






Implementing Guidelines on Ease of Doing Business and Transparent Procurement
Draft Guidelines on the use of Digital Signatures in the Department of Agriculture
Draft Guidelines on the use of Digital Payment in all Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations of the Department of Agriculture
Draft Guidelines on Inspection And Acceptance Policies For The Procurement Of Goods In The Department Of Agriculture – Central Office (DA-CO)
Process Flow and Procedures for the Financial and Management Service and the Administrative Service
Business Process Review and Synthesis for the Automated Government Service Management System for DA Regulatory Agencies
Process Flows of the Department of Agriculture’s Regulatory Agencies
Procurement Division
Process Flow

Key Strategy 17 | Ease of Doing Business and Transparent Procurement



ADMINISTRATIVE ORDER
No._______________
Series of 2021
SUBJECT : IMPLEMENTING GUIDELINES ON EASE OF DOING BUSINESS AND EFFICIENT GOVERNMENT SERVICE DELIVERY OF THE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
These implementing guidelines aim to improve the delivery of services of the Department of Agriculture (DA) relative to the current systems, processes and procedures, both manual and automated, in accordance with the Republic Act (RA) No. 11032 or also known as Ease of Doing Business and Efficient Government Service Delivery Act of 2018 and its Implementing Rules and Regulations (IRR) Further, it aims to streamline the current systems and procedures of the DA in order to facilitate prompt actions or resolution of all its transactions with efficiency. It likewise seeks to resolve the perennial problem of delays and long procedures in accomplishing government transactions.
With the promulgation of RA No. 11032 and its IRR, the DA shall ensure streamlined procedures and simplified requirements to guarantee the immediate delivery of services to its stakeholders. The same shall facilitate prompt actions on government transactions with efficiency and promote integrity and accountability, thereby ensuring a citizen-centric delivery of services.
1. Article I, Section 27 of the Constitution provides that the State shall maintain honesty and integrity in the public service and shall take positive and effective measures against graft and corruption.
2. RA No. 11032 otherwise known as the Ease of Doing Business and Efficient Government Services Delivery Act of 2018, dated May 28, 2018, amending RA No. 9485, provides a program for the adoption of simplified requirements and procedures that will reduce red tape and expedite business and nonbusiness related transactions in the government.
3. CSC-ARTA-DTI Joint Memorandum Circular No. 2019-001, dated July 17, 2019, the Implementing Rules and Regulations of RA No. 11032 otherwise known as the “Ease of Doing Business and Efficient Government Service Delivery Act of 2018”.
4. Memorandum issued by the Secretary pertaining the composition of task forces to implement the 12 key strategies under the “One DA” approach.
5. Special Order (SO) No. 142, Series of 2021, Designation of Focal Persons for the Ease of Doing Business Task Force.

These Guidelines shall apply to the DA Central Office, Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations and cover all transactions serving both internal and external stakeholders, which include services enlisted in the DA Citizen’s Charter including current systems, processes and procedures, both manual and automated, among others, which shall be classified in either of the three (3) categories (simple, complex, highly technical) or under exemptions.
This Administrative Order (AO) shall provide guidelines in compliance with relevant laws, rules, and regulations, specifically, it aims to:
1. Review and enhance the existing policies relevant in streamlining the process of delivery of DA’s services;
2. Identify and classify processes as well as transactions that fall under the categories of simple, complex, and highly-technical as well as determine those which are requiring exemptions;
3. Prioritize the DA’s critical services for the streamlining and process improvement;
4. Provide implementing mechanisms to ensure compliance with relevant laws, rules, and regulations; and
5. Establish an organizational unit to monitor effective implementation of the requirements set forth by relevant laws, rules, and regulations.
1. Citizen’s Charter – refers to an official document, a service standard, or a pledge, that communicates, in simple terms, information on the services provided by the government to its citizens pursuant to Section 6 of RA 11032. It describes in detail the comprehensive and uniform checklist of requirements for each type of application or request, procedure to obtain a particular service, person/s responsible for each step, maximum time to conclude the process, document/s to be presented by the applicant or requesting party, if necessary, amount of fees, if necessary, and procedure for filing complaints.
2. Citizens/ Clients/ Stakeholders – refers to persons or entities whose interests and values are addressed by the DA, and therefore includes not only the citizens of the Philippines, but also all the stakeholders, including but not limited to, users, beneficiaries, other government offices and agencies, and the transacting public.
3. Complete requirements – refer to all the necessary or appropriate documents that are required to be submitted together with an application form by the applicant or requesting party, which fully satisfy the formal and substantive requirements of the relevant law. For processes that involve several stages with different requirements per stage, it is complete when the applicant or requesting party has fully satisfied or submitted all the requirements necessary for each stage, as enumerated in the Citizen’s Charter of the agency.


4. Complex transactions – refer to applications or requests submitted by applicants or requesting parties of a government office which necessitate evaluation in the resolution of complicated issues by an officer or employee of said government office, such transactions to be determined by the office concerned (7 Working Days).
5. Compliance Cost Analysis - refers to the analysis of the costs that are incurred by businesses or other parties at whom regulation may be targeted in undertaking actions necessary to comply with the regulatory requirements, as well as the costs to the government of regulatory administration and enforcement.
6. Electronic Signature - refers to a distinctive mark, characteristic and/or sound in electronic form, representing the identity of the person and attached to or logically associated with the electronic data message or electronic document or any methodology or procedures employed or adopted by a person and executed or adopted by such person with the intention of authenticating or approving an electronic data message or electronic document.
7. Fixer - refers to any individual or a group of individuals whether or not officially involved in the operation of a government office or agency who has/ have access to people working therein, whether or not in collusion with them, facilitates speedy completion of transactions for pecuniary gain or any other advantage or consideration.
8. Government Services - refer to processes or transactions between applicants or requesting parties and DA involving applications for any privilege, right, reward, license, clearance, permit or authorization, concession, or for any modification, renewal or extension of the enumerated applications or requests, which are acted upon in the ordinary course of business of the agency or office concerned. This includes frontline services enrolled in the existing Citizen's Charter (whether or not related to business), corresponding back-end/support services and regulatory functions related to permitting, licensing and issuance of a privilege, right, reward, clearance, authorization or concession.
9. Highly technical application or transaction – refers to transaction that requires the use of technical knowledge, specialized skills and/or training in the processing and/or evaluation thereof (20 working days).
10. Processing Time - refers to the time consumed by the DA from the receipt of an application or request with complete requirements, accompanying documents and payment of fees to the issuance of certification or such similar documents approving or disapproving an application or requests. For processing that involve several stages, each stage shall have its own processing time. The processing time commences on the date/time that the applicant has satisfactorily completed the previous stages and all the requirements for the stage being applied for, and has paid the applicable fees, if any.
11. Prescribed processing time - refers to the maximum period of three (3) working days for simple, seven (7) working days for complex, and twenty (20) working days for highly technical transactions given to complete its process. It shall also include the period when a transaction has been extended for justifiable reasons.
12. Regulatory Impact Assessment (RIA) - refers to the tool to design and evaluate policies, laws and regulations that are targeted, proportionate, accountable, transparent and consistent. It involves systematic processes that examine the expected consequences of a range of alternative policy options that could be used to address a particular policy problem or issue. The policy options shall include evidence-based information_ to decision-makers, regulators and stakeholders. It aims to reduce unnecessary regulatory burdens and costs to enhance the quality of existing regulations and regulatory proposals.
13. Report Card Survey (RCS) 2.0 - refers to an evaluation tool that provides a quantitative measure of actual government service user perceptions on the quantity, efficiency and adequacy of different government services, as well as a critical evaluation of the office or employee. It is an instrument that also solicits user feedback on the performance of government services, for the purpose of exacting public accountability, and when necessary, proposing change. It shall be used to measure management support in institutionalizing agency service delivery reforms.
14. Simple transactions - refer to applications or requests submitted by applicants or requesting parties to the DA which only require ministerial actions on the part of the public officer or employee, or that which present only inconsequential issues for the resolution by an officer or employee of said government office (3 Working Days).
15. Time and Motion Study - refers to the tool to track the progress of customer interface, processing, queuing and waiting times, and linked processes that are within and beyond the control of the service office. It is an essential step in the process mapping of services for the formulation and/or updating of the Citizen's Charter.
16. Zero Contact Policy - refers to the policy that government officers or employees shall have no contact, in any manner, unless strictly necessary with any applicant or requesting party concerning the subject application or request.
1. The DA Central Office and Field Offices, Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations shall commence with the reengineering of their systems and procedures in compliance with the provisions in the Ease of Doing Business and Efficient Government Service Delivery Act of 2018.




2. The DA Central Office and Field Offices, Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations shall aim to achieve the following improvements for each of their critical services/processes:
a. Reduction in the number of signatories to not more than three (3);
b. Simplification of application forms or documentary requirements;
c. Progressive reduction in the turn-around time in accordance to the set standards and completion of the transaction within standard timelines;
d. Automation or computerization of applicable services/ processes;
e. Reduction in costs, if any; and
f. Clear feedback mechanisms and client satisfaction measurement.
3. A Citizen’s Charter shall be developed and updated in accordance with the rules and regulations issued by Anti-Red Tape Authority (ARTA). Likewise, the Citizen’s Charter shall be in the form of a handbook, information billboards such as touchscreens, interactive information kiosks, electronic billboards, posters, tarpaulins, standees or any other readable materials that could be easily understood.
4. The DA Central Office and Field Offices, Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations shall adopt a zero-contact policy, thus, concerned employees shall limit interaction with an applicant or requesting party unless such interaction is strictly necessary for the processing of the request or application.
5. For the acceptance of applications or requests and the action of offices, the concerned office shall adhere to the provisions stipulated in Section 9(a) and Section 9(b)of RA No.11032, respectively, and as applicable.
6. A Quality Management System (QMS) shall be established in line with the Department's Quality Management Program (QMP) and in conformity with the Government Quality Management Systems Standards (GQMSS).
7. The Integrity Management Program of DA through the Agriculture Dialogue and Information Network Groups or ADING, a system that will monitor and evaluate the agrifishery policies, programs, and projects, shall be strengthened by establishing an effective monitoring systems.
8. The Public Assistance Desk (PAD) shall be strengthened to receive feedback where an officer or employee who is knowledgeable in government services shall be available for consultation and advice. The desk shall be attended to even during break time. There shall also be a hotline number, short message service, or other mechanisms by which the clients may adequately express their complaints, comments or suggestions.
9. To ensure prompt action on complaints and grievances, the DA shall develop an Integrated Grievance Redress Monitoring System (IGRMS) which shall be used for efficient monitoring and systematic resolution of complaints. The IGRMS covers all grievance platforms of the DA. (PAD, 8888 Citizens' Complaint Hotline and walk-in clients).

1. Preparatory
a. The DA Central Office and Field Offices, Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations shall come up with their list of critical services and/or transactions for Ease of Doing Business together with its relevant flowcharts containing detailed steps to complete these services and submit the same to the Task Force of Ease of Doing Business (TFEODB) for compilation into an inventory;
b. Criteria for simple, complex and highly technical transactions shall be issued by the TFEODB and thus, identified critical services and/or transactions with its flowcharts shall be reviewed, assessed and categorized based on said criteria;
c. Compliance cost analysis, conduct of time and motion studies and evaluation of improvement of all services shall be undertaken by the DA Central Office and Field Offices, Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations;
d. The Citizen's Charter and a report on the process of the identified critical services and/or transactions using the standard template provided by ARTA shall be prepared by the DA Central Office and Field Offices, Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations for submission to their respective heads for approval prior to submission to the TFEODB;
e. An appropriate system or mechanism for the legal use of electronic or digital signature shall be developed by the Information Communication and Technology Service (ICTS) as provided under the RA No. 8792 or Electronic Commence Act of 2001 and related issuances of the DA;
f. A standard feedback mechanism and client satisfaction measurement shall be developed by the TFEODB in collaboration with the concerned offices for the process improvement of the identified service/transactions;
g. The DA Central Office and each Field Office, Bureau, Attached Agency and Corporation shall conduct their own Regulatory Impact Assessment (RIA) for purpose of reviewing, simplifying, modifying, modernizing regulations, laws, and issuances to reduce regulatory burden and cost. This applies to existing regulations or regulatory changes that are outdated, redundant, and adds undue regulatory burden to the transacting public; and
h. The location of offices providing these government services and feasibility of establishing one-stop shops shall be reviewed by all Heads of Field Offices, Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations


a. The DA Central Office and each Field Office, Bureau, Attached Agency and Corporation shall regularly conduct process reviews and process reengineering to determine what and how they will reduce their number of signatories to a maximum of three (3). In relation to documents, identify number of documents necessary. The same shall also-reduce their processing and waiting time; identify and automate their processes; and receive client's feedback for the services rendered;
b. The Citizen's Charter shall be posted immediately in all respective Offices (physical representation) and in the DA Website;
c. The implementation of the approved Citizen's Charter, particularly on the procedures/steps, time, documentary requirements , and fees shall be monitored and reviewed regularly;
d. A Regulatory Impact Statement (RIS) shall be prepared before new regulations are introduced, or an existing regulation is modified or repealed. When necessary, a proposed regulation may undergo pilot implementation to assess regulatory burden and cost; and
e. Duties and responsibilities enumerated under the institutional mechanisms of this AO shall be carried out by concerned offices and regularly monitored by the TFEODB
a. The Citizen/Client Satisfaction Report as prescribed by ARTA shall be prepared and submitted to the head of office for approval prior to submission to the TFEODB;
b. The DA and its regulatory agencies shall use the Report Card Survey (RCS) 2.0 to effectively measure the overall performance of the Department and compliance with RA No. 11032, its IRR and other ARTA issuances;
c. For complaints and grievances, the IGRMS shall be used for efficient monitoring and systematic resolution of complaints.
a. The head of Office, Bureau, Attached Agency and Corporation shall be responsible for approving all reports as stipulated in these guidelines prior to submission to the TFEODB or the designated office/unit; and
b. The aforementioned Report shall be submitted to the Secretary for approval prior to submission to the ARTA.

1. Task Force on Ease of Doing Business (TFEODB)
a. Take the lead role in the implementation of the RA No. 11032 and its IRR as well as these guidelines within the Department;
b. Identify management support, and provide technical assistance to comply with the provisions of the law;
c. Provide advisory to the Secretary relevant to the implementation of the EODB;
d. Facilitate the inventory of the Department's critical, services and/or transactions for EODB;
e. Review and endorse the final critical services and/or transactions for the DA streamlining and process improvement to the Secretary for approval;
f. Oversee and validate the overall implementation of EODB and other streamlining efforts to further ensure the compliance thereof;
g. Serve as the Arbiter for grievance; and
h. Other tasks that may be assigned to the TFEODB.
2. Committee on Anti-Red Tape (CART)
a. Conduct of compliance cost analysis, time and motion studies, evaluation and improvement of all the agency's services, and reengineering the same;
b. Subject to the Guidelines/National Policy on Regulatory Management System to be issued by ARTA:
b.1 Notify ARTA of every formulation, modification, and repeal of regulations, ordinances or other related issuances;
b.2 Conduct post-implementation assessment and review of existing regulations, ordinances or other related issuances, undertake Regulatory Impact Assessment (RIA);
b.3 Prepare a Preliminary Impact Assessment (PIA) whenever there is an intent to formulate, modify, or repeal a regulation and submit to the ARTA;
b.4 Produce a RIS upon completion of each RIA and submit to ARTA for review and assessment;
b.5 Refer the ARTA's policy option recommendations to the appropriate decisionmakers within the agency; and
b.6 Submit an inventory and electronic copies of all existing (both in-effect and repealed) regulations and issuances to populate the Philippine Business Regulation Information System (PBRIS).

c. Ensure effective knowledge transfer, or information dissemination among office employees on ARTA-related trainings, briefings, or such related matters obtained by office staff within sixty (60) days from the end of the training;
d. Register new regulations and issuances to the following, if applicable, within fifteen (15) days from issuance:
d.1.UP Office of the National Administrative Register (UP ONAR); and
d.2. Official Gazette for publication.
e. Set up the most current and updated service standards and indicate in the Citizen's Charter in accordance to the prescribed template issued by ARTA, and submit the same to ARTA to populate Anti-Red Tape Electronic Management Information System (ARTEMIS);
f. Monitor and periodically review the DA Citizen's Charter, specifically: procedures/steps, time, documentary requirements, and fees;
g. Ensure that an updated Citizen’s Charter, should there be any change, is posted not later than March 31st of each year;
h. Ensure the compliance of the DA on the zero-contact policy in accordance with the law;
i. Ensure the compliance of the agency's external and internal services with the prescribed processing time as mandated by RA No. 11032 or the agency's mandate under special law;
j. Develop and foster a client feedback mechanism and client satisfaction measurement;
k. Report to ARTA not later than the last working day of January of each year the results of the Client Satisfaction Survey for each service based on the guidelines to be issued by ARTA;
l. Establish and manage a Public Assistance Complaints Desk or ARTA Helpdesk to effectively receive complaints, feedback and monitor customer satisfaction via hotline numbers, short message service (SMS), information and communication technology, or other mechanism where clients may adequately express their complaints, comments, or suggestions. The CART must ensure that complaints forwarded by the Presidential Complaints Center, Civil Service Commission’s Contact Center ng Bayan, and Complaints Action Center of ARTA are acknowledged, received, responded, to and/or acted upon by the DA within the designated period by the intended recipient;
m. Serve as overall coordinating body for the establishment of an Electronic Business One Stop Shop (e-BOSS) in compliance with the mandate under R.A. No. 11032, its IRR, and other issuances by ARTA. The CART must facilitate and assist various departments and offices involved during the development and implementation of e-BOSS, including logistical and personnel requirements, security of the system, development of a communication plan, implementation of contingency measures, and protection of data and information, as applicable;
n. Coordinate with the DA’s communications/public relations office the dissemination of ARTA Information, Education, and Communication materials for public consumption; and

o. Perform such other functions, duties, and responsibilities under R.A. 11032 (amending R.A. No. 9485), its IRR and other issuances issued by ARTA.
a. Establish an ARTA Unit to be composed of representatives of all Divisions. The ARTA Unit shall be responsible for the following:
a.1 Proactive review and standardization vis-a vis establishedcategories/classification of transactions;
a.2 Provision of parameters for Citizen's Charter;
a.3 Periodic determination of the percentage reduction in the processes;
a.4 Regular provision of recommendations for the enhancement that shall respond to the EODB requirements, ISO Certification, and other QMP requirements;
a.5 Monitor and oversee the streamlining process/EODB implementation; and
a.6 Perform other tasks as may be assigned.
b. Lead in identifying, facilitating and streamlining of its existing systems and processes as required under Section VI (2);
c. Consolidate and compile all reports prior to submission to the TFEODB Secretariat or the designated office/unit;
d. Provide the needed management support and guidance;
e. Recommend to the TFEODB for onward recommendation to the Secretary the appropriate working schedules to ensure that all stakeholders or clients who are within their premises prior to the end of official working hours are attended to and served even during lunch break and after regular working hours; and
f. Provide other support and assistance to the DA's TFEODB as the needs arise.
a. Monitor and evaluate the streamlining and process improvement of the DA's services including the client satisfaction report using the reporting template provided by ARTA and RCS 2.0;
b. Consolidate and prepare the agency report on the process improvement of the critical services;
c. Monitor the submission on the status of the identified critical services and/or transactions;
d. Prepare and submit report, as approved by TFEODB, to Office of the Secretary on the status of those critical services and/or transactions;
e. Monitor and review all submitted Citizen's Charter and the implementation of the same, particularly on the procedure/steps, time, documentary requirements, and fees; and
f. Facilitate the submission of necessary documents and reports to the ARTA.



a. Adhere to the general policies of this AO and perform the tasks indicated in the implementing procedures hereof;
b. Regularly conduct regulatory impact assessment to review, simplify, modify, modernize regulations, issuances to reduce regulatory burden and cost;
c. Periodically review and harmonize existing issuances and regulations and repeal unnecessary and redundant policies to lessen regulatory burdens to the transacting public;
d. Regularly update the Citizen's Charter of their critical services and/or transactions and post the same immediately in their respective Offices (physical representation) and in the DA Website;
e. Accept and assess the written applications, requests and/or documents submitted by requesting parties to ensure a more expeditious action on the request;
f. Assign a unique identification number to a particular request and issue an acknowledgement receipt;
g. Act on the request within the prescribed processing time stated in the Citizen’s Charter;
h. Implement the feedback mechanism and client satisfaction measurement for the process improvement of the identified service/transactions;
i. Identify permanent and alternate focal persons for the implementation of this guideline to be part of the ARTA unit set to be established under Section Vlll (2)(a) of this AO;
j. Ensure that all personnel wear the ARTA Identification Card at all times;
k. Ensure that contact numbers are updated and reachable at all times; and
l. Perform other tasks inherent to its functions and mandate as may be deemed necessary in relation to the implementation of the EODB.
a. Facilitate the internal capacity and capacity building of the Department in relation to the implementation of EODB;
b. Provide agency orientation on the salient features of EODB to the DA Central Office and its regulatory agencies;
c. Undertake preparations for the change of working schedules as may be recommended and subsequently inform the Civil Service Commission on the adoption of such working schedules;
d. Ensure that all employees/staff/personnel and even regular/temporary external service providers of the Department are provided with Identification Cards bearing the full name, position title, name of office, and the Office seal or logo,if any, apart from DA's logo. This must be readable and available immediately on Day 1; and
e. Perform other tasks inherent to its functions and mandate as may be deemed necessary in relation to the implementation of the EODB.

a. Maintain and update the posting of Citizen's Charter in the DA Website reflecting the Department's enhanced service standards for all government services to citizens and other government agencies;
b. Ensure that contact numbers are posted and regularly updated in the website;
c. Lead the development of automation systems of all transactions and processes;
d. Lead the conduct of capacity building on the business process maps and process reengineering;
e. Develop and maintain information systems for the identified transactions/processes;
f. Provide the required ICT equipment and other support needed to the implementation of automated transaction and dissemination of Citizen's Charter (information billboards such as touchscreens, interactive information kiosks, and electronic billboards);
g. Formulate guidelines for the use of electronic or digital signature as provided under RA No. 8792 or Electronic Commence Act of 2001; and
h. Perform other tasks inherent to its functions and mandate as may be deemed necessary in relation to the implementation of the EODB.
a. Review all documents relative to the RA No. 11032 and its IRR;
b. Determine whether the complaints are viable to undertake administrativeproceedings;
c. Conduct administrative hearing upon receipt of complaint from transacting public and/or internal clients, subject to existing rules and procedures stipulatedin CSC Rules on Administrative Cases; and
d. Perform other tasks inherent to its functions and mandate as may be deemed necessary in relation to the implementation of the EODB.
1. The following shall constitute violations of these guidelines:
a. Refusal to accept applications or requests with complete requirements submitted by an applicant or requesting party without due cause;
b. Imposition of additional cost and requirements other than those listed in the Citizen's Charter;
c. Failure to give the applicant or requesting party a written notice on the disapproval of an application or request;
d. Failure to render government services within the prescribed processing time on any application and/or request without due cause;
e. Failure to attend to applicants or requesting parties who are within the premises of the office concerned prior to the end of official working hours and during lunch break;
f. Failure or refusal to issue official receipts; and
g. Fixing and/or collusion with fixers in consideration of economic and/or gain or advantage.
2. Penalties
a. First offense shall be charged with administrative liability with six (6) months suspension, however in case of Section IX (1) (g), the penalty under Section Section IX (2) (b) shall apply.
b. Second offense shall be charged with administrative and criminal liability of dismissal from the service, perpetual disqualification from holding public office, and forfeiture of retirement benefits, and imprisonment from one (1) year to six (6) years with a fine of not less than Five Hundred Thousand Pesos (P500,000.00) but not more than Two Million Pesos (P2,000,000.00).
All previous issuances inconsistent with these implementing guidelines shall be deemed accordingly repealed.
XI. EFFECTIVITY
This Order shall take effect immediately and shall remain in force until revoked in writing.
Done this _________ day of __________________ 2021.

WILLIAM D. DAR, Ph.D. Secretary

DRAFT GUIDELINES ON THE USE OF DIGITAL SIGNATURE IN THE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE

MEMORANDUM CIRCULAR
No. _________________________
Series of 2021
SUBJECT: GUIDELINES ON THE USE OF DIGITAL SIGNATURE IN THE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
The Commission on Audit (COA) has issued the COA Circular 2021-006 dated September 6, 20211 entitled "Guidelines on the use of Electronic Documents, Electronic Signatures, and Digital Signatures in Government Transactions", which allows the use of digital signatures in government transactions following the existing laws, rules and regulations.
“The Republic Act No. 8792 or the Electronic Commerce Act of 200012 provides for the legal recognition of electronic signatures and imposes strict requirements before an electronic signature qualifies as a handwritten signature. The same law allows electronic transactions in government and allows appropriate government entities to adopt and promulgate rules, regulations, or guidelines to specify the use of an electronic signature, the type of electronic signature required, the manner the electronic signature shall be affixed to the electronic data message or electronic document, and the control processes and procedures as appropriate to ensure adequate integrity; security and confidentiality of electronic data messages or electronic documents or records of payments.
The Government Procurement Policy Board (GPPB) in its Resolution No. 16-20193 allowed and approved the use of digital signature in all GPPB issuances and in procurement-related documents. Similarly, the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) issued Revenue Memorandum Circular No. 29-20214 which allows the use of electronic signatures on BIR Forms 2304, 2306, 2307 and 2316, The Anti-Red Tape Authority intensifies its drive to streamline the processes in all government entities and take advantage of technology, especially in the event of a disaster or any state of emergency such as the COVID-19 pandemic as it allows government officials to approve transactions and make payments without necessarily being physically present. Furthermore, COA Circular No. 2004-006 dated September 9, 2004 implies admissibility of digitally-signed documents in audit.”
This circular, therefore, is issued to provide policies and guidelines in the use of the Digital Signature in the Department of Agriculture.
This Circular shall apply when DA officials and employees issue electronic documents in lieu of paper documents, where the signature of an authorized signatory is required. Nothing in the Circular shall be construed as prohibiting an office from submitting paper documents, or a combination of paper and electronic documents.
This issuance covers all the following DA offices: Central Office, Regional Field Offices (RFOs), Bureaus, and Attached Agencies and Corporations.
A trusted third party validates a person’s identity and either generates a public/private key pair on their behalf or associates an existing public key provided by the person to that person. Once a CA validates someone’s identity, they issue a digital certificate that is digitally signed by the CA. The digital certificate can then be used to verify a person associated with a public key when requested.
Digital certificates
Digital certificates are analogous to driver licenses in that their purpose is to identify the holder of a certificate. Digital certificates contain the public key of the individual or organization and are digitally signed by a Certificate Authority (CA). Other information about the organization, individual, and CA can be included in the certificate as well.
Digital Signature
A mathematical algorithm used routinely to validate the authenticity and integrity of a message (e.g., an email, a credit card transaction, or a digital document). Digital signatures create a virtual fingerprint that is unique to a person or entity and are used to identify users and protect the information in digital messages or documents.
Electronic Signature is also known as e-signature, refers to data in electronic form, which is logically associated with other data in electronic form and which is used by the signatory to sign.
PKI consists of the policies, standards, people, and systems that support the distribution of public keys and the identity validation of individuals or entities with digital certificates and a certificate authority.
PNPKI Philippine National Public Key Infrastructure
4.1 Designation of Focal Person
4.2. Documents allowed to use digital signature
The following are the documents allowed for use of the digital signature:
a. Under the COA Circular 2021-006 General Principles and Guidelines1 item 2: “When under existing rules a document requires a signature, the use of electronic signature (including digital signature) on the electronic document shall be an accepted alternative and shall be equivalent to the signature of a person on a written document such as, but not limited to, procurement-related documents, Disbursement Vouchers, Requisition and Issuance Slips, Purchase Orders, Contracts, and Memoranda among others.”
b. Under the GPPB RESOLUTION NO. 16-20193, the following are the Procurement related documents allowed to use the digital signature:
i. Issuances such as Resolutions, Circulars, Policy Matter Opinions, and Minutes of the Meeting;
ii. Issuances including but not limited to: (a) Project Procurement Management Plan; (b) Annual Procurement Plan; (c) Request for Quotation; (d) Request for Proposal; (e) Philippine Bidding Documents; (f) Invitation to Bid; (g) Request for Expression of Interest; (h) Supplemental/Bid Bulletin; (i) Notice of Postponement of Bid Opening; (j) Notice of Eligibility or Ineligibility; (k) Notice of Short Listing; (l) Abstract of Quotations; (m) Abstract of Bids as Read; (n) Abstract of Bids as Calculated; (o) Bid Evaluation Report; (p) Notice to Bidder with the Lowest Calculated Bid; (q) Post-Qualification Report; (r) Notice of Postdisqualification; (s) Notice of Award; (t) Approval of Higher Authority; (u) Notice to Proceed; (v) Reply to Motion for Reconsideration and Protest; (w) Bids and Awards Committee (BAC) Resolutions; (x) Blacklisting Order; (y) Procurement Monitoring Report; and (z) Agency Procurement Compliance and Performance Indicators.
c. Other DA documents as identified:
i. Administrative Documents such as Memorandum, Leave Application Forms, Daily Time Record, Accomplishment Report;
ii. Financial documents such as Vouchers / ROA:
iii. Other documents such as IPCR/ OPCR/ SPCR, Market Studies, and Justification.
4.3. BAC-related documents and transactions
4.4. Responsibilities of a Digital Signature Holder
Owning a digital signature comes with responsibilities. The following are the responsibilities of the DA personnel with a digital signature:
a. Prepare and submit the application form and mandatory requirements to the Cybersecurity Bureau- Digital Certificate Division of the DICT or online at https://sites.google.com/dict.gov.ph/pnpki/ors. (The process and requirements are listed in the Annex B attached in this circular);
b. Attend the scheduled interview by the DICT;
c. Download and installation of the digital certificates;
d. Installation of the Adobe Acrobat Reader and other software required in using the digital signature;
4.5. Responsibilities of the Information and Communications Technology Service (ICTS) as Technical Support
a. In coordination with the Cybersecurity Bureau- Digital Certificate Division of the DICT, ICTS will conduct trainings or orientation and disseminate information on the use of digital signature as authorized herein;
b. Assist DA employees in the downloading and installation of the digital signatures;
c. Answer queries and concerns related to the application, download, installation and use of digital certificates;
d. Monitor status of DA digital signature applicants and users; and
e. Provide other technical assistance.
4.5 Responsibilities of the DA Office ICT Units
a. Facilitate the enrolment of their respective offices.
b. Assist employees in their respective offices in the downloading and installation of the digital signatures;
c. Answer queries and concerns related to the application, download, installation and use of digital certificates;
d. Monitor the status of application in their respective office and submit report to ICTS at <insert email> <insert frequency of reporting>;
e. Provide other technical assistance.
4.6 Limitation of use for the Contract-of-Service (COS) Personnel
The DA COS will be allowed to use digital signature only on the following conditions:
a. Daily Time Record (DTR); Accomplishment Report (AR); and Job Completion/ Satisfaction Certification
b. Travel reports
c. Others documents that may be allowed
SECTION 5. Unauthorized and Illegal use of the Digital Signature
The punishment for the Employee who found for unauthorized and illegal use of the digital signature will be subject to administrative disciplinary actions to be determined by the Administrative Service, Data Privacy Protection Officer, and DA Legal Service subject to the policy that will be issued by the DICT
Aside from this Memorandum Circular, an Operating Unit can craft its own internal policies and guidelines in accordance with its Operating Unit’s function.
This Order shall take effect immediately.
Done this ___ day of ___________ , 2021 in Quezon City, Philippines.
WILLIAM D. DAR, Ph.D. Secretary
1. COA Circular 2021-006 dated September 6, 2021
https://coa.gov.ph/index.php/2013-06-19-13-06-41/1-circulars/category/9178-cy-2021
2. Republic Act No. 8792 or the Electronic Commerce Act of 2000
https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2000/06/14/republic-act-no-8792-s-2000/
3. Government Procurement Policy Board (GPPB) in its Resolution No. 16-2019
https://www.gppb.gov.ph/issuances/Resolutions/GPPB%20Resolution%20No.%20162019.pdf
4. BIR Revenue Memorandum Circular No. 29-2021
https://bit.ly/3rkJdcB
5. Guidelines on the Application and Issuance of PNPKI Digital Certificates For External Clients During the State of Public Health Emergency
https://dict.gov.ph/wpcontent/uploads/2020/04/SIGNED_DEPARTMENT_CIRCULAR_NO_6_GUIDELINES_ON_THE_AP PLICATION_AND.pdf
PNPKI – Individual Certificate - https://dict.gov.ph/pnpki-individual-certificate/
For Subscribers, Registration Authority (RA) shall ensure that the identity information is verified by prior compliance with the following:
1. Complete registration at the Online Registration System (ORS) portal or Duly accomplished application form (for bulk application);
2. Online face-to-face verification with the applicant;
3. Birth Certificate or valid Philippine Passport; (softcopy)
4. 1 passport size photo taken within the last six (6) months; (softcopy)
5. Unified Multi-Purpose Identification (UMID) compliant card. (softcopy) *
Note: File name of documents (softcopy) must be in this format:
Lastname Firstname_Document Type (e.g. Dela Cruz Juan_Passport or Dela Cruz Juan_UMID)
* In the absence of UMID-compliant card, ANY TWO of the following cards are allowed as valid IDs based on BSP Circular 608 series of 2008
● Passport
● Driver’s License
● Professional Regulation Commission (PRC) ID
● National Bureau of Investigation (NBI) Clearance
● Police Clearance
● Postal ID
● Voter’s ID
● Government Service Insurance System (GSIS) e-Card
● Social Security System (SSS) Card
● Senior Citizen Card
● Overseas Workers Welfare Administration (OWWA) ID
● OFW ID
● Seaman’s Book
● Alien Certification of Registration/Immigrant Certificate of Registration
● Government Office and GOCC ID, e.g. Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP ID), Home Development Mutual Fund (HDMF ID)
● Certification from the National Council for the Welfare of Disabled Persons (NCWDP)
● Department of Social Welfare and Development (DSWD) Certification
● Integrated Bar of the Philippines ID
● Company IDs Issued by Private Entities or Institutions Registered with or Supervised or Regulated either by the BSP, SEC or IC
● Tax Payer Identification Number (TIN);
● Phone number (mobile and/or landline);
● Email address owned by the individual or authorized by the owner for use by the subscriber; and
● Consent to verify and share the information submitted (included in the application form).
For bulk application and other inquiries, please email info.pnpki@dict.gov.ph or the PNPKI Cluster Team Offices in the Region.
PNPKI – Agency Certificate - https://dict.gov.ph/pnpki-agency-certificate/
Juridical applicant’s information shall be verified with prior submission of the following:
1. Duly accomplished application form;
2. Online face-to-face verification with the authorized representative;
3. Birth certificate of the applicant printed on security paper for Filipino citizen or Alien Certificate of Registration (ACR) card for a foreigner;
4. Tax Payer Identification Number (TIN);
5. Authorization Letter/Board Resolution naming the authorized representative/s to apply for a digital certificate in behalf of the agency;
6. Consent to verify the information submitted; and
7. Verified e-mail address owned by the organization or authorized by the owner of the email address to be used by the organization.
Additional Requirements:
For a government agency:
1. Government Service Insurance System (GSIS) registration number
For non-government entities:
1. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) business registration for corporation and partnership, DTI Certificate of Business Name Registration for single proprietorship or Cooperative Development Authority (CDA) registration for cooperatives;
2. Business Permit issued by the Local Government Unit (LGU); and
3. Social Security System (SSS) Employer Clearance
For further inquiries and submission of application requirements, please email info.pnpki@dict.gov.ph or the PNPKI Cluster Team Offices in the Region.
As per Department Circular 006 dated April 02, 2020 - Guidelines on the Application and Issuance of PNPKI Digital Certificates For External Clients During the State of Public Health Emergency -
https://dict.gov.ph/wpcontent/uploads/2020/04/SIGNED_DEPARTMENT_CIRCULAR_NO_6_GUIDELINES_ON_THE_AP PLICATION_AND.pdf
E-Filing of Application for External Clients
Application Form and Supporting Documents :
1. All interested applicants may download the application Form and find the list of supporting documentary requirements , at the official DICT website : https://dict.gov.ph/pnpki
2. USer of official Email Addresses - the applicant shall use his/her official email address to file and submit his/her application and supporting documents to the PNPKI official email address info.pnpki@dict.gov.ph in accordance with the procedures provided in this circular. The application email shall bear the proper description i.e. “ PNPKI Application of (Name of Applicant) “ or nay similar phrase similar thereto indicated in the email title or subject field. The application email thread , shall be as far as practicable
Bulk Application
i. Documentary Requirements. The following are the documents a DA personnel need to complete to be able to apply for a digital signature.
1. Duly accomplished application form -A fillable application letter can be accessed through this link: https://dict.gov.ph/wpcontent/uploads/2019/04/PNPKI-Individual-CertificateApplication-Form-fillable.pdf
2. Personal appearance of the applicant;
3. Birth Certificate or valid Philippine Passport. (Photocopy)
4. 1 passport size photo taken within the last six (6) months
5. Unified Multi-Purpose Identification (UMID) compliant card. (Photocopy)*
6. Phone number (mobile and/or landline);
7. Email address owned by the individual or authorized by the owner for use by the subscriber; (highly encouraged to use official govmail address, username@da.gov.ph)
8. Latest copy of a bill containing the address of the applicant where the PIN, which will be used to activate a digital certificate, shall be mailed; and
9. Consent to verify and share the information submitted.
*(In the absence of UMID-compliant card, ANY TWO of the following cards are allowed as valid IDs based on BSP Circular 608 series of 2008)
● Passport
● Driver’s License
● Professional Regulation Commission (PRC) ID
● National Bureau of Investigation (NBI) Clearance
● Police Clearance
● Postal ID
● Voter’s ID
● Government Service Insurance System (GSIS) e-Card
● Social Security System (SSS) Card
● Senior Citizen Card
● Overseas Workers Welfare Administration (OWWA) ID
● OFW ID
● Seaman’s Book
● Alien Certification of Registration/Immigrant Certificate of Registration
● Government Office and GOCC ID, e.g. Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP ID), Home Development Mutual Fund (HDMF ID)
● Certification from the National Council for the Welfare of Disabled Persons (NCWDP)
● Department of Social Welfare and Development (DSWD) Certification
● Integrated Bar of the Philippines ID
● Company IDs Issued by Private Entities or Institutions Registered with or Supervised or Regulated either by the BSP, SEC or IC
** Please refer to the DICT Department Circular 06, series of 2020 at https://dict.gov.ph/wpcontent/uploads/2020/04/SIGNED_DEPARTMENT_CIRCULAR_NO_6_GUIDELINES_ON_THE_APPLICATION_AND.pdf which provides guidelines on alternative means of application and issuance of PNPKI digital certificates.
ii. Application Process. After completing the documentary requirements the DA official or employee can now proceed to the application proper.
A. Validity of the Digital Signature
a. How long signature?
b. How do DA personnel re-apply for digital signature?
c. When the DA personnel lost his password, will the DA personnel reinstall again the certificate?
d. Why is it important to have a Digital Signature nowadays?
e. Why are digital signatures considered secure?
f. What are the PNPKI Services?
g. What is the importance of Digital Signature?
h. Advantages of Digital Signature
B. PNPKI FAQs
a. What is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)?
b. Why is it called ‘public key’? Does it mean open and unrestricted?
c. Why do I need a PKI?
d. What is a digital certificate?
e. How can I have a digital certificate?
f. Do I have to pay for it?
g. Where can I use a digital certificate?
h. How do I use a digital certificate?
i. Do I have an option not to use it?
j. When can I use a digital certificate?
k. Who can avail of a digital certificate?
l. Can I apply for other people’s certificate?
m. Where can I use a digital certificate?
n. How long can I use the digital certificate?
o. How do I renew and how long is the process of renewal?
p. Where can I store the digital certificate?
q. What types of certificates are issued?
r. What if I lose my certificate?
s. What if the subscriber resigns, retires or exits from government service?
t. What are my responsibilities as digital certificate holder?
u. How long is the application process?
v. Is it possible to have multiple certificates?
w. How big is a digital certificate?
x. What is the best browser to use when using PKI?
y. What is the best email provider to use when encrypting and signing emails?

Draft Guidelines on the use of Digital Payment in all Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Corporations of the Department of Agriculture



MEMORANDUM CIRCULAR
No. ____________________________
Series of 2021
SUBJECT: GUIDELINES ON THE USE OF DIGITAL PAYMENT IN ALL BUREAUS, ATTACHED AGENCIES AND CORPORATIONS OF THE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
The Department Agriculture (DA) is mandated to promote agricultural development by providing the policy framework, public investments, and support services needed for domestic and export-oriented business enterprises.
To fulfill these mandates and to provide the utmost ease, convenience and security to all its clients, the DA introduced the DA portal with an online payment facility where clients can manage and pay their fees/charges online anytime and anywhere so long as there is internet connections.
In line with this, the DA recognizes the emergence of technological advancement in financial transactions and its role in increasing the efficiency, security, and ease of use in making payments.
Section VI (4) of Memorandum Circular No. 2020-06, Series of 2020 of the Anti-Red Tape Authority provides that all Government Agencies are required to set up a payment gateway to accept digital payments (credit cards, debit cards, prepaid/e-money, and/or bank transfer) for the acceptance of all permits, licensing, and other fees. As an immediate short-term solution, electronic payments may be accomplished initially by providing direct payment to the agency’s designated account for such payments after confirming the agency’s capability for matching payments and invoices.
Under Commission on Audit (COA) Circular No. 2013-007, government agency shall acknowledge the electronic receipt issued by the digital payment gateway as proof of payment by the clients. Upon the reconciliation by the Cashier or Authorized Official of the validity of the electronic payment, a separate electronic official receipt (eOR) or a scanned version of the written official receipt shall be issued by the government agency and be transmitted electronically to the payee.
Subsequently, in line with the zero-contact policy of RA No. 11032 or Ease of Doing Business and Efficient Delivery Act of 2018, all agencies provide alternative digital payments options through service agreements with BSP – regulated private and/or public Payment System Providers (PSP) or Electronic Payment and Collection System Providers (EPCSs), such as but not limited to EGov Pay,

Land Bank Link.Biz, GCash, PayMaya, Coins.Ph, DragonPay, Omni-Pay, BancNet, for digital payment acceptance and electronic Official Receipt (eOR) provision, and restrict over-the-counter payments to highly exceptional cases. These service providers will allow agencies to better reconcile payment information through the provision of reference information specific for each transaction, with at least the provision of payment instructions that includes a payee name, payment type (such as license or permit paid for), and a transaction identification number.
These Guidelines shall apply to all payment collection services of the following: Bureau Of Agricultural and Fisheries Engineering, Bureau of Agriculture and Fisheries Standard, Bureau of Animal Industry, Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources, Fertilizer and Pesticide Authority, Bureau of Plant Industry, National Meat Inspection Service, Philippine Fiber Industry Development Authority, National Dairy Authority, National Tobacco Administration, Philippine Coconut Authority, Philippine Fisheries Development Authority, and Sugar Regulatory Commission
1. Electronic Official Receipt (eOR) – refers to a proof of payment generated/issued through an Electronic Payment and Collection System (EPCS) with unique or sequential reference numbers that can be validated using the same system. More specially, the eOR refers to an evidence of payment for collection received by the above mentioned agencies under DA from clients generated through the agency’s electronic collection system.
2. Electronic Payment and Collection System (EPCS) – refers to a system that accepts and processes Electronic Payments, authenticates the payor and payee, validates availability of funds and executes the appropriate debit and credit instructions for the fund source and destination accounts, generates and forward electronic proof of payment or eOR to the payor, or allows secure access thereto and creates, retains and safeguards the resulting detailed electronic transaction records which are accessible by authorized personnel.
3. Originator or client – refers to a person by whom, or on whose behalf, the electronic document purports to have been created, generated and/or sent. The term does not include a person acting as an intermediary with respect to that electronic document.
4. Addressee or DA – A person who is intended by the originator to receive the digital payment. The term does not include a person acting as an intermediary with respect to that electronic document.



5. Intermediary or Payment Service Provider (PSP) – refers to a person who, on behalf of the addressee provides digital payment services to the originator. It is also a bank or non-bank e-money issuer duly authorized by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP)
For quick access to digital payments, the DA shall place in the home page of its website, a hyperlink and/or a Quick Response (QR) Code to their digital payment platforms. The use of QR Codes by PSP is provided for by BSP Circular No. 1055 series of 2019 entitled Adoption of National Quick Response (QR) Code Standard.
Thus, the digital payment may be accessed through the hyperlink and/or a Quick Response (QR) Code of digital payment platforms provided at DA website via https://www.da.gov.ph.
Likewise, the digital payment may be accessed from ___:00 AM to ___:00 PM, Philippine Standard Time (PST), ______ (_______) days a week, subject to service periods, maintenance time, computer, telecommunication, electrical or network failure, and/or any other reasons beyond the control of the DA
1. The client will make digital payment/s to the DA through the use of services provided by the PSP
2. When digital payment has been completed by the client, the DA shall immediately acknowledge receipt of the same through issuance of eOR.
The said eOR shall have the following minimum data content:
a. Name of the Department/ Bureaus/ Attached Agencies issuing the receipt
b. Location and location code
c. Date and time of receipt
d. Nature of collection
e. Amount received
f. eOR Number (a unique and sequential number generated by the system for every eOR issued)
g. Transaction Number (number generated for every transaction accepted by the system which does not necessarily pertain to the generated eOR. It may include cancellation of eOR, etc.)
h. Mode of payment
i. Order of Payment Slip Number or Assessment Number 1

Digital payment shall be deemed complete upon receipt by the client of eOR from the DA that the payment has been accepted/completed
3. In case of error in digital payment, the digital payment service provider or the DA must place within the digital payment system platform an option available to the client to cancel a completed digital payment within 24 hours, if the originator did not intend to make such digital payment. In such a case, the reasons that shall be acceptable for the cancellation of the completed digital payment made by the client shall be, but not limited to, the following:
a. Accidentally clicking/tapping on the option of making an electronic payment.
b. The client erroneously/accidentally paid for the wrong service.
Nothing in this Section shall preclude the DA from allowing a longer period of time for the client to cancel the digital payment completed.
All errors within the system or the transfer of information in digital payments on the part of the DA or digital payment service provider shall not prejudice the client in any manner.
In any case where there is error of payment by the client, the same amount he/she has paid shall revert to is account without any penalty or interest.
4. Collection of the DA shall be deposited to the ________________________________.
1. The DA or digital payment service provider shall have no authority to modify or alter the content of the electronic data message or electronic document received or to make any entry therein on behalf of the client, any third party who shall retain the electronic document or as necessary for the purpose of delivering the service.
2. Denial of the legal effect of payment for the sole reason that it is not in physical form of payment.
3. Making any provision in the terms and conditions to be accepted by the client before proceeding to digital payment which shall have the effect of a waiver of the any of the prohibited acts in this Circular.
All previous issuances inconsistent with this Policy shall be deemed accordingly repealed.
It shall be the duty of the DA – Information and Communications Technology Service (ICTS) to monitor the compliance of digital PSP with the requirements under this Circular.
The provisions under this Circular is without prejudice to application of pertinent laws, rules and regulations being implemented by other government regulatory agencies.
This Circular shall take effect fifteen (15) days after its publication in a newspaper of general circulation and shall be deposited thereafter with the Office of National Administrative Register (ONAR) of the University of the Philippines Law Center.
Done this ___ day of ___________ , 2021 in Quezon City, Philippines.

WILLIAM D. DAR, Ph.D. Secretary

Inspection And Acceptance Policies For The Procurement Of Goods In


MEMORANDUM ORDER
No._______________
Series of 2021
SUBJECT : INSPECTION AND ACCEPTANCE POLICIES FOR THE PROCUREMENT OF GOODS IN THE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE – CENTRAL OFFICE (DA-CO)
These Policies aim to set standards, consolidate and update the existing rules and procedures of the Department of Agriculture (DA) relative to the inspection and acceptance of goods, in line with the Republic Act (RA) No. 9184 and its 2016 Implementing Rules and Regulations (IRR). It also aims to ensure the submission of documentary requirements prescribed by the Government Accounting Manual (GAM) for National Agencies.
Further, the implementation of the herein prescribed policies shall assist and guide the DA Central Office (CO) Inspection Committee (IC) and the Supply and Property Officer/Section to ensure that the delivered goods are properly inspected and received for the use of recipient units. Likewise, to equip the inspectors with updated knowledge and sufficient understanding and discipline in the area of inspection which is a crucial element of the procurement process.
These Policies shall apply to the pre-delivery, delivery, and post-delivery inspection and acceptance of procured goods of the DA-CO, including purchases through cash advances/reimbursement and others being bought regardless of procurement methods and value/amount.
The Secretary of the DA shall designate an IC through a Special Order to be composed of the following:
The Team Leader and Assistant Team Leader of the IC shall occupy a permanent position who shall be responsible to lead the inspection of all procured goods of the DACO.
Moreover, the Team Leader or Assistant Team Leader shall be the signatory in the inspection portion of all the Inspection and Acceptance Report (IAR) (Annex “A”) regardless of the amount and procurement method. In the absence of the Team Leader, the Assistant Team Leader shall attend in the inspection and sign in the said IAR in order to ensure that no delay in the inspection service.

The General Services Division (GSD) Permanent Member, who should occupy a permanent position, is indispensable pursuant to its explicit responsibility in providing support services relative to the supplies and properties of the DA-CO, aside from the custody and accountability for all supplies and properties. The GSD Permanent Member shall also focus on the receiving and checking with respect to the quantity of the units/items delivered in accordance with the approved specifications.
All Regular Members, with permanent status, are selected from the DA-CO for their expertise and technical knowledge to the subject goods. Their permanence and availability are crucial to avoid delay in the inspection of supplies and materials delivered.
The Internal Audit Service (IAS) personnel, as regular member, has a vital role in ensuring checks and balances in ethical, economical, efficient and effective operations within the DA. This will help strengthen the accountability among the concerned personnel and improve the quality and quantity of outputs necessary in the delivery of public service. Further, there will be ascertainment that the assets and other resources of the DA are fully accounted for and are safeguarded from any losses.
The IC shall perform the following functions:
1. Attend the Pre-Inspection Conference wherein specific tasks are designated to each member in accordance with inspection references and accomplish the Pre-Delivery Inspection Report (Annex “B”);
2. Attend the Post-Inspection Conference wherein the findings and results of the inspection are duly discussed and accomplish the Post-Delivery Inspection Report (Annex “C”);
3. Prepare the inspection references prior to the scheduled inspection such as but not limited to the following: a) copies of technical specifications; b) inspection and test protocols sourced from the bidding documents of the project; and c) the necessary measuring and testing instruments;
4. Familiarize with the technical specifications of the goods for inspection and test protocols before proceeding to the inspection site;
5. Check the completeness and authenticity of the documents presented by the supplier;

6. Conduct physical inspection of the goods, and check whether the technical specifications, quantity and standards as indicated in the perfected Contract/Purchase Order/Work Order are met;
7. Perform trial and operation test on equipment, computers and other related goods. In addition, require the supplier to demonstrate operation of the equipment and observe its performance;
8. Check and verify the inclusion of warranty certificate and instructional manual;
9. The Team Leader or Assistant Team Leader shall sign the IAR indicating the condition that the delivery is in accordance with the approved quantity, quality and specifications.
10. Prepare and submit promptly a report to the End-User and Head of the Procuring Entity (HoPE) whenever findings or assessment are found not in accordance with the contracted quantity and specifications;
11. Submit assessment reports and policy recommendations concerning the inspection;
12. Attend meetings, conferences and training programs as may be required by the DA; and
13. Perform other duties and responsibilities related to the foregoing.
The inspection shall not proceed without the presence of the Team Leader or Assistant Team Leader and the members thereof
a. Upon delivery, the GSD shall sign the “Received” portion of the Delivery Receipt from the supplier and forward the same to the IC for inspection of the goods.
b. A brief pre-inspection conference shall be conducted to designate the specific tasks to the IC in accordance with inspection references.
c. The pre-delivery inspection of goods shall be conducted by the IC and the IAR shall be accomplished at this stage by the members thereof. The findings and result of the pre-delivery inspection, including the inspection method used, shall be summarized in the Pre-Delivery Inspection Report

a. The IC shall then conduct the inspection of the delivered goods in accordance with the approved technical specifications and the applicable manual or inspection and test Protocol, if any.
b. If the goods conform to the technical specifications and the delivery receipt, the Team Leader or the Assistant Team Leader of the IC shall sign the IAR. Rejected goods, if any, shall be notated in the IAR and returned to the supplier for rectification or replacement.
c. The Team Leader or the the Assistant Team Leader shall sign, specify the date of inspection, and put a check “” mark in the “inspection” portion of the IAR, indicating that he/she has inspected, verified and found in order the items delivered as to quantity and specifications. Then, the Supply and Property Officer/Section shall acknowledge receipt of the items by indicating in the “Acceptance” portion of the IAR, his/her name, signature, date of acceptance, and a check “” mark whether the delivery is complete or partial as to quantity;
d. Pursuant to GAM for National Government Agencies, the IAR shall be prepared in four (4) copies and distributed as follows:
Original – Supplier (to be attached to the Disbursement Voucher)
Copy 2 – Inspection Officer/ Committee
Copy 3 – Accounting Division/Unit (to be attached in the Journal Entry Voucher setting up payables)
Copy 4 – Supply and Property Section/Unit
a. A post-delivery inspection shall be conducted by the IC during installation, commissioning, start up, or initial use within the warranty period stated in the contract or purchase order or work order, which commences to run from the date of issuance of a Certificate of Final Acceptance (Annex “D”). This post-delivery inspection shall not bar claims for any latent or hidden damage that may be exhibited during the warranty period which shall render the supplier liable for replacement.
b. The post-delivery inspection is intended to ensure that all accepted goods are free from manufacturing defects and with the right quality as described in the technical specifications.
i. Goods are considered defective when they are “unfit for the use for which it is intended” or its fitness for such use is diminished to such an extent that, had the vendee been aware thereof, he would not have acquired it or would have given a lower price for it ” 1


ii. Under the Government Procurement Manual (GPM) Volume II, a defect can either be(i) a patent defect, which is one that is apparent to the buyer on normal observation, or (ii) a latent defect, which is one that is not apparent to the buyer by reasonable observation. Both latent and patent defects are covered by the warranty observation expressly required in RA No. 9184 and its 2016 IRR
iii. Ordinary wear and tear due to normal usage of the goods is excluded from the coverage of the supplier’s warranty obligation.
iv. Upon completion of inspection, the IC shall prepare a Post-Delivery Inspection Report stating therein the quality and condition of the goods and a recommendation to the HoPE for claims against the warranty should there be manufacturing defects discovered in the goods inspected.
The documents enumerated hereunder shall be used to record and report inspection and acceptance activities of the DA-CO. Each of these documents should present clearly and truthfully the information relating to the transaction or activity that it is meant to represent and validate. Only the signing officer who is physically present may sign the form. By affixing his/her signature thereto, he/she effectively certifies that he/she personally witnessed the delivery and/or inspection and acceptance of goods, and that the details and information provided in the documents are true and correct of his personal knowledge.
1. Pre-delivery Inspection Report
This document shall state, among others, the findings and result of the pre-delivery inspection. It shall state the quantity of accepted and rejected items, if any, and the reason(s) for rejection.
2. Inspection and Acceptance Report 2
This form shall be used to document the inspection and acceptance of goods. The inspection portion of the IAR must be signed by the Team Leader or the Assistant Team Leader. The acceptance portion must be signed by the the Supply and Property Custodian, who must be physically present during the inspection.
3. Post-Delivery Inspection Report
This report presents the inspection conducted by the IC within the warranty period for the purpose of insuring that the goods received are free from manufacturing defects. It shall state briefly the condition of the goods as inspected and the recommendation to the HoPE for claims against the warranty should there be manufacturing defects discovered.

2 Appendix 62, GAM Vol. 2

This document certifies that the goods had been inspected and accepted as reflected in the IAR, and that the goods conform to the technical specifications as stipulated in the contract. The issuance of this certificate shall cause the release of the performance security, provided DA-CO has no claims against the supplier. It must be prepared and certified by the Supply and Property Officer/Section and noted by the end-user.
The HoPE shall continuously gather feedback and monitor the implementation of this Order.
The IC shall ensure that these Policies are strictly enforced in the conduct of inspection and acceptance of goods procured by the DA-CO. Reports or recommendations may be submitted to the HoPE for further enhancement of these Policies Reports may include practical observations made, difficulties or issues encountered, assessment of the adoption of procedure and proposals for additional measures.
All previous issuances inconsistent with these Policies shall be deemed accordingly repealed.
This Order shall take effect immediately and shall remain in force until revoked in writing.
Done this _________ day of __________________ 2021.
WILLIAM D. DAR, Ph.D. Secretary


Supplier Project
Contact No.
Date of Inspection

Notes, if any:
Team Leader/Assistant Team Leader Inspection Committee


Supplier
Project
Contact No.
Date of Acceptance
Warranty Period

Notes, if any:
Team Leader/Assistant Team Leader Inspection Committee
This is to certify that the units of for the Project ____________ under Contract No. , and with the total Contract Price of ______________________________________________ (Php_______) were inspected and accepted as reflected in the Inspection and Acceptance Report dated ______________________.
It is further certified that the said goods conform to the technical specifications stipulated in the Contract.
This Certificate is hereby issued for the purpose of releasing the performance security to the Supplier, _________________________________________________.
Issued this ____ day of _____________________, 2021.
CERTIFIED BY:

Supply and Property Officer/Section
NOTED BY:
End-User


1. Financial and Management Service
2. Administrative Service


The Financial and Management Service (FMS) is the Department’s vital support service responsible for handling the budgetary, financial, and management improvement matters of the Department. Based on existing laws, rules and regulations, it has a central role to play in: (1) providing effective and efficient procedures to safeguard public funds and assets; (2) ensuring timely release of public funds; and (3) in providing top management critical information in resource decision making.
The FMS provides management with reliable, timely and accurate financial reports, data and analysis for information, decision-making, planning, control and reportorial obligations to government instrumentalities and outside interested parties.
FUNCTIONS
• Coordinate with the Planning and Programming Division of the Planning and Monitoring Service regarding the preparation of agency plans and programs.
• Conduct the regular monitoring of fund releases and disbursements made by the operating units/ offices under the Department.
• Oversee the preparation of budgets and financial plans with all DA operating units/offices.
• Direct close coordination with the DBM, COA, Bureau of Treasury, Congress and other fiscal agencies of the National Government.
• Conduct consultations/coordination with all the operating units/offices of the Department with regard to their fiscal requirements.
• Develop plans and programs relative to management improvement in the Department.
• Examine the administrative organization of the Department and provide recommendations for improvement.
• Maintain and update the Department organization and other manuals.
• Conduct management surveys of the organizational structure, manpower and operations, and conduct studies on special problems, as assigned.
• Review existing methods, systems and procedures/processes, and provide recommendations for improvement.
• Develop new and improved management systems and provide staff supervision over the implementation of such improvements, as well as conduct trainings on the application of the system/s.
• Develop staffing standards and manpower requirements for the department.
• Perform such other functions as may be provided by law.
Review of Standard Operating Procedures
• Based on issuances of new circulars, memoranda and orders affecting government procedures, review existing Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) manual.
• Validate with concerned offices the effect of these new issuances on their operations/ functions.
• Incorporate the steps/procedures essential to the transaction/process and updates the existing SOP manual.
• Write the draft SOP of that particular transaction.
• Review and edit the draft SOP.
• Approve the draft SOP.
• Finalize the SOP of a particular transaction.
OFFICE OF THE SECRETARY
Issue Order Re : Updating of SOP
Special Order Directing the Management Division to update the Manual
OFFICE OF THE
OFFICE OF THE
Preparation/Updating of Organizational Structures and Functions
• Review existing structures, issuances and circulars to determine their obsolescence.
• Validate with concerned office any changes/modifications in their organizational structures, functions and/or activities in conformity with the new issuances.
• Update existing structures or make a draft of the organizational structure/functions of the office concerned based on their submission.
• Review and edit the written materials.
• Approve the draft organizational structure and functions.
• Finalize the manual.
FUNCTIONS
• Monitor budget utilization throughout the Department, analyze financial data to ensure the effective and efficient use of public funds, and provide the top management timely and accurate data for sound decision making.
• Consolidate and prepare the annual budget proposals, provide assistance to legislators in the authorization of the agency budget, and prepare and submit budget execution documents to oversight agencies.
• Prepare, for the Central Office, the Statement of Allotment Obligation and Balances, and other Financial Accountability Reports.
• Analyze, consolidate and prepare the Department-wide Statement of Allotment Obligation and Balances and other Financial Accountability Reports.
• Analyze, consolidate and prepare Department-wide annual budget proposals, activity recasts, program structure changes, allotment and all other budgetary documents, as required by oversight agencies.
• Design, develop, implement and/or update budget monitoring tools and standards.
• Provide technical assistance to top management in the presentation of the Department’s budget to legislators and other oversight committees.
• Responsible for the collection, analysis and documentation of budget data that enable users and top management to make sound decisions.
• Responsible for reports generation as regard to the financial position vis-à-vis appropriation of the Department.
• Performs other functions as maybe provided by law.
Preparation of Budget Proposals
• Issue the Budget Call/Budget Ceiling.
• Prepare and issue guidelines for the preparation of plan and budget proposals.
• Prepare the plan and budget proposals based on issued guidelines and baseline budget.
• Present budget proposal in the DA internal Budget Hearing.
• Conduct internal Budget Hearings.
• Revise plan and budget proposals and submit the proposals to the PMS/FMS.
• Review and consolidate plan and budget proposals and return it to the concerned agency for revision, if necessary.
• Approve and submit the budget proposals to DBM.
• Evaluate/analyze the DA's Budget Proposal and conducts Technical Budget Hearings.
• Prepare the Budget Recommendation for DA's comment and/or revision.
• Review and consolidate the Recommended Budget or return it to the concerned agency for revision.
• Analyze the DA's comment and/or revisions and prepare and submit the National Expenditure Program (NEP) to the President.
• Submit the NEP to Congress.
• Evaluate the proposal and conduct Congressional Budget Hearings then draft House Bill and submit to Senate.
• Evaluate the NEP against House Bill, conducts Senate Budget Hearings and draft a version of the Senate Bill.
• Conduct conference to come up with a common Bill.
• Sign the Bill into law called the General Appropriations Act or GAA.
TECHNICAL STAFF BUDGET AND PLANNING DIV.
Formulates guidelines in crafting Plans and Budget Proposals upon receipt of the Budget Call
• Provide copies of GAA to government agencies.
ADMINISTRATIVE OFFICER
Conducts on-line submission (per OUs account) of actual obligation through the DBM website
Conducts on-line submission of budget proposal (OSBP) in the DBM website
Submits the consolidated and OSBP generated budget proposal to DBM
Presents the consolidated budget proposal to CSO
Prepares other documents as needed and instructed during technical budget hearing
Request for Obligation of Allotments
Conducts and attends DA-DBM consultative Review
Submits forward estimates to DBM
Reviews, analyzes and consolidates the proposals submitted by DA Operating Units
Submits all budgetary requirements needed by Senate and Congress
• Receive and record the Obligation Request and Status (ORS).
• Process ORS with complete supporting documents.
• Posts Transaction in the Budget System and Central Control (Unified Account Code Structure (UACS)/Object Code).
• Review the ORS with complete supporting documents.
• Sign the ORS.
• Certify the copy.
• Release the documents to Accounting Division (Obligation of Allotments).
Conducts internal budget hearing for the Department
Conducts technical review of plans and budget proposals by cluster
Conducts briefing with Secretary in preparation to Congress and Senate Hearing
Attends budget briefing/hearing as requested by various legislators
Endorsement of Special Budget Request (SBR)
• Receive the Special Budget Request.
• Check the attached supporting documents as to completeness and appropriateness.
• Review/process/analyze and prepare endorsement to the DBM.
• Review the endorsement letter and affix initial on the document. e. Sign the SBR.
• Record the endorsement letter in the log book.
• Forward the endorsement and SBR to office of FMS Director for initial.
ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANT START
Receives and checks the completeness of the required supporting documents
ADMINISTRATIVE OFFICER
Analyzes the correctness of the attachments’ content; and prepares the endorsement letter
ASSISTANT CHIEF, BUDGET DIVISION
REVIEWS
Returns to budget analyst for revision
START Preparation of Memorandum regarding Submission of BEDs 1 & 3, ) per Operating Units (OUs) based on NEP
ADMINISTRATIVE OFFICER
Affixes initial on the second page of the endorsement letter to certify that documents attached are complete and endorsement is correct.
Signs the briefer attached and affixes initial on the second page of the endorsement letter CHIEF, BUDGET DIVISION
Conducts online submission of BEDs 1 & 3 (per OUs account) in the Unified Reporting System (URS) of DBM
Reviews and anlayzes the URS generated reports (BEDs 1 & 3) of OUs
Print the URS generated consolidated reports and the per OUs ; prepares endorsement letter
CHIEF, BUDGET DIVISION
Signs the URS generated BEDs 1 & 3 as the preparer: - Central Office - Consolidated
Affixes initial: - Endorsement letter
ASEC. FOR FINANCE
Affixes initial for the approving authority:
- Consolidated URS generated BEDs 1 & 3
- endorsement letter
Signs the URS generated BEDs 1 & 3 as the preparer: - Central Office - Consolidated DEPARTMENT CHIEF ACCOUNTANT
Signs the URS generated BEDs 1 & 3 as the preparer: - Central Office - Consolidated PLANNING OFFICER
USEC. FOR ADMIN & FINANCE
Signs the URS generated BEDs 1 & 3 as the approver: - Consolidated
Signs the endorsement letter
Issuance of Advice of Sub-Allotment (ASA)
ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANT
Records the signed endorsement letter for monitoring
DIRECTOR, FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Signs the URS generated BEDs 1 & 3 as the approver: - Central Office
Affixes initial for the approving authority:
- Consolidated URS generated BEDs 1 & 3 - endorsement letter
Submits duly endorsed, signed and printed copy of the Consolidated CPR to DBM and BTr LIAISON OFFICER
• Receive the Memorandum request and check the attached supporting documents.
• Review/process/analyze and prepare/assign the control number of the ASA.
• Record the ASA to the respective individual electronic control and RAO
• Enter the ASA in the central master control.
• Examine and review the ASA and affix signature on the document.
• Record the ASA in the log book and forward it to the office concerned.
• Approve the ASA and forward it to Budget Division.
• Receive the signed ASA and prepare 3 photocopies for distribution.
• Make an electronic copy of the ASA and forward it to Records Division.
• Mail the original approved ASA and furnish copies to COA and Accounting Division.
ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANT
Records the endorsement letter and forwards to the Office of the Director for Finance for initial.
DIRECTOR, FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Receives the endorsed printed and signed copy of the Consolidated CPR DEPARTMENT OF BUDGET AND MANAGEMENT (Receiving)
ADMINISTRATIVE OFFICER START Preparation of Memorandum regarding Submission of Cash Planning Report (CPR) per Operating Units (OUs)
DEPARTMENT CHIEF ACCOUNTANT
Signs the CPR as the preparer: - Central Office - Consolidated
Analyzes and consolidates submitted CPR based on NEP
Online submission of the consolidated CPR in the Bureau of Treasury (BTr) website
PLANNING OFFICER
Signs in coordination with the prepaparer: - Central Office - Consolidated
Prints the manually consolidated CPR together with the submission of the OUs; and prepares endorsement to DBM
CHIEF, BUDGET DIVISION
Signs the CPR as the preparer: Central Office Consolidated
Affixes initial: endorsement letter
USEC. FOR ADMIN & FINANCE
Signs the CPR as the approver: - Consolidated
Signs the endorsement letter
ADMINISTRATIVE ASSISTANT
Records the signed endorsement letter for monitoring
DIRECTOR, FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Signs the CPR as the approver: Central Office
Affixes initial for the approving authority: - Consolidated CPR - Endorsement letter
LIASON OFFICER
Submits duly endorsed, signed and printed copy of the Consolidated CPR to DBM and BTr
ASEC. FOR FINANCE
Affixes initial for the approving authority: - Consolidated CPR - Endorsement letter
DEPARTMENT OF BUDGET AND MANAGEMENT (Receiving)
Receives the endorsed printed and signed copy of the Consolidated CPR
FUNCTIONS
• Advise top management on financial matters.
• Process all claims for payment.
• Verify the correctness and accuracy of reports related to finance submitted by the various operating units under the Department.
• File and maintain basic and subsidiary accounting records and books of accounts of the Office of the Secretary to reflect accurate and current financial information required by existing auditing rules and regulations and by management.
• Prepare, analyze and interpret Financial Statements and Reports.
• Provide adequate and timely financial information critical to the management of the Office of the Secretary.
• Perform such other functions as may be provided by law.
1. Disbursement Section
• Preparation of Disbursement Vouchers and processing of all claims for payment and insuring validity, propriety, mathematical accuracy and completeness of documents.
• Verification of liquidation vouchers/reports as to its accuracy and completeness of supporting documents.
• Monitoring and reporting of Accounts Payable.
• Preparation of remittances to government regulatory bodies (GSIS, HDMF, BIR, etc.) and insuring its prompt filing and remittances.
• Preparation of certificates of remittance/deductions to be issued to employees and other concerned parties.
• Preparation of Certificates of Tax Withheld for issuance to concerned parties.
2. Bookkeeping Section
• Analysis and verification of financial transactions as to correctness of journal entries including mathematical accuracy.
• Recording and posting of financial transactions from the source documents to the books of original entry.
• Preparation of financial statements such as: Trial Balance; Balance Sheet; Income Statement; Cash Flow; Detailed breakdown of Disbursements; Statement of Government Equity; Schedule of Subsidiary Ledger Balances; Statement of Bank Reconciliation; Aging of Accounts Payable; Aging of Cash Advances; and Notes to Financial Statement.
- Monthly monitoring of cash advances and preparation and issuance of demand letters thereof.
3. Consolidation and Analysis Section
• Financial analysis and interpretation of all financial reports for all funds of the fourteen (14) Regions, seven (7) Bureaus and three (3) Foreign Assisted Projects under the Department.
• Consolidation of financial statement and other financial reports.
• Provide reports to government regulatory bodies (COA, DBM, Congress, Senate, etc.).
• Monitoring and reconciliation of all funds transferred to Bureaus, RFUs, Attached Agencies and Corporations.
• Monitoring and consolidation of all reports of compliance of annual audit findings and observation memoranda of COA.
• Consolidation of reports for all the Bureaus and RFUs under the Department, as required from time to time.
• Preparation and reconciliation of Notice of Transfer Allocation (NTA) with Bureaus and Regional Offices under the Department.
• Analysis and posting of financial transactions to subsidiary ledgers or different funds.
• Consolidation of action taken on the Audit Observation Memoranda (AOM) and Consolidated Annual Audit Report issued by COA.
• Preparation/submission of various reports aside from the regular reports being requested by COA and DBM from time to time.
• Monitoring of cash utilization of Regions and Bureaus under the Department.
1. Certification of Availability of Funds
• Receive the ORS from the Budget Division and assign a reference number.
• Evaluate and assess claims for payment and its attached supporting documents and affix initial.
• Review the evaluation and assessment made by the staff and affix initials.
• Confirm and/or add comments as to lack of requirements.
• Update the data in the Tracking System.
• Release the ORS and CAF to the concerned office.
2. Air Fare (under special arrangement with Airlines Companies)
• Receive the claim (ORS) and assign a reference number.
• Evaluate and assess the claim and attached supporting documents then affix initial.
• Check for unliquidated travel claims/unaccounted plane tickets.
• Review the evaluation and assessment made by the staff.
• Confirm and/or add comments as to lack of requirements.
• Update the data in the Tracking System.
• Release Claims (ORS) and PAL Travel Order to the concerned employee.
• Receive the ORS from Budget Division and assign a reference number.
• Evaluate and assess the claim and its attached supporting documents then affix initial.
• Review the evaluation and assessment made by the staff and affix initial.
• Confirm and/or add comments as to lack of requirements.
• Sign the documents.
• Update the data in the Tracking System.
• Release the Disbursement Voucher to the concerned employee and/office
Above Php 5M to Php 50M Php 500k and below
Regional Director, Bureau Director or Head of Attached Agency and Corporation
Above Php 500k to Php 5M
4. Liquidation Reports
Assistant Regional Director, Assistant Bureau Director or Assistant Head of Attached Agency and Corporation
RECEIVING AND RELEASING PERSONNEL
Liquidation Report (LR) and Assigns Reference # and LR#
Regional Director, Bureau Director or Head of Attached Agency and Corporation
Assistant Regional Director, Assistant Bureau Director or Assistant Head of Attached Agency and Corporation supervising the Finance and Administration Unit
• Receive the Liquidation Report and assign a reference number.
• Evaluate and assess the claim and its attached supporting documents and affix initial.
• Review the evaluation and assessment made by the staff and affix initial.
• Confirm and/or add comments as to lack of requirements.
• Sign the documents.
• Update the data in the Tracking System.
• Release the Liquidation Report to the concerned employee.
& Assesses Claim and Supporting Documents
5. Validation of Bank Account and Preparation of Letter of Intent
• Receive the Liquidation Report and assign a reference number.
• Evaluate and assess the claim and its attached supporting documents and affix initial.
• Review the evaluation and assessment made by the staff and affix initial.
• Confirm and/or add comments as to lack of requirements.
• Sign the documents.
• Update the data in the Tracking System.
• Release the Liquidation Report to the concerned employee.
Administrative and Finance Division or the next Higher Position supervising the Administration and Finance Group
The Administrative Service (AS) provides the Department with economical, efficient and effective administrative support services in the policy formulation and implementation, particularly on areas of personnel administration and management, human resource development, records, information, general services/security and procurement.
• The Administrative Service spearheads the continuing development of Department-wide standardized systems and procedures to improve the quality and efficiency of administrative services at all levels of implementation. It is responsible for managing the assets of the Department, generating income from these assets and providing an efficient procurement program.
• The Administrative Service provides staff support services in administration and management.
The Administrative Service has six (6) divisions:
• Personnel Division
• Procurement Division
• Records Division
• Human Resource and Development Division;
• Agriculture and Fisheries Information Division; and
• General Services Division.
FUNCTIONS The Personnel Division shall be responsible for providing the Department with economical, efficient and effective service relating to human resource management and administration.
• Advises management on human resource management policies and administration;
• Assists the management in the formulation of human resource policies and programs;
• Develops and administers human resource programs which include selection and placement, classification and pay, performance evaluation, personnel relation and discipline, leave administration and employee welfare benefits, awards and incentives;
• Acts on all matters concerning recruitment, placement, promotions, transfer, attendance, performance evaluation, leave of absence, appointments and other human resource concern;
• Maintains personnel records and statistics; and
• Performs such other functions as may be provided by law.
Step 1
• Posting of Application Schedule and Requirements
• 18-25 Years Old
• Good Health Condition
• Must not be related by consanguinity or affinity to any offical or employee in the office
• Must not be a previous participant to the DA SYIP/GIP (no participant shall be recruited/ accepted more than once)
• For Students : College level or high school graduate
• For Out-of-school-youth : should not have ceased for more than 2 years
• For differently abled individuals : shall be able to perform office works (e.g. typing/ encoding, sorting, photocopy. etc.
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
• Distribution of forms and interview
• Examination
• Posting of successful applicants
• Orientation and deployment
• Actual work in offices (45 working days)
• Closing ceremony
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
• Submission of required documents
• Endorsement from school addressed to the highest HRMO
• Curriculum Vitae / Resume of Student Applicant
• Telephone call coordination with offices for possible assignment / placement of the student trainee
• Preparation and approval of endorsement letter to the concerned office
• Acceptance by the student applicant / coordination with the school
• Inform student application of his/her acceptance to the office
• Place of Assignment
• Possible scope of work
• Orientation and signing of the rules and regulations for on the job trainees
• Report for first day of training
The Personnel Division shall notify the newly appointed or promoted employee with regard to his/her approved appointment and shall require him/her to submit the following requirements:
Newly appointed employees
• Fully accomplished Personal Data Sheet (CSC Form 212, Revised 2017)
• Attachment to CSC Form 212 (Work Experience Sheet)
• Authenticated Eligibility/License
• Authenticated Diploma and Transcript of Records
• Medical Certificate (CS Form No. 211, Revised 2018)
• Three (3) original copies of Sworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net Worth (SALN)
• NBI Clearance
• Individual Performance Commitment and Review (IPCR) –Targets
• Office Clearance (Contract of Service under DA-CO, Bureaus, and Attached Agencies)
• Resignation Letter (Contract of Service under DA-CO)
• Position Description Form (In new position)
• Oath of Office
• Assumption to Duty
Promoted employees (within DA-CO)
• Fully Accomplished Personal Data Sheet (CS Form 212, Revised 2017)
• Attachment to CSC Form 212 (Work Experience Sheet)
• Authenticated Eligibility/License
• Position Description Form (In new position)
• Oath of Office
• Assumption to Duty
Promoted employees (outside DA-CO)
• Fully Accomplished Personal Data Sheet (CS Form 212, Revised 2017)
• Attachment to CSC Form 212 (Work Experience Sheet)
• Authenticated Eligibility/License
• Authenticated Diploma and Transcript of Records
• Medical Certificate (CS Form No. 211, Revised 2018)
• Three (3) original copies of Sworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net Worth (SALN)
• NBI Clearance
• Office Clearance
• Authority to Transfer
• Position Description Form (In new position)
• Oath of Office
• Assumption to Duty
01
02
The employee signs his/her approved appointment paper.
Where to get?
• Personnel Division
All new/promoted employees shall attend the 2 day classroom-type orientation.
Another orientation shall be attended by rank and file employees
To be conducted by the Human Resource Development Division (HRDD).
Components:
• Overview of the DA-CO as an organization and generally includes the history, vision, mission, culture, organizational structure, and its mandates.
• Topics on leave privileges, employee benefits, Pagibig benefits, GSIS benefits, and other workplace practices.
• Strategic Performance Management System
• Learning and Development
• RA 6713 (Rules Implementing the Code of Conduct and Ethical Standards for Public Officials and Employees)
03
The employee shall submit additional requirements for the processing of initial salary.
04
Issuance of agency employee number and registration in the biometrics system/ bundy clock by the Personnel Division.
Newly appointed employee:
• Pag-ibig ID
• Philhealth ID
• BIR 1905
• BIR 2316
Promoted employee (outside DA-CO)
• Pag-ibig ID
• Philhealth ID
• BIR 1905
• BIR 2316
• Certificate of last salary received
• Certificate of Leave Credits
• Service Record
• On the first week at work, the employee shall be officially introduced to his/her place of assignment and will be exposed to the actual operations of his/her division.
• The Supervisor shall discuss the division/office targets, roles, and responsibilities as well as performance expectations/work targets and provide the schedule of activities for the new employee. The Supervisor shall also mentor the new employee on the crafting of the Individual Performance Commitment and Review (IPCR) to ensure that he/she understands the targets.
• The immediate superior shall discuss the six (6) months probationary period.
• A progress review meeting shall be conducted at the end of the employee’s first month of service. The Supervisor and his/her other subordinates shall provide feedback on the employee’s performance.
• During the first three (3) months, the new employee shall attend learning and development interventions for him/her to skillfully dispense his/her duties and responsibilities.
• Performance Evaluation. On the last days of the third month, the supervisor shall meet with the new employee to discuss the latter’s progress. It shall be stressed that as a new employee, he/she is under the probationary status. As such, he/she is required to have a “Very Satisfactory” ratings on his/her performance evaluation.
1. A performance check shall be conducted to ensure that the new employee performs his/her best. Learning and development interventions shall be continuously provided.
2. Upon completion of the six (6) months onboarding process, the new employee’s performance shall again be evaluated by the supervisor. The results of the IPCR and behavior evaluation report shall serve as basis for his/her retention or development.
1. There shall be equal employment opportunity for men and women at all levels of position in the agency, provided they meet the minimum requirements of the position to be filled.
2. The Unified Merit Promotion Plan shall cover positions in the first, second and third levels and shall also include original appointments and other related personnel actions.
3. When a position in the first, second or third level becomes vacant, applicants for employment who are competent and qualified shall be considered for permanent appointment.
• Filling of vacant positions in the Department shall be made after compliance with the required at least ten (10) calendar days of publication and posting of the said vacant positions.
• The publication of a particular vacant position shall be valid until filled up but not to extend beyond nine (9) months reckoned from the date the vacant position was published.
4. The following positions are exempt from the publication requirement:
• Primarily confidential positions;
• Positions which are policy determining;
• In case of reorganization;
• Highly technical positions;
• Other non-career positions;
• Third level positions (Career Executive Service); and
• Positions to be filled by existing regular employees in the agency in case of reorganization.
5. Human Resource Merit Personnel and Selection Board (HRMPSB) for first and second level positions shall be established in every agency.
6. All candidates for appointment to first and second level positions shall be screened by the HRMPSB.
7. For vacancies in the first and second levels, all qualified next-in-rank employees shall be automatically considered candidates for promotion to the next higher position. Those who are qualified but not next-in-rank shall have to apply in writing.
8. The comparative competence and qualification of candidates for appointment shall be determined on the basis of:
8.1 PERFORMANCE
• For appointment by promotion, the performance rating of the appointee for the last rating period prior to the effectivity date of the appointment should be at least very satisfactory.
• For appointment by transfer involving promotion, the performance rating for the last rating period immediately preceding the transfer from the former office or agency should be at least very satisfactory.
8.2 EDUCATION AND TRAININGS
• include educational background, successful completion of training courses accredited by the Civil Service Commission, scholarships, training grants and others which much be relevant to the duties of the position to be filled.
8.3 EXPERIENCE AND OUTSTANDING ACCOMPLISHMENTS
• include occupational history, relevant work experience acquired either from the government or private sector and accomplishments worthy of special commendation.
8.4 PSYCHO - SOCIAL ATTRIBUTES AND PERSONALITY TRAITS
• refer to the characteristics or traits of a person which involve both psychological and social aspects. Psychological includes the way a person perceives things, ideas, beliefs and understanding and how such person acts and relates these things to others and in social situations.
8.5 POTENTIAL
• refers to the capacity and ability of a candidate to assume the duties of the position to be filled and those of higher or more responsible positions.
The Distribution of percentage weights are allocated as follows:
To join the Department of Agriculture, you must have undergone the screening process for the recruitment and selection of its personnel, in accordance with standards and guidelines set by the Civil Service Commission as the central personnel agency of the government.
When screening applicants, the department uses qualification standards for a class of positions in terms of education, training and experience, civil service eligibility, psychosocial attributes, potential and other qualities required for efficient performance.
Applicants should submit complete set of required documents:
1. Personal Data Sheet (PDS);
2. CSC Eligibility/Licensure Exam (PRC);
3. Diploma & Transcript of Records;
4. Certificate of trainings/seminars attended;
5. Certificate of Employment (for non gov’t applicants);
6. Service Record (for gov’t employees);
7. Performance Evaluation (IPCR) for applicants applying for promotion; and
8. S.O./designations that an applicant is performing managerial or supervisory functions (for chief/assistant chief of division positions).
1. Evaluation of applicants based on documents submitted;
2. Qualification Assessment Forms of applicants will be forwarded to the Division Chief (DC) concerned where vacancy exists for further evaluation. The DC will rate the applicants in two (2) factors: Psychosocial attributes and potentials by administering exam and/or interview;
3. Upon the return of the duly accomplished evaluation form, the PSB Secretariat (Personnel Division) will rank the applicants according to the results submitted by the Division Chief;
4. The Personnel Selection Board will convene, evaluate and interview applicants and come up with the shortlist of candidates;
5. Short list of candidates will then be forwarded to the appointing authority for signature; and
6. Preparation of appointment.
Publication of Vacant Positions Checking of
Documentary Requirements
The Department shall continuously search, screen and reward deserving employees to motivate them to improve the quality of their performance and install excellence in public service. As such the following types of incentives shall be regularly awarded:
1. Loyalty Award - granted to an employee who has served continuously and satisfactorily the agency for at least ten (10) years. The recipient shall be entitled to cash award of P1, 000.00 per year. Succeeding awards shall be given every five (5) years thereafter. Aside from cash award and plaque, a lap emblem/loyalty pin/pendant/ring in the amount not exceeding P10, 000.00 shall be given.
Other tokens such as watches, necklace with pendant, ring and the like not exceeding the amount of P15,000.00 may also be given to those employees who have rendered twenty five (25) to forty (45) years of service, subject to the approval of the Committee and funds availability.
2. Personnel Development Award - This award shall be given to officials and employees of the Department of Agriculture who have finished Bachelors, Masteral or Doctoral Degrees through their own personal expenses. The award shall be:
10,000.00 for Bachelor’s Degree
15,000.00 for Masteral Degree
20,000.00 for Doctoral Degree
Awarding shall be done during the DA Anniversary Celebration.
3. Length of Service Incentive - given to an official/employee who has rendered at least three (3) years of continuous satisfactory service in the same position. The salary adjustment shall be incorporated pursuant to Circular No. 1 s. 2012 issued jointly by the Civil Service Commission and Department of Budget and Management under Section 6 thereof.
4. Performance-Based Bonus - given to officials/employee in accordance with their contribution to the accomplishment of the Department’s overall targets and commitments to motivate higher performance and greater accountability. This incentive shall follow relevant existing guidelines.
5. Other incentives which the DA PRAISE Committee may recommend on the basis of special achievements, innovative approaches to assignments, exemplary service to the public and recognition by an outside group of a particular achievement.
To develop, capacitate and retain highly competent and professionalized DA personnel for effective and efficient public service delivery. It plans, programs, conducts and evaluates training programs and implement other HRD intervention and activities in the department.
FUNCTIONS
• Formulates and recommends policies, plans and programs for the development of the human resource program of the department;
• Prepares SOP/guidelines for the management, operation, implementation and evaluation of the human resource program of the Department;
• Arranges, facilitates, conducts and coordinates formal in-house trainings, seminars, workshops, symposia, conferences (Technical/Non-Technical, local and international) and selects and invites resource speaker;
• Designs and administers continuing Staff Development Plan including scholarships and other short-term training courses, study grants and in-house training programs for all employees of the Department;
• Conducts researches, studies, surveys on attitude and morals of the employees in the organization; identifies the causes of factors adversely affecting their attitude and morals; and recommends solutions;
• Develops training materials for manpower development, organize programs to upgrade and strengthen job skills and competence;
• Conduct studies and periodic surveys to determine the training needs;
• Devises means for the evaluation of the effectiveness of designed training programs;
• Selects and evaluates candidates/participants to any seminar, training, observation, study tour, and scholarship, technical and non-technical courses for both foreign and local;
• Develops monitoring and evaluation scheme to all scholars / awardees of training and scholarship program; and
• Coordinates inter-departmental socio-cultural and healthy lifestyle development program.
*Please refer to the Learning and Development (L&D) Manual for the detailed standard and operating procedures of the Division.
1.1) All permanent officials and employees may avail of opportunities for local/overseas scholarships and other training grants including attendance to seminars, conventions, conference and training to enhance and upgrade their professional and technical knowledge, skills, and competencies.
1.2) Human Resource Development Program refers to activities aimed at enhancing career programs and personnel growth which include scholarships, study grants, study leave, trainings, seminars, workshop, conferences and conventions. Scholarship and other Training Grants (local and overseas) shall include those offered directly to the Department by the Commission on Higher Education (CHED) for Degree Courses and the Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA)for non-degree course and those which may be solicited by the Department from foreign foundations, universities, study centers and other institutions.
1.3) Foreign Scholarships and Training Programs (FSTP) - is a component of the Overseas Development Assistance (ODA) extended to the Philippines by foreign donor countries or foreign institutions based on the identified training needs of the Department in accordance with the National Development Thrust and Strategies.
1.4) Self-solicited scholarship, training grants, and continuing Professional Development Program for all Regulated Professions accredited by the CPD Council may be allowed on highly meritorious cases as may be determined by the Agency Head thru the PDC.
1.5) Scholarship/Training Programs are classified into:
a) Bilateral Programs – Australia, Belgium, China, Federal Republic of Germany, Indonesia, Italy, Israel, India, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Thailand, The Netherlands, Pakistan, Russia, Singapore, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and United State. b) Special Programs – United Nations Agencies, ASEAN/EU Scholarship Program, Japan Scholarship Program and other regional organizations.
2.1) Invitations coursed through the Office of the Secretary and referred to the Human Resource Development Division for proper processing as DA OSEC PDC Secretariat. These include the following:
a) Local Trainings and Conventions from DAP, CSC and other CSC accredited training institutions.
b) Full Scholarship grant from UP Econ., AIMS, DAP, Phil. Business for Education (PBED), Phil. Public Safety College (PPSC), Center for Space Science & Technology in Asia and the Pacific (CSSTEAP) and Southeast Asian Regional Center for Graduate Study and Research in Agriculture (SEARCA).
c) Foreign Scholarship that is fully funded by the sponsoring country/institutions through their respective agency or indorsed by the DFA.
d) Foreign Scholarship that is not fully funded by the sponsoring country through their respective agency, directly from the sponsoring country or indorsed by the DFA.
2.2) Invitations directly coursed to the Office of the Human Resource Development Division for proper processing such as the following:
a) Foreign Scholarship Training Program (FSTP) indorsed by TESDA, CHED, KOICA and JICA Special Project for Young Leaders in the Philippines.
b) Direct full grant invitations coming from the donor country/organization and/or through its representative, coursed through the DFA.
2.3) Other commitments of the Department such as Codex, WTO, BIMP-EAGA, ASEAN and APEC are coursed through the Office of the designated Focal Person.
3.1) Degree courses such as Diploma, Master’s Degree and PhD coming from Sponsoring Agency/Organization through CHED and direct invitation coming from the donor countries and/or through its representative.
3.2) Technical courses from the sponsoring country/representative through TESDA and direct invitation coming from the donor country & coursed through DFA.
4. Required Documents for Application
4.1) Nomination letter signed by the authorized signatory of the DA-Scholarship Committee or Personnel Development Committee.
4.2) Certification from the Head/Manager of the HRD, and has no pending service obligation from the previous scholarship previously enjoyed.
4.3) Certification from the Legal Officer/Personnel Officer that the nominee has no pending administrative and/or criminal case.
4.4) Personal Date Sheet to include list of training programs and seminars attended both foreign & local.
4.5) Statement of Present/Actual Duties and Responsibilities (including past involvement) relevant to the course/program signed by the immediate superior.
4.6) Medical Certificate indicating that the nominee is fit to travel and to undergo foreign training abroad.
4.8) Duly accomplished prescribed application form with passport size photos on white background (handwritten application forms will not be accepted).
4.9) Photocopies of Passport (official or personal/old or new).
4.10) Inception/ Country Report.
5. Application Procedure
All invitations and information for scholarships, study grants, trainings and attendance to trainings, seminars, conventions and conferences, both local and foreign, sent to the different offices of the Department must be forwarded to the PDC and must be properly disseminated by the Human Resource Development Division to all offices in the Department.
5.1) All applications for scholarship and participation in training courses, conventions, seminars, and conferences shall be coursed through and endorsed to the PDC for deliberation and approval.
5.2) Upon receipt of the nominations from the different units in the DA-Central Office, the documents of the nominees shall be transmitted to the DA-PDC Secretariat for screening and evaluation.
5.3) The PDC Secretariat shall prepare a Comparative Assessment Data on all nominees to determine whether they meet the qualifications prescribed for the scholarship or training grant to which they have been nominated and the requirements under III-6 hereof.
5.4) The following Evaluation/Assessment Criteria shall be used by the DA-PDC in determining the most qualified nominee: Weight A. Job Relevance
Performance
6. Application/ Availment for Scholarship and Attendance to Trainings, Seminars, Conferences and Conventions
6.1) Availment of all human resource development programs shall be based on the applicants’ need and career path. Priority shall, however, be given to applicants (1) who have not availed of any scholarship, study grant, training, seminar, workshop, conference or convention for the last two years; and (2) whose functions are relevant to the programs.
6.2) Local training, seminar, convention and conference can be availed of by an employee at least once a year, except when his/her attendance is necessary as official representative or focal person and in other meritorious cases to be determined and evaluated by the DAOSEC PDC.
6.3) Application for scholarship, training, seminar, conventions and conference whether sponsored by and/or funded by DA-OSEC or other government and non-government institutions, should not prejudice the duties and responsibilities of the employees/applicant. Hence, prospective trainees/applicants should secure recommendation from their Chiefs of offices.
6.4) Attendance of personnel in authorized human resource development programs shall be on official time.
6.5) Participants or beneficiaries of any human resource development program shall be relieved of all duties and responsibilities for the duration of the program.
6.6) To avail of any Human Resource Development Programs, the applicant:
a) Must have rendered at least two (2) years of service in the government at the time of nomination or as prescribed by the donor country;
b) Must hold a permanent appointment at the time of nomination;
c) Must have obtained a Very Satisfactory performance rating for two consecutive periods preceding the nomination;
d) Must have no pending administrative and/or criminal case;
e) Must have no pending nomination/approved application for scholarship in another program/course;
f) Must have already rendered the required service obligation for a scholarship previously enjoyed;
g) Must be physically fit to travel and undergo training/study both local and abroad; and
h) Must have a college degree and/ or sufficient demonstrated ability and experience related/ relevant to the course applied for and must meet the position level, age, education and experience required and specified by the donor country/ organization/course (for Foreign Scholarship Training Program applicants);
6.7) DA officials and employees may be authorized to participate in conventions, seminars, conferences, symposia and such other activities conducted by non-government organizations or private institutions for a fee, as part of the human resource development program of the Department, chargeable against DA funds. The registration or participation fee shall not exceed P 2,000 per day for each participant. (National Budget Circular No. 563 dated April 22, 2016, items 3.1 and 3.2).
6.8) There shall be no discrimination in the development and availment of scholarship of DA officials and employees on account of gender identity, sexual orientation, age, civil status, disability, religion, ethnicity or political affiliation.
7.1 The applicant shall not withdraw from the nomination and once accepted shall complete the course and should not be allowed to cancel or terminate the scholarship/training without justifiable reason and without giving prior notice to and getting the approval from the donor institution, TESDA or the donor country/organization.
8.1 Requirements for Nomination
a) Nomination Letter signed by the duly authorized Official of the concerned work unit.
b) Duly accomplished Application Forms and other required documents as stated in the disseminated invitation/announcement.
8.2 Other documents required for Selection/Screening
a) Inception/country report shall be submitted if required by the donor country.
8.3 Interview
a) Qualified nominees are required to appear personally for an interview to be conducted by the Scholarship Committee of the sponsoring agency (TESDA & CHED).
b) The date of interview is stated in the invitation. However, if there is a change on the scheduled date, the sponsoring agency will inform directly the applicant/agency concerned.
9.1) After the selection process conducted by the donor country through the sponsoring agency (CHED-TESDA), they shall send the acceptance letter to the concerned office/agency.
9.2) Upon receipt of the letter of acceptance, the HRDD will immediately notify the nominating DA work unit by telephone and/or through an official letter.
9.3) The staff assigned shall immediately send the acceptance letter and its attachments which shall be the basis in requesting for a Travel Authority to be signed by the DA Secretary.
9.4) The HRDD shall inform the scholar on the required documents needed in the preparation of Travel Authority.
9.5) Upon the approval of the Travel Authority, the HRDD will inform the scholar on the documents needed to secure official passport, visa requirements, travel tax exemption and schedule of the pre-departure briefing.
10. Effects of Failure to Complete the Foreign or Local Scholarship Grant
a) A Scholar who will not be able to complete the grant after the extended term/period may continue his/her studies at his/her own time and expense. He/she may file a leave of absence, subject to the approval of his/her Head of Office to enable him/her to complete the grant within six (6) months. Otherwise, the scholar will refund to the sponsoring agency/DA all expenses defrayed for his/her studies including salaries and allowances he/she received while on study grant. No employee shall be authorized to apply for any study/scholarship grant until after rendering the required service obligation on the previous grant attended. (E.O. No. 367, series of 1998).
11. Effects of Failure of Scholars to Render Service Obligation
a) In case the scholar fails to comply with the foregoing conditions of the Training/Scholarship Service Contract through his/her fault or willful neglect, resignation, voluntary retirement and other causes within his/her control, he/she shall refund to his/her Office the amount defrayed by the Philippine Government and the Sponsor.
Proportionate refund shall be allowed, provided that the GRANTEE has served his/her office/agency at least 75% his/her total service obligation.
12.1) The scholars are briefed on the preparation of other documents needed for his/her travel as well as the training materials to be brought to the program as per CHED or TESDA instructions.
12.2) The donor embassy/sponsoring agency prepares and conducts pre-departure briefing for the scholars. The briefing provides information on:
a) Country of destination i.e. language, history, currency, climate, etc.;
b) Details of training program to be attended;
c) Conduct and behavior of the scholar while on training;
d) Itinerary of travel and arrival details in country of training (if provided by Embassy/Donor);
e) Reminder for the scholar to always carry proper documentation;
f) Submission of post travel/training report to authorized agency on mother unit;
g) Who to contact in time of emergency; and
h) Reminder for the scholar to report her/his presence to the Philippine Consulate/Embassy where the training program is to be conducted.
12.3) The scholar is expected to study the guidelines. He/she is advised to attend the pre-departure briefing at the local embassy or sponsoring agency on other details of his/her travel award.
13. Foreign Diplomatic Concern of a Filipino Scholar
13.1) There shall be no withdrawal once a nominee is accepted by the donor country;
13.2) The scholar must acquaint his/her self to the culture and values of the donor country. Thus, he/she must attend the pre-departure orientation;
13.3) The scholar must attend the language course required and conducted by the donor country;
13.4) Scholars are required to conduct themselves with discipline and abide by the rules, regulations and guidelines as stipulated by both the nominating government and the donor country;
13.5) The scholar must observe the rules and regulations of the accommodation and shall not change the accommodation designated by the donor organization;
13.6) The scholar must report to the Philippine Embassy/Consulate upon arrival and be in touch with them from time to time;
13.7) The scholar must communicate regularly with the sponsoring agency/institution for any circumstances/status update on academic, financial and social life in her/his new environment;
13.8) No scholar shall be engaged in any political activities and/or apply for any form of employment for profit or gain while undergoing the academic requirement for his/her study grant;
13.9) For extension of validity of official passport /and or extension of stay of the scholar abroad, the scholar should file request for extension through the head of his/her work unit addressed to the Secretary, Department of Agriculture with the following attachments:
a) Letter of recommendation/request of extension from the course adviser/director or any authorized personnel of the academic institution;
b) Travel Authority previously approved by the Secretary; and c) Duly notarized Training/Scholarship Contract.
14. Academic Responsibilities of a Scholar
14.1) To live up to the terms and conditions of the grant;
14.2) To conduct himself in such a manner as not to bring disgrace or dishonor to himself or to his country;
14.3) To keep up with the standards of scholarship or accomplishments;
14.4) To abide by the rules of the university/institution/establishment in which the participants are selected to undergo the training/ study as well as participate in all course-related activities including submission of periodic assessments/test conducted by the institute;
14.5) To submit to the head of his office and the DA-Scholarship Committee his/her official transcript of grades at the close of each quarter or semester;
14.6) To return immediately upon the termination of his scholarship;
14.7) To submit to the head of his office and the committee a report on his/her study/training within (30) days after his/her return to duty; and
14.8) To submit a Re-Entry plan or proposal for the application of newly acquired skill or expertise to his/her office and the committee.
15.1) Culture is central to the experience of living/studying overseas. International students in the donor country certainly share similar experiences of cultural adjustments and transitioning while pursuing their studies. No matter how well the donor country representative prepares the incoming students before leaving, they still experience some kind of culture shock and find ways to adopt and survive. Here are some guides that may help scholars adjust to a new environment:
a) Attend to the pre-departure orientation, usually held at the office of the donor country representative to provide them with details on the donor country, conditions of the training/degree course to be attended and other matters;
b) Involved yourselves in various welfare activities such as sports program, exposition of the donor country traditional cultures and language/conversation classes etc;
c) When you feel “overwhelmed”, you should talk to someone who has the time and patience to listen and then gradually into groups where you will meet new people”. Or you may want to hang out with people from a common background, other international students who can empathize with your feelings;
d) Be patient and open-minded. It takes time to learn a new language, slang, or to get used to the food, customs, and live in a culture. Don’t hesitate to ask questions. Don’t be afraid to talk to people. Try to initiate a conversation at appropriate times. Sometimes a simple greeting/ gesture can go a long way in fitting-in. It shows your effort of learning the culture;
e) Stay active and healthy, get involved, and be inclusive. Although you may feel comfortable speaking your language, hanging out with friends from your own country, and participating in the international student organization, it is advised to include different nationals in your activity or discussion. Avoid building an exclusive club of your group. Be proud to be your cultural ambassador. Most likely, nationals from other country are eager to learn from you about your culture. Eat, sleep and exercise to stay both physically and mentally healthy. This will sustain a positive attitude while adjusting and adapting to a new culture; and
f) Remember that you come to study in that country not only for grades and degrees, but also for social life and cultural appreciation. Allow yourself to be integrated into an on and off campus community, and participate in departmental and student activities.
16. Allowances & Expenses
16.1) Round-trip air ticket.
16.2) One-way domestic trip expenses from the participants’ residence to the location of the PDOS.
16.3) Other allowances
a) Outfit allowance
b) Book allowance
c) Shipping allowance
d) Free Medical care
e) Living allowance
16.4) The specific details for each allowance are to be discussed during the PDOS.
17. Entitlements of Scholars
17.1) Pre-departure expenses - E.O. 77 series of 2019
17.2) Clothing allowance - E.O. 77 series of 2019
18. Job Report/Country Report
18.1) Accepted Candidate shall prepare Country/Job Report describing the current situation in your respective country. The following are the expected content of the country/job report:
a) Personal information (Name, job, what you expect from the course and additional information you want to add);
b) Basic information on your country (Population, industries, economic situation, related laws and politics, culture etc.);
c) Information on your organization (Role of your organization/department/agency, organizational chart, budgetary situation, strategies and systems to support regions, territories/scope of your organization/department/agency; and
d) Current situation of regional development, especially product development/promotion (Existing and potential products, existing and potential market, problems and suggested solution on the problem).
19. Travel Report
19.1) Legal Basis
a) Executive Order 367
b) Malacañang Circular No. 7
c) DA-Memorandum Order No. 03 series of 2017
d) DA Memorandum Order dated August 7, 2017- Prescribed Travel Report Format
20. Travel Report Format
DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
OFFICE OF THE SECRETARY
HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT DIVISION
Official Travel Report
(Degree Course, Training, Seminar, Conference, Study Visit/Tour, Symposium & summit)
Name of Participant: Office /Agency: Position/Designation Course/Training Title:
Duration: Sponsor: Place/Country:
I. General Evaluation (Procedure, Content/Topics Discussed, Delivery, Comment on the conduct of the Program and Applicability to Philippine situation).
II. Problems Encountered:
III. Recommendations/Suggestions:
IV. Re-Entry Plan/Action Plan:
21. Monitoring and Evaluation
21.1) The HRDD maintains a file copy of each scholar’s foreign travel authority and duly accomplished scholarship/training contract.
21.2) The HRDD staff concerned evaluates and facilitates action on request of scholar for:
a) Extension of validity of passport
b) Transfer to another course and/or another degree
22. Data Management and Information System
22.1)The HRDD inputs/encode all data for monitoring and evaluation purposes.
22.2)The HRDD Staff updates all files including course availed of by the nominees and scholars.
23. Guidelines for Action Plan/Oral Report
23.1) Re-Echo Seminar
a) Returning scholar shall render a re-echo-seminar/oral report to her/his respective agency/office to transmit the information learned from the training attended.
b) Scholars should conduct Oral Report/Presentation on the Training/Non-Degree/Degree Course attended in their respective office within 90 days upon return.
23.2) Re-Entry Plan (REP)/Re-Entry Action Plan (REAP)/Action Plan (AP)
a) All scholars/grantees shall submit a Re-entry Plan/Re-Entry Action Plan/Action Plan to the DA-OSEC PDC through the Human Resource Development Division within 30 days upon returning to duty for proper monitoring.
b) Action plan aimed to alleviate the problems you face in your organization, utilizing the knowledge and skills obtained in the training program attended.
24. DA Scholar Post Evaluation Questionnaire
24.1) The questionnaire is designed for DA Foreign and Local Scholarship Grant beneficiary to evaluate the impact of the training/degree course attended and to assess the extent of application and effectiveness of the knowledge and skills acquired from the training/degree course inserted as letter B.
25. COMMON PROVISIONS ON LOCAL AND FOREIGN SCHOLARSHIP
(DA Memo. No. 9, series of 2018)
The following provisions shall apply to both local and foreign scholarships: 25.1 Effects of Administrative Cases
a) When a scholar is formally charged prior to enrolment with an administrative offense where the penalty is suspension or dismissal, he/she shall be automatically disqualified to avail of the grant.
When a formal charge is filed after enrolment, a scholar shall be allowed to continue his/her studies, unless the charge is for a grave offense and the evidence of guilt is strong.
b) When a scholar is subsequently found guilty of an administrative offense and dismissed from the service, he/she shall refund to the sponsoring agency/DA all expenses incurred including salaries and allowances received while studying.
25.2 Effects of Incomplete or Failing Grades of the LSP-BDC Scholars
a) In case an LSP-BDC scholars receives an incomplete grade in a particular semester or terms, he or she shall still be allowed to avail of the scholarship grant for the next semester/trimester or summer term as the case maybe.
b) In case the LSP-BDC scholar receives a failing grade in any subject the scholarship grant shall be discontinued. He/she shall refund to the CSC all expenses incurred and to DA all remuneration such as salaries and allowances received for the period covered.
25.3 Effects of Discontinuance of Studies for LSP Scholars
a) In case the LSP-BDC scholars discontinue their studies or fail to complete the course due to their own fault or willful neglect, except those due to illness or health reasons, they shall (1) refund to the CSC all expenses incurred and to DA all salaries, allowances and emoluments received for the period covered; and (2) be barred from participating in future scholarship examinations or assessment processes.
26 Other added LSP guidelines for both LSP-MDP and LSP-BDC
26.1 In the event that the scholar fails to (1) complete the degree or discontinue his/her studies; or (2) fails to fulfill/render the service obligation stipulated in the contract through his/her own fault or willful neglect, resignation, voluntary separation or transfer, the scholar shall refund to the:
a) Civil Service Commission the actual full amount defrayed for his/her study grant. However, in case the scholar completed his master’s degree and opted to transfer to another government agency, he/she shall no longer refund to the Commission the amount spent for his/her studies.
b) DA all salaries and other remunerations received while on scholarship.
26.2 Refund of all expenses, e.g., salaries and allowances may be condoned in any of the following instances:
a) Separation from government due to:
- Abolition of the office; or
- Involuntary phase-out of the position being held by the grantee due to reorganization; or
- Death or permanent disability
26.3 The proportionate refund of the monetary value of the scholar’s service obligation to the agency shall be allowed after he/she has rendered at least fifty (50%) of the total service obligation in the agency. (CSC. M.C. No. 18, series of 1998).
26.4 The mode of payment whether on installment basis and/or through salary deduction, shall not exceed three (3) years. An agreement, duly executed in an affidavit shall be effected between the scholar and the CSC or between the scholar and the agency. (CSC. M.C. No. 18, series of 1998)
27 Consequences of Failure to Complete the Foreign or Local Scholarship Grant
27.1 A Scholar who will not be able to complete the grant after the extended term/ period may continue his/her studies at his/her own time and expense. He/she may file a leave of absence, subject to the approval of the Head of Office to enable him/her to complete the grant within six (6) months. Otherwise, the scholar will refund to the sponsoring agency all the expenses defrayed for his/her studies and to his/ her agency the salaries, allowances and emoluments he/she received while on study grant. No employee shall be authorized to apply for any study/scholarship grant until after rendering the required service obligation on the previous grant attended. (E.O. No. 367, series of 1989).
28 Consequences of Failure to Render Service Obligation (E.O. No. 367, series of 1989)
28.1 In case the scholar fails to comply with the foregoing conditions of the Training/Scholarship Service Contract through his/her fault or willful neglect, voluntary resignation, optional retirement and other causes within his/her control, he/she shall refund to his/her Office the amount defrayed by the Philippine Government and the Sponsor.
Proportionate refund shall be allowed, provided that the GRANTEE has served the Department of Agriculture at least 75% of his/her total service obligation.
29. APPLICATION FOR THE GRANT OR AVAILMENT OF STUDY LEAVE
29.1 Applicant/s must possess all the qualifications as provided for under CSC Memorandum Circular No. 21, series of 2004 as amended.
29.2 Applicant/s for the study leave must submit proofs of completion corresponding to the purpose of the leave such as:
For Board/Bar Examination
Certification of Grades from the School/University, Professional Regulation Commission (PRC) Supreme Court For Thesis/Dissertation Writing - Approval Sheet of the Thesis/Dissertation by the panel and Dean of the graduate school and a copy of the approved thesis outline/proposal (Chapters 1,2 & 3)
29.3 Applicant/s must secure a favorable recommendation from the Head of the Division/Department/Office.
29.4 All applicants for study leave both local and foreign must pass through the Committee for evaluation and approval, to ensure that the course and/or the thesis proposal are relevant to the official duties and responsibilities of the applicant as well as to the mandate of DA.
29.5 The Head of the Unit or the Supervisor shall ensure that the existing duties and responsibilities of the grantee are properly delegated and assigned, so as not to hamper the operations/functions of the unit/division/department for the duration of the study leave.
29.6 A grantee can avail of the study leave only once, and no extension beyond the approved period shall be allowed, except under meritorious cases to be determined and evaluated by the Committee. However, in case of approval of extension, all existing government rules in the availment of Leave of Absence shall apply.
29.7 The grantee need not be rated during the period of his/her study leave; the performance rating prior to the grant of the study leave shall be used instead, as necessary.
29.8 Prior to the commencement and consummation of study leave the DA and Grantee shall execute a Study Leave Service Contract to be prepared and provided by the Personnel Division.
29.9 In case the official or employee fails to render in full the service obligation referred to in the contract on account of voluntary resignation, optional retirement, separation from the service through his own fault, or other causes within his control, he/she shall refund the gross salary, allowances and other benefits received while on study leave based on the following formula:
R = (SOR- SOS) X TCR
SOR WHERE R = REFUND
TCR = TOTAL COMPENSATION RECEIVED (GROSS SALARY, ALLOWANCES AND OTHER BENEFITS RECEIVED WHILE ON STUDY LEAVE)
SOS = SERVICE OBLIGATION SERVED
SOR = SERVICE OBLIGATION REQUIRED
The official/employee beneficiary of the study-leave shall inform the Department of Agriculture in writing, through the Personnel Office, of his failure to pursue his studies or his failure to take the bar/board examination for which reason the study leave was granted. 29.10 The service obligation to the Department shall be as follows:
Period of Grant Service Obligation
One (1) month Six (6) months
Two (2) to Three (3) months One (1) year
More than three (3) months to six (6) months Two (2) years
29.11 The grantee/scholar is required by the Committee to submit Action Plan, Re-Entry Plan (REP) or Re-Entry Action Plan (REAP) and render an oral report or re-echo seminar in addition to their Post Training Report for Foreign Travel which should be submitted within 30 days upon his/her return using a prescribed format for Official Travel Report. For local seminar, training and conference, grantees are required to submit Certificate of training/ Attendance and Learning Application Plan approved by their immediate supervisor.
29.12 Monitoring of DA-Central Office Scholars thru CHED and TESDA will be undertaken by the Human Resource Development Division (HRDD). HRDD shall maintain a DA-Scholar Profile and conduct Post Evaluation Survey for Returning Scholars as part of their impact assessment.
29.13 HRDD will also consult and coordinate with scholar’s immediate supervisor to ensure that all learning gained from the scholarship program indicated in the submitted Action Plan (AP), Re-Entry Plan (REP) or Re-Entry Action Plan (REAP) will be significantly applied in their respective office/organization.
29.14 Returning scholars who will render re-echo seminar/oral report in their respective offices must coordinate with the HRDD for monitoring and evaluation purposes.
FUNCTIONS
• Takes custody and is accountable for all the disbursements, collections and deposits, supplies, properties, and plant and equipment owned by the Department;
• Maintains and supervises janitorial, security and other related services;
• Be in the frontline of general services activities such as possible imminent destruction or damage to supplies, properties and structures, threat of security;
• Provides policy guidance on the maintenance and disposition of assets, utilization and storage of supplies, materials and equipment in accordance with government prescribed standards;
• Manages and supervises the transportation, general utility and maintenance services for the Department;
• Manages and supervises the buildings and grounds of the Department;
• Receives and distributes supplies and equipment of the Department and conduct periodic inventories of same;
• Receives and collects cash, process payment of salaries of DA employees and the Department’s obligations;
• Supervise the janitorial and security services of the Department; and
• Procures other general services of the Department.
• To provide a clear policy and guidelines related to the maintenance and other general administrative services;
• To facilitate a smooth and immediate service delivery of support services needed by the Department;
• Identify the responsibilities, accountabilities and authority of the concerned personnel involved.
As part of the General Services Division’s ongoing effort to simplify and enhance the control of the Department’s operational processes the following policy guidelines must be observed;
The General Services Division of the Department of Agriculture has two major functions; Manage the DA Motor Vehicles and facilitation of the maintenance of the building and equipment.
• Managing the DA Motor vehicles refers to the assigning of drivers through dispatch to transport the passengers to the requested destination and handles registration, including repair and maintenance of various DA motor vehicles.
• Facilitating the building and Equipment Maintenance involves the following services;
- Controls the delivery of basic utilities and other services needed by the Department this includes water and electricity, distribution of newspapers, provision of drinking water, leasing of photocopying machines, etc.
- Supervises the implementation of all the contracted services to make sure a good housekeeping and security within the premises.
- Maintenance and repair of equipment including the preparation of job order and job estimates necessary for the maintenance, repair and renovation of facilities and oversees the implementation of such repairs;
- Prepares all the necessary documents needed for the processing of payments for the job orders and services rendered; and
- Assist in the preparation of special events (eg., DA-Anniversary, World Food Day, National Rice Awareness Month, DA Annual Affairs, Tienda- Market and other activities).
Fuel Allocation
• Monthly Fuel Allocation
Official Vehicle
Secretary / Back Up
Chief of Staff / Undersecretary
• Request for additional allocation of fuel for provincial trips shall be subject to the approval by the Chief, General Services Division. The Chief, General Services Division is tasked to implement and monitor the strict compliance and monthly summary report of fuel consumption shall be submitted by the drivers by using the official form (Annex A);
• Fuel Allocation is through the Fleet Card System;
• All request for vehicles shall be filed one (1) day in advance, for Metro Manila and three (3) days, for provincial travel to enable the Motor Pool Section to coordinate and prepare the vehicle to be used and shall be made on a “First come – First serve” basis. Emergency requests shall be entertained subject to the approval of the Chief, General Services Division;
• The requesting party shall fill up the official Vehicle Request Form (Annex B) for the complete detail of the travel prior to the approval of the Chief, General Services Division;
• If the request form is approved the Dispatcher will issue vehicle Trip Ticket (Annex B-1).
• The Secretary shall be allowed one (1) official vehicle, two (2) back-up vehicles and two (2) staff vehicles.
• Undersecretaries, Assistant Secretaries, Service Directors, Chief of Staff/ Head Executive Assistant and Program Directors/ Project Managers shall be allowed one (1) official vehicle each.
• Undersecretaries are entitled to one (1) staff and one (1) back-up vehicle, the latter subject to the approval of the Secretary.
• The Assistant Secretaries are entitled to one (1) staff vehicle, the latter subject to the approval of the Secretary.
• Other critical offices and units may be allowed one (1) service vehicle upon the request of the concerned head of office/ unit subject to the availability of vehicle and the approval of the Secretary.
• Vehicles for staff used shall be parked in the DA’s compound after office hours or after their official use, unless issued by a Travel Order.
• Officials and officers are entitled to the services of assigned drivers except when there is no available driver in the pool or the official and officer has opted personally drive the vehicle. In the event that the official or officer shall need the services of a driver a corresponding request shall be made to the Chief, General Services Division.
Assignment of Drivers Mechanic
• The Pool Section/ Mechanic shall schedule and conduct periodic and regular preventive maintenance check-up of all official vehicles.
• The DA Mechanic shall issue to the driver a Certificate of Roadworthiness for every vehicle scheduled for provincial trips, prior to the issuance of trip ticket.
• The Mechanic shall prepare a pre-repair inspection (Appendix 3-1) and Job Order (Appendix 3-2) for every finding that needs to be repair on DA motor vehicles.
• As soon as a defect or problem on any vehicle is observed and detected, the assigned driver or user of the vehicle must immediately report the problem to the DA Mechanic.
• Drivers are required in every request for travel outside Metro Manila or provincial trips to secure a Certificate of Roadworthiness of the vehicle to be used.
• Dispatch vehicles shall be parked in DA’s compound after office hours or after their official use, unless issued by a Travel Order.
• Only passengers officially list in the trip ticket shall be allowed to ride the vehicle. Drivers are instructed to report any violation of this procedure to the Chief, General Services Division.
Drivers Emergency Repair
• The Emergency repair is defined as the repairs necessary to prevent further damage of the vehicle.
• On the case of vehicle defect on the road within Metro Manila the DA-GSD authorized mechanic shall prepare a pre-repair inspection (Appendix 3-1) and Job Order (Appendix 3-2) on the findings that needs to be repaired immediately.
• On the case of vehicle defect outside Metro-Manila, the assigned driver of the said vehicle may rush to a nearest auto-shop for its immediate repair.
• The assigned driver/ end-user will prepare the Certificate of Emergency Purchase/ Repair (Appendix 4).
• After the repair has been made, the GSD-Authorized Mechanic and Inspector shall prepare a Post-repair inspection report.
• On the case of repair of the Building, Plumbing, Ground etc., the DA-GSD authorized engineer/carpenter/plumber/electrician shall prepare a pre-repair inspection (Appendix 3-1) and Job Order (Appendix 3-2) on the findings that needs to be repaired immediately
Electricity and Water
• Lights should be turned off before leaving the office or after the official working hours.
• Lights in certain comfort rooms shall be monitored/ turned off if natural light is available.
• Lighting facilities inside the building and/ or perimeter fences should be consistent with security requirements of the office and should be turned on not earlier 6:00pm and shut off not later than 5:00am the next day.
• to achieve maximum efficiency all lights and air conditioning units should be cleared/ maintained regularly.
• The Pool Services and Building Maintenance section shall adopt a systematic monitoring plan to detect immediately leaking faucets and the likes which should be reported immediately to the Pool Services and Building Maintenance Section. The latter shall immediately cause the repair thereof and preparation of Job Order and estimates of the materials to be used.
• The use of water for watering of plants/ lawn and/ or cleaning/ washing of vehicles should be systematically done so as to avoid wastage.
Issuance of Pre-Paid Cards shall be limited to the following with the corresponding cell card limits based from the approved Memorandum of the Secretary:
End User
Secretary
Undersecretary
Assistant Secretary
Chief of Staff
Director
Division Chief
Assistant Division Chief
Section Chief
Liaison Officer
Technical Staff
*Section Chief (prerogative of Division Chief)
*Technical Staff (with corresponding approved Special Order)
Monthly Allocation
php 30,000.00
php 2,500.00
php 2,500.00
php 2,500.00
php 1,500.00
php 1,200.00
php 900.00
php 600.00
php 500.00
php 500.00
• No employee shall be allowed to sleep/ stay overnight inside the DA building/ offices, unless emergency in nature. In such cases, permission/ notification should be made with the office Assistant Secretary for Administration for coordination. No employee rendering overtime services shall stay 9:00pm unless authorization therefore is coordinated with the office of Assistant Secretary for Administration. The security guard on duty is hereby instructed to see to it that this is complied with and recorded in their daily guards’ report for record purposes.
• All vehicles entering the DA compound shall be properly logged. Drivers of vehicles other than those belonging to the DA or its staff shall be required to leave identification card with the date guard and shall be issued a DA gate pass, which will be surrendered upon egress.
• Only persons with legitimate purpose shall be allowed to enter the DA office/ building premises. Guard on Duty shall maintain a record book for this purpose.
• No supplies/ materials/ equipment shall be taken out of DA building/ premises unless a duly approved Gate Pass therefore signed by the Chief, General Services Division is presented to the guard on duty. No personal equipment shall be allowed entry into the DA premises for repair purposes.
• The Security Detachment is hereby instructed to coordinate with the duly designated Building Administrator on the checking/ inspection of DA offices/ rooms/ premises inside the compound.
• In anticipation of security measures during emergencies such as fires, natural calamities, etc. the guard shall be properly informed/ trained on how to operate the Main Power House (for electricity) and Main Gate Valve (for water).
• Wearing the DA ID by employees shall be strictly enforced. The Security detachment shall adopt the two way lane at the entrance and exit gates (one for employees and another for visitors only) for proper and orderly inspection.
• For proper monitoring and security reasons, the sticker system for DA-RP vehicles, DA-officials, and DA-employees shall be enforced. Only current employees, (Permanent/ Contract of Service (COS), with valid appointment/ contract shall be issued car sticker and are authorize to park their car in the DA premises. DA-visitor may park his vehicle on the Visitor parking on a first-come-first serve basis and shall not be occupied by the DA-officials/employees.
Conference Room and Dormitory
Conference Room
• The reservation of the Conference room located at the 4th Floor of the DA- New Building is on a first-come-first-served basis with minimum of 30 pax.
• The requesting office must submit to the GSD-Maintenance Section the accomplished Conference room request form (Annex __) with the attached Memorandum or Notice of Meeting signed by the supervisor of the concerned requesting unit.
• The end-user shall assign focal person to coordinate with GSD regarding the following;
a. Audio and meeting equipment shall be provided by the requesting party;
b. Physical arrangement shall be coordinated with Ms. Rosario Ladera at least one (1) day prior to the event/meeting;
c. Tables and chairs used shall be inspected and counted with Ms. Ladera;
d. Clean as you go and turn off lights and aircon units;
e. Coordinate with GSD – Maintenance regarding catering services for the proper usage of pantry and elevator; and
f. Food requested for the meeting shall be prepared outside the DA premises.
• Cancellation of reservation shall be coordinated to the GSD-Maintenance Section at 928-8741 to 46 local 2837 three (3) days prior to the event/meeting.
• DA has the right to cancel reservations with prior notice.
Dormitory
• Only trainees and transient/s on official government business are allowed to stay in DA dormitory.
• The Request for reservations and payments for dormitory stay should be made during office hours, and not to be made to the assigned dormitory or the Client Center front desk officer as part of the transparency requirements of all government offices under the Anti Red Tape Act. As a matter of policy, no transactions with the dormitory staff are allowed before and after office hours.
• Transient/s need to fill up the registration form at the DA dorm office upon the arrival
• Check-in time is 3 o’clock in the afternoon and check-out time is 12 noon. An accommodation of early arrivals and late departures with advance reservation depends on the availability of the room.
• Occupy only the bed paid in difference to the other room occupants except when the whole room has been booked and paid for. Additional beds occupied shall be added to the final bill.
• Guest should observe quiet hours and courtesy to other guests, especially with those sharing room. The use of headphones is encouraged for music and video games. Guest sharing the room with others should strive to make a concerted effort to work towards and fair living arrangement.
• The following are prohibited inside the room:
• Use of illegal drugs and drug paraphernalia.
- Toxic Chemicals
- Fire Arms
- Smoking
- Gambling
- Food
- Pets
- Drilling of nail holes and affixing of adhesive tapes in any part of the room.
- Transfer of beddings and furniture to another room.
- Cooking inside the room is not allowed. Bringing in of portable cooking appliances like rice cooker, toaster, oven, and deep fryer is prohibited. Other open fire like incense and candles are not allowed. Ironing of clothes inside the room is not allowed.
• Visitors are not allowed inside the dormitory rooms.
• The guest/s are responsible for the condition of the room and its furnishing. Missing and damaged items will be charged to the guest/s. Report missing items and damages that needs to be repaired to the dormitory staff to avoid being additionally charged.
• The dormitory does not provide laundry services.
• Turn-off lights and air-conditioning units when leaving the room for the day’s activity.
• Room keys should be surrendered to the reception counter or to the assigned security guard every time one leaves the DA premises. Dormitory guest/s who losses the key will shoulder the cost of key duplication. Key duplication is to be arranged with DA GSD office with contact number 920-4075.
• The Dormitory and Conference Rooms are for the official use of DA Office of the Secretary, Bureaus, Attached Agencies and Attached Corporations. Conference Rooms are to be used only for meetings, trainings, workshops and seminars. Dormitory can be used by the transient/s who will attend DA activities. It caters on a FIRST COME-FIRST SERVED BASIS.
• Booking notice for dorm accommodation: At least 3 working days advance notice either phone call or written confirmation.
• Booking notice for conference rooms: At least 3 working days advance notice either phone call or written confirmation.
• Note: Reservations are considered tentative and will be held at least 3 working days for dorm accommodations while 3 working days for Function rooms.
• In the event that no confirmation is made, the dormitory management will automatically cancel the said reservation unless an agreement is drawn prior to the signing of the forms.
• Cancellation can be made either phone call or written confirmation at least 3 working days prior to the scheduled check in date.
The Records Division shall be responsible in providing the Department with efficient, effective and economical records management.
FUNCTIONS
• Formulates, evaluates, updates and implements policies and guidelines on records management.
• Prompt delivery of mails and communications received for the Department and its employees.
• Provides systematic control of handling incoming mails and correspondence and dispatch outgoing/signed communications.
• Services the documentary reference and information requirements of top management, action officers and the general public.
• Provides messengerial/liaison service for the department.
• Ensures proper storage of inactive records and prompt disposal of absolute, valueless records and preserves vital and permanent records for archival purposes.
• Provides systematic control of handling incoming mails and correspondence and dispatches outgoing/signed communications.
• Safeguards the seal and official records of the Department.
• Represents the Department in the presentation of documents in Court and other administrative body(with the assistance from the Legal Service)
• Authenticates official records when necessary.
1. Receive, post date of receipt, and initial all correspondences including telegrams and personally addressed correspondences.
2. Encode control numbers and record the correspondences.
3. Supervise/check the documents to be released.
4. Send correspondences to the concerned party.
1. Receive documents.
2. Forward the communication to the assigned Records Division personnel and record the correspondence.
3. Classify and release communications to the concerned party. If correspondence to be released pertains to cases, sealed order, decisions, keep file copies for reference.
4. Keep files and compile according to office, date, and file classification
Records Clerk
Records Officer
Chief,
Records Clerk
NOTES:
• Acted communications refer to: MOA or contracts; case related documents; and released documents to Bureaus, Attached Agencies/Corporations, Regional Field Units, and other outside offices.
• Original of all case related documents, MOA, and contracts are stored in the Records Division. The photocopies of outgoing acted documents for Bureaus, Attached Agencies/Corporations, Regional Field Units and other outside offices are kept in the office.
• For case related documents, require copies need prior approval/clearance of legal service.
• DA COA are provided with the certified true copy of the Contracts/MOAs.
III. Release of DA Issuances
1. Receive issuances.
2. Analyze and assigned numbers.
3. Provide photocopies.
4. Dissemination (if for public information, provide UP Law Center a copy)
5. File proof of receipt, original are encoded to Database, file Original
NOTES:
• DA Admnistrative issuances (original) are on file in the Records Division. If the issuances are for public information, UP Law Center will be provided Certified True Copies.
and assign
Certify True copy for UP Law Center CHIEF, RECORDS DIV.
1. Pick up mails from post offices’ boxes and bring them to Records Division.
2. If registered, log to logbook. If ordinary, arrange according to office and forward to concerned office/person.
• Envelopes marked “personal”, “private”, or “confidential” are to be delivered unopened.
V. Issuance of Certified Copies of Documents
1. Concerned party forwards request to the appropriate Records Division staff.
2. If the requested documents pertain to legal matters, refer to the Legal Division for approval or clearance.
3. If the request is approved or cleared, requesting party shall be provided certified copies.
Records Clerk / Chief Records Division
Chief, Records Division Legal Division
Records Custodian
1. End-user forwards request for retrieval of past records.
2. Inform the Records Officer.
3. Approve request.
4. If approved, Records clerk will get the documents from the storage room.
5. If documents pertain to legal cases, approval or clearance must be secured from Legal Division.
6. If approved, provide all requested previous records.
• “Issuance” refers to Special Orders, Memoranda, Circulars, Administrative Orders, and other documents of the same nature.
• The Records Division keeps the original copies of court documents, Special Orders, Memoranda, Circulars, Administrative Orders, and other documents of the same nature.
• “Release” usually refers to acted communications to be disseminated to Bureaus, Attached Agencies/Corporations, Regional Field Units, and other outside offices.
• Court documents usually refers to case-related documents.
Records Clerk
Records Officer / Chief, Records Division
Chief, Records Division
Records Clerk End-user
Chief, Records Division / Records Clerk
Invetory fo Records and Preparation of Records Disposition Schedule
1. Records clerk segregates permanent records from temporary records.
2. Records clerk compiles files according to office, subject/date and label
3. Records clerk arranges alphabetically all compiled records or by series for proper sequencing.
4. Records clerk prepares the records inventory and appraisal report for review of the Records Division Chief.
5. Send to NAP for approval.
6. Once Records Inventory is approved, it will be the basis for the preparation of Records Disposition Schedule.
7. Preparation of RDS for approval.
Records Clerk / Records Officer / Chief, Records Division
Records Clerk / Records Officer / Chief, Records Division
Records Clerk / Records Officer / Chief, Records Division NAP
Chief, Records Division
Records Staff / Chief, Records Division
Chief, Records Division / NAP
1. The concerned office shall accomplish the NAP Form and submit to the office of the Director for Admnistrative Service, for signature.
2. Sign the NAP Form and forward it to the Records Division.
3. Compile all the NAP Forms to be evaluated.
4. Transmit the letter and all NAP Forms.
5. Appraise and examine the disposable records of the requesting agency then prepare and submit Analysis Report based on his/her evaluation.
6. Submit to Executive Director the NAP recommendation
7. Issue Authority to Dispose of Records and notify the requesting agency of the approval
8. Supervise the segregation of valueless records and be responsible for the safekeeping of the valueless records until their actual disposal.
Records Officer / Chief, Records Division
Director, Administrative Service
Records Clerk
Records Clerk
NAP Records Management Analyst
Chief of the Management Services Division (RMSD)
Executive Director of NAP
Records Clerk / Records Officer / Chief, Records Division
9. Records clerk will dispose the records in the presence of NAP Officers and the Resident Auditor from the COA.
10. Issue an official receipt to the buyer.
11. Prepare Certificate of Disposal signed by three (3) witnesses who will be given a copy each.
Records Clerk/Chief Records Division, NAP Officers, COA Resident Auditor, Official Buyer Cashier NAP Authorized representative
The Agriculture and Fisheries Division (AFID) is the communication arm of the Department of Agriculture, particularly its banner programs - Rice Program, Corn/Cassava Program, High Value Crops Development Program, Livestock Program, and other programs and projects of the Department geared towards the development of the rural farming and fishing sectors, as well as related industries.
The Information group’s primary concern is to establish and maintain thru quad-media the positive image of the Department to sustain the people’s thrust to the government.
AFID has three sections: Editorial, Audio-Visual and Graphics, and the Library.
AFID has twenty-four (24) approved plantilla positions thru the Rationalization Plan and five (5) Contract of Service/Job Order workers to implement the information advocacy initiatives of the Department.
Conceptualization, development, writing, and production of various IEC materials such as brochures, pamphlets, leaflets, flyers, coffee table books, komiks, wall calendars, desk calendars, planners, posters, magazines, tarpaulins, info kits, billboards, among others.
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. If the request is approved, it will be forwarded to the Editorial Section Chief. If not, the requesting office will be notified.
• The Editorial Section Chief will then assign an Information Officer to facilitate the request. The Info Officer will gather/research information materials needed and draft the PR and IEC material.
• The Editorial Section Chief will then edit and check the draft the PR and IEC material. After which, the Info Officer will input all the corrections. The Editorial Section Chief will again check the write-up. If approved, it will be forwarded to the Division Chief for further review and approval.
• The Division Chief will forward the revised PR or write-up to the requesting office for approval. If there are comments and suggestions from the requesting office, the info officer will edit and incorporate it on the write-up.
• The Editorial Section Chief will review and forward the approved final PR to the requesting office. The write-up of the IEC material will be forwarded to the Audio Visual and Graphics (AV&G) Section Chief for layout. The AV&G Section Chief will assign a graphic artist to design and layout the materials. The layout artist will prepare the designs and layouts of the materials.
• The AV&G Section Chief will then check, review, and edit the materials for appropriate format, size, text, style, color, etc. before submission to the Division Chief.
• If the material is approved, the AFID chief will send them back to the requesting office for review and final approval. If there are comments and suggestions, the layout artist will again edit and incorporate the corrections.
• If there will be no more suggestions and comments, the Division Chief will then forward the approved IEC material to the requesting office. Process
Provides editorial assistance to bureaus, attached agencies, corporations, foreignassisted projects, and regional offices to ensure consistent messages of DA materials for production.
Flow:
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. If the request is approved, it will be forwarded to the Editorial Section Chief. If not, the requesting office will be notified.
• The Editorial Section Chief will then assign an Information Officer to facilitate the request. The Information Officer will edit and validate the data.
• The Editorial Section Chief will edit and check the drafted write-up/IEC materials. After which, the Info officer will input all the corrections.
• The edited write-up/IEC material will be given to the Editorial Section Chief for final review and if there will be no more suggestions and comments this will be forwarded to the Division Chief for further review and approval.
• The Division Chief will send the edited write-up/IEC material to the requesting office.
Fill-out and file request for editing of write-up/material or send the letter of request
Approve and forward request to the Editorial Section Chief
Assign a staff to do the request
Edit and validates the data
Edit and checks the draft
Input all the corrections
Check approve and forward the edited write-up/material to the AFID Chief
Check approve and send the edited write-up/material to the requesting office
The Audio Visual and Graphic Arts (AV&G) Section handles requests for video presentations, preparation for radio programs/segments, photo and video coverages, design and layout of various IEC materials and office forms, and requests for sound system, and AV equipment during meeting and DA events.
1. Preparation and Management of TV and Radio Programs/ Segments
Preparation of newscasts and program/segments, information materials for radio broadcast, scripts, and replies to listeners’ correspondences/queries.
Process Flow:
For Radio Program/Segment:
• The Radio Producer Announcer (RPA) will prepare program/ segment outline for approval by the AV&G Section Chief.
• With the approved outline, the RPA will gather news materials coordinate with the resource persons, prepare guide questions for approval by the AV&G Chief and proceed with the script.
• The AV&G Section Chief will review and edit the script and return it to the RPA. The RPA will rewrite the script based on the comments and suggestion and then return it to the AV&G Section Chief for approval, then to the Division Chief.
• The approved script will be used by the RPA for the interview with resource person on-air and schedule of the radio program/segment.
For TV Program/Segment:
AUDIO VISUAL AND GRAPHIC ARTS SECTION
Agriculture and Fisheries Information Division
Media Production Specialist III
Scriptwriter II
Broadcast Program Announcer
Administrative Assistant IV
Creative Arts Specialist I
Audio Visual Aid Technician III
Photographer II
Audio Visual Equipment Operator III
Administrative Assistant II
• The AFID Technical Working Group (TWG) will prepare program/segment outline for approval by the AV&G Section Chief.
• With the approved outline, the TWG will gather news materials coordinate with the resource persons, prepare guide questions for approval by the AV&G Chief and proceed with the script.
• The AV&G Section Chief will review and edit the script and return it to the TWG. The TWG will rewrite the script based on the comments and suggestion and then return it to the AV&G Section Chief for approval, then to the Division Chief.
• The approved script will be used by the TWG for the production of the program/segment.
2. Request for Video Presentation
DA provides assistance to bureaus, attached agencies, corporations, and DA banner programs in their in-house production of AV/video presentations.
Process Flow:
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. If the request is approved, it will be forwarded to the AV&G Section Chief. If not, the requesting office will be notified.
• The AV&G Section Chief will then assign an AV staff to handle the AV/video presentation. The AV&G Section Chief, requesting office representative/s, and assigned AV staff will conduct a meeting for the conceptualization and preparation of materials needed for the AV presentation.
• If a script is needed, the AV&G Section Chief will assign a writer to prepare. The AV&G Section Chief will then review, comment, and give suggestions on the script. After which, the writer will incorporate the comments and suggestions on the prepared script. The revised script will be forwarded to the requesting office for their review and comments. If there are comments and suggestions from the requesting office, the writer will incorporate these and finalize the script.
• With the final script, the AV staff will proceed with the gathering of materials (photos and footages) through photo and video shoot in the identified places.
• The AV staff will review and edit the photos and footages taken consistent to the approved AV/video script.
• The AV&G Section Chief will review, approve, and send the initial AV/video presentation to the requesting office for review and comment.
• If there are comments and suggestions, the AV staff will again edit and incorporate these on the AV/video presentation.
• The edited AV/video presentation will be given to the AV&G Section Chief for final review and if there will be no more suggestions and comments, will be forwarded to the Division Chief for further review and approval.
• The Division Chief will then send the approved AV/video presentation to the requesting party.
3. Request for Photo Coverage
This includes documentation of regional engagements of DA officials and other agri-related events, meetings, courtesy calls, and taking photographs of agricultural products for IEC materials.
Process Flow:
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. If the request is approved, it will be forwarded to the AV&G Section Chief. If not, the requesting office will be notified.
• The Division Chief will forward the approved request to the AV&G Section Chief and assign a photographer to cover the event.
• The photographer will cover the assignment and select good shots for printing, media release, and social media and web uploading after the coverage. The selected photos will be processed (process color corrections and other necessary alterations) and submitted to the AV&G Section Chief for evaluation and approval.
• The AV&G Section Chief will then assign a writer to put caption on the approved shots for editing and approval.
• The AV&G Section Chief will submit the edited and approved photo caption to the Division Chief for approval.
• The Division Chief will forward the captioned photo to the Press Office for dissemination to media outlets and uploading in social media platforms.
4. Request for Video Coverage
Includes documentation of the Secretary and other DA officials activities, success stories of the farmers, fishers, agri-entrepreneurs, among others, production of corporate videos, and video coverages on DA events.
Process Flow:
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. If the request is approved, it will be forwarded to the AV&G Section Chief. If not, the requesting office will be notified.
• The Division Chief will forward the approved request to the AV&G Section Chief.
• The AV&G Section Chief will calendar or schedule the event and will assign an AV crew to cover it and a writer to prepare a factsheet.
• The AV crew and assigned writer will cover the assignment on the scheduled time.
• After the coverage, the writer will prepare the factsheet or video release for AV&G Section Chief approval.
• The videographer will edit the video consistent with the factsheet.
• Upon approval of the AV&G Section Chief and the Division Chief, footages will be taken for media release, and social media and web uploading.
• The AV crew will dub and release/distribute copies to all TV stations.
5. Request for Voice-Over of Video Productions/AVPs
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. If the request is approved, it will be forwarded to the AV&G Section Chief. If not, the requesting office will be notified.
• The AV&G Section Chief will then assign an AV staff to handle voice-over
• If a script is needed, the AV&G Section Chief will assign a writer to prepare. The AV&G Section Chief will then review, comment, and give suggestions on the script. After which, the writer will incorporate the comments and suggestions on the prepared script. The revised script will be forwarded to the requesting office for their review and comments. If there are comments and suggestions from the requesting office, the writer will incorporate these and finalize the script.
• With the final script, the AV staff will proceed with the voice-over consistent with the approved script.
• The AV&G Section Chief will review, approve, and send the initial voice-over to the requesting office for review and comment.
• If there are comments and suggestions, the AV staff will incorporate these in the voice-over. If there will be no more suggestions and comments, it will be forwarded to the Division Chief for further review and approval.
• The Division Chief will then send the approved voice-over to the requesting party.
Process Flow: 6. Request for
Includes design and layout of information advocacy collaterals, IEC materials, and other official forms/documents (Annex), calling cards, routing slips, etc.
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. If the request is approved, it will be forwarded to the AV&G Section Chief. If not, the requesting office will be notified.
• The Division Chief will forward the approved request to the AV&G Section Chief.
• The AV&G Section Chief will assign a layout artist to do the design and layout.
• The layout artist and a representative from the requesting office will conduct a meeting for the conceptualization of the design.
• The layout artist will execute the agreed concept and submit it to the AV&G Section chief for comments and suggestions.
• The layout artist will incorporate the comments and suggestions and submit it to the AV&G Section Chief for approval.
• After review and approval, the AV&G Section Chief will send the design to the requesting office for review, comments, and suggestions.
• The layout artist will incorporate the corrections and suggestions of the requesting office in the final layout and submit it to the AV&G Section Chief for review.
• The AV&G Section Chief will forward the final layout to the Division Chief for review and approval. If there are corrections still, it will be returned to the layout artist for revision. If there is none, the Division Chief will send it to the requesting office.
7. Request for Ad Supplement
Process Flow:
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. The program coordinator will check if there is available AFID budget to fund the request. If none, fund allocation will be sourced from the requesting party.
• The assigned writer/s will prepare needed write-ups/materials for review and approval of the Chief and the requesting party. If no more corrections, the layout will be sent to the publishing company.
**If materials are already prepared upon request by therequesting party (i.e guidelines, memo circulars), this will be sent to the concerned publishing company for layout to determine the size it will occupy in the newspaper. Then PRAS will be prepared and submit to the online procurement system of the Department.
8. Request for Sound System, and other AV Equipment
Process Flow:
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. If the request is approved, it will be forwarded to the AV&G Section Chief. If not, the requesting office will be notified.
• The Division Chief will forward the approved request to the AV&G Section Chief.
• The AV&G Section Chief will calendar the request then will assign a staff as the AV operator.
• The AV operator will prepare the requested equipment, test run, and bring the same to the event’s venue.
• The AV operator will install and operate the equipment until the event ends then repack and bring the equipment back to the office.
9. Request for Printing, Cutting, and Binding of Various IEC and Office Materials
Process Flow:
• The requesting office must fill out and file/send request. The request form or letter will be forwarded to the Division Chief. If the request is approved, it will be forwarded to the AV&G Section Chief. If not, the requesting office will be notified.
• The Division Chief will forward the approved request to the AV&G Section Chief.
• The AV&G Section Chief will assign a layout artist and a printing machine operator/staff to facilitate the request.
• The layout artist will check the specifications of the material to be printed, adjust the settings according to the printer’s capability and capacity while the printing machine operator/staff will execute the request.
• The assigned printing machine operator/staff will prepare the materials needed, check the machines, adjust the settings, and do the request.
• The printing machine operator/staff will submit the final output to the AV&G Section Chief.
• The AV&G Section Chief will send the final output to the requesting office.
The Library Section aims to provide easy access to agricultural information and to disseminate updated materials to library users.
• Accession Number – A unique identifier assigned to and achieving initial control of, each acquisition.
• Accession Record Book – The official record of each volume added to the library including date and number of accessions, author, title, place, publisher, date of printing and copyright, volume, size and number of pages and cost.
• Call Number – A number, letter, symbol, or combination of these, indicating the specific location of a work in a library, especially the combination of classification symbol and the designation of the author.
• Card Catalog – A file of cards of uniform size arranged in some definite order and listing the items in the collection of a library or group of libraries, each card typically identifying a single item.
• Catalog Card – An individual entry in a library catalog containing bibliographic information, including author’s name, book title, and even approximate location.
• Cataloging – The process of creating metadata representing information resources, such as books, sound recordings, moving images, etc.
• Cataloger – A Librarian who classifies publication according to a categorical system.
• Circulation Desk – A place in the library, which provides lending services and facilities for return of loaned items.
• Closed Shelf – A library stacks with access restricted to the staff of the library or a limited group of library users.
• Computer File Librarian (CFL) – A person who works in the data library and keeps track of the non-print materials stored and logged out for use. Also known as a “File Librarian”.
• Indexing (service) – A service that assigns descriptors and other kinds of access points to documents.
• Librarian – A person who works professionally in a library, providing access to information, provide instruction on information literacy to users.
• Library of Congress Classification – A classification system that was first developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries to organize and arrange the book collections of the Library of Congress.
• Library of Congress Subject Headings –Integral part of bibliographic control, which is the function by which libraries collect, organize, and disseminate documents.
• Monograph – A highly detailed and thoroughly documented study or paper written about a limited area of a subject or field of inquiry.
LIBRARY SECTION
Agriculture and Fisheries Information Division
Librarian III
Librarian II
Librarian I
Computer File Librarian
• Non-print Materials – Not printed, not occurring in, being, or involving printed matter.
• Online Public Access Catalog (OPAC) – an online database of materials held by a library or group of libraries.
• Periodicals – Is anything that comes out with regular issues. Examples of these are daily newspaper, weekly news magazine, and monthly journal.
• Philippine Standard Commodity Classification – A detailed classification of all imported and exported commodities being used for tariff and statistical purposes.
• Serials – A publication in any medium issued in successive parts bearing numerical or chronological designation and intended to be continued indefinitely.
• Vertical file – A collection of resource materials, such as pamphlets, clippings from periodicals, and mounted photographs, arranged for ready reference.
• Weeding out – A systematic removal of resources from a library based on selected criteria.
Cutting and clipping of agri-related articles published in the daily broadsheets and tabloids.
Staff Responsible: Computer File Librarian/Librarian
Process Flow:
• Receive the newspaper.
• Count the newspapers upon receipt and sort these for reading and clippings purposes.
• Stamp mark of ownership on newspapers and staple one set for reading purposes.
• Browse agri-related articles, cut and paste these on bond papers for newspaper clippings.
• Stamp mark of ownership to all pasted news clippings
• Prepare list/title cover of news clippings and scan all clippings including the title cover.
• Photocopy the newspaper clippings and submit all photocopied clippings to the Press Office.
• E-mail the scanned copy of newspaper clippings to all DA officials and concerned staff.
• Assign subject headings to pasted newspaper clippings.
• File clippings in the Vertical Files Collection arranged alphabetically by subject.
• Weed-out of five (5) year old newspaper clippings.
Recording of newly acquired publications (Purchased and Donations)
Process Flow:
• The CFL will receive the publication and record its information on the record book.
• The CFL will bring all the recorded publications to the Cataloger (Librarian) for cataloging.
• If the publication was donated, the Librarian will prepare an acknowledgment letter.
Staff Responsible: Librarian Process Flow:
• Mark stamp of ownership to the library materials. Perform the following:
- Provide cards for serials, pamphlets, brochures and IEC materials and file on the Records Cards.
- Record the details of the book/monograph in the accession record book and assign accession number to the publication.
• Catalog and classify the library materials according to the Library of Congress Classification Scheme.
• Print/write the call number on the spine for books and on the upper left-corner of the cover page for serials, pamphlets, brochures and IEC materials.
• Provide book card and book pockets to the publications.
• Encode the bibliographic data and print complete set of catalog cards.
• File the book/monograph on the shelf according to call number and the serials for indexing.
• File the catalog cards on the card catalog.
Library-Classifying Newspaper Clippings and Pamphlets, Brochures and other IEC Materials
Mark books with stamps of ownership upon receipt of new ones
Assigns accession number
Catalogue and classify the books according to the Library of Congress Classification Scheme
Check the catalogue and classification of books
Print the call number on the spine of the book
Prepare book cards and book pockets
Type and file catalogue cards
Check the typed catalogue cards
File the book
Charging-Out of Books
Accomplish and sign the researcher’s slip
Sign the book card
Search the books requested on the shelves
File the Borrower’s Card in the circulation tray
Process Flow:
• Select articles for indexing and perform indexing procedures.
• Assign subject according to Library of Congress Subject Headings and Philippine Standard Commodity Classification.
• Encode and print complete set of indexed cards.
• File the serials on the shelf according to call number.
• File the indexed cards on the index catalog card arranged alphabetically by subject.
5. Library Digitization
Process Flow:
• Label the library received materials and scan for digital format.
• Crop the scanned library material.
• Save back-up file for scanned folder.
• Export file from PDF to TIFF.
• Review the image of the scanned material for quality control using Scan Tailor Software.
• Convert file from TIFF to PDF and final review the file.
• Save file in the Network Attaché Storage for master file back-up.
*Additional procedures will be added when the OPAC/Library System is available.
6. Borrowing of Library Materials
Process Flow:
• Library users will register on the log book provided at the circulation desk upon entry.
• The library user will select his/her material from the card catalog and will fill-out Researcher’s Slip and bring it to the circulation desk.
• The library staff will retrieve the library material listed on the researcher’s slip and give it to the library user.
• After using the library materials, the library users will place the material/s used on the designated area.
*The DA Library practices a closed-shelf policy system.
*All library collections are strictly for ROOM-USE only for non-DA researchers.
7. Charging-out of Library Materials
Process Flow:
• The library users will do the borrowing procedures :
• Library users will register on the log book provided at the circulation desk upon entry.
• The library user will select his/her material from the card catalog and will fill-out Researcher’s Slip and bring it to the circulation desk.
• The library staff will retrieve the library material listed on the researcher’s slip and give it to the library user.
• The library user will fill-out the necessary information on the book card.
• The librarian will stamp the due date on the book card and file at the circulation tray.
• The borrower is allowed to check-out with a maximum of five (5) books.
• The following materials are strictly for ROOM-USE only.
- Reference materials (dictionaries, encyclopedias, etc.)
- Periodicals, journals, magazines, newspapers and vertical files.
- Non-print materials (audio-visual materials such as CDs, DVDs, etc.)
Details/Notes: All permanent DA Employees are allowed to check-out library materials.
8. Charging-in of Library Materials
Process Flow:
• The borrower will return the borrowed library material/s to the Librarian/CFL at the circulation desk.
• The Librarian/CFL will check the condition of the borrowed material/s.
• The Librarian will pull out the corresponding book card from the circulation tray, stamp the returned date and place it back in the book pocket.
• Keep the researcher’s slip and return the library material on the shelf.
Process Flow: 9. Renewal of Library Material/s Borrowed
• The borrower will return the library material/s borrowed to the Librarian/CFL at the circulation desk and request for the renewal.
• The Librarian/CFL will check the condition of the library material/s.
• The Librarian will pull out the corresponding book card from the circulation tray and stamped with the returned date.
• The borrower will fill-out again the necessary information on the book card and researcher’s slip.
• The librarian will stamp the due date on the book card and give the materials to the borrower.
10. Lost/Damaged Library Materials
Process Flow:
• The borrower is required to replace the lost/damaged material with the same bibliographic information (title, author, edition/volume, year of publication).
• In case the library material is no longer commercially available:
- The old edition maybe replaced with the newest edition.
- Can be replaced by a material with the same title and subject which cost not lower than the lost/damaged material.


Business Process Review and Synthesis for the Automated Government Service Management System for DA Regulatory Agencies
WORKSHOP ON AUTOMATED GOVERNMENT SERVICE
MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (AGSM)
for DA Regulatory Agencies Prepared by the Information and Communications Technology Service

The role of information & communications technology (ICT) in the current generation is very useful and powerful. ICT has become a vital and integral part of every sector of society. It can fast track communication processes and serves as the main prime mover of data which are vital in strategic planning and policy-making. With the application of ICT, one can make sophisticated and comprehensive databases that can contain all imaginable pieces of data it can store, update and even analyze information that serves as bases for solutions to current or future problems.
To reinforce the need for the digitalization of Philippine Agriculture, the Agriculture and Fisheries Modernization Act (AFMA) of 1997 (RA 8435) mandates the Department to set-up a national information network (NIN) from the central office down to the regional, provincial and municipal offices and shall likewise link various research institutions, cooperatives, other private sector, and other government agencies for easy access to data on agriculture and fisheries research technology.
The law also gave the power to ensure the provision of the necessary information technology, IT training, and basic infrastructure requirements as well as establish suitable telecommunications links with capable private sector service providers. The Philippine Department of Agriculture (DA) is also mandated to explore and innovate mechanisms to ensure cost recovery and sustainability, where recoveries are applied to the improvement and sustainability of the NIN and its associated training programs without disregarding equity in access to the NIN, particularly by small and subsistence farmers and fisherfolk and their associations. As we embark on DA Secretary William D. Dar’s journey as servant-leader, we will continue to harness the power of information and communications technology (ICT) to maximize agricultural production and increase the income of our clientele.
Now more than ever, the digitalization of the agriculture sector should be at the tip-of-the-spear in the battle against COVID-19 and the fight for food security. The use of technologies that integrate production from farms to consumers and provide tools and information for decision-makers to improve productivity and cost-efficiency is now a necessity. It is imperative that we don’t get left behind as we transition to Philippine “Agriculture 4.0” and the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR).

Rationale
A business process review (BPR) enable institutions to design workflows that reduce human error, manual work and process completion times while increasing employee bandwidth and enabling business continuity. It brings clear definition of process automation and its benefits. During a business process review, the analyst will breakdown everything you do day-to-day and document these activities. The reviewer will the elicit information from the employees that are involved in these important processes (Wacker, 2021) The aim of the BPR is to quickly understand the regulatory agencies’ capacity or degrees of freedom to execute and automate certain processes. The identification of the current ICT capabilities and resources will outline the key areas of concern including key drivers and whether ICT is an enabler or constraint. If resources and capabilities are incorrectly assessed, sound and logical strategy might be rendered useless and performance measurement systems might be adversely affected.
The workshop is part of the strategic implementation plan relative to OneDA reform agenda under Ease of Doing Business and Transparent Procurement strategy. One of the measures of this 17th strategy is the automation of the regulatory processes of the Department. It states that the DA will continue to pursue “internal cleansing”, strengthen and synchronize efforts to institute a more transparent, technology-driven processes and procurement system. The DA will also aid agripreneurs, especially medium and small Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), in reducing the cost and effort of complying with the regulatory burdens of doing business.

The general objective of the workshop is to develop processes/ systems and models that will simplify, streamline, and harmonize procedures, requirements and at the same time, maximize the use of existing technology for continued effective and more efficient government service delivery to the public. Specifically, the workshops aims to:
1. Identify and review business processes or systems for automation in DA Offices and come up with a prioritization list for development; and,
2. Determine various factors that will affect the successful development.
The event is critical in recognizing the selection of the processes that will support the streamlining of the current systems and procedures. This will simplify the business operations of the organization.

A small team from the ICTS was mobilized to facilitate the conduct of the workshop. The group also conceptualized and determined the different tools and activities that will be performed. This was followed by the adoption, simplification and testing of workshop tools, particularly the templates/ instruments. An estimated 128 personnel from various DA regulatory agencies, including senior officials, resource speakers and support staff were invited as face-toface participants while at least 200 individuals joined the sessions through an online platform. They are mostly technical personnel, Regional Technical Directors for Research and Regulations, heads of agencies and finance officers. During the agency group discussion 1, they identified the processes for automation using the workshop template. The tool captured the processes, description, data collected, data shared proposed mode of development and prioritization for automation for each respective agency. They are classified whether exclusive to their office (internal ICT project), common with other offices (cross-agency ICT project) or interconnecting/ sharing of data.
For the agency group discussion 2, each of the 11 regulatory agencies consolidated their perceived challenges and corresponding strategies for the automation of their processes. Part of the discussion were problems in terms of manpower, technology, environment, and other resources. The factors which may hinder the automation/ systems development as well as the other considerations which affects the successful implementation of the system. They were also given a chance to list activities that may help achieve the automation of their agency’s priority processes and tactics that will ensure the effective streamlining and re-engineering leading to computerization. Essentially, it is but proper to document these activities for future reference. This will greatly help in enhancing the capacity of the existing ICT personnel resources thus assuring its continuity and sustainability in supporting the operations of DA.

The expected outputs of the workshop are the identified and prioritized business processes for automation of the regulatory agencies and the strategies to develop and implement the information systems to support the current initiatives of the DA including specifically for regulatory agencies.
Due to time and resources constraints, only 2 days were allotted for the workshop. There were 11 DA regulatory agencies that participated in the workshop. They are the Bureau of Agriculture and Fisheries Engineering (BAFE), Bureau of Agriculture and Fishery Standards (BAFS), Bureau of Animal Industry (BAI), Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (BFAR), Bureau of Plant Industry (BPI), Fertilizer and Pesticide Authority (FPA), National Meat Inspection Service (NMIS), Philippine Fiber Industry Development Authority (PhilFIDA), National Tobacco Administration (NTA), National Dairy Authority (NDA), Philippine Coconut Authority (PCA), Philippine Fisheries Development Authority (PFDA) and Sugar Regulatory Administration (SRA)
The outcome of the workshop, seeks to picture the capabilities of DA to automate its regulatory processes. It reflects a macro perspective of the current situation of the ICT network for the entire Department. Although this workshop may have its shortcomings, it is safe to say that it will give a good description of the true state of automation in the DA as a whole. It can be used as an indicator and a planning tool to find out the gaps and overlaps relative to information technology support in the DA’s programs. Take note that the workshop was not intended to give a detailed analysis on the present status of automation in DA. Rather, it hopes to provide a glimpse of the DA ICT’s impact in the automation of DA processes. This will greatly help in future ICT planning, policy analysis and in the design of appropriate interventions.
The result of the workshop for processes that are exclusive to each DA regulatory agency shows that the priority for automation are their certification processes (23.5%). This is followed by licensing (17.3%), registration (14.8%), monitoring/ inspection (11.1%), accreditation (9.9%) and clearance (4.9%). The rest and least priority are the monitoring/ reporting, and payment portals. The highest ranked category of processes can be streamlined, harmonized, integrated and developed into a single window or online portal depending on the decision of the ease of doing business task force and the available resources.

2. Common with other agencies (Cross ICT project)
In terms of the identification and prioritization of processes for system development, monitoring/ inspection processes got the highest rank with 22.6%. The payment portals was pegged at 18.5% followed by permits, certification, collection, accreditation, clearance and registration, respectively as shown in figure 10. Among the processes/ systems prioritized are document tracking, property/ inventory management, online payments, government accounting, certifications, laboratory services and payroll.

3. Interconnecting and sharing data
For processes that interconnect and share data, figure 11 shows that almost half of the agencies’ priority for automation are their certification processes (41.2%), followed by licensing (17.6%), accreditation (11.8%), registration (11.8%), and the rest. Again, all these processes can be harmonized, integrated and developed into 1 single window or online portal depending on the decision of the ease of doing business task force and the available resources.

The result of the agency discussion 2 were consolidated, grouped and ranked into 5 categories. These are a.) infostructure, connectivity & equipment, b.) ICT learning & development (L&D), c.) ICT human resource, d.) digital policy & standards, and e.) budget/ financial constraints (figure 12).

When it comes to automation of regulatory processes, the main issue for the participants were infostructure, connectivity and equipment (38%). This was primarily attributed to poor or weak internet connectivity, lack/ limited hardware and developed regulatory information systems/ portals as well as insufficient online payment providers just to name a few. To mitigate this, they recommended to promote closer collaboration/networking with the Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT) and the private telecommunication companies. It also includes and acquisition of increased internet bandwidth as well as additional capital investments in ICT infrastructure and applications. They further opined that the DA needs to strengthen partnerships with public and private stakeholders in the regulatory environment.
ICT learning and development (27%) comes next as the perennial problem for the participants of the workshop. The limited awareness of stakeholders on digital solutions, stakeholders’ hesitancy/ resistance to adapt ICT and lack of ICT knowledge and skills among regulatory personnel were among the perceived threats to digitalize the regulatory sector. Accordingly, their recommendation were to conduct information & education campaign (IEC) and knowledge transfer, develop an ICT capacity development program for DA regulatory agencies, implement customized trainings to enhance digital competencies and transform mind sets, and to carry-out organizational capacity evaluation. Third in the list are the problems pertaining to ICT human resource (15%). The limited/lack of IT personnel, unavailable IT plantilla positions and the lack of manpower complementation/ mismatched capabilities were some of the issues which was raised by the regulatory agencies during the event. For the participants, these can be alleviated by hiring of additional manpower or creation of ICT units or interim ICT units/ office and by proposing additional staff positions to the Department of Budget and Management (DBM). Fourth in the list were the difficulties on ICT policies & standards (11%). The reasons cited were the lack of interoperability for similar processes/ systems, “un-harmonized” regulatory procedures and threats on cybersecurity and data privacy. The proposed solutions were the creation of technical working groups (TWGs) for harmonization of regulatory processes, conduct of in-depth business process analysis, treamlining and/or re-engineering, ISO/ IEC 27001 - information security management system certification and conduct of data privacy impact assessment. lastly, budget/ financial constraints (9%) represented the last group of obstacles towards automation. The limited funding support for digitalization and poor planning in the preparation of ICT budget proposals were the key drawbacks that were mentioned during the workshop. The participants reiterated that additional funding assistance for ICT should be given and that digital agriculture should be elevated as one of the major programs of DA.
Other recommendations
The recommendations of ICTS technical staff, resources speakers, panelists and other stakeholders were also summarized and consolidated as shown in the following bullets:
• Identify and prioritize processes/ systems first before you can streamline and automate;
• Fast-track onboarding of DA regulatory agencies in the TradeNet/ national single window (NSW);
• Explore possible arrangements with value added service providers (VASPs;
• Push collaboration with existing payment gateways;
• Strengthen corporate social responsibility (CSR) collaborations and linkages with the private sector;
• Establish close networks with DICT, DOF and other relevant partners through adoption of their digital solutions (online payment platforms, e-BPLS, digital official receipts, etc.);
• Automate priority regulatory processes through possible donor/ grant funding;
• Adapt good practices of neighboring countries on computerization of regulatory procedures;
• Prioritize harmonization and integration of regulatory processes to promote efficiency and economies of scale;
• Rollout and upscaling of existing regulatory and other systems (eg. UCAS, etc.);
• Sharing of existing regulatory information systems for possible inclusion in the DA Digital Command Center;
• Conduct of a deeper business process analysis (the workshop saw only the macrocosm of the regulatory issues and concerns);
• There should be a policy and a data repository in place to prevent the resubmission of renewal application forms to streamline the process;
• Always use the ease of doing business law and ARTA as “lens” in the automation of processes;
• Consider internet-of-things (IoT) in the machineries, security features, cloud service, security batches/ blockchain, and document tracking system (DTS);
• Conduct a survey and impact assessment of current processes particularly on getting feedback from clients; and,
• Traceability system should be included in the automation process.




Process Flows of the Department of Agriculture’s Regulatory Agencies



• Bureau of Agriculture and Fisheries Engineering (BAFE)
• Bureau of Plant Industry (BPI)
• Bureau of Animal Industry (BAI)
• Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (BFAR)
• Bureau of Agricultural and Fisheries Standards (BAFS)
• National Meat Inspection Service (NMIS)
• Sugar Regulatory Administration (SRA)
• Philippine Coconut Authority (PCA)
• Fertilizer and Pesticide Authority (FPA)
The recently conducted Seminar-Workshop on Automated Government Service Management System for the Regulatory Agencies of the Department of Agriculture (DA) became an avenue for a comprehensive discussion of all the regulatory process flows of the following bureaus, attached agencies, and corporations of the DA:
• Philippine Fiber Industry Development Authority (PhilFIDA)
• Philippine Fisheries Development Authority (PFDA)
• National Dairy Authority (NDA)

The Bureau of Agriculture and Fisheries Engineering (BAFE), under the Agricultural And Fisheries Mechanization (AFMECH) Law of 2013, is mandated to “Coordinate and monitor the enforcement of the standard and other regulatory policies on agricultural and fishery engineering; Implement accreditation and registration scheme for agriculture and fisheries machinery, tools and equipment, in coordination with technology generators; Promulgate and implement accreditation guidelines for testing centers; and Issue permits to operate to agriculture and fishery tools and equipment manufacturers, fabricators, assemblers and importers.”
During the seminarworkshop, they featured five (5) regulations where four (4) are highlytechnical, taking up 20 working days for its respective processing periods: Permit to Operate, Certificate of Conformity, Certification of Test Engineers, Accreditation of Testing Centers. AMTEC Test Exemption, as a complex transaction, takes seven (7) working days.
The Permit to Operate is issued to any Manufacturer, Fabricators, Assemblers, Dealers, Distributors, Importers, and Exporters (MFADDIEs) who have completed pertinent submissions and have been reviewed, inspected, and evaluated by DA-BAFE and Regional Agricultural Engineering Division (DA-RAED).






The Bureau of Plant Industry (BPI), as a regulatory agency, is divided into the following: National Seed Quality Control Services (NSQCS), Plant Product Safety Services Division (PPSSD), National Plant Quarantine Services Division (NPQSD), and Biotechnology Office.
The National Seed Quality Control Services (NSQCS) follows the Seed Industry Development Act of 1992 and provides quality assurance and control services for seed and distribution, seed research, and seed training in seed quality control towards sustainable agriculture and environmental protection.
The Plant Product Safety Services Division (PPSSD), under the Food Safety Act of 2013 (Republic Act 10611), targets strengthening the food safety regulatory system in the country to protect consumer health and facilitate market access of local foods and food products, and for other purposes.
The National Plant Quarantine Services Division (NPQSD) is tasked to prevent the entry of quarantine/exotic plant pests into the country, prevent further spread of those already present, and enforce the compliance with the phytosanitary requirements of importing under the Plant Quarantine Law of 1978 (Presidential Decree 1433).
The Biotechnology Office is in charge of preventing the introduction, incursion, establishment, and subsequent spread of plant pests by regulating the international and domestic movements of plants and plant products under P.D. No. 1433. It also under the DOST-DA-DENR-DOH-DILG Joint Department Circular No. 1, Series of 2016.
The NPQSD oversees granting the License to Operate for the importer and exporter, which is a requirement for the importation and exportation of agricultural commodities and application for Sanitary and Phytosanitary Import Clearance (SPSIC).
The office is also responsible for issuing the Phytosanitary Certificate (PC), the License to Operate for Quarantine Treatment Provider, Packaging Facilities - for export, and the Certificate of Registration for Farmers or Growers.
The PPSSD, NSQCS, NPQSD, and DA-RFOs are issuing the Certificate of Good Agricultural Practices (GAP), a requirement for food safety/consumer preference and local and export purposes and signed by the BPI Director.
The Biotechnology Office is in charge of the Issuances of Biosafety Permits, a prerequisite for importing GM products for direct use, field trial, and commercial propagation.
NSQCS accredits seed growers and as well as issues Seed Certification.
BPI / NPQSD License to Operate (Importer) Requirement for importation of agricultural commodities and application for Sanitary and Phytosanitary Import Clearance (SPSIC) signed by BPI Director
-Submission of application with the required documents (TradeNet)
- Review and evaluate application forms
-Scheduling of inspection
-Inspection of Warehouse facility
-Orientation to DA Trade System
- Preparation of COR, CRR, PQSC
- Signing of certificate
- Payment of fees
- Endorsement to DA trade system
Importer details, exporting country detail, commodity details to be imported, cold storage license
or not
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BPI / PPSSD License to Operate (Cold Storage Warehouses)
Requirement for cold storage warehouse operation and application for license to operate (importer)
- Submission of notarized application form together with required documents
-Receipt and evaluation of documents
signed by BPI Director
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BPI / NPQSD Sanitary and Phytosanitary Import Clearance (SPSIC)
Requirement for importation of agricultural commodities
signed by BPI Director
BPI / NPQSD License to Operate (Exporter) Requirement for exportation of agricultural commodities
signed by BPI Director
-Payment of fees
-Scheduling and issuance of notice of inspection
-Conduct of inspection, preparation of reports, submission to AC -TWG for evaluation
-Issuance of License to Operate
-Uploading, review, and evaluation of List of Importables (LOI) (DA- Intercommerce)
- Input port conditions and send to the NPQSD Chief (LOI)
- Review and endorsement of application (LOI) to the BPI Director
- Payment of fee - Review and approval by Plant Quaratine reviewer - Issuance of SPSIC
-Submission of notarized application form together with the requirement
- Review and evaluation of application forms
- Schedule of Orientation
- Inspection of Office
- Report and recommendation by the PQO
- Final evaluation of certificate
BPI / NPQSD Phytosanitary Certificate (PC) Requirement for exportation of agricultural commodities and application for Licence to Operate (Exporter)
signed by BPI Director
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BPI / NPQSD License to Operate (Quarantine Treatment Provider)
Requirement for treatment of agricultural commodities to be exported/imported and application for Licence to Operate (Exporter)
signed by BPI Director
- Submission of application for inspection and phytosanitary certification
-Review and evaluation of application (Prohibited commodities, treatment required, other requirements)
- Treatment and inspection of commodity
- Payment of fees
- Issuance of Phytosanitary Certificate
- Submission of notarized application form together with required documents
- Schedule of visit of site/facility/office
-Treatment demonstration
- Endorsement to the NPQSD Chief
- Preparation of license to operate with corresponding QTP code
- Payment of fees
- Issuance of license
Warehouse capacity, commodity stored, importer details (accreditation)
if licensed or not
details, plant and plant product details
approved or not
details, plant and plant product details
exporter/import er details, plant and plant product details
BPI / NPQSD License to Operate (Packaging Facilities - for export)
BPI / NPQSD Issuance of Certificate of Registration for Farmers or Growers
Required facility for exportation of agricultural commodities and application for Licence to Operate (Exporter)
signed by BPI Director
- Submission of notarized application forms together with other required documents
- Review and evaluate application form
- Schedule of orientation of packing facility Operator
- Inspection of packing facility/ies
- Report and recommendation
- Final evaluation and preparation of certificate
- Signing of license
- Payment of fees
Requirement for exportation of agricultural commodities and application for Licence to Operate (Exporter)
signed by BPI Director
BPI / PPSSD, NSQCS, NPQSD DA-RFOs Issuance of Certificate of Good Agricultural Practices (GAP)
Requirement for food safety/consumer preference and local and export purposes
signed by BPI Director
- Issuance of License to operate
- Submission of notarized application form together with required documents
- Review and evaluation of application forms
- Schedule of orientation of growers/farmers
- Inspection of farms
-Report and recommendation by the PQO
- Final evaluation
- Preparation, signing, and issuance of certificate
-Submission of application to DA-RFO and endorsement to BPI-PPSSD
-Evaluation of the application
-Notice of Inspection
-Inspection
Process/Preparation of Inspection report
-Submission of report to PHILGAPCC
-evaluation of reports by GAP
details,
BPI / Biotechnology Office Issuances of Biosafety Permits
if approved or not
2 OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
CC and recommendation for certification
Requirement before importing of GM products for direct use, field trial and commercial propagation
signed by BPI Director
BPI / NSQCS Accreditation of Seed Growers Seed growers (SG) applying for seed certification should be accredited by BPI.
signed by BPI Director
-Issuances of certificates signed by BPI Director farmer details, pesticide and other inputs used, commodity planted
-Application with required docs -Risk Assessment of CNAs and STRPS
-DA-BC summarized report
-Issuances of Biosafety Permits for Direct Use, Field Trial and Commercial Propagation Technology developer; technical dossier and tabulated risk assessment
-Submission of application with the required documents
-Payment of fees
-Verification of submitted docs
-Inspection of field and postharvest facilities by SI
-Verification and endorsement by NSQCS Regional Office and RFOs
-Issuance of certificate of accreditation
or not
BPI / NSQCS Accreditation of Seed Growers
BPI / NSQCS Seed Certification
Seed growers (SG) applying for seed certification should be accredited by BPI.
signed by BPI Director
Requirement for ensuring seed quality (RA 7308, Seed Industry Dev't Act of 1992) and for procurement by DA projects
signed by BPI Director
-Submission of application with the required documents
-Payment of fees
-Verification of submitted docs
-Inspection of field and postharvest facilities by SI
-Verification and endorsement by NSQCS Regional Office and RFOs
-Issuance of certificate of accreditation
-Submission of application with the required documents
-Payment of fees
-Verification of submitted docs
-Preliminary and final field inspections by SI
-Packaging, sampling, and seed testing of samples
-Issuance of seed test results and seed tags
-Tagging of certified seeds SG details, planting data, bags tested, bags passed, NSIC registration
| COMMON WITH OTHER OFFICES (CROSS AGENCY)
Submission/ verification of documentary requirements BPI clients to submit authenticated documentary requirements to be verified proof of registration, license, accreditation, certification
Client to pay license, accreditation, certification fees and other fees via Online

The Bureau of Animal Industry (BAI) has the Animal Feeds, Veterinary Drugs and Biologics Control Division (AFVDBCD), Animal Health and Welfare Division (AHWD), and the National Veterinary Quarantine Services Division (NVQSD) issuing licenses and permits.
The AFVDBCD has online, electronic, and virtual processes. Its online orientations follow a scheduling system and digital certificate issuance, which is required to apply for a License to Operate. For the issuance of the electronic order of payment, the AFVDBCD, the process involves email requests for electronic order of payment, issuance of an order of payment, and then the sending of official receipt to the client once the payment has been made.
The License to Operate registration is also applied online.
The procedure for Licensing of Establishments outlines the scheduling of inspection of establishment, entry meeting at the site, inspection of documents, facility inspection, and exit/closing meeting. For those who will not be able to comply, the company will submit a corrective action.
Virtual inspection for licensing of establishments is also employed where scheduling, entry photo documentation, validation, facility inspection, and exit documentation are parts of the process.
As for the Certificate of Feed Product Registration (CFPR) application, it can also be done online, where they will have to register on the BAI website and upload documents to be reviewed. Once compliant, the application will be endorsed to pass through the Head of Licensing, Registration and Certification Section (LRCS) and the BAI Director/OIC Assistant for Regulations and Disease Control for approval.
Lastly, the Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Clearance requires online registration on the BAI website, where they also have to upload needed documents. After evaluation, once the application is complete and correct, it will be endorsed to the Supervising Agriculturist. The Supervising Agriculturist will then endorse it to the BAI Director/OIC Assistant for Regulations and Disease Control for approval.
The AHWD has the following frontline services:
1. Accreditation of Animal Show Veterinarians
2. Animal Research Permit
3. Animal Show Permit
4. Registration of Animal Facilities
5. Registration of Animal Show Organizer
6. Swine Breeder Farm Accreditation Program (SBFAP)
7. Small Ruminant Breeder Farms Accreditation Program (SRBFAP).
8. Gamefowl Breeder Farm Accreditation Program
9. Beef Cattle Breeder Farms Accreditation Program (BCBFAP)
10. Pigeon Club Certification
11. Poultry Farm Certification
Poultry Hatchery Certification
GAHP Certification Program
Licensing of Livestock
Poultry and By-Products Handlers 16. Registration of Land Transport Carriers
The validity of the Poultry Farm and Gamefowl Farm certificate is for two (2) years, Hatchery and Aviary certificates both for one (1) year, and Duck, Quail, and Pigeon Club certificates for six (6) months. The Handler’s License and Transport Carrier Registration are both valid for one (1) year.
STEP 1 (START)
schedule of
every Tuesday of
Client will receive Digital Certificate the following week signed by AFVDBCD Chief (END)
Note: The Certificate is a requirement before the establishment can apply for LTO
of
The NVQSD accredits commercial importers/ exporters of live animals, animal products, and byproducts (except frozen meat), issues SPS Import Clearance for animal products and by-products, SPS Import Clearance for live animals (except dogs and cats), SPS Export Clearance for live animals (except dogs and cats), Veterinary Health Certificate/ International Veterinary Certificate for the export of animal products (Fully Processed Products including Canned Goods and Frozen Poultry), Commodity Clearance Certificate, Veterinary Health Certificate/International Veterinary Certificate for the export of Dogs and Cats, local Shipping Permit for live animals, animal products and by-products, and Import Permit for Dogs and Cats.
STEP 1 (START)
Client will request an Electronic Order of Payment thru emails
STEP 4 Client will pay thru https://www.landbank.com/
STEP 5
Once the payment is made, Client will email the transaction Slip and issued Order of Payment to BAI Cashier (bai.cashier@gmail.com).
STEP 2
Administrative Support Staff will issue an Order of Payment once the following requirements are met.
STEP 3
Client will receive an Electronic Order of Payment form noreply@bai.gov.ph
STEP 6 (END) BAI Cashier will send a copy of Official Receipt to client email.
Note: The Official Receipt is a requirement before the establishment can apply for LTO
STEP 5
Reject Application
Schedule for Inspection of Establishment
Exit Photo Documentation
Compliant?
Yes No
Facility Inspection (Video Presentation) / Photo Documentation
Entry Photo Documentation
Company will submit corrective action
START END
CFPR ONLINE REGISTRATION PROCESS FLOW
PROCESS FLOW OF CFPR ONLINE REGISTRATION
STEP 1 (START)
Client will register to http://baireg.intercommerce.com.ph
Compliant?
Validation of Documents
For re-inspection (if necessary)
STEP 2
Client will receive confirmation from INS for their registration
STEP 4
CFPR Reviewer will evaluate the attached documents for its correctness and completeness
STEP 5
CFPR Reviewer will endorse the application to Head of Licensing, Registration and Certification Section (LRCS)
STEP 8
Client to print CFPR
STEP 3
Client will upload necessary documents and submit the application
STEP 6
Head of LRCS will endorse the CFPR
STEP 7
BAI Director/OIC Assistant for Regulations and Disease Control will approved the application













Receive and Review Filledout Application Form & Documents

Conduct Inspection and Evaluation of Facility (Onsite/ Virtual)
Prepare Certificate of Registration



Review and Sign for Approval of Certificate
Sign for the Approval of Certificate
Prepare Order of Payment
Issue Official Receipt
Release Certificate of Registration

The Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (BFAR) has presented a number of their processes for automation. Under the Fisheries Inspection & Quarantine Division (FIQD) are the following: (a) Registration of establishment for the Exportation of Fish and other Fishery/Aquatic Products, (b) Issuance of Export Commodity Clearance (ECC) for live food fish, live ornamental fish, shells and shellcrafts and its derivatives, and fresh, chilled, frozen fish and fishery/aquatic products, (c) Health Certificate for Export of Fresh Chilled and Frozen Fishery Products, (d) Health Certificate for Export of Live Food Fish and Live Ornamental Fish, (e) Health Certificate (HC) for transboundary movement of fish and fishery/aquatic products, (f) Accreditation of Importers, and (g) Manual issuance of Sanitary Phytosanitary Import Clearance (SPSIC) under FAO 259 Wet Market.
The Fisheries Inspection & Quarantine Division and the Fisheries Inspection Section (FIQD-FIS) are the ones in charge of the License to Operate for Cold Storage Warehouses, Inspection of Fishery/Aquatic Products/ Establishments (New Applicant) for Registration and Issuance of HACCP/GMP/SSOP/Vessel Certificate (New Applicant), Inspection of Fishery Establishment for Export of Fishery/Aquatic Products for Issuance of Certificate of HACCP/GMP/SSOP/Vessel (Renewal of Certificates), Accreditation of Importer, Pre-shipment inspection, 2nd Border Inspection (Post Border Inspection), and Registration of Traders/ Exporters of fishery / aquatic products.
The BFAR-FIQD- Quarantine oversees the Registration of Exporter’s Facility for Live Aquatic Animals, Pre-shipment Inspection of Live Aquatic Animals for the Issuance of Health Certificate, and Inspection for the Registration of Importer’s Facilities and Pre-arrival of Live Aquatic Animals.
DA-BFAR Regional Field Offices supervise the granting of Certificate of Clearance (COC) for Commercial Fishing Vessel to Depart and Issuance of Fisherman’s License.
The Fisheries Regulatory and Licensing Division is in charge of the Digital or online payment of Commercial Fishing Vessel License (CFVL) fees with the capacity to issue an official electronic receipt.
In partnership with the Philippine Fisheries Development Authority (PFDA), BFAR facilitates the Online payment gateway for clients to pay license and other fees online and validate applicants for SPSIC and other pertinent Documents for importation.
The issuance of a Local Transport Permit is also under BFAR, in cooperation with the BAI and BPI.
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BFAR- FIQDCertification Registration of establishment for the Exportation of Fish and other Fishery/Aquatic Products
BFAR- FIQDCertification Issuance of Export Commodity Clearance (ECC) for live food fish, live ornamental fish, shells and shellcrafts and its derivatives, and fresh, chilled, frozen fish and fishery/aquatic products
Registration of Establishment as Exporter of Shell and Shell Crafts (including by-products and its derivatives
Export Commodity Clearance (ECC) for fish and fishery/aquatic products provides documented evidence that the product is not derived from Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing, and compliant to aquatic wildlife conservation regulations, and other relevant fishery laws
Shell and Shell Crafts (including byproducts and its derivatives
Fish Exporter Details, Commodity Details
Status of establishment that exports
Customer
1
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BFAR- FIQDCertification Issuance of Health Certificate for Export of Fresh Chilled and Frozen Fishery Products
BFAR- FIQDCertification Issuance of Health Certificate for Export of Live Food Fish and Live Ornamental Fish
BFAR- FIQDCertification Issuance of Health Certificate (HC) for transboundary movement of fish and fishery/aquatic products
Health Certificate provides documented evidence that the products have been cultured, harvested/collected, handled, transported, manufactured, packed, stored and distributed under established SPS and/or food safety standards and in accordance with relevant rules and regulations.
Health Certificate (HC) for transboundary movement of fish and fishery/aquatic products provides documented evidence that the products have been cultured, collected/harvested, handled, transported, manufactured, packed, stored and distributed under established Sanitary Phytosanitary (SPS) and in accordance to relevant rules and regulations.
Exporter details; Fish and fishery/aquatic products details
Exporter details; Fish and fishery/aquatic products details
Trader/Client details; Fish and fishery/aquatic products details
details In-house 1
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY PROCESS
BFAR- FIQDCertification Accreditation of Importers Accreditation of importers for fishery business establishments secures that the Fishery Aquaculture Business Operators (FABOs) comply with the Sanitary Phytosanitary (SPS) measures, food safety standards and BFAR laws and regulations to export fish and fishery/aquatic products
BFAR- FIQDCertification Manual issuance of Sanitary Phytosanitary Import Clearance (SPSIC) under FAO 259 Wet Market
The (SPSIC) provides documented evidence and ensures that the product is imported based on its approved purpose under established SPS and food safety standards and in accordance to relevant rules and regulations.
Importer details; Fish and fishery/aquati c products details
KYC details In-house 1
Customer KYC details In-house 1
Customer KYC details In-house 1
Importer details; Fish and fishery/aquati c products details
Status if accredited or not In-house 1
Customer KYC Details In-house 1
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BFAR-FIQD-FIS License To Operate for Cold Storage Warehouses
BFAR-FIQD-FIS Inspection of Fishery/Aquatic Products/Establishments (New Applicant) for Registration and Issuance of HACCP/GMP/SSOP/Vessel Certificate (New Applicant)
OFFICE
BFAR-FIQD-FIS Inspection of Fishery Establishment for Export of Fishery/Aquatic Products for Issuance of Certificate of HACCP/GMP/SSOP/Vessel (Renewal of Certificates)
BFAR-FIQD-FIS
Process of licensing of cold storage warehouses prior to operate Application Form data and documentary requirements/ inspection report
HACCP Approval and Recognition Process of Fishery / Aquatic Establishments / Vessels
Application form data and documentary requirements/ins pection report
License to operate/ inspection report On-line application 1
Certificate of HACCP implementatio n / Certificate of Inspection / Inspection Report On-line application 1
HACCP Approval and Recognition Process of Fishery / Aquatic Establishments / Vessel
Accreditation of Importer Facility inspection and verification of volume or capacity requirements of processing / canning and institutional buyer’s
Application form data and documentary requirements/inspection report
Certificate of HACCP implementation / Certificate of Inspection / Inspection Report On-line application 1
Application form data and documentary requirements, inspection report
Importable fish specie and volume or quantity of import intended for endorsement to intercommerce On line application 1
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BFAR-FIQD-FIS Pre-shipment inspection
BFAR-FIQD-FIS 2nd Border Inspection (Post Border Inspection)
Inspection conducted prior to loading to refrigerated or nonrefrigerated container van of fishery/aquatic products destine for export
Application form data and documentary requirements/inspection report
Inspection Report On-line application and inspection 1
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY PROCESS
BFAR-FIQD-FIS Registration of Traders / Exporters of fishery / aquatic products
Inspection conducted for incoming imported fishery / aquatic products at the cold storage warehouses for the enforcement of FAO 195 and FAO 259
Documentary requirements such as eRFI, Notice of Release, Health Certificate, SPSIC, Bill of Lading, Commercial Invoice), violation such as co-mingling, thawing or temperature abuse, misdeclare and other) and inspection report
Inspection report and Incident report if there is any violation
Automation of inspection report using mobile phone 1
DESCRIPTION/ DETAILS
Inspection conducted of physical facility of traders / exporters that has no fishery establishment or facility
Application form data and documentary requirements/inspection report
Certificate of Registration / Inspection Report
Online application 1
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BFAR- FIQDQuarantine 1. Registration of Exporter’s Facility for Live Aquatic Animals
OFFICE
DA-BFAR (Regional Field Offices) Certificate of Clearance (COC) for Commercial Fishing Vessel to Depart
Exporter’s facility for the export of live aquatic animals (ornamental fish / food fish) should be registered (please see attached diagram)
-Exporters details
- Common violation/noncompliance of exporters to SPS/ DA-MC 15/ other country’s requirements
- Data of exported live products (species/volume/ amount) biggest/highest importing countries of live aquatic animals
-Status if registered or not
- Top exported live aquatic animals
-Data of exported live products (species/vol ume/amoun t) biggest/high est importing countries of live aquatic animals On-line registration of exporters’ facility 1
Issuance of Certificate of Clearance (COC) for Commercial Fishing Vessel prior to Departure
DA-BFAR (Regional Field Offices) Issuance of Fisherman’s License This authorizes the fisherman to engage in commercial fishing activity
DA-BFAR FRLD Digital or online payment of Commercial Fishing Vessel License (CFVL) fees with the capacity to issue electronic official receipt
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BFAR- FIQDQuarantine 2. Pre-shipment Inspection of Live Aquatic Animals for the Issuance of Health Certificate
Payment of application and license fees for the issuance of CFVL
Inspection of Exporter’s facility for the export of live aquatic animals (ornamental fish / food fish) for the issuance of health certificate (please see attached diagram)
-List of Commercial Fishing Vessels with Valid CFVL -Registered and Licensed Commercial Fishing Vessel or not Out source with other agencies 1
Amount of fishing license/permit /certificate fees collected.
-Exporters details
-Health Certificate Issued
-biggest/highest importing countries of live aquatic animals
Amount of fishing license/permi t/certificate fees collected. In-house or outsource 1
-Status of compliance of exporters
- Top exported live aquatic animals
-Data of exported live products (species/volume /amount)
-biggest/ highest importing countries of live aquatic animals Virtual Inspcection of the Facilities 1
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY PROCESS
BFAR- FIQDQuarantine 3. Inspection for the Registration of Importer’s Facilities and Pre-arrival of Live Aquatic Animals
Inspection of Importers’s facility for the import of live aquatic animals (ornamental fish / food fish) for registration (please see attached diagram)
-Importers details
-Species imported
-biggest/highest exporting countries of live aquatic animals to the Philippines
-Status of compliance of importers
- Top imported live aquatic animals
-Data of imported live products (species/volu me/amount)
-biggest/ highest exporting countries of live aquatic animals Virtual Inspcection of the Facilities 1
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BFAR- FIQDQuarantine Inspection for the Registration of Importer’s Facilities and Pre-arrival of Live Aquatic Animals
Inspection of Importers’s facility for the import of live aquatic animals (ornamental fish / food fish) for registration (please see attached diagram)
-Importers details
-Species imported
-biggest/highest exporting countries of live aquatic animals to the Philippines
-Status of compliance of importers
- Top imported live aquatic animals
-Data of imported live products (species/volu me/amount)
-biggest/ highest exporting countries of live aquatic animals Virtual Inspcection of the Facilities 1
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
BFAR- FIQDQuarantine Inspection for the Registration of Importer’s Facilities and Pre-arrival of Live Aquatic Animals
Inspection of Importers’s facility for the import of live aquatic animals (ornamental fish / food fish) for registration (please see attached diagram)
-Importers details
-Species imported
-biggest/highest exporting countries of live aquatic animals to the Philippines
-Status of compliance of importers
- Top imported live aquatic animals
-Data of imported live products (species/volu me/amount)
-biggest/ highest exporting countries of live aquatic animals
Inspcection of the Facilities 1
COMMON WITH OTHER OFFICES
Online payment gateway BFAR, PFDA Client to pay License fees and other fees via Online
Issuance of SPSIC BFAR, BAI, BPI The (SPSIC) provides documented evidence and ensures that the product is imported based on its approved purpose under established SPS and food safety standards and in accordance with relevant rules and regulations.
Issuance of Local Transport Permit BFAR, BAI, BPI Local Transport Permit (LTP) acts as traceability for the commodities from their origin which an essential risk management tool enabling individual members of supply chain to quickly identify problems and to promptly disseminate this information to affected parties.
Commodity Details, Traceability
List of Accredited Fish Importers and Cold Storages BFAR, PFDA Validation of applicants for SPSIC and other pertinent Documents for importation
Commodity details, Traceability
Required to ensure that only accredited fish importers are allowed to import fishery products

The Bureau of Agriculture and Fisheries Standards (BAFS) processes for automation include the Certificate of Registration (COR) for companies engaged in organic inputs (soil amendments & biocontrol agents) and integrated farms for the production of organic commodities, Certificate of Product Registration (CPR) for organic inputs (soil amendments and biocontrol agents) which should be registered, Experimental Use Permit (biocontrol agents) for organic biocontrol agents (OBCA) which should undergo efficacy trials under local conditions before application for CPR, and Trade Regulatory Government Agencies (TRGAs) permits.
| EXCLUSIVE /BAFS
Bureau of Agriculture & Fisheries Standards (BAFS)
Certificate of Registration (COR)
Companies engaged in organic inputs (soil amendments & biocontrol agents) and integrated farms for the production of organic commodities
Organic Certificatio n and documenta ry requireme nts
Electronic system on status of applicatio n and registry published in the website
In-house 1 (with BAFS initiated system in place and ready for launching by December 2021)
| EXCLUSIVE / BAFS
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY PROCESS PROCESS DESCRIPTION/ DETAILS
Bureau of Agriculture & Fisheries Standards (BAFS)
Certificate of Product Registration (CPR)
PROCESS OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
Experimental Use Permit (biocontrol agents)
BAFS/ FPA
Organic inputs (soil amendments and biocontrol agents) shall be registered
Organic biocontrol agents (OBCA) shall undergo efficacy trials under local conditions prior to application for CPR
For soil amendments and integrated organic farms- Organic Certification and documentary requirements For biocontrol agents- efficacy trial, OC and documentary requirements
Product and its raw materials are allowed for organic production, % acceptable efficacy, MSDS, active ingredient specifications, other pertinent requirements
| INTERCONNECTING AND
DATA SHARED OFFICE NAME/AGENCY
TradeNet.go v.ph for Organic Input Importation & Exportation Permit Trade Regulatory Government Agencies (TRGAs)
PROCESS
Online application, processing and issuance of trade permits
This process is required prior to import and export. The TradeNet platform serves as the system in generating the permits and giving real-time updates of status of applications
Electronic system on status of applicatio n and registry published in the website
Electronic system on status of application and registry published in the website
In-house 1 (with BAFS initiated system in place and ready for launching by December 2021)
In-house 1 (with BAFS initiated system in place and ready for launching by December 2021)
Bill of Lading, Packing List, Organic certification, Invoice and documentary req’ts Outsourced (governmen t initiated) 1 (BAFS is officially onboarded in the platform last August 2021, awaiting approval of the guidelines and other minor req’ts

The National Meat Inspection Service (NMIS) is a specialized regulatory service attached to the Department of Agriculture that oversees all meat inspection and meat hygiene matters as guided by laws and issuances.
Its processes which are exclusive to the office, are the following:
1. AIPLIRS (Automated In-Plant Line Inspection System)
2. Express (Disease Reporting System,
3. Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS)
4. Document Tracking System (DTS)
5. Human Resource Information System (HRIS)
6. Property and Inventory Management System
The AIPLIRS (Automated In-Plant Line Inspection System) works as a tool for the real-time collection of slaughter data.
Express Disease Reporting System monitors the spread of notifiable diseases through collecting and analyzing data.
Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is a system that records, manages, stores, monitors, and analyzes the submitted laboratory samples for testing.
Document Tracking System (DTS) functions as an electronic dynamic routing slip that aims to monitor the status of documents in the agency.
The Human Resource Information System (HRIS) provides fast access to personnel Information and works as a tool for assessing the competencies of the personnel.
The Property and Inventory Management System is a web-based system that will manage the NMIS logistics inventory. It will be a repository for the property numbers of different assets in all NMIS offices.
Processes standard with other offices are the a) Online Payment Gateway and b) eNGAS - e-New Government Accounting System (NGAS).
The Online Payment Gateway is an avenue for clients to pay for regulatory fees through the web.
The eNGAS - e-New Government Accounting System (NGAS) is an accounting software developed by the Commission on Audit for financial transactions and records, which is still in the process of adoption.
The NARIS (NMIS Accreditation and Registration Information System) is one of the processes of interconnecting and sharing data. The NMIS -Accreditation and Registration Division (ARD) provides for the automated application for an NMIS License to Operate (LTO) for meat establishments / Meat Transport Vehicle (MTV) Registration / Reporting and generation of GMP, GOP, HACCP Audit Reports. It offers e-Registration of NMIS Meat Transport Vehicle (MTV) and e-Reporting Info System (GMP, GOP, HACCP).
Lastly, NMIS – Meat Import Export Division (MIED) leads the Meat Import Licensing Portal (MILP), an information system that focuses on providing a fast and efficient automated platform to all applicants of License to Import of Meat Commodity, and the Electronic Certificate of Meat Inspection (eCOMI), an information system that gives easy and contactless transactions for applications of certification of imported meat to be distributed locally as fit for human consumption and also providing the agency a platform for traceability.
















The Sugar Regulatory Administration (SRA), under the helm of Executive Order No. 18, dated May 28, 1986, upholds its role of “promoting the growth & development of the sugar industry through greater participation of the private sector and to improve the working conditions of the laborers” through employing processes accessible to its clientele.
RA 10659 or the Sugarcane Industry Development Act of 2015 furthers, uplifting the “competitiveness of the sugarcane industry and maximize the utilization of sugarcane resources, and improve the incomes of farmers and farmworkers, through improved productivity, product diversification, job generation, and increased efficiency of sugar mills.”
The SRA’s processes for automation unique to the agency include the following:
1. Application of License-to-operate (LTO) as a trader, mill/refinery, bioethanol producer, and warehouse registration
2. Application of Import/Export Clearance
3. Application of Shipping Permits
4. Its online payment channel where clients pay License fees and other fees thru any Landbank Branch or bank transfer is one process it shares with other agencies.
The SRA also allows clients, researchers, and other agencies to secure copies of the List of traders for the Crop Year (CY) and previous CYs and Accredited CBW/Exporters/Importers/Food Processors with approved SRA Clearances for their imported sugar for the month.
EXCLUSIVE /UNIQUE
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY PROCESS
SRA Application of Licenseto-operate(LTO) as trader, mill/refinery, bioethanol producer and warehouse registration.
Application of Import/Export Clearance
Application of Shipping Permits
*(IN HOUSE, LEASED OR OUT SOURCE)
Issuance of LTO as Traders/ Importers/ Exporters of sugar/ molasses/ muscovado, Fructose, Bioethanol Producers and Warehouse Registration
Issuance of Import and Export Clearance to Importers/ Exporters prior withdrawal from BOC for imports and export of regulated products
Issuance of shipping permit to Trader for the shipment of sugar from one port to another.
Applicant details and requirements
Status of trader application Approved or Disapproved
Applicant and shipment details and requirements
Applicant and Shipment details and requirements
Status if approved/ disapproved.
source 2
Status if approved/ disapproved Out source 3
(COMMON WITH OTHER OFFICES (CROSS AGENCY)
/ AGENCY
Online payment SRA
Client to pay License fees and other fees thru any Landbank Branch or bank transfer Payment details (Name of Applicant, Nature of Transaction, Date of Payment, Amount Paid
| INTERCONNECTING AND
*(IN HOUSE, LEASED OR OUT SOURCE)
DATA SHARED OFFICE NAME/AGENCY
Licensed traders SRA Client, researchers and other agencies to secure a copy of the needed list of trader
Accredited CBW/Exporters/Imp orters/Food Processors
*(IN-HOUSE, LEASED OR OUT-SOURCE)
SRA Client, researchers and other agencies to secure a copy of the needed list of Accredited CBW/Exporters/Impo rters/Food Processors with approved SRA Clearances for their imported sugar for the month

Customer details and other information mentioned in data collected
Out-source 1
List of traders for the Crop Year (CY) and previous CYs.
List of Accredited CBW/Exporters/Importer s/Food Processors with approved SRA Clearances for their imported sugar for the month
Name of Licensed Trader and other basic information
Name of CBW/Exporters /Importers/Food Processors with their corresponding volume of approved imports, destination
In-house 1
In-House 2
The Philippine Coconut Authority (PCA) allows for the a) Registration of Coconut & OilPalm Products (Copra, HuskedNuts, Buko, Charcoal, Seedlings, Oilpalm) Traders and Lumber Processor, Lumberyards, Chainsaws, Sawmills, b) Registration of Coconut Food and Non- Food Processors, Trader/ Exporters, Trade Intermediary without Processing Activity, c) Accreditation of Coconut & Oil Palm Seednuts/ Seedlings Producers/ Nursery Operators. d) Permit to Cut Coconut Trees, and Permit to Transport, e) Commodity and Export Clearance for Coconut and Oilpalm Products, and f) processors Inventory and Purchase Reports for PCA Fee Collection. PCA also has a system created for easy monitoring of programs and projects - Enhancing Coconut Famers Survival and Recovery thru Economic Support (Ensures).
Common processes with other agencies include the Payroll System, Human Resource Management Information System, Asset & Procurement Management, Document Tracking System, and the Financial Account Management System.
The National Coconut Farmers and Registry System, intended for generating a complete and accurate coconut farmers and farm workers’ registry and to establishing and maintaining a data bank that will serve as a repository of essential information on coconut farmers and farmworkers in the country, and the Trade and Market Information Data, which covers the Issuance of Commodity and Export clearance for Coconut/ Oil Palm Products, are both PCA processes which interconnect and share data with other agencies.
Philippine Coconut Authority
Registration of Coconut & OilPalm Products (Copra, HuskedNuts, Buko, Charcoal, Seedlings, Oilpalm) Traders and Lumber Processor, Lumberyards, Chainsaws, Sawmills
Registration of Coconut Food and Non- Food Processors, Trader/ Exporters, Trade Intermidiary without Processing Activity
Accreditation of Coconut & Oil Palm Seednuts / Seedlings Producers/ Nursery Operators
Philippine Coconut Authority Permit to Cut Coconut Trees, and Permit to Transport
Commodity and Export Clearance for Coconut and Oilpalm Products
and
Pursuant to P.D. No. 1468 and P.D. 1644 the PCA is to regulate the marketing and export of coconut and palm oil products in furtherance to the rationalization of coconut oilmilling industry.
Business Name, Contact Details, Capital, Area of Operation, capacity of operation, equipment, warehouse/s
Pursuant to P.D. No. 1468 and P.D. 1644 the PCA is to regulate the marketing and export of coconut and palm oil products in furtherance to the rationalization of coconut oilmilling industry.
Business Name, Contact Details, Capital, Area of Operation, capacity of operation, equipment, warehouse/s
Application, Food Safety Standards Compliant
The accreditation shall promote the production of good quality of planting materials. It aims to accelerate the development of coconut plantation and nurseries as sources of sustainable planting materials with geneticl quality.
Business Name, Contact Information, Farm Location, Farm size, Volume of Production, Equipment, Warehouse
An export champion, thus it becomes mandatory to step in and regulate the unabated and indiscriminate cutting of the coconut trees.
Business name, contact information, farm size, number of trees to cut, Origin, volume of lumber, Vessel, destination, date of transport, consignee, Period of Effectivity
Pursuant to P.D. No. 1468, the PCA is to regulate the marketing and export of coconut and palm oil products in furtherance to the rationalization of coconut oilmilling industry.
of fees per kg for every raw materials purchased by Coconut processing plants and submission of market reports
Business name, contact information, commodity, date of production, Lot/Batch No. Volume, Date of Loading, Port of loading, Destination, Contract No. Date of Sale, Consignee
PROCESS
Document Tracking System DA and Attached Agencies
Automation of the process of accessing, searching and editing documents and enables you to control who views or edits a document.
Administrative, Operations, and Financial Documents
Administrative, Operations, and Financial Data
Financial Account Management System DA and Attached Agencies
Software and processes to manage assets, income, and expenses.
Disbursements, Procurement, Travelling and allowances.
Disbursements, Procurement, Travelling and allowances.
National Coconut Farmers and Registry System
Philippine Coconut Authority, DA (RSBSA)
Masterlist of Registered Coconut Farmers, CrossCheckin g
To generate a complete and accurate coconut farmers and farm workers' registry and to establish and maintain a data bank that will serve as a repository of essential information on coconut farmers and farm workers in the country
Trade and Market Information Data PCA, DOF, BOC Issuance of Commodity and Export clearance for Coconut/ Oil Palm Products
Automation of the Application and issuance of Commodity Clearance Trade and

The Fertilizer and Pesticide Authority (FPA) has the following processes, a) Licensing of Fertilizer And Pesticide Handlers, b) Registration Fertilizer And Pesticide Products, c) Issuance of Experimental Use Permits for Fertilizer and Pesticide, d) Accreditation for individual, Accredited Responsible Care Officer (ARCO), Certified Pest Applicator (CPA), Accreditation of Fertilizer and Pesticide Researcher, and Accreditation of Safety Dispenser (ASD), Vat Exemption Certificate, and Certification Authorizing Importation Of Pesticide (CAIP).
- Importer, Exporter, Distributor, Manufacturer, Procesor, Formulator, Indentor Repacker etc )
1. Application Form downloadable at the FPA website, and Other Documentary Requirements are submitted to regulatory divisions and verified for correctness and completeness.
2. Bill form issued to client For payment of fees.
3. Receive and process Application
4. Notify client of approved application
5. Release license
Company profile: (Name of company, address, contact info)
Regulated documents (SEC, DTI – for capitalization verification , proof of business ) for new application List of
handlers ( expiry of license)
FPA REGISTRATION FERTILIZER AND PESTICIDE PRODUCTS
Fertilizer (Traditional, Non-traditional)
Agricultural Pesticide (Herbicides, Insecticide, Fungicide.. etc )
1. Application Form downloadable at the FPA website, and Other Documentary Requirements are submitted to regulatory divisions and verified for correctness and completeness.
2. Bill form issued to client For payment of fees.
3. Receive and process Application
Technical evaluation of test data (Non-traditional and pesticide)
4. Notify client of approved application
5. Release certificate
Company profile: (Name of company, address, contact info)
Product profile: (Brand name, label, NPK composition for Fertilizer, Active ingredients for Pesticide, etc.)
Bioefficacy data
FPA REGISTRATION FERTILIZER AND PESTICIDE PRODUCTS
Fertilizer (Traditional, Non-traditional)
Agricultural Pesticide (Herbicides, Insecticide, Fungicide.. etc )
FPA ISSUANCE OF EXPERIMENTAL USE PERMITS FOR FERTILIZER AND PESTICIDE
1. Application Form downloadable at the FPA website, and Other Documentary Requirements are submitted to regulatory divisions and verified for correctness and completeness.
2. Bill form issued to client For payment of fees.
3. Receive and process Application
Technical evaluation of test data (Non-traditional and pesticide)
4. Notify client of approved application
5. Release certificate
Company profile: (Name of company, address, contact info)
Product profile: (Brand name, label, NPK composition for Fertilizer, Active ingredients for Pesticide, etc.)
Bioefficacy data
List of registered products( expiry of registration)
2
1. Application Form downloadable at the FPA website, and Other Documentary Requirements are submitted to regulatory divisions and verified for correctness and completeness.
2. Bill form issued to client For payment of fees.
3. Receive and process Application
Technical evaluation of test data (Non-traditional and pesticide)
4. Notify client of approved application
5. Release certificate
Company profile: (Name of company, address, contact info)
Product profile: (Brand name, label, NPK composition for Fertilizer, Active ingredients for Pesticide, etc.)
Bioefficacy data
2
*no shared data due to proprietary information
OFFICE NAME / AGENCY
FPA Accreditation for individual
- Accredited Responsible Care Officer (ARCO) - Certified Pest Applicator (CPA) - Accreditation of Fertilizer and Pesticide Researcher
- Accreditation of Safety Dispenser (ASD)
FPA VAT EXEMPTION CERTIFICATE
CERTIFICATION AUTHORIZING IMPORTATION OF PESTICIDE (CAIP)
1. Application Form downloadable at the FPA website, and Other Documentary Requirements are submitted to regulatory divisions and verified for correctness and completeness.
2. Bill form issued to client For payment of fees.
3. Receive and process Application
4. Notify client of approved application
5. Release license
TRADENET PLATFORM
Company profile: (Name of company, address, contact info)
Applicant profile (Name, Training date) List of accredited individual( expiry of accreditation)
4
Company profile: (Name of company, address, contact info)
Shipping Details (Bill of Lading, Commercial/ Proforma Invoice, Packing List, Broker Name/ TIN, Quantity Commodity, etc)
Pesticide Import Price and Volume per use report (Annual, Semestral, Monthly)
Import and Export Price/Volume report (Annual, Semestral, Monthly)

The Philippine Fiber Industry Development Authority (PhilFIDA) issues the following:
1. Registration and Licensing of Fiber Traders/Processors
2. Certificate of Fiber Inspection (CFI)
3. Permit to Transport Fiber (PTF)
4. Fiber Inspection



The Philippine Fisheries Development Authority (PFDA) ‘s processes are divided into the following: a) Fish Port and Other Post-Harvest Facilities Operation Services, b) Fishery Post-Harvest Facilities Construction Services, c) General Administrative and Support Services, and d) Information Management.
Fish Port and Other Post-Harvest Facilities Operation Services include the following information systems (IS): a) Accreditation IS, b) Harbor IS, Market IS, c)Market IS, d) Port Maintenance and Refrigeration IS, e) Billing IS, f) Cashiering IS, g) Contact Monitoring IS, h) Online Contract Monitoring IS, and i) Client and Visitor Entry IS.
For the Fishery Post-Harvest Facilities Construction Services, PFDA has an Online Project Monitoring IS. The General Administrative and Support Services has:
Those which are still for development are the following: a) Document Management
and e) Accounting
For the Information Management System, PFDA has the following: a) Modified Integrated Corporate Reporting System, b) Executive Management Dashboard, and c) PFDA Corporate Information System Portal.

Process Flow PORT ACCREDITATION SYSTEM

Process Flow
PERMIT TO CONDUCT BUSINESS (PTCB)


The National Dairy Authority (NDA) has the following processes exclusive to their agency: a) Registration of Dairy Business Operator, b) Application for NDA-LTO, and c) Laboratory services.
The collection of fees and Issuance of Certificate of Registration/ LTO are common with other offices.



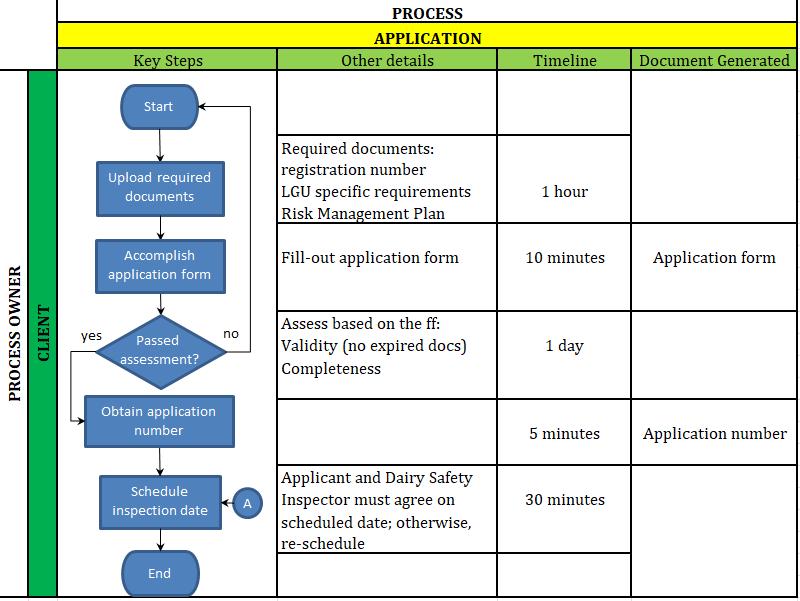



Procurement Division Process Flow

FUNCTIONS
• Undertakes the DA-wide procurement;
• Oversees procurement activities of the DA regional offices and staff bureaus;
• Acts as the BAC Secretariat;
• Reviews and updates the submitted APP of the DA OSEC, all regional offices and staff bureaus;
• Acts as secretariat for the procurement of all requirements of the DA OSEC, regional offices and staff bureaus pursuant to existing general memorandum order;
• Acts as the Central Repository of all up to date procurement related information and GPPB resolution issuances, circulars and events and disseminate the same to all parties requiring information;
• Transacts with the PS-DBM in behalf of the Procuring Entity;
• Ensures that all procurement and bidding documents are properly documented in order to provide an audit trail of the procurement process;
• Provides administrative support to the BAC and the technical working group, if necessary; and
• Manages and undertakes procurement upon prior resolution of the BAC and the approval of the head of the agency or the duly designated officer.
*Please refer to the Procurement Manual for the detailed standard and operating procedures of the Division.
Procurement activities, the period of which cannot be shortened.
Posting of Invitation to Bid
Conduct of Pre-Bid Conference
Conduct of Opening of Bids
Seven (7) calendar days pursuant to Section 21.2.1
Twelve (12) calendar days prior to the Opening of Bids pursuant to Section 22.2
Twelve (12) calendar days after the Pre- Bid Conference pursuant to Section 22.2
Procurement activities, the period of which can be shortened.
From Opening of Bids to the issuance of Notice of Award
From the Opening of Bids to the issuance of Notice to Proceed
Three (3) Months (pursuant to Section 38.1)
“The procurement process from the opening of bids up to the award of contract shall not exceed three (3) months, or a shorter period to be determined by the Procuring Entity concerned. ”
One Hundred Twenty (120) calendar days from the Opening of Bids (pursuant to Section 28 and discussed in NPM 18-2012)
“The validity of the bid security is material at the time of the issuance of the NOA since the validity of the bid security signifies that the bidder’s bid or offer still stands at the time the procuring entity awarded the contract The validity of the bid or offer is vital because the NOA or the act of acceptance by the procuring entity will be rendered nugatory and ineffectual when there is no longer an “offer” to accept.
(G.R. No. 212381) Jacomille vs Abaya et. al, states as follows:
“This period is not merely directory but mandatory in character. There is nothing in the law which states that the 3-month period can be disregarded. Non- compliance with the period will certainly affect the validity of the bidding process.”
The Notice of Award must be issued within the bid validity period. Otherwise, the act of acceptance by the Procuring Entity will be rendered nugatory and ineffectual as there is no longer an offer to accept.
A. Republic Act (R.A.J 9184 otherwise known as Government Procurement Reform Act (GPRA) and its 2016 Revised Implementing Rules and Regulations (RIRR);
B. Government Procurement Policy Board (GPPB) Resolutions and Non-Policy Opinions or Matters;
C. Relevant Commission on Audit (COA) Circulars; and
D. Other Related Laws and Pertinent Jurisprudence On Government Procurement.
This Manual is applicable to all procurement process undertaken by all DA Offices, Staff Bureaus and Regional Field Offices
A. Head of Procuring Entity (HoPE]
B. Bids and Awards Committee (BAC):
- BAC Chairperson
- BAC Vice-Chairperson
- Regular Members
- Provisional Members
- End-user
C. Technical Working Group (TWG)
D. Procurement Division/BAC-Secretariat
DEFINITION OF TERMS:
Alternative Modes of Procurement - approved methods of procurement by the HoPE, which used in certain conditions or exceptional cases to promote economy and efficiency, subject to the conditions set forth by RA 9184 and its 2016 RIRR.
Annual Procurement Plan (APP) - document that consolidates the submitted Project Procurement Management Plan (PPMPs) by the various end-users and approved by the Head of Procuring Entity (HOPE). It reflects the entirety of the procurement activities that will be undertaken by the Procuring Entity within a calendar year.
Bid Security - bond posted by the bidder during the opening of bids, payable to the Procuring Entity as a guarantee that the successful bidder shall, within ten (10) calendar days from the receipt of the Notice of Award, enter into contract with the Procuring Entity and furnish the performance security.
Bidding Documents - refer to the documents issued by the Procuring Entity as the basis for bids, furnishing all information necessary for a prospective bidder to prepare a bid for the Goods, Infrastructure Projects and/or consulting services required by the Procuring Entity.
BED No. 4 (Annual Procurement Plan for Common Use Supplies and Equipment [APP-CSE])Projected monthly procurements in terms of quantity and cash requirements. This shall be categorized into items available at Procurement Service (PS) stores and those items not available at PS. Purpose: Basis of the PS in projecting inventory requirements, scheduling of procurement activities, and overall management of the central procurement of common-use goods. It also serves as Agency Procurement Request (APR), subject to issuance of guidelines.
Competitive/Public Bidding - method of procurement which is open to participation by any interested parties which consist of the following process: Advertisement, Pre-Bid Conference, Receipt and Opening of bids, Evaluation of Bids, Post-Qualification, and Award of Contract, the specific requirements and mechanics of which shall be specifically provided in this Manual.
Consulting Services -refers to services for Infrastructure Projects and other types of projects or activities of the government requiring adequate external technical and professional expertise that are beyond the capability and/or capacity of the government to undertake, such as, but not limited to: (i) advisory and review services; (ii) pre-investment or feasibility studies; (iii) design; (iv) construction supervision; (v) management and related services; (vi) other technical services or special studies.
Goods and Services - refer to all items, materials and general support services, except consulting service and infrastructure projects, which may be in the nature of equipment, furniture, stationary, materials for construction, office materials and supplies, or personal property of any kind, including non-personal or contractual services such as the repair and maintenance of equipment and furniture, as well as trucking, hauling, janitorial, security and the like.
Highest Rated/Rank Bid (HRB) -the Highest rate amongst the submitted bids after undertaking the detailed evaluation of the technical proposals of the bids and ranking the bids from Highest to lowest and will be subject to Negotiation. (For Consulting Services).
DEFINITION OF TERMS:
Highest Rated and Responsive Bid (HRRB) - after the HRB undergone post-qualification and complies with and responsive of all the requirements and conditions as specified in the Bidding Documents.
Infrastructure Projects/ Civil Works - include the construction, improvement, rehabilitation, demolition, repair, restoration and maintenance of roads and bridges, railways, airport, seaports, communication facilities, civil works components of information technology [projects, irrigation, flood control and drainage, water supply, sanitation, sewerage and solid waste management system, shore protection, energy/ power and electrification facilities, national buildings, and other related construction projects of the government.
Lowest Calculated Bid (LCB) - the lowest amongst the submitted bids after undertaking the detailed evaluation of the financial component of the bids and ranking the bids from lowest to highest.
Lowest Calculated and Responsive Bid (LCRB) - after the Lowest Calculated Bid has undergone post-qualification and responsive to all the requirements and conditions as specified in the Bidding Documents.
National Expenditure Program (NEP) - this contains the details of spending for each Department and Agency by program, activity for project, and is submitted in the form of a proposed General Appropriations Act (GAA).
Performance Bond/Security - a security, to be submitted by the winning bidder, to guarantee the faithful performance under the contract in accordance with the Bidding Documents.
Procurement Monitoring System (PMS) - a digital application or tool developed in-house used to monitor procurement process and activities. It may be used as an audit trail in procurement and in compliance with the principle of transparency in government transactions.
Procurement Planning - involves the preparation/updating of the agencies PPMPs by the individual project, the consolidation of all PPMPs into the APP, and approval of the APP by the HOPE.
Procurement Planning Group - unit of the Procurement Division who is tasked to review, verify and consolidate the submitted PPMPs and BED 4 of each end-user.
Project Procurement Management Plan (PPMP) - the detailed planning of requirements prepared by each end-user for the whole calendar year. These PPMPs will be submitted to the Budget Office for inclusion in the DA Budget proposal which in turn, will then be submitted for approval of the Head of Procuring Entity (HOPE).
Procurement Request Action Slip (PRAS) - a document created by the End-users in initiating their procurement requests included in the approved Annual Procurement Plan (APP).
Purchase Request (PR) - a document created by the End-users in initiating their procurement requests not included in the approved APP. PR is considered a revision of the approved APP.
Pursuant to Sections 4.2,4.4 and 4.5 of the 2016 RIRR of R.A. 9184, the following shall not apply:
A. Any Treaty or International or Executive Agreement to which the GoP is a signatory affecting the subject matter of the Act and this IRR shall be observed. In case of conflict between the terms of the Treaty or International or Executive Agreement and this IRR, the former shall prevail. (Section 4.2 of 2016 RIRR of R.A. 9184)
B. Procurement of Goods, Infrastructure Projects and Consulting Services funded from Foreign Grants covered by R.A. 8182, as amended by R.A. 8555, entitled “An Act Excluding Official Development Assistance (ODA) from the Foreign Debt Limit in order to Facilitate the Absorption and Optimize the Utilization of ODA Resources, Amending for the Purpose Paragraph 1, Section 2 of R.A. 4860, As Amended,” unless the GoP and the foreign grantor/foreign or international financing institution agree otherwise. (Section 4.4 (a) of 2016 RIRR of R.A. 9184)
C. Acquisition of real property which shall be governed by R.A. 107523, entitled “An Act Facilitating the Acquisition of Right-Of-Way Site or Location for National Government Infrastructure Projects,” and other applicable laws, rules and regulations. (Section 4.4 (b) of 2016 RIRR of R.A. 9184)
D. Public-Private sector infrastructure or development projects and other procurement covered by R.A. 6957, as amended by R.A. 7718, entitled “An Act Authorizing the Financing, Construction, Operation and Maintenance of Infrastructure Projects by the Private Sector, and for Other Purposes,” as amended: Provided, however, That for the portions financed by the GoP, in whole or in part, the provisions of the Act and this IRR shall apply. (Section 4.4 (c) of 2016 RIRR of R.A. 9184)
E. Direct financial or material assistance given to beneficiaries in accordance with the existing laws, rules and regulations, and subject to the guidelines of the concerned agency. (Section 4.5 (a) of 2016 RIRR of R.A. 9184)
F. Participation in local or foreign scholarships, trainings, continuing education, conferences, seminars or similar activities that shall be governed by applicable COA, CSC, and DBM rules. (Section 4.5 (b) of 2016 RIRR of R.A. 9184)
G. Lease of government-owned property as lessor for private use. (Section 4.5 (c) of 2016 RIRR of R.A.9184)
H. Hiring of Job Order Workers. (Section 4.5 (d) of 2016 RIRR of R.A. 9184)
I. Joint Venture under the revised NEDA Guidelines (GOCC and Private Entities), and Joint Venture Agreements by LGU with Private entities. (Section 4.5 (e) of 2016 RIRR of R.A.9184)
J. Disposal of Property and Other Assets of the Government. (Section 4.5 (f) of 2016 RIRR of R.A.9184)
Preparation and submission of Project Procurement Management Plan (PPMP)
Submission of draft PPMP for Budget Preparation to the Budget Division and Procurement Division
Consolidation of draft PPMPs into the Indicative APP for the following year for attachment to the budget proposal
Finalization of the draft PPMP based on the approved NEP
Submission of Finalized PPMP by the End-User to the Procurement Division
Consolidation of finalized PPMP into the APP (with procurement timelines and mode of procurement)
Forwarding of the APP to the Budget Division for availability of funds, (for purposes of procurement)
Indicative APP recommended by the BAC for approval by the HOPE.
Posting of approved Indicative APP in the DA Transparency Seal
Dissemination of approved Indicative APP for the incoming year to End-users
Revision of the Indicative APP to the final APP
Submission of the Final APP to the GPPB
End-user / Chief of Offices
End-user / Chief of Offices
Procurement Division 1st Qtr of the year 1st Qtr of the year 1st Qtr of the year
End-user / Chief of Offices
End-user / Chief of Offices
Procurement Division - Planning Section and Purchasing Section with the BAC Budget Division
1st week of August before the effective calendar year
August 15 before the effective calendar year
1st week before September of the effective calendar year
3rd week before September of the effective calendar year
4th week before September of the effective calendar year
September 30 before the effective calendar year
Procurement Division - Planning Section
Procurement Division - Planning Section
October before the effective calendar year
October before the effective calendar year
31st of January of every year
Preparation and submission by the End- users of the APP-CSE thru the system developed by the 1CTS based on the NEP and APP-CSE form for the succeeding year by the DBM-Procurement Service
Printing of the consolidated APPCSE for signature and funding
Forwarding of the APP-CSE to the Budget Division for availability of funds and GSD- Property Section for signature
APP-CSE recommended by the BAC for approval of the HOPE
Submission of approved APP-CSE to DBM-PS and posting in the DA Transparency Seal
End-user / Chief of Offices including the Regional Offices and Bureaus
Procurement Division - Planning Section
Procurement Division
September before the effective year
1st week of October before the effective year
2nd week of October before the effective year
3rd week of October before the effective year
October 31 before the effective calendar year
Preparation and submission of PR and PPMP thru the PMS by the Endusers
Consolidation of submitted PPMPs into the Revised APP
Forwarding of the APP to the Budget Division for availability of funds.
Revised APP recommended by the BAC for approval by the HOPE.
Dissemination of approved Indicative APP for the incoming year to End-users
Submission of the revisions in the APP to the GPPB
End-user / Chief of Offices
Procurement Division - Planning Section
Procurement Division
Procurement Division - Planning Section
Procurement Division - Planning Section
Quarterly or as the need arises
Quarterly or as the need arises
Quarterly or as the need arises
Quarterly or as the need arises
Quarterly or as the need arises
July of the effective year and January of the succeeding year
Creation of PRAS with attachment of APP and Terms of Reference/ Technical Specifications/Scope of Work (if needed) and submission through PMS
Verification, approval and number assignment of PRAS
Submission of the hard copies of PRAS together with the Annual Procurement Plan, Terms of Reference/Technical Specifications/ Scope of Work of the requirement (if necessary) to the Procurement Division
Receipt, encode and confirmation of documents attached with the PRAS as enumerated in Step 3
Certification that the request is included in the APP and updating the status in the PMS
Forwarding of PRAS to the Budget Division for earmarking of funds
Earmarking of Funds
Receipt of Earmarked Funds for updating of status in the System and indorsing to the Purchasing Section.*
Preparation of draft Bidding Documents and schedule of Procurement Activities
Conduct of Pre-Procurement Conference
Result of Preliminary Conference:
-If no clarifications or queries were raised, prepare the final version Bidding Documents and proceed to next step.
-If there are queries that need to be addressed and clarified, the PRAS and supporting documents will be returned to End-User for compliance.
Routing of Bidding Documents for approval of the BAC Chairperson (review and initial) NOTE:
This presumes that all the queries or clarifications raised during the preliminary conference were all clarified by the end- user prior to routing and approval of the bidding document
Receipt of Approved Bidding Document and updating of status in the PMS
End-user / Chief of Offices
Procurement Division
- Planning Section
End-user / Chief of Offices
Procurement Division
- Monitoring Section
Chief, Procurement Division
Procurement Division
- Monitoring Section
Budget Division
Procurement Division
- Monitoring Section
Procurement Division
- Purchasing Section
Procurement Division
- Purchasing Section, BAC, TWG and Enduser
BAC through the BAC Secretariat/ Procurement Division
- Purchasing Section
Four(4) months prior to the intended delivery date of the requirement 1 day
BAC Chairperson and Procurement Division
- Monitoring Section
Procurement Division
- Monitoring Section
1 day 1 day 6 days
