4 minute read
HL Maths - Applications & Interpretations
HL Maths - Applications & Interpretations
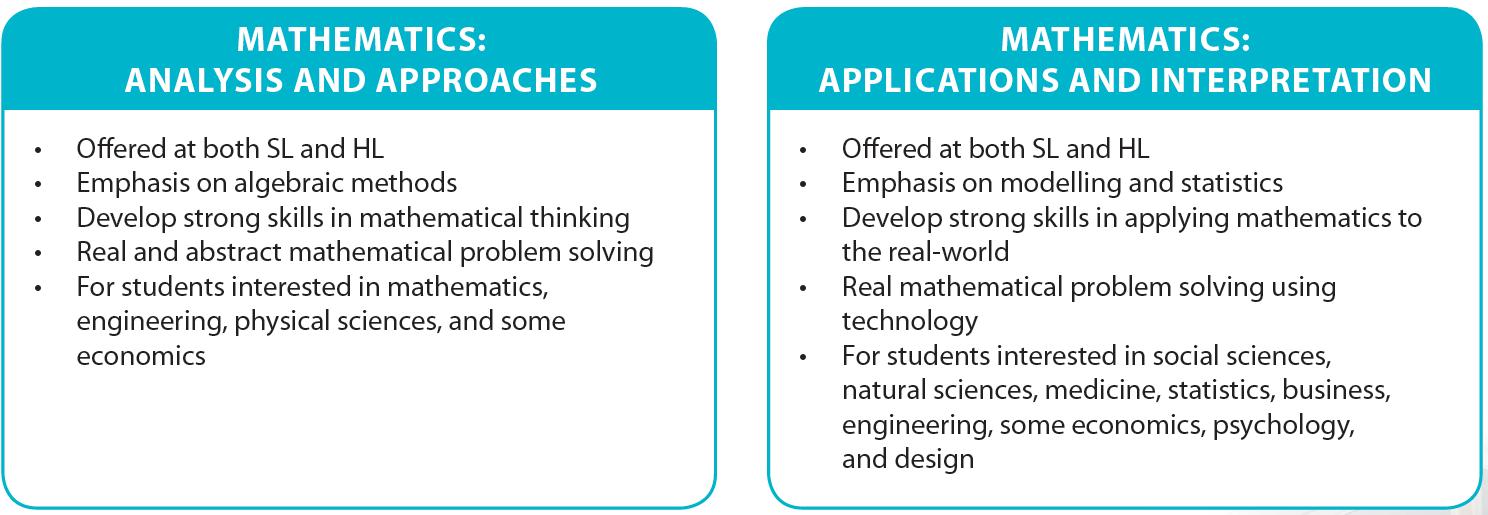
Comparison between the two courses:
This is a course which had its first examination in 2021 and is appropriate for students who wish to take a HL course in mathematics but prefer the more practical side with modelling using technology, statistics and algorithms. Their preferred choice of study at university will probably have significant mathematical content. For example, business, economics, natural sciences.
Aims:
The mathematics courses aim to contribute to students' personal attributes, subject understanding and global awareness by enabling them to: 1. develop a curiosity and enjoyment of mathematics and appreciate its elegance and power 2. develop an understanding of the concepts, principles and nature of mathematics 3. communicate mathematics clearly, concisely and confidently in a variety of contexts 4. develop logical and creative thinking, and patience and persistence in problem solving to instil confidence in using mathematics 5. employ and refine their powers of abstraction and generalization 6. take action to apply and transfer skills to alternative situations, to other areas of knowledge and to future developments in their local and global communities 7. appreciate how developments in technology and mathematics influence each other 8. appreciate the moral, social and ethical questions arising from the work of mathematicians and its applications 9. appreciate the universality of mathematics and its multicultural, international and historical perspectives 10. appreciate the contribution of mathematics to other disciplines, and as a particular “area of knowledge” in the TOK course 11. develop the ability to reflect critically upon their own work and the work of others 12. independently and collaboratively extend their understanding of mathematics
Course Description: This course caters for students with a very good background in Mathematics who are confident in a range of analytical and technical skills. The majority of these students will be expecting to include Mathematics as a major component of their university studies, either as a subject in its own right or within courses such as economics, physics, engineering and technology. Others may take this subject because they have a very strong interest in mathematics and enjoy meeting its challenges and engaging with its problems. There is also a strong emphasis on statistics and mathematical modelling, particularly using technology. The course covers five broad areas of Mathematics: number and algebra, geometry and trigonometry, functions, statistics and probability, and calculus. The students will need a graphical display calculator (GDC) which will be used throughout the course. Students will complete an internal assessment worth 20% of their final grade.
Students will learn to develop their mathematics for describing our world and solving practical problems. They will also learn to harness the power of technology alongside exploring mathematical models. They will enjoy mathematics in more practical contexts such as statistics and using algorithms to solve problems.
Graphic Display Calculator (GDC)
Students are required to use a GDC throughout the course and during their exams. In Tanglin we use the TI n Spire CX, and all students are expected to buy this particular model. It is available for sale in the school shop.
Requirements:
To follow the Maths Applications HL course, students should be expecting to achieve a level 9 or 8 at IGCSE Mathematics. Most importantly they need to be very motivated and interested in mathematics, in particular modelling, using technology and statistics, but still with a firm understanding of functions and calculus.
Career Path:
The study of mathematics is excellent for developing critical thinking, problem solving and being analytical in one’s response to a number of diverse problems. It requires application and dedication and helps students develop independence. As such, it is invaluable in any career but particularly important in careers requiring Mathematics as a major component. These careers include engineering, the actuarial profession and other financial sectors, economics, IT, computer programming and systems administration, research and development and statistical analysis. Intelligence agencies require top class mathematicians, as do many other careers. HL Applications particularly suits courses containing practical uses of Mathematics e.g. engineering, Computer Science, Biology, Chemistry, Geography and some Economics courses.
Comparison between this course and A-Level
The main difference is in the assessment. A Level questions can be more structured. IB questions vary in style and bring many topics into one problem. Sometimes there are aspects that a student may not have seen before in order to test problem solving skills. Another difference is the internal assessment that is required for IB. No coursework is required for A Level. Also, A Level does not require confident use of a graphical calculator, whereas IB does.
Assessment
The course is assessed with three papers, one non-calculator and one calculator worth 60%, a third paper with two extended modelling questions worth 20% and an "exploration" worth 20%. The exploration is a piece of written work undertaken in Term 3 of Year 12 which investigates an area of mathematics of their choosing.
Contact for further information:
Mr Chris Hollingworth: chris.hollingworth@tts.edu.sg Mrs Sarah Aldous: sarah.aldous@tts.edu.sg