Power BITutorial for Beginners
This Power BI beginners tutorial covers the basic learning techniques of data visualization Considering the audience as beginners, this tutorial starts from scratch, thus eliminating confusion related to the topic
In addition, this tutorial assumes that the user is proficient with the advanced formulas and concepts of MS Excel
What is Power BI?
Power BI is a business intelligence tool that helps convert raw data into meaningful insights through dashboards, reports, and applications (apps) It helps visualize data from a variety of visual elements available
For example, an organization may want to create a finance dashboard that displays profits, inventories, cash-in-hand, operating expenses, and so on.Alternatively, a sales dashboard shows the number of units sold in a particular region, earnings of a location, discounts and schemes offered to the general public, and so on
The datasets are uploaded in the Power BI followed by visualizing and selecting the most appropriate representation Auser-friendly visualization helps ease the analysis of data
The desktop version of Power BI is free of cost. Besides, one can also try the SaaS (software as a service) and the mobile supporting app
TheAvailability of Power BI
The Power BI desktop is available on the Microsoft website Alternatively, it can be downloaded from the following link
https://powerbi microsoft com/en-us/desktop/
Note: Prior to downloading, verify whether your Excel is 32-bit or 64-bit.Thereafter, the corresponding version must be installed
Getting Started with Power BI Desktop
The steps for getting started with the Power BI desktop are listed as follows:
Once the Power BI desktop has been installed, type “Power BI” in the search box, as shown in the following image. Click on the “Power BI desktop”.

Power BI takes some time to load. In the meantime, the “initializing model” is visible on the screen, as shown in the following image

The “sign-in” window, as shown in the following image, appears

Cancel the registration or the “sign-in” window and a complete Power BI file opens
Power BI Desktop User Interface

Let us understand the Power BI user interface.The elements of the user interface are listed as follows:
● There are four tabs on the ribbon–Home, View, Modeling, and Help These are similar to the menu options of MS Excel

● In the working area of the Power Bi desktop view, there are three icons on the left side of the screen.These are–“report,” “data,” and “model.”

In the following pointers (a to c), the “report,” “data,” and “model” tabs are discussed
a By default, the “report” workspace is visible, as shown in the following image In this workspace, all the visualizations of data are created.
b In the “data” tab, the uploaded data table information is visible

c. In the “model” tab, the relationship between two or more data tables can be seen.This is the case when more than one data table is uploaded
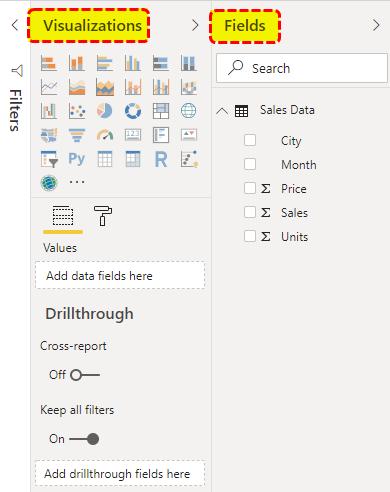
On the right-hand side of the page are two tabs, “visualizations” and “fields ” By using these “visualizations,” we can create reports and dashboards from the “fields.” “Fields” are the column headings of the uploaded data table

The Procedure of Uploading Data
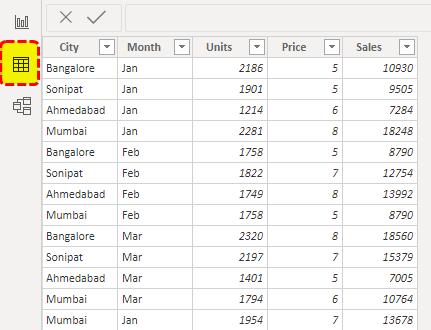
Let us learn how to upload the data to the Power BI desktop The succeeding image shows a sample dataset prepared in Excel.The steps to upload the given dataset are listed as follows:
Step 1: Keep the data ready in any of the mentioned file extensions–Excel, text/csv, xml, json, pdf, etc The current dataset is in Excel format
Step 2: In the Home tab, click on the “get data” drop-down list
Select the appropriate option depending on the type of data source Since our data is in Excel format, we choose the same.

Step 3: Choose the desired file from a location on the computer Go to the saved folder and select the file. Click “open” to upload the data.


Step 4:The “navigator” window opens, as shown in the succeeding image In this, we can edit the data using Power Query
.Alternatively, we can upload the data as it is.
Step 5: Select the worksheet name (sales data) where the data resides At the bottom, there are two options–the “load” and “transform data.” For editing the dataset, choose “transform data,” else click the “load” option
Step 6: In the “Data” option, the entire data table can be seen, as shown in the following image

An Example of Creating Visualizations
Once the data is uploaded, we can create visualizations.The following steps serve as an example for such visualizations:
Step 1: In “fields,” all the data headings can be viewed

Step 2: To create overall sales numbers, choose the “card” visualization.

Step 3: Under “fields,” select “sales” to see the total sales numbers in the card, as shown in the following image.

Step 4:To create a city-wise representation, choose the clustered column chart visualization icon. In “axis,” select “city,” and in the “value” field, select “sales.” Likewise, you can use the different visual elements to create the desired dashboard

The Reasons for Using Power BI
The Power BI has a number of features which are of interest to a data professional.The reasons to learn Power BI are listed as follows:
Power BI is one of the best visualization tools consisting of in-built dashboards and reports

The combination of Excel and Power BI is a powerful mix Aquick analysis is possible as the data refreshes automatically when the source is online. Power BI desktop is a major development of the power view of Excel
Note:The refreshing time can be scheduled if the data uploaded to the Power BI is offline
Here we learning about What is Power BI, How to install and theArchitecture of Power BI and for more details visit this blog Power BI Tutorial
