initial 58 community batteries through the Business Grants Hub. This round is now closed, with DCCEEW now assessing applications.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 8
NEWS No. 407319937
Meter security seals Contact us for more information about our comprehensive range of key cabinets. Trackable Serial Numbering Expose Unauthorised Access
Key management
WINNER OF THE BEST TASTING TAP WATER IN VICTORIA COMPETITION
The winner of the 2023 Ixom Best Tasting Tap Water in Victoria competition was announced at the Water Industry Operators Association of Australia (WIOA) conference in Bendigo.

Watersure – Victorian Desalination Plant took home the title, after competing against the other two Grand Finalists for Victoria, Falls Creek Alpine Resort and North East Water –Benalla WTP.
Water samples were subjected to a blind taste test and rated according to the Water Tasting Wheel, which outlines some of the attributes that water professionals use when judging water such as colour, clarity, odour and taste.
This year’s Victorian judges included Utility Magazine’s new Editor, Katie Livingston; Warrick Green from Ixom; Doug Moorby, Manager Utilities at Narromine Shire, NSW; and Kyra Sunnex from NZ Tour Group.
Watersure will now go on to battle it out against the best from other states for the Australian title in November 2022.
The winner of the national competition will then represent Australia at the annual Berkeley Springs International Water Tasting Competition in West Virginia, USA.
WIOA Managing Director, George Wall, said the competition recognises and acknowledges the individuals and organisations that are stepping up,

some in very trying circumstances, to make sure their communities are supplied with safe drinking water every day.
“We want to use the competition to let people know the great work that is going on in local communities around Australia, and help to shape and secure Australia’s water future,” Mr Wall said.
Mr Wall also acknowledged Ixom’s support of the Best Tasting Tap Water competition.

“Thanks to Ixom’s unwavering commitment and support of the industry, we have been able to continue running the competition.”


UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 9
NEWS
WA RESIDENTS TO RECEIVE STANDARD POWER SUPPLY ALLOCATION
The Western Australia State Government has announced an across-the-board power supply allocation will soon be in place for regional and metro areas across the South West Interconnection System (SWIS).

Western Australia Energy Minister, Bill Johnston, announced the standard power supply allocation and said it will meet the evolving energy needs of Western Australians.
“We’ve listened to the community and sought advice on how we can best serve the power supply demands of Western Australians now and in the future,” Mr Johnston said.
“I’m pleased to announce that we now have one equitable power supply allocation across the network – that means regardless of whether you live regionally or in the metro area, everyone will have the same standard supply.
“Western Power has successfully undertaken a trial to test this and ensure network infrastructure is built for increased rural loads.
“The comprehensive assessment used Advanced Meter Infrastructure data to verify that a standardised connection service can be applied across the network safely and reliably.
“The new standard demonstrates Western Power’s commitment to transforming the network to facilitate the growth of renewables and electrification.”
Western Power will now offer a standard connection service capacity of 63 amps for small-use, single-phase (240V) connections regardless of location, ensuring that all homes and businesses across the entire network have the same allocation.
The increase to regional supply followed Western Power’s trial, which successfully established that a standardised supply allocation could be managed in a safe and reliable way for community benefit.
The 24-week trial involved seven regional local government areas ensuring that a representative sample of a diverse range of rural customers with different energy needs was included.
The trial enabled the installation of a 63 amp-rated main switch circuit breaker for all new single-phase connections to the network, or when altering an existing electrical installation.
Data from 140,000 single-phase meters across the network was analysed to understand load demand and network usage in metro and rural areas, which proved that existing electrical infrastructure could accommodate increased rural load requirements.
The installation of a main switch circuit breaker is critical in providing overload protection for a household if its capacity is exceeded. It prevents more widespread outages and damage to equipment, ensuring that the whole community has safe and equitable access to power supply.
The one standard supply will enable greater electrification and uptake of renewables and aligns with state and national compliance frameworks including Australian standards.
Electrical contractors are required to assess household demand requirements when adding new circuits for property owners and apply for an upgraded supply allocation where necessary.
NEWS
10


email: AU.sushisensor@yokogawa.com website: www.yokogawa.com/au Phone: +1300 558 965 Wireless IoT sensing for industrial processes from the benchmark for quality & reliability Digital Transformation Without Compromise
THE LARGEST SOLAR FARM IN AUSTRALIA HAS FINISHED CONSTRUCTION
The Western Downs Green Power Hub in Queensland has reached the end of construction on the largest solar farm in Australia.
Totalling more than one million solar panels, the 400MW Western Downs Green Power Hub has the capacity to power the equivalent of 235,000 Queensland homes and is connected to the Queensland SuperGrid by a new 275kV line built by Powerlink.
Queensland Premier, Annastacia Palaszczuk, said, “Queensland is leading the charge with renewable power so it’s no surprise that the sunshine state is now home to the largest solar farm in the country.

“I’m pleased we can deliver clean, reliable and affordable energy to every Queenslander because we own our power lines and the majority of power generation,” Ms Palaszczuk said.
Located near Chinchilla, the Queensland Government’s publicly owned CleanCo Queensland has signed a power purchase agreement with owners Neoen for 80 per cent of the power generated at the site.
Deputy Queensland Premier, Steven Miles, said, “Queensland is building the infrastructure and delivering more clean, green power generation and more jobs.
“We are blazing a trail when it comes to green energy and the capacity this solar farm will be able to produce
is a testament to the Palaszczuk Government’s vision for Queensland.
“Our Energy and Jobs Plan means more opportunities for businesses, more skilled jobs and more growth, especially for our regional communities.”
The completion of panel installation will allow the final testing and commissioning phase of the project to begin to get it to full capacity.
Managing Director of Neoen Australia, Louis de Sambucy, said, “We are delighted to have completed the panel installation of the largest solar farm in Australia at Western Downs, and we’re excited about the strong contribution that this asset will make to Queensland’s rapidly accelerating energy transition.”
Construction of the project has also delivered a huge boost to Queensland’s regional economies, with an estimated $800 million in economic activity.
The solar farm is another major investment towards delivering 70 per cent renewable energy by 2032 under the Queensland Energy and Jobs Plan
Assistant Minister for Hydrogen Development and the 50 per cent Renewable Energy Target by 2030, Lance McCallum, said, “The renewable energy being generated is already supplying some of CleanCo’s biggest customers including Coles, BHP, and Westfield shopping centres.
“This is our Queensland Energy and Jobs Plan in action, delivering more jobs in more industries, affordable power, lower emissions, and stronger economic growth,” Mr McCallum said.
CleanCo CEO, Tom Metcalfe, said, “The renewable energy generated by the Western Downs Green Power Hub will supply some of CleanCo’s biggest customers including Coles and BHP.
“Projects like these complement CleanCo’s portfolio of fast ramping, flexible gas and hydro generators to provide our customers with 24/7 reliable clean energy.
“We are proud to support renewable energy projects like the Western Downs Green Power Hub that deliver great local employment opportunities and economic outcomes in regional Queensland.
“The renewable solar energy generated here in Queensland’s Western Downs will contribute to the longterm sustainability of Queensland industries and communities, helping them to thrive in a net zero future.”
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 12
NEWS
WESTERN DOWNS GREEN POWER HUB IN QUEENSLAND. PROVIDED BY THE QUEENSLAND GOVERNMENT.
VIC WATER RECYCLING PLANT GETS GLOBAL RECOGNITION
South East Water’s Boneo Water Recycling Plant has been shortlisted for Water Reuse Project of the Year at the 2023 Global Water Awards, the only Australian project to be selected.

The project will compete against initiatives from the USA, Singapore and the Philippines at the 2023 Global Water Awards with winners announced at the Global Water Summit, held in Berlin in May 2023.
South East Water’s General Manager Liveable Water Solutions, Charlie Littlefair, said the global recognition for the Boneo upgrade shows that a sustainable approach to technology solutions provides benefits to customers, community and environment.
“This innovative upgrade of our Boneo plant will support the region’s growing community until 2050. We’ve increased its capacity to treat 50 per cent more wastewater, which provides a drought-proof source of high-quality recycled water for local farmers.
“It also supports peak sewage inflows in the area during the summer months and allows the connection of more
than 16,000 aging septic systems to sewer – a known cause of groundwater and waterway pollution in the region,” Mr Littlefair said.
In 2022, South East Water completed a $150 million upgrade of its Boneo Water Recycling Plant in a joint venture with John Holland, SUEZ and Beca (JHSB).

The upgrade transformed the Boneo Water Recycling Plant into a circular ecosystem, which reduces emissions and supports sustainable agriculture by making better use of the nutrient and energy rich by-products of the water recycling process.
The upgrade delivers a suite of innovative energy efficient technologies and biogas-driven combined heat and power (CHP), reducing the utility’s reliance on grid electricity by 30 to 40 per cent and contributing to a corporate emissions reduction target of 45 per cent by 2025.


The major upgrade is funded by a commitment South East Water made in its five-year Customer Commitment 2018–23 to stay ahead of challenges like population growth and climate change.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 13
NEWS
BONEO WATER RECYCLING PLANT – AERIAL VIEW OF UPGRADE. COURTESY OF SOUTH EAST WATER.
DRINKING WATER QUALITY REPORT PROVIDES INSIGHT TO NT’S WATER
The Drinking Water Quality Report 2022 details the water quality management system for the 91 locations Power and Water services across the Northern Territory, recognizing Power and Water’s commitment to providing safe, sustainable, and secure drinking water to all Territorians.

The annual report provides details about water quality management, including progress on delivering improvements to drinking water quality.
Over the past few years, Power and Water has developed and implemented a bespoke drinking water quality management system that aligns with industry best practice and responds to the Territory’s unique environments.
Power and Water’s Executive General Manager Water Services, Steven Porter, said, “Power and Water is committed to providing access to safe, sustainable and secure drinking
water to all Territorians, regardless of where they live.
“Power and Water’s passionate experts continually strive to improve water quality services across urban and remote communities, and that commitment was recognised with an Organisational Excellence Award at the 2022 NT Water Awards and as a finalist at the OzWater Awards.”
Power and Water has a central role in delivering the Northern Territory Government’s $28 million program to improve water quality and security in remote communities, including addressing the high levels of naturally occurring elements like uranium and nitrate in some communities’ drinking water.
“Construction of an ion-exchange water treatment plant in Laramba, about 200km west of Alice Springs, was completed in December 2022,” Mr Porter said.
Next Level Radar
Providing the highest confidence in level measurement in the most challenging conditions
● Easy installation and confidence in your data with the REFLECTTILT TM LED indicator

● Configure REFLECT™ with your application parameters using the secure browser-based Bluetooth® connection and user-definable range
● Accurate and repeatable FMCW radar technology for the most challenging conditions, even in the presence of dust, temperature changes, moisture, pressure and chemicals
“The plant, which will reduce the levels of uranium in the community’s water supply, is in the final stages of commissioning.”
Power and Water is also partnering with the University of New South Wales to trial membrane Capacitive Deionisation (mCDI) technology in Ali Curung to remove natural contaminants from groundwater.
View the annual Drinking Water Quality Report 2022 at www.powerwater.com.au.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 14
NEWS
™
REFLECT
Introducing
PULSARMEASUREMENT.COM
Contact us for a quote today! For more details, contact: oceania@pulsarmeasurement.com
Work management software with
Xugo is a cloud-based solution that powers the compliance, control and vegetation management activities across your business.

With Xugo you can:
Access the insights needed to take actions, implement programs and meet your regulatory requirements

Create, manage, schedule and allocate work cases and tasks
Build your own forms and workflows
Visualise work progress
Capture complaints, incidents, and feedback directly from your customers and your teams
Store your complete collection of information relating to inspections, tasks, incidents, maintenance history, safety and environmental checks, investigations and analysis


Run and publish interactive reports
Engage with your mobile teams wherever you are via Xugo’s app in real-time
Scan to learn how Xugo makes utility regulatory compliance easy




Configurable to fit your requirements, and with an Australian-based team on hand to assist and enhance your workflow, Xugo delivers effciency benefits without disrupting your business model.

people at the heart Transform your utility’s workflow with powerful works management software
AUSTRALIA’S HYDROGEN INDUSTRY COULD GENERATE $40B BY 2040
Anew report from the National Energy Resources Australia (NERA) and Arup has revealed that Australia’s hydrogen industry has the potential to generate $40 billion in domestic GVA by 2040 and create tens of thousands of jobs per year by 2040.
The report, Powering Up: Seizing Australia’s Hydrogen Opportunity by 2040, is the first comprehensive analysis of Australia’s hydrogen supply chain and the hydrogen equipment, technology and services (HETS) opportunity from a national perspective, outlining crucial actions needed to support Australia’s future hydrogen economy.

The study builds on modelling developed by Arup for the yet-to-be-released National Hydrogen Infrastructure Assessment (NHIA) to consider one possible configuration of the hydrogen supply chain in 2040.

Key findings reveal an enormity of potential economic benefits for Australia, with the hydrogen industry capable

of generating nearly one per cent of national GVA and supporting 58,000–72,000 jobs by 2040, most of which would be created in regional areas.


By 2040, Australian hydrogen demand could soar to 9.5MMT, almost ten times the current global production, with 46 per cent designated for export markets. To meet this demand, massive infrastructure development will be needed, including a five-fold increase in Australia’s solar and wind capacity, thousands of electrolysers and compressors, and more than 5,000 hydrogen storage tanks. The required infrastructure investment is estimated to be between $340 –$420 billion, with an annual investment of $25–$30 billion between 2025 and 2040.
NERA CEO, Miranda Taylor, said realising the full potential hydrogen presents for Australia requires significant investment to foster local capabilities, job creation and decarbonisation efforts, particularly in regional areas.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 16
tenders@lancogroup.com.au | www.lancogroup.com.au | 1300 1 LANCO (1300 152 626) Civil and Infrastructure Engineering | Project Management NEWS
“The hydrogen supply chain could drive Australia’s future economic growth and position the country to become a global leader in hydrogen. Our opportunity extends far beyond producing and exporting molecules. Rather, homegrown HETS businesses can offer cutting-edge technology and expertise across supply chain segments, such as hydrogen storage. But seizing this opportunity requires a robust local supply chain.

“The Powering Up report highlights the urgency of swift and strategic action to develop the strong hydrogen supply chain required, and provides actionable recommendations to help Australia take hold of its hydrogen opportunity, such as investing in regional capability, incentivising overseas manufacturers to onshore their capabilities, and securing annual infrastructure investment,” Ms Taylor said.
Ms Taylor emphasised that the report’s findings underscore the importance of strategic initiatives like the NERA-initiated hydrogen technology cluster network.
“The national network of 17 hydrogen clusters are pivotal in connecting emerging regional hydrogen industries in Australia, and promoting early HETS sector development, coordinated supply chains, and accessible entry points into hydrogen for local businesses. And, with 90 per cent of hydrogen industry jobs projected to be in regional areas, it is essential to develop local capabilities and supply chains to support this growth.
“As NERA’s tenure as Australia’s energy resources Industry Growth Centre concludes in July, we are transitioning the vital national leadership role for these regional networks to the Australian Hydrogen Council (AHC). This partnership allows AHC to build on existing momentum and continue to support the HETS sector’s crucial growth, connecting Australia’s emerging HETS supply chain and innovative businesses with major corporations at the forefront of hydrogen innovation,” Ms Taylor said.
PRODUCT
•4K UHD video and images
•HD dense Lidar & 360 degree pro ling Sonar

•HD PTZ camera and HD 360 degree camera
•PointVision®software : view & measure without lag
• Pr oprietary AI: image ltering, see below the waterline
•Advanced SLAM functionality: “Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping”
•Beta level AI for data mining of imagery and sensor data
•Client portal for interpretation and report generation
•Data can be delivered RAW and also in multiple formats
CAPABILITIES
•Can be tted with a range of arms and sensors to meet the precise survey needs of each client


•UAM Tec’s open architecture makes ROGER’s modularity exible and adaptable to mission requirements
•Manhole entries from 0.6 meters width and up

• Tunnels from 0.6 meters and up

•All shapes of tunnels
•Distance from 0 to 1KM
•Up to 400mm water submersion on base version
•All water types including low visibility environments.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 17
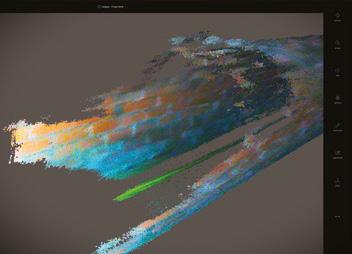
Introducing R.O.G.E.R, the Remotely Operated Ground Exploration Rover developed by UAM Tec for capturing high resolution data in non- ooded and partially ooded tunnel environments
4K UHD 360 DEGREE VIDEO LiDAR - POINT CLOUD ZOOM FROM SAVED FILE
assets
greater accuracy than
before. Get in touch for more imformation. UAM Tec Headquarters Unit 5/ 11-15 Rocklea Drive Port Melbourne Victoria 3207, Australia Craig Smales 0408 837 066 sales@uamtec.com NEWS
Available now to help you understand the condition of your underground
with
ever
MELBOURNE WATER’S WINNEKE TREATMENT PLANT POWERED BY NEW SOLAR FARM
Melbourne Water is making an effort to reduce carbon emissions while also increasing energy production for the Winneke Water Treatment Plant through the construction of the Winneke Solar Farm.

The 19,000 panel farm will deliver 12,400 MWh/annum, the equivalent of about 2,500 households’ yearly demand. All the energy produced will be used by the treatment plant and pumping stations. Any excess energy will be fed into the public grid for external use.
The total estimated carbon reduction is 12,000 TCO2-e/annum.

In an Australian first, Melbourne Water has utilised terrain tracking sensors for the solar farm’s construction. These sensors allowed the construction to occur on a slope, which otherwise would have required extensive earthworks, impacting financial viability.
By avoiding extensive earthworks, the panels were installed with minimal ground disturbance – a key restraining factor owing to water purity and soil runoff.
In order to maximise energy production in a limited area, the panels rotate on a pivoting bar which follows the movement of the sun. Additionally, the panels are bifacial, capable of generating energy from both sides of the panel.
This solar farm is an example of the Victorian Government’s commitment to decarbonisation and achieving a 50 per cent reduction of emissions by 2025, and net zero by 2030.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 18
NEWS
FEDERAL GOVERNMENT WELCOMES RENEWABLE ENERGY STORAGE ROADMAP
The CSIRO has released its Renewable Energy Storage Roadmap, emphasising the need for major investment in storage technologies to meet the growing demand for cheaper renewable power.


Federal Minister for Science and Industry, Ed Husic, said the Government is pressing ahead with its ambitions to see domestic battery manufacturing capabilities ensure homes and businesses can access cheap and reliable renewable energy into the future.
“Large-scale uptake of battery storage and battery manufacturing will be vital in the nation’s transition to net zero and to Australia becoming a world leader in clean energy,” Mr Husic said.

“The Government recognises the pivotal role that cheap, widely available energy storage will need to play in the transition to renewable power. That’s why the Government is delivering the Australian Made Battery Plan, spearheaded by the development of Australia’s first National Battery Strategy.
“By 2030, the battery manufacturing industry has potential to be worth nearly $17 billion and create more than 61,000
jobs, according to the Charging Ahead report from the Future Battery Industries Cooperative Research Centre.
“As the CSIRO roadmap emphasises, we need a pipeline of projects using diverse technologies to unlock the full potential of our renewable energy resources.
“That means there’s a huge opportunity for new systems and technologies to be developed here to manage the production, storage and use of renewable energy.”
The Federal Government continues to implement other initiatives focused on bringing cheaper renewable energy to homes and businesses and meeting Australia’s international emissions obligations.
This includes reaching 82 per cent renewables in Australia’s energy grid by 2030, which will be achieved through our $20 billion Rewiring the Nation Fund through deals with states and territories, as well as unlocking around $10 billion of investment in clean dispatchable power through the Capacity Investment Scheme.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 19
URD ELECTRICAL PILLARS +61 8 9378 1077 sales@rimco.net.au www.rimco.net.au ● Manufacturing Pillars in Australia for over 40 years ● Quality Assured to ISO 9001:2015 ● Pillars comply with AS/NZS 61439 ● Manufactured from proven, durable materials for Australian conditions ● Residential and Commercial applications. ● Minimal installation area required for Pillars ● Supplied Australia Wide NEWS
The MAPT produces an averaged differential pressure (DP) signal proportional to the square of the flow rate. The DP output is normally piped to a Differential Pressure transmitter in order to generate an electrical signal proportional to the flow rate.


The outer impact tube has a number of pressure sensing holes facing upstream which are positioned at equal annular points in accordance with a log-linear distribution. The ‘total pressures’ developed at each upstream hole by sum of the impact
of the flowing medium and the static pressure are firstly averaged within the outer impact tube and then to a second order (and more accurately) averaged within the internal averaging tube. This pressure is represented at the head as the high pressure component of the DP output. The low pressure component is generated from a single sensing hole located on the downstream side of the outer impact tube, measuring static pressure.
The MAPT is an improvement on the round sensor design due to the unique profiled flats which are positioned
around the downstream hole in order to define the separation point at which the flow lines separate as the fluid passes around the outer impact tube. This feature creates a stable pressure area at the downstream pressure sensing hole, thereby maintaining a more constant flow coefficient at high velocities enabling a very wide range of flow measurement (turndown).
Options include the inclusion of a thermowell for temperature measurement of the measured product.







AMS have been suppliers of instrumentation and calibration equipment to all industries since 1973 representing some of the world’s leading manufacturers of the equipment in their field.








UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 20
The MAPT is a multiport self-averaging flow meter with a design based on the classical pitot tube concept of fluid flow measurement.
INSTRUMENTATION & CALIBRATION
SPECIALISTS
PTY LTD
Flow Measurement Specialists www.ams-ic.com.au sales@ams-ic.com.au MCMENON AVERAGING
NEWS | Sponsored editorial For further information contact AMS Instrumentation & Calibration Pty Ltd on 03-9017 8225, or Freecall (NZ) 0800 442 743, alternatively on e-mail: sales@ams-ic.com.au or visit our web site at www.ams-ic.com.au.
www.ams-ic.com.au
PITOT TUBES


DID YOU KNOW? DENSO AUSTRALIA OFFERS THE MOST COMPREHENSIVE TIME-PROVEN RANGE OF LONG-TERM CORROSION PROTECTION SOLUTIONS. THIS NOW INCLUDES THE NEXT GENERATION OF TRULY SURFACE TOLERANT, VISCO-ELASTIC COATING SYSTEMS WHICH DEMONSTRATE AMAZING ‘SELF-HEALING’ COATING CHARACTERISTICS IDEALLY SUITED TO THE WATER INDUSTRY AND WATER PIPELINES. MORE THAN YOU THINK www.densoaustralia.com.au 77 – 95 National Boulevard Campbellfield Victoria 3061 AUSTRALIA TEL: +61 (0) 3 9356 7600 FAX: +61 (0) 3 9356 7699 EMAIL: denso@densoaustralia.com.au CONTACT YOUR LOCAL EXPERT NOW DENSO (AUSTRALIA) PTY LTD CORROSION PREVENTION
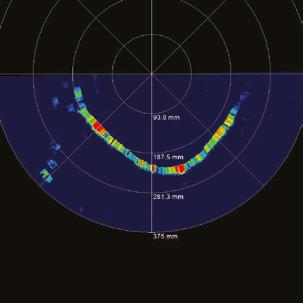
THE TRUTHS AND MYTHS OF MULTI ARRAY GROUND PENETRATING RADAR FOR UTILITY DETECTION


Amulti array ground penetrating radar is a GPR that has multiple antennas set close together. For instance, the Raptor 45 Cart has 8 channels, and the Raptor 45 Road system has 18 channels. There are some benefits to having many antennas close together, such as:

1. The array will see changes in direction of a service more clearly
2. It eliminates the need to scan multiple times reducing time in acquisition
3. An array can see voids easier, as it has a larger area to pass over showing irregularities below that a single or dual channel GPR would not show as clearly

4. Some array can move at legal speeds up to 110km in Australia, reducing locate times
Multi Array GPR does not eliminate other technologies used for locating underground services. Professional locate companies use many technologies like EMF and PWG, to name just a few. This avoids missing crucial services using just one technology.

Multi Array GPR’s are not immune to poor soils, and services can easily be missed no matter how good the array is. Good data quality relies on good soils.
Software is another important part of Multi Array systems. Having fancy videos showing 3D images doesn’t assist in getting info out to AutoCAD or 12D. Software should allow you to gather data quickly post-process, and then convert it to your preferred system or point cloud.
Let’s remove all the marketing hype and look at the facts and benefits of multi array ground penetrating radar when used in large environments.
NEWS | Sponsored editorial
Build and Close Out Utilit y Construction Projects



Locusview's technology manages the entire utility infrastructure construction process from planning to execution and closeout. Faster, Safer, Smar ter Faster Reconciliation 90% Backlog Reduction See How It Works 70% © 2023 Locusview Inc. All rights reserved. | locusview.com/faster
INNOVATIVE NEW EXCAVATOR GPR TECHNOLOGY
RodRadar Australia has introduced the all-new, revolutionary Live Dig Radar (LDR) Excavate.

Fully integrated into an excavator bucket, the LDR Excavate brings RodRadar's unique high-resolution, ground-penetrating radar imaging into the operator's cabin during excavation and earthworks projects.
Available in three size configurations, the RodRadar LDR Excavate is compatible with most makes and models of excavator sized one to 18 tonnes.

The only solution of its kind worldwide, the Live Dig Radar provides real-time, precise data on the location of underground utility infrastructure, automatically and directly alerting the excavator's operator with simple-to-understand notifications.
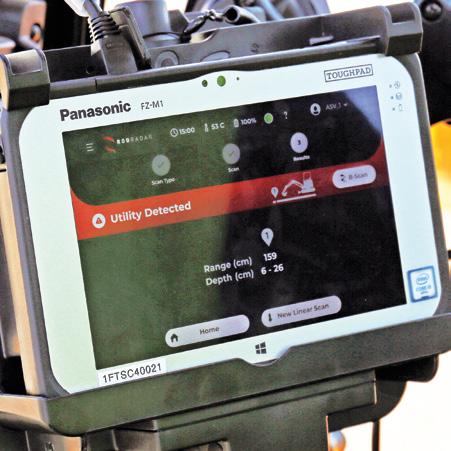
The technology, although complex in scientific design, is simple to use; connect the LDR-integrated bucket to a compatible excavator, link the bucket to the supplied tablet which is mounted inside the operator cabin, then make sequential excavations into the earth to scan the ground below. As the bucket digs and makes contact with the ground, the built-in radar technology delivers highly accurate, real-time, easy-to-understand data to the tablet about underground utility locations and depths.
The technology’s aim is to provide holistic prevention of costly and unsafe utility damage, and exceptional improvement of project efficiency and productivity.
AVOIDING DANGEROUS AND COSTLY UTILITY STRIKES
Each year, underground infrastructure damage costs the global construction industry more than $150 billion AUD – including billions invested in less effective alleviation methods – with utility strikes during excavation, causing dozens of deaths and hundreds of injuries.
RodRadar Australia’s innovative Live Dig Radar is a dramatic improvement over current widespread excavation technologies and processes, overcoming their inherent limitations.
In February 2023, RodRadar Australia partnered with distributors ASV Sales & Service and STM Trucks & Machinery to conduct preliminary LDR Excavator Demonstration Days in Sydney and Newcastle. As part of each demonstration, utility services were buried underground in various earth compositions, and attendees were invited to find and unearth the utilities using the Live Dig Radar in-situ.
With more than 50 industry representatives in attendance – hailing from fields including construction, risk assessment, workplace health and safety, utility management and government – the LDR technology was met with extensive positive feedback.
A government agency representative in attendance said, “The accuracy of the radar was spot on. The LDR would work well in our operations and is exceptional new technology.”
In addition, Michael Owen from major construction body RTC Group, said, “[The LDR] would be very helpful for safety, and also a time saving device – and also looks to be easy to use.”
Furthermore, RodRadar’s Live Dig Radar is garnering exceptional acclaim on the global stage. Florida-based Haskell – a pioneering architecture, engineering and construction firm – has become the first contractor in the United States to deploy the technology.
Cutler Knupp, Managing Director of Haskell's innovation and venture capital arm, Dysruptek, said, "RodRadar's Live Dig Radar technology is a game changer. The accuracy has been impeccable, and it's already helping Haskell to identify subsurface conditions that we were not aware of before."
RodRadar Australia will roll out the new LDR Excavate nationwide throughout 2023.
24 UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU NEWS | Sponsored editorial
Visit www.rodradar.com.au for further information regarding the product, demonstration opportunities and stock availability.


TM
THE FUTURE OF WATER MANAGEMENT WITH URBAN UTILITIES’ NEW CEO

After more than three decades in the resources sector, Paul Arnold is now at the helm at one of Australia’s largest water service providers, Urban Utilities. Formerly the Chief Executive and Managing Director at Energy Resources of Australia based in the Northern Territory, Mr Arnold made the 2,200km journey back home to South East Queensland where he took up the role of Urban Utilities CEO in September last year.
Mr Arnold joined the organisation at a pivotal time as the water industry continues to respond to the challenges of climate change and population growth, and with less than a decade until Urban Utilities’ service region hosts the Olympic and Paralympic Games.
“This is undoubtedly one of the most exciting times to be part of the South East Queensland water industry,” Mr Arnold said.
“Our region has a lot to look forward to, including hosting the Olympic and Paralympic Games in 2032, but we’re also facing some pretty fundamental short and long-term challenges as a sector, which we need to work together to solve.”
As he forges ahead in his first year as Urban Utilities CEO, Mr Arnold has shared his vision for the role, what led him to make the change from natural resources to water and the key challenges and opportunities he’s observed for both Urban Utilities and the broader industry as utilities around Australia work to achieve a sustainable water future.
FROM NATURAL RESOURCES TO WATER
Before joining the team at Urban Utilities, Mr Arnold spent 35 years in the resources and energy sectors, spanning operations, project development and execution, stakeholder relations, Indigenous engagement and business development.
This experience has helped him arrive in his leadership role at Urban Utilities with a unique perspective and clear priorities, accompanied by a deepseated curiosity to gain greater insight into the Australian water sector.

“One might ask how a mining engineer ended up running a water utility,” Mr Arnold said.
“Throughout my career in natural resources, I’ve been passionate about
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 26
INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
The future of water management drew Paul Arnold to the industry – here’s why Urban Utilities’ new CEO thinks now is the most exciting time to work in water.
the protection of the environment and the repair of country.
“One of the things that drew me to the water industry, and specifically to Urban Utilities, was its unwavering commitment to service and environmental leadership.
“Being born and first raised in central Queensland and then growing up in Brisbane from school age, I’m also thrilled to be working in a role that will help shape the future of water and enhance livability here in Queensland.”
PEOPLE, SAFETY AND WELLBEING
Before joining Energy Resources of Australia as CEO and Managing Director, Mr Arnold also held a variety of operations, commercial, business analysis and major project development roles with Rio Tinto and BHP, spending five years as a Director of the Queensland Resources Council.
“When I think about some of the learnings I’ve gathered over the years, the most obvious and important one that every industry should focus on is safety,” said Mr Arnold.
“Safety is a fundamental value in caring for our people and it’s a priority I have brought with me to the role as Urban Utilities CEO.
“What I’ve learnt about the water industry so far is that, like in mining, our people are often navigating the same high-risk activities as they complete
their essential work, such as working in tunnels and confined spaces, at height, with high-pressure equipment or beside mobile and heavy equipment.
“As a leader in this business, I know what an important role I can play to help ensure we have the best processes and support structures in place to look after our people’s mental and physical health.
“We also know that safe organisations are efficient and productive organisations, they go hand-in-hand.”
The connection to purpose of those in the water industry is something that has stood out to Mr Arnold since starting the role.
“At Urban Utilities we are committed to showing up in the moments that matter, and shaping the moments to come, and I have been continually impressed by the passion that is evident in the people I meet and work with every day,” he said.
“Regardless of their role, be it a contact centre operator, field worker, treatment plant operator or engineer, I see genuine care for our customers, community and country and a true passion to deliver our purpose of enriching quality of life.”
COLLABORATION AND PARTNERSHIPS KEY TO SOLUTIONS
Joining Urban Utilities amid the organisation’s ongoing recovery from
the February 2022 flood event means Mr Arnold understands all too well the increasing challenges for the water sector posed by climate change.
“Last year's floods are an example of how our industry is both planning for climate change and living with its impacts in real time,” he said.
"We’re thinking about the future impact of climate change on behalf of our customers.
“While this is most certainly a challenge, it’s also an opportunity for us to think about how we can deliver our services differently and make decisions now that will support our customers through the impacts of climate change.
“There’s also an important seat at the table in supporting government and the broader community in some of the decisions we have to make to protect ourselves from climate extremes.
“Another challenge for the industry is aging infrastructure. At Urban Utilities, we’re looking at ways we can get beyond age as the driver of asset performance, which means making use of emerging technologies and data analytics to improve both the way we maintain and rejuvenate our assets.”

Mr Arnold said the strong commitment to share best practice and learn from each other is a real positive for the water industry as it looks to meet common challenges.
“Since becoming Urban Utilities’ CEO, I’ve discovered that one of the defining features of this sector is its collective desire to drive sustainable water management. We share this common goal of doing our best for our customers and communities,” he said.
“Now more than ever, we need to collaborate and build our collective skills and knowledge so we’re best placed to achieve a resilient, secure and affordable water future.”
SHAPING AND GROWING OUR FUTURE
Urban Utilities has released its water leadership plan, Our Water Way, which outlines how the utility is preparing to meet the challenges of both climate change and population growth and ensure water security for generations to come.
“This is not just a local issue. Around Australia and the world, the way we use and look after water is
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 27
INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
becoming more of a priority and we’re proud to play our part in supporting a secure water future for South East Queensland,” Mr Arnold said.
The Our Water Way plan outlines Urban Utilities' aim to reshape the water cycle from the traditional ‘catchment to sea model’ of water use, to a more circular model that manages water more sustainably.
“Water is at the heart of our much-loved lifestyle in South East Queensland. Our quality of life – our jobs, businesses and our communities – depend on it and that’s why we’re planning well ahead for the future,” Mr Arnold said.
“Our plan is about caring for the water we have today and creating the water we need for the future.
“Caring for the water we have today involves always using water efficiently in our homes and businesses and encouraging waterwise communities.
“Creating the water we need for the future is about grasping every opportunity to use our valuable and finite water resources more than once. To achieve this, we're focused on increasing our use of recycled water for
industry, agriculture and irrigation and keeping our water closer to home by treating and managing water nearer to where it’s used.
“Across our region, it also involves looking to other more resilient, climateindependent sources of water to help supplement our drinking water supplies, including desalination and purified recycled water, which can be produced in our region using the Western Corridor Recycled Water Scheme.

“We’re already exploring opportunities to design and build innovative and sustainable water and wastewater infrastructure for key Olympic and Paralympic precincts that will form part of our network to support activities such as cooling and greening.”
Urban Utilities last year announced its commitment to reach net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2032, which will support the region to host a climate-positive Olympic and Paralympic Games.
To reach net zero, the utility plans to further improve energy efficiency, increase its renewable energy use, and invest in beneficial local offset projects.
BUILDING TRUST A KEY FOCUS
Mr Arnold said another priority he had identified for the role included further building trust with Urban Utilities' customers, communities and stakeholders.
“We’ve been entrusted with billions of dollars of assets by our communities,” he said.
“By providing safe and efficient water and wastewater services every day and by encouraging shared understanding, we will continue to build trust.

“As a water utility, we are stewards of the most precious natural resource our planet has, and I believe it’s important to bring our customers on the journey to support that shared understanding as we work towards a secure water future, together.
“I am relishing this opportunity to work with the passionate people at Urban Utilities and across the water sector as we ensure our communities continue to enjoy safe and reliable water and wastewater services every day and into the future, whatever the weather.”

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 28
INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
93% of the Australian population captured
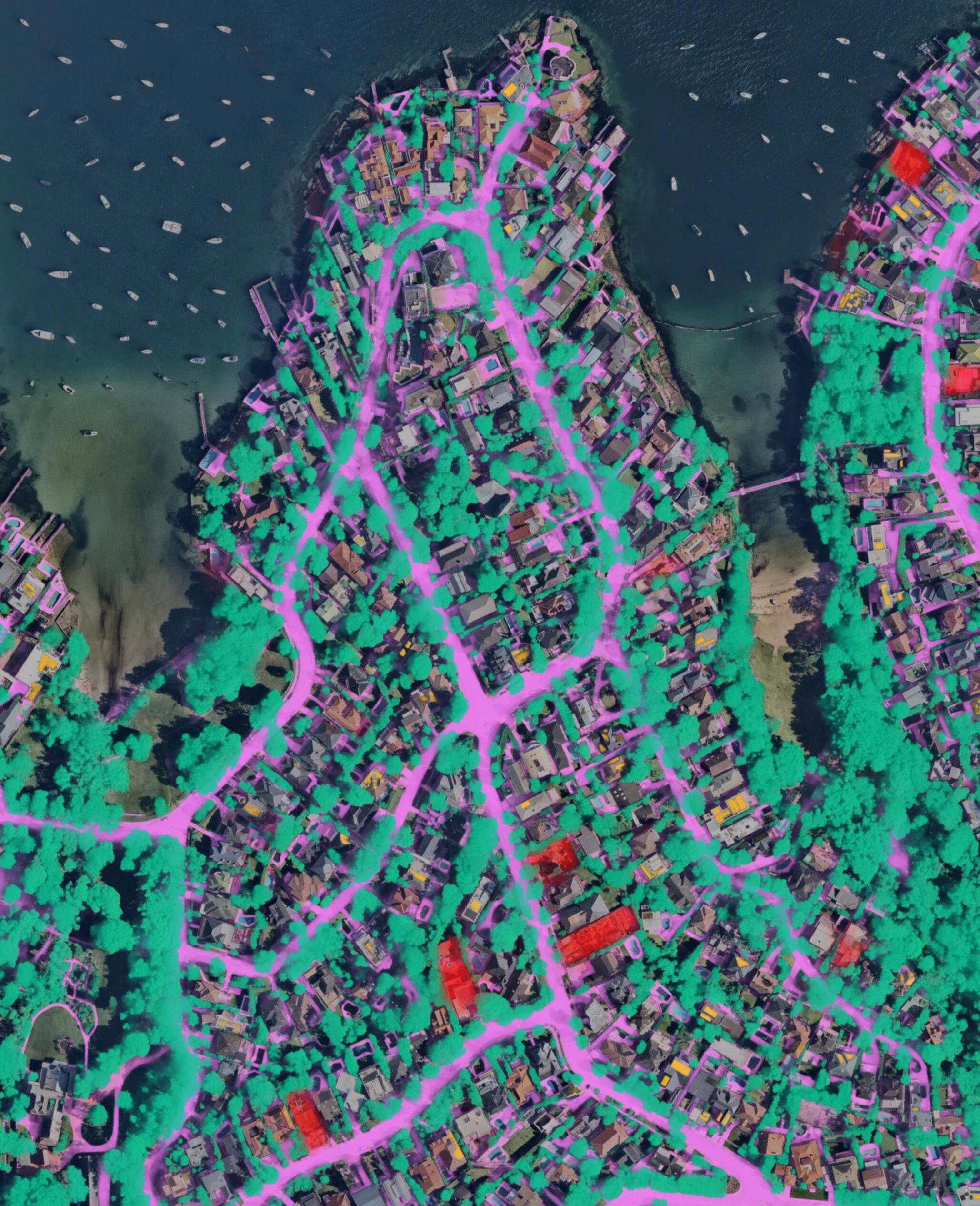
FOR MORE INFORMATION: Scan here to email Myles from our business development team to discuss how Nearmap can enhance your workflow. www.nearmap.com/industries/aerial-photography-utilities VAUCLUSE, NSW AU
ENRICH YOUR DECISION MAKING WITH CURRENT LOCATION INTELLIGENCE
SOLUTIONS TO MITIGATE CREATING INNOVATIVE FLOOD DAMAGE
Each day, EJ solutions play a vital role in the development and maintenance of public and private infrastructure.
In early 2022, a series of floods hit South East Queensland and coastal New South Wales. Media reports estimate upwards of $2.5 billion in damages related to the floods. Businesses and residents impacted are still trying to rebuild over a year later.
A major rain or tidal event can overload your stormwater and sewer systems. The extreme pressure within the system often results in dislodged access covers. The result is a lifethreatening safety hazard for both motorists and pedestrians. These open pits are hidden if the area is submerged under even a small amount of flood water.
CREATING A SOLUTION
EJ has invented an access assembly designed to solve this problem. In everyday use, the MAESTROTM cover is secured shut by an engineered torsion bar design. Once subjected to a large back pressure surge, such as a flood, the cover will act as a relief valve allowing itself to hinge open.
Due to specially designed hinges, even when relieving pressure, the cover is retained in the frame, keeping the street safe and preventing accidents. Furthermore, once the pressure subsides, the MAESTROTM cover will simply close and lock safely under passing traffic.
The MAESTROTM product is already widely in use across New Zealand, with councils and governments embracing the resilient design. This investment in MAESTROTM products paid dividends in the recent flooding and cyclone hitting the North Island. After these events, while infrastructure was being assessed, cleaned up and sometimes rebuilt, the MAESTROTM products shut closed and went back to business as usual.
PROVIDING UNRIVALLED EXPERTISE
There is a comprehensive range at EJ including cast and fabricated products, which serve a vast range of industries such as construction, water distribution and telecom.

The EJ foundries and workshops around the world use the latest integrated technology and lean processes, and EJ has a century of experience in craftsmanship delivering quality products.
As a global presence, EJ draws from a wide range of expertise and resources, to provide users with access solutions that are specifically tailored to their unique requirements.
The EJ MAESTROTM cover is a testament to the EJ advantage. EJ has designed access solutions made to work for Australians, helping to keep the public safe and reducing damages during challenging times.
30 UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU INDUSTRY INSIGHTS | Sponsored editorial
Across Australia and the globe, EJ is relied upon to design, manufacture and distribute exceptional access solutions for vital infrastructure projects. These projects support the stormwater, wastewater and telecommunications networks necessary in modern society.

The EJ Advantage –innovative solutions to upgrade stormwater and sewer systems with MAESTRO™ covers. Engineered to Perform. Visit ejco.com to learn more about the resilient designs by EJ. QLD | 07 3216 5000 NSW | 02 9757 3862 VIC | 03 9792 5144 WA | 08 9209 2930 au.info@ejco.com
MITIGATING CYBERSECURITY THREATS IN WATER AND WASTEWATER

As more critical infrastructure is connected to the internet or accessible to staff, it is increasingly targeted by cybercriminals interested in breaching operational technology (OT) networks to lay the groundwork for future attacks.
A cyberattack on water and wastewater treatment facilities can temporarily stop operations and have huge consequences, not only for the water authority and the community it serves, but also the nation's overall economy.
RISKS FROM LEGACY TECHNOLOGIES AND INSIDER THREATS
Many water infrastructure systems still rely on outdated technology and managers are often under-resourced. Managers must invest in modernising and regularly upgrading their systems and can seek external assistance from cybersecurity experts.
Many employees are also unaware of cyberattack risks, while another threat is current or former employees with malicious intent. Water infrastructure systems are increasingly interconnected and often use third-party vendors and contractors, which makes them more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
RISK MITIGATION MEASURES
The specific mitigation measures each facility decides to implement will depend on its unique security risks. However, there are some key mitigation measures that most water infrastructure managers should implement as best practice: Segmentation into zones: This should be practiced in every plant to help limit access to safety systems. For example, a demilitarised industrial zone (IDMZ) with firewalls and data brokers can securely segment the plantwide network from the enterprise network. Also, using virtual LANs (VLAN) and a layer-2 or layer-3 switch hierarchy can create functional sub-zones to establish smaller domains of trust and simplify security policy enforcement.
Physical access: Many organisations use RFID cards to control facility access, but physical access security should go further. Lock-in, block-out devices should be used to prevent the unauthorised removal of cables and to close unused or unnecessary ports. Control cabinets should also be locked to restrict walk-up and plug-in access to the industrial automation and control system devices.
Network-integrated safety and security: CIP Safety™ and CIP Security™ are extensions to the common industrial protocol (CIP), which is the application-layer protocol for EtherNet/IP™. CIP Safety allows safety devices to co-exist on the same EtherNet/IP network as standard devices and enables a safe shutdown during a denial-of-service attack. In addition, CIP Security incorporates data integrity and confidentiality into EtherNet/IP communications.
Asset and change management: Asset management software can automate the discovery of new assets and centrally track and manage configuration changes across an entire facility, including within safety systems. It can detect real-time malicious changes, log those activities and report them to key personnel. If unwanted changes are made, the software can access archived copies of a device program for fast recovery.
ENSURING SAFETY THROUGH SECURITY
The security landscape is ever-changing, so it’s important to partner with a company that is trustworthy to manage the constantly evolving risk. NHP works closely with Rockwell Automation and Claroty to provide comprehensive cybersecurity solutions beyond just network security, and its industrial security portfolio and services will help you assess, implement and maintain ICS security within operations and enable transformational technologies that rely on enterprise connectivity. Organisations that want to stay ahead of these risks must comply with the latest standards, conduct a comprehensive risk analysis and implement risk mitigation measures using the latest technologies.
For more information, contact NHP in Australia on 1300 647 647 or nhpsales@nhp.com.au or in New Zealand on 0800 647 647 or sales@nhp-nz.com.
literature.rockwellautomation.com/idc/groups/literature/documents/wp/safety-wp035_-en-p.pdf blog.cyble.com/2022/05/04/water-and-wastewater-treatment-facilities-vulnerable-to-cyber-attacks/
32 UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU INDUSTRY INSIGHTS | Sponsored editorial
An increasing reliance on technology in water and wastewater infrastructure management has resulted in cybersecurity challenges becoming a significant concern in the sector, and one that must be addressed to ensure a safe and reliable water supply.


Future proof your protection system with NHP ACB retrofitting services nhp.com.au | nhpnz.co.nz 1300 NHP NHP | 0800 NHP NHP nhpservice@nhp.com.au | sales@nhp-nz.com ■ Increase system safety and reliability ■ Minimise production downtime ■ Reduce operational costs NHP’s Services and Solutions team can customise solutions to suit specific requirements or work within your existing switchboard environment to provide a costeffective solution, engineered according to relevant Australian and New Zealand standards and recognised industrial practices. Find out more
USES LASER-GUIDED TUNNEL BORE FOR SEWER INSTALLATION COLIBAN WATER

The opportunity to use the tunnel bore was recommended by local contractor, R&R McClure, in its tender submission. According to Coliban Water’s Manager of Infrastructure, Corey Bourne, they suggested using the laser-guided bore to ensure accuracy when installing the section of sewer trunk main on flatter areas of land.
“The laser-boring technique is similar to what is used in the Melbourne Metro Tunnel Project - only on a much smaller scale,” Mr Bourne said.
“While creating the micro-tunnel required for this project, the technology has proven successful and allowed us to constantly monitor and manoeuvre the machine for accuracy.
“One of the major benefits was the added control it gave our crews where there was little tolerance for vertical deviation.
“It also allowed us to avoid open trenching for this project, limiting disruption to local residents, roads, vegetation and natural habitat.”
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 34 INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
Regional Victorian water authority, Coliban Water, has used a state-of-the-art laser-guided tunnel bore to install a new 507m section of sewer trunk main in White Hills, in suburban Bendigo.
R&R McClure worked closely with subcontractor, S&Z Australia, and German company, Bohrtec, which developed the technology.
A Bohrtec expert visited Australia in February 2023 to train onsite crews about operating the bore. It was the first time the machine had been used in regional Victoria, after it was used once before on a Melbourne project.
Mr Bourne said the project team was able to keep abreast of the latest innovations, equipment and construction methodologies thanks to the use of new technology such as this.
“This has provided a great development and learning opportunity for Coliban Water staff and our contractors,” Mr Bourne said.
Having committed to improving environmental outcomes in its Environment and Sustainability Policy, Coliban Water continues to focus on its environmental management systems by adopting best available science and technical innovations.
“The added control and accuracy the bore made it a good choice for this project over other trenchless technologies,” Mr Bourne said.
WORKING TO OVERCOME CHALLENGES
While trenchless technology and the laser-guided bore have come with benefits, using the machine has not been without its challenges.

“This machine needed to sit in a pit, whereas other trenchless technology such as horizontal directional drills can sit on the surface,” Mr Bourne said.
“This means a larger pit was required on-site to house the machine while it drilled the micro-tunnel. In the future, there may not always be space available to do this.”
The machine’s German origins could add a further challenge for Australian crews.
“Any additional parts or attachments need to come from Germany,” Mr Bourne said.
“So, if there is a change on site, such as ground conditions, there could be delays.”
CATERING FOR BENDIGO’S GROWING POPULATION
The new sewer trunk main in White Hills replaces part of the aging East Bendigo sewer trunk main. It will improve the network’s capacity to carry sewage from the growing suburbs of Strathfieldsaye, Junortoun, parts of Strathdale and East Bendigo.
The new trunk main will accommodate greater flows and enable wastewater to be better distributed between two smaller mains that carry waste to the Bendigo Water Reclamation Plant in neighbouring Epsom.
Final work is currently being completed with the last connections being put in place. The project is one of a number Coliban Water is undertaking to cater for population growth in the Bendigo region.

The five-kilometre Epsom-Huntly Pipeline, due for completion in Autumn 2023, will increase water network capacity for Epsom and Huntly, north of Bendigo.
Phase One of works at the Bendigo Water Reclamation Plant are due to commence in 2024, while surveying work has commenced on a new pipeline to connect Golden Square with the growing suburbs of Maiden Gully and Marong.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 35 INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
Visit connect.coliban.com.au for more information on Coliban Water’s projects.
THINK YOU KNOW HOW TO WORK NEAR GAS PIPELINES?
THINK AGAIN
APA owns and operates networks that deliver half of the natural gas used in Australia. Work conducted by other utilities is one of the most common forms of unauthorised works near APA pipelines. Apart from the risk of personal injury or death, damage to gas pipelines may result in legal action. If you are planning any work around APA’s gas transmission pipelines, ask yourself and your team if the following common mistakes sound familiar.
I’ve worked around gas pipelines before – I know what I can and can’t do.
Even experienced people may not know they are working around high pressure gas transmission pipelines. Each case can have very different levels of risk. There are also many other pipeline operators with their own requirements. Don’t assume that previous experience will apply.
My work won’t be a problem – I’ll just go ahead without checking for underground services.
Unauthorised excavation is one of the leading causes of risk to APA’s pipelines and coatings. Work should also not block line-of-sight between the pipeline marker signs, or restrict access for patrols and maintenance. APA transmission pipeline easements often run through private property. The terms of the easements typically provide for APA access along the easement and prevent placement of structures or obstructions. APA will not unreasonably stop work, but will work with you and the landowner to keep adequate access. It’s only a quick job. I won’t get caught, and even if I do, nothing will happen.
APA regularly patrols its pipelines. It is highly likely that your works will be
detected. The work will be stopped. You will need to reinstate the site and wait until you have the right authority. You may then be responsible for the significant cost of any works that are required to check and repair pipeline integrity. Penalties may also apply under state pipeline legislation. Hitting the pipeline won’t cause death or injury.
Australia has not experienced any death or injury from damage to a gas transmission pipeline, but there have been cases of rupture and ignition resulting from third party interference. Overseas, third party interference has caused many fatalities and serious injuries.
I only scratched the pipeline, it will be fine.
Damaging the coating or the pipeline itself in any way diminishes its integrity. It can reduce the wall thickness or create a pathway for corrosion to form, leading to future failure. So any suspected pipeline strike requires APA to check and maintain pipeline integrity. The pipeline is deep enough that my works will be clear.
Depth of cover varies throughout a pipeline’s life due to earthworks, erosion and subsidence. Excavation can easily extend to the depth of transmission pipelines. APA needs to confirm pipeline depth before authorising works.
The landowner has done the Before You Dig, so I’m OK to go.
Using the Before You Dig service at www.byda.com.au is the essential first step, but your duty of care doesn’t end there. Get a copy of the Before You Dig response, even if someone else has made the enquiry. Read the response carefully to ensure that the enquiry is current, and that you have completed all required actions. If a transmission
pipeline is affected this means calling APA to discuss your proposed works. The pipeline marker signs show the exact location of the pipeline.
Marker signs are usually offset and not located directly above the pipeline. I’ll just get a locator service to find the pipeline and then I can proceed safely.

Third party location of APA assets is not allowed. The company is happy to schedule an on-site location for your project or works. Work within set criteria requires APA authorisation. In some cases, APA supervision during works is also required. Supervision is scheduled according to availability, so please plan your works to allow for this. I can use vacuum excavation without needing to contact the pipeline operator.
Vacuum and hydro excavation can damage pipeline coating. Any of these activities around APA assets require supervision by one of the company’s permit issuing officers, and must observe strict pressure limits.
INDUSTRY INSIGHTS | Sponsored editorial 36 UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
Safety is vital when working near gas pipelines, which in the worst case can result in death or injury. Here, Australia’s largest pipeline operator APA outlines some common mistakes people make when working near its 15,000km of transmission pipelines.
TRANSMISSION PIPELINES OFTEN RUN THROUGH PRIVATE PROPERTIES APA has seen the risks, expense and time caused by these misconceptions. Contact APA on 1800 103 452 or at apaprotection@apa.com.au to discuss any of these points. APA will come to your workplace and present to your company on the risks and requirements when working around gas transmission pipelines.





eillance Communications e… Harnessing the power of natural resources to make autonomous sensing, thinking and action available anywhere, anytime... for more information 1300 802 960 www.spectur.com.au
THE ROLE OF DIGITAL CONNECTIVITY IN INDUSTRY 4.0
Connectivity plays a vital role in supporting and improving industrial and operational environments today, and more importantly, underpins long-term digital transformation strategies.
In the short term, connectivity can help provide local and remote visibility across your entire network, allowing you to monitor operations.

THE IMMEDIATE VALUE OF CONNECTIVITY
Once connected to a network, an asset providing field and control data suddenly gives new operational insights to the asset operators. This new flow of data enables real-time decision making and can reduce response time to potential asset issues, minimising downtime.
Companies can monitor various productivity and heath parameters of an asset, or its deployed environment, with multiple diagnostic features. Possible data points include temperature, pressure, level, and many other discrete and analogue field signals. Crucially, connectivity provides the infrastructure necessary to enable this flow of data.
WHAT MAKES UP THE CONNECTIVITY LAYER?
Every operating environment is unique, and the connectivity layer designed for the specific requirements of an industrial environment could include the following:
• Wired communication networks, or wireless communications
• Network routing, switching, segmentation and traffic management
• Redundant or mesh networks where high availability and reliability in critical applications is required
• Private and mobile network communications to enable connectivity in remote and difficult to reach areas
CONNECTIVITY CHALLENGES
Of course, there are challenges associated with creating a successful connectivity layer. Some key considerations are ensuring the reliability, security, and scalability of your network. We suggest:
• Defining your requirements early, including what data needs to be generated (and why), the amount of data, the number of devices, the required bandwidth, and the expected growth over time. This will help you determine the necessary capacity and scalability for the network
• Designing a resilient network architecture that minimises single points of failure and maximises redundancy. Redundancy will also help ensure that the network can handle increased traffic and data loads as it grows
• Using network hardware components that are specifically designed for industrial environments, have a proven track record of reliability, and are specifically built to meet IEC 62443 or ISA-95 cybersecurity standards
There are many more considerations in addition to the above, which is why we suggest working with an operational technology specialist who understands critical operating environments and industrial networking. They can provide the prescription and the recommendation of the steps required to achieve a robust and future-proofed connectivity infrastructure.
LONG-TERM BENEFITS
A layer of robust and reliable connectivity now provides the foundation for the integration of digital technologies into all aspects of an operation. Asset data can also be used to develop predictive maintenance models and asset anomaly detection.
With data points pulled from across operations, predicting your overall performance becomes much easier, meaning that you can manage your business with more confidence. A clearer understanding of downtime and rate losses from accurate and accessible data gives greater confidence that you can meet future production targets, business efficiency and profitability.
Connectivity is the key to unlocking the full potential of Industry 4.0. It enables the seamless integration of advanced technologies, the collection and analysis of data, and the creation of more dynamic and responsive operations.
If you need help building, optimising, or scaling connectivity, book a discovery session with Madison Technologies’ technical team. Visit www.madison.tech or phone 1800 72 79 79.
By now, many of us have heard the term Industry 4.0. The promises of using technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) to create a more interconnected, automated, and intelligent operational environment are inspiring and exciting. With this in mind, connectivity is the foundation layer and first step to digital transformation.
INDUSTRY INSIGHTS | Sponsored editorial 38
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
Technology solutions for connected utilities.
Digital transformation is creating efficient, reliable and sustainable Australian utilities.

Camera, IoT Loggers and Edge Devices .


o Intelligent Camera
o Data Loggers
o Edge Computers
o Sensors
Connectivity.
o Wired
o Wireless
o Mesh Networks
o LTE/Mobile
o Protocol Gateways

Platforms & Applications .
o On Premise
o IIoT Platforms
o Visualisations
o Analytics
Cybersecurity.
o Secure technology for IEC 62443 standards



Connect and protect people, assets and the environment
With a 30-year legacy of providing resilient industrial technology solutions, our experience connecting and protecting people, assets and the environment means we’re the preferred partner for solving IIoT, industrial networking, cybersecurity, asset management and asset visibility challenges.
Find out more.
P 1800 72 79 79 www.madison.tech
FOUR PRACTICAL WAYS TO IMPLEMENT EFFECTIVE COMPLIANCE PROGRAMS
INCREASING REGULATION
Most utility businesses operate under licence conditions, codes, and state and commonwealth legislation. Those who draft and enforce such regulatory obligations have little understanding of how challenging it is for businesses seeking to do the right thing and comply.
When looking at compliance, one of the first (and most difficult) steps to take is to understand all the applicable obligations and their applications in different business models and at different points in operation. That is a step that continually needs to be taken as a business expands and regulation changes.
Regulation is largely reactive rather than proactive as it seeks to prevent the re-occurrence of conduct or outcomes that are deemed to be negative, whether to consumers, the environment, employees, or society at large. Therefore, most regulation is prescriptive following a set formula which is: c (Compliance) = x (Action) in y (Circumstances).
The challenge then becomes understanding what x requires and when y is present. A comprehensive and current obligations register is critical for complex businesses, such as utilities. Separately, there are various principles that underpin regulatory obligations i.e. the rationale behind regulation. Those principles need to be understood and an effective compliance program addresses not only prescriptive regulation but the principles behind that regulation.
PRACTICAL SOLUTION 1: PRIORITISE COMPLIANCE
The single factor that is most important in determining the success or otherwise of a compliance program is the attitude of upper management and the leadership team.
Boards set priorities by their words and actions. Compliance needs to be one of those priorities in the same way that revenue generation usually is. In larger businesses, there are typically many layers between the board and employees who carry out the day-to-day functions that are critical in determining compliance or otherwise.
Setting compliance as a priority allows a culture of compliance to develop. That means that all employees understand the importance of compliance, the need to act in a compliant manner, and to call out potential and actual non-compliance.
PRACTICAL SOLUTION 2: EMBED COMPLIANCE IN DECISION MAKING
Compliance is a critical component of decision-making. There is no point in having a compliance program that is well-staffed but where compliance staff have no say in the decisions a business makes.
To embed compliance in decision making, those with expertise should be involved in all critical decisions, including price changes and entry and exit from markets. That means involving your compliance team in operational and financial meetings and ensuring that they understand changes that are occurring in your business and your industry.
PRACTICAL SOLUTION 3: RESOURCE COMPLIANCE
The resources that a compliance function requires include internal and external expertise, access to databases and registers and other compliance tools.
Understandably, it can be difficult to justify spending more on what is seen by some as a cost centre. Compliance should be resourced if a business wants to operate in a compliant manner, to avoid penalties, and to have a good reputation with regulators and other stakeholders.
The financial justification for spending more on compliance is the reduction in the likelihood of a penalty or other enforcement outcome and the cost of that penalty or other enforcement outcome.
For example, for energy retailers, a civil penalty breach may result in a penalty that is the greater of: i) $10 million, ii) ten per cent of global turnover, or iii) three times the benefit received by the business from the breach. Would it be justified to spend $300,000 on a compliance system if it is going to reduce the likelihood of a $10 million breach by ten per cent?
PRACTICAL SOLUTION 4: CHECKLISTS
The simple checklist is a powerful tool that can be employed in compliance. Your compliance staff should be asked to develop checklists for all areas of operation and for key changes in the business. Checklists should be kept up to date and reviewed on a consistent basis. The simple checklist allows a business to review and confirm compliance quickly.
Compliance is a tricky and complex process, but it’s possible to navigate with the right approach. The quantity and complexity of regulation is only set to increase, and there is never a better time to examine your compliance program than right now.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 40
The utility sector is one of the most regulated in the country, if not the world. The quantity and complexity of regulation applying to the industry is increasing daily, as are the penalties for non-compliance. Compliance is moving from an abstract concern to an area requiring direct and focused attention. This article explores four practical ways that leaders in utility businesses can implement effective compliance programs.
INDUSTRY INSIGHTS | Sponsored editorial

NEW HIGH-VOLTAGE TRANSMISSION LINE POWERING SA’S EYRE PENINSULA
Homes, businesses and communities across South Australia’s Eyre Peninsula now have a more secure power supply following the completion of Eyre Peninsula Link.
Delivered by South Australia’s Transmission Network Service Provider (TNSP) ElectraNet, Eyre Peninsula Link is a new 270km double-circuit 132kV highvoltage transmission line from Cultana to Port Lincoln, via Yadnarie, constructed with 500 new transmission towers and upgrades to five ElectraNet substations.
ElectraNet Chief Executive, Simon Emms, said after two years of construction and over five years of planning, the new line is now powering the Eyre Peninsula.
“Eyre Peninsula Link is a significant, $320 million investment in the region, giving residential and business electricity users a more secure and reliable power supply,” Mr Emms said.
“As well as improving supply reliability, the new line future-proofs the region’s high-voltage electricity supply to support growth and renewable energy development, which will deliver substantial benefits now and into the future.”

THE NEW AND OLD TRANSMISSION LINES ON EYRE PENINSULA. THE OLD LINE WILL BE REMOVED BY THE END OF 2023. DEMAND MANAGEMENT 42
The Eyre Peninsula’s old transmission line was more than 50 years old and needed substantial investment to replace worn out components to ensure customer reliability. Following comprehensive investigations, it was determined a new transmission line was the best and most cost-effective solution to delivering reliable electricity supply to customers across the Eyre Peninsula into the future.
“Our process to get to the final option of building the new line involved comprehensive stakeholder engagement, an economic assessment of a range of available options and public consultation,” Mr Emms said.
“The information and feedback we gained through this consultation played an important role in arriving at the final outcome.
“It was then a matter of engaging a primary contractor to undertake the works. Downer was contracted to conduct the detailed design and construction of the project, following an Early Contractor Involvement engagement which involved the preliminary design works and critical procurement activities.”
LOCAL AND COMMUNITY INVOLVEMENT
Ensuring that local and South Australian businesses had the opportunity to be involved in supporting the project’s delivery was a key objective for both ElectraNet and Downer.

“During the project’s initial stages, COVID-19 restrictions were in place across South Australia, so ElectraNet and Downer hosted several online forums for interested businesses to find out more about the project and the work packages that were available,” Mr Emms said.
“These forums provided a really good opportunity for Eyre Peninsula and South Australian-based businesses to hear from and speak with the project team and register their interest to be involved in its delivery.
“About $57 million was spent with South Australian businesses, of which more than $22 million was with Eyre Peninsula businesses.
“There were about 200 workers on average involved in delivering the project, peaking at 300 early in 2022. These
were workers who were spending money locally on things like food and drink, accommodation and fuel, which has been great for the local economies.
“Local subcontractors and suppliers represented about 15 per cent of the workforce, delivering works ranging from fencing through to minor civil works along the transmission line route.”
Mr Emms said Eyre Peninsula Link has been one of the biggest construction projects undertaken by ElectraNet and he would like to thank everyone that supported its delivery.
“When undertaking a project of this scale, support and collaboration from everyone who is impacted by or delivering it is vital,” Mr Emms said.
“Specifically, I would like to thank the Barngarla Determination Aboriginal Corporation (BDAC) for the significant contribution it has made to the project and its steadfast support in the important role of protection of cultural heritage in the field. BDAC has been a major contributor to the success of the project.
“ElectraNet recognises the huge commitment this project was for the Barngarla community and sincerely thank them for their efforts.
“We also appreciated the ongoing support from ElectraNet landholders, local councils and the substantial hours of work dedicated by the entire ElectraNet and Downer project teams.
“The project’s delivery was a really good example of how collaboration drives positive outcomes for everyone involved.
“Despite the challenging weather conditions and ongoing impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, the project was successfully delivered, which was a huge achievement and a credit to all involved.”
The cost of the new transmission line was largely offset by avoiding the cost of refurbishment works on the existing transmission line and annual Port Lincoln generator network support payments, resulting in minimal net price impact for customers.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
DEMAND MANAGEMENT 43
ELECTRANET EYRE PENINSULA LINK PROJECT DIRECTOR, DAVID TANSELL AND ELECTRANET CHIEF EXECUTIVE, SIMON EMMS AT THE PORT LINCOLN SUBSTATION.
ACHIEVING RENEWABLE-FIRST CONTROLS
By Daniel Watson, Automation Solutions Innovator, Yokogawa
Arguably the largest issue currently garnering attention in the utility and process control space is that of energy. Oil shortages, fuel and electricity price spikes and the unprecedented halt of the electricity trading market on the east coast of Australia last year have jolted us from our COVID-19 haze drawing focus once again to the topic of renewables and what role they can play. For so long just seen as an environmental saviour, now there is wider appeal in lowering the cost of energy, improving the quality of power and meeting carbon neutrality.
The latest Integrated System Plan (ISP) from AEMO highlights looming step changes, the most promising of which is the forecast of total renewables generation at 83 per cent by 2030. However, to achieve this some major investment in the grid is required. Investment that needs to be focused on latest technology use for more intelligent control.
There are three key areas that need to be addressed as part of the energy transition: management and increased penetration of distributed energy resources (DERs); increasing independence from the grid; and reliable dispatchable power. The Yokogawa PXiSE controller is
designed to solve all these challenges in a logical and renewable first manner. Other controllers are often aimed at making renewables fit into the existing grid, whereas the PXiSE vision is focused on 100 per cent renewables, 100 per cent of the time, taking a more advanced controls approach.

DISTRIBUTED ENERGY RESOURCES
Part of the AEMO plan is to address increased penetration of DERs. Projects like Edge and Symphony help to give a commercial mechanism for leveraging household resources, but we also need platforms to maximise their potential and control their impact on the grid, for many this is a utility problem, and utilities are looking for DER Management Systems (DERMS), like PXiSE, to solve this challenge. DERs are at the stage where they are creating issues during peak periods by supplying more power than the grid requires, potentially more than the power network can handle, and causing stability issues where the voltage is pushed high, even leading to restricting the amount of rooftop solar. The concept of Dynamic Operating Envelopes (DoEs) through DERMS was introduced to give a safe maximum operating window to individual resources.
Distributed energy resources such as solar and wind are pivotal for reaching net zero energy goals, however, the intermittent nature of these renewables can cause an influx of many un-coordinated distributed energy resources that can threaten the reliability of a power grid. However, the solution lies in intelligent and advanced control platforms that take a renewable-first approach.
44 DEMAND MANAGEMENT | Sponsored editorial
Taking a renewable first approach will aim to focus on maximising the power supplied by these DERs, in the case of Horizon Power the household DERs can supply 100 per cent of the renewable energy on the grid. This control is possible by integrating the grid generation/despatch controls with the DERMS controls, and by ingesting weather forecasts it is possible to shut down all hydrocarbon generators and leverage only the DERs with a battery for stability – no need for load banks or synchronous condensers.
GRID INDEPENDENCE
To help the energy transition one key step that can be taken is to cut the level of dependency on the grid and traditional generation. This is particularly important for commercial and industrial facilities, remote towns and communities, however, is equally applicable to residential use. The Victorian Government has already announced the development of islanding remote community microgrids to combat the impact of natural disasters.
Independence relates to the amount of power demanded from the grid and the level of reliance on it, especially during peak periods. With the increased DER penetration, the daytime energy supply is high, thus being a consumer during this period can be advantageous, and being a supplier during the evening demand peaks can be financially beneficial.
It is possible to actively control the power at your point of grid connection so that users can decrease demand without physically needing to cut the cord. For example, at Santa Rosa Junior College in California the PXiSE Microgrid controller is designed to maximise the potential of behind the meter renewable generation and storage as well as control HVAC to manage the power across the point of interconnection netting them $330,000USD in annual energy savings and $170,000USD in demand charges.
There are additional positives to increasing independence, in the case of the Santa Rosa college they are now able to island the site from the grid, meaning the college can continue to function in the event of a power outage as the campus is supplied completely by renewables. Combining DER control gives the ability to perform demand response and load enabling to ensure that operations can continue for days while disconnected.
RELIABLE DISPATCHABLE POWER
The grid runs on a fine balance of supply and demand. This balance has been achieved through a network of power generation assets that have a continual fuel source, such as coal or gas. When looking to run a renewable-first grid this level of dispatch needs to be achieved through storage such as a battery and pumped hydro.

Wind and solar have a capacity factor of approximately 30 per cent meaning that a significant oversupply of these resources is needed to meet the average demand. The storage is used to compensate when there is a drop in the renewable output, and smart deployment of storage can be used to pick up the intermittency, and act as long duration supply either overnight or during longer periods of cloud cover.
In the case of a microgrid, or a facility looking to have grid independence, the variability in the renewable resources can result in ten to 15 per cent more fuel usage if no storage is used and this can also cause greater power instability. In some of the Pacific Island projects PXiSE found it was normal to have frequency fluctuations of +/-1Hz, mostly due to renewable variability and diesel not being able to ramp quickly enough.
The solution to this is a co-located battery with very high speed, and forward planning controls. The battery can be used as a shock absorber for the system as well as a safety net. High speed controls of an appropriate battery can keep frequency variations to less than +/-0.01Hz and with automated planning and forecasting the battery state of charge can be optimised and maximised to ensure that the most renewable energy is used before we fall back to hydrocarbon-based resources.
The Australian energy transition has been spurred on by a few drivers, with frequent bushfires and floods highlighting a need for change, as is rising energy costs and aging infrastructure. The cost of doing nothing is now outweighing the cost of the change. Anyone exposed to the spot price market during 2022 would be very aware of the volatility in the market currently, and in many cases the cost of renewables would have been offset by the power prices. Through a few simple planned steps and approaches to redesigning the grid, a renewable-first grid can be setup, hopefully halting the rising electricity prices.
45 Sponsored editorial | DEMAND MANAGEMENT
more information, please visit www.yokogawa.com/au.
For
KEEPING WATER SERVICES FLOWING
amid rare river flood
This past summer, communities along the River Murray in South Australia experienced flooding not seen in decades. Harnessing a combination of proactive planning, extensive infrastructure assessments and a hands-on community engagement approach, SA Water was able to largely maintain essential services throughout this generational natural event, including an uninterrupted drinking water supply.
Peaking at around 190 gigalitres per day at the South Australia/ Victoria border, a significant rise in normal river flows presented an equally significant risk to SA Water’s nearby sizeable water and wastewater network operations, which are relied upon by thousands of homes and businesses.

Stretching more than 2,500km in length across three states, the River Murray is an important source of water for irrigation and agriculture, and habitat for native fish and birds.
For SA Water and the communities living and working along it, the Murray is the source of billions of litres of safe and clean drinking water each year.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 46 WATER
MANAGEMENT
With half of SA Water’s 80 drinking supply systems across metropolitan and regional South Australia using water from the River Murray, the utility’s General Manager of Operations, Chris Young, said it inherently brings a sizable network of river-based treatment plants, pump stations and major pipelines.
“Having seen the significant flooding impacts faced by communities and interstate water utilities upstream, it was evident a rapid flood response was needed to protect our asset base from flood damage, and maintain water and sewer services for customers,” Mr Young said.
“This included a comprehensive assessment process to examine each of our water and wastewater assets stationed along the River Murray, allowing us to highlight any potential impacts that rising water levels posed to our normal operations and take action where required.”
Among SA Water’s most at-risk assets identified was its raw water pump station at Cowirra in South
Australia’s Murraylands region, which pumps untreated water from the River Murray to the nearby water treatment plant. The resulting safe and clean drinking water is then delivered to customers in the towns of Cowirra, Pompoota and Ponde.


“With forecasts predicting water levels not seen since the 1950s, we collaborated across the organisation to design and construct an four-metre-high earth bank levee around the pump to isolate the infrastructure as an island,” Mr Young said.
“A further 200 one-tonne sandbags were also delivered by helicopter with assistance of the State Emergency Service to further safeguard this important infrastructure from damage.
“This early intervention and creative efforts of our people ensured that normal water services were able to be maintained to hundreds of customer properties throughout the duration of this natural event, which is a terrific outcome in such complex circumstances.”
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 47 WATER MANAGEMENT
WATER MANAGEMENT
LOCKS AND WEIRS GET BACK IN BUSINESS
On behalf of the Murray-Darling Basin Authority, SA Water manages Locks One to Six in South Australia as well as Lock Seven at Rufus River and Lock Eight at Wangumma in New South Wales, and Lock Nine at Kulnine in Victoria.
The locks and weirs play a key role in regulating the flow of water down the river system, while providing a safe channel of passage for boats, kayaks, and other river vessels.
CASE STUDY: PROTECTING MANNUM’S SEWERS
Sitting around 90km east of Adelaide, Mannum was one of South Australia’s most impacted riverside townships as a result of the flood event.

The low-lying topography of the area meant parts of SA Water’s underground sewer network and associated pumping stations were set to be inundated by rising river levels, presenting the risk of sewage overflows impacting customer properties and the surrounding environment.
“To protect the town’s wider wastewater network from damage, our operational and stakeholder engagement teams worked closely with more than 120 residents to proactively disconnect their wastewater services, temporarily preventing their ability to use showers, toilets and sinks,” Mr Young said.
“This involved inserting a bung and fibreglass seal at each customer’s
sewer connection, with locals instead able to access temporary bathroom and shower facilities at our nearby operational depot.
“A further 61 customers identified in flood-affected areas were able to continue using their wastewater service throughout the flood event, and this is the result of us being able to implement temporary wastewater pumping and tank infrastructure where possible.
“Within just a matter of weeks of the flood’s peak, our crews and contract partners were able to assess and safely restore normal wastewater services to all properties, enabling them to resume using their toilets, showers, kitchen sinks and dishwashers as normal.
“This is a credit to the efforts of our team collaborating with the community of Mannum in difficult circumstances to ensure that normal services could be maintained for the largest number of customers, for the longest time possible.”
“With water levels during the flood set to inundate all of our locks and weir structures, our River Murray Operations team took early action in closing the lock chambers, removing sections of the weirs using our on-site cranes, and disconnecting vital hydraulic and electrical cables to prevent significant damage,” Mr Young said.
“Boats could then instead safely travel across the top of the adjacent weir structure, without the need to pass through the concrete lock chamber.
“Working with the state’s Department for Environment and Water in observing the water levels for many months, our team was able to rapidly access each lock chamber to complete the necessary electrical and hydraulic testing when safe to do so, and allow each site to open for business as usual in late February and early March.
“Our team of lockmasters – or ‘lockies’ – have missed the opportunity to chat with locals and travellers using the locks throughout the busy summer months, and are excited to be back helping people on their river journey.”
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 48
SA Water provides the state’s most important and essential service – the delivery of safe, clean water and dependable sewerage services. It is a corporation owned by the people of South Australia, and is committed to providing its 1.7 million customers with trusted water services that represent excellent value. It invests $300 million a year in sustaining and enhancing its state-wide network, to ensure that it continues to play an integral role in South Australia’s social and economic development.
Protect your critical assets with the most reliable systems made in Australia.







Century Yuasa has been protecting critical power assets for 30 years with our local design, construct and onsite teams. Our DC systems are built with the best of global technologies and supported with the globally recognised Yuasa VRLA batteries which are the only batteries you can genuinely rely on to protect your critical assets and business services year after year.



To learn more about Australia’s own DC power systems, maintenance services, and the Yuasa range of VRLA batteries, visit our website.

For enquiries call 1300 364 877 https://cyb.com.au/industries-markets/industrial

WATER MANAGEMENT: are utilities security guards or stewards?
Water is at the heart of our much-loved Aussie lifestyle – our quality of life, our jobs, our businesses, and our communities all depend on it and this resource is central to how our cities, towns, and regions grow and develop. Without the water cycle, there is no lifecycle.
But when it comes to water management, are utilities security guards or stewards?
SECURITY VERSUS STEWARDSHIP
Water security means protecting water resources proactively, and considering the political, economic and social factors – including the impact of climate change and
population growth – that influence water availability and quality. It also means securing climate-independent sources of water and planning infrastructure and strategy around those factors.
Water stewardship, on the other hand, means managing water ethically and sustainably, and involves working with local communities, customers, and stakeholders to develop innovative ways to use water responsibly and beneficially for both the environment and communities.
Urban Utilities’ focus is on both concepts side-by-side to ensure that water is protected and conserved for generations to come.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
50
With climate change, population growth, and industrial development placing pressure on our finite water supplies, the challenges water utilities face are growing more complex, and there has never been a more urgent time for innovative and sustainable solutions to manage our most precious resource. Recycling water is one of the key ways that utilities can keep up with this demand and minimise their impact on the environment.
WATER MANAGEMENT | Sponsored editorial
RECYCLED WATER: A SMART AND SUSTAINABLE SOLUTION
One of the key elements of Urban Utilities’ roadmap to net zero by 2032 is recycled water – water that has been used once and then treated to remove contaminants, making it safe for reuse, rather than returning it to the environment.
Adding recycled water to the mix eases pressure on our drinking water supplies, reduces nutrients in waterways, and improves the well-being and liveability of communities. Recycling water can also reduce energy use, which leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Urban Utilities currently provides recycled water to hundreds of customers in its service region, mainly for agriculture and irrigation. Among other things, the water is used to green sports fields, support farmers, revive country racetracks, and grow koala habitats.
The utility also supplied recycled water to Brisbane Airport Corporation to support the construction of its second runway, saving more than 500 Olympic-sized swimming pools of drinking water in the process.

EMBRACING GROWTH AND OPPORTUNITY
If water isn’t sustainable, industry isn’t sustainable.
Over the past year, Urban Utilities has experienced rapid growth in demand for recycled water from industrial customers who are committed to sustainability and water stewardship.
Several major international companies have recently announced sustainability strategies that prioritise water stewardship, and this trend has been mirrored at the local level too.
Urban Utilities recently reached out to several of its biggest commercial water users to learn more about their sustainability goals, and was happy to hear that all of them have set sophisticated targets – with most having specific water stewardship goals.
The utility is thrilled to be an enabler of this important and rapid shift toward more environmentally responsible business practices.
There are also some emerging green industry players who plan to use non-potable water sources to make eco-friendly products like cardboard pulp, green hydrogen, and concrete.
Urban Utilities currently recycles an average of around 10,000ML of water every year, but this output will likely need to increase to meet customers’ changing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) needs.
Customers with a commitment to sustainability aren’t just setting the standard but shaping the future, and Urban Utilities aims to support them every step of the way.
BRISBANE 2032 AND BEYOND
Brisbane being announced as the Host City of the 2032 Olympic and Paralympic Games has also accelerated the pace of change in this service region.
Brisbane is set to be the first climate-positive Olympic and Paralympic Games, and Urban Utilities is thrilled to be playing its part to ensure that large-scale, global events can be done sustainably.
The utility is excited to explore opportunities to design and build innovative and sustainable water and wastewater infrastructure for key precincts that will benefit the community long after the closing ceremony.
Despite the challenges ahead, Urban Utilities is determined to secure a diverse water supply for its customers and communities, including by looking into climate-independent water sources like desalination and purified recycled water, for both residential and industrial use.
As a water utility, Urban Utilities has an opportunity and a responsibility to pursue sustainable water solutions, and is excited to work with like-minded industry partners and commercial customers to help them meet their ESG needs.
After all, waste is only waste if it’s wasted!
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
51 Sponsored editorial | WATER MANAGEMENT Discover how Urban Utilities is moving beyond reuse and how recycled water can help you meet your ESG needs, by visiting urbanu.com.au/wvum.
PROCURING INNOVATIVE WATER ASSET MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY
By introducing sustainable management strategies into an asset’s entire lifecycle, utilities can ensure the long-term success and resilience of their operations. This requires prioritisation of the procurement and delivery of innovative technology, which can maximise efficiency and performance reliability of assets, as well as their ability to withstand climate challenges.
Leading water and wastewater management solutions company, SUEZ, has released a new strategic plan for 2027, focusing on innovation and technologies within water management. The strategy highlights a focus on the research and development of new technology in water and wastewater treatment, which can then be provided to treatment plants.
Every new technology brings changes to the core principles of the water industry, and utilities are intensifying their efforts to adopt innovative technology. This involves a continuous cycle of discovering, examining, procuring and adopting innovation to improve asset capacity, operate more efficiently, improve customer service and provide long-term cost-effective solutions.
Bringing technology experience from across the globe, SUEZ’s General Manager of Innovation and Performance, Eric Garcin, highlighted that technological innovation is a key driver of sustainability, economic growth and human wellbeing.
“Technological innovations bring a myriad of opportunities, not only from an operational efficiency standpoint, but from a social, economic and sustainability perspective,” he said.
“While the benefits of innovation may cause short-term doubts, coupled with incumbent interests resisting change, with the right expertise, procuring innovative technology can lead to more growth and prosperity over the long haul. Moreover, the positive social and environmental implications can spread across entire territories.”
NEW STRATEGIES FOR PLANT UPGRADES
Victorian utility, South East Water, contracted joint venture John Holland, SUEZ and Beca to deliver an upgrade of its Boneo Water Recycling Treatment Plant. SUEZ led the procurement strategy for the project, bringing a sustainable approach to technology solutions and operational services to maximise the efficiency and performance reliability of the plant.
Initial works focused on incorporating leading low-energy nutrient removal and energy recovery processes to help South East Water achieve its emissions reduction target of 45 per cent by 2025.

With the plant's construction, the joint venture prioritised modernising the plant by utilising several breakthrough technologies, including optimised anaerobic digestion, Nitrite Shunt, and anammox sidestream. These helped reduce South East Water’s reliance on grid electricity and improved capacity to serve the local community's needs.
The project also prioritised transforming a conventional linear wastewater treatment plant into an ‘ecosystem’ that creates circular solutions. This involved reducing treatment expenses (including energy and chemicals) and decreasing its carbon footprint, whilst increasing revenues from water, biosolids utilisation, energy recovery and nutrient recovery.
PROCUREMENT FOCUSED ON COLLABORATION AND INNOVATION
The procurement strategy allowed the joint venture to manage the interface risk of designing and constructing a complex technology upgrade, which resulted in Australia’s first SUEZ Biofactory.
The Boneo project provided an outline of the key success factors for enabling innovation that can be replicated for different utilities. These included clear communication,
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
52 WATER MANAGEMENT | Sponsored editorial
The key to Australian water utilities dealing with the impacts of climate change is the use of innovative technology in water and wastewater treatment and management. Procuring the right technology for your utility’s specific operations is essential to bring sustainability and innovation goals from ideas to reality.
a collaborative approach, interactive sessions, desire for leading-edge technology, a long O&M period, not requiring a tender conforming to the reference design, and a true focus on best whole-of-life cost.
Given the collaborative nature of the joint venture, as well as the commitment from the designer, constructor and operator during the full contract term, Boneo was a huge success. It prioritised performance through innovation, bringing South East Water one step closer to its commitment of net zero emissions by transforming traditional methods of wastewater treatment.


South East Water’s General Manager - Liveable Water Solutions, Charlie Littlefair, stated that collaboration played a key role in generating new ideas and promoted knowledge-sharing, which led to the procurement of innovative technology.
“For our Boneo project, SUEZ made sure that collaboration was at the core of our approach to innovation,” said Mr Littlefair.
“By bringing together people with different ideas, views and experiences, the joint venture spurred new ideas, creating a joint momentum for disrupting the traditional way of doing things.”
In contrast, a typical design and construct contract usually has the designer selecting equipment that optimises the capital cost, often at the expense of operational cost and/or integrity. Whereas, in the Boneo arrangement, the contractor was responsible for the O&M phase and integrated the Net Present Value into decision making, leading to the best whole-of-life cost.
Peter Segura, SUEZ’s O&M Manager for the Boneo WRP Project, said that by working openly with South East Water throughout the project, SUEZ was able to ensure that all parties were comfortable with the innovative technology being used.

“Clear communication was important to everyone involved – we needed to work together to ensure that South East Water
ultimately received an asset that achieved their objectives and optimised capital costs, without compromising integrity,” Mr Segura said.
“We held interactive sessions with South East Water to test new technology and concepts, which helped us to come up with solutions that best met their needs.”
The benefits of SUEZ’s approach to the project and the implementation of technological solutions included decreased project costs, reduced carbon footprints, and lowered energy consumption. As a result, this provided other treatment plants with a blueprint to use when procuring new technology to produce the best outcomes.
Rachael Nuttall, Business Development Manager at SUEZ, said, “We want our approach to innovation and solutions to serve as a roadmap for Australia’s utilities and provide an outline for how we can transform procurement in water and wastewater treatment.
“This will require a desire for leading-edge technology across the sector, and a collaborative approach between our customers and communities.”
Procuring innovative technology helps utilities overcome their current sustainability challenges whilst future-proofing their assets. This enables them to gain the most value across the entirety of their assets’ lifecycle by creating customised solutions that best meet their sustainability, financial and social needs.
For more information, please visit www.suez.com/en/australia-new-zealand.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
53 Sponsored editorial | WATER MANAGEMENT
Sydney Water
INSTALLS NEW IOT SENSORS IN MAJOR ROLLOUT
The agreement will see Sydney Water spend $15 million dollars to install over 26,000 blockage detection devices across 4,600km of wastewater infrastructure by June 2024. Sydney Water has already installed 9,000 devices across its wastewater network. The sensors detect about 20 blockages in the gravity wastewater network per month on average, saving approximately $400,000 in incident costs. Sensors are installed on existing wastewater infrastructure and frequently send back data readings. These data readings are preconfigured to trigger an alarm when certain thresholds are met to indicate a potential blockage. These alarms allow Sydney Water to act on the issue before a wastewater overflow occurs.

As the system detects blockages in wastewater pipes before they lead to wastewater discharge into customer properties and the environment, incidents can be avoided that could pose a public health risk and incur massive clean-up costs and result in reputational damage. The devices from project partner Kallipr and Metasphere are data loggers attached to sensors that communicate regular data readings. The loggers are pre-configured to alert operators when the data indicates that a potential blockage has occurred. This allows a rapid response from Sydney Water, resulting in more efficient management of its assets.
Head of Operational Technology at Sydney Water, Craig Earl, said he is excited about the multi-million dollar initiative.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 54
WATER MANAGEMENT
SYDNEY WATER’S INSTALLATION OF ONE OF 26,000 BLOCKAGE DETECTION DEVICES AROUND SYDNEY.
“This is a transformational project for Sydney Water. We’re stepping into the Internet of Things with internet connected devices. We’re leading the industry on some of this new deployment which is resulting in massive savings via early detection of blockages in our wastewater network,” Mr Earl said.

“We’ve worked with other utilities around the country and industry partners as well. We’re really focused on that Australian ability to drive innovation, not just nationally but on a global scale as well.”
SIGNIFICANT COST SAVINGS
Sydney Water’s Internet of Things Manager, Christoph Prackwieser, said the cost savings generated by the sensors have been considerable.

“So far, around 400 blockages at environmentally high-risk sites have been identified and cleared. We are saving $400,000 a month in avoidance costs with this technology,” Mr Prackwieser said.
Mr Earl said the results have been pleasing, with the data from the 9,000 devices currently installed creating a return every month on cost avoidance, plus the added benefit of protecting the environment.
The majority of blockages are caused by tree roots penetrating pipes or access chambers, although grease and wet wipes also contribute to blockage build-up.
The sensors can withstand high humidity and water immersion. The more than five year battery life reduces the need for maintenance and site visits significantly. The devices can reliably and securely record and send data from remote and difficult-to-access areas by operating on the NB-IoT network.
DRIVING WASTEWATER NETWORK DIGITISATION
Mr Prackwieser said the Internet of Things technology is a game changer.
“The Internet of Things is a monitoring technology which allows us to securely connect these devices via the internet to our systems. It’s been working very well and has generated good outcomes,” Mr Prackwieser said.
Mr Earl said the placing of the sensors is of paramount importance, so the utility has been very strategic about their placement, as it’s about maximising the ability to protect the environment.
“So many of our assets are around creeks and streams or places like Sydney Harbour where we’re installing these sensors, we’re ensuring we protect these special places,” Mr Earl said.
More than 8,800 sensing devices have been installed in the past 18 months, and the deployment work continues at a rate of between 160 and 210 devices a week. Sydney Water envisages there will ultimately be tens of thousands of devices in the field.
Installing the devices will allow Sydney Water to build on its highly successful wastewater management project. It is driving the digitisation of its existing wastewater networks and allowing for proactive management of blockage events within the infrastructure.
Mr Earl said he’s proud to be a part of the initiative and constantly shares his findings with his family.
“They know how passionate I am about this project and listen to my stories. They say to me ‘yes Dad, yes Dad’. They know it's something that excites me and it excites me because I know we’re making a difference to this great city,” Mr Earl said.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 55
Sydney Water is undertaking the first wastewater monitoring Internet of Things (IoT)
deployment
of its scale in Australia, which is saving hundreds of thousands of dollars per month in potential blockages.
WATER MANAGEMENT
CRAIG EARL, SYDNEY WATER HEAD OF OPERATIONAL TECHNOLOGY (LEFT) AND CHRISTOPH PRACKWIESER, SYDNEY WATER INTERNET OF THINGS MANAGER (RIGHT) WITH ONE OF 26,000 BLOCKAGE SENSOR DEVICES.
EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE IN WATER TREATMENT
Sodium hypochlorite (NaCIO) is a corrosive chemical and powerful oxidizer that is often used as a bleach and a disinfectant. Due to its reactive nature, it needs to be stored carefully. Liquid storage solutions provider, Polymaster, supplies safe-storage tanks for this chemical to be used in water treatment plants, and has shared some key information about when this chemical is used and how to store it safely.
HOW IS SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE USED IN WATER TREATMENT?
When sodium hypochlorite is added to water it starts a process called chlorination, which eliminates harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. This process is commonly used in municipal water systems to ensure the water is safe to drink and use.
It can be used to remove things from the water such as dissolved iron, manganese and hydrogen sulphide, which give the water an unpleasant taste and odour, and can stain clothing and fixtures. It also controls algae and other organic growth in reservoirs, water tanks, and other water storage facilities.
HOW DO YOU STORE IT?
Sodium hypochlorite is a highly reactive and corrosive chemical that requires special handling and storage. It’s important that it’s stored within a tank or container that is built for the purpose of holding aggressive chemicals, such as Polymaster’s self-bundled and process tanks.
These tanks have a specific gravity (SG) of two, even though you only need up to 1.5SG, and are UV stabilised and chemical resistant, meaning that they are not prone to corrosion. If you were to put this chemical within a normal polyethylene rainwater tank with a lower SG of one it would essentially dissolve, resulting in leaks.

Store sodium hypochlorite in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and other chemicals, using containers made of compatible materials. Ensure that the sodium hypochlorite containers are labelled with the proper hazard warnings.
When it comes to storing sodium hypochlorite, what you are storing it with is also important. It should not be stored with acids or any other chemicals that can react with it. This includes other acid-based chemicals (e.g. sulfuric and nitric) as these release a toxic chlorine gas when they come into contact with sodium hypochlorite that can cause serious respiratory problems; any kind of organic compound such as oil, gas or alcohol, as chlorine gas can be released and create a fire hazard; and certain metals such as iron, aluminum, and zinc, which can also create a fire hazard.
By following these guidelines, water treatment plant operators can ensure the safe and effective use of sodium hypochlorite in their facilities.
For more information, contact Polymaster’s chemical team on 1300 062 064.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
One key component of the water treatment process is the disinfection of water, which is often achieved through the use of sodium hypochlorite. Although it is a powerful disinfectant, it is also highly reactive. This article explores how sodium hypochlorite is used in water treatment plants, best practices for storing it, and guidelines for safe handling.
56 WATER MANAGEMENT | Sponsored editorial

1800 062 064 | polymaster.com.au Secure IBC storage & decanting solutions
unique Enclosed IBC Bund solves many of the problems
with IBC storage and chemical/fluid decanting in a weather resistant, purpose-built enclosure.
Full weather protection – stops rain entering the enclosure Æ Easy forklift loading with wide forklift access from both side and back Æ 250ltr day tank Æ Lockable cabinet to keep system secure Æ Venting by two sides Æ Viewing windows incorporated into the doors Æ 110% bund capacity complies with AS3780 Æ Low-level alarm available Æ Chemical resistant – high grade polyethylene construction View Video
Polymaster’s
associated
Æ
BUILDING TRUST, DRIVING INNOVATION, AND DELIVERING VALUE IN THE WATER SECTOR
 By Ryan Collins & Kareen Moraes, Graduate Engineers from Greater Western Water
By Ryan Collins & Kareen Moraes, Graduate Engineers from Greater Western Water
On 23 February, 2023, 180 people from across the water industry joined together for the second SWAN Asia-Pacific Alliance Workshop in Melbourne.
WATER MANAGEMENT 58
SWAN – the Smart Water Networks Forum – is the leading global hub for the smart water sector. The event drew in utility and industry experts from across Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Korea, Malaysia, and several European countries. It focused on how to optimise data-driven solutions to generate important outcomes for customers and minimise risks by improving compliance reporting and monitoring.
Three core themes shaped the nature of discussion:
• People driving change
• Technology as an enabler not disruptor
• The value of the process, the Digital Transformation Journey
As young professional graduates at Greater Western Water assisting with the event, these themes particularly resonated with us since we could access the current innovation taking place and understand its potential for greater use in the future.
THE IMPORTANCE OF PEOPLE IN DRIVING CHANGE
“Make your last 10 per cent, your first 10 per cent.”
One of the core tenants for driving change in the water industry via smart water solutions is the placement of people at the centre of the design philosophy.

In his keynote, Damian Wells, Managing Director of Coliban Water, focused on the 2022 Victorian floods.
“Trust can be gained in teaspoons, but lost in buckets,” Mr Wells said.
“The public gets to decide what’s of value.”
Customers are the most imperative people to get on board when implementing smart water solutions; at the end of the day, they are the ones who pay the price to implement new technologies and are the most impacted when technologies do not work as planned. The key challenge is ensuring the community’s buy-in, such as by improving the data and water literacy levels and removing jargon from messaging.
Another key issue is equity as summarised by Sean Cohen, Head of Smart Metering at SUEZ Australia & New Zealand.
“Make your [project’s] last ten per cent your first 10 per cent,” Mr Cohen said.
Such a mindset can help tackle complex and unexpected challenges.
TECHNOLOGY AND DATA AS AN ENABLER, NOT A DISRUPTOR
A reminder that “the bots don’t connect the dots.” Technology and data form the engine of the Smart Water Ecosystem by representing a compilation of “what if’s” that can be refined to help inform business decisions. Technology is the bridge that refines data into implementable solutions, which can then empower changes to people and process. The use of technology and data is growing in importance across the industry to assist in asset management, the demonstration of compliance, and the optimisation of projects/service delivery solutions.
The most impressive emerging solutions we saw that we think will impact the water industry are artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and digital twins (DT). AI and ML are exceptionally powerful for sorting and assessing
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 59
WATER
IMAGE CREDIT: JANE TYZACK PRESENTATION AT THE SECOND SWAN APAC ALLIANCE WORKSHOP
MANAGEMENT
large quantities of data and can greatly assist utilities in their decision-making process. The development of DT models further allows utilities to streamline their asset management processes and significantly increase visibility of key issues moving from reactive to proactive asset management. However, the integration of these solutions requires buy-in from key stakeholders through adequate change management frameworks.
Our key takeaway is that technology will never replace humans and should be an enabler, not disruptor.
As said by Damian Wells, “the bots don’t connect the dots.”
IT’S ABOUT THE PROCESS, THE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION JOURNEY
Having “A clear structure, priorities, and understanding adoption personas.”
A final key takeaway from the discussions was around the utility digital maturity journey. Process change is a continuous cycle that has people at its core, as pointed out by Jenny Francis, Executive Manager, Digital at Hunter Water.
Similarly, Klir’s Business Development Manager, Cillian O’Neil, said that the adoption of processes that drives change is thoroughly intertwined with utilities’ risk maturity journey, requiring an understanding of ways to monetise, prevent, and manage risk in a continuous cycle.
Another compelling case for driving greater perspective analysis for compliance reporting was demonstrated by Michael Howden, Data + Insights Manager at Taumata Arowai (New Zealand’s Water Services Regulator). Mr Howden expanded on the process of real-time reporting through condensing their drinking water guidelines into lines of code that is then fed into the API to enable analysis and determine the compliance.
A last value proposition for an outcome-driven process use was made through a technical case study of Bolivar’s North Wastewater Master Plan. As Optimatics’ Product Manager, Lucy Pocock explained, their software was able to provide an optimised master plan that focused on important main upgrades based on different input functions from over 4,000 iterations. This improved cost savings by leveraging intelligent automation, cloud computing, and evolutionary algorithms.

However, it was essential that the ‘process’ be thoroughly informed by the organisation’s risk appetite, comprehensive change management guidance, and system transparency. Thus, an effective framework for process implementation needs to be grounded in structure, prioritisation, and the understanding of the people impacted by the process.
The second SWAN APAC Workshop was a resounding success, bringing together regional industry leaders to share knowledge around the key themes of building trust,

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 60
WATER MANAGEMENT
IMAGE SOURCE: PATRICK BONK PRESENTATION AT SECOND SWAN APAC ALLIANCE WORKSHOP.
driving innovation, and delivering value. These topics were explored through the lenses of people, technology and data, and processes.
The overall sentiment was the need for collaboration and championing smart water solutions to ensure benefits to the community and country, while ensuring that the appropriate
change management frameworks are in place to support technology adoption. This is needed to ensure long-term water sustainability.
As said in the Workshop by Indigenous elder, Uncle Bill, “It is not what the river can do for us, but what we can do for the river.”
To view the workshop presentations and photos, swan-forum.com/publications/2nd-swan-apac-workshop.
To Learn more about the SWAN APAC Alliance, visit swan-forum.com/asia-pacific-alliance.
Link-Seal
Pipe Penetration Seal Solutions


Link-Seals offer hundreds of solutions to seal pipe penetrations ranging in size from 10mm to 3.6 metres diameter.


Link-Seals are suitable for most types of pipes including PVC, HDPE, Copper and Steel.
Resistant to water, oil, gas, aggressive chemicals and fire.
Projex Group helps calculate the right Link-Seal size and model for your application.
Link-Seal
mail@projex.com.au 1800 001 114
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 61
IMAGE SOURCE: CILLIAN O’NEILL PRESENTATION AT THE SECOND SWAN APAC ALLIANCE WORKSHOP.
WATER MANAGEMENT
In 2020, Franklin Harbour District Council implemented a new 23km gravity-fed water scheme to supply up to 200kL of water a day to a large remote farming area north-west of Cowell in South Australia, overcoming challenges around a mountain range separating the area to the connection point.

The scheme had to deal with the fact that the farming area was separated from the closest SA Water connection point by a substantial mountain range, and that the SA Water connection site and mountain range both had limited existing infrastructure and connectivity.
Monitoring and automation solutions company Station Innovation helped the Franklin Harbour District Council implement the scheme. Station Innovation’s equipment is made to operate reliably in harsh Australian conditions, even without external power or connectivity.

To solve these problems, the Council designed a multistage pumping operation that pressure feeds water 2.2km from the 40mm SA Water connection point via a 100mm PVC pipe to a 200L base tank and pump station (tanks $26k, sheds $5k) at an elevation of 80m.
WATER SCHEME
From there, water is pumped a further 4km to an intermediate 200kL tank and pump station at elevation of 180m, and finally to the Apex 500kL tank station at an elevation of 283m. From there, it is gravity fed for 23km to connect farms to the mains water supply.
CRITICAL COMPONENT OF THE WATER SCHEME
Station Innovation’s EcoSAT remote monitoring and control units are an essential part of this innovative scheme. The pumping stations, each with two (Xylem Lowara GVH20/15SV11, $32k) pumps in a duty/standby mode, cannot be operated using pressure switches due to the high (100m) static heads inherent in the system.
Instead, tank levels and pump operations have been monitored and controlled without fault for over three years using Station Innovation’s EcoSAT remote SCADA system (VFD controllers and SCADA $86k).



Operators view the level, status and history of each tank and pump online, and remotely control pump operations and adjust alarm (high and low) trigger levels.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 62
WATER MANAGEMENT | Sponsored editorial
& Velocity measurement Continuous Biofilm Monitoring Sample Biofilm growth signal over time LEVEL METERS BIOFILM ANALYSER ANALYTICAL CONTROLLERS PROCESS INSTRUMENTS PULSAR • Lightweight, compact design • No interruption to service • ATEX Ex mb Zones 1 & 2 approval • Minimal installation costs • Maintenance-free • RS485 Modbus • IP68 • Non-contacting • Cost-effective • Ultrasonic Transmitters and Controllers • Point Level Switches • Sludge Level Systems • Wireless Systems • Early detection of Bacterial Growth on surfaces • Monitoring & optimisation of sanitation requirements. NEW TURBIDITY MONITOR BINTECH SYSTEMS WATER SOLUTIONS 1300 363 163 sales@bintech.com.au www.bintech.com.au For more information on Station Innovation and its remote monitoring and control units, please visit www.stationinnovation.com.au or contact 1300-781-134
REMOTE AUTOMATION INFRASTRUCTURE TRANSFORMS DISTRIBUTED
TO THE CORE CLEV

THE TRACTOR THAT HELPS KEEP YOU ONE STEP AHEAD.

The Vermeer RTX1250i2 Ride-on Tractor helps bring intelligent features to the forefront of your job. Offering selfidentifying, intelligent i2 attachments, the RTX1250i2 automatically recognises the i2 attachment and adjusts the machine’s controls according to the operational needs of the attachment. With a plow depth of 106.7cm (with tracks) and a reel carrier capacity of more than 2,200kg - all supported by an optional climate-controlled cab boasting a quiet, comfortable ride - productivity is at your fingertips. Contact your local Vermeer Australia team to try it for yourself.

VERMEERAUSTRALIA.COM.AU | 1300 VERMEER Vermeer and the Vermeer logo are trademarks of Vermeer Manufacturing Company in the United States and /or other countries. Product specifications are subject to change by OEM. © 2023 RDO Equipment Pty Ltd (trading as Vermeer Australia). All Rights Reserved.
IN STOCK
BENEFITS AND CHALLENGES OF RENEWABLE TRANSMISSION LINE SENSORS
By Mikayla Bridge, Utility Magazine
The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) is providing major funding to help New South Wales Transgrid and Infravision trial sensors that will increase capacity to support renewable energy and improve the efficiency of existing transmission lines. Utility spoke with Dan Sturrock, ARENA’s Director in Business Development & Transactions, to discuss the project’s opportunities and challenges.
The critical trial will involve the deployment and testing of Infravision’s Next Generation Line Monitoring System sensors on selected transmission lines on the Transgrid network in New South Wales.

The Next Generation Line Monitoring System consists of a sensor stack that can be installed by drone on transmission lines to provide real time microclimate data such as wind speed/ direction, temperature and any sagging of conductors.
ARENA is providing $732,493 in funding for the $1.8 million Infravision project. ARENA’s portion of the funding will assist Infravision to develop, test and trial its hardware and proprietary software to process the data.
“Infravision identified a clear opportunity to improve the efficiency of existing network assets with a relatively simple and low cost solution that can efficiently and reliably determine a real-time dynamic-line rating (DLR) of transmission lines,” Mr Sturrock said.
Infravision’s line monitoring technology consists of a sensor stack that can be installed by drone on transmission lines to provide real time microclimatic data which can unlock additional transmission line capacity. This data can be used to calculate a DLR that provides a more accurate and responsive measurement of transmission capacity, allowing higher volumes of electricity to be safely dispatched when conditions are suitable.
“Safe line capacity can be affected by wind, temperature and nearby vegetation. Line sag caused by hot weather or high energy flows can cause cables to hang lower than usual, bringing them closer to trees and urban infrastructure that may be located below,” Mr Sturrock said.
“At scale or deployed strategically in congested areas of the grid, this technology could provide the means for the market operator to reduce constraints or curtailment, which in turn will facilitate greater renewable energy export into the grid, potentially delaying and reducing the need for significant network investment upgrades.”
DLR will become increasingly important in a grid with increasing renewable energy generation. Network congestion and curtailment is likely to
ENERGY NETWORKS 64
be a major consideration for planned renewable energy zones where significant volumes of power flows are expected during peak solar hours or periods of high generation.
MAJOR CHALLENGES WITHIN THE TRIAL
Part of ARENA’s funding requirements is the opportunity to share knowledge and learnings with the energy sector. ARENA will work with Infravision to develop and deliver these outcomes.
If any challenges do arise from Infravision’s ongoing trial, Mr Sturrock said they will be captured in the knowledge sharing reports that will be made publicly available on ARENA’s website.
“The value of Infravision’s project to ARENA will be in determining whether the proposed technology solution can calculate a real-time DLR with reliability,” Mr Sturrock said.
“This will provide broader benefits to market participants in optimising technology solutions to determine DLRs and improving the commercial case for the adoption of these solutions by network owners. This will ultimately provide better tools to determine the potential ability of the technology to reduce renewable energy curtailment.”
RENEWABLE BENEFITS FOR THE INDUSTRY
As a major trial with government funding, the project’s results – if successful – are likely to have broad benefits to existing industry challenges.
“The industry’s existing approaches to working out the operating limit of transmission lines is quite crude and lacking in accuracy. More accurate approaches can be costly, such as using LiDAR (the same technology employed by Infravision) and helicopters,” Mr Sturrock said.

“Other options – such as ‘sag monitors’ – can be expensive and require line outages to install. Their installation process can also expose workers to safety risk if they need to climb the towers.
“Infravision has discovered a market niche that doesn’t yet have significant competition or available alternative technologies that are fit for purpose. The market’s need for technologies
that enable an accurate DLR is clear and increasing.”
This can also be said for data quality and fidelity on transmission lines across Australia.
“Deploying, testing and enhancing a fleet of next generation line sensors on the New South Wales transmission network will provide Transgrid with much higher fidelity data on these lines,” Mr Sturrock said.


“In the 2022 Integrated System Plan, the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) identified $12.7 billion of new transmission projects required to underpin the transition to renewable energy over the next decade.
“Transgrid’s trial could generate valuable outcomes for network operators, by reducing constraints on renewable energy generators, which also improves network utilisation.”
KEY MESSAGES FROM THE TRIAL
When asked what key message he hopes utilities and communities will take away from Infravision’s trial, Mr Sturrock said, “We’re hoping people will see why investment in Australian
companies, particularly startups, is a great way to ensure Australia achieves net zero emissions by 2050.
“The electricity transition is going to require new generation and transmission on a massive scale. Infravision’s integrated Dynamic Line Rating solution can help get the most out of existing transmission lines.”
Allowing an increased flow of electricity through existing assets reduces the need for new infrastructure, keeping down costs for network operators and consumers.
“Infravision is a great example of an Australian startup providing practical solutions to unlocking a higher penetration of renewable generation sooner which can be applicable to the National Electricity Market and other electricity networks across the world,” Mr Sturrock said.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
65 ENERGY NETWORKS
VIRTUAL ASSET ASSESSMENT: DIGITAL INTELLIGENCE SOLVING NETWORK CHALLENGES
The COVID-19 pandemic, technological advancements, and regulatory changes, as well as the shift towards renewables, and a declining workforce, have created a state of upheaval across industries. The utility sector was slow to adopt automation in the past. However, the recent retirement of experienced workers who are not being replaced has sparked a change in this trend. As the number of industrial assets and the data they generate grows at an exponential rate, utilities are looking for ways to inspect assets with fewer staff.
RAPID ASSESSMENT PROCESSING
When a New South Wales based power utility turned to Altavec’s AIMS Virtual Asset Assessment (VAA) tool, it knew the cloud-based platform could streamline the process of capturing and analysing images of assets. AIMS VAA uses images taken by helicopters, drones, or field inspectors, and automatically associates them with the appropriate assets based on the image metadata. Rapid and streamlined processing takes less than 24 hours with images captured on one day are uploaded and ready to review by the next. This eliminates the need for manual association and makes the process more efficient.
But the technology application goes further, it now accelerates the utility inspection department workflows, optimising asset performance and ensuring networks stay compliant and reliable. The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Machine Learning (M) algorithms now automated asset inspection within the Altavec AIMS VAA platform. Virtual asset inspections and defect identification are now performed automatically, thus filling the gap created by the shortage of skilled workers.
INSIGHTS TO RECOMMENDATIONS
AI pulls actionable insights from complex data sets and delivers recommendations to inspection teams. For example,
AI can estimate an asset's current state based on prevailing environmental and usage conditions without requiring a physical inspection. Predictive maintenance is now possible, improving asset reliability by identifying risks and providing the information needed to fix critical assets before they fail. The use of ML algorithms for data intelligence is rapidly advancing - consider that ML is like having a team of experts working around the clock to analyse data sets and pull the most valuable insights. The larger the data set, the more accurate the predictions, as machine learning is not biased towards one sample, in fact the more data accessible by the ML algorithm the more accurate the predictions and insights become.
Technologies such as ML and AI provide deeper insights into each asset's condition. With this information, maintenance strategies are optimised to increase the assets' lifespan, minimise the need for replacement parts or equipment, and focus the efforts of skilled asset workers.
REAL RESULTS
Our customer, a New South Wales energy utility, saw its asset inspection program successfully transformed using AIMS VAA. A 40 per cent increase in the number of asset inspections and a 30 per cent savings on current asset maintenance programs was realised. This resulted in measurable operational time and cost savings, improved safety outcomes, and enhanced network accuracy. Better asset management and decision-making was enabled, helping the utility to operate more efficiently and effectively.
An extension of the program is now underway - asset inspections via AIMS VAA now cover an expanded part of network operations, further streamlining maintenance and repair processes, improving customer satisfaction whilst optimising the overall management of network assets.
Network problems solved, that’s the purpose of Tech Mahindra Altavec.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 66 ENERGY NETWORKS | Sponsored editorial
To learn more, please visit www.altavec.com or email solutions@altavec.com.
Utilities across Australia and the globe are increasingly turning to the potential of digital data and digital intelligence to assess the condition of assets. The use of digital technologies and data analytics is disrupting traditional business models, changing the way linear assets are designed, built, inspected, and operated.


ENDEAVOUR ENERGY PIONEERS INNOVATION WITH ITS DIGITAL TWIN
Millions of people in Sydney’s Greater West and beyond rely on Endeavour Energy to provide a safe and reliable electricity supply around the clock. To combat the challenging conditions of the region’s harsh environment –subject to heat waves, flooding, drought and wildfires – Endeavour Energy has embraced technology and dramatically improved customer outcomes after it became the first electricity network in Australia in 2022 to deploy an engineering grade ‘digital twin’ of its physical poles and wires network.
A‘digital twin’ is a virtual model designed to reflect a physical object, process or system that includes relational interactions with data and simulations.
Developed in partnership with leading cloud-based engineering analytics platform Neara, the digital twin has revolutionised Endeavour Energy’s response to critical emergency events by accurately identifying clearances between rising floodwaters and power lines from the office, rather than onsite inspections, freeing up field resources to perform other critical functions.
Endeavour successfully deployed the digital twin during four successive record-breaking floods along New South Wales' Hawkesbury River in 2021–22, using the digital twin’s advanced analytics and risk modelling to eliminate 300 hours of inspection time and help speed up recovery. These extreme floods saw up to 7,000 customers residents and businesses in Western Sydney left without power for up to a week as Endeavour Energy used past flood records and manual calculations to predict future flood levels in order to proactively switch off power to areas that were likely to be submerged as floodwaters rose.
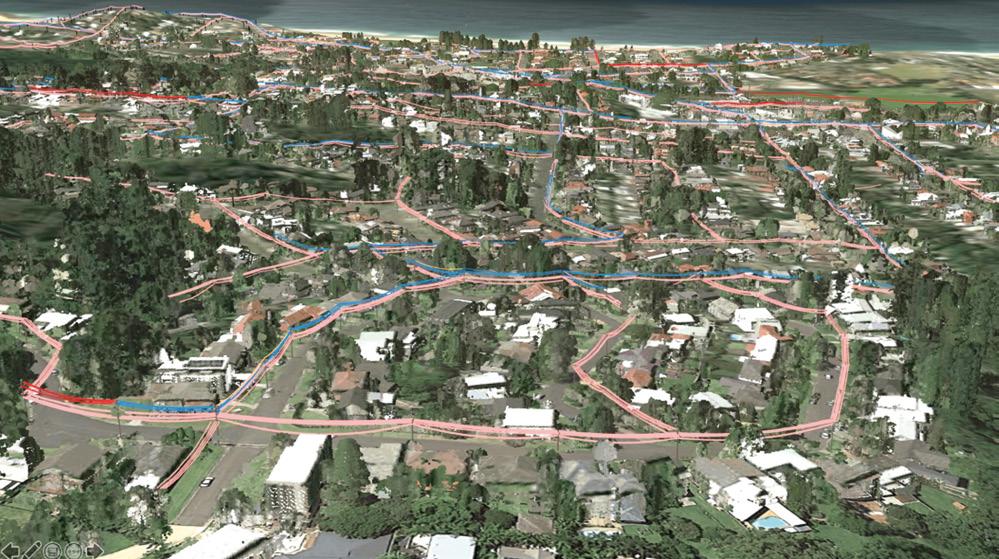

During floods, this is a critical public safety step to ensure that residents and emergency workers are not exposed to live power lines hidden beneath raging flood waters. This was based on ‘best estimates’ in areas where the Hawkesbury/ Nepean floodplain was submerged with floods reaching up to 14m – higher than most of the power poles in the area and stretching as far as the eye could see.
Endeavour Energy embarked on a trial to initiate a new system that would revolutionise the way it delivered power and supported communities in times of crisis.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 68
ENERGY NETWORKS
ACCURATE DATA CLASSIFICATION
After the first flood, Endeavour Energy used modelling of flood levels over its network digital twin to develop a virtual flood overlay across the modelled 3D network, based on data collected and manually calibrated through visual inspections, helicopter flights, Google Earth and the digital twin. This information was refined in subsequent flooding events to provide a more accurate picture of the impact of floodwaters on Endeavour Energy’s network, and to share that information with customers.
IDENTIFY AT-RISK ASSETS
Using Neara’s physics-enabled software, Endeavour Energy can now assess where assets are at risk from multiple factors, including high tension and encroachment risk. With this information, the utility can identify high-risk and high-priority areas of its network when simulating extreme weather events – such as high wind, extreme heat, rising floodwater and wildfire – to understand the impact on its network. For example, the digital twin can also be used to see how cables might sag in hot temperatures, which feeders might be impacted first as flood water rises, and which poles might be most at risk of failure in high winds.
During flood recovery, the digital twin has allowed Endeavour Energy to maintain safe clearances between the floodwaters and the high voltage network. It is used in conjunction with a purpose-built inspection app that brings back real-time information from the field to the control centres that coordinate the on-ground inspection and repair works between teams and partners. This has improved response times as well as worker and public safety.
It has enabled Endeavour Energy to quickly inspect and restore flooded properties, dramatically reducing the time it takes to restore essential electricity supplies to flood-affected customers so that they could start rebuilding their lives and communities sooner.

However, identifying weather-related risk is not the only thing Endeavour Energy is doing with this technology.
VEGETATION MANAGEMENT
Vegetation management is an ongoing responsibility for utilities with overhead infrastructure. LiDAR data captures network assets and vegetation. Once the data is classified, the result is an extremely accurate representation of network assets and the objects around them.
Unlike buildings, vegetation grows and changes over time. Not only must utilities ensure that vegetation – such as trees – does not grow into power lines, they also need to ensure that the vegetation does not present a fall-in risk. Endeavour Energy’s digital twin includes a physics-based calculation to determine whether nearby trees might fall onto a power line, and these are highlighted across the whole network so that engineers and contractors can easily identify and prioritise hazardous tree removals.
REPLACE AND MAINTAIN ASSETS
Endeavour Energy has been able to deliver more efficient asset replacement and maintenance regimes using the digital twin. With high-quality LiDAR data already captured by most utilities to understand vegetation encroachment, the next logical step is to use the data to extract more value by applying it to other use cases.
With its interactive 3D digital model, Endeavour Energy has been able to understand loading scenarios, so that it can optimize asset maintenance workflows. Having a rich asset database allows for better asset replacement strategies by prioritising the highest-risk and highest-impact assets and tackling them prudently.
INVEST IN THE MODERN GRID
With so much time and money saved through the efficiencies introduced by the digital twin, Endeavour Energy can invest more time on strategising for the future. The utility is committed to planning a modern grid where batteries, microgrids and solar integrate seamlessly with the distribution network’s traditional poles and wires. By first designing digitally and stress testing the 3D model in a risk-free environment, Endeavour Energy can ensure that the decisions it makes are right the first time with new construction projects.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 69
ENERGY NETWORKS
OVERCOMING CHALLENGES IN PORT MELBOURNE
network augmentation project
A new innovation precinct in Fishermans Bend is set to position Victoria as a global leader in engineering, manufacturing and design. However, before the redevelopment work could start, there was the complex task of augmenting the existing power network. Daly’s Constructions had to innovate to combat weak ground conditions, traffic management constraints and to navigate 150 existing underground services.
The General Motors Holden (GMH) site situated in Fishermans Bend in Port Melbourne was one of the cornerstone locations for car and propulsion systems manufacturing in Australia for more than 60 years. Following the factory’s closure in 2016, the Victorian Government pledged $179.4 million to redevelop the site into a technology precinct that will place Victoria at the forefront of global innovation.
To facilitate the precinct’s development, Daly’s Constructions was engaged by Powercor Network Services
on behalf of CitiPower to augment the existing 66kV and 11kV networks. The contract, awarded in July 2022, saw Daly’s Constructions responsible for the installation of the 2.2km long dual circuit 66kV conduit bank; the design, manufacture and installation of two 18t precast joint bays; 66kV cable hauling; the installation of the 2.5km of optic fibre cable and 2.6km of full depth road remediation.
The company was also in charge of project management and construction planning, as well as obtaining DoT/VicRoads approvals and traffic management.

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
ENERGY NETWORKS | Sponsored editorial
70
THE MISSION
The design consisted of a dual 66kV circuit, one to be used for the GMH site redevelopment and the other to support future CitiPower works. Due to the complexity of the project, detailed planning had to be conducted prior to mobilisation. These preparations included:
• Safe excavation procedures within sandy soils
• Traffic impact analysis and traffic management planning along Salmon Street, Cook Street and Todd Road
• Procedures to navigate the numerous underground utilities and service crossings, including existing oil-filled 66kV cables
• Liaising with and obtaining works consents/ approvals from:
» Department of Transport (DoT)/VicRoads
» City of Melbourne
» National Heavy Vehicle Regulator
» Development Victoria
» Local businesses directly impacted by works
dewatering the trench, which saw the removal and disposal of more than 150,000 litres of groundwater in a single shift.
Another challenge was the traffic management required to facilitate the works. To mitigate the traffic impact, Daly’s Constructions divided the work into six separate stages that involved full road closures of Salmon Street, Cook Street and Todd Road, which are the main access roads into and out of the Port of Melbourne. With the land-locked nature of the roads in the area, the staged diversions involved sending oversized vehicles around the site.
Approximately 150 existing services were crossed along the 2.2km route with zero damage. These assets included large stormwater drains and water mains, to live 66kV oilfilled power cables, gas services and optic fibre transmission cables, several of which were not present on the tender design and Dial Before You Dig (DBYD) information. Daly’s Constructions remained in constant communication with the Powercor Network Service project team to manage alignment changes and to ensure that the circuit rating was maintained.
One of the most challenging sections was at the intersection of Salmon Street and Cook Road, in particular the section beneath the Salmon Street bridge. In this 15m section Daly’s Constructions had to navigate existing 66kV oil-filled cables, large stormwater drains, gas mains, and optic fibre cables. This was completed safely over three shifts with no outages required on the existing 66kV cables, which was a great outcome for the client.
Another key innovation was the use of precast concrete joint bays instead of in-situ construction. The joint bays weighed 18t each and were designed by Daly’s Constructions to meet Powercor Network Services jointing requirements. The use of precast joint bays saved time and cost, and assisted in relieving the pressure Daly’s Constructions faced to reopen the roads and restore traffic.
INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS
One of the key challenges experienced during the project was excavating in sandy soils common to the Port Melbourne area, and navigating more than 150 underground services and utilities.
Due to the weak ground conditions and large zone of influence adjacent to the trench the risk of the trench collapsing was very high, which required the use of special, aluminium shoring boxes. In addition, Daly’s Constructions’ experienced operators needed to mitigate the trench sidewall from subsiding, and prevent sand from falling into the trench prior to the placement of fluidised thermal backfill (FTB). The team also had to manage the shallow water table and
Other achievements included the removal of more than 12,000 tonnes of contaminated spoil to EPA requirements, installation of the 2.2km long dual circuit 66kV conduit bank in less than six months, managing procurement of more than 5,000m3 of fluidised thermal backfill and the completion of nine 750m 66kV cable hauls in six days.

Daly's Projects Manager, Givantha Silva credits the success of the project to close collaboration between Daly’s Constructions and the Powercor Network Services project team.
"This collaborative approach allowed for effective planning and permitted our skilled workforce to deliver the project on time and to a high standard," Mr Silva said.
The completion of the Fishermans Bend 66kV and 11kV project will facilitate the future works at the GMH innovation precinct that will place Victoria at the forefront of global innovation.
For more information, please contact Daly’s Constructions on (03) 9360 9485 or visit dalysconstructions.com.au.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
Sponsored editorial | ENERGY NETWORKS
71
UNITYWATER ON A GREEN PATH TO
With a growing population, a changing climate and the desire to improve the liveability of South East Queensland front of mind, Unitywater has harnessed the power of science, technology and Mother Nature to implement key infrastructure projects that will help reduce the utility’s operating footprint. Unitywater Executive Manager Sustainable Infrastructure Solutions, Daniel Lambert, expands on some of the projects and key milestones that the water utility is delivering.
Mr Lambert said Unitywater is proud of its sustainability goals, pledging to achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2050.
“In addition, we’re the first water utility in Australia to commit to zero nutrients diverted or offset from waterways by 2050,” Mr Lambert said.
Mr Lambert said that Unitywater was committed to sustainability while enhancing water and wastewater services for its communities.
“We are continuously looking for ways to reduce our operating footprint, use the natural environment to help us do our job and beneficially reuse water,” he said.
A RELIABLE WATER SUPPLY FOR WAMURAN FARMERS
One of Unitywater’s flagship projects, the Wamuran Irrigation Scheme, will be complete and operational by mid2024 and will provide year-round water security for farmers to cultivate thousands of hectares of land while sustainably recycling water from the Caboolture South Wastewater Treatment Plant.

Mr Lambert praised the progress made in the past 12 months and said that in 2023, additional pipe will be installed with more than 1.7km drilled underground using horizontal directional drilling (HDD).
“In its first stages the scheme will deliver about 2.6GL of recycled water each year – the equivalent of 1051 Olympic swimming pools,” he said.
“We’re installing 17km of new pipe, which will connect to an existing 5km section that was completed as part of early project works. Once completed, the 22km pipeline will supply Class A recycled water to farms in the Wamuran region.
“As the Moreton Bay region continues to grow and we produce higher volumes of recycled water, we will be able to connect additional customers to the scheme.”
The scheme will divert recycled water from the Caboolture River, preventing 11t of nitrogen and 1.8t of phosphorus from entering the waterway.
ENVIRONMENTAL RESTORATION IN PROGRESS IN CABOOLTURE
Mr Lambert said he was looking forward to the recently announced $8 million Caboolture River Nutrient Offset Project coming to life.
“It will see 30,000 seedlings planted, 1.6t of nutrients offset per year, and 34t of carbon offset per year from our Burpengary East Wastewater Treatment Plant,” he said.
“The massive forecast population growth in the area will put pressure on the environment and on wastewater infrastructure and this project will provide offsets for the equivalent of an additional load on the treatment plant of 5,500 people.
“Unitywater is committed to working closely with community, First Nations groups and stakeholders and assessing each of our projects from a community, environmental and economic perspective.
“This project will remediate 2.4km of eroding riverbank and is set to be one of Australia’s largest nutrient offsetting river rehabilitation projects in an estuarine environment, increasing biodiversity and fish habitat in the process.”
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 72 SUSTAINABILITY
ACHIEVE SUSTAINABILITY GOALS
YANDINA CREEK WETLAND – A GREEN ENGINEERING SOLUTION
Mr Lambert said another of Unitywater’s projects, Yandina Creek Wetland, helped improve water quality while being an environmental attraction for the community.
“Yandina Creek Wetland is on former cane farming land that we’ve restored to a wetland,” he said.
“It removes nutrients and sediments from the river, improving water quality and overall river health. In 2020 we constructed a walkway and bird viewing hide for the community to come and enjoy this beautiful site.
“This project helps offset the nutrients discharged to the Maroochy River following treatment of the local community’s wastewater.”

OYSTER FARMS TO IMPROVE WATER QUALITY
Mr Lambert said Unitywater wasn’t afraid to innovate and was currently working to progress an Oyster Reef Restoration project where oysters will ‘clean’ waterways and improve water quality by absorbing nitrogen.
“We are working with our partners to begin a five-year trial, which will help achieve significant nutrient offset targets ahead of schedule,” he said.
TOTAL WATER CYCLE MANAGEMENT THROUGH ‘WATER MATTERS’
In a bid to ensure a healthier, more liveable future in South East Queensland, Unitywater is preparing its total water cycle management plan, Water Matters, with its partners and covering key waterways in the Noosa and Sunshine Coast regions.
“Water Matters is part of our strategic planning for a future with further climate variability affected by increased severity and frequency of floods and rising sea levels,” Mr Lambert said.
“This plan focuses on four major waterways including Northern Pumicestone Passage, Mooloolah River, Maroochy River and Burgess Creek in Noosa, exploring options for potable water, recycled water, storm water run-off and natural waterways.
“We are committed to adaptive infrastructure planning to support the needs of our communities and ensure we’re providing reliable and sustainable water and wastewater services,” Mr Lambert said.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 73 SUSTAINABILITY TO
THE EQUIPMENT MAKING VEGETATION MANAGEMENT SUSTAINABLE
These days, individuals and organisations are being urged to consider their choices and make decisions with sustainability in mind. As such, utilities are seeking products and equipment providers that demonstrate a clear understanding of the long-term impacts of their offerings.
Acknowledging this, Vermeer has put a great deal of effort, research and development into making sure its range of equipment is sustainable, and contributing to a circular economy.
Tree and vegetation management around powerlines is an essential and potentially life-saving task completed by organisations and utilities throughout Australia. Not only does this reduce the risk of bushfire, but contact between trees and powerlines can also result in electric shock and power outages, which can lead to property damage and even injury and death.
Powerline clearing is a crucial, never-ending, sometimes backbreaking job that requires hours of manual labour. Additionally, this work results in a great deal of remaining branches and tree cut offs which are usually disposed of and often go to waste.

Vermeer’s range of wood chippers and stump grinders have been proven to be faster and more effective at getting the job done, with the team priding the equipment on its sustainability features.
By using Vermeer equipment, utilities can recycle the resulting wood chips and mulch for an abundance of reuse applications, including being used in compost, creating footpaths, kindling for lighting fires, and providing a shockabsorbing, biodegradable surface for children to play on at playgrounds.
CHIPPING AWAY AT WOOD WASTE
Vermeer’s range of wood chippers – from the seven inch disk through to the 18 inch drum chipper – offer the perfect equipment for any vegetation management job.
Boasting a range of specifically-engineered, exclusive features, Vermeer’s wood chippers prioritise efficiency, operator safety and ease of operation.
The patented feed sensing system of Vermeer’s wood chippers allow for increased operator productivity while reducing the strain on vital engine parts. It can also monitor engine rpm and automatically stops and reverses the roller when feeding larger, hardwood material.
TAKING THE BACKACHE OUT OF STUMP REMOVAL
With Vermeer’s stump grinder range, stump removal is no longer the time-consuming chore it once was. The equipment offers a time-saving, convenient and reliable option for utilities working on vegetation clearing and management around powerlines.
The equipment is tough and easy to use, with a Vermeerexclusive system that sweeps away tree stumps, one pass after another.
While ease of use, reliability and convenience are all important characteristics to look for when selecting equipment for a project, sustainability is becoming an increasingly sought after quality by operators around the country, especially in the utility industry.

Offering usability, convenience and reliability plus sustainability ensures that Vermeer keeps ahead of the competition and provides equipment options that don’t cost the environment.
For more information on how Vermeer products can enable sustainable vegetation management for powerlines, call 1300 VERMEER or visit www.vermeeraustralia.com.au.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
Asset management is a key responsibility of utilities across Australia, and arguably the most important and critical of these is vegetation and tree clearing around powerlines. Vermeer’s range of equipment offers sustainable vegetation management choices for utilities, and recycling options for project byproducts.
74 SUSTAINABILITY | Sponsored editorial




Easy transportation Simple implementation Operator and equipment safety 1300 FMT FMT (368 368) Melbourne 1/53-57 Rimfire Drive Hallam VIC 3803 Brisbane 2/5 Percy Drive Brendale QLD 4500 Perth 3/48 Hardey Road Belmont WA 6104 The water supply operator’s kit H2O WATER KIT
GIPPSLAND WATER POWERS TOWARDS A 100 PER CENT RENEWABLE FUTURE

THE NEW SOLAR INSTALLATION AT GIPPSLAND WATER FACTORY BRINGS A THIRD RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCE TO THE SITE. SUSTAINABILITY 76
The site treats 20 million litres of wastewater from nine towns and major industries each day, servicing the needs of more than 48,000 customers and 300 local businesses. The latest solar panel installation was another important step towards the organisation’s target of being fully powered by renewable energy by 2025.
Now that the system is installed and running, Gippsland Water is in the unique position of having three types of renewable energy powering the water factory.
The site was already powered in part by a biogas cogeneration engine, which uses gases produced from the wastewater treatment process to generate power, as well as a hydroelectric generator, which captures energy from water.
This mix of renewable energy sources reduces the organisation’s electricity costs, saving almost a million dollars every year, keeping downward pressure on Gippsland Water’s customers’ bills.
Gippsland Water uses a dedicated and purpose-built control system to manage the combination of the three renewable generators on a daily basis.
WHY THIS SITE FOR A LARGESCALE SOLAR PROJECT?
The Gippsland Water Factory is Gippsland Water’s most energy intensive facility to operate, making up about 35 per cent of the organisation’s total electricity consumption. This makes it an obvious target for largescale renewable energy projects.
The site was also a good option for a solar installation because it didn’t require preparation. This meant that a ground mounted installation was straightforward and easier to execute.
Gippsland Water found promising results when it researched how the site’s existing hydroelectric generator
and biogas generator could work together with a solar installation. These insights, combined with assessments of the organisation’s energy generation opportunities and consideration of renewable and financial returnon-investment, indicated that the project had strong potential to bring multiple benefits.
RESEARCH AND CONSULTATION
Working within construction environmental management plans and environmental and cultural heritage studies enabled Gippsland Water to manage the risks to the environment and heritage values of the area, ensuring that the project had minimal environmental impact.
Once the research phase was complete, Gippsland Water embarked on a consultation phase before progressing the project.
The consultation involved meeting with and providing information to direct neighbours of the property, as well as early engagement with stakeholders including the local council, West Gippsland Catchment Management Authority and the Victorian Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action.
A GREAT RESULT
The new solar system produces enough energy at its peak capacity to completely power the site, which is capable of consuming 2,000kW of electricity at any time.
With the new solar installation, the total generation capacity of the site reaches 3,040kW, which is comprised of:
• 1,125kW produced by an embedded diesel generator
• 330kW via the biogas generator
• 385kW from the hydroelectric generator
• 1,200kW generated via the solar system
By using the biogas generator, hydro generator and solar system at the same time, the Gippsland Water Factory can potentially generate more than 1,000kW of excess energy to go back into the grid.
In times of critically high demand in the grid, the site’s diesel generator can be turned on by the Australian network operator as a back-up.
The Gippsland Water Factory is the organisation’s seventh site to be powered by solar, with systems already installed at the Warragul, Traralgon and Tyers water treatment plants, Warragul and Moe wastewater treatment plants, and the Traralgon office.

LESSONS LEARNED
While the planning process was extensive and detailed, the outcomes are significant. Coordinating energy generation technologies is complex and takes a lot of careful planning to ensure that everything is operating smoothly. Network protection requirements were onerous for this project because the energy generation capacity exceeds 1,500kW. Gippsland Water had to learn about controlled tripping with other network protection equipment, which gives the distributed network provider control over electricity generation at the site.
This meant that Gippsland Water had to understand the impact it would have on site operation and electricity generation if the network tripped, and make sure the site would continue to have reliable energy sources at all times.
Gippsland Water has already seen the benefits of this learning process in subsequent projects and is keen to openly share its experience and learnings with others in the sector.
For more information on Gippsland Water’s renewable energy sources, visit www.gippswater.com.au/climate-change.
Gippsland Water’s latest $3 million project sees the utility switching on more than 2,000 solar panels at its largest wastewater treatment plant, the Gippsland Water Factory in Morwell.
SUSTAINABILITY 77
INCREASING AUSTRALIA’S DIGITAL CAPABILITIES AND SUSTAINABILITY
The company has committed to a target of 100 per cent renewable electricity purchases from December 2025. This commitment is underpinned by membership of the RE100 – a global renewable electricity initiative comprising 407 of the world’s largest businesses. NBN Co was the first Australian telecommunications company and first Australian Government Business Enterprise to join RE100.
Supporting this commitment, and as a significant consumer of electricity in Australia, nbn has entered into its first renewable Power Purchase Agreement (PPA). The company signed a 10-year PPA at a new solar farm in the Riverina area of New South Wales in July 2022.

When operational, which is expected to be in mid-2023, the 260 hectare site will generate enough electricity to power the equivalent of 27,000 Australian homes.
The nbn PPA equates to approximately 90 Gigawatt hours per annum – which is more than 62 per cent of the expected power generated by the solar farm. This will take the company’s renewable electricity purchases in New South Wales to 100 per cent from mid-2023.
nbn is also setting Scope 1, Scope 2 and Scope 3 emissions targets. These targets have been submitted to the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) and await validation. They build on, and underpin, the company’s earlier TowardsZero Carbon Ambition program and three-year roadmap, which see it working towards:
• Reducing annual energy use by 25 Gigawatt hours by December 2025
• A target of purchasing 100 per cent renewable electricity from December 2025
• Using electric or hybrid vehicles where suitably available by 2030
AUSTRALIAN FIRST FOR GREEN BONDS
The company established a Sustainability Bond Framework in February 2022 to enable the issuance of green, social and sustainability bonds. In April 2022, nbn generated proceeds of $800 million through the successful issuance of its first Green Bond in the domestic market.
In March 2023, it successfully raised $2.1 billion from its debut European Green Bonds issuance in debt capital markets. The EUR benchmark Green Bonds were priced on 6 March 2023, with $1.2 billion of six-year bonds and $947 million of ten-year bonds. The combined proceeds will be fully allocated to eligible green projects undertaken as part of the company’s commitment to energy efficiency in line with its Sustainability Bond Framework
The transaction makes NBN Co the first Australian Government Business Enterprise to issue Green Bonds in Europe. nbn’s network investment plan is designed to significantly reduce the number of copper connections in the network, which is central to its plan to improve customer experience and reduce maintenance and operating costs.
Fibre is inherently more capable of delivering faster upload and download speeds and is generally more reliable than copper connections. So, as it rolls out new fibre deeper into the network, not only is nbn delivering faster speed capabilities and greater energy-efficiency, it is also making the network more reliable and resilient.
nbn’s goal is to enable around 10 million premises, or up to 90 per cent of homes and businesses on the fixed line network, to access nbn’s highest residential speed tiers with wholesale download speeds of 500Mbps to close to 1Gbps by the end of 2025.
The raising follows the company’s commitment, as outlined in its 2023 Corporate Plan, to deliver greenhouse gas emissions reductions consistent with meeting or exceeding the Australian Government’s commitment to net zero emissions by 2050.
Regardless of the retail service you purchase, the actual wholesale speeds delivered by nbn’s highest wholesale speed tiers of 500 to close to 1000 Mbps will be less than 1Gbps due to equipment and network limitations and the peak information rate may fall anywhere in this range. In addition, the HFC Home Ultrafast bandwidth profile downstream service provided to retail providers is a ranged profile with a maximum sustained information rate of 750Mbps. A customer’s experience, including the speeds actually achieved over the nbn network, depends on some factors outside nbn’s control (like equipment quality, software, and how the customer’s retail service provider designs its network) and the nbn technology used for the customer’s connection.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
NBN Co is taking action to address the inherent risks climate change poses to its operations, network continuity and service obligations. By embedding sustainability in all its activities, it aims to deliver on its purpose to lift the digital capability of Australia, while enabling long-term social, economic and environmental value for all stakeholders.
SUSTAINABILITY | Sponsored editorial 78
Made to be sustainable
nbn is committed to driving positive change for Australia. We are continually improving our transparency across diversity, inclusion, safety, governance, and sustainability including a roadmap towards zero emissions by December 2025.


We are focused on delivering positive and sustainable outcomes for Australia now and into the future.

Make nbn part of the plan Find out how nbn can do more for your build Visit nbn.com.au/ourimpact
HOW QLD’S LARGEST SEWER WAS UPGRADED WHILE THE CITY SLEPT
Over 100 years since its inception, Brisbane’s S1 Main Sewer underwent an ambitious seven-year upgrade. By harnessing the power of innovation, Urban Utilities and its delivery partner, Interflow, have given new life to a hidden but essential piece of infrastructure.
Deep under Brisbane’s bustling CBD lies the city’s oldest and largest sewer pipeline. Averaging 1.5m in diameter, the S1 Main Sewer runs a total of 12km, stretching from Toowong to the Eagle Farm pump station, and is buried eight stories beneath the ground.
Completed back in 1924, the S1 serves well over 750,000 people, carrying 60 percent of the city’s sewage. To put that in perspective, more than 60 Olympic-sized swimming pools of wastewater travel through the system daily.
A lot has changed in Brisbane over the last 100 years, so it’s no surprise that the S1 would eventually need an upgrade to meet the needs of the growing city.
AN ASSET SEVEN YEARS IN THE MAKING
The works involved rehabilitating a section of the pipeline between James Street in Fortitude Valley to the Eagle Farm pump station, spanning a 5.7km distance.
Owner of the asset, Urban Utilities, first awarded the rehabilitation works to leading pipeline infrastructure company, Interflow, back in 2015.
Since then, Interflow has relined 40 individual sections (averaging 160m) of pipeline using a spiral-wound lining system.
Fast forward seven years and the S1 Main Sewer upgrade is now complete, with Brisbane’s largest sewer asset ready to serve its community for generations to come.
OPERATING UNDERNEATH A BUSTLING CBD
To reduce community disruption and minimise traffic impacts on the busy road, the works took place at night. This meant all traffic lanes could operate undisrupted during peak travel periods. It also meant crews needed to move on and off the busy road each night to allow full lane access in the morning.
Interflow’s Project Manager during the program’s early phases, John Adamo, said, “We developed a portable set up that could be quickly assembled and removed, giving us more time to make progress on relining the S1 within our small nighttime working window from 8pm to 5am.
“Once we had sewer access, we would mobilise a gantry set up straight over the access chamber using a small crane, which could easily take it on and off the worksite daily.
“We did something similar for our grouting team, too. We imported a special trailer and built a mobile grout plant on it.”
By making their set up portable, Interflow was able to work in the peak of the night within a small working window, allowing little disruption to Brisbane’s traffic network.

GOING DEEPER UNDERGROUND
On projects of this scale, it is not unusual for conditions to change along the way, and in this case it led the delivery team to seek new solutions in order to adapt.
Interflow’s Development Manager, Boris Graljuk, said, “As we moved further through the sewer, the pipelines were getting deeper.
“This meant there was an increase in the external forces on the pipeline.”
Working closely with technology partner, Sekisui Rib Loc Australia, Interflow identified an innovative way of reinforcing a spiral-wound liner with steel.
“Spiral lining is performed by winding an interlocking strip of PVC into an existing pipe to form a smooth, continuous pipe,” Mr Graljuk said.
“The new solution, called RibSteel, involved clipping stainless steel strips into the outside of the PVC strip in the lined pipe, which makes it exceptionally strong.”
With the last line now complete, the S1 Main Sewer is ready for its next chapter, and the impressive, yet hidden, piece of infrastructure will go on to serve the Brisbane community for generations to come.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 80
INSPECTION, CCTV & CONDITION ASSESSMENT | Sponsored editorial
To learn more about Interflow and the work it does in Brisbane and across Australia and New Zealand, visit interflow.com.au.
All night long: Queensland’s oldest and largest sewer was upgraded while the city slept
Read on to learn how we rehabilitated this 100-yearold sewer







INSPECTION, CCTV & CONDITION ASSESSMENT
CONCRETE SOLUTIONS FOR AUSTRALIA’S FUTURE PIPELINES
By Tess Macallan, Journalist, Utility Magazine
Aging infrastructure and rising sewerage temperatures pose increasing risks for corrosion of concrete sewerage pipes around the world. Failing pipes are a significant threat to utility operations, public health and the environment. However, there could soon be a solution. Professor in Structural Engineering at the University of South Australia STEM, Yan Zhuge, is leading a project focused on a self-healing concrete that could help prevent future pipelines from corroding.
Over the past five years Prof Zhuge has attracted more than $4 million worth of grants and published 149 journal papers. In 2018 she won the South Australian Innovation Award in Engineering for her research on using waste in concrete.
Prof Zhuge’s latest project is focused on developing a self-healing concrete that can be used in sewage pipes.
The project is being partially funded by a $501,504 Australian Research Council grant and involves researchers from the University of South Australia and University of Queensland.
Prof Zhuge said this technology could transform the pipeline industry and Australian utility operations.
“The idea of self-healing concrete is not new. It has been around for five or six years,” Prof Zhuge said.
“The problem was that it wasn’t suitable for sewage pipes. Our idea uses a product that is more suitable for sewage pipes.”
Corrosive acid from sulphur-oxidising bacteria in wastewater, along with excessive loads, internal pressure and temperature fluctuations are cracking pipes and reducing their lifespan.

Surface coating is a common method for fixing deteriorating concrete, however, it is labour intensive and costly. Another issue is that it is temporary – 20 per cent of repairs fail
after five years and 55 per cent fail after ten.
In 2018, SA Water approached the University of South Australia to find a way to prevent the exorbitant amount of sludge at drinking water treatment facilities across its network from going to landfill.
During tests conducted by Prof Zhuge and her team, they found that the water treatment sludge was resistant to corrosion due to its high aluminium content.
This led to Prof Zhuge researching a way in which microcapsules composed of water treatment sludge and calcium hydroxide powder could be embedded into concrete during
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 82
the mixing process, counteracting the corrosive effect of wastewater on concrete pipes.
“Sludge waste shows promise to mitigate microbial corrosion in concrete sewer pipes because it works as a healing agent to resist acid corrosion and heal the cracks,” Prof Zhuge said.

Prof Zhuge said the idea of selfhealing concrete with microcapsules is straightforward.
“During crack propagation, the shell of microcapsules is triggered for release of the healing agents, activating a healing process.
“The amorphous SiO2 and Al2O3 in sludge can react with calcium hydroxide in the presence of water to form solid gel (precipitated from water) to fill the cracks. The carbonation of calcium hydroxide can cause the formation of solid CaCO3 to fill the cracks as well,” Prof Zhuge said.
CHALLENGES ALONG THE WAY
Prof Zhuge said the challenge is in finding the right material for the shell. If the material is too soft, it might break during the concrete mixing process. If the material is too hard, it may not rupture when self-healing is required.
“Most studies have focused on using the mechanical force to trigger the shell to release the healing agent, but as failure modes with microbially induced corrosion (MIC) are sensitive to pH change, our composites are designed with pH sensitive shells.
“The material we selected exhibits an inert behaviour in an alkaline environment (high pH values), but is able to degrade in dilute aqueous acid solution,” Prof Zhuge said.
The exact name of the material for the shell remains confidential. The project is ongoing, with testing still needed to explore the potential of the technology. Prof Zhuge said the methodology is aiming for “early detection and early fix”.
“We still don’t know how wide a crack could be repaired as we haven’t done any testing yet. I don’t think it could close the crack wider than 0.5–1mm or even less,” Prof Zhuge said.
A SUSTAINABLE SOLUTION
Unfortunately this self-healing technology only applies to new pipelines and can’t be used for existing aging pipelines. However, while the current methods are costly and only temporary fixes, self-healing concrete could be implemented as a long-term sustainable solution.
Many Australian utilities have pledged to reach net zero emissions by 2050. In order to achieve this target along with interim targets laid out over the next few decades, the industry must shift to a circular economy.
Prof Zhuge said self-healing concrete could help support this transition by providing a new market to use recycled sludge.
“Mainland Australia alone has about 400 drinking water treatment plants, with a single site generating up to 2,000t of treated water sludge annually. Most of that is disposed of in landfill, costing more than $6 million
each year, as well as causing severe environmental issues,” Prof Zhuge said. Disposing a single tonne of sludge in landfill releases approximately 29.4t of carbon dioxide emissions, much higher than cement production.
“This technology will not only extend the lifetime of concrete structures, saving the Australian economy more than $1 billion, but it will promote a circular economy as well by reusing sludge that would normally end up in landfill,” Prof Zhuge said.
Prof Zhuge said she hopes that the project will encourage Australia’s pipeline industry to be more welcoming of new ideas.
As for the utility industry, more companies should consider adopting net zero targets. By working closely with researchers like Prof Zhuge and her team, utilities can use research and development to discover more sustainable, circular solutions.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 83 INSPECTION,
& CONDITION ASSESSMENT
CCTV
Boosting security for TELECOMMUNICATION ASSETS
Working with leading telecommunication provider Optus, Spectur has delivered surveillance solutions to protect critical assets from theft and vandalism. After three years of partnering together, Optus and Spectur will extend their collaboration to boost security for vulnerable telecommunication assets and support Optus’s commitment to strengthening mobile network security.
Optus has updated its Statement of Works with Spectur through an existing Variation Order agreed by both parties. The existing value of works was $956,000 and was updated to the value of $2,023,758.
On top of that, the two-year Statement of Works, which was due to expire on 16 November 2023, has been extended under the updated agreement and will now expire on 31 December 2025.
This updated agreement expands on the multi-year rollout of Spectur hardware, and services that will be used to protect and maintain assets for Optus.
Spectur has provided turnkey solutions with hardware, software and services including surveillance systems, installation, relocation, maintenance, monitoring and software subscriptions, all of which will be used to boost protection for vulnerable assets and sites.
PARTNERING WITH TELECOMMUNICATION LEADERS

Spectur has been working with Optus since 2021 when the initial works order was signed. With wireless 3G/4G solarpowered surveillance systems, Spectur has been providing security solutions for assets across Australia.

During the initial trial, Optus utilised Spectur camera and sensor systems to protect mobile phone tower sites. With multi-system functionality to deter criminals from stealing or damaging equipment, Spectur surveillance systems successfully reduced theft and vandalism at the site, while
also providing reliable security that could not be interrupted by power failures.
Since then, Optus has embarked on a program and installed Spectur security systems across the country to help reduce crime at other critical assets.
Spectur Managing Director, Gerard Dyson, said Spectur has been supporting Optus and its associated companies since 2020.
“Over this time we have continued to work with Optus to improve and update our hardware, software and reporting systems, to suit their operations,” Dr Dyson said.
“This relationship and the positive impact that Spectur solutions have had in reducing theft, vandalism and disruption, has led to a continuation and expansion in the deployment of Spectur platforms.
“A key part of our strategy is to grow our income from institutional contracts. We see this step-up in our engagement with Optus as a validation of the return on investment that we can deliver for blue-chip customers.”
PROTECTING REMOTE ASSETS WITH ACTIVE SURVEILLANCE
The Optus network comprises more than 10,000km of fibre connecting state capitals and regional centres, with an additional 24,000km within metropolitan and fibre serving centres, making it a leading telecommunication organisation.
84 UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU INSPECTION, CCTV & CONDITION ASSESSMENT
With some asset locations, it can be difficult for teams to reliably secure every site from theft and vandalism with traditional, non-active surveillance systems or security personnel. If intruders manage to break in and steal or damage valuable equipment and assets, this could potentially disrupt critical telecommunication services.
Spectur’s surveillance systems are designed to do more than just capture footage. Spectur security solutions incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) to autonomously respond to threats that are captured by the cameras and sensors.
Once a threat is detected, the system can deploy the appropriate response to deter intruders, including identifying suspicious activity and behaviours.
RELIABLE SURVEILLANCE FOR REMOTE APPLICATIONS
For isolated locations where setting up surveillance cameras can be impractical or even impossible, critical infrastructure is vulnerable to theft and damage. Optus has ten million customers Australia-wide, which makes its assets crucial to providing telecommunication services to 40 per cent of the population.

Telecommunications networks located in remote areas can have limited internet and power access. These sites often depend on wired electricity and limited internet and mobile reception. Sometimes asset owners can set up fences, deploy drones or hire security personnel, but these solutions can become expensive or impractical.
With Spectur’s remote security solutions, Optus has a reliable surveillance and condition monitoring system to
protect critical assets. Each Spectur camera platform is powered with solar panels and a rechargeable battery and has an in-built 3G/4G modem to transmit data.
This means Spectur’s security solutions are entirely wireless and self-contained to support off-the-grid functionality. This offers utilities a surveillance option that is not a risk of failing due to power outages or poor reception.
With remote monitoring capabilities, asset owners can use the live-feed in the Spectur app to check sites from anywhere and at any time..
For organisations like Optus, this peace of mind can make all the difference when monitoring hundreds of sites across the whole country.
SUPPORTING ESSENTIAL SERVICES
Leaving telecommunications assets vulnerable to damage or theft is not a risk worth taking considering the high demand and need for mobile and internet access. With autonomous security solutions, Spectur can support critical infrastructure and essential services in Australia and New Zealand.
Through the expansion of its Variation Order with Optus, this partnership ensures Spectur will continue to offer the telecommunications giant reliable and autonomous security solutions that can protect assets.
With additional Spectur surveillance systems preventing theft and damage at these critical sites, Optus can keep essential mobile and internet services running for users around the country.

85 UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU Sponsored editorial | INSPECTION, CCTV & CONDITION ASSESSMENT
This sponsored editorial is brought to you by Spectur. For further information, please visit spectur.com.au.
SPACERS ASSISTING WITH CORROSION MANAGEMENT
Ignoring the effects of corrosion can be costly for asset owners, and planning for corrosion control and mitigation has many advantages, including extending the life of an asset and reducing maintenance time and costs.
STOPPING CORROSION
According to kwik-ZIP Managing Director, Jason Linaker, an appropriate spacer system is one simple tool that asset owners can employ as part of their corrosion management system.
“Choosing an appropriate spacer system can help mitigate the effects of corrosion on new and rehabilitated pipelines,” Mr Linaker said.
“Spacers made from inert materials such as high-grade thermoplastic are the best choice for pipeline installations as they are resistant to the effects of corrosion.”
This is particularly important in harsh environments where spacers made from other materials such as metal do not hold up as well.
“For instance, some areas may have acid sulphate soils (ASS). A metallic spacer would be subject to severe corrosion if it were to come into contact with ASS. Even stainless steel
is subject to accelerated corrosion from such soil conditions,” Mr Linaker said.
While corrosion can be transferred via the metallic spacer to the steel pipeline itself, inert non-metallic pipe spacers are resistant to such conditions. Corrosion can also be transferred when a new pipe is inserted into an old pipe for rehabilitation. This transfer can occur if the new pipe is made from steel, or if metallic spacers are used.
Even if the new pipe is not steel, corrosion can still breach the grout seal around the new pipe.
“Inert non-metallic spacers are resistant to the transfer of pre-existing corrosion, ensuring they remain intact throughout the life of the pipe,” Mr Linaker said.
THE KWIK-ZIP ADVANTAGE
kwik-ZIP spacers are one of the only Australian-owned spacers on the market. Designed and developed by drilling professionals, the kwik-ZIP range of spacers is manufactured from an engineered thermoplastic blend, which is characterised by its high resistance to corrosion, even when in contact with organic substrates for long periods of time.
“kwik-ZIP casing spacers will protect pipes, make installation easier and extend the life of your asset, and now with WSAA approval for two product series, choosing the right spacer for longevity and success is even easier,” Mr Linaker said.
The HDX and HDXT Series casing spacers can be used for medium to heavy weight pipe materials including steel, ductile iron, GRP, FRP, concrete, PVC and PE. Furthermore, it’s suitable for both pressure and non-pressure pipelines in grouted and ungrouted installations.
The spacers incorporate low friction, high abrasion resistant wear pads, attached to load sharing runners. The number of segments required for each spacer is determined by the outside diameter of the carrier pipe.
Although small relative to the entire pipeline infrastructure, kwik-ZIP spacers make a large difference in the overall success of pipeline installations and corrosion management.

INSPECTION, CCTV & CONDITION ASSESSMENT | Sponsored editorial 86 UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
All pipelines are exposed to a range of physical, climatic and chemical elements that can cause corrosion. This is often exacerbated in harsh environments, where pipelines are exposed to high salt levels or extreme temperatures that can accelerate the rate of decay.
more information, please visit kwikzip.com.
For


Is your pipe spacer compliant? Call us for details on ordering P (08) 9725 4678 sales@kwikzip.com www.kwikzip.com The only casing spacers successfully appraised by WSAA HDX and HDXT KWIK-ZIP’S HDX & HDXT CASING SPACERS COMPLY WITH WSAA PRODUCT SPEC #324 - CASING SPACERS; REFER WSAA PRODUCT APPRAISAL REPORT #1523
VEGETATION MANAGEMENT THAT'S AHEAD OF THE PACK
Meeting strict and increasingly complex regulatory requirements is perhaps one of the greatest challenges faced by most modern utilities. The inherently high-risk nature of the sector means it is highly regulated across a number of facets, with vegetation management being an area requiring particular attention. Meeting the challenge of adhering to vegetation regulatory requirements is too complex a task to be left to manual processes; which is where work management software comes in to simplify the process.
Energy network operators spend many millions of dollars managing vegetation proximity to powerlines annually, in order to mitigate the risks of service disruptions and serious hazards like bushfires, and maintain mandated clearances.

Given the potentially catastrophic effects that can be seen when vegetation adjacent to powerlines is left unchecked, it’s clear to see why the industry has developed
such strict regulatory standards when it comes to managing vegetation.
And while incredibly important, the task for utilities to meet these regulatory requirements can be quite challenging.
This is where work management software (WMS) comes in. WMS provides utility businesses with tools to effectively and efficiently track and manage their compliance-related activities. It also streamlines reporting, ensuring the required records are on-hand when the regulator comes knocking.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
VEGETATION MANAGEMENT | Sponsored editorial
88
ENSURE YOU’RE READY FOR THE REGULATOR
Vegetation management regulatory frameworks and operating standards vary considerably between states and across energy networks.
The appropriate clearance distance to prevent interaction varies depending on a range of criteria. These include:
• The voltage of the powerline
• The location of the powerline (whether it is in a bushfire risk area etc.)
• The type of conductor (fully insulated, covered or bare)
• Span length (longer spans will sag and swing more under hot/windy conditions)
Vegetation management is also impacted by differences in climate, geography and vegetation growth characteristics.
Over decades, various regulatory frameworks and standards regarding vegetation management have developed in the different Australian states and territories. Even for networks under the jurisdiction of the national electricity market (NEM), there remain variations in regulation and standards.
Within the NEM, the Australian Energy Regulator (AER) provides economic regulation, deciding on the revenue allowable for network service providers. These allowances are intended to be sufficient for an efficient Network Service Provider (NSP) to maintain their network in a safe, reliable and affordable manner, consistent with technical compliance obligations determined by state technical regulators.
The vegetation management technical compliance requirements themselves are set and regulated by respective state governments through technical regulators or government departments. Differences between regulations in each jurisdiction originate from prior decisions by these bodies, which may have been driven by countless different factors over the years.
In addition to regulations directly specifying vegetation clearances, a range of state and commonwealth legislation can indirectly affect vegetation management program design, management and cost in different jurisdictions. These may pertain to considerations such as environmental protection, protection of threatened native species or Aboriginal cultural heritage, biosecurity, heritage significance, chemical handling, and/or road use and safety. The penalties imposed by regulators for any compliance failures also vary based on a multitude of factors.
KEEPING IT ALL IN CHECK WITH WORK MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE
Vegetation management is a task too complex to be left to manual processes.
To ensure energy network utilities meet their regulatory requirements, an automated, digitised solution is a must; and Xugo is a cloud-based work management solution that is recognised as being best-of-breed when it comes to vegetation management.
Xugo connects teams and processes, enables work programs, ensures processes run smoothly, and
strengthens compliance with regulations, policies and standards across a business. Xugo provides the data accessibility and visibility needed for effective compliance control and enterprise risk management.
With Xugo, users can manage all of the works associated with vegetation management, including creating and assigning tasks for planning, scoping, auditing and cutting. Users can schedule and track various activities in progress; as well as review audit results and other critical operational progress information via scheduled and dashboard reporting. Out in the field, contractors and service providers can track all of the work they undertake remotely by connecting to Xugo via mobile devices.
In addition, crews can utilise the Xugo app, which offers significant offline capability in locations where network connectivity is challenging. It’s a rich experience that tailors to the prevailing conditions; wherever your crews may be.
“Xugo provides utilities with the confidence to manage all aspects of their vegetation management program,” said Matthew Croft, General Manager of SFI Allegro, developer of the Xugo software.
“Services that can be undertaken with Xugo include annual planning, coordination of LiDAR collection and analysis, field service activities, reporting and contractor payments to help minimise fire risk, improving network reliability and enabling compliance management with current regulations.
“Xugo functions as the authoritative data source and tracks and allocates work to provide transparency on the status across every vegetation network span.
“Importantly, Xugo can also be easily interfaced with corporate systems, for asset, network and financial information.”

By managing your compliance-driven data, Xugo powers your compliance framework and increases visibility of your safety, quality, regulatory and enforcement programs. Xugo streamlines compliance activities, including carrying out inspections, safety checks, audits and incident investigations (including those from customers), as well as the processes involved in compiling reports for regulators. Compliance can be tracked in real-time to drive continuous improvements.
The team at Xugo can configure the software to your business needs, allowing flexibility and full integration with your current operations, procedures and policies. Additionally, this adaptability ensures that Xugo can evolve in response to any enterprise changes. The solution is also scalable, ready to grow with your business.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 89 Sponsored editorial | VEGETATION MANAGEMENT
Scan to learn how Xugo can help your business manage its vegetation compliance activity.
THE POWER OF
MANAGEMENT IN

VEGETATION MANAGEMENT
90
OF VEGETATION
THE RED CENTRE

VEGETATION MANAGEMENT
91

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 92 VEGETATION MANAGEMENT
You might not expect wild storms, gusty winds and heavy rains in the desert regions of Central Australia, yet they occur frequently during late spring and summer. The storms can cause significant destruction, and the town of Alice Springs – the region’s largest, with a population of 28,000 – often feels the full force of these unexpected events with little warning.
The Northern Territory’s Power and Water Corporation is committed to public safety around all electricity infrastructure, ensuring that the community has a reliable power supply. To help prepare and protect Alice Springs from the destructive power of these storms, Power and Water invests in strategic vegetation management practices and community engagement to help build understanding about why it is needed.
Power and Water Senior Manager Service Delivery South, Gavin Kahl said, “Trees, shrubs and other vegetation present a significant risk to powerlines, as falling branches or trees can damage them and bring them down.”

“During past storm events, we’ve seen trees and tree debris blown onto powerlines, properties and roads, causing substantial damage and leaving customers without power for many hours while we work to safely bring the network back on.
“To reduce these dangers, clearance standards have been set for how much trimming is necessary, while at the same time trying to maintain greenery, shade, cooling and privacy where possible.”
To successfully deliver the vegetation management program, Power and Water must manage a diverse set of challenges and issues, working closely with the community and peak organisations.
One challenge is managing native trees that seed in sacred or culturally significant sites close to powerlines.
To address this, Power and Water works with organisations such as the Aboriginal Areas Protection Authority (AAPA) to ensure that any culturally significant trees are identified and managed appropriately.
Alice Springs is home to numerous well-established old trees that create the sense of an oasis in the desert, alongside many species planted as the town has developed that are not suitable to be in close proximity to powerlines.
“Broader community engagement is essential to help educate and notify residents and key stakeholders about the need for vegetation management, while balancing power supply reliability and public safety with the community’s environmental values,” Mr Kahl said.
“This engagement also offers the opportunity for any concerns to be discussed directly with a Power and Water representative before each program of work begins. Local government organisations, environment and community groups, Indigenous organisations and local media are all included.”
Power and Water has engaged an experienced contractor who employs a qualified arborist to assess each tree within a power span (pole to pole). This helps them gauge whether
VEGETATION MANAGEMENT
it will have an effect on the power infrastructure or disrupt access to powerlines.
Mr Kahl explained that before works commence near homes, affected residents will receive a card in their letterbox to notify them once the assessment has been completed. “We also advertise extensively in the weeks leading up to work starting to raise awareness of the program,” he said.
This approach has seen improved engagement with customers and a reduction in complaints from residents about trimming trees and branches around powerlines.
As part of the vegetation management program, a tree replacement project has been introduced using suitable native species sourced locally. An unsuitable species or hazardous tree is replaced with two more appropriate native shrubs and once the saplings are established the original tree is removed.
“This initiative is a progressive and positive outcome for the community and Power and Water, protecting the power network and maintaining the greenery in Alice Springs’ urban areas that are so valued by the community,” Mr Kahl said.
Vegetation maintenance work is conducted every two years in urban areas and every four years in rural areas to prepare for future severe weather events.
In late 2022, Alice Springs was hit by two sudden, successive wild storm cells that left thousands of people without power after trees, branches, debris and roofing materials damaged powerlines.
“These storms were the most severe the town has experienced in recent times,” Mr Kahl said.
“Our crews worked around the clock to repair the damage and restore services within just a few days.
“If not for the work delivered through the vegetation management program, things could have been much worse than they were.”
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 93
Vegetation management is a vital part of helping to protect the Alice Springs community from the impacts of severe weather.
AUGMENT VEGETATION MANAGEMENT WITH SATELLITE IMAGERY
From roads and railways to power lines and pipelines, encroaching vegetation can cause downtime, damage and catastrophes. Utility vegetation management remains a huge line item in most annual budgets, involving manual inspection of thousands of infrastructure miles. But it’s mainly reactive maintenance, leaving very little focus on prevention. Satellite technology provides a great opportunity to augment existing methods, offering more scalability, reliability, and flexibility.
Satellites can capture long corridor lengths frequently and in a single pass. This approach drives efficiency and savings, and removes the constraints of LiDAR and UAV photogrammetry. You can identify risk areas for further investigation with helicopter optical imagery, LiDAR, and UAV photogrammetry to avoid costly image capture of the entire infrastructure.
Or task a satellite for a specific time and specify cloud coverage, which improves reliability and predictability, and reduces risks from bad weather. Furthermore, using satellites for the most inaccessible points of infrastructure maximises compliance and minimises the risk of danger to employees.
Satellites offer different types of useful data; optical satellites take imagery in the visible or near-visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum using existing radiation. When optical satellites take imagery of the same point from two or three different locations, those images are combined to construct digital surface models, which are important for utility vegetation management.
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) sensors capture imagery by transmitting microwaves at a target and catching the backscattered
signals at any time, day or night. SAR’s microwaves can penetrate clouds, haze, dust, or canopies and dense vegetation, to give information on different layers of vegetation. Elevation data can be used to track differences in elevation (height or volume) and ensure that hazards such as vegetation encroachment are monitored, predicted, and mitigated, minimising damage.
INTELLIGENT VEGETATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
A great example of rethinking vegetation management with satellites comes from AI-first SaaS company, AiDash. Geospatial developer platform and marketplace, UP42, helped AiDash transform the process for its customer, a Fortune 500 utility company that wanted to improve vegetation management along lines spanning over 80,000km. AiDash’s client relied on a traditional approach, with trimming cycles spanning four to five years and including manual data collection. This time-consuming process gave it minimal predictive capabilities for future outages, damages, and costs.

To solve the problem, AiDash developed a proprietary AI model called the Intelligent Vegetation Management System (IVMS), with satellite imagery from UP42. Through the UP42 platform,
AiDash accessed both archive and very high resolution (50cm) Airbus Pléiades imagery of utility lines, providing detailed coverage for the customer’s remote asset monitoring needs. AiDash was able to predict species’ growth rates in each feeder across different utility towers and different height levels. The company prepared a three to five-year trim plan for the entire network with an accuracy of over 85 per cent, improving system reliability by 15 per cent and reducing its annual budget for vegetation management by 20 per cent.
There are countless more potential applications for vegetation management – from combining weather data with multispectral data to forecast strong winds affecting trees, to analyzing the state of the surrounding forests for risk of fires. With the recent emergence of dedicated geospatial platforms offering easy access to complex data, satellite imagery has proven to be the complementary tool of choice by many utility operators and solution developers, enabling more targeted and efficient solutions.
For more information, please visit www.up42.com.
94 UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
VEGETATION MANAGEMENT | Sponsored editorial


TOOWOOMBA COUNCIL TURNS THE TAP ON FOR SMART WATER METERS

External consultants were engaged, a proof of concept trial was undertaken and in March 2023, the first of the smart water meters were installed.

As a strong advocate for water conservation, TRC Waste and Water Committee Chair, Cr Rebecca Vonhoff, said she was delighted to see the project moving to this next stage.
“After progressing the project from the first concept stage, it’s great to see we are now at a point where smart water meters are being installed at homes throughout the region,” Cr Vonhoff said.
“This is something we have spent a lot of time and money on as it has such a significant impact on our community.”
When Council first engaged an external consultant, it outlined the following key objectives:
• Monitoring water usage to inform short and long-term business decision making
• Seeking opportunities to align with the Demand Management Strategy
• Ensuring functional objectives are specific to the operating context of TRC
• Keeping the current billing system intact
In addition to the identified objectives of the business case itself, Council also expressed other desired outcomes that included:
• Minimising re-reads, misreads and estimated bills
• Providing detailed consumption data to customers
• Reducing staff time dedicated to meter maintenance
• Replacing aging/failing infrastructure
• Utilising new technology to deliver better demand management outcomes
“Once Council was satisfied it had established clear objectives for the program, the next steps were to find a company that could deliver this solution and to begin a proof of concept trial,” Cr Vonhoff said.
“As part of the trial, almost 2,000 smart water meters were installed in 65 different suburbs/towns, covering 102 of the 106 routes Council uses.
“With an area of almost 13,000km² that includes a large number of rural properties, it was important we knew the technology would work at all of these locations.
“From a technology perspective, the devices met Council’s objectives and any areas where there were potential blackspots, our consultants were tasked with finding solutions before we began the full rollout.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 96
Toowoomba Regional Council (TRC) is in the process of implementing an automated water meter reading system that helps conserve water, supports operations and improves the customer service experience for its customers throughout the region.
SMART METERS
“While it was pleasing to see the technology solution in place, the real benefit we saw in the trial was through the water loss identified through potential leaks.”
Leaks detected on the customer side of the supply network were on average in the range of 12 per cent from the data available.
The largest leaks were referred to the Rates and Revenues Section of Council for immediate follow-up and investigation.
“This suggested substantial improvements could be gained by giving approval for the smart water meters program to be rolled out more broadly,” Cr Vonhoff said.
“This will likely be the most significant change in operational improvements and greatly assist with the region’s water security.
“There is no doubt water is our most precious resource so it’s crucial we’re doing everything we can to further strengthen our position.
“When you think back to 2010 when our combined dam levels were around seven per cent, the thought of now being in a position where we can identify opportunities like this to improve our water security, the answer was fairly straight forward – this was something we simply had to do.”
Council approved the full implementation of the Smart Water Metering Solution across all water connections in the Toowoomba Region at the Ordinary Meeting of Council on 15 November 2022.


Approval was given for the rollout of 66,000 meters in total, with the first of the meters in the ground from March 2023.
“With the meters now being installed, attention has turned to making sure our community is part of this journey with us,” Cr Vonhoff said.
“This is a significant shift from how we read water meters.
“The digital reading of these smart water meters will provide residents with analytics that will alert them and our team to any significant spikes in usage.
“In addition to the new water meters, residents will be able to download an app to monitor their own usage.
“With customers being able to access data through the app, it’s anticipated they will be able to better understand their own water habits, making them more aware of their water consumption.
“This helps residents take more ownership of the role they can play within the Toowoomba Region.
“As meters are constantly recording all flow, the theft of water will also become less likely which is again another opportunity to improve our water security.”
Over the next three years as meters are installed, Council’s Water Operations and Planning team will systematically gain visibility of network performance as meters are deployed.
As meters are deployed in zones, leaks on Council assets will become easier to find as zone balancing can be achieved. The sum of all meters should match the Council zone meter. Discrepancies in these zones help narrow likely sources of leaks on Council infrastructure.
Knowing where and how much water is moving and when is key information for hydraulic modelling. These data points could vastly improve hydraulic modelling and help improve future demand management and planning for future infrastructure replacement and renewal programs.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 97
SMART METERS
SMART WATER METERING:

BUSINESS TRANSFORMATIONAL, NOT JUST REMOTE METER READING
Sure, within a SWM project the meter metrology, battery life, telemetry and ultimately the data delivery by the Meter Data Management Systems (MDMS) are all important. But if we broaden the view and examine the meter insights and implications on business processes, a range of new perspectives are revealed.
NEW DATA INSIGHTS WARRANT NEW ACTIONS
Moving from quarterly meter readings to hourly meter readings means you have a wealth of new data to yield insights, which both creates new questions and warrants new action. Such as:
• Zero water flow over seven days: if the meter is transmitting, has it been removed indicating water theft?
• Continuous high flow: Do we inspect the meter? Is the meter the right size?
• Leaks: How many times should we follow up a customer? Do they still get a rebate once notified? How should we advise them?
WHICH SYSTEM IS THE NEW MASTER
The introduction of new systems to capture and manage your water meters and customers may mean the traditional master data source you have relied on may not be as up to date as the MDMS. Fields in the MDMS, such as the meter serial number, will likely be more up to date than in the Asset Management System (AMS), which traditionally has stored these.
Your billing system will leverage the meter reading from the MDMS, but what about change of ownerships and new tenants on lease properties. The integration between your CRM/billing systems and identifying what data is the master, are key considerations that ensure minimal use of daily or weekly manual processes to align the differing systems.
SYSTEM INTEGRATION
What integration between the MDMS and your AMS is needed beyond billing?
The MDMS can identify customer-side water leaks. Systems like Aqualus Water from Taggle, can both detect and manage the customer SMS or mail communications to end consumers. If you’re using a CRM for end customer management, you’ll want to consider integration to provide your customer management team the single view of the customer.
IMPORTANCE OF DISTRICT METERED AREAS (DMAS)
Non-revenue water is often a major driver of the business case for smart water metering, a portion of this comes from monitoring DMAs and mass balance calculations. Setting DMAs up should be considered in the initial scope of work as additional network meters might be required to clearly define DMA areas.
Once DMA’s are in place, network losses can be easily quantified and investigated. Network losses can be significant and identifying any mains breaks quickly or before they escalate can deliver valuable savings.
POLICY CHANGES
What policies need to change from these new capabilities? Having new data and providing leak notifications to customers has implications to customer requests for bill relief.
Should a customer who has been notified of a leak, but not actioned it, be allowed bill relief? How much time should the customer be given to fix their leak? Does the customer have to sign up to the customer portal to get the relief and ensure that future leaks are quickly identified?
IMPORTANCE OF INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL STAKEHOLDERS’ ENGAGEMENT
SWM projects have the potential to touch a range of initially unforeseen, but in the future key, stakeholder groups. With more than 65 deployments to date, Taggle encourages customers to bring the broader organisation on the Smart Water Metering journey. To achieve the business outcomes desired, council or utility staff and the community need to be educated and engaged with the project.
For more information, please visit taggle.com.
98 UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU
SMART
| Sponsored editorial
When examining a Smart Water Metering (SWM) project, the initial focus is often the smart meter, communications and meter management software. However, Taggle Systems has found long-term project and business success is driven by other considerations.
METERS
Promoting best practice in water management by building the knowledge, skills and networks of operators.

• Listen to the experience of others through the latest “operational” technical and research based information through platform and poster presentations.
• View and discuss the latest advances in technical equipment, products and services with suppliers and trade consultants.



• Update their knowledge and skills through interaction with fellow water industry employees.

19 & 20 JULY SUNSHINE
All industry personnel involved in the operation and maintenance of water related infrastructure for the management, conveyance, treatment, discharge and reuse of water and trade wastes should attend this conference.
• 20+ speakers over 2 days
• 90 of the world’s leading water suppliers on display



Supported by Hosted by

Prime Sponsors
• Ixom 2023 Water of Origin - QLD v NSW

• Queensland main tapping competition
Media Partners

us at our 2023 QLD
Join
Water Industry Operations Conference & Exhibition QLD
COAST www.wioaconferences.org.au info@wioa.org.au 03 5821 6744 BE COVIDSAFE
THE NEXT GENERATION OF ENERGY STORAGE
By Shane Rattenbury, Minister for Water, Energy and Emissions Reduction
The ACT is electrifying and shifting to a zero emissions future. Creating a strong and stable distributed energy system is a critical focus for this work. Energy storage, mainly through batteries, is a key priority as we transition from fossil fuel gas. The ACT Government’s Next Generation Energy Storage program (Next Gen) has been a major factor in encouraging energy storage development and increasing the number of household batteries available in the ACT. This program has now concluded, but its impacts will be long lasting for our Territory.
The ACT has a history of taking bold action and being a global leader in responding to climate change. When we launched the Next Gen program in 2016, it was the largest deployment of battery storage in Australia. This $20 million multi-year initiative aimed to grow the ACT's battery industry, add 36MW of power storage into the electricity grid, and help reach our goal of having 100 per cent renewable electricity by 2020 – a target we have achieved and will continue to maintain.
The Next Gen program has been a resounding success. Over the past seven years, it has accelerated the ACT’s battery marketplace and contributed invaluable data to battery and network integration research. In early 2023, the program reached its target of 5,000 rebates. It has already added 28MW of storage to the grid, with the full 36MW expected to be reached by late 2023 or early 2024 as the final installations are completed.
The program launched with just four battery installers in the ACT. Now there are 24 installers, with around 50 jobs created for retailers and installers, including apprenticeships and training initiatives. As a result of the Next Gen program, the ACT's battery market has developed to the point where

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 100 ENERGY STORAGE
ACT has become a leader in energy storage with the successful completion of the Next Generation Energy Storage program and investment in large-scale batteries
it can operate independently in an atmosphere of healthy rivalry and high demand.
Thanks to the Next Gen program, the ACT has a battery installation density of 2.9 per cent, meaning that about one in 30 ACT homes has battery storage. This is one of the highest domestic battery densities in the world and more than three times the national average. These adoption rates show that there is consumer demand for household batteries, and suggest we are on our way to seeing batteries becoming commonplace in existing homes and new builds along with other distributed energy resources such as solar panels and, increasingly, EV chargers.

SIGNIFICANT INDUSTRY IMPACT
Next Gen has had a lasting effect on research that will benefit the renewable energy industry beyond the ACT. As a direct result of the program, the Australian National University now hosts a critical mass of research expertise in battery and network integration through its Battery Storage and Grid Integration Program. This was made possible through access to data from the Next Gen program, as well as support provided by the ACT Government’s Renewable Energy Innovation Fund
The key to the program’s success is that it aligns with other ACT Government initiatives, including the Sustainable Household Scheme through which participants can access zero-interest loans to make energy-efficient upgrades to their homes, including batteries. Launched in 2021, the scheme has meant that households could combine their Next Gen rebate with a zero interest loan to avoid upfront costs and start saving right away.
Building on the success of the Next Gen program, energy storage technology will continue to transform the way we use electricity. In the ACT, increased energy storage will be essential to ensuring the reliability of our electricity supply and providing power during times of high demand. Energy storage capabilities will also become increasingly important when large fossil-fuel generators fail and cause supply issues across eastern Australia.
LARGE-SCALE BATTERY INVESTMENT
We are continuing to build energy storage capability by investing in large-scale batteries. This work will provide a variety of energy storage options to the ACT electricity grid. In February 2023, the ACT’s first grid-scale

battery, a 10MW/20MWh system secured through reverse auction in 2019, became fully operational. Developed and owned by Global Power Generation, the battery has enough storage to power approximately 3,000 homes for two hours and helps to smooth and stabilise electricity supply.
In the same round of reverse auctions, the ACT Government secured a 100MW/250MWh battery built and owned by Neoen. This battery will further modernise and stabilise the ACT grid, and we expect it to become operational this year.

In addition, the ACT Government has recently announced a partnership with Eku Energy to deliver a large-scale battery of up to 250MW as part of the Big Canberra Battery program. We’re also considering the role that smaller neighbourhood-sized batteries have in our grid and are working with industry to assess proposals for small-scale batteries of up to 1MW. We expect these batteries to supply electricity to schools and other government buildings and play an important role in meeting our target for net zero emissions from ACT Government operations by 2040.
Building energy storage capability requires bold, strategic leadership combined with an integrated policy approach, investment in research and innovative technologies, and effective partnerships with industry that deliver the best outcome for communities.
While there is still much to be done, I’m proud of what we have achieved so far both through the Next Gen program and complementary initiatives. Continuing to focus on energy storage in the ACT will be crucial as we work to electrify our city and rapidly reduce emissions to meet our target of net zero emissions by 2045.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 101 ENERGY STORAGE
THE ACT'S BATTERY MARKET HAS DEVELOPED TO THE POINT THAT IT CAN OPERATE INDEPENDENTLY IN AN ATMOSPHERE OF HEALTHY RIVALRY AND HIGH DEMAND.
BATTERIES HELP TO INCREASE HOUSEHOLD ENERGY RESILIENCE AND ADD ENERGY STORAGE TO THE GRID.
THE ACT’S FIRST GRID-SCALE BATTERY WAS SWITCHED ON IN FEBRUARY 2023 AND IS NOW FULLY OPERATIONAL AS PART OF THE NATIONAL ELECTRICITY MARKET
HOW RESEARCH IS CREATING NEW KNOWLEDGE FOR THE ENERGY TRANSITION
 By David Norman, CEO, Future
Research Centre
By David Norman, CEO, Future
Research Centre
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 102 FUTURE FUELS
David Norman, CEO of Future Fuels Cooperative Research Centre (CRC), explains how industry-led collaborative research is transforming the Australian energy industry’s knowledge of hydrogen and biomethane, at a time when this knowledge is vital.
Fuels Cooperative

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 103 FUTURE FUELS
UNIVERSITY OF WOLLONGONG’S SAFE(TI) LABORATORY PHOTO: APA GROUP
A NEW ERA OF AUSTRALIAN RENEWABLES
The transition to net zero is asking the Australian industry some difficult questions, but the answers can be found through research and development, and utilities need to make a long-term pivot that puts research right at the core of their businesses.
When a group of far-sighted Australian energy companies started Future Fuels CRC in 2018, there were many unknowns about the use of hydrogen or biomethane as new gaseous fuels in Australia’s energy networks.

As we worked out the details of our three research programs, that list of unknowns became more focused and defined. Five years later, those industry-led research programs have already profoundly changed, now delivering the new knowledge needed to unlock the first stage of demonstration and development projects and driving the industry forward. As our research continues, this will underpin the next-stage and commercialisation projects as the renewable gas industry develops across Australia.
Back in 2018, the challenge in front of us was to understand how existing infrastructure could be repurposed to use net zero fuels like hydrogen and biomethane. This would mean a top to bottom transformation of the networks; the continued safe operation of these networks, how our communities could accept and use them, the economics, the engineering, the materials science of the steel and plastics in the pipes and equipment, the operation of millions of home and industrial appliances and the workforce skills needed to carry this out.
These are just some of the issues covered in over one hundred research projects being completed by a community of almost seven hundred university researchers, engineers and industry advisors.
The great value of CRC is that it creates communities that can then carry forward its research. They are also a community for interfacing with overseas institutions working on similar research, ensuring we optimise knowledge exchange and avoid duplication of activity wherever possible.
Our community involves six of Australia’s leading research universities working as integrated teams with specialists from more than 80 companies and every state’s technical regulation teams. It's important that this effort is broad because directly participating in research raises the skills of all the industry participants. This means this research process is developing knowledge not just in energy companies but across the supply chain in construction companies, equipment suppliers and engineering consultancies.
Future Fuels CRC is supporting 50 PhDs and masters, whose students not only deliver our projects, but who will themselves become future leaders in research and industry. We are already seeing this as our PhD students complete their projects and start to transition into roles in industry, government and career research. We aren’t just creating workforce skills; this research program is creating the future workforce itself.
CRC’S CRITICAL RESEARCH AREAS
Well-directed research can find ways to overcome the multi-dimensional issues that many utilities face. Just a few of our research areas show how these complex issues can
be worked on using a combination of research techniques to unlock the new knowledge needed:
• Economists are modelling how biomethane could scale up in Australia, using dynamic models to identify regions with the highest feedstock potential and lowest barriers to network connection. Sociologists are surveying and understanding public acceptance trends on using biomethane and our engineering researchers can understand and quantify the effects on infrastructure and appliances of any bio-impurities in the biomethane supply.
• Combustion engineering researchers are evaluating and testing how appliances operate on blends of hydrogen and natural gas and pathways to higher levels with a 100 per cent hydrogen supply. This covers appliances from the smallest home cooker to the largest industrial process burner and gas-powered turbines.
• Steel and polymer scientists are evaluating the integrity and operational parameters of using hydrogen in Australia’s distribution and transmission networks. We have a representative sample of the most common ‘vintages’ of plastic pipes at our sandpit test facility at Deakin University undergoing long-term testing with hydrogen at operational pressures. Our Safe(Ti) (Stress Assessment of Future Energy Transport Infrastructure) lab at the University of Wollongong is one of the few facilities in the world that can test pipeline steels’ physical properties in a pressurised hydrogen environment. These test facilities are providing the operational data that will underpin the transition to future net zero networks.
• Researchers at the University of Queensland, RMIT and University of Adelaide are unlocking the social acceptance and regulatory issues that will define how our communities engage with new energy infrastructure. In many ways, this is the most important part of all research as it is the combination of end users, voters and their representatives who have always defined how and where infrastructure is implemented and provide its regulatory and social licenses to operate.
• Multi-system modelling by the University of Melbourne is preparing the industry for a future network system in which renewable gas and electricity are thoroughly integrated with energy moving from one vector to another, depending on the lowest cost transmission option or the final product needed by the user.
Utilities are now all participating in the transition to net zero, and there are plenty of unknowns ahead. However, it does not have to stay that way. Australia has world-class universities, engineers and technical experts, and they can be brought together to give your organisation the new knowledge it needs. Future Fuels CRC is not alone; there are many colleagues in other CRCs and research groups operating in the energy, water and utilities areas, so bring them into your organisation and find ways to put research at the core of your business.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 104 FUTURE FUELS
FUTURE FUEL’S CEO,DAVID NORMAN
The missing link in your B2B Marketing Strategy
While traditional trade publications have quality audiences and high levels of trust, they can lack the full range of services to guarantee a return on your investment. And while traditional marketing agencies offer the latest marketing techniques, they don’t have the audience or the industry understanding the B2B sector needs.
Monkey Media is the missing link that brings together a trusted brand and powerful audience, with a complete agency offering.

TO FIND OUT MORE SCAN THE QR CODE NOW
How to Australiagetback IN THE GLOBAL HYDROGEN RACE
Since the release of the National Hydrogen Strategy in November 2019, Australia and the world have changed. The pandemic, war in Ukraine, natural disasters, and rising inflation have highlighted the vulnerability of supply chains and resulted in a renewed focus on building domestic capabilities, sovereign manufacturing and energy and resource security.
We have also witnessed a shift in the global discussion towards clean energy and hydrogen. Significant financial incentives and policy approaches have been announced by various countries across the globe, demonstrating a shift in focus towards transitioning energy systems to be prepared for the future.
The introduction of the US Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is already starting to increase US capacity and competitiveness in new and emerging industries, driving significant government and private investment in both large scale infrastructure projects and smaller, high-risk technology commercialisation.
The IRA has changed the game since it was signed in to law, just a few short months ago, and conversations in Australia are no longer about how we do not want to fall behind in the hydrogen race – we have already fallen behind other countries (Canada, India, the EU and others) who continue to announce new policies backed by significant financial incentives, with each pushing for first mover advantage. Where companies and investors have choices among a range of projects, we are already hearing that Australian projects are being de-prioritised due to lack of policy certainty and financial support.
The speed and delivery of the global energy transition has obvious constraints such as available land and permitting times, accessible infrastructure (including transmission lines and ports), availability of technology, equipment and materials, and access to skilled technical and trades people. While Australia is fortunate to have some of these vital
elements onshore, we would also be reliant on other nations to develop a hydrogen industry at scale.
The challenges and competition for global investment are unlikely to be met by Australia simply attempting to outspend the larger jurisdictions (if that were even possible or politically palatable). The Australian response to the policy and funding challenges set by the IRA and other policies must be strategic and targeted, and policy needs to consider and support elements of project development that are not necessarily reliant on direct cash incentives.
There needs to be a further demonstration of seriousness from the Federal Government if we are not to fall further back in the queue for capital, equipment and the mobile workforce, and it should be signalled now, while a revised National Hydrogen Strategy is being developed.
Australia has an opportunity to shift the focus to job creation, retention of manufacturing capability, and assisting heavy industry to decarbonise. The hydrogen strategy can usefully shape the planning and regulatory environment and help in the development of investable propositions to attract a range of co-investors.
We hope that the revised strategy will provide a detailed plan for the transition that clearly outlines the targets, costs and timing for an effective transition and reconsiders the best range and combination of long-term economic mechanisms to develop the industry.
Specifically, it is pivotal that the revised strategy explicitly values and supports the development and commercialisation of new technologies and industries to ensure that there is a pipeline of technologies and researchers in Australia.
Additionally, the Federal Government should consider establishing a case manager approach within governments to assist project developers and funders in tying all potential sources of support together, as well as assist in the coordination of planning and approvals.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 106
FUTURE FUELS
FUTURE FUELS
By Dr Fiona Simon, CEO, Australian Hydrogen Council

WHERE DO WE GO NOW?
So, what can Australia do right now that will have an immediate impact on the Australian hydrogen industry?

In the immediate term, there are low regrets policy actions that Australia can take.
Firstly, incentivise hydrogen production in areas where Australia has a competitive advantage, such as the production of chemicals (ammonia, urea, methanol). The Federal Government needs to underwrite demand for these strategically important and hydrogen-dependent industries.
Secondly, increase and expand ARENA funding for trials and demonstrations looking at decarbonisation of the production processes for carbon intensive, trade exposed industries, such as aluminium and iron ore refineries.
Finally, develop bespoke joint support packages between Australia and its trading partners that underwrite trade and support necessary infrastructure to assist the development of export supply chains.
Reform needs to be timely – and it needs to be implemented over the next 20 (or even better, 15) years if the country is to remain on track to achieve net zero and transform the economy for a carbon constrained future. This type and amount of investment and work requires centralised policy coordination in order to ensure that the needs of citizens and nation are being met.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 107
As the world-wide discussion shifts towards clean energy and hydrogen, Fiona Simon, CEO of the Australian Hydrogen Council, explains how Australia can rejoin the hydrogen race and what it can do that will have an immediate impact on the Australian hydrogen industry.
YARRA VALLEY WATER’S TRENCHLESS TECHNOLOGY

INNOVATOR EXPLORES CRITICAL INNOVATIONS
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 108
MICROTUNNELLING
By Ash Hamer, Major Projects Manager, Yarra Valley Water, and Australasian Society for Trenchless Technology’s Young Person of the Year 2022

The trenchless industry is an essential part of delivering infrastructure for Yarra Valley Water customers. Its assets (mainly sewer mains) have been getting larger and more complex over the past decade due to population growth. Here, Yarra Valley Water’s Major Projects Manager, Ash Hamer, explains how the utility has relied heavily on trenchless construction methods to deliver more than $200 million worth of work to expand and improve Melbourne’s water and sewer network over the past ten years.
Protecting cultural heritage is very important to us as we work to deliver our essential services – it’s part of our commitment to caring for Country. We always endeavour to avoid disturbing environmentally sensitive areas and Aboriginal cultural heritage during our construction work. With trenchless technology there’s less digging, which significantly reduces potential damage. It can be complex work due to ground conditions, so it’s important that we work closely with our delivery partners to manage key risks,
reduce impacts to the community and environment and ensure successful outcomes.
One of our most significant recent achievements is delivery of the $80 million Lockerbie Main Sewer Project – one of Yarra Valley Water’s largest ever capital works projects. It runs over 9km between Donnybrook and Wallan in Melbourne’s north. As part of the project design, we worked with our design partner Jacobs and the Wurundjeri Woi-wurrung Cultural Heritage Corporation to identify the

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 109
MICROTUNNELLING
potential impact that excavation might have on culturally sensitive areas.
Trenchless drilling technology was used to minimise disruption to sensitive sites along the construction route. Where areas could not be avoided, we went beyond what is required in a standard Cultural Heritage Management Plan by establishing a collaborative research paper to better understand the significance of the stony rises in this region.
We typically use micro tunnelling and horizontal directional drilling across our major projects. Our focus is on micro tunnelling for large diameter sewer construction such as for Lockerbie (DN1400 to DN600) and our Amaroo (DN1600), Kalkallo Creek (DN1200), Epping (DN1600 – 1800), Donnybrook East (DN1000 to DN600), and Donnybrook Link (DN 800) projects.

Utilising horizontal directional drilling on the Doreen transfer main meant that we could limit the need for vegetation removal, which reduced our impact on the environment. Epping Main sewer was a highlight due to the depth being 40m and therefore requiring significant logistics to just get the drilling and tunnelling machines in place. We’ve also been leading the implementation of glass reinforced plastic pipe, which has successfully supported delivery of projects while ensuring longevity of assets.
WORKING AROUND EXISTING INFRASTRUCTURE
As well as cultural and environmental sensitivity, another factor that determines the use of trenchless technology on our projects is the presence of existing infrastructure, such as buildings or roads. Trenchless becomes more economical and safer than open cut trenching when the depth exceeds about eight metres.
Trenchless technology can have its challenges due to the risk of unexpected ground conditions that can be encountered. For example, construction in the northern growth corridor around Donnybrook is especially difficult due to high strength rock from multiple lava flows intersected with mixed/soft ground conditions that make tunnelling challenging.
Ensuring that we carry out appropriate ground investigations and risk discussions is critical to setting up these projects for success. There needs to be significant collaboration between clients, designers, suppliers, and contractors to ensure successful project delivery.
Trenchless technology is critical to the future of the water and utilities sector. The combination of aging infrastructure and population growth means that our work will increasingly need to be completed in more built-up areas.
This will require innovation and technology to renew and install essential infrastructure for the future. Trenchless technology also has a key role in reducing a project’s carbon footprint by limiting the backfill needed for open trenching (backfill being a significant contributor of embodied energy).
As the industry continues to develop and grow there are exciting times ahead for trenchless technology in Australia. As a utility, it’s important that we continue to engage with the trenchless industry across all spectrums so we can deliver our work with the least possible impact. Only by working together will we be able to achieve our commitment to caring for Country and deliver on our purpose to support the health and wellbeing of our customers, and create a brighter future for communities and the natural environment.
UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 110
MICROTUNNELLING
All The Way
We have a range of jetting trucks to suite your application.



Safe, reliable, and cost effective.

1800 816 830 enviroline.net.au

UTILITY • MAY 2023 WWW.UTILITYMAGAZINE.COM.AU 111 MICROTUNNELLING
AUSSIE INNOVATION
The water jetting specialists
EDITORIAL SCHEDULE & ADVERTISERS INDEX
23 JUNE 2023
NOVEMBER 2023
EVENT DISTRIBUTION
WIOA NSW ALL ENERGY
MAJOR FEATURES
RENEWABLES
DISASTER MANAGEMENT
CORROSION
RETAIL, BILLING & CRM
SPECIAL FOCUS
LAND ACCESS
TRANSFORMERS & SUBSTATIONS
PIPELINE INTEGRITY & LEAK DETECTION
SAFETY
DAMS
FEBRUARY 2024
EVENT DISTRIBUTION
WIOA SA
MAJOR FEATURES
BIG DATA
CYBER SECURITY
SOLAR
WATER
WIOA VIC
SPECIAL FOCUS
MAPPING, GIS & SURVEYING
UTILITY LOCATION
SEWER REHABILITATION
EMBEDDED NETWORKS
DISTRIBUTED GENERATION
CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE
SALES DEADLINE
15 SEPTEMBER 2023
EQUIPMENT & MACHINERY
HORIZONTAL DIRECTIONAL DRILLING (HDD)
INTERESTED IN WORKING WITH UTILITY MAGAZINE?
SCAN TO DOWNLOAD
OUR MEDIA KIT.
SALES DEADLINE
8 DECEMBER 2023
EQUIPMENT & MACHINERY DRONES SWITCHGEAR
SECTION 112 UTILITY • MAY 2023 Access Detection 22 Altavec 67 AMS Instrumentation & Calibration 20 APA Group 36 Bintech Systems 62 Century Yuasa 49 Compliance Quarter 41 Daly's Constructions (Australia) 70-71 Denso (Australia) 21 Eco Detection OBC EJ Australia 31 Emtivac Engineering 9 Enviroline Group 111 FMT-Field Machine Tools 75 Harcor 8 Interflow 81 Kwik-Zip 87 Lanco Group 16 Locusview 23 Madison Technologies 39 MM Electrical Merchandising IFC Monkey Media 105 nbn 79 Nearmap Australia 29 NHP Electrical Engineering Products 33 Pezzimenti Trenchless 5 Polymaster 57 Projex Group 61 Pulsar Measurement 14 RIDGID Australia 13 Rimco 19 RodRadar Australia 25 Spectur 37, 84-85 Station Innovation 62 Steel Mains IBC SUEZ 52-53, 95 Taggle Systems 98 Toshiba International Corporation 18 UAM Tec 17 UP42 94 Urban Utilities 50-51 VEGA Australia 7 Vermeer Australia 63, 74 WIOA 99 Xugo 15, 88-89 Yokogawa Australia 11, 44-45
MAJOR FEATURES WATER MANAGEMENT DEMAND MANAGEMENT ENERGY NETWORKS SUSTAINABILITY SPECIAL FOCUS INSPECTION, CCTV & CONDITION ASSESSMENT MOBILITY VEGETATION MANAGEMENT ENERGY STORAGE FUTURE FUELS EQUIPMENT & MACHINERY SMART METERS MICROTUNNELLING SALES DEADLINE 29 MARCH 2024 EVENT DISTRIBUTION WIOA QLD OZWATER LOCATE EVENT DISTRIBUTION IMARC
MAJOR FEATURES WATER OPERATIONS AND TREATMENT STORMWATER ASSET MANAGEMENT SMART GRIDS SPECIAL FOCUS GAS PIPELINES TRENCHLESS TECHNOLOGY IoT AND SCADA WASTE MANAGEMENT IRRIGATION EQUIPMENT & MACHINERY PIPE & CONDUIT PUMPS, VALVES & FILTERS SALES DEADLINE
MAY 2024
AUGUST 2023
SINTALOCK® II - A REVOLUTIONARY JOINT DESIGN FOR AN EVER-EVOLVING WATER PIPELINE INDUSTRY


A step forward into the future of the water industry, Steel Mains’ Sintalock® Type II Rubber Ring Joint is an Australian-made fully restrained joint for high pressure water pipelines that goes further beyond today’s standards than any other joint in the market.
With no need to enter the pipe for welding or lining reinstatement, safety is optimised while corrosion protection is fully enhanced and laying rates are maximised.
www.steelmains.com




YOUR LAB IN THE FIELD
Fully integrated solution
• Automated water quality testing

• Multiparameter system
• Laboratory grade precision and accuracy
• Self-calibrating and resistant to biofouling
• Automated cloud-based reporting
• Easily integrated into SCADA systems
• Early warning system in near real-time
• Mains and solar powered autonomous operation

• Low cost user-replaceable reagent fluids and consumables
• Designed to enable installation of additional parameter sensors
Nitrite (NO2-)
Nitrate (NO3-)
Phosphate (PO4-)
Chloride (Cl)
Carbonate (CO3)
Fluoride (F)
Sulphate (SO4)
Ammonium (NH4+)
Magnesium (Mg)
Potassium (K)
Calcium (Ca)
Reduce cost, risk and delay. High frequency automated measurement at a fraction of grab sample analysis cost.
More information ecodetection.com













































































































 By Dominic Adams, GM Networks, Energy Networks Australia
By Dominic Adams, GM Networks, Energy Networks Australia


























































































































































 By Ryan Collins & Kareen Moraes, Graduate Engineers from Greater Western Water
By Ryan Collins & Kareen Moraes, Graduate Engineers from Greater Western Water

























































































 By David Norman, CEO, Future
Research Centre
By David Norman, CEO, Future
Research Centre





















