4 minute read
2 Requirements process
2.1 Overview and process diagram
This process links closely with the design and development process and provides essential inputs to it. From a quality viewpoint, it is important that everything we do is based on a clear understanding of what the customer wants, and the other factors that must be taken into account when designing, developing, producing, testing, releasing and supporting our products and services.
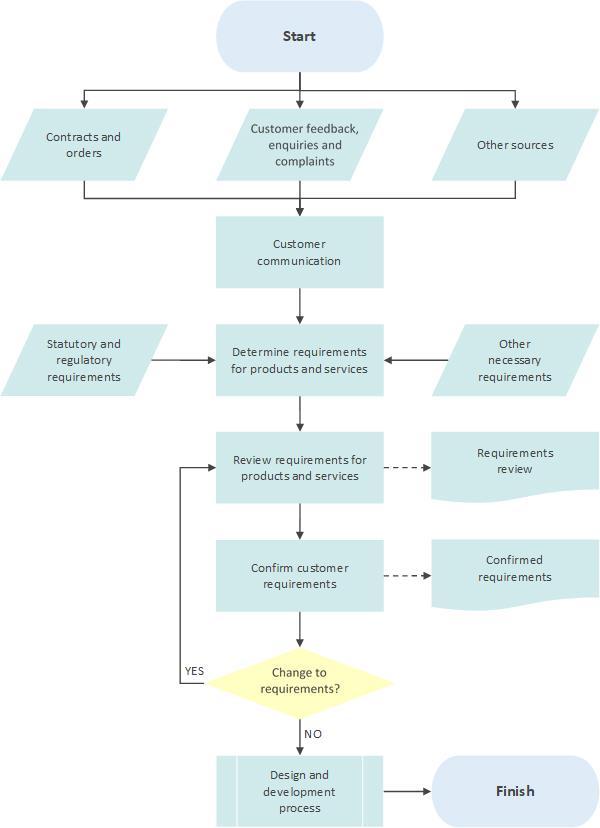
The key to establishing the requirements for products and services is customer communication, and this takes place in several ways, including pre-sales enquiries, regular contact as part of ongoing service delivery and via more formal methods such as surveys and complaints.
From this managed communication, a set of detailed requirements are identified that the products and services must meet if they are to be acceptable to the customer. Other factors are also considered, such as legal and regulatory guidance in order to arrive at a full set of requirements.
These requirements are then reviewed to ensure that they can be delivered and that we, as an organization, are not placing ourselves in a situation of unacceptable risk. As part of this, the requirements are confirmed with the customer before design and development commences.
Lastly, changes to the requirements, which may occur at any stage, are managed so that their implications are recognised and allowed for.
The process of establishing requirements is shown in Figure 1.
2.2 Requirements process diagram
Figure 1: Requirements process diagram
2.3 Process inputs
The following areas may act as inputs to the requirements process at one or more stages:
Customer details and contacts Customer enquiries Customer feedback Customer complaints Customer contracts Statutory requirements Regulatory requirements Policies on products and services Changes to requirements
These may come from different sources.
2.4 Process activities
The following activities are carried out as part of this process.
2.4.1 Customer communication
As part of identifying requirements for products and services, various forms of communication will happen with customers. These will include:
Handling of pre-sales enquiries about our organization and its products and services The provision of information about existing products and services, and about our capabilities in the relevant areas Regular meetings with existing customers as part of an established relationship Customer feedback surveys and discussions Complaints raised about our products, services or other aspects of our organization Arrangements regarding the handling of property belonging to the customer Discussions about risk and appropriate actions to take if they occur
This communication will be via a variety of channels, including email, telephone, face-toface meetings, online methods such as chats, survey forms and social media.
Based on the level of communication with customers and the results from that, requirements for products and services will be identified and documented. These could be at the generic level i.e. applying to all customers, or at the customer-specific level e.g. in the case of bespoke services.
Incorporated into these customer requirements will also be any other requirements from sources such as relevant laws and regulations, best practice standards, industry guidance etc. as well as requirements that, based on our organization’s experience, have been found to be desirable.
Current claims for our current products and services, and our capabilities in creating new ones, will be evaluated against the identified requirements to make sure that they can be met i.e. that our organization is not “over-promising” to the customer.
Prior to committing to supply the products and services involved, a formal review will be conducted to ensure that our organization has the capability to meet the requirements as specified by the customer and as defined by ourselves, also taking into account customer expectations (which may be unstated) and any external standards that are intended to be worked to.
Particular attention will be paid to those cases where the new requirements are different from previous ones e.g. from the same customer, in order to confirm that the differences are genuine and not due to a misunderstanding.
2.4.4 Confirm customer requirements
If no written indication of requirements has been provided by the customer, there must be communication with the customer to check that our understanding of requirements is accurate and that nothing has been omitted or inadvertently included.
2.4.5 Changes to customer requirements
If requirements are changed after being initially identified, a clear definition of the changes must be created and the implications of these changes assessed, as a minimum, in terms of viability, cost and timescale. Any consequences of the change to requirements, such as a revised price, must be communicated to the customer and agreed before progressing to design and development.
2.5 Process outputs
The major outputs of this process are as follows:
Documented requirements definition Review of requirements Customer confirmation of requirements Documentation of changes and their approval
These outputs will be included as part of the QMS.


