





Academic Authors: Ayushi Jain, Neha Verma
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh
Project Lead: Jatinder Kaur
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First impression 2023
Second impression 2024
Third impression 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Tekie Computer Science Teacher Manual 2
ISBN: 978-81-984519-4-1
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
Uolo’s Tekie program offers a coding-focused curriculum for grades 1 to 8, preparing students for the technology-driven world. We present a carefully crafted Teacher Manual to assist teachers in delivering effective and engaging lessons to students. Rather than prescribing teaching methods, the manual provides examples and demonstrates how and why teachers can apply these examples in their classes.
The Teacher Manual includes a suggested implementation plan to help teachers navigate the curriculum better throughout the academic year. Within the academic year, the Tekie program prescribes the following types of chapters and sessions:
Familiarisation: this period builds familiarity with the Tekie program and the digital platform.
Theory: these periods are dedicated to the Computer Science Theory chapters. These topics are mostly delivered in the classroom.
Tools: these periods are dedicated to the Computer Tools chapters. These topics involve almost equal numbers of classroom and computer labs sessions.
Coding: these periods are dedicated to the Coding chapters. These topics have more computer lab sessions.
Additional Hands-on Time: these are additional computer lab periods that teachers can use to revise topics or dedicate for completion of projects.
Revision: these are additional classroom periods that teachers can use to revise topics or cover syllabus backlogs.
Each chapter in this manual is structured to provide a comprehensive lesson plan. The chapters are divided into multiple sessions, each following the Warm up, Engage, Build, and Sum up (WEBS) strategy. The Warm up phase sets the stage for learning by connecting to prior knowledge and building curiosity. The Engage phase captures the students’ attention and motivates them to participate actively. In the Build phase, questions from various sections are discussed to build the understanding of the students. Finally, the Sum up phase reinforces learning through easy-to-recall activities and questions. Time duration for each section has been suggested based on the requirements of the students. Additionally, an answer key for every chapter is provided to assist teachers in assessing their students’ understanding and guiding their learning effectively.
Lastly, we understand that the Indian education landscape is quite diverse. To suit the needs of all types of schools, we have built-in extra higher-order chapters in the content books. These extra chapters are clearly marked in the table of contents of this manual. We suggest that the teacher completes the main chapters first and then move to higher-order optional chapters only if there is sufficient time left in the academic year and learners are ready for more challenging content.
We hope that this teacher manual will empower teachers to use the curriculum effectively, support the learning of all students thoroughly, create learning opportunities and design interactive learning environments that cater to the students’ needs and interests.
1 How Computers Help Us ������������������ 1
Understanding Computers
Advantages of a Computer
Disadvantages of a Computer
Where We See Computers
Starting a Computer
Shutting Down a Computer
2 Different Parts of a Computer ������� 14
Input Devices
Output Devices
Storage Devices
Input, Process, and Output Cycle
3 Typing Using Keyboard ������������������ 23
Computer Keyboard
Alphabet and Number Keys
Special Keys
Combination Keys
4 Fun with Mouse ������������������������������� 33
Understanding the Mouse
Tiny Tech Game
Holding a Mouse
Mouse Pointers and Using the Mouse 5 Introduction to Paint���������������������� 41
Introduction to MS Paint and Shapes Tool 1
Introduction to MS Paint and Shapes Tool 2
Using Shapes Tool 2
Using Shapes Tool 3
Saving and Opening a Drawing 1
Saving and Opening a Drawing 2
6 Colouring in Paint ��������������������������� 54
Colouring a Drawing 1
Colouring a Drawing 2
More Tools in MS Paint 1
More Tools in MS Paint 2
7 AI: Introduction to Robots* ����������� 63
Robots and Their Types
AI Game
High-tech Robots in Our World
Fun with AI: Using Chatbot
1 Introduction to Coding������������������� 71
Block-based Coding and Commands
What Is a Sequence?
What Is an Algorithm?
Tour to Puzzle Code Studio
2 Introduction to Sprite �������������������� 79
Introduction to Sprite and Sprite Lab
Creating a Scene 1
Creating a Scene 2
Adding a Behaviour
3
Understanding Events and Actions
Setting up the Second Scene 1
Setting up the Second Scene 2
Setting up the Second Scene 3 4 Loops in Coding*
Concept of Loops and Repeat Loop
Continuing with Project

38

In Avora, a magical land, it’s the first day of school. Mel, a smart robot, and Conji, a young wizard, become friends as Elder Wizard and Elder Robot teach that magic and technology go hand-in-hand. Mel introduces Conji to computers in the lab, explaining parts like the mouse and keyboard, while Conji shows Mel magical spells to control lights. They learn that both magic and technology require careful use.
Trouble begins when Lord Ero, an evil wizard, steals all the computer mouses to make Avora dull and colourless. Mel, Conji, and their friend Eva hide a computer in the Memory Palace, safe from Lord Ero’s spells. When Elder Wizard falls ill, Mel and Conji make a get-well-soon card using Paint. However, Lord Ero uses dark magic to drain Avora’s colours. The trio and Elders combine their knowledge of magic and technology, using Paint to restore the colours. Ms. Idea suggests linking the computer to Avora, enabling actions on the computer to affect the real world. Mel colours Avora on the computer while Conji and Eva support with spells, successfully bringing back the colours. The Elders praise their teamwork.
As they celebrate, Lord Ero reappears, casting a destructive spell. Eva blocks it, and they realise they need AI to strengthen their powers. Mel explains AI and demonstrates its benefits, helping them weaken Lord Ero. With his defeat, the peace returns to Avora.
● Elder Robot and Elder Wizard are talking to Mel and Conji.
● Mel takes Conji to the Computer Lab and show him the world of gadgets.
● Conji asks Mel about computers, as he is not aware of computers.
● Mel tells Conji that a computer is an electronic device that helps them to play games, draw pictures and find information. Mel then shows him a computer.
● Conji is surprised to see a computer and asks Mel to tell him more about it.
This chapter is divided into the following classroom sessions
5. Starting a Computer
6. Shutting Down a Computer
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe a device, an electronic device, and a computer.
● tell the uses of computers.
Keyword
● Computer: A computer is an electronic device that helps us do many things.
Ask the students about different devices around them. Tell students what a device, electronic device, and computer are. Also discuss uses of computers.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
● Ask the students about different devices around them.
● Tell them about electronic devices.
● Now, build the concept by introducing them to computers.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Describe a device, an electronic device, and a computer.
Tell the uses of computers.
15 mins
Explanation
Tell the students that the devices are things that help us to do specific tasks. Then tell them about electronic devices and computers, as given on page 4.
Tell them that a computer is used for playing games, watching videos, etc., as given on page 4.

● What are the uses of computers?
Correct Responses: playing games, watching videos, etc.
● Can you draw a picture using a computer?
Possible Responses: Yes/No
Correct Response: Yes. You can draw a picture on a computer.
● Ask the students to answer to the question “What are the things you like to do on a computer?” asked in the Think and Tell section on page 4.
Possible Responses: drawing pictures, playing games, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising that a computer is an electronic device that helps us do many things. A computer is used for playing games, watching videos, drawing pictures, listening to music, and finding information.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 3, and 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 1
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Ask the students what a computer is and its uses.
Ask them what can be the possible advantages of a computer.
● tell the advantages of computers. 5 mins
Tell them that a computer can do many things for us, then discuss the advantages of a computer.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students what a computer is and its uses.
● Ask them what can be the possible advantages of a computer. Tell them computers help us know about new things.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Explanation
Tell the advantages of computers. Tell the students that a computer can do many things for us, as given on page 5.
● Tell any one advantage of a computer.
Possible Responses: We can share information and talk to each other using a computer. / It can store a large amount of data, like pictures, music, videos, and games. (Answers may vary.)
● Name one way a computer helps us with entertainment.
Possible Responses: watching cartoons, playing games, etc.

● Ask the students to answer the question “Is doing many things on a computer at the same time an advantage?” in the Think and Tell section on page 5.
Possible Responses: Yes/No
Correct Response: Yes, it is an advantage since it saves our time.
● Conclude the session by summarising that a computer can do many things for us. It is used to store a large amount of data, play games, watch cartoons, share information, etc.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 1
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Based on the topics they have learnt, ask the students what can be the possible disadvantages of a computer. Tell them that the computers are very useful but they also have some disadvantages. Thereafter, discuss the disadvantages of a computer.
● tell the disadvantages of computers. 5 mins
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Based on the topics they have learnt, ask the students what can be the possible disadvantages of a computer.
● Ask the students if they know that using a computer for a long time can make their eyes weak. 15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Tell the disadvantages of computers. Tell the students that computers are very useful but they also have some disadvantages, as given on page 6.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1A section and encourage the students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.

● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ‘Consequences of using a computer for a long time’.
Possible Response: Using a computer for a long time can cause many health problems, such as headaches, strain on our eyes, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising that the computers are very useful, but they also have some disadvantages, such as causing health, security, and environmental problems.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter, as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 4 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Ask the students where they have seen the computers. Discuss the places where computers are used. Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework 5 mins 15 mins 7 mins 3 mins
● describe the places where computers are used. 5 mins
● Ask the students where they have seen the computers.
● Now, build the concept by discussing any one place where computers are used.
Explain the following concepts: Learning
Describe the places where computers are used. Tell the students that in today’s world, computers are used everywhere, such as in schools, banks, hospitals, etc., as given on page 7.
● Read aloud the questions in the Do It Yourself 1B section and encourage the students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. a. Banks: To let us take money out from our account.
b. Schools: To help us learn new things.
2. Option c

● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic “How can computers help us in doing our homework and creating projects?” given in the Discuss section on page 8.
Possible Response: Computers allow finding information quickly, and the projects look neat when done on a computer.
mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that in today’s world, computers are everywhere, and they help us in many places. In banks, they help us take out money and send money to others, etc. In school, computers help us learn new things. In hospitals, computers help make medical reports. At airports and stations, they help us book tickets. In stores and offices, computers help make orders and bills.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter, as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 2
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 3, and 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 3 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 2
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 4 and 5
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● tell the steps to start a computer.
Ask the students if they have ever turned on a TV.
Discuss the various steps to start a computer.
Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students whether they have turned on a TV or any other electronic device.
● Now, build the concept by telling the students if they know the steps to start a computer.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning
Tell the steps to start a computer. Tell the students about the various steps in starting a computer, as given on pages 8 and 9.
● Read aloud Question 1 provided in the Do It Yourself 1C section and encourage the students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.


● In which step you should press the ON button on the monitor to start a computer?
Possible Responses: Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, Step 4, or Step 5.
Correct Response: Step 4
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ‘Can we start a laptop the same way as we start a computer?’.
Possible Responses: Yes/No
Correct Response: No. Starting a laptop is a bit different from starting a desktop computer with separate components. With a laptop: we press the power button on the laptop itself. There is no need for a separate main power button, UPS switch or CPU switch, as laptops are self-contained units.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that to start a computer, we need to follow these steps: Switch on the main power button > Press the ON button on the UPS > Press the ON button on the CPU > Press the ON button on the monitor > Wait for the computer to start. Once your computer is ‘Awake’, you can use it.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● shut down a computer.
Ask students whether they can turn off a computer directly by pressing the power button, just like a TV.
Discuss the various steps to shut down a computer.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students whether they can turn off a computer directly by pressing the power button, just like a TV.
● Now, build the concept by discussing the steps to shut down a computer.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Shut down a computer. Tell the students about the various steps involved in shutting down a computer, as given on page 9.
● When should we shut down a computer?
Correct Response: We should shut down a computer when it is not in use.

● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ‘What are the electronic devices that can be shut down?’.
Possible Responses: televisions, lamps, toys, mobile phones, etc. Sum Up 3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising the following steps to turn off a computer: First, click on the Start button. Then, find the Power icon at the bottom left-hand side of the menu that pops up. Click on Shut down.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
C. Who Am I?: Question 5
In Avora, a magical land, it’s the first day of school. Mel, a smart robot, and Conji, a young wizard, become friends as Elder Wizard and Elder Robot teach that magic and technology go hand-in-hand. Mel introduces Conji to computers in the lab, explaining parts like the mouse and keyboard. Conji shows magical spells to Mel to control lights. They learn that both magic and technology require careful use. Trouble begins when Lord Ero, an evil wizard, steals all the computer mouses to make Avora dull and colourless. Mel, Conji and their friend, Eva hide a computer in the Memory Palace, safe from Lord Ero’s spells. When Elder Wizard falls ill, Mel and Conji make a get-well-soon card using Paint. However, Lord Ero uses Dark Magic to drain Avora’s colours. The Trio and the Elders combine their knowledge of magic and technology, using Paint to restore the colours. Ms Idea suggests linking the computer to Avora, enabling actions on the computer to affect the real world. Mel colours Avora on the computer while Conji and Eva support with spells, successfully bringing back the colours. The Elders praise their teamwork. As they celebrate, Lord Ero reappears, casting a destructive spell. Eva blocks it, and they realise they need AI to strengthen their powers. Mel explains AI and shows its benefits, helping them weaken Lord Ero. With his defeat, the peace returns to Avora.
● After understanding computers, Mel and Conji enter the magical room.
● Conji teaches some magic spells to Mel. Meanwhile, Elder Wizard appear in the room using magic.
● Mel is surprised to see this trick and asks, “How do you remember all the spells?”.
● Conji tells her that they look for the spells in the magic books, which are stored in the Wizard Library.
● Mel relates this to how they use storage devices, but Conji is unaware of storage devices and asks Mel about them.
● Mel tells him that to understand storage devices, he should first know the different parts of a computer.
● Elder Wizard asks Mel to tell Conji about the parts of a computer.
This chapter is divided into the following classroom sessions
1. Input Devices
2. Output Devices
3. Storage Devices
4. Input, Process, and Output Cycle

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define the different input devices.
● identify different input devices.
● explain the uses of different input devices.
Keywords
● Device: A device is a tool that helps us do a specific task.
● Input devices: Input devices help us tell a computer what to do. Input devices provide ways to ‘talk’ to the computer.
Ask the students what a device is.
Ask the students if they have observed different devices of the computer. Discuss what input devices are and explain different input devices, such as the keyboard, mouse, and microphone. Tell them the uses of each device. Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students what a device is.
● Ask the students if they have observed different devices of the computer.
● Now, build the concept by discussing what input devices are.
Explain the following concepts:
Define the different input devices. Tell the students that input devices help us tell a computer what to do, as given on page 20.
Identify different input devices.
Explain the uses of different input devices.
Tell them about different input devices, such as a keyboard, mouse, and microphone, as given on pages 20 and 21.
Explain to them the uses of the keyboard, mouse, and microphone as given on pages 20 and 21.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 2A section and encourage the students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 1. T 2. T 3. T 4. T 5. F
● What are the uses of a mouse?
Correct Responses: Selecting items, clicking on items to open them, etc.
● Which device is used to record your voice?
Possible Responses: Keyboard/Mouse/Microphone
Correct Response: Microphone
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic “Can you name a few devices that you have seen in the classroom?”.
Possible Responses: Computer, laptop, projector, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising that there are three types of devices in a computer: the input devices, the output devices, and the storage devices. The input devices, such as a keyboard, a mouse, or a microphone, enable us to communicate with a computer. The keyboard allows us to type, the mouse allows us to point and click, and the microphone enables us to use our voice to tell the computer what to do.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2 and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5
E. Answer the Following: Question 1
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define output devices.
● identify different output devices.
● explain the uses of different output devices.
Keyword
● Output devices: Output devices show the results of what we want from the computer.
Ask the students to think about how the computer shows the results of commands given by the input devices.
Discuss what output devices are and explain different output devices, such as the monitor, printer, speakers, and headphones. Tell them the uses of each device.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Action Plan
Ask the students to think about how the computer shows the results of commands given by the input devices.
Now, build the concept by discussing what output devices are.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Define output devices. Tell the students that output devices show the results of what we want from the computer, as given on page 22.
Identify different output devices.
Tell them about different output devices, such as monitors, printers, speakers and headphones, as given on pages 22 and 23.
Explain the uses of different output devices.
Explain to them the uses of monitor, printer, speakers, and headphones, as given on pages 22 and 23.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 2B section and encourage the students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 1. Monitor 2. Speaker 3. Keyboard 4. Mouse (From top to bottom)
● Name the device that shows you the result of your input.
Possible Responses: Monitor/Printer/Keyboard/Mouse
Correct Response: Monitor
● Which device is used when more than one person wants to hear the sound and music?
Possible Responses: Microphone/Headphones/Speaker
Correct Response: Speaker
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ‘Difference between Input and Output Devices’. Correct Response: Input devices help us to tell a computer what to do. Whereas output devices show the results of what we want from the computer.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that computers show us things with output devices. The monitor helps us see text, videos, images, and what we are doing on our computer. A printer is used to print pictures and text on paper. Speakers are used when more than one person wants to hear the sounds and music, while headphones are just for one person.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 3
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 3, and 5
D. Answer the Following: Questions 2 and 4
E. Apply Your Learning: Question 3

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define storage devices.
● identify different storage devices.
● explain the uses of different storage devices.
● Storage devices: The devices used to store information on the computer are known as storage devices.
Ask the students how they store their clothes and toys. Discuss what storage devices are and explain to the students the different storage devices, such as the hard disk, CD/DVD, and pen drive. Tell them the uses of each device.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Ask the students how they store their clothes and toys.
● Now, build the concept by discussing how, similarly, we can store our school projects, songs, and games on computers.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Define storage devices. Tell the students that a computer is used to store information on the computer, like our favourite songs, school projects, films, and games. Then introduce them to storage devices, as given on page 23.
Identify different storage devices.
Explain the uses of different storage devices.
Discuss different storage devices, such as the hard disk, CD/DVD, and pen drives, as given on pages 23 and 24.
Explain to them the uses of hard disk, CD/DVD, and pen drives, as given on pages 23 and 24.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● Name the devices that are round in shape.
Possible Responses: Monitor/Printer/Keyboard/Mouse/CD/DVD
Correct Responses: CD and DVD
● Which storage device is also known as a flash drive?
Possible Responses: Microphone/Speaker/Pen drive/Hard disk/CD
Correct Response: Pen drive
● Which device looks like a box?
Correct Response: Hard disk
● What is the full form of a CD?
Correct Response: Compact Disc
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ‘How is a hard disk different from a pen drive?’.
Possible Responses: A hard disk is larger and is not as portable as a pen drive whereas pen drives are small and can easily fit in a pocket.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that on a computer, we can save things like our favourite songs, school projects, films, and games. This is called data. This data is kept safe on storage devices. A hard disk is like a big box inside the computer that keeps everything safe. CDs and DVDs are round discs that also store things. Pen drives store lots of files and can be carried around easily.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2 and 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2 and 4
E. Answer the Following: Question 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain the IPO cycle.
Ask the students if they have ever grown plants, then discuss how a seed grows into a healthy plant. Discuss the IPO cycle with the students. Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students if they have ever grown plants, then discuss how a seed grows into a healthy plant.
● Now, build the concept by discussing how, similarly, a computer works by telling them about the IPO cycle.
Explain the following concepts:
Explanation
Explain the IPO cycle. Tell the students that a computer works in three phases—input, process, and output, often referred to as the IPO cycle. Explain to them using relevant examples, as given on pages 25 and 26.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 2C section and encourage the students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic “Can you think of another example for the IPO cycle” given in the Discuss section on page 27.
Possible Responses:
Input—Water, Ice Tray, and Refrigerator Process—Freezing of Water Output—Ice Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that computers function through an (IPO) cycle—Input, Process, and Output. The input is what we provide to the computer, such as information or commands. The process is what the computer does with this input, like performing calculations. The output is what the computer gives us back, like displaying information on the screen, printing a document, etc.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 1
E. Answer the Following: Question 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 4 and 5

In Avora, a magical land, it’s the first day of school. Mel, a smart robot, and Conji, a young wizard, become friends as Elder Wizard and Elder Robot teach that magic and technology go hand-in-hand. Mel introduces Conji to computers in the lab, explaining parts like the mouse and keyboard. Conji shows magical spells to Mel to control lights. They learn that both magic and technology require careful use. Trouble begins when Lord Ero, an evil wizard, steals all the computer mouses to make Avora dull and colourless. Mel, Conji and their friend, Eva hide a computer in the Memory Palace, safe from Lord Ero’s spells. When Elder Wizard falls ill, Mel and Conji make a get-well-soon card using Paint. However, Lord Ero uses Dark Magic to drain Avora’s colours. The Trio and the Elders combine their knowledge of magic and technology, using Paint to restore the colours. Ms Idea suggests linking the computer to Avora, enabling actions on the computer to affect the real world. Mel colours Avora on the computer while Conji and Eva support with spells, successfully bringing back the colours. The Elders praise their teamwork. As they celebrate, Lord Ero reappears, casting a destructive spell. Eva blocks it, and they realise they need AI to strengthen their powers. Mel explains AI and shows its benefits, helping them weaken Lord Ero. With his defeat, the peace returns to Avora.
● Conji and Mel walk towards the Computer Lab to see the parts of a computer.
● Curious Mel asks Conji to teach her magic. So, she asks Conji to increase the size of the computer keys.
● Conji tells her to use the “JUMBO RUMBO!” spell.
● Accidentally, due to overexcitement, Mel uses the spell incorrectly. She spells it “JUMBO MUMBO!”.
● After her spell, all the keys of the keyboard go missing, and Mel gets scared.
● But, Conji knows reverse spells too. So, he uses “JUMBO MUMBO REVERSIO!” to get back all the keys.
● Surprisingly, all the keys appears, but by looking at them, Conji becomes confused.
● He asked Mel to explain the keys on the keyboard.
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what keys are.
Keyword
● Keyboard: It is an input device. It has lots of buttons, called keys
Ask the students to look at the picture of the keyboard and call out the names one by one, written inside each square.
Describe the keys. Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students to look at the picture of the keyboard and call out the names one by one, written inside each square.
● Now, build the concept that the keyboard is an input device. It has lots of buttons, called keys, on it.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Describe what keys are. Discuss with the students that the keyboard is an input device. It has lots of buttons, called keys, on it. It helps us type letters, numbers, and symbols on the computer, as given on page 35.

● Ask the additional questions to the students to check their understanding.
1. Can you see numbers on these keys?
Possible responses: Yes/No
2. Can these keys have the alphabets of your name?
Possible response: Yes
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ‘What is a keyboard?’.
Correct Response: A keyboard help us to type letters, numbers, and symbols on a computer using keys.
● Conclude the session by summarising that the keyboard is an input device. It has lots of buttons, called keys, on it. It helps us type letters, numbers, and symbols on the computer.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 1
Learning Outcomes
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe and show alphabet keys on the keyboard.
● describe and show number keys on the keyboard.
Keywords
● Alphabet keys: The alphabet keys are the keys with letters on them.
● Number keys: The number keys are the keys with numbers on them.
Ask the students what are alphabets?
Explain the number and the alphabet keys to the students. Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students what are alphabets?
● Now, build the concept by telling them what alphabet keys are.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Describe and show alphabet keys on the keyboard.
Describe and show number keys on the keyboard.
Explanation
Tell the students that the alphabet keys are the keys with letters on them. There are 26 alphabet keys, one for each letter in the English language, as given on page 35.
Explain to them that the number keys are the keys with numbers on them. There are 10 number keys, from 0 to 9, as given on page 36.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 3A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 1.






● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ‘How many alphabet keys and number keys do we have?’.
Possible Responses: 25, 30, 45
Correct Response: We have 26 alphabet keys and 10 number keys on the keyboard.
● Conclude the session by summarising that the alphabet keys are the keys with letters on them. There are 26 alphabet keys, one for each letter in the English language. The number keys are the keys with numbers on them. There are 10 number keys, from 0 to 9.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2 D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2, 3, and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1 F. Apply Your Learning: Question 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe special keys.
● discuss about the Backspace key.
● explain the Delete key.
● discuss the Punctuation keys.
● explain the Spacebar key.
● describe the Caps Lock key.
● discuss the Enter key.
● explain Arrow keys.
Keywords
● Backspace key: The backspace key helps us remove the text or objects before the cursor.
● Delete key: The delete key also helps us to remove text or objects but when they are after the cursor.
● Punctuation keys: Punctuation keys are used to add punctuation symbols.
● Spacebar: The spacebar is the largest key on the keyboard that adds space between two words.
● Caps Lock key: Caps Lock key is used to type letters in capital.
● Enter key: The Enter key is used to move the cursor to a new line while typing.
● Arrow keys: The arrow keys are used to move the cursor in the direction of the arrow.
Ask the students to check the keyboard image and calculate how many keys do we have in total.
Describe Special keys. Explain the types of special keys.
Action Plan
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students to check the keyboard image and calculate how many keys do we have in total.
● Now, tell them that the keyboard has a total of 104 keys.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe special keys. Tell the students that special keys are used to do particular tasks, as given on page 37.
Discuss about the Backspace key.
Explain to them that the backspace key helps us remove the texts or objects before the cursor, as given on page 37.
Explain the Delete key. Discuss with them that the delete key helps us to remove text or objects, but only when they are after the cursor, as given on page 37.
Discuss the Punctuation keys.
Explain the Spacebar key.
Describe the Caps Lock key.
Elaborate on punctuation keys as they are used to add punctuation symbols, as given on page 38.
Describe how the spacebar key adds a space between two words, as given on page 38.
Explain to them that the caps lock key is used to type letters in capital, as given on page 38.
Discuss the Enter key. Tell them that the enter key is used to move the cursor to a new line while typing, as given on page 39.
Explain Arrow keys. Elaborate on arrow keys and explain that they are used to move the cursor in the direction of the arrow, as given on page 39.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 3B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. a. Caps Lock b. Spacebar

2. b. Shift
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ‘How many special keys do we have?’.
Possible Responses: 7, 8, 9
Correct Response: We have 7 special keys on the keyboard.
● Conclude the session by summarising that we use 7 special keys on the keyboard, such as the Backspace key, Delete key, Punctuation keys, Spacebar, Caps Lock key, and Enter key.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3, 4, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2 and 3
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 5

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe the combination keys.
● discuss symbol keys.
Keywords
● Combination keys: The combination keys are the keys when two or more keys are pressed together.
● Symbol keys: Symbol keys are the keys where symbols are written above the numbers.
Ask the students how they can type the symbols.
Describe the combination keys. Explain the symbol keys.
Group discussion
Action Plan
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
Warm Up
● Ask the students how they can type symbols.
● Now, build the concept that symbol keys are used to type symbols.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Describe the combination keys. Tell the students that the combination keys are the keys when two or more keys are pressed together, as given on page 39.
Discuss symbol keys.
Explain to the students that the symbol keys are the keys where symbols are written above the numbers, as given on pages 39 and 40.
● Read aloud the question provided in the Do It Yourself 3B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 3.
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ’How many symbol keys do we have?’. Correct Response: 9 Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the combination keys are the keys when two or more keys are pressed together. The symbol keys are the keys where symbols are written above the numbers.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 4 and 5
E. Answer the Following: Question 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2 and 3

In Avora, a magical land, it’s the first day of school. Mel, a smart robot, and Conji, a young wizard, become friends as Elder Wizard and Elder Robot teach that magic and technology go hand-in-hand. Mel introduces Conji to computers in the lab, explaining parts like the mouse and keyboard. Conji shows magical spells to Mel to control lights. They learn that both magic and technology require careful use. Trouble begins when Lord Ero, an evil wizard, steals all the computer mouses to make Avora dull and colourless. Mel, Conji and their friend, Eva hide a computer in the Memory Palace, safe from Lord Ero’s spells. When Elder Wizard falls ill, Mel and Conji make a get-well-soon card using Paint. However, Lord Ero uses Dark Magic to drain Avora’s colours. The Trio and the Elders combine their knowledge of magic and technology, using Paint to restore the colours. Ms Idea suggests linking the computer to Avora, enabling actions on the computer to affect the real world. Mel colours Avora on the computer while Conji and Eva support with spells, successfully bringing back the colours. The Elders praise their teamwork. As they celebrate, Lord Ero reappears, casting a destructive spell. Eva blocks it, and they realise they need AI to strengthen their powers. Mel explains AI and shows its benefits, helping them weaken Lord Ero. With his defeat, the peace returns to Avora.
● Mel, Conji, and Eva discover Lord Ero’s plan to steal the computer mouse in the Computer Lab.
● They decide to seek help from Elder Wizard to prevent Lord Ero from causing any trouble in Avora.
● The group aims to save all the computer devices to protect Avora’s future from Lord Ero’s mischief.
● Conji suggests using magic, while Mel considers locking the mouse in the Computer Lab and giving the keys to Elder Robot.
● Concerned about Lord Ero using magic to open the lab, they decide to ask Elder Wizard for a special spell to hide the mouse.
● The trio heads to Elder Wizard, trusting that Lord Ero cannot alter the spells used by Elder Wizard.
● Conji and Eva think about why a mouse is important to Lord Ero.
● Elder Wizard tells Mel to explain about the mouse to Conji and Eva.

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe a mouse and its parts.
Keyword
● Pointer: When you move the mouse, an arrow also moves on the computer screen. This arrow is called the pointer.
Warm
Ask the students to name the main parts of a computer. Tell the students about the mouse and its parts. Also, tell them about the mouse pointer.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins 15 mins 7 mins 3 mins
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students to name the main parts of a computer. Then, build the concept by describing a mouse.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
15 mins
Explanation
Describe a mouse and its parts. Explain to the students that a mouse is used to operate many things on the computer and it has three parts—a left button, a right button, and a scroll wheel. Also, tell them about the mouse pointer, as given on page 50.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 4A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.

● Ask the students to answer the question “Is the mouse an input device?“ asked in the Think and Tell section given on page 50.
Possible Responses: Yes, the mouse is an input device.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the mouse is used to perform any action on the computer screen. When you move the mouse, an arrow also moves on the computer screen. This arrow is called the pointer. A mouse has three parts: a left button, a right button, and a scroll wheel.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2 and 3
E. Answer the Following: Question 1 Correct Response: 1.
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Demonstrate to the students how to play the game for which the link is provided on the panel.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Tiny Tech Game.
● Show the Learning slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
● perform various actions using a mouse by playing fun-based interactive games. 15 mins Engage
● Demonstrate to the students how to play the game for which the link is provided on the panel.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
● Conclude the chapter by summarising that we have to play the game to practice the mouse buttons.

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● hold a mouse.
Can you think of the things in our daily lives where holding them in the right way is important?
Tell the students how to hold a mouse properly.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Can you think of things in our daily lives where holding them in the right way is important?
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Hold a mouse. Tell the students that to hold a mouse properly, you need to put your hand on top of it as given on page 51.
● Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding: Name the parts of the below figure:
Correct Responses:
Index Finger
Left Button
Thumb
Build
Right Button
Middle Finger
Other Two Fingers
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic “Does the mouse work when it is in the air? Why or why not?” provided in the Discuss section as mentioned on page 51.
Possible Responses: No, a computer mouse doesn’t work in the air because it needs a surface to move on. The mouse has a special sensor underneath that senses movement when it’s on a flat surface like a desk or a mouse pad.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that to hold a mouse properly, place your index finger on the left button and your middle finger on the right button. Your thumb and the other two fingers should rest on the sides of the mouse. This grip ensures comfortable and effective control of the mouse.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1
Additional Questions
Q1. Where should your index finger be on a mouse while holding it?
Q2. Where should your middle finger be on a mouse while holding it?

Learning Outcomes
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe a mouse pointer.
● explain different actions using a mouse.
Keyword
● Mouse pointer: The mouse pointer is the little arrow on the monitor that moves when we move the mouse.
What do you notice on the computer screen when you move the mouse around?
Describe to the students about the mouse pointer. Also, explain different actions using a mouse. Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● What do you notice on the computer screen when you move the mouse around?
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Describe a mouse pointer. Tell the students that the mouse pointer is the little arrow on the monitor that moves when we move the mouse as given on page 52.
Explain different actions using a mouse.
Explain to the students that the mouse can perform three functions which include clicking, scrolling and drag & drop, as given on pages 52 and 53.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 4B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. Do It Yourself 4B
Match the following. 1
Left-click
Right-click
Drag
Keep holding the left button to do this.
Place an object at a new place on the monitor.
Open a list of options.
Drop Select an item.
2. a. F b. T c. F
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic ‘How do you make the mouse move on the computer screen?’
Possible Response: I slide it on the table! Or I move it with my hand!
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the mouse pointer is the little arrow on the monitor that moves when we move the mouse. To use a mouse effectively, left-click to select items and right-click for a list of choices. Scrolling involves moving the scroll wheel up and down to navigate pages on the monitor. Double-clicking the left button quickly opens the selected item. Drag and drop files by selecting them with a left-click, holding the left mouse button, moving the mouse, and releasing the button to place the file where the pointer is.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 4 and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 2, 3, 4 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2, 3, 4 and 5

In Avora, a magical land, it’s the first day of school. Mel, a smart robot, and Conji, a young wizard, become friends as Elder Wizard and Elder Robot teach that magic and technology go hand-in-hand. Mel introduces Conji to computers in the lab, explaining parts like the mouse and keyboard, while Conji shows Mel magical spells to control lights. They learn that both magic and technology require careful use.
Trouble begins when Lord Ero, an evil wizard, steals all the computer mouses to make Avora dull and colourless. Mel, Conji, and their friend Eva hide a computer in the Memory Palace, safe from Lord Ero’s spells. When Elder Wizard falls ill, Mel and Conji make a get-well-soon card using Paint. However, Lord Ero uses dark magic to drain Avora’s colours. The trio and Elders combine their knowledge of magic and technology, using Paint to restore the colours. Ms. Idea suggests linking the computer to Avora, enabling actions on the computer to affect the real world. Mel colours Avora on the computer while Conji and Eva support with spells, successfully bringing back the colours. The Elders praise their teamwork.
As they celebrate, Lord Ero reappears, casting a destructive spell. Eva blocks it, and they realise they need AI to strengthen their powers. Mel explains AI and demonstrates its benefits, helping them weaken Lord Ero. With his defeat, the peace returns to Avora.
● Mel and Conji go to their classroom only to find that Elder Wizard has not come to teach the students.
● Mel and Conji get worried as the Elder Wizard is always present to teach his class. They start suspecting that Lord Ero might have done something wrong.
● They then decide to meet Elder Robot, who informs them that Elder Wizard has fallen sick, but he will be okay soon.
● Mel thinks of making him a get-well-soon card.
● Conji wants to get the crayons from the art class. But Mel suggests using Paint to make him the card as this will save them from going all the way to the art class.
● Conji does not know what Paint is.
● Mel then explains to Conji that Paint helps draw in a computer.
This chapter is divided into the following classroom and lab sessions
1. Introduction to MS Paint and Shapes Tool 1
2. Introduction to MS Paint and Shapes Tool 2
3. Using Shapes Tool 2
4. Using Shapes Tool 3 5. Saving and Opening a Drawing 1
6. Saving and Opening a Drawing 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what MS Paint is.
● start MS Paint.
Keywords
● explain different parts of MS Paint.
● draw a line and a curve using the shapes tool.
● MS Paint: MS Paint lets us draw and colour on the computer.
● Shape: A shape is a figure that is made of lines or curves.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Ask the students to draw their favourite fruit on a paper using a pencil.
Discuss what MS Paint is. Explain to them how they can start using Paint. Also, get them familiar with different parts of a Paint window. Also, tell them how to draw a line and curve using the Shapes tool. Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Ask the students to draw their favourite fruit on a paper using a pencil.
● Now, build the concept by introducing them to MS Paint.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
15 mins
Explanation
Describe what MS Paint is. Ask the students to match the shapes with their correct shadows. Tell the students that we can draw these shapes on the computer using MS Paint, as given on page 63.
Start MS Paint. Explain the steps to start MS Paint to the students, as given on page 63.
Explain different parts of MS Paint.
Tell the students about different parts of the MS Paint window, such as the title bar, drawing area, ribbon, etc., as given on page 64.

Draw a line and a curve using the Shapes tool.
Tell the students that the Shapes tool is used to draw many shapes easily. Also tell them the steps to draw a line and a curve, as given on pages 65 to 68.
● Read aloud the question provided in the Do It Yourself 5A section and encourage the students to solve the question. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Response:

● Name the space where you draw in MS Paint.
Correct Response: Drawing area
● Which bar shows the name of your MS Paint file?
Correct Response: Title bar
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic, ‘My Favourite Drawing in MS Paint’.
Possible Responses: hut, robot, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising that MS Paint lets us draw and colour on the computer. Tell the steps to start MS Paint. Tell them about different parts of MS Paint such as the title bar, tabs, ribbon, drawing area, etc. Also, instruct them on how to draw a line and a curve.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 3 and 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 and 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what MS Paint is.
● start MS Paint.
● explain different parts of MS Paint.
● draw a line and a curve using the Shapes tool.
Keywords
● MS Paint: MS Paint lets us draw and colour on the computer.
● Shape: A shape is a figure that is made of lines or curves.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Discuss what MS Paint is. Demonstrate to them how they can start using Paint. Also, get them familiar with different parts of the Paint window. Also, tell them how to draw a line and curve using the Shapes tool.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page.
Action Plan
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Introduction to MS Paint and Shapes Tool 2.
● Show the Learning slides or the video and discuss the concepts shown on the panel.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe what MS Paint is. Tell the students that we can draw the shapes on the computer using MS Paint, as given on page 63.
Start MS Paint.
Explain different parts of MS Paint.
Draw a line and a curve using the Shapes tool.
Demonstrate the steps to start MS Paint to the students, as given on page 63.
Tell the students about different parts of the MS Paint window, such as the title bar, drawing area, ribbon, etc., as given on page 64.
Tell the students that the Shapes tool is used to draw many shapes easily. Demonstrate to them the steps to draw a line and a curve, as given on pages 65 to 68.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students' understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
7 mins
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students. Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that MS Paint lets us draw and colour on the computer. Tell the steps to start MS Paint. Tell them about different parts of MS Paint, such as the title bar, tabs, ribbon, drawing area, etc. Also, instruct them on how to draw a line and a curve.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● draw a rectangle.
● draw a circle.
● draw a polygon.
● draw a hut.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Ask the students to give examples of some objects that are rectangular in shape. Discuss that, similar to lines and curves, we can also draw a rectangle, a circle, and a polygon using the Shapes tool. Also tell them how to draw a hut in Paint.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Action Plan
Warm Up
● Ask the students to give examples of some objects that are rectangular.
● Now, build the concept by discussing the rectangle, circle, and polygon shapes.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
5 mins
15 mins
Explanation
Draw a rectangle. Tell the students various steps to draw a rectangle, as given on pages 68 and 69.
Draw a circle. Tell the students various steps to draw a circle, as given on pages 69 and 70.
Draw a polygon. Tell the students various steps to draw a polygon, as given on pages 70 and 71.
Draw a hut. Tell the students various steps to draw a hut, as given on pages 71 and 72.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 5B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: Do It Yourself 5B
Q2. 1. POLYGON 2. OVAL 3. CURVE 4. RECTANGLE 5. LINE
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students based on the topic, “What things can you draw using the shapes we learnt?” provided in the Discuss section, as given on page 71.
Possible Responses: house, tree, car, etc.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to draw a rectangle, circle, and polygon shapes. Revise the concept of a polygon: a polygon is a shape with many sides. A triangle is a polygon with three sides. A square is a polygon with four sides.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 2
C. Who Am I?: Questions 3 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 1
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● draw a rectangle.
● draw a circle.
● draw a polygon.
● draw a hut.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Discuss that, similar to lines and curves, we can also draw a rectangle, a circle, and a polygon using the Shapes tool. Also, demonstrate to them the steps to draw a hut in Paint.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page.
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Using Shapes Tool 3
● Show the Learning slides or the video and discuss the concepts shown on the panel.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
15 mins
Explanation
Draw a rectangle. Demonstrate to the students various steps to draw a rectangle, as given on pages 68 and 69.
Draw a circle. Demonstrate to the students various steps to draw a circle, as given on pages 69 and 70.
Draw a polygon. Demonstrate to the students various steps to draw a polygon, as given on pages 70 and 71.
Draw a hut. Demonstrate to the students various steps to draw a hut, as given on pages 71 and 72.

● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
7 mins
Build
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students. Sum
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to draw a rectangle, circle, and polygon shapes. Revise the concept of a polygon: a polygon is a shape with many sides. A triangle is a polygon with three sides. A square is a polygon with four sides.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● save a drawing.
● open a drawing.
Tell the students the importance of saving something. Explain the concept of why we need to save our work and also explain that sometimes we need to open our saved file to make changes to it.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign
● Explain to the students that we need to save our work so that it can be seen again later.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Save a drawing. Tell the students the importance of saving a drawing, and then tell them the steps to save a drawing, as given on pages 72 and 73.
Open a drawing. Tell the students the various steps to open a saved drawing, as given on pages 73 and 74.
● Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
1. To save an MS Paint file, click on the tab and then select the option.
2. To open a saved file in MS Paint, click on the File tab, and then select the file, and finally, select the option.
Correct Responses: 1. File, Save as 2. Open

● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic, ‘By what name should we save our drawing?’.
Possible Responses: our name, favourite animal, superhero, etc.
Correct Response: We should give the file a name that reflects the content of the drawing.
● Conclude the session by summarising that it is important to save a drawing, revise the steps to save a drawing and open a drawing.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
C. Who Am I?: Question 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2 and 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● save a drawing.
● open a drawing.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Demonstrate to the students how to save and open a file. Attempt the activity on the Assignment page.
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Saving and Opening a Drawing 2.
● Show the Learning slides or the video and discuss the concepts shown on the panel.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
15 mins
Explanation
Save a drawing. Tell the students the importance of saving a drawing, and then demonstrate to them the steps to save a drawing, as given on pages 72 and 73.
Open a drawing. Demonstrate to the students the various steps to open a saved drawing, as given on pages 73 and 74.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.

● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students. Sum Up 3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that it is important to save a drawing, revise the steps to save a drawing and open a drawing.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
In Avora, a magical land, it’s the first day of school. Mel, a smart robot, and Conji, a young wizard, become friends as Elder Wizard and Elder Robot teach that magic and technology go hand-in-hand. Mel introduces Conji to computers in the lab, explaining parts like the mouse and keyboard. Conji shows magical spells to Mel to control lights. They learn that both magic and technology require careful use. Trouble begins when Lord Ero, an evil wizard, steals all the computer mouses to make Avora dull and colourless. Mel, Conji and their friend, Eva hide a computer in the Memory Palace, safe from Lord Ero’s spells. When Elder Wizard falls ill, Mel and Conji make a get-well-soon card using Paint. However, Lord Ero uses Dark Magic to drain Avora’s colours. The Trio and the Elders combine their knowledge of magic and technology, using Paint to restore the colours. Ms Idea suggests linking the computer to Avora, enabling actions on the computer to affect the real world. Mel colours Avora on the computer while Conji and Eva support with spells, successfully bringing back the colours. The Elders praise their teamwork. As they celebrate, Lord Ero reappears, casting a destructive spell. Eva blocks it, and they realise they need AI to strengthen their powers. Mel explains AI and shows its benefits, helping them weaken Lord Ero. With his defeat, the peace returns to Avora.
● Avora becomes colourless because of Lord Ero’s magic spell.
● Mel, Eva, and Conji are playing games when this happens.
● They go to the council room to ask the Elders for help.
● Ms Idea has a plan to use a computer to bring back colours.
● Elder Robot says computer actions can change things in Avora.
● Elder Wizard tells them Lord Ero’s spell won’t work inside the Memory Palace.
● They decide to use MS Paint, a computer program, to colour Avora.
● Eva wants to use crayons, but they chose MS Paint instead.
● Ms Idea will teach them how to use MS Paint for colouring.
This chapter is divided into the following classroom and lab sessions
1. Colouring a Drawing 1
2. Colouring a Drawing 2
3. More Tools in MS Paint 1
4. More Tools in MS Paint 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● use MS Paint to colour a drawing.
● use the Fill with color tool to fill colour in a drawing.
Keyword
● Fill with color: This tool is used to fill colour in a closed shape.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Ask the students to draw any shape on their notebooks and then colour the shape.
Explain the students to colour a drawing using Fill with color tool.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
Warm Up
● Ask the students to draw any shape on their notebooks and then colour inside the shape. Relate the concept that they can use fill with color tool to fill colours in a closed shape.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Use MS Paint to colour a drawing.
Use the Fill with color tool to fill colour in a drawing.
Explanation
Tell the students that we can add different colours in different shapes. as given on page 83.
Tell the students that filling shapes with colours helps children better understand and recognise different shapes. Explain the Fill with color tool and steps to fill colour inside a shape to students as given on page 84.
● Ask the following questions from students to check for understanding.
1. Which tool is used to fill colour in a shape?
Correct response: Fill with color tool
2. From where you can select the colors to fill colour in a shape?
Correct response: Colors group
7 mins
● Ask the students to answer to the question “What did you like the most about MS Paint, and why?” asked in the Think and Tell section on page 84.
Possible response: I like both drawing and coloring the most in MS Paint because it is fun and easy to make pictures using different tools and colors.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising the use of fill with color tool and the steps to do so.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 1
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 3
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 2
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● use MS Paint to colour a drawing.
● use the Fill with color tool to fill colour in a drawing.
Keyword
● Fill with color: This tool is used to fill colour in a closed shape.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Demonstrate to the students how to colour a drawing using Fill with color tool.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Colouring a Drawing 2
● Show the Learning slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Use MS Paint to colour a drawing.
Use the Fill with color tool to fill colour in a drawing.
Explanation
Explain to the students that we can add different colours in different shapes as given on page 83.
Tell the students that filling shapes with colours helps children better understand and recognise different shapes. Explain the Fill with color tool and steps to fill colour inside a shape to students as given on page 84.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
12 mins
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
● Conclude the session by summarising the use of fill with color tool and the steps to do so.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
3 mins

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● use Text, Eraser, Colour Picker, and Brushes tools in MS Paint.
Keywords
● Text tool: The Text tool lets you add letters and numbers to your drawings.
● Eraser tool: The Eraser tool is used to erase things you do not want in your drawing.
● Colour picker: The Colour Picker tool allows you to pick the colour of an object without going into the colour section.
● Brushes: Brushes help you to make different lines, shapes, and textures, just like real paint brushes.
Ask the students do they write the name of drawing when they draw something in their notebook?
Explain Text, Eraser, Colour Picker, and Brushes tools in MS Paint. Explain the steps to use the tools to make the drawings bright and beautiful.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Ask the students do they write the name of drawing when they draw something in their notebook?
● Now, build the concept of tools in MS Paint used for making the drawings interesting.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Use Text, Eraser, Colour Picker, and Brushes tools in MS Paint.
Tell the students that the Text tool lets you add letters and numbers to your drawings. Eraser tool is used to remove mistakes in our drawings. The Colour picker tool allows us to pick the colour of an object and the brushes are used to make different lines, shapes, and textures, just like real paint brushes. Explain the steps to use the Eraser tool, Colour picker, and Brushes to the students as given on pages 85 to 87.
● Read aloud the question provided in the Do It Yourself 6A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 1. F 2. T 3. T 4. F
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students based on the topic “What can you write using Text tool in Paint”?
Possible Response: We can write words, sentences, or numbers using the Text tool.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that in MS Paint, we can use the Text tool to put letters and numbers, use the Eraser tool to fix mistakes, use the Colour picker to pick the colour of an object without going into the colour section, and brushes to make different lines, shapes, and textures, just like real paint brushes.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2, 3, and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 3, 4, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 3, 4, and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 2, 3, and 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2, 3, and 4

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● use the Text tool, Eraser, the Colour Picker, and the Brushes tools in MS Paint.
Keywords
● Text tool: The Text tool lets you add letters and numbers to our drawings.
● Eraser tool: The Eraser tool is used to erase things you don’t want in your drawing.
● Colour picker: The Colour Picker tool allows you to pick the colour of an object without going into the colour section.
● Brushes: Brushes help you to make different lines, shapes, and textures, just like real paint brushes.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Discuss various tools in MS Paint. Demonstrate to the students the steps to use Text tool, Eraser tool, Colour picker tool, and Brushes.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on More Tools in MS Paint 2
● Show the Learning slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
10 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Use the Text, Eraser, the Colour Picker, and the Brushes tools in MS Paint.
Explanation
Demonstrate to the students the steps to use Text, Eraser, Colour picker and Brushes as given on pages 85 to 87.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
12 mins
Build
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that in MS Paint, you can use Text tool to put letters and numbers, use Eraser tool to fix mistakes, use Colour picker to pick the colour of an object without going into the colour section, and brushes to make different lines, shapes, and textures, just like real paint brushes.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.

In Avora, a magical land, it’s the first day of school. Mel, a smart robot, and Conji, a young wizard, become friends as Elder Wizard and Elder Robot teach that magic and technology go hand-in-hand. Mel introduces Conji to computers in the lab, explaining parts like the mouse and keyboard. Conji shows magical spells to Mel to control lights. They learn that both magic and technology require careful use. Trouble begins when Lord Ero, an evil wizard, steals all the computer mouses to make Avora dull and colourless. Mel, Conji and their friend, Eva hide a computer in the Memory Palace, safe from Lord Ero’s spells. When Elder Wizard falls ill, Mel and Conji make a get-well-soon card using Paint. However, Lord Ero uses Dark Magic to drain Avora’s colours. The Trio and the Elders combine their knowledge of magic and technology, using Paint to restore the colours. Ms Idea suggests linking the computer to Avora, enabling actions on the computer to affect the real world. Mel colours Avora on the computer while Conji and Eva support with spells, successfully bringing back the colours. The Elders praise their teamwork. As they celebrate, Lord Ero reappears, casting a destructive spell. Eva blocks it, and they realise they need AI to strengthen their powers. Mel explains AI and shows its benefits, helping them weaken Lord Ero. With his defeat, the peace returns to Avora.
● Colours return to Avora, restoring the kingdom’s beauty and harmony.
● The trio relaxes in the garden, enjoying the blend of magic and technology.
● They express joy, saying magic and technology are beautiful together.
● Suddenly, Lord Ero reappears, casting a powerful and destructive spell.
● Eva blocks the spell, saving her friends from harm.
● The Mel realizes they need AI to strengthen their magical powers.
● Mel explains AI and demonstrates its benefits to the Eva and Conji.
● Using AI-powered enhancements, they weaken Lord Ero’s strength.
● After a fierce battle, Lord Ero is finally defeated.
● Peace return to Avora, and the trio celebrates their victory.
This chapter is divided into the following classroom and lab sessions
1. Robots and Their Types
2. AI Game
3. High-tech Robots in Our World
4. Fun with AI: Using Chatbot
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe robots.
● explain about different types of robots.
Keywords
● Robot: A robot is a machine that can do things on its own.
● AI: AI gives machines, or robots, the ability to learn and do things on their own, just like humans do.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Have you ever seen a robot in a movie or a cartoon? Tell the students about the robots and explain about different types of robots.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Action Plan
Warm Up
● Have you ever seen a robot in a movie or a cartoon?
● Now, build the concept by explaining what robots are.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Describe robots. Tell the students that a robot is a machine that can do things on its own. Also, describe to them that robots can do all the smart things using AI, which stands for artificial intelligence as given on page 96.
Explain about different types of robots.
Describe to the students that there are different types of robots such as humanoid robots, animal robots, industrial robots, and service robots, as given on pages 96 and 97.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 7A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their books.
Correct response:
1. ARTIFICIAL
2. INTELLIGENCE
3. ROBOT
4. MACHINE
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic “Have you seen any robot. If yes, which type of robot and where?
Possible Responses: Yes, I have seen a service robot, in a restaurant.
● Conclude the session by summarising that a robot is a machine that can do things on its own and they can do all these smart things using AI, which is Artificial Intelligence. With AI they are able to understand and think. Also, tell them about various types of robots such as humanoid robots, animal robots, industrial robots, and service robots.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 3, and 5
C. Who Am I? Questions 4 and 5
D. Write T for True or F for False: Questions 3, 4, and 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1, 2, and 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● play the AI game.
Let the students revise the chapter. Demonstrate to the students how to play the game for which the link is provided on the panel.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page Conclude the concepts
Warm Up
● Instruct the students to go to the Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on AI Game.
5 mins
● Show the Learning slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
10 mins
Engage
● Demonstrate to the students how to play the game for which the link is provided on the panel.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
12 mins
● Instruct the students to click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity. Then, click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
● Instruct the students to click on the Confirm button to submit their work when they are done with the activity. Sum
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that you have to follow the instruction given on the panel to play the AI game.

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe different high-tech robots in our world.
What do you think? Who invented the robots?
Tell the students about various high-tech robots in the world.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
Action Plan
Warm Up
● What do you think? Who invented the robots?
● Now, build the concept by explaining about different high-tech robots.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Describe different high-tech robots in our world.
Explanation
Tell the students about different high-tech robots, which includes Sparko, Roomba, Sophia, as given on pages 97 and 98.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
1. Name 3 different types of high-tech robots.
Correct Responses: Sophia, Sparko and Roomba
2. What type of robot ‘Roomba’ is?
Correct Response: Robotic Vacuum Cleaner
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic ’Different new age robots’.
Possible Responses: New-age robots are smart machines that work on their own, like robot vacuums, delivery drones, or farming robots that pick fruits.
● Conclude the session by summarising that some of the different high-tech robots in our world are Sparko which was the first robotic dog, Romba, a robotic vacuum cleaner and Sophia, the first human like robot.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3,4, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 4
C. Who Am I? Questions 1, 2, and 3
D. Write T for True or F for False: Questions 1 and 2
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 3 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● play the fun with AI game.
Let the students revise the chapter. Demonstrate to the students how to play the game for which the link is provided on the panel. Attempt the activity on the Assignment page. Conclude the concepts
● Instruct the students to go to the Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Fun with AI: Using Chatbot
● Demonstrate to the students how to play the game for which the link is provided on the panel.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
● Instruct the students to click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity. Then, click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
● Instruct the students to click on the Confirm button to submit their work when they are done with the activity.
● Conclude the session by summarising that you have to ask your question to Chai, and it will answer you. Chai will not only write your answer in the chat box, but it will also read it out for you.
This chapter is divided into the following lab sessions
1. Block-based Coding and Commands 3. What is an Algorithm?
2. What is a Sequence? 4. Tour to Puzzle Code Studio
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what coding is.
● explain block-based coding.
● tell about Code.org.
● describe commands.
Keywords
● Coding: Coding is a language that is used to talk to a computer.
● Block-based coding: The coding language that uses blocks to give instructions is called blockbased coding.
● Command: A command is an instruction that tells a computer what to do.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Explain to them what coding is; tell them about block-based coding; introduce them to Code.org; and tell them what commands are.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page.
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework

5 mins
Warm Up
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Block-based Coding and Commands.
● Show the Learning slides or the video and discuss the concepts shown on the panel.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Describe what coding is. Introduce the students to the coding language, as given on page 1.
Explain block-based coding.
15 mins
Explain the concept of block-based coding to the students, as given on page 1.
Tell about Code.org. Tell the students that Code.org is a fun coding platform where you can learn to use colourful blocks, as given on page 2.
Describe commands. Describe the concept of commands to the students, as given on page 2.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
7 mins
Build
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that a computer needs us to talk to it in a language called coding language. Block-based coding uses colourful blocks to give instructions. Code.org is a fun coding platform where we’ll use these blocks to make characters move, play games, and tell stories. Commands are like instructions for the computer. We’ll use code blocks as commands to make the computer do different things.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 1
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 1

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what a task is.
● follow a sequence.
Keywords
● Task: A task is a piece of work that needs to be done.
● Sequence: A sequence is when we do things step by step in an order.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Discuss the concept of sequence by giving a real-life example. Attempt the activity on the Assignment page. Conclude the concepts Assign homework
Warm Up
Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on What is a Sequence? Show the Learning slides or the video and discuss the concepts shown on the panel. 15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Describe what a task is. Give any task to the students to accomplish, and then describe to them what a task is, as given on pages 2 and 3.
Follow a sequence. Ask the students how they follow the steps to get ready for school. Then tell them that we follow a particular sequence to do a task. Tell them about fixed and flexible sequences, as given on page 3.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1A section and Do It Yourself 1B section to encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: Do It Yourself 1A



● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
7 mins
Build
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that every day, we do lots of tasks, like brushing our teeth or playing with toys. A task is a piece of work that needs to be done. When we do things step-by-step in order, it’s called a sequence. Sometimes, there’s only one way to do a task; it’s a fixed sequence. Other times, there can be many ways to do a task, and that’s called a flexible sequence.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2, 3, and 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 2 and 3

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe an algorithm.
Keyword
● Algorithm: The set of steps, in an order, to solve a problem is called an algorithm.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Discuss the concept of algorithm by giving a real-life example.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page.
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on What is an Algorithm?
● Show the Learning slides or the video and discuss the concepts shown on the panel.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Describe an algorithm. Explain to the students that the set of steps in order to solve a problem is called an algorithm, as given on pages 3, 4, and 5.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students. Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that a problem is like a puzzle that needs solving, and there can be more than one way to solve it. Each way has steps to follow, called an algorithm.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 4 and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 to 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 5

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
● run Puzzle Code Studio and solve the puzzles. 5 mins
Explain the four important parts of the Puzzle Code Studio. Attempt the activity on the Assignment page. Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Tour to Puzzle Code Studio.
● Show the Learning slides or the video and discuss the concepts shown on the panel.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Run Puzzle Code Studio and solve the puzzles.
Explanation
Explain to the students that the Puzzle Code Studio on Code.org is the playground where we code to solve the given puzzles. There are four main parts of the Puzzle Code studio, as given on page 6.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that Puzzle Code Studio is the coding playground on Code.org. It has four important parts: the Play Area where things happen, the Toolbox with all the code blocks for giving commands, the Workspace where we drag and connect the blocks to make things work, and Instructions that give us hints about what to do next.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 2

This chapter is divided into the following lab sessions
1. Introduction to Sprite and Sprite Lab
2. Creating a Scene 1
3. Creating a Scene 2
4. Adding a Behaviour
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe elements required to create a story.
● explain what a sprite is.
● describe what a sprite lab is, and what its three parts are.
Keywords
● Sprite: A character in coding is called a Sprite.
● Sprite lab: A Sprite Lab is where we can create our own stories and games.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Describe to the students the elements required to create a story. Explain what a sprite and sprite lab is. Also, explain the three parts of the sprite lab.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts

5 mins
Warm Up
● Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Introduction to Sprite and Sprite Lab.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
15 mins
Describe elements required to make a story. Describe to students that a story is made up of various elements, such as characters, problems, settings, and events, as given on page 12.
Explain what a sprite is. Explain to them that a character in coding is called a sprite. The astronaut will be the main sprite in our story, as given on pages 12 and 13.
Describe what a sprite lab is, and what its three parts are.
Correct Responses:
a. 5 b. 2 c. 2
Describe to the students that a Sprite Lab is where we can create our own stories and games. Tell them about its three parts: Play Area, Toolbox, and Workspace, as given on page 13.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 2A section to encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
● Show the Learning slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel. Build
7 mins
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that a story is made up of various elements such as characters, problems, settings, and events. A character in coding is called a sprite. We can create our own stories and games in Sprite Lab. Its three parts are Play Area, Toolbox, and Workspace.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 5
E. Answer the Following: Question 1

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● make scenes for the exciting journey of the astronaut in Sprite Lab.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Demonstrate to the students how to create a scene in Sprite Lab. Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Creating a Scene 1. Show the Learning slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
Engage
Explain the following concepts: Learning Outcome Explanation
Make scenes for the exciting journey of the astronaut in Sprite Lab.
Demonstrate to the students how to make scenes for the exciting journey of the astronaut in Sprite Lab. Tell them that we will have two scenes: one for the start of the story and another for reaching Mars. Also, tell them the algorithm to set up the first scene, as given on pages 14 to 16.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps of the algorithm to make scenes for the exciting journey of the astronaut in Sprite Lab.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 4, and 5

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● follow the algorithm to code the first scene.
Warm
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Demonstrate to the students the steps to code the first scene.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Creating a Scene 2
Show the Learning slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel. 15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome Explanation
Follow the algorithm to code the first scene.
Demonstrate the steps to code the first scene as per the algorithm by dragging and dropping various code blocks from the Toolbox to the Workspace, as given on pages 17 and 18.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to follow the algorithm to code the first scene.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 3, and 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 2
E. Answer the Following: Questions 3 and 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● add behaviour to a sprite.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Demonstrate to the students how to add behaviour to a sprite. Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Adding Behaviour
Show the Learning slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Add behaviour to a sprite.
Explanation
Demonstrate to the students the steps to add behaviour to a sprite by dragging the code blocks from the Behaviours section in the Toolbox and dropping them into the Workspace. Tell them how to make the astronaut sprite move to the right to reach the rocket, as given on pages 19 and 20.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students. Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to add behaviour to a sprite.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
3 mins
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 3 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 3
E. Answer the Following: Questions 2 and 5

This chapter is divided into the following classroom and lab sessions
1. Understanding Events and Actions
2. Setting up the Second Scene 1 3. Setting up the Second Scene 2 4. Setting up the Second Scene 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain what events and actions are using real-life examples.
● explain what events and actions mean in coding.
Keywords
● Event: An event tells you when an action will happen.
● Costume: A costume sets the appearance of a sprite.
Ask the students what they do when their hands are dirty.
Explain to the students what events and actions are using real-life examples; also explain to them what events and actions are in coding. Think and Tell Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Ask the students what they do when their hands are dirty.
● Now, build the concept by telling them for every event there is an action. So, if your hands are dirty, you must wash them.
Explain the following concepts:
Explain what events and actions are using real-life examples.
Explain what events and actions mean in coding.
Tell the students that an event tells you when an action will happen. For example, being hungry is an event, and eating food is an action, as given on page 26.
Explain that in coding, an event tells you when an action will happen, and an action is something that happens as a result of the event. For example, in the scene where an astronaut reaches the planet Mars when it touches the rocket, touching the rocket is the event and reaching the planet Mars is the action, as given on page 27.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 3A section to encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
● Ask the students to answer to the question “Are mouse clicks and keypress events too?” asked in the Think and Tell section on page 26.
Possible response: Yes, mouse clicks and key presses are events that a computer can use to do actions.

● Conclude the session by summarising that an event tells you when an action will happen. Events are important in coding too. For example, in a car game, clicking the arrows to make the car go to the left or right is the event. The car moving to the left or right is the action.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1, 2, and 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 3, and 4
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1 and 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 4 and 5
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● set an event and action scene using code blocks.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Demonstrate to the students how to set an event and action scene using code blocks.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Setting up the Second Scene 1
Show the Learning Slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Set an event and action scene using code blocks.
Explanation
Demonstrate to the students how to set a scene of an astronaut reaching the planet Mars when it touches the rocket, using different code blocks, as given on pages 28 and 29.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.

● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to set a scene of an astronaut reaching the planet Mars when it touches the rocket using various code blocks.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 2
E. Answer the Following: Question 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, and 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● set an event and action scene using code blocks.
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Demonstrate to the students how to set an event and action scene using code blocks.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Setting up the Second Scene 2
Show the Learning Slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Set an event and action scene using code blocks.
Explanation
Demonstrate to the students how to set a scene of an astronaut change the costume of the sprite, using different code blocks, as given on page 29.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.

● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to set a scene of an astronaut to change the costume of the sprite using various code blocks.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 4 and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 4 and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 4 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2 and 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● set an event and action scene using code blocks.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Demonstrate to the students how to set an event and action scene using code blocks.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Setting up the Second Scene 3
Show the Learning Slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Set an event and action scene using code blocks.
Explanation
Demonstrate to the students how to set a scene of an astronaut to stop moving the astronaut when it touches the rocket, using different code blocks, as given on page 30.
● Ask the questions provided on the slides one by one to assess the students’ understanding. Discuss the answers to the questions with the students. If necessary, ask additional relevant questions.

● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to set a scene of an astronaut to stop moving the astronaut when it touches the rocket, using different code blocks.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
C. Match the Following: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 5
This chapter is divided into the following classroom and lab sessions
1. Concept of Loops and Repeat Loop
2. Continuing with Project
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe a loop.
● define a repeat loop.
Keywords
● Loop: A loop is an action of doing something, again and again, until the task is complete.
● Repeat loop: A repeat loop is used when we want to repeat the task a certain number of times.
Ask the students to stand up and sit for five times. Describe a loop to the students. Discuss a repeat loop with them. Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign
Action Plan
Warm Up
● Ask the students to play an instruction game where they will be standing and sitting for five times.
● Now, relate the concept that if they sit and stand again and again, then it is called a loop.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe a loop. Discuss with the students that a loop is an action of doing something again and again until the task is complete, as given on page 37.
Define a repeat loop. Tell the students that a repeat loop is used when we want to repeat the task a certain number of times, as given on page 38.
● Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
1. When we want to repeat a task a certain number of times, then it is called?
Possible Response: Repeat Loop
2. What is called an action of doing something again and again?
Possible Response: Loop
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students based on the topic ‘Examples of loop’.
Possible Responses: Writing a sentence for three times, bouncing the ball, skipping for 5 minutes, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising that a loop is an action of doing something again and again until the task is complete. Also, summarise that when we repeat something for a specific number of times it is called a repeat loop.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● Add a background to the project.
● Add the people to the Mars background.
Keyword
● Random location: It is not a fixed place.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Let the students watch the video or the learning slides related to the topic on the digital panel.
Describe loop to the students. Discuss repeat loop with them.
Attempt the activity on the Assignment page
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework 5 mins 8 mins 14 mins 3 mins
5 mins
Warm Up
Instruct the students to go to Tekie’s Digital platform and open a Lab session on Continuing with Project.
Show the Learning slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slides in the panel.
8 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Add a background to the project.
Add the people to the Mars background.
Explanation
Demonstrate to the students how to set the background in the project using the set background to block, as given on pages 39 and 40.
Show them how to add people on the Mars background at a random location by using the random location block, as given on pages 41 and 42.

● Read aloud the question provided in the Do It Yourself 4A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to solve the answers in their book.
Possible Response: 2
● Which block helps us to move at a random location?
Possible Response: random location block
● Which block will help Reema repeatedly cycle around for four times?
Possible Response: repeat loop block
● Instruct the students to attempt the assignment by clicking on the Assignment tab.
● Explain the activity to the students.
● Conclude the session by summarising how to set the background in the project, using the set background to block. Also, tell them how to use the random location block.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 3, and 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, and 3
D. Write T for True or F for False: Questions 1 and 2
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. entertainment 2. schools 3. main power 4. Shut down 5. security problems
B. Tick () the Correct Option. 1. a. 2. c.


c.

C. Who Am I?
Computer 2. Computer 3. Hospital 4. Bank 5. Shut down
D. Write T for True and F for False. 1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. A computer is an electronic device that helps us do many things.
2. Computers are used in:
a. Banks b. Schools c. Hospitals d. Airports and stations e. Stores and offices.
3. Some advantages of computers are: storage, connectivity, information, calculation, and entertainment.
4. Some disadvantages of computers are: health problems, security problems, and environmental harm.
5. Sometimes using computers is not good for us as it can cause health problems like headaches and weak eye sight.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Some uses of a computer are:
a. Playing Games b. Watching Videos c. Drawing Pictures d. Listening to Music e. Finding Information

2. To start a computer:
● Switch on the main power button.
● Press the ON button on the UPS.
● Press the ON button on the CPU.
● Press the ON button on the monitor.
● Wait for the computer to start.
3. Some disadvantages of computers are: Health Problems, Security Problems, and Environmental Harm.
4. He should use a computer to book train tickets.
5. Computers are used in:
a. Banks: To help us send money to other accounts.
b. Schools: To help us learn new things.
c. Hospitals: To prepare and print medical reports.
d. Airports and stations: To help us in booking tickets.
e. Stores and offices: To keep a record of the number of items in shops.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Speakers 2. input 3. monitor 4. pen drive 5. keyboard
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. Keyboard
2. b. Hard Disk
3. a. Printer
4. a. Pen Drive
5. c. Mouse
C. Who Am I?
1. Headphones 2. DVD 3. Speakers 4. Hard Disk 5. Monitor
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. Input devices help us to tell a computer what to do. Input devices provide ways to ‘talk’ to the computer.
2. Output devices show the results of what we want from the computer.
3. We need storage devices to store data in the computer, like our favourite songs, our school projects, films, and games.
4.
Speakers are used when more than one person wants to hear the sounds and music. They are meant for only one person to listen to sounds and music, without disturbing others. They are usually bigger. They are smaller in size.
5. The IPO (Input, Process, and Output) cycle tells us how a device works. Input is what we give to the computer, Process is what the computer does with the input, and the Output is what the computer gives us back.
An example of a IPO cycle is:
Example 1: Washing Machine
Input: We put dirty clothes in the washing machine. Process: The washing machine washes the clothes.
Output: We get clean clothes.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Aman should use a pen drive to save his photos because a pen drive is a small stick-like device that can be carried around easily.
2. Riya must use a keyboard to type a letter on the computer.
3. Aarav is using a monitor to watch the film.
4. Yes, making a sandwich follows an IPO cycle.
Input: Toaster, bread, and cheese to make a sandwich
Process: Place cheese between bread slices and toast it in a toaster.
Output: A sandwich is made.
5. Input: Keep a glass of water in the refrigerator.
Process: Lowering the temperature of water until it freezes.
Output: Ice in the glass.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. alphabet 2. numbers 3. backspace 4. uppercase 5. line
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. Typing words
2. d. Spacebar key
3. b. Moving the cursor in different directions
4. d. Shift key
5. a. Press the Shift key and that number key together.
C. Who Am I?
1. Enter key
2. Backspace key
3. Caps Lock key
4. Spacebar key
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. F 4. T 5. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. The spacebar is used to add a space between two words.
2. The Caps Lock key is used to type letters in capital.
3. The Delete key helps us remove text or objects, but only when they are after the cursor.
4. Examples of special keys are the Backspace, Delete, Punctuation, Spacebar, Caps Lock, Enter, and the Arrow keys.
5. When we press two or more keys together, they become combination keys. For example, we can type symbols by pressing and holding the Shift key and then a number key.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Riya must use the Caps Lock key to type her name in capital letters.
2. To add the exclamation mark (!), Raj should press the Shift key and ‘1’ number key together.
3. Aarav should press the Shift key and the ‘/’ key together to add a question mark at the end of the sentence.
4. The letters on the keyboard are in a different order than the book because the keys are arranged in such a way that they make typing letters easier.
5. Naina must use the arrow keys to move the character of the game on the screen.

Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Mouse 2. Pointer 3. Left button 4. Right button 5. Scroll wheel
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. Left button 2. Double click 3. Scroll 4. 5. Index finger
C. Who Am I?
1. Mouse 2. Pointer 3. Scroll wheel 4. Right button 5. Left button
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. a. It helps control the pointer on the monitor.
b. It helps you click on things you want to open or use on the computer.
2. With one left-click, we can select an item and by clicking the left button two times very quickly we can do a double-click.
3. Left-clicking an item selects and opens it on the monitor.
4. Drag and drop allows you to move items using a mouse. Moving the mouse without leaving the left mouse button is called dragging. When you release the left button, you will see the file is placed where the pointer is. This is called dropping. This way of moving the file is called drag and drop.
5. Clicking the left button two times, very quickly, is called a double-click. When we double-click the left mouse button, it will open the selected item.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Aarna can drag and drop the item using a mouse.
2. The arrow is called a pointer.
3. Scroll wheel is used for lowering down the page.
4. The left button on the mouse is used to open items on the page.
5. Conji clicked the right mouse button to open a list of options.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Start 2. Title Bar 3. Drawing Area 4. Polygon 5. File, Save as
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. a.

2. d.

C. Who Am I?
1. MS Paint 2. Ribbon 3. Shapes 4. Shift 5. Save as
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. F 5. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. MS Paint lets us draw and colour on the computer.
2. Title bar, tabs, ribbon, drawing area
3. We should save a drawing in MS Paint so that you can always see it again later.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. MS Paint 2. Circle 3. Save the file
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Tools 2. Color picker 3. Eraser 4. Text
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. d. 2. c. Draw with different line styles 3. b. Fills the shape with a colour
4. a. 5. b. Removes mistakes from the drawing
C. Who Am I?
1. Colors group 2. Fill with color tool 3. Text tool 4. Color picker tool 5. Eraser tool
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. F 5. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. We can use the Fill with Color tool to make our shapes colourful.
2. The Eraser tool is used to fix mistakes in our drawings.
3. The Color picker tool allows us to ‘pick’ the colour of an object without going into the Colors section.
4. The Text tool allows us to write in our drawings.
5. We need to colour our drawing because it looks more attractive and real.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. The Fill with color Tool is used to add colours to the picture.
2. Sahiba can use the Eraser tool.
3. Simran can use the Text tool to write the text.
4. Nikhil can select the same colour by using the Color picker tool.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. AI 2. humanoid 3. Sparko 4. vacuum 5. Sophia
B. Tick () the correct option.
1. b. Roomba
2. b. Look and move like humans
3. a. Artificial Intelligence
4. d. None of these
5. b. Service robots

C. Who am I?
1. Sparko 2. Roomba 3. Sophia 4. AI 5. Robots
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. F
E. Answer the following questions.
1. A robot is a machine that can do things on its own.
2. Different types of robots are humanoid, animal, industrial, and service.
3. Sparko, the first robotic dog, can walk and run, wag its tail like a real dog, play games, listen to us, and bark like a real dog.
4. AI gives machines, or robots, the ability to learn and do things on their own, just like humans do.
5. Sophia was developed in Hong Kong in 2016.
F. Apply your learning. 1.
Do it yourself
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Coding 2. Command 3. Sequence 4. Flexible 5. Play area
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. Toolbox 2. c. Algorithm 3. c. Play area 4. b. 5. c.


Who Am I?

D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. F 3. T 4. F 5. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. A command is an instruction that tells a computer what to do.
2. A sequence can be a:
Fixed sequence: There is only one way to do the task.
Flexible sequence: There can be more than one way to do the task.

F. Apply Your Learning.



Which block can be used to change the costume of a sprite?
Chapter-2 Introduction to Sprite Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
Four 2. Sprite 3. Location 4. Size 5. Behavior
B. Tick () the Correct Option.



b. Toolbox C. Who Am I? 1. Location Icon 2. setting size to 250 3. Moving east block 4. Sprite begins (Behaviour) block 5. Sprites
D. Write T for True and F for False. 1. F 2. T 3. T 4. F 5. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. A character in coding is known as a sprite.
The Run button helps to run the code.

5. b. Right
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. a. set background to b. make new
2. set background to block
3. Size
4. a.
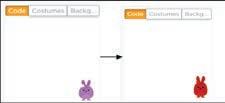
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Event 2. Action 3. when touches 4. Costume 5. change costume to
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. a. An event tells you when an action will happen.
2. c. Prepare for exam
3. a. Your TV will turn on.
4. a. Mop the floor
5. d. When the astronaut touches the rocket
C. Match the Following. C Match the Following.







An
2 You cannot change the behaviour of a sprite.

D.
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1.




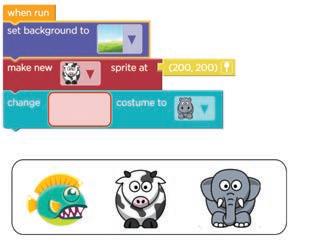

3 The repeat loop is used when we want to repeat a task a number of times.
4 Using a repeat loop, your code will become . 5 A location is not a fixed place.
B Tick () the Correct Option.
1 Which block is used to do a task a certain number of times?
3 The repeat loop is used when we want to repeat a task a number of times.
4 Using a repeat loop, your code will become .
5 A location is not a fixed place. B Tick () the Correct Option.
1 Which block is used to do a task a certain number of times?
Chapter Checkup
2 Which code will show the given picture in the Play Area?
A. Fill in the Blanks.
Loop 2. Stop 3. Certain 4. Shorter 5. Random B. Tick () the Correct Option.
c.
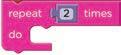
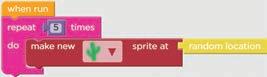
2 Which code will show the given picture in the Play Area?
3 Which is the correct picture of the Play Area for the given code?

Who Am I? What I Do?


Am I?
makes the germ sprites appear, as shown in the given picture?
I can set or change the background as you want.
I can set or change the background as you want.
I can do a task, again and again, for a certain number of times.
I can do a task, again and again, for a certain number of times.
I can place a sprite anywhere in the Play Area.
I can place a sprite anywhere in the Play Area.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
CO24CB0204_P1.indd 52


1. Using a repeat loop, your code will become shorter.
2. A loop is an action of doing something, again and again, until the task is complete.
3. The repeat loop is used when we want to repeat a task a certain number of times.
4. Reading a book is not an example of a loop because we do not read the same page again.
F. Apply Your Learning.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Computer 2. Microphone 3. Pen drive 4. Delete
B. Tick () the correct option.
1. c. Printer 2. a. Shift Key 3. a. Shut Down
Am I? the background again and again, for of times. anywhere in
C. Write T for True and F for False. 1. T 2. T 3. F 4. F
D. Answer the Following Questions.
1. A mouse is used to point at things on the computer screen.
2. Computers help teachers to make time tables and report cards.
3. Punctuation keys are used to add punctuation symbols. These symbols are the question mark (?), exclamation mark (!), full stop (.), comma (,), semi-colon (;), and colon (:).
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. Caps Lock Key
2. Yes, Input: Orange, Juicer Process: Making juice
Output: Orange juice
3. Online Banking
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Pointer 2. Ribbon 3. Fill with color 4. Robot
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. Right button 2. c. Line tool 3. c. Text tool
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. F 4. F
D. Answer the Following Questions.
1. The left mouse button is used to click on, select, and open items on the monitor.
2. The Eraser tool is used to remove mistakes in our drawings.
3. The different types of robots are: Humanoid, Animal, Industrial, and Service.
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. Fill with color tool 2. Shapes tool 3. Left-button
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Coding 2. Order 3. Costume 4. Repeat
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. Events Section 2. b. Clicking a mouse 3. a. Creating stories and games
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. T
D. Answer the Following Questions.
1. Event: Pressing a doorbell. Action: The doorbell rings.
2. A loop is an action of doing something, again and again, until the task is complete.
3. The set of steps in an order to solve a problem is called an Algorithm.
E. Apply Your Learning.
1.




This teacher manual has been designed to implement Tekie, the storytelling-based Coding and Computer Science program. The manual consists of lesson plans within each chapter that teachers transact within classrooms and computer labs. Each lesson is based on a research-based ‘WEBS’ framework that simplifies pedagogical practices for teachers and enables them to deliver effectively.
• Sharp Lesson Planning: Each lesson plan focuses on specific sub-learning outcomes within a chapter and are designed for delivery within the stipulated class or lab time.
• Real-life and Application-based Questions: Additional questions that link Computer Science to real-life contexts and assist teachers to develop learners’ conceptual understanding and application skills.
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East.
• Support and Detailed Solutions: In-depth solutions for in-class and post-class activities to reinforce learning. hello@uolo.com
ISBN 978-81-984519-4-1
