

I’m an Architect and Computational Designer. Click to visit my website.




I’m an Architect and Computational Designer. Click to visit my website.

Urban Design I Game Simulation I Climate Change Responsive
DRL Thesis I Studio Bhooshan Team of three I 2023-24
Involved in Urban Research & Design, 4D land use simulation, Spatial Design
This thesis is an attempt to create a set of rules for bottom up cities on the coast. Currently 8/10 mega cities are on the coast and around 40% of world population lives within 100km on coast because of trade, tourism and resources available near the sea. As per world bank urban development report, 1.2 million sq km of new urban area is expected by 2050, we believe that will be on the coast because of the advantages it has to offer for a city growth. But location of coast also comes with an issue of flooding. 1/4th of the world population is exposed to flood already and it will increase every decade. Currently cities are using barriers to protect, but they costs a lot and only a temporary solution to this inevitable issue. Whereas cities like Amsterdam, are resilient by design, built with a network of communally funded canals which grew over time period of 800 years. The thesis was a response to current issues of coastal cities using game simulations like City Skylines. A prototypical simulation system which can be applied to any location with global rule sets applied to local context.

Amsterdam- Land Use
Amsterdam has 400 years old canal houses which are mixed use. Warehouses, retail , office and residence all in one house, sufficient for nuclear families. The houses were narrow and long because the canal frontage was expensive.
Still most of the land use in Amsterdam is mixed use. 4D land use simulation is a set of rules to design coastal cities around the globe considering economy and climate. The rules sets and studies allows local context for bottom up growth of cities.


Players
Its a multiplayer game simulation, where one is community player who is responsible for infrastructure and other players are representatives of RICO who buy land and purchase buildings.

Communal Player
Infrastructure built + tax collected

Residential Representative
Land Bought

Industrial Representative
Land Bought + Construction

Commercial Representative Pass!

Office Representative Construction
Land Value
After each player buy and build over it, land value of other parcels. After each level of population and built area , value range of all the parcels increases.
3X 30X





Economic Calculations
The economy flow rule sets where back-end calculations give each building a cost and a maintenance cost and tax from residents to get final revenue for each player




Ψ - (Tax)
The community player receives tax from the other players and pays for infrastructure cost for the city. He has special buildings like cruise terminals etc to buy on parcels which unlocks like other buildings.
Ψ - (Land Cost)(Construction Cost )
Ψ + (Rent)(Maintenance Cost)
Ψ + (Tax)

Ψ - (Infrastructure Cost)








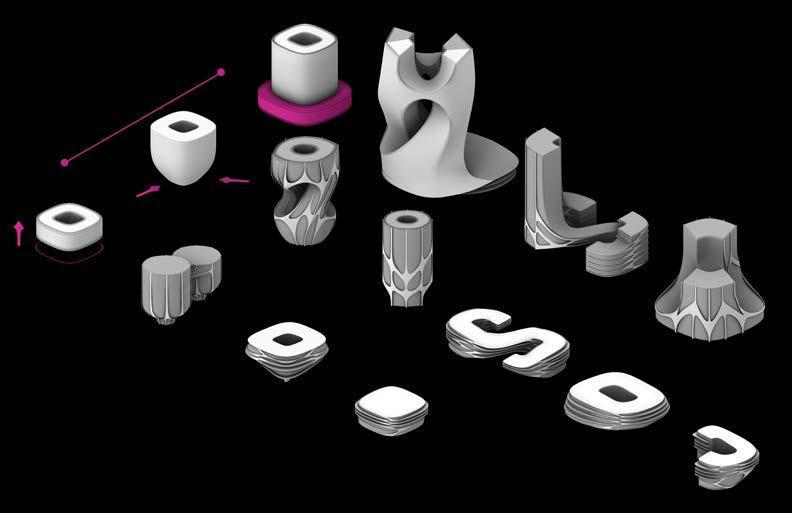
Game simulation can later be replaced by designed spaces and buildings. Considering The brief, a catalogue of buildings was proposed considering the distance from the sea , where closest buildings are designed with elevated roads and stilts, whereas buildings on the rear end are fully built on ground. There are special buildings as well like cruise terminal which will be placed by communal player.
Intertidal Upland


Game Play Instance

Architectural Interpretitions

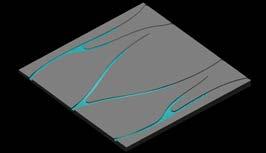
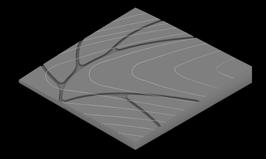
First Part of research is centered to the canal planning, with studies of Venice and Amsterdam. Amsterdam’s canals grew over time of 800 years in radial pattern, segment by segment.
This study involves different canal planning in segments which can also grow over time with respect to existing context as a part of 4d land use simulation.

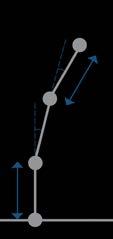
This is the angle study of first segment with respect to the coast, higher angle to the perpendicular direction of coast increases inundation at the mouth.
All the segments further that, with respect to previous one was studied for the velocity of water. Local angles allows global curvature.
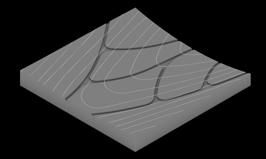
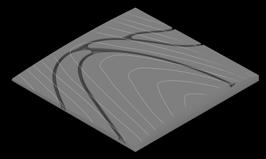
Another method to study the canal planning in segments was through length of segments with same angle in all cases, moderation of length is needed to maintain the curvature.




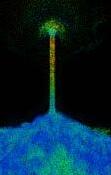

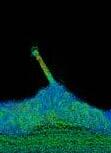











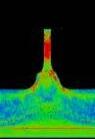



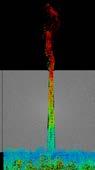





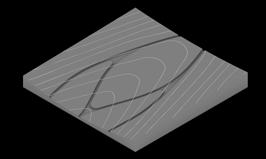
This study shows different coastline conditions to plan the mouth of canal. More recessed parts of coastline receives higher velocity of flow. Other is the angle study of the recessed portion, narrow angles receives higher current. This allows to plan first segments of canals. Third study is a global study of nodes and width which helps in controlling inundation and velocity.












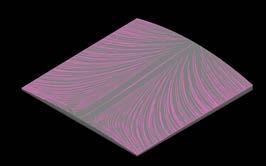
Iteration 01 - Surface Run off
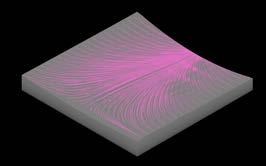
Iteration 02

Iteration 03

Iteration 04

Iteration 05

Canal Design Simulation

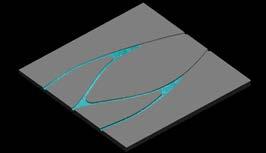

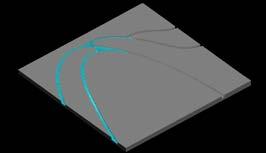





Next step of study was to study the canal design with respect to terrain in both high and low water current. As proof of concept, physical tests were done in a tank of 1200mm X 900mm.
A prototypical terrain was chosen with designed canals according to rule sets and tested under the case of low current and urban sinks were mapped.
Under high current situation, recessed coastlines zones receives high inundation with respect to others, hence needs more sensitive approach while design treatment.
Other condition was tested under heavy rainfall which is responsible for of flooding. To test if canals can channelize the water to the sea during low currents.
Same urban sinks appeared during this instance as well, which confirms the areas in both conditions needs to treated separately under urban design approach.






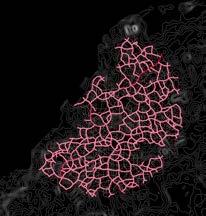







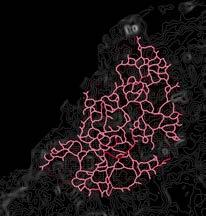















Gaziabad, India
Honorable Mention I INSDAG Competition
Team of four I Fall-2019
Involved in concept and design development, Structural details, 3d model and rendering
This project was a design competition as well as an academic project. The competition was focused on the use of steel as an innovative material in an international cricket stadium. The process involved complete understanding of stadium design, traffic management on site as well as building level and steel as a substantial construction material. It was designed for a capacity of 45,000 people in 33 acres.
As structure was the primary challenge of given problem, it was divided into two different parts, shell and core, keeping in mind that the region of project comes under zone-iv of seismic zones in India, dividing the structure makes it less bulky and more safe. Under Planning of a stadium, intend of the study was traffic management of all types of user groups, consisting of General public, VIPs, Players, Media, Office staff, staff associated with areas like restaurant. Dimensions of catenary arches were studied with physical models made from chains, corresponding to the dimensions required in span for planning.

Form is derived with the help of critical radiation analysis over pavilions and pedestrian ring. The intention for each iteration was to reduce direct sun exposure and innovate with shell structure. Shell structure is designed with a web of steel catenary arches. With paneling of ETFE and solar panels. The whole massing was placed in the center of the site to be accessed from all the sides to reduce traffic and easy escape.

2. Radiation analysis on stands and pedestrian ring with an approach of covering all the pavilions and pedestrian ring with shell.

4. Radiation analysis after the introduction of primary structure form.

6. Radiation analysis on the shell, to target the region of high dry bulb radiations throughout the year.

1. Radiation analysis on stands and pedestrian ring over block form of stadiums

3. Introducing web of repetitive catenary arches in shell structure to make the vision practically possible

5. Division of web into two layers, which reduces connections by 50%, making arches more stable and overall structure light.

7. Introducing solar panels on most affected area to come as an energy producing membrane. Rest of the area is covered by ETFE as an energy efficient material




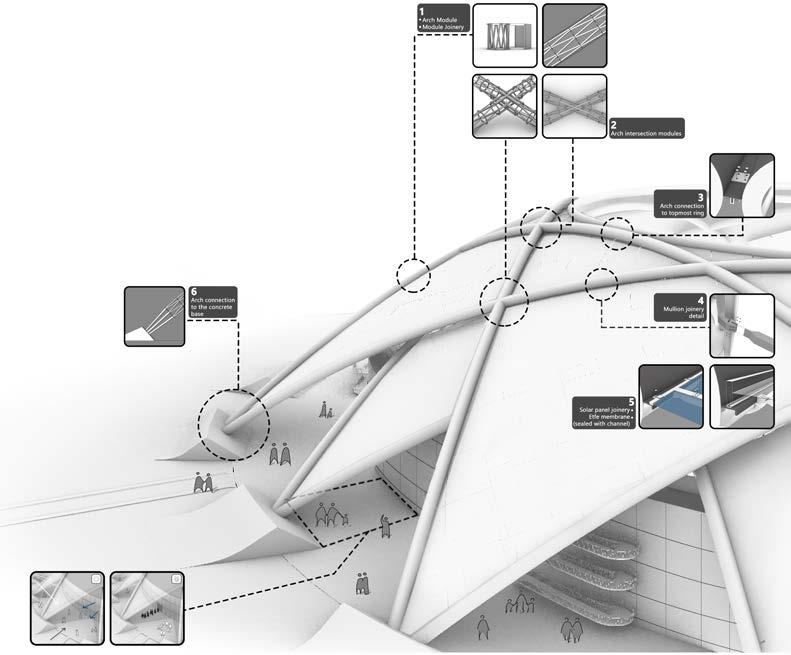
Structural details
All the arches covers a span of 240 m with maximum rise of 49m, both the shells are connected with shock absorbers at a height difference of 1m.


Spatial and Interior Design I Completed
Hauz Khas, Delhi
Professional Work I Team of two I Spring 2022 Responsible for concept and design development
This project aims to change the vocabulary of fitness and create an adrenalized identity through nature’s free forms. Client wanted an unconventional space for gym, that can become a trademark for their brand.
The free form of the design is introduced to the user, gradually, as they uncover its different levels. It starts from the flooring in the cardio zone, to decrease monotony and add to the palpating rush of the user. As one climbs to the strength zone, they are greeted with the cascading elliptical ceiling, enveloping the user in its own experience. Each experience is blanketed in an elliptical geometry for a binding identity. The buzzing nature of the design is balanced with shades of white, to create a calming balance, while certain spaces are splashed with a wooden texture, to avoid symmetry.








Walls were removed and reception table was designed around the columns to blend them in.




This project was a challenge for the team in replicating those free forms from drawings to site. We explored different ways for the same to coordinate with the local workers. False ceiling and floor pattern was done smoothly by projecting it on a grid. Whereas the reception table did not come as it was designed. Details were designed with metal framework and cladding, but on site, details were changed due to budget and worker’s proficiency with fluid geometries.





Bhimtal, Uttarakhand
Aim of the design was to blend with the natural context of the site, using similar materials and textures of wood, rubble stone etc. The project has freedom of design in 3d but the site had restrictions in sense of area and shape, which did not allow much freedom in planning. Client wanted a welcoming, peaceful and rejuvenating spatial experience for the guests. We tried to achieve that with the warmth of local materials, and exposing common spaces to the unobstructed vistas, to provide that experience inside out. Furniture was also selected considering minimalism and texture. I majorly worked in the initial phase of design, including planning, working drawings for services and selection of materials.








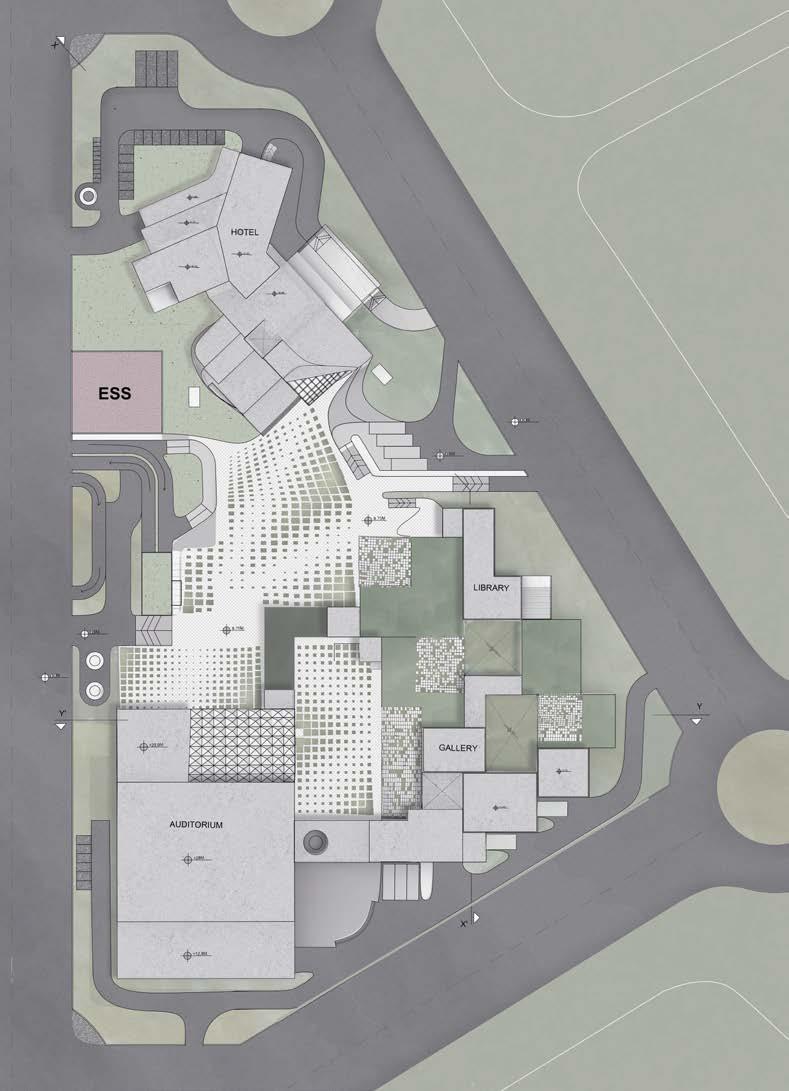
District Centre-II, Rohini, New Delhi, India
Bachelor thesis project I Fall 2020
Guide- Ar. Tarun GuptaMy thesis is an response to the situation of pandemic of covid-19, when there was nothing else bigger than the issue of lack of infrastructure and amenities. I believe, the pandemic has caused serious consequences that can be an opportunity to review individual as well as collective choices, and priorities. Most of the architecture today shows evidences of how humans have responded to infectious disease by redesigning our physical spaces. For example, the bubonic plague motivated the urban revival of renaissance. Cholera and typhoid influenced sanitary reform, water and sewage systems during industrial era.
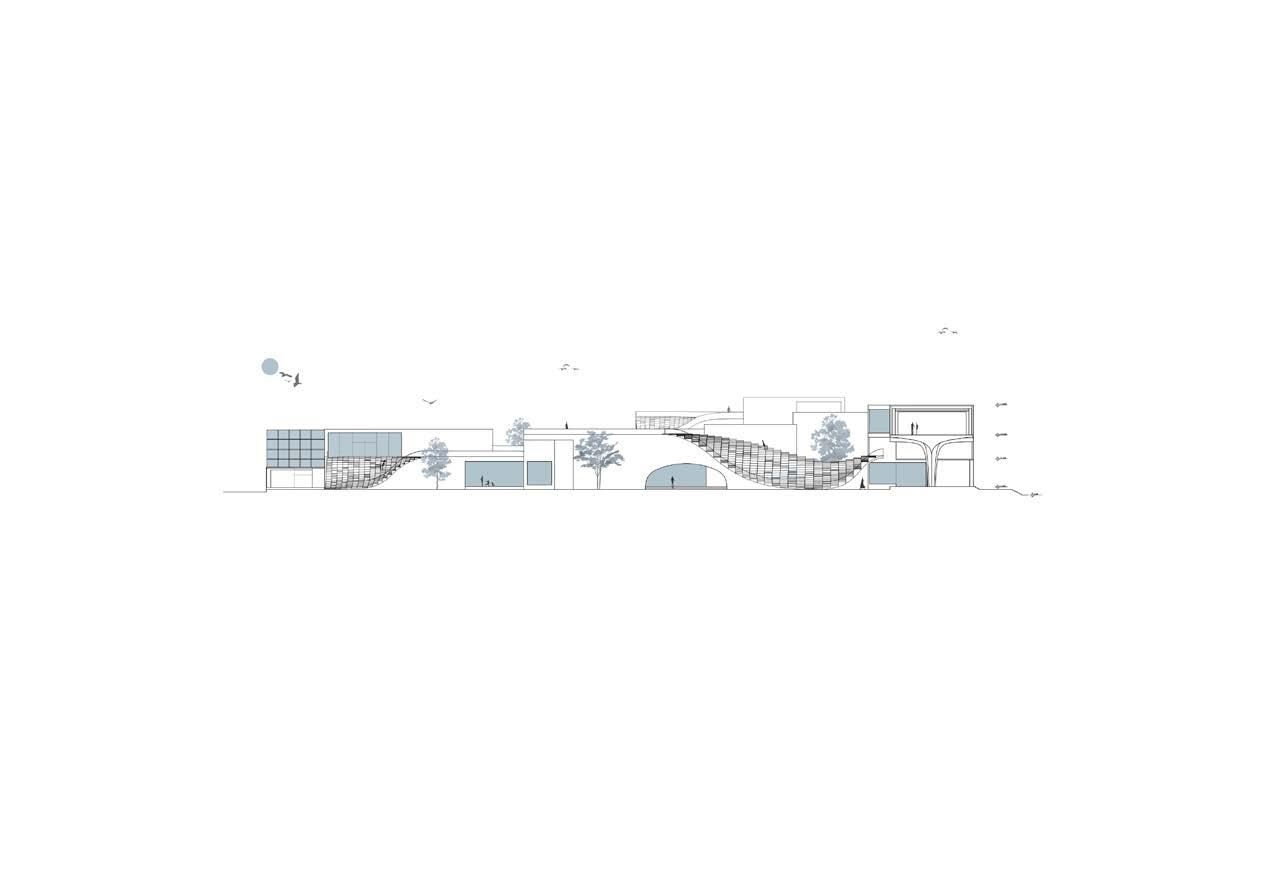
My area of focus was to suggest modified approach and sensibility for design of future public buildings. The project is a socio-culture center involving three major components- hotel building, exhibition and an auditorium. In the time of emergency, hotels and large covered spaces were used as hospitals and relief zones, similarly this is an attempt to design spaces to be reused adaptively during situations like this in future. Study also focused on, if the public buildings are closed, the built up can be used as landscape
Area of research majorly covered rules and perception for the building type, study of disease transmission and methods of prevention, consideration of issues, like lack of hospitals, fear of infection as new psychosocial problem and artificial intelligence.


1. Shortest paths between various elements were determined.

3. Taking in account the social distancing, green patches are used in between to create buffer spaces between individuals.

2. Path is created with an idea of maximum green patch.

4. Through generative design, zones were created portraying major green or hard scape area requirement.





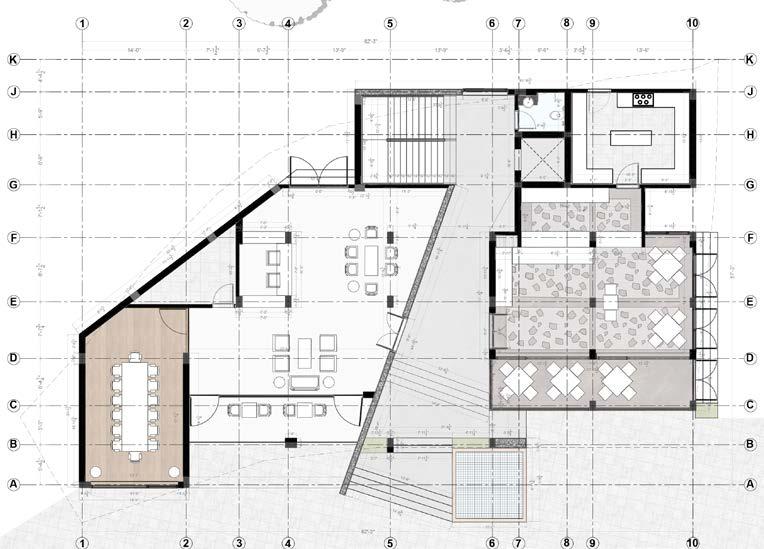
Dining Area
Walkable Roof
Exhibition Area
Walkable Roof Kitchen
Restaurant Entry Library
Restaurant Service/ Storage
Adaptive Courtyard
Workshop Area
Entrance Foyer/ Ticket Counter
Souvenir Shop Check Point
Library Entry
Restroom
Entry

Walkable Roof Courtyard
Balconies were designed keeping in mind the lack of greens in high rise buildings, especially to the upper floors which only experience the chaotic life of Delhi. So, there are sharing gardens in the balconies which provides a stay close to nature even on higher floors, without compromising privacy. Fewer balcony connections, preventing transmission again.





