SkyEnergy is always researching for other innovative ways how mini-grid can stay economically sustainable and environmentally safe for customers.
Kenya government is playing a key role by providing a conducive environment for mini-grid operators and overall renewable energy sector through adoption by enacting energy act.
SkyEnergy is directly making impact by taking Solar power to businesses in the rural communities and offering cost-effective payment solutions so that our customers in the rural communities will not feel overburdened paying upfront high cost of Solar capex
SkyEnergy stakeholders engagement has been one of key governance by bringing everyone onboard to discuss our services and or products and listening to communities need and challenges
What role do you see mini-grids playing in Kenya's overall energy mix, and how do you think the Kenyan government can support their development and integration into the national grid?
Mini-grid as a sector has played significant role in Kenya's renewable energy transition to sustainable electricity since it's adoption in Kenya There are 3 mode of mini-grid delivery in Kenya i e Solar Rural electrification, off-grid electrification and Solar Home System. Rural electrification is a government program to electrify institutions such as Schools etc where Off-grid is operated by IPP and focusing in delivering electricity to hard-to-reach communities where grid doesn't exist Where SHS is providing PayGo Solar for homes in Rural communities across the country These combination of Solar delivery modes has seen many Kenyans have access to electricity
Kenya government is playing a key role by providing a conducive environment for mini-grid operators and overall renewable energy sector through adoption by enacting energy act 2019. This Act is allowing operators and investors to operate with ease Kenya is the first country in Africa to have actualized and regulate mini-grid sector Also, the first to adopt mini-grid Tariff which is now being adopted by many counties in SSA. Currently Kenya is working on a Net Metering policy that will allow excess power to be sold to national grid

How will SkyEnergy Africa measure the success of its mini-grid projects in Kenya, and what metrics will you use to evaluate their impact on the communities they serve?

SkyEnergy's success in Kenya and region is through customer centric delivery Our Mini-grid is focusing on Product Use by delivering Solar power to high dependency sectors such as healthcare clinics and SMEs in the rural and offgrid communities SkyEnergy is directly making impact by taking Solar power to businesses in the rural communities and offering cost-effective payment solutions so that our customers in the rural communities will not feel overburdened paying upfront high cost of Solar capex
How will you engage with customers and stakeholders in the mini-grid projects, and what kind of services or products do you plan to offer beyond basic electricity access?
SkyEnergy stakeholders engagement has been one of key governance by bringing everyone onboard to discuss our services and or products and listening to communities need and challenges We incorporate all views into every project or products we're rolling-out.
SkyEnergy is currently working with our product partners to rollout innovative solar solution in Kenya and the region This will see mini-grid take a complete different twist because Skyenergy's
Solar Solution is total renewable energy power and more importantly, it's sustainable, no pollution like Diesel or gas Gensets
Can you talk about any challenges you've faced while implementing mini-grid projects in Kenya, and how have you addressed these challenges?
Most challenges we faced always a robust Solar PV solution that can work anywhere and in any environment community awareness and adoption to using Solar as the sole source of power and some don't think Solar can power their machines especially the business communities. However, we have been able to overcome this by continually addressing and educating the community on use of Solar power.
How does SkyEnergy Africa plan to ensure that the mini-grids are sustainable over the long term, both financially and environmentally?
SkyEnergy is always researching for other innovative ways how mini-grid can stay economically sustainable and environmentally safe for customers It's one of the reasons why SkyEnergy is working with innovative partner to rollout renewable energy solar solution in Kenya and subsequent SSA targeting healthcare and SME sectors across SSA This solution will revolutionize the entire mini-grid sector because of it's adaptability and mobillity to work in any environment and geography including rural and off-grid communities and can be used across multiple sectors

PowernSun is a customer centric company, our in-house technical expertise and rigorous quality check parameters helps us to bring quality product and component to the customers.
Our pursuit of innovation is characterized by an in-depth understanding of solar technology and an agile approach to delivering innovative and reliable products and services to our clients

We developed in house expertise of Global Material Sourcing experience and expertise to handle KW to MW Projects Supply and Management
We strive to bring the latest technology, products, and services under one umbrella
Which are some of your bestselling products and why?
Powernsun is a customer centric company our, in-house technical expertise and rigorous quality check parameters helps us to bring Quality product and component to the customers
Major Brands -Sungrow, SMA, JA Solar, LONGi ,Trina and Many More.
What makes Power n Sun the best solution provider in the market?
Our pursuit of innovation is characterized by an in-depth understanding of solar technology and an agile approach to delivering innovative and reliable products and services to our clients In one word, we strive to bring the latest technology, products, and services under one umbrella
Tell us about the services and products offered by Power n Sun in Africa.
We are dealing with top brands from different verticals All brands have global footprints, strong service network and prompt response time
Lead Acid Battery – Luminous battery
PV Panel – JA Solar, LONGi & Trina
Inverter -Sungrow, Solpalnet, SMA, Sineng, Luminous, Solinteg, Focus and Polaris

What are some challenges you face in your day-to-day work as a Solar distributor and how do you mitigate them?

As we know in Solar business reliability of components is major constraint, we as a Power n Sun developed in house expertise of Global Material Sourcing experience and expertise to handle KW to MW Projects Supply and Management
Where can customers find more information about your services in Africa?
PowernSun presence across Africa region, we have office in RSA (South Africa), for more information visit our Official websitewww powernsun co za and Our social media accounts
Powernsun is a customer centric company our, inhouse technical expertise and rigorous quality check parameters helps us to bring Quality product and component to the customers."

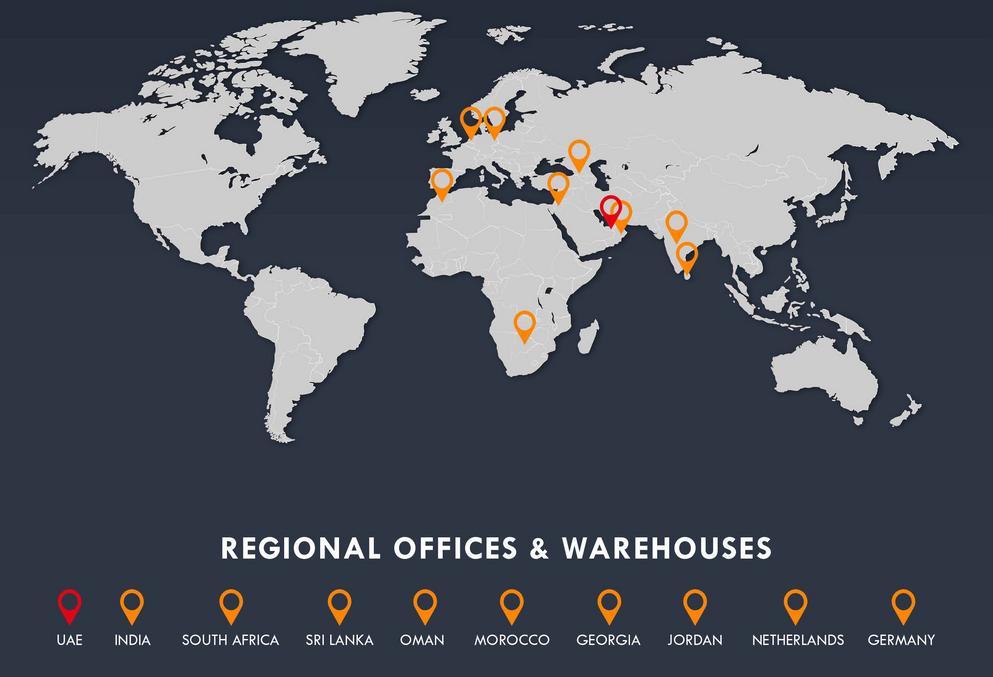
In the renewable energy world, Powernsun is a renowned market player in the distribution segment of solar products The company takes pride in its significant success track record of 10 years in the Middle East, South Africa and Southeast Asia accelerates it to expand its solid footprint in more than 50+ green energy enthusiastic countries around the globe.
The story of Powernsun starts as a subsidiary of Orange overseas FZE, which was started in 2013, under Hamriyah free zone, United Arab Emirates, by Mr Lokesh Kumar, to deal with power and power generation products, mainly import and export in the middle east and Africa region In 2017, Power n Sun solar equipment’s trading LLC was formed as 100% subsidiary of Orange overseas FZE, registered in Dubai as a limited liability company

The Group has been growing year on year and has shipped 1200 Megawatts of solar products by the end of February 2023 In 2021, the group opened their branch office in India, and in 2022 Q1 in Oman and Q3 in South Africa and Q4 they have successfully to opened a subsidiary in the Netherlands, Germany, Morocco and Georgia to manage their business in India, Africa, and Europe respectively
Africa with its maximum sunny days and proximity to the equator facing challenges such as higher energy prices and possible shortages cumulatively inspiring African countries in moving toward renewable energy generation powernsun believes a continent that possesses 60% of the best global resources in the world, holds great scope for solar energy generation
The continent has sunlight year around, it is observing a sharp peak in solar power generation, a 14% growth year-over-over, as per the report of AFSIA Africa is evolving with its largest solar energy potential and the governments and international bodies are supporting consumer market the green energy initiatives, that paves way for easy business operation This stands as another evident reason for Powernsun to choose Africa market for its service expansion
With a regional office in Johannesburg and warehouses in Johannesburg/Durban, we are fully geared up with a rich product catalog to serve the highly informed and well-updated markets of the Southern African region, covering from Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Botswana, Zambia, Malawi, Namibia, Angola, Mauritius, and Madagascar
In North Africa, we have a history of serving the needs of aspirational markets of Morocco, Egypt, Algeria, Tunisia, South Sudan, Ethiopia, and Djibouti Recently, the company has participated in the three-day Solaire Moroc 2023 event.
With a strong commitment to serving the entire solar needs of Africa, Powernsun has aspired to have a strong presence in the markets of Eastern & Western Africa especially Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Malawi, and Zambia, Nigeria, Ghana, Senegal, Burkina Faso, Cote de Ivory, and Togo to provide energy storage solutions and various other solar products
Creating a regional presence is a part of their overall and long-term strategy as solar business is driven by many regional and economic factors Presently the group operates from its headquarters in Dubai and has 60+ employees across the continents
Africa is evolving with its largest solar energy potential and the governments and international bodies are supporting consumer market the green energy initiatives, that paves way for easy business operation."


As a company that fully embraces global best practice ESG principles, it is important for Tatanga Energy to ensure that all its projects are sustainable and socially responsible.
There is enormous scope for ‘mini grids’ to play an expanded role in improving access to energy in Zimbabwe, particularly in rural and peri urban settings.

A key success factor is to ensure that the electricity generated by projects is affordable and the community has or can be assisted to have the means to procure the electrical output of the project whether it is used for productive or residential usage
Tatanga Energy actively engages with local communities and its customers to better understand their evolving energy needs.
How does Tatanga Energy plan to design and implement its minigrid projects in Zimbabwe, and what factors will you consider when selecting project locations?
There is enormous scope for ‘mini grids’ to play an expanded role in improving access to energy in Zimbabwe, particularly in rural and peri urban settings At first screening, the ideal mini grid site candidates are typically clustered around rural and peri urban communities, where it is not currently economically or technically feasible to extend the national grid
Despite the undoubted socio- economic benefits of extending electrification to underserved communities, the uptake of mini grids in Zimbabwe has been slow However, a few mini grids have been implemented with varying degrees of success There are a few key learnings from the implementation of the few actively functioning mini grid projects in Zimbabwe that Tatanga Energy and any other developer that is interested in this emerging space should consider incorporating in the design, implementation and selection of new mini grid projects
The first and perhaps the most important factor to consider is the level of current and projected economic activity in the community Without a doubtful whether a deployed on a
commercial basis Other factors that need to be considered include the population density of the community, average incomes and the nature of existing economic activity A soft factor that is often overlooked is a feeling of community ownership of the project Without active community participation, involvement and a general sense of ownership, mini grid projects often end up as white elephants.
What kind of business models does Tatanga Energy plan to use for its minigrid projects in Zimbabwe, and how do you anticipate generating revenue from these projects?
We believe that there is no ‘one size fits all’ mini grid business model This lends to the utilization of a number of different business models as influenced by each project’s unique characteristics In many case we would envisage a hybrid model whereby third parties, typically Development Finance Institutions and sub governmental agencies such as the Zimbabwean Rural Electrification Agency (‘REA’), are brought in to tackle any viability gaps in the project Addressing these viability gaps could include structured support to assist to reduce the end user tariff to ensure its affordability to the targeted off-takers
There are also a number of possible revenue models with the most basic being the vending of electricity to end users via a network of split meters A key success factor is to ensure that the electricity generated by projects is affordable and the community has or can be assisted to have the means to procure the electrical output of the project whether it is used for productive or residential usage
How does Tatanga Energy plan to ensure that its minigrid projects are environmentally sustainable and socially responsible?
As a company that fully embraces global best practice ESG principles, it is important for Tatanga Energy to ensure that all its projects are sustainable and socially responsible
Access to modern energy and the intensity of its usage are widely recognized as good indicators of a communities level of development It is now increasingly evident that it is difficult – some would say impossible - to sustainably deliver quality healthcare, education or other social services without reliable and affordable energy. It is also challenging to generate much needed sustainable and scaled employment opportunities without electrification The widespread deployment of mini grids can thus be termed a great predictor and equalizer of a communities ability to leverage opportunities to better their lives
In order for the full benefits of mini grids to be realizable it is important that the twin goals of deploying environmentally sustainable and socially responsible projects are met Tatanga Energy seeks to ensure that it meets these goals by ensuring it embeds best practice ESG principles in the foundations of all its projects Typical tools utilized include the IFC Performance Standards to both assess and improve the environmental and social performance of projects utilizing an outcomes based approach Adherence to the IFC Performance Standards is a rigorous process and can be quite involved but leads to more predictable and balanced project outcomes The main value of the process once implemented is the systematic approach to the identification and management of risks and upsides through the project’s lifecycle
How does Tatanga Energy plan to engage with local communities and customers to understand their energy needs and preferences, and how will you tailor your minigrid solutions to meet these needs?

Tatanga Energy actively engages with local communities and its customers to better understand their evolving energy needs Engagement can be both individual or collective through workshops, focus groups and forums It is dangerous to implement these type of projects without widespread consultation as a number of general assumptions that a developer may make could prove costly or even fatal to the success of the projects
Can you discuss any partnerships or collaborations that Tatanga Energy has formed in the minigrid space, and how have these partnerships supported your project development?

The development of a mini grid project invariably requires a number of different parties to collaborate effectively towards the successful execution of the projects Potential project partners range from community leaders, businesses that are active in the community Rural Electrification Agencies Development Funding Institutions and EPC contractors
In the case of the recently commissioned St Patrick’s mini grid, which comprises of a 157 kWp solar array plus a 300 kWh battery storage system, a number of different parties collaborated over a period oof approximately 6 months to bring the project to fruition The project sponsor was the Anglican Diocese of Central Zimbabwe with Trinity Church Wall Street, a United States based Anglican Parish and Charity, providing the bulk of the viability gap funding The project was constructed by Solar Energy Partners All partners contributed extensively and collaboratively towards the successful and timely implementation of the project It is anticipated that the project which was highly successful and delivered on a fast track basis will be replicated across a number of different institutions in the near future.

JA Solar was awarded "Top Brand PV South Africa 2023" in the module category from the Energy Research institute EUPD Research in Cape Town during the “Experience & Connect

Boat Cruise Networking Event” in Cape Town JA Solar is a tier 1 manufacturer of high-performance PV products with a cumulative shipment of 115GW across the globe by the end of 2022 Q3


From DeepBlue 3 0 to DeepBlue 3 0 Pro and the latest DeepBlue 4 0 X launched in May last year, JA Solar has adopted half-cut, PERC, bi-facial, ntype and other leading technologies and manufacturing techniques in its DeepBlue series solar modules. They have been well-proven for high conversion efficiency, high power output and robust reliability in many solar projects across Africa
South Africa’s current electricity crisis has been described as “a perfect storm” and many are turning to solar power as the country enjoys an average of eight hours of sunshine every day Currently JA Solar enjoys the largest PV module market share in South Africa and its modules have been well adopted in utility scale, commercial & industry and residential solar projects
The certificate was handed over to Hadyr Koumakpai – General Manager Africa, Daniel Pasker - Sales Manager South Africa, Cindy LiuSales Director South Africa and Victor Musau - Technical and Marketing Manager by EUPD Research CEO Markus A W Hoehner

JA Solar enjoys the largest PV module market share in South Africa and its modules have been well adopted in utility scale, commercial & industry and residential solar projects.

Carbon credits, also known as offsets, are certificates that represent one ton of CO2e that have been either prevented from being emitted from the atmosphere or removed from it To verify the climate impact of projects, they must be independently verified and meet certain standards Individuals and corporations can trade the certificates they generate and sell them to others who want to offset their carbon emissions and claim towards their climate targets

There are two types: voluntary markets and compliance markets Companies and governments are required to account for their greenhouse gasses emissions through compliance markets There are several types of compliance markets, including 'cap-and trade system' and baseline and credit system
In voluntary markets, project developers create projects that do not emit certain pollutants (e g, landfill gas management and treatment) or that remove CO2e from our atmosphere (e.g. afforestation, direct air capture) An independent 3rd party verification body or validation body (VVB) verifies that the project meets the standards of a standard setter. Once the project has been certified, carbon credit are issued in a amount that is equal to its mitigation impact The carbon credits are then sold by the developer to governments, individuals, and companies These carbon credits can be traded multiple times on secondary markets through intermediaries, such as OTC platforms or carbon exchanges. Credits can be held until they are retired. A credit becomes retired when it is used to meet its climate targets of any corporate or any government or any individual. This is called 'claiming' the climate effect towards the goals
Voluntary carbon markets are in demand and should grow by 15x by 2030 1, owing to an increase in corporate net zero commitments VCMs are expanding beyond North America and Europe, as new markets develop in Asia, Latin America and the Middle East
Voluntary carbon markets are witnessing the emergence of new types of projects driven by the necessity for carbon removals to address residual carbon emissions in hard-to-abate sectors The use of new technology to remove carbon is complementing existing nature-based methods. Direct Air Carbon Capture and Storage is an example of a chemical process that captures and separates carbon dioxide directly from air
Different types of major Carbon Credit projects in Africa
African voluntary carbon markets are expanding at a 36% CAGR between 2016 and 2021 2 However, carbon markets remain underutilized as a means to finance climate finance. Only five african countries have received 65% of the credit issued in the last 5 years (Kenya Zimbabwe, DRC Ethiopia, Uganda, and Uganda) Low activity has been seen in many of the countries that have the greatest potential Only the Democratic Republic of the Congo, out of the high-potential countries (including Angola and Nigeria as well as Sudan and Tanzania), has announced significant carbon credit deals There are almost no local validation/verification bodies (VVBs) and almost all credits from Africa are certified by global bodies VERRA, Gold Standard and other players are the global standard bodies.

AUTHOR:
ABIGAIL BOTSHA Head, Marketing & Business Development in GVE Projects Ltd
CClimate change isn't just a passing concern or fad in Africa It is a daily reality that affects millions of people, particularly those living in remote and rural areas with limited access to modern energy services Even in Nigeria, climate change is an ever-increasing threat that


exacerbates existing issues of poverty, underdevelopment, and social inequality Sixty (60) million people are lacking access to electricity, and the country's energy sector is heavily reliant on fossil fuels However, mini-grids offer a practical solution to help reduce carbon footprints and mitigate global warming which is ideal for developing climes because they can provide reliable, affordable, and clean energy to remote and underserved communities
According to the Rural Electrification Agency (REA) of Nigeria, as of October 2021, there were over 150 mini-grid projects operational in the country, providing electricity to over 100,000 people with GVE Projects Ltd having deployed a sizable number of mini-grids in that lot. The REA aims to connect 40 million Nigerians to electricity by 2030, with minigrids expected to play a significant role in achieving this goal In terms of the impact of mini-grids on carbon emissions in Nigeria, a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) estimates that mini grids in the country could potentially reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 1 3 million tonnes per year by 2030, equivalent to taking 280,000 cars off the road Also, GVE’s Wuse Market Project is set to power over 2000 SMEs to displace about 3,000 petrol/diesel generators thereby mitigating significant amounts of Green House Gases and transforming Wuse Market into Nigeria's first 100% green and generatorlargest black nation of the world
Since 2010, the Energy and Environment Partnership (EEP) has funded over 70 Kenyan mini- grids These solar biomass mini-grids power more than 40,000 rural residents Mini-grids replaced diesel generators, reducing carbon emissions by over 5,000 tons per year. Also, Tanzania's Rural Energy Agency (REA) promotes mini-grids in remote and underserved areas The program has installed over 100 mini-grids that power over 50,000 people Solar, hydro, and biomass mini-grids reduce carbon emissions by over 8,000 tons per year
In addition to reducing carbon footprints, mini-grids can mitigate the effect of climate change in Africa In droughts and other extreme weather events, mini-grids can power water pumping, irrigation, and other agricultural processing Mini-grids can power health clinics and schools, which improve the quality of life in rural areas most affected by climate change
Mini-grids can significantly reduce Africa's carbon footprint and global warming They solve the continent's energy poverty and climate change issues while boosting economic growth and job creation However, financing, policy and regulatory frameworks can be complex and inconsistent in many African countries, and community engagements to ensure mini-grids meet community needs and aspirations remain obstacles
In conclusion, the implementation of mini-grids represents a promising pathway toward achieving sustainable development goals and mitigating climate change.

It is clear from recent market trends that both p- and n-type solar cell efficiency will increase. But it is essential that you understand the basics of these cell types from an investor's or end user's standpoint The base of a solar cell with a p-type type semiconductor is present in the p-type cell, and vice versa for ntype cells This is because the doping of wafers (both mono- and multi-) results in a difference in base. This is required to make a semiconductor junction that conducts current flow The wafer is either doped with phosphorus (leading to n-type wafer) or boron (leading to p-type wafer).
Advantages & Disadvantages
P-type cells have economies of scale This is due to the demand for p type solar cells in the market Because the whole value chain, from sand to solar cells, is optimized for p-type solar cells, this is a huge advantage.
P-type cells have a cost competitiveness to its competitor The current market situation may make the initial cost a significant determining factor, giving p-type an advantage
The main benefit of an n-type cell is its efficiency The n-type cell can produce more power and thus generate more revenue

They are also less susceptible to module degradation compared to P-type solar modules This allows a longer life expectancy for modules made with such cells They are also less susceptible to impurities than p-type cells.

The thirdly levelized cost for electricity (LCOE), which is the ratio of total energy cost to plant's life expectancy, can be quite significant It may even exceed the plant's return on investment (ROI) in some cases.
PERC, like other cell technologies, is available in both p and n-type There are still many challenges to be overcome, the most important being Light Induced Degradation and Light enhanced Temperature Induced Degradation for p-type cells. LID and LeTID have been shown to significantly reduce the power output of the PERC module It takes a lot of effort to improve the few practical ways that LID &LeTID can be eliminated However, N-type PERC cells are LID &LeTID-free


Nigeria recently passed the Climate Change Act (2021) and the Energy Transition plan (2022) which establish a target to reduce GHG by 47 percent in 2030, relative to base case, achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 and generate 30 GW of energy by 2030 with 30% renewable energy.
Gabon has committed to being a carbon neutral country beyond 2050 With international support, Gabon pledges to continue its net carbon absorption of no less than 100 million tCO2e annually beyond 2050. Gabon also plans on issuing large volumes of carbon credits
Togo’s nationally determined contribution (NDC) established an unconditional target to reduce emissions up to 6 Mt CO2e, 21% below business as usual (BAU) by 2030.
Mozambique has shared a commitment to reduce emissions by 40 MtCO2e until 2025
Malawi’s NDC established a target to reduce emissions by 12 8-18 1 MtCO2e below business as usual by 2030

Kenya’s NDC established a target to reduce emissions by 32% below business-as-usual by 2030, corresponding to 46 MtCO2e.






HONORARY AWARD:
Le Commissariat aux Energies Renouvelables et à l’Efficacité Energétique (CEREFE)
COMPANY EXCELLENCE AWARDS:
Best Solar Company of the Year - Module


JA Solar
Best Solar Company of the Year- Distributor





Securité 2000 Technique
TECHNOLOGY EXCELLENCE AWARDS:
Best Solar Technology of the Year
JA Solar
MASTERS OF CORPORATE LEADERSHIP AWARDS:
Best Solar Company of Year- EPC
EVOTRIK