





Education is a dynamic field, continuously evolving to meet the ever-changing demands of the modern world. Keeping pace with these advancements, the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) periodically revises its curriculum to ensure that students receive the most relevant and up-to-date knowledge.
In light of the recent syllabus updates for Information Technology (Subject Code 402), we have undertaken a revision of our existing book to incorporate these changes. While the core structure of the book remains intact, certain chapters have been modified to align with the latest curriculum requirements. To facilitate a seamless transition, we are providing this Supplementary Booklet, which includes the revised chapters.
This booklet ensures that students have access to accurate and updated content, enabling them to confidently prepare for their academic assessments. It retains the same clarity and practical approach as the main textbook, ensuring that learners continue to develop both their theoretical understanding and hands-on IT skills effectively.
We remain committed to delivering high-quality educational resources that empower students in their learning journey. We sincerely hope that this supplement serves as a valuable addition to your studies, helping you stay aligned with the most recent curriculum changes.


The Track Changes feature in LibreOffice Writer is a powerful tool that allows users to monitor modifications made to a document. This is very useful for long documents that are being worked on simultaneously by more than one user, as it provides a systematic way to track edits, comments, and revisions. When Track Changes feature is enabled, any addition, deletion, or formatting change is recorded, making it easy to review and revert modifications, if needed.
To enable Track Changes in LibreOffice Writer, go to Edit > Track Changes > Record. Once activated, any change made to the document will be highlighted. Insertions will be in a different colour, deletions may possibly be formatted in strikethroughs, and changes in formatting will be set up with special markers. Users can also add comments to specific sections, providing additional context for suggested changes.
Collaboration Track Changes feature offers a means through which several users can review and edit a document, which would even allow the same document to be edited without any confusion. Modifications made are easy to spot by every contributor so that nothing will be missed.
Improved Document Control It allows a user to see who made a change and when a modification was made. It is particularly useful in professional and academic settings where the version control plays a dire role.
Efficient Review Process Instead of manually comparing different document versions, users can quickly review, accept, or reject changes, saving time and effort.
Clear Communication The ability to add comments and suggestions directly within the document helps maintain clear communication between authors, editors, and reviewers.
Maintains Document Integrity With Track Changes, users can review each change purposely before finalising the document, ensuring only essential changes are there, thus keeping up the quality of a document.
To view the Track Changes toolbar, select View > Toolbars > Track Changes. The Track Changes toolbar will appear at the bottom left corner of the Writer window. Let us quickly learn about the various options in the Track Changes toolbar.

1 Show Track Changes Displays all tracked changes in the document
2 Record Track Changes Enables or disables the tracking of document modifications
3 Previous Track Change Moves to the previous tracked change in the document
4 Next Track Change Moves to the next tracked change in the document
5 Accept Track Change Confirms and applies the selected tracked change
6 Reject Track Change Discards the selected tracked change
7 Accept All Tracked Changes Approves and applies all changes in the document
8 Accept Track Change and select the next one Accepts the current change and moves to the next one
9 Reject Track Change and select the next one Rejects the current change and moves to the next one
10 Manage Track Changes Opens a dialog box for reviewing all tracked changes
11 Insert Comment Adds a comment at the selected position in the document
12 Insert Track Change Comment Adds a comment specific to a tracked change
13 Protect Track Changes Locks the Track Changes feature to prevent unauthorised modifications
14 Compare Non-Track Changed Document Compares a document without tracked changes to another version
15 Merge Track Changed Document Merges tracked changes from multiple versions into a single document
Before sending a document for review, it is essential to prepare it correctly to ensure a smooth reviewing process. LibreOffice Writer provides several tools to facilitate this. The first step is enabling the Track Changes feature, ensuring that all edits made by reviewers are recorded.
To prepare a document for review and start tracking changes:
• Select Edit > Track Changes > Record option.
• Alternatively, click the Record button on the Track Changes toolbar.
To prevent users from disabling the Track Changes feature, the document can be protected with a password. Follow the given steps:
• Create a new document in LibreOffice Writer.
• From the main menu, select Edit > Track Changes > Protect or alternatively, click the Protect Track Changes button on the Track Changes toolbar.
• The Enter Password dialog box appears.

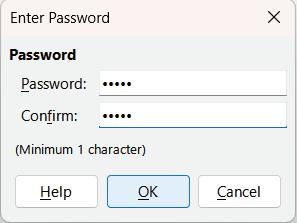
• Enter the same password in both the Password and Confirm text boxes, then click OK.
• Once the document is password-protected, any user attempting to disable Track Changes will be prompted to enter the password.
The document can now be shared with various users to record their changes.
After activating the Track Changes feature, now the users can start recording their changes. You can notice the following changes:
• Any deleted text will appear with a strikethrough.
• Added text will be highlighted in a different colour.
• When you hover the mouse over a change, a tooltip appears displaying details such as the author’s name, the modification made, and the date and time of the change.

To stop recording changes, deselect the Record option by clicking Edit > Track Changes > Record or clicking the Record button on the toolbar.
In collaborative document editing, multiple reviewers may suggest modifications to improve clarity, correctness, or overall quality. Once all the changes have been made, the original author has the responsibility to review them and decide whether to accept or reject each change. This step ensures that the final document reflects the intended message while incorporating valuable feedback.
You can perform the following actions on the document:
Accept or Reject Individual Changes
As you review the document, you may find some suggestions helpful, while others might not align with your original intent. To make a decision:
• Click on the highlighted change.
• Choose Accept Track Change if you agree with the suggestion, or Reject Track Change if you want to discard it.
When working with a document containing multiple edits, it can be time-consuming to manually locate each change. To make this process easier:
• Use the Previous Track Change and Next Track Change buttons to jump between modifications.
Accept or Reject All Changes at Once
If you are confident in the suggested changes and want to apply them quickly, you can:
• Click Accept All Tracked Changes to approve all modifications in one go.
• Click Reject All Tracked Changes to discard all suggestions at once.
This option is useful when working on a document with trusted collaborators, where most changes are expected to be beneficial. However, it is always a good practice to skim through the changes before making a final decision.
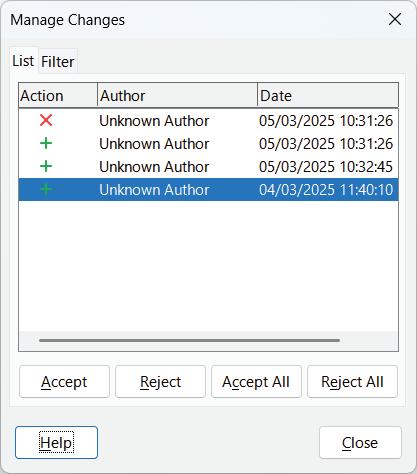
For a more detailed overview of all modifications, you can:
• Click the Manage Track Changes button, which opens the Manage Changes dialog box.
This dialog box provides a list of all modifications in the document, allowing you to review them efficiently. It also offers buttons to accept or reject changes directly from the list, making it a valuable tool for handling large-scale revisions.
Comments are an interesting feature in LibreOffice Writer that allow users to provide feedback, ask questions, or highlight areas that require attention. Instead of making direct changes, reviewers can leave comments for the document author to consider. Comments are commonly used in collaborative writing, academic papers, and business documents where multiple people need to provide input.
To add a comment:
• Select the text where feedback is needed.
• Go to Insert > Comment or press Ctrl + Alt + C
• A text box appears in the margin where comments can be entered. Each comment is associated with a specific user, and the date and time of the comment are recorded.
• Users can reply to existing comments, creating a discussion thread that makes collaboration more effective.
• Additionally, comments can be formatted or deleted once they are no longer needed.

• If there are multiple comments added by different reviewers, then they appear in different coloured comment boxes.

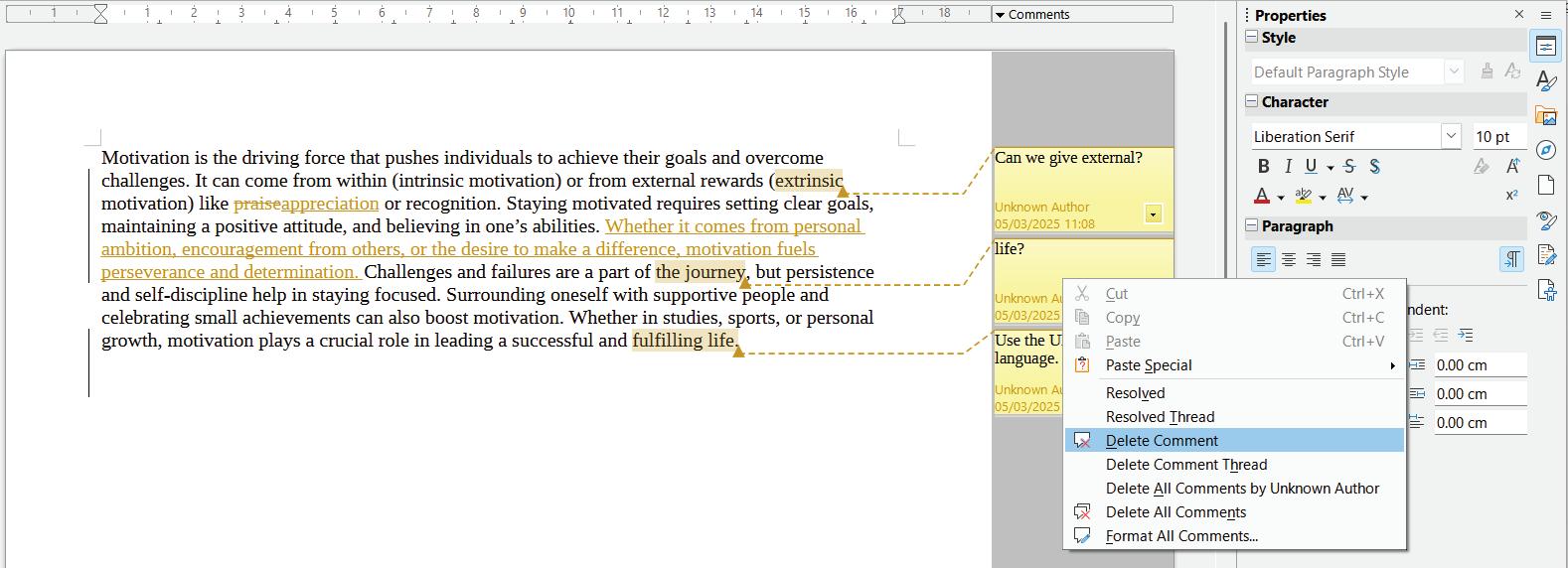
Once comments have served their purpose, they can be deleted to keep the document clean and organised. LibreOffice Writer offers multiple ways to remove comments, depending on user preferences.
• To delete a single comment, right-click on it and select Delete Comment.
• To remove multiple comments, navigate to Edit > Track Changes > Manage and select Delete All Comments. This ensures that all feedback is cleared in one step. You can delete all the comments by a particular reviewer as well as all the reviewers as needed.
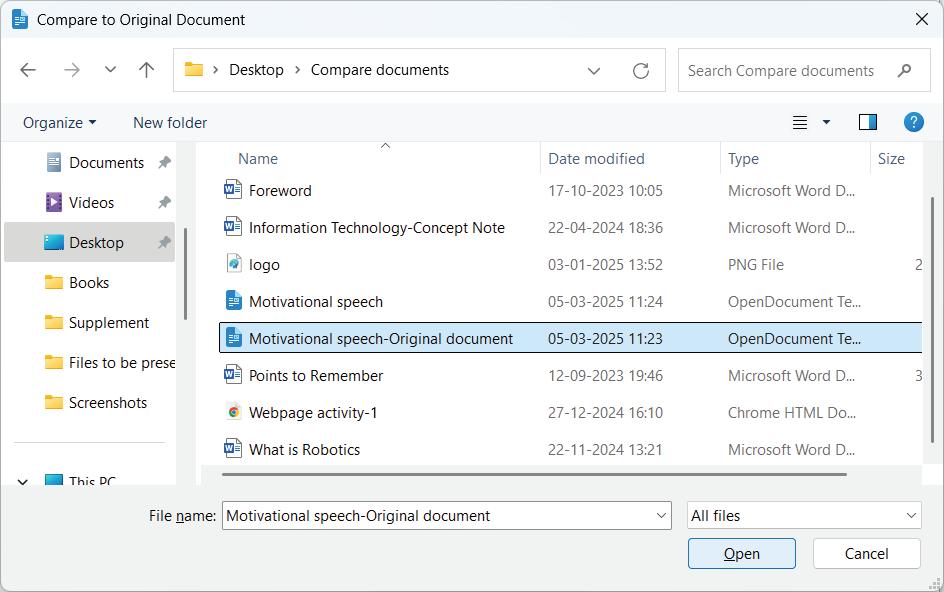
LibreOffice Writer provides a Compare Documents feature that allows users to identify differences between two versions of the same document. This is particularly useful when reviewing revisions or merging edits from different contributors.
To compare documents:
• Open the original version and navigate to Edit > Track Changes > Compare Document. Alternatively, you can select the Compare Non-Track Changed Document option from the Track Changes toolbar.
• The Compare Documents dialog box appears.
• Select the modified version, and LibreOffice Writer will highlight differences, such as added, deleted, or changed text.
This feature helps in tracking progress, ensuring that important edits are not overlooked. It is especially valuable in academic, legal, and business settings where document accuracy is critical.
After comparing, users can choose to accept or reject changes, similar to the Track Changes feature. This makes it easier to manage document versions without manually reviewing line-by-line differences.
(Individual Activity)
Open LibreOffice Writer and create a short paragraph about your favourite hobby. Enable the Track Changes feature and make at least five modifications to your text (adding, deleting, and formatting changes). Add comments to explain the reasoning behind each modification. Finally, review your changes and accept or reject them as necessary. Take a screenshot of the final document with tracked changes and comments.
(Group Activity)
Create a group of three to four students. Each member will take turns making changes to a shared document using the Track Changes feature in LibreOffice Writer. Follow these steps:
1. The first student will write a short passage on a given topic (e.g., “The Importance of Technology in Education”).
2. The second student will review and modify the text using Track Changes, adding comments to explain their suggestions.
3. The third student will accept or reject the changes while ensuring document clarity and coherence.
4. The final student will use the Compare Documents feature to check differences between the original and the final version.

A Select the correct option.
1 What is the primary purpose of the Track Changes feature in LibreOffice Writer?
a To permanently modify the document without review
b To track and review edits made to a document
c To delete unnecessary content automatically
d To create multiple versions of the same document
2 Which option enables the Track Changes feature?
a File > Save As
c Insert > Comment
b Edit > Track Changes > Record
d Format > Paragraph
3 What happens when a user adds a comment in LibreOffice Writer?
a The comment replaces the selected text
b The comment is inserted in the text itself
c A text box appears in the margin with the comment
d The document is automatically saved
4 How can you remove all comments in a document?
a Delete them one by one manually
b Edit > Track Changes > Manage > Delete All Comments
c Restart LibreOffice Writer
d Save the document in a different format
B Fill in the blanks with the most suitable words.
1 The feature allows users to track and review modifications made to a document.
2 To insert a comment, go to Insert > or use the shortcut Ctrl + Alt + C.
3 The Compare Documents feature helps users identify differences between two versions of the
4 To accept or reject all tracked changes at once, use the option.
C State whether the following is True or False. Correct the statements that are false.
1 The Track Changes feature in LibreOffice Writer allows users to track and review edits made by multiple users.
2 Once a change is made with Track Changes enabled, it cannot be reverted.
3 Comments are directly inserted into the text rather than appearing in the margin.
4 The Compare Documents feature automatically accepts all changes made between two versions.
D Answer the following questions.
Q1. What are the benefits of using the Track Changes feature in collaborative editing?
A1. The Track Changes feature allows multiple users to review and edit a document while keeping a record of modifications, ensuring clarity and efficiency in collaboration.
Q2. How can a document be protected to prevent users from disabling Track Changes?
A2. A document can be protected by selecting Edit > Track Changes > Protect and setting a password. This prevents unauthorised users from disabling Track Changes.
Q3. Describe the steps to accept or reject a tracked change in LibreOffice Writer.
A3. To accept or reject a change, click on the modified text, then select Accept Track Change or Reject Track Change from the toolbar.
Q4. Explain the steps involved in comparing two documents using the Compare Documents feature in LibreOffice Writer. How does this feature help in document review?
A4. To compare two documents in LibreOffice Writer:
• Open the original document.
• Go to Edit > Track Changes > Compare Document
• Select the modified version of the document.
• LibreOffice Writer will highlight differences such as added, deleted, or changed text.
• The user can then review, accept, or reject changes as needed. This feature helps in reviewing changes systematically without manually comparing versions.
Q5. Imagine you are part of a team working on an important report. Your team members have suggested several changes using the Track Changes feature. How would you efficiently review their edits, communicate your feedback, and finalise the document while maintaining document integrity?
A5. To efficiently review the team’s edits:
• Navigate through the changes using the Previous Track Change and Next Track Change buttons.
• Accept or reject each modification while ensuring clarity and accuracy.
• Use comments to ask for clarification or suggest further refinements.
• If necessary, use the Manage Track Changes dialog box for a comprehensive review.
• Once all changes are finalised, save the document and communicate with the team to ensure alignment before submission.
2. False. Changes can be reverted by accepting or rejecting them.
3. False. Comments appear in the margin, not directly in the text.
4. False. The Compare Documents feature highlights differences but does not automatically accept changes.







You must have read in newspapers or seen in news reports about incidents like factory fires, security breaches at offices, or workplace accidents leading to injuries. These incidents highlight the importance of maintaining a safe and secure work environment. Ensuring workplace safety is not just a legal requirement but also a moral responsibility of organisations. For example, consider a case where a manufacturing plant did not follow proper safety protocols, leading to a fire that caused severe damage to property and endangered employees’ lives. Such incidents serve as reminders of why strict safety measures, proper training, and emergency preparedness are essential in every workplace. A proactive approach to workplace health, safety, and security can prevent accidents, protect employees, and ensure smooth business operations.

Every organisation is responsible for developing a safe working environment for its employees. Occurrence of accidents, diseases, and hazards will disrupt operations, lower productivity, and above all, may put lives at risk. Just as is the case for management alone, it is employees’ task for providing safety to their workplace.
A positive workplace encourages the health of employees and improves productivity, reducing hazards. Employees should not only depend on safety officers or management to ensure their safety instead, take personal responsibility for their own health and security.
Ignoring safety measures may lead to physical injuries, health complications, and even legal ramifications or financial losses for the organisation. Strong health and safety security programs will foster a caring culture in an organisation, hence improving morale and productivity.
The chapter will look into the importance of workplace safety, hazards associated with it, and common practices for ensuring a safe and healthy environment.
A healthy workforce is the foundation of a productive and successful organisation. Employee health goes beyond just physical well-being; it encompasses mental and social well-being too. Organisations must prioritise workplace health to prevent illnesses, reduce absenteeism, and create a positive work environment.
A well-maintained workplace contributes to good physical health. Organisations should ensure:
Cleanliness and Hygiene: A clean office reduces the spread of germs and infections. Workspaces, common areas, and restrooms must be regularly cleaned and sanitised.
Proper Ventilation and Air Quality: Adequate ventilation and air conditioning help maintain a comfortable indoor environment, reducing respiratory issues.
Access to Clean Water and Nutritious Food: Employees must have access to purified drinking water and a cafeteria serving fresh, healthy meals.
Ergonomic Workstations: Proper desk arrangements, comfortable chairs, and correct screen heights can help prevent posture-related issues and muscle strain.
For instance, an IT company that provides adjustable desks and ergonomic chairs to its employees helps them avoid back pain and fatigue, ultimately improving productivity.
A workplace that supports mental health ensures reduced stress levels and increased job satisfaction. Organisations can:
• Encourage work-life balance by promoting reasonable working hours and breaks.
• Offer counselling services or mental health workshops to help employees deal with stress.
• Create a supportive work culture where employees feel valued and heard.
For example, a company implementing an employee assistance program with mental health professionals allows workers to seek help confidentially, leading to a healthier work environment.
A safe workplace protects employees from injuries, accidents, and health risks. Organisations must identify potential hazards and take steps to minimise them.

A hazard is anything that can cause harm, while a risk is the probability of that hazard leading to an accident. Common workplace hazards include:
• Slippery floors that may lead to falls.
• Faulty electrical wiring that can cause fires or electric shocks.
• Heavy machinery or equipment that requires proper handling.
For instance, in a warehouse setting, improper stacking of goods can lead to accidents. Companies should implement clear guidelines for storage and lifting techniques to prevent injuries.
To maintain workplace safety, organisations should:
• Conduct regular safety training to educate employees on emergency procedures.
• Ensure proper signage and warnings for hazardous areas.
• Provide personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves, helmets, and safety glasses where required.
• Perform routine safety inspections to identify and fix risks promptly.
For example, a construction firm that mandates the use of helmets and harnesses for workers operating at heights reduces the likelihood of serious injuries.
Security is essential to ensure employees feel safe from potential threats such as unauthorised access, theft, or cyberattacks. A well-implemented security system helps build trust among employees and protects company assets.
Organisations must have measures in place to protect employees and company property. These include:
Access Control Systems: Using ID badges, biometric scanners, or security personnel to monitor entry and exit.
Surveillance Cameras: Installing CCTV cameras in key areas to deter potential threats.
Emergency Response Plans: Having clear procedures for handling security breaches or workplace violence.
In today’s digital world, securing company data is as crucial as physical security. Companies must:
• Implement strong password policies and two-factor authentication.
• Train employees to identify phishing scams and cybersecurity threats.
• Regularly update firewalls and antivirus software to protect sensitive information.
Employee Security and Workplace Ethics
Employees should feel safe from harassment, discrimination, and workplace bullying. Organisations must:
• Establish zero-tolerance policies against harassment.
• Encourage employees to report security concerns confidentially.
• Conduct background checks before hiring new employees.
A workplace with strict anti-harassment policies ensures a positive and respectful environment for all employees.
Organisations establish health, safety, and security policies to create a safe and compliant work environment. These policies outline the necessary procedures to prevent workplace hazards, ensure employee well-being, and maintain security standards in accordance with legal and regulatory requirements.
A health, safety, and security policy is more than just a document—it reflects our organisation’s responsibility and dedication to protecting our employees, visitors, and the broader community. This policy serves as a guiding framework to:
• Promote Workplace Safety: Implement measures that prevent accidents, injuries, and potential hazards.
• Support Employee Well-being: Foster a culture where physical and mental health are valued and protected.
• Ensure Security: Safeguard employees, data, and assets from potential threats.
By adhering to these policies, we can work together to maintain a secure and healthy workplace for everyone.
The health, safety, and security policy is designed to:
• Prevent workplace injuries and illnesses.
• Identify and mitigate potential hazards.
• Ensure compliance with government regulations.
• Foster a culture of safety and awareness among employees.
• Provide clear procedures for responding to health, safety, and security concerns.

The health, safety, and security program consists of essential elements that guide an organisation toward achieving a secure work environment. These include:
• Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to government-mandated health, safety, and security standards.
• Health and Hygiene Protocols: Guidelines on cleanliness, sanitation, and disease prevention.
• Emergency Preparedness: Fire drills, evacuation plans, and first aid training.
• Security Measures: Access control, surveillance systems, and cybersecurity policies.
• Ergonomics and Workplace Design: Guidelines on proper workstation setup to prevent strain and injuries.
• Incident Reporting: Procedures for reporting accidents, injuries, or security threats.
A well-defined policy ensures that employees understand their responsibilities and know how to react in case of an emergency.
Organisations implement these policies to:
• Ensure Employee Well-being: A structured safety framework protects employees from workplace hazards, fostering trust and productivity.
• Align Safety with Business Goals: Safe work environments reduce absenteeism, improve efficiency, and enhance overall performance.
• Prioritise Stakeholder Welfare: A commitment to safety demonstrates that the company values people as much as profits, strengthening reputation and employee retention.
• Define Roles and Responsibilities: Clear accountability ensures proactive risk management at all levels.
• Comply with Legal Regulations: Adhering to OH&S standards set by the Government of India helps avoid legal issues and promotes best practices.
• Prevent Workplace Injuries and Illnesses: Identifying risks and implementing preventive measures reduces medical costs, compensation claims, and lost workdays.
A typical OH&S policy in IT companies includes:
Investing in Safety Resources: Providing ergonomic workspaces, mental health programs, and regular safety audits.
Ensuring Compliance and Best Practices: Going beyond legal requirements by adopting industry-leading safety standards.
Setting Objectives and Evaluating Performance: Defining measurable OH&S goals with regular progress assessments.
Preventing Workplace Hazards: Addressing risks like ergonomic strain, stress, and electrical hazards through proactive measures.
Enhancing Awareness and Competency: Conducting safety training, first aid programs, and emergency preparedness sessions.
Government laws outline the minimum health, safety, and security standards that companies must follow. Employers are required to implement policies that meet these regulations and ensure a safe workplace for all employees. Compliance with these laws helps prevent workplace hazards and ensures accountability.
Every organisation should establish a health, safety, and security committee responsible for:
• Identifying workplace hazards.
• Assessing risks and proposing mitigation strategies.
• Regularly reviewing and updating safety procedures.
• Ensuring all employees comply with safety protocols.
For the policy to be effective, organisations must:
• Regularly review and update health, safety, and security measures.
• Encourage employee participation in safety initiatives.
• Conduct periodic audits and risk assessments to maintain a safe workplace. By implementing a comprehensive health, safety, and security policy, organisations can create a safer work environment, reduce risks, and comply with legal obligations, ultimately fostering a culture of well-being and protection for all employees.
Hazards, in the context of workplace safety, are conditions or situations that have the potential to cause harm to employees, ranging from minor injuries to life-threatening incidents. These hazards can stem from various sources, including the nature of the work, the environment, equipment, and even human factors. Let us understand this concept with the help of different types of workplace hazards and their sources prevalent in the work sector.
Common major types of hazards are:
• Physical Hazards
• Electrical Hazards
Let us learn about these hazards one by one.
• Fire Hazards
• Health Hazards
These hazards arise from the physical environment or setting of the workplace and the materials used while working. For instance, on construction sites across India, workers are exposed to various hazards, such as falling from heights, due to improper scaffolding or inadequate safety equipment. Additionally, improper handling of heavy machinery or tools can lead to accidents resulting in injuries or even fatalities.
Numerous accidents are caused by falls and slips at work every year. Falling from a height due to negligence is a common cause of death, particularly in India. According to the World Health Organization, falls are the second-leading cause of unintentional injury deaths worldwide. Construction workers are more likely to get seriously injured from a fall since they work at heights with unprotected roof edges. It is important that proper safety equipment and safety gear be put in place to ensure the safety of the workers.

1. Poor lighting in the workplace can cause employees to trip and fall as they cannot see any obstacles in their way.
2. Uneven floor surfaces make it difficult to walk and can lead to falls and slips.
3. Wet or slippery floors often cause a person to slip, and that can also sometimes lead to severe injury.
4. Trailing cables on the floor can also cause a person to trip and fall, which can lead to several injuries.
5. Poor housekeeping in an untidy workplace with improper storage of material can cause hindrances in walking.
6. Weather conditions such as heavy rain can make the floors wet. It can also sometimes lead to slips and falls.
By following certain measures, we can prevent falls and slips in the workplace.
Proper Lighting: Lighting is a major cause of falls and slips. If a space is well illuminated, everyone can see objects around them and walk properly without tripping over anything.
Stairways: It is the riskiest location and has the highest number of falls. Stairs must have proper handrails and lighting, be free of any unsecured objects, such as nails, and the presence of slippery substances like oil, water, banana peels, etc.
Manage Cables and Wires: Slips and falls are common in the workplace due to the abundance of cables and wires lying loose. To eliminate the risk of slipping due to loose and running wires on the floor, all cables should be secured to the corners of the floor or hung with pins along the walls.
Signage: Adequate signage plays an important part in the prevention of falls and slips. With proper signage, one can identify which areas require special attention. These signs provide a clear warning to the employees and also bring the issues to the attention of the employer.
Proper Footwear: Wearing footwear appropriate for the work environment decreases the chances of slipping and falling. People often wear uncomfortable or slippery shoes to work, causing them to fall and injure themselves.
Proper Equipment: Proper equipment, such as good-quality ladders and stools, allows workers to access places at a certain height. Employees who don’t use proper equipment are more likely to fall and injure themselves.
Cleaning Spills: If something has been spilled unintentionally, then that should be cleaned immediately so that nobody falls because of that. Proper signs should be placed around the area to make people aware.
Check Floor Conditions: The state of the floor should always be monitored, and any necessary repairs should be undertaken immediately. Many people slip and fall on uneven floors, which results in injuries.
The human body is a good conductor of electricity, and when a body part comes in contact with an exposed electric wire, it suffers an electric shock. Electric shocks can cause injuries ranging from minor shocks to more fatal consequences. The amount of current passed by the shock causes harm to the body.
Electrical safety refers to the techniques, rules, and precautions used to avoid accidents that can occur while using electricity. It includes a variety of techniques and processes aimed at ensuring that electrical systems, equipment, and appliances are used, installed, and maintained in a manner that reduces the risk of electrical hazards.
Electrical safety is essential in both home and industrial settings because electricity can be extremely dangerous if handled without caution or if any electrical equipment is not properly maintained. Handling electrical appliances can pose a significant risk to workers, especially those whose jobs require them to work near high-voltage areas.
1. Electric shocks
2. Electrical fires due to short circuits
3. Overloaded circuits due to using too many appliances for a longer period of time
4. Exposed wires and conductors
5. Improper grounding of wires
6. Using electricity in wet conditions such as rain and snow
7. Faulty electrical equipment that can cause electric shocks
8. Inadequate wiring at various places
9. Lack of electrical safety training
Employee
It is a misconception that minor or non-fatal incidents do not have to be recorded. People believe that minor workplace events, such as a cut from a sharp table edge, need not be documented. However, it is actually crucial to document every accident in a workplace, no matter how big or small, so that safety measures can be tracked easily in the future.
Electrical safety procedures must be taught to employees in order to safeguard them from occupational hazards. Employee training and awareness of electrical safety measures are essential because electrical accidents can cause severe injuries or even fatalities. All the employees should be trained in electrical hazards, equipment, safety regulations, and standards.
Risk Assessment
It is the methodical process of detecting risks in the workplace, assessing the severity of the risk associated with it, and putting into place reasonable control measures to either eliminate or minimise such risks.
Cables, plugs, sockets, and other flexible leads and connectors get damaged easily. Inspect electrical systems, equipment, and wiring on a regular basis to discover and resolve any problems, such as damaged cables, frayed wires, loose connections, or symptoms of overheating.
Proper Wiring
Ensure that the wiring is correctly installed and has adequate capacity for the load. Replace the damaged wires with new ones on a regular basis. Cable connectors or couplers should be used in place of tape to connect wires.
Emergency Equipment
Have fire extinguishers and first-aid kits readily available, and ensure that employees know their locations and how to use them in case of electrical fires or accidents.
Electrical
Install suitable safety signs and labels to warn employees about electrical hazards, such as high-voltage regions or electrical equipment that requires specific measures. Signs or reminders to turn off electricity when not in use should be installed.
Protective equipment, including helmets, gloves, goggles, and masks, safeguards employees from workplace electrical hazards, ensuring their safety and well-being.

Fire-related hazards are very common at workplaces, and they can take place due to a number of reasons, including short circuits, electrical failures, carelessness, or flammable chemicals. Fire safety has a pivotal role in safeguarding both workplaces and homes. It includes a range of measures designed to prevent the initiation and spread of fires while also providing secure means for individuals to evacuate during emergency situations involving fire. Fire safety refers to the steps used to control and minimise the risks associated with fires. Fire safety at the workplace is required to prevent any hazards that can occur in a setting that involves chemicals, electricity, or fire. A company should implement stricter safety protocols to protect its employees and prevent fire-related accidents.
Some of the major causes of fire at a workplace are:
Electrical Malfunctions
Electrical fires can be caused by faulty wiring, overloaded circuits, or damaged electrical equipment.
Human Error
Workplace fires can also be caused by accidents or carelessness on the part of employees, which includes electrical faults, improper storage of inflammable materials, etc.
Faulty Equipment or Machinery
If equipment and machinery are not properly maintained, they may experience mechanical failures that produce heat and cause short circuits, thereby leading to fire.
Chemical Hazards
Fires can start in environments where dangerous chemicals or materials are handled and stored carelessly or without proper knowledge. This can lead to chemical reactions, spills, leaks, etc., and initiate fires.
Intentional Acts
Workplace fires can also be purposefully started by someone with bad intentions. It can also cause a lot of harm to people and property.
To maintain a safe working environment, it is necessary to follow proper fire safety rules:
Safety Equipment
Install sprinklers, fire alarms, fire extinguishers, and smoke detectors in the workplace. Smoke detectors can detect smoke in the vicinity; fire alarms generate sound and alert people about the danger; and sprinklers help extinguish the fire. Also, fire extinguishers help control the fire. This equipment is essential for the safety of a workplace and the people working there.
Clean Environment
Maintaining a clean environment is essential because clutter in the environment contributes to the spread of fire. A clean workplace offers space for people to move around freely, and in case of an emergency, it helps in quick
evacuation. A congested environment allows fire to spread easily and makes it harder for people to move and evacuate the place quickly. In case where the work involves extensive use of inflammable chemicals and items, it is advised to store them safely.
Faulty wirings and overloaded sockets are two of the most common causes of fires. Electrical cables should always be maintained by replacing the damaged ones quickly. Employees should be watchful regarding overheated equipment and strangely smelling electrical lines. When electrical appliances are not in use, they should be turned off. Warning signs are very important where high-voltage wires are stored.
Proper signs will help the employees know what they should do if they are in danger. Signs indicating the location of a fire extinguisher, emergency numbers, and the way to an emergency exit are essential for employees’ safety. They are the simplest techniques for spreading awareness, as people can easily comprehend what is being communicated.
Staff members should be aware of fire evacuation procedures and the precautions they need to take during a fire emergency. For this, fire drills should be conducted every three months by a certified professional who should inform the participants about safe evacuation techniques and how to use tools like fire extinguishers. Understanding safety measures can help avert disasters.
Chemicals should be stored in labelled, airtight containers, away from heat sources and incompatible substances, and in a well-ventilated area, following all the safety guidelines.
Employees should be instructed to refrain from using inflammable materials in the vicinity of explosive zones. Avoid sparks and open flames, use safe equipment, and make sure there is adequate ventilation to prevent explosions in hazardous locations.
It is the methodical process of detecting risks in the workplace, assessing the severity of the risk, and putting into place reasonable control measures to either eliminate or minimise such risks.









101 is the fire safety helpline number in India. By calling this number, you can get connected to the nearest fire station.

The well-being of workers is a crucial aspect of workplace safety, encompassing not only their physical health but also the condition of their internal systems, such as the respiratory, cardiovascular, and nervous systems. Health hazards exist in various work environments and can affect different parts of the body, often in ways that are not immediately visible. Many workplaces contain risks that may impact employees’ health. For instance, continuous exposure to high noise levels in industrial settings can lead to hearing impairment over time. Similarly, working in environments with intense lighting or exposure to harmful fumes and vapours can cause damage to the eyes and respiratory system. In more severe cases, prolonged exposure to hazardous substances can lead to chronic conditions, such as lung damage due to inhalation of toxic chemicals.
Identifying and mitigating these hazards is essential to ensure a safe and healthy working environment. Employers must take preventive measures such as providing protective gear, implementing safety protocols, and ensuring proper ventilation to minimise the risks associated with workplace hazards.
Working with computers for extended periods can pose various health risks if proper precautions are not taken.
Poor Posture and Musculoskeletal Issues
• Incorrect desk setups or prolonged sitting can cause discomfort and chronic pain.
• Repetitive movements (typing, mouse usage) may lead to muscle strain and fatigue.
Eye Strain and Vision Problems
• Prolonged screen exposure and glare can cause dryness, headaches, and blurred vision.
• Regular breaks, screen brightness adjustments, and proper lighting help reduce strain.
Cybersecurity Threats
• Risk of data breaches and online threats in digital workspaces.
• Safe online practices include avoiding suspicious links, using strong passwords, and protecting sensitive data.
Preventive Measures
• Maintain ergonomic seating and desk setup.
• Take periodic breaks for stretching and simple exercises.
• Follow cybersecurity guidelines to ensure physical and digital well-being.
Common sources include:
• Poorly Maintained Equipment: Broken machinery, faulty electrical outlets, and worn-out office furniture.
• Inadequate Lighting: Poor visibility increases the risk of accidents.
• Cluttered Workspaces: Loose objects and scattered cables can cause tripping hazards.
• Unsafe Handling of Chemicals: Improper storage and use of hazardous substances.
Handling Office Equipment
• Proper training on operating office machines.
• Routine checks to prevent malfunctions.
• Keeping workstations organised to avoid accidents.
Handling Heavy Objects
• Using correct lifting techniques to prevent injuries.
• Storing heavier items at waist level to reduce strain.
Workplace stress can result from excessive workloads, tight deadlines, or conflicts with colleagues. Employers should promote:
• Breaks and flexible schedules to reduce mental fatigue.
• Conflict resolution training to maintain a positive work environment.
• Wellness programs to support employee mental health.
A safe working environment includes:
Proper Ventilation: Clean air reduces respiratory issues.
Adequate Lighting: Prevents eye strain and improves focus.
Noise Control: Reduces distractions and enhances productivity.
Hazard control strategies include:
Elimination: Removing hazards entirely (e.g., replacing toxic chemicals with safer alternatives).
Substitution: Using a less hazardous option.
Engineering Controls: Installing ventilation systems, noise insulation, or proper workstation setups.
Administrative Controls: Implementing training programs and workplace policies.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Providing gloves, masks, helmets, and other protective gear.

Keep all work areas clean and organised to prevent accidents.
• Ensure that emergency exits remain accessible at all times.
• Follow fire safety protocols and evacuation plans.
• Store all cleaning chemicals in tightly sealed containers and place them in designated cupboards.
• Dispose of garbage daily to maintain hygiene and prevent hazards.
• Ensure that all areas are well-lit to reduce the risk of accidents.
• Avoid wearing loose clothing or jewellery when operating machines.
• Use protective gear (goggles, masks, gloves, safety glasses, hairnets, etc.) as required.
• Follow proper lifting techniques to prevent injuries.
• Do not distract individuals working near fire, machinery, tools, or equipment.
• Always turn off machines before leaving the workspace.
• Do not tamper with electrical controls or switches.
• Operate machines or equipment only after receiving proper training and authorisation.
• Inspect electrical equipment and repair damaged wires or plugs before use.
• Avoid using equipment that sparks, smokes, or appears damaged.
• Cover all food properly with a lid, plastic wrap, or aluminium foil.
• Do not smoke in designated ‘No Smoking’ areas.
• Report any unsafe conditions or actions to your supervisor immediately.
• Participate in regular safety training sessions to stay updated on best practices.
Poster Making on Safety Measures (Group Work)
Get into groups of five to six students each. Each group should choose one of the four situations given below. In your group, discuss the safety norms related to the selected situation that should be followed at the workplace to prevent accidents and protect workers. Design a poster mentioning the safety measures for the chosen situation and present it to the whole class.
Situation 1 – To avoid fire in a company
Situation 2 – To prevent your co-worker from slipping
Situation 3 – Safety norms for high-voltage areas
Situation 4 – Safety norms for working in a chemical factory
A Select the correct option.
1 Why is workplace safety important?
a To prevent accidents
c To improve employee well-being
2 Which of the following is NOT a common workplace hazard?
a Slippery floors
c Faulty electrical wiring
3 What is the purpose of a workplace security system?
a To prevent theft and unauthorised access
c To decrease the number of employees
B Fill in the blanks.
b To increase productivity
d All of these
b Ergonomic workstations
d Heavy machinery
b To increase work pressure on employees
d To eliminate the need for safety policies
1 helps employees feel secure and motivated at work.
2 Electrical hazards can be caused by wiring.
3 A workplace boosts employee morale and productivity.
4 Proper and help in preventing slips and falls.
C State whether the following is True or False. Correct the statements that are false.
1 Fire drills are unnecessary if there are fire extinguishers.
2 Cluttered workspaces can cause accidents.
3 Employees should only depend on management for their safety.
4 Proper ventilation and clean drinking water are not necessary for workplace health.

Answer the following questions.
Q1. Define workplace hazards and give two examples.
A1. Workplace hazards are potential sources of harm or danger that can cause injury, illness, or damage in a work environment. They can be physical, chemical, biological, or ergonomic in nature. Two examples are:
1. Slippery floors: Can cause slips and falls.
2. Faulty electrical wiring: Can lead to electrical shocks or fires.
Q2. Mention two ways organisations can promote mental well-being at the workplace.
A2. Organisations can promote mental well-being by:
• Encouraging work-life balance by allowing flexible working hours and regular breaks.
• Providing counselling services or mental health programs to help employees manage stress and emotional well-being.
Q3. Explain at least three workplace safety measures that help prevent injuries and accidents.
A3. Workplace safety measures are essential to ensure a secure and productive work environment. Three key measures include:
• Conducting Regular Safety Training: Employees should be trained on emergency procedures, first aid, and how to use safety equipment like fire extinguishers. This helps them respond effectively to workplace hazards.
• Providing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Employers should supply appropriate PPE such as gloves, helmets, safety glasses, and masks to prevent injuries from workplace risks.
• Ensuring Proper Housekeeping: Workspaces should be kept clean and free of hazards such as wet floors, clutter, or loose cables. Proper signage should be placed in hazardous areas to warn employees.
Q4. Rahul works in an IT company where employees complain of back pain and fatigue. What ergonomic changes should the company implement to improve workplace health?
A4. The company should provide ergonomic workstations, including adjustable desks, comfortable chairs, and proper screen heights. They should also encourage employees to take short breaks and maintain correct posture.
Q5. A factory worker notices exposed electrical wires near a wet floor area. What immediate actions should be taken to prevent an accident?
A5. The worker should report the issue to the management immediately, place warning signs around the area, and ensure the wires are repaired by a professional before resuming work in that space.
C 1. False. Fire drills are necessary even if there are fire extinguishers to ensure employees know emergency procedures.
2. True.
3. False. Employees should take personal responsibility for their own safety along with management efforts.
4. False. Proper ventilation and clean drinking water are essential for workplace health.
Cleanliness and good health in any workplace are a prerequisite for the motivation of employees. Good air quality and clean water enhance the capabilities of all workers to be focused and effective in their assignments. While air conditioning provides comfort in temperature in many offices, purification of air from dust and other impurities is equally important. Proper ventilation, regular maintenance of air filter systems, and introduction of indoor plants can improve air-quality.
Contamination of water is another issue to address by companies. Water-borne diseases increase absenteeism in the workplace, which in turn reduces productivity. Safe drinking water must be ensured by city organisations; factories, besides regular checking of their plumbing systems, should encourage hygienic practices amongst their employees.

A clean workplace can be said to include dust-free and clean desktops, proper disposal of waste material, and pest control, all of which combine to create a healthier and more productive work environment.
There are three kinds of pollution monitoring analyses used for air and water:
Physical Analysis: Observing the colour, smell, and temperature of air and water.
Chemical Analysis: Testing for the presence of harmful substances like increased carbon dioxide in the air or high pH levels in water.
Biological Analysis: Checking for bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms that can affect health.
By monitoring air and water pollution regularly, organisations can make timely decisions that help in keeping the environment clean.
For a healthy and pollution-free workplace, it is essential that companies should follow these steps:
Reducing Air Pollution
• Limit work practices that generate dust or toxic gases, indoor incineration of waste, high-emission, and inefficient machinery.
• Limit the number of vehicles into the office premises so that carpooling, cycling, or electric vehicles can be utilised.
• Organise a “No Vehicle Day” once a week to reduce emissions, public transport, or any alternative means of transportation, including walking.
• Ensure proper maintenance of air-conditioning units, ban the use of aerosol sprays, and provide eco-friendly cleaning products that minimise the release of such pollutants like ozone.
• Install air-purifying devices inside the workplace and encourage the use of indoor plants that help absorb the pollutants and particulate matter in the conventional air.
• Monitor air quality types regularly so that a workplace can be kept safe and healthy for its employees.
Preventing Water Pollution
• Ensure that all sewage and wastewater get a high-quality treatment before the final disposal, employing advanced filtration and recycling to decrease environmental hazards.
• Avoid excessive use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides; these chemicals often seep into the groundwater; promote organic alternatives in any landscaping done for the office.
• Provide filtration systems that will supply drinking water free from contaminants, and perform regular testing for water safety.
• Initiate conservation measures that may include awareness in water conservation, daily fixing of leaks in water systems, and installation of devices that reduce water consumption.
• Make sure industrial discharge and chemicals that cause contamination of water sources are safely disposed of.
• Encourage employees to join the campaign for water conservation, including rainwater harvesting, and to minimise plastic waste that pollutes water bodies.



Maintaining a clean workplace is essential not only for health and safety, but for performance and presentation. A disorganised work environment may lead to accidents, inefficiency, and a plethora of hazards to staff health. Good hygiene also fosters a sense of professionalism while generating an inviting atmosphere.

Bad personal hygiene in the workplace may also mean that germs spread, a lot of sick days undertaken by the staff, and a lot of things that would directly decrease productivity. Furthermore, dusty and cluttered workplaces can cause equipment to malfunction and may lead to its deterioration. Keeping cleanliness ensures workplaces are safer and more productive.
Following are a few major workplace cleanliness practices: Keeping the Work area Clean and Organised: Workers are supposed, from time to time, to keep their desks clear of clutter by putting files, tools, and other materials away. A tidy desk will help with less stress and more focus.
Cleaning the Floor: Spilled drinks, piles of papers, or loose wires can present a slip-and-fall hazard in the workplace. One way to avoid this is to clean up spills as soon as they occur and ensure that the floor is dry.
Keeping Walkways Free of Clutter: Blocked walkways with furniture, boxes, or cables can make tripping hazards, inhibiting people from passing smoothly. Hallways and emergency exits should remain unlocked to facilitate smooth movement and a swift response in case of emergencies.
Checking and Maintaining Lights and Fixtures Regularly: Good illumination is extremely important for good vision and safety. Bad lighting, such as over-burnt bulbs or flickering systems, can lead to eye strain and accidents.
Adopting Good Waste Disposal Practices: Trash bins should be placed in well-situated places and emptied frequently to mitigate the bad odour and discourage pests and vermin. Recycling should be encouraged to raise the environmental awareness of all.
Sanitising Shared Areas and Equipment: Frequent sanitisation of commonly used items such as keyboards, telephones, doorknobs, and the lunch area works to minimise the spread of bacteria and viruses.

























Ergonomics is the science of designing and arranging workplaces, products, and systems to fit the people who use them. It focuses on improving efficiency, comfort, and safety by reducing strain, fatigue, and the risk of injury. Ergonomics considers factors such as body posture, repetitive movements, lighting, and workstation layout to create a healthier and more productive work environment.
By applying ergonomic principles, organisations can enhance employee well-being, prevent musculoskeletal disorders, and boost overall performance.

So here are some common ergonomic problems and their causes along with effective solutions:
Problem
Cause
Sore lower back There is either no lower back support or poor posture
Stiff neck Looking at the monitor uncomfortably, that is, from an angle
Wrist pain Incorrect keyboard height or absence of wrist support
Dry eyes Not blinking enough, staring at the screen for too long
Eye strain Bright screen, glare, or improper lighting
Shoulder pain Poor desk or chair height, unsupported arms
Solution
Put in place a backrest, small pillow, or ergonomic chair that has lower back support. Maintain a proper posture while seated.
Position the monitor at eye level, distance of an arm length away, do not tilt your neck.
Use a wrist rest, adjust keyboard position, and ensure elbows are at a 90-degree angle.
Take breaks regularly (20-20-20: Every 20 minutes, look at an object 20 feet away for 20 seconds), blink often, and use artificial tears or eye drops if needed.
Adjust the brightness of the screen, and use an antiglare filter, get the screens located further from the light source directly behind them, and ensure ambient lighting is proper.
Adjust the chair height so that the arms of the user lie on the desk. If available, use an armrest to assist.
Tingling in fingers Long typing without breaks, improper wrist position Practice taking breaks frequently, stretch those fingers and hands, and have the wrist in a neutral position while typing.
Leg discomfort Sitting for long periods without movement
Use a footrest so that feet can be flat on the floor, and take short breaks to walk every now and then.
By following a few ergonomic principles, employees can enhance their comfort, productivity, and overall health at work while sidestepping the risk of work-related injuries:
Use a Chair That Can Be Adjusted: A chair that is adjustable for height, armrest position, and lumbar support can be set at the right height and in the proper posture for reducing pressure on the body.
Keep Feet Flat: Allowing both feet to be flat on the floor helps relieve stress leg strain and improve circulation.
Maintain Proper Posture As Much As Possible: Keeping the back straight, relaxing the shoulders, and holding the wrist in a neutral position while working at a comfortable distance from the body can help reduce strain on muscles and joints.
Take Short Breaks: Throughout the day, take time out to stretch and stand up; go around a bit now and then; preferable frequently every hour to keep from becoming stiff and fatigued.
Use Ergonomic Accoutrements: Try one of the many ergonomic keyboards, mouse, or standing desks to support better posture and lessen discomfort.
Arrange the Workspace: Keep frequently used items within a hand’s reach to avoid overstretching and reaching.
Computers have become an essential part of our daily lives, but prolonged use can lead to several health and safety issues. These problems can affect not only physical well-being but also mental health and overall productivity.
By following proper ergonomic practices and safe computer usage guidelines, individuals can minimise discomfort and prevent injuries.
Sitting for long hours with poor posture can cause pain and stiffness in the neck, back, and shoulders. This discomfort can lead to chronic musculoskeletal disorders if not addressed.
The following are some prevention tips:
Adjust Your Chair and Monitor: Ensure the top of the screen is at eye level and about an arm’s length away. This prevents neck strain caused by looking too high or too low.
Maintain a Neutral Posture: Sit with your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and elbows at a 90-degree angle to reduce strain on muscles.
Position the Keyboard and Mouse Correctly: Keep them at a height where your wrists remain straight and relaxed while typing or clicking.
Take Frequent Breaks: Stand up and stretch every 30–60 minutes to relax your muscles. Simple neck and shoulder stretches can reduce stiffness and improve circulation.
Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS)
Occupational overuse syndrome, is also known as repetition strain injury (RSI).
It is defined as performing the same movement repeatedly—such as typing, clicking a mouse, or using a touchscreen. It can cause pain, numbness, and inflammation in the fingers, wrists, and arms.
The following are some prevention tips:
Keep Wrists Straight while Typing: Avoid bending your wrists upward or downward to prevent unnecessary pressure on the joints.
Avoid Gripping the Mouse Too Tightly: Hold it gently to reduce muscle tension. Using a larger mouse can help prevent overuse of small hand muscles.
Use an Ergonomic Keyboard and Mouse: These accessories are designed to reduce strain on the hands and wrists. A split keyboard, for example, allows a more natural hand position.

Sitting for long periods without moving can cause poor circulation, leading to swelling, numbness, or even deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in severe cases.
The following are some prevention tips:
Keep Feet Flat on the Floor or Use a Footrest: This helps maintain proper blood circulation and reduces leg fatigue.
Avoid Crossing Your Legs for Long Periods: This can restrict blood flow and lead to numbness or discomfort.
Stand up and Stretch Every Hour: Simple exercises like calf raises, ankle circles, or walking a few steps help improve circulation.





Staring at a screen for too long can cause dry eyes, blurred vision, and headaches. This condition is often referred to as Computer Vision Syndrome (CVS).
The following are some prevention tips:
• Adjust screen brightness and contrast to comfortable levels to minimise eye strain. A screen that is too bright or too dim can lead to discomfort over time.
• Reposition the screen to reduce glare from overhead lights, windows, or other bright surfaces. Using an antiglare screen protector can also help.
• Maintain a proper viewing distance by keeping the monitor about 18 to 24 inches (45 to 60 cm) from your eyes. The top of the screen should be at or slightly below eye level.
• Blink frequently to keep your eyes moist and prevent dryness caused by prolonged staring. Consider using artificial tears if your eyes feel dry.
• Wear anti-glare glasses or blue light-blocking lenses when working on a computer for long periods to reduce strain and protect against harmful light exposure.
• Keep your screen clean by regularly wiping away dust and fingerprints, which can cause visual discomfort. A clean screen ensures clear visibility.
• Use appropriate lighting such as a desk lamp with soft lighting to improve visibility and reduce contrast issues between the screen and the surrounding environment.
• Choose comfortable screen settings with text that is sharp and easily readable. Adjust font size, contrast, and background colour for better visibility.
• Take regular eye breaks following the 20-20-20 rule—every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet (6 meters) away for at least 20 seconds. This helps reduce eye fatigue.
• Position your monitor properly to avoid reflections from sunlight or artificial lighting. Use curtains, blinds, or reposition your desk if necessary to minimise glare.
Frequent headaches can result from muscle tension, poor posture, or eye strain caused by prolonged screen exposure. Staring at a bright screen for extended periods, incorrect monitor positioning, and uncorrected vision problems can all contribute to discomfort.
To reduce the risk of headaches:
• Ensure proper posture by keeping your neck aligned with your spine while working.
• Adjust screen brightness and contrast to a comfortable level to prevent eye strain.
• Schedule regular eye exams to detect and correct any vision problems that might contribute to headaches.
• Stay hydrated and take short breaks to stretch and relax your muscles.
Prolonged use of computers can lead to a lack of physical activity, increasing the risk of obesity and related health concerns. In children, excessive screen time is a significant contributing factor to weight gain, as it reduces time spent on outdoor activities and exercise.
To maintain a healthy balance:
• Incorporate regular movement into your daily routine— stand up, stretch, or walk around every hour.
• Engage in physical activities such as jogging, cycling, or sports to counteract the sedentary effects of computer use.
• Maintain a healthy diet by avoiding excessive snacking while using a computer.
• Set screen time limits, especially for children, and encourage outdoor play and physical activities.
Excessive screen time and workplace pressure can lead to increased stress levels, affecting both mental and physical health.
Stress caused by prolonged computer use may result in:
• Difficulty concentrating and reduced attention span.
• Increased fatigue, dizziness, and burnout.
• Sleep disturbances due to excessive exposure to blue light before bedtime.
• Emotional strain, irritability, and anxiety over workload or deadlines.
To manage and prevent stress-related issues:
• Take frequent breaks and practice deep breathing or relaxation techniques.
• Engage in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or mindfulness exercises.
• Follow a balanced schedule with time allocated for work, leisure, and rest. Make time for hobbies and personal activities.
• Talking to someone can ease mental strain and improve well-being. If stress becomes overwhelming, seek professional help and explore treatment options, including therapy or prescribed medication if needed.
Laptops offer portability and convenience, making them a preferred choice over desktop computers. However, prolonged laptop use can lead to discomfort, strain, and injuries due to poor ergonomics. Unlike desktops, where the screen and keyboard can be adjusted separately, laptops have a fixed design that often forces users into awkward postures.
The increasing use of laptops has led to a rise in musculoskeletal issues such as neck pain, back pain, wrist strain, and eye fatigue. Since laptops are designed for shortterm use, long periods of working on them without proper adjustments can cause:
• Neck and back pain from constantly looking down at the screen.
• Wrist and shoulder strain due to improper keyboard and trackpad positioning.
• Eye strain and headaches from poor screen positioning and prolonged screen time.
• Overheating-related discomfort when using laptops on laps or soft surfaces.

• Use a laptop docking station or an external monitor, when possible, to maintain a comfortable screen height and posture.
• Opt for a wireless keyboard and mouse to allow flexible positioning and reduce strain on wrists and shoulders.
• Use a cushioned wrist rest to prevent strain while typing and reduce pressure on the median nerve, lowering the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
• Angle your keyboard slightly to keep your wrists in a neutral position, reducing tension on your forearm muscles.
• Keep your laptop cool by ensuring proper airflow—avoid placing it on pillows or blankets, which can block vents and cause overheating.
Good and ergonomic workstation design prevents discomfort, fatigue, and the development of long-term health problems. The basic ergonomic and safety needs to be met are for screens, regardless of whether it is a desktop, notebook, tablet, smartphone TV, or video monitor, to allow for user well-being and productivity.
Display Screen (Monitor)
• Modern LED or LCD monitors of sufficient size with adequate spacing between characters and lines should be used.
• The display could not flicker or distort and hence is one of the greatest causes of eye strain.
• Glare screen protectors or anti-glare coatings can save oneself from reflections or other visual problems to enhance visibility.
• Adjust screen brightness and contrast to lessen eyestrain.
• Centre the monitor so as to be in line with the eyes and maintain an arm’s distance to avoid neck strain.
Keyboard

• Keyboard positioned so that it is adjustable and is kept at a distance from the screen to allow for the natural resting position for both hands and fingers, so no wrist strain.
• A slight angle of inclination for the keyboard and adequate wrist support will help avoid tension in the upper limbs and hands.
• The keys not too far to read even while typing, should be high contrast and have a clear identification.
• Matt finish prevents glare from the keyboard which contributes towards distractions and eyestrain.

• Use of an ergonomic mouse or touchpad to reduce repetitions of work strain injuries.
• The desk should be spacious, stable, and low-reflective surface for reduced glare and arranged in flexible placements of equipment.
• Document holders should be adjustable and positioned at eye level to avoid often moving the head up and down and from side to side.
• The desk has to have enough room for all necessary equipment so that users can keep their work areas uncluttered and organised.
• The chair must be stable, height-adjustable, and support the lower back to promote a good posture.
• The users must be at least flat-footed on the floor or must be able to use a footrest for support.
• Make it easy for users to move around in the chair and encourage them to shift positions now and then in order to avoid stiffness.
• There must be plenty of space in which free movement can occur; this would allow users to assume different postures during the working day.
• Users must be able to stretch and change their sitting position without any restriction.
Illumination
• The workstation must have sufficient lighting so that there is adequate contrast between the screen and surroundings.
• Reflective surfaces separate lighting glare from the monitor by placing the monitor perpendicular to the window rather than directly toward the window, providing adequate blinds or curtains to control natural lighting.
• Do not sit in front of a bright light source, such as a window, overhead lighting, or shiny surfaces reflecting on the screen.
Noise and Thermal Comfort





• If the use of machines is unavoidable, noise from equipment must be kept within limits, lest it distract users. If not, they may have to use noise-cancelling earphones to keep their minds focused.
• No equipment should get unduly hot, as it may be uncomfortable and inefficient. The equipment must have a good ventilation and cooling system to control the amount of heat generated.
It is important to handle computers and electrical devices safely to prevent accidents and equipment damage.
• Always unplug devices before repairing them. This prevents electric shocks and protects the components from accidental damage.
• Keep cords organised to avoid tripping hazards. Using cable organisers helps in keeping wires neatly arranged and prevents unnecessary accidents.
• Never use electronic devices with wet hands. Water and electricity are a dangerous combination and may cause serious harm.
• Use surge protectors to prevent damage from power fluctuations. This safeguards devices from sudden voltage spikes and extends their lifespan.



Activity 1: Workplace Cleanliness Survey (Individual Activity)
Ask students to observe the cleanliness of their classroom or home workspace. Have them check for factors like desk organisation, waste disposal, air quality (dust levels, ventilation), and lighting conditions. Instruct students to note three areas that need improvement and suggest practical ways to enhance cleanliness and productivity. Conduct a class discussion where students share their observations and recommendations.
Activity 2. Ergonomic Workstation Setup (Group Activity)
Divide the class into six groups. Each group will assess their study or computer workstation at home or in school based on ergonomic principles. Ask them to evaluate chair height, monitor positioning, wrist support, and overall comfort. Encourage students to make necessary adjustments, such as repositioning their monitor to eye level or using a cushion for back support. Have them write a short reflection on how these changes improved their comfort and posture.
A Select the correct option.
1 Which of the following is NOT a type of pollution monitoring analysis?
a Physical Analysis
c Mechanical Analysis
2 What is one way to reduce air pollution in the workplace?
a Increase indoor incineration of waste
b Chemical Analysis
d Biological Analysis
b Use high-emission machinery
c Install air-purifying devices and indoor plants d Allow unrestricted vehicle entry into office premises
3 Why is good air and water quality essential in the workplace?
a To make the office look good
c To reduce electricity bills
B Fill in the blanks.
b To improve employee focus and effectiveness
d To eliminate all types of pollution completely
1 A clean workplace includes desktops, proper waste disposal, and pest control.
2 analysis involves checking for bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms in air and water.
3 Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS) is also known as .
4 To prevent water pollution, offices should encourage as an alternative to chemical pesticides.
C State whether the following is True or False. Correct the statements that are false.
1 Poor workplace hygiene can lead to increased productivity.
2 The 20-20-20 rule suggests taking a break every 20 minutes, looking at an object 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
3 Reducing the use of aerosol sprays helps in maintaining clean air in the workplace.
4 Sitting in one position for a long time improves posture and prevents health issues.
D Answer the following questions.
Q1. What are the three types of pollution monitoring analysis used for air and water?
A1. The three types of pollution monitoring analysis used for air and water are:
• Physical Analysis: Observing the colour, smell, and temperature of air and water.
• Chemical Analysis: Testing for harmful substances like increased carbon dioxide in the air or high pH levels in water.
• Biological Analysis: Checking for bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms that can affect health.
Q2. List two ways to maintain cleanliness in a workplace.
A2. Two ways to maintain cleanliness in a workplace are:
1. Keeping the work area clean and organised by regularly clearing clutter and properly storing materials.
2. Adopting good waste disposal practices, such as using trash bins efficiently and promoting recycling.
Q3. Explain the importance of office ergonomics and list three common ergonomic problems along with their solutions.
A3. Office ergonomics improves employee health, productivity, and comfort by preventing injuries, reducing fatigue, and enhancing efficiency. It also helps minimise the risk of musculoskeletal disorders.
Three common ergonomic problems and their solutions:
• Sore Lower Back: Caused by poor posture or lack of support.
Solution: Use an ergonomic chair with lumbar support or a small pillow.
• Eye Strain: Due to screen brightness, glare, or improper monitor placement.
Solution: Adjust brightness, use an anti-glare screen protector, and position the monitor at eye level.
• Wrist Pain: Caused by incorrect keyboard height or lack of support.
Solution: Use a wrist rest, adjust keyboard height, and keep wrists in a neutral position.
Q4. A company notices that many employees are suffering from frequent headaches and dry eyes. What measures can be taken to address this issue?
A4. The company should adjust screen brightness and contrast, encourage employees to follow the 20-20-20 rule, and provide anti-glare screen protectors. Ensuring proper lighting and regular eye breaks can also help reduce strain.
Q5. An office manager wants to improve air quality in the workplace. Suggest three measures that can be implemented.
A5. The office manager can:
• Install air-purifying devices and indoor plants to absorb pollutants.
• Reduce the use of aerosol sprays and encourage eco-friendly cleaning products.
• Ensure regular maintenance of air-conditioning units and ventilation systems.
C 1. False. Poor workplace hygiene can lead to decreased productivity.
2. True.
3. True.
4. False. Sitting in one position for a long time can cause posture-related health issues.


and emergencies can strike anytime and anywhere, even when they are least expected. Therefore, it is important to take the necessary precautions. To tackle such accidents and emergencies, organisations follow safety plans to keep their people safe and secure. Also, policies and procedures are laid out to make sure that the business is able to recover from such incidents.
An accident is an unplanned, unexpected, and unintended event that typically results in damage or injury. When someone’s body suffers physical harm or damage due to an accident or attack, it is called an injury. Both accidents and injuries can take place anytime or anywhere and can even lead to fatalities. Therefore, it is important to control such accidents at workplace and make sure that minimal harm is caused to the people involved in them. A workplace accident cannot be anticipated by anyone and threatens the safety of every individual associated with the organisation including the employees, employers, and customers. It can cause serious physical or environmental damage and even disturb the functioning of an organisation.
There can be different types of accidents and the impact of these accidents can also vary from person to person.
Vehicle-related Accidents Accidents and serious injuries due to the crashing of vehicles on and off the premises happen quite frequently. Such accidents usually involve cars, trucks, or even small vehicles. These accidents and injuries can have a long-lasting impact on the people affected by them.
Machine-related Accidents While operating, maintaining, or cleaning the machines and equipment, workers can get injured. These results are due to inadequate training, a lack of safety equipment, and malfunctioning equipment. Sometimes, workers get pulled inside the equipment or get crushed while shifting or rolling the equipment.
Slips, Trips, and Falls Accidents or injuries can happen when an employee slips on a wet or slippery floor while walking or running. They can either fall from heights or trip over obstacles, such as protruding nails and boards, bunched-up floor mats, uneven stairs, etc.
Fire and Explosions At any workplace or organisation, accidents might occur due to fire or other explosive substances. There can be different reasons for such explosions, such as faulty electrical systems, gas leaks, or improper storage of flammable materials.
Violence Any kind of physical argument or confrontation can turn into violence at the workplace. Some industries such as healthcare, law enforcement, etc. are at risk of violence and assaults from customers, coworkers, or outsiders.
Chemical Spillage Workers can be exposed to hazardous chemicals and toxic fumes due to accidental spills, which can lead to respiratory problems, irritation in the eyes or skin, chemical burns, and other health issues.
Structural Collapse An accident where the infrastructure of any organisation collapses or is disrupted is known as a structural collapse. This can injure the people working in the organisation due to the collapse of a roof or a wall.
Electrical Incidents Accidents involving electric shocks or burns fall under the category of electrical incidents. Electrocution can result from faulty wiring, damaged equipment, or improper use of electrical devices.
Confined Space Accidents When workers enter confined spaces, such as tanks or sewers, they are at a high risk due to a lack of oxygen, toxic gases, and other physical hazards. These situations are highly dangerous.









An emergency is a sudden and often unforeseen situation or event that needs immediate attention and action. An emergency situation might pose a sudden risk to life, property health etc. and needs intervention to mitigate the losses and reduce the negative consequences.
A situation of emergency can:
1. threaten the employees, customers, or the public
2. disrupt or shut down the operations
3. cause physical or environmental damage
There are various types of emergencies that may occur at home, school, or workplace. Hence, it becomes essential requirement to have an emergency plan to minimise their consequences.
Natural Disasters These include accidents or events that are caused by nature and are often uncontrollable. They pose a threat to human life, property, and the environment.
Earthquakes: Sudden shaking of the ground caused by the movement of tectonic plates.
Floods: Overflow of water onto normally dry land, often due to heavy rainfall, storm surges, or dam failures.
Wildfires: Uncontrolled fires in forests, grasslands, or urban areas, often exacerbated by dry conditions and high winds.
Tsunami: A series of large ocean waves generated by sudden and powerful disturbances beneath or near the ocean’s surface. (continued...

Weather-related Emergencies
These are situations that arise due to extreme or unusual weather conditions.
Medical Emergencies
Public Health Emergencies
These are sudden and often life-threatening situations that require immediate medical attention.
Severe Storms: Thunderstorms, hailstorms, and blizzards that can cause damage, power outages, and transportation disruptions.
Extreme Heat or Cold: Prolonged periods of excessively high or low temperatures, posing health risks.
Tornadoes: Violently rotating columns of air extending from thunderstorms to the ground.
Hurricanes, Typhoons, and Cyclones: Powerful tropical storms with strong winds and heavy rains.
Cardiac Arrest: Sudden loss of heart function, requiring immediate CPR and defibrillation.
Stroke: Sudden interruption of blood flow to the brain, necessitating rapid medical attention.
Severe Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis due to allergies, often requiring epinephrine administration.
These are situations or events that pose significant risks to the health and well-being of a community, region, or even the entire population. These emergencies can be caused by infectious diseases, environmental factors, or other health-related issues.
Security and Safety Emergencies
Fire Emergencies
Environmental Emergencies
They encompass a range of critical situations that pose safety and security related threats to individuals, organisations, or communities.
They are critical situations that involve the uncontrolled outbreak of fire, posing risks to people, property, and the environment
They are critical events or situations that have the potential to cause significant harm to the environment, wildlife, and human health.
Pandemics: Widespread infectious disease outbreaks, such as COVID-19.
Epidemics: Regional outbreaks of contagious diseases.
Biological Threats: Deliberate release of biological agents or accidental exposure to hazardous materials.
Terrorist Attacks: Acts of violence or sabotage carried out by individuals or groups for political, religious, or ideological reasons.
Civil Unrest and Riots: Public demonstrations escalating into violent or destructive events.
Building Fires: Uncontrolled fires in residential or commercial structures.
Wildfires: Uncontrolled fires in natural areas.
Oil Spills: Accidental or deliberate release of oil into the environment, posing ecological and economic risks. Chemical Contamination: Pollution or exposure to hazardous chemicals in the environment.
Think about any natural disaster that you have witnessed or heard about. Discuss its impact with your classmates.
Various safety measures can help prevent accidents and emergencies from occurring at a workplace. These measures include following the right procedures and training the staff adequately. Creating a safe workplace is a continuous process that requires commitment from all levels of the organisation. Here are a few ways to prevent accidents:
1. Risk assessment is an integral part of the safety measures required to prevent accidents. It is important for employers to identify potential hazards at all locations through regular inspections and risk assessments.
2. Organisations should ensure the supply and maintenance of proper protective equipment, like helmets, gloves, safety goggles, etc., to avoid any dangerous exposure to hazardous substances.
3. Employees should always be alert and attentive. They should be involved in safety programs, and their feedback should be recognised immediately.
4. There is a need to implement comprehensive safety policies and procedures regarding different hazards. All employees should be equipped with proper training and information regarding these policies.
5. Use clear and visible signage to indicate hazardous areas, safety precautions, and emergency procedures.
6. An emergency response plan, along with emergency evacuation strategies, should be developed and communicated effectively to all employees.
7. Practice drills should be conducted regularly in the workplace. Everyone should be aware of the evacuation routes, procedures for reporting injuries, emergency alarms, meeting points, etc.
8. All the machinery, tools, and equipment should have a maintenance schedule and be monitored accordingly. Any defects or malfunctions should be addressed promptly.
9. Foster open communication regarding safety concerns and encourage employees to voice their ideas for improvement. Update your safety policies regularly as per the latest technology and feedback.
Handling accidents effectively at a workplace is extremely important because they can occur anytime, in spite of safety measures or regulations in place. When such a situation arises, it should be handled carefully without blaming any particular individual. Effective accident management involves a timely response to minimise the harm caused and prevent future accidents. The following steps should be followed to handle an accident at the workplace:
Ensure Immediate Safety It will always be the first priority to ensure the safety of the injured or affected individuals and distance them from any ongoing hazardous situation.
Call for Medical Assistance If there are multiple or severe injuries in an accident, emergency services should be called for medical assistance. They should be informed about the number of injured individuals and the nature and extent of their injuries.
Provide First Aid Trained first aiders should provide immediate first aid to the injured individuals and try to stabilise their condition until medical help arrives.
Secure the Accident Scene The accident site should be isolated or cordoned off in case of serious accidents to avoid any further damage. The equipment should be shut down if necessary.
Notify Relevant Authorities Management or supervisors should be informed immediately without any delay so that they can initiate appropriate response procedures and coordinate with higher authorities as required by law.






























Document the Accident Accident should be documented accurately with all the details in place, like the date, time, location, individuals involved, witnesses, etc. This documentation will be helpful for further investigation and understanding the causes of the accident.

Support Injured Workers Support injured employees financially or provide them with good medical treatment, if necessary. Make a plan for them to return to work as per their convenience.
Conduct a Detailed Investigation After ensuring the well-being of all the employees, conduct an investigation to find out the root cause of the accident. Use any preserved physical evidence to identify the exact reason behind such a dangerous situation.
Implement Corrective Actions After the investigation is successfully conducted, implement corrective actions on the basis of the findings. It may include changes in procedure, equipment, safety protocols, or training in order to prevent such accidents.
Review and Improve Safety Protocols Safety policies and procedures should be regularly reviewed and improved according to the lessons learnt from accidents and new proactive measures should be incorporated.
Injuries can happen to anyone at any time, from a minor cut to a serious accident, and we do not always have a doctor or a hospital nearby. First aid is the first and immediate care or assistance given to an injured person right after the accident or until hospital assistance arrives. First aid’s main objectives include preserving lives, preventing the condition from worsening, and facilitating recovery, with trained individuals providing initial assistance. It contains all of the basic medicinal aspects required for dealing with an immediate crisis. First-aid kits are mandatory in every location, and the government recommends that they be kept everywhere, including school, home, or the office. Using a first-aid kit is a life skill that requires a blend of common sense and simple technology.
Dial 108 for calling an ambulance in case of a medical emergency.
First aid is necessary in an emergency situation because it helps conceal wounds and treat minor injuries until medical assistance arrives.
The following are some further reasons why first aid is important: Life Skill
First aid is a basic life skill that everyone should learn. Injuries are not optional; they can occur at any time, and one should be prepared to handle such situations in a medically appropriate manner.
Life
Every year, many individuals lose their lives due to lack of first-aid knowledge. First aid can help control injuries in the early stages and, if administered promptly, can save lives. Heart attacks and choking are two of the most common life-threatening conditions, and first aid has the potential to save lives from these two.
Nobody can foresee an accident, and they can occur in schools, at workplaces, or even on the road. Keeping a first-aid kit can be beneficial in reducing the impact of some major accidents.
When someone is hurt, every second counts, and if those seconds are wasted on calling the hospital and waiting for them to arrive, then that person can die. First aid can help treat the injury at the initial stage. For example, if a person is hurt in an accident and is bleeding excessively, his life can be saved by controlling the bleeding immediately by covering it with cotton and a medical gauge; otherwise, a person can lose his life due to blood loss.
Imagine that one of your coworkers fainted in front of you at work. How will you provide first aid to them?
At a workplace, any accident or injury can happen that needs immediate treatment and cannot be delayed until reaching the hospital. These situations can occur at the workplace and require immediate first aid:
• Seizures
• Accidents
• Cuts
• Heart attacks
• Food Poisoning
• Burns
• Bites and stings
• Sprain
• High fever
• Other medical emergencies
A first-aid kit is a box that contains all the necessary supplies to provide initial treatment for injuries, illnesses, and emergencies. A well-stocked first-aid kit helps to respond effectively and quickly to situations ranging from minor injuries to serious medical conditions.
A basic first-aid kit should contain the following items:
• Bandage
• 10 adhesive cloth tapes
• A bottle of antiseptic liquid
• A thermometer
• Instant heat and cold pack
• An antibiotic ointment
• Cotton
• Scissors
• Tweezers
• A packet of pain reliever tablets
• Surgical gloves








These are the benefits of providing first-aid training to the employees:
Rapid Response in Emergency





All jobs may not be hazardous in nature, but it is the responsibility of all employers to keep their workers safe and provide a secure working environment. The employer has a moral and legal duty to ensure that workers receive first-aid instructions.
When staff members are trained in first aid, they can assist one another and act more quickly in an emergency. They learn about the procedures to follow and how to lower the risk of suffering a serious illness or injury.
First-aid training makes workers more aware of workplace safety, which reduces accidents and injuries because they take the necessary precautions and are informed of what to do in an emergency.

If employees are trained regarding first aid, then they are safe at the workplace and also at home. They can assist a friend or relative; they can educate others about safety; and in the event of an accident or other emergency, they can help their family members and friends.
Adhere to Legal Obligations
Every employer who offers first-aid instruction at the workplace adheres to the law, which specifies that employers are required to train staff members and set up first-aid kits, tools, and other safety equipment at the workplace.
Physical Hazards Unequipped Construction Site
Chemical Hazards Pesticide use in agriculture
Biological Hazards Taking care of a patient who is infected by a communicable disease
Ergonomic Hazards Improper office workstations
Psychosocial Hazards Medical professionals or policemen
Fire and Electrical Hazards Faulty wiring in a shop
Workers may fall, leading to injuries.
Improper handling can harm agricultural workers’ health and can cause diseases like skin irritation, rashes, etc.
Risk of contracting diseases like COVID-19 due to inadequate protection while patient interactions.
Poor ergonomics or repetitive tasks can cause back and neck pain.
Stress can affect mental health and well-being.
Fire risk increases due to a poor electrical setup.
Understanding these diverse sources of hazards in the workplace is crucial for both employers and employees. By identifying and preventing these risks, we can collectively create safer and healthier work environments, ultimately promoting employability skills that prioritise the well-being of the workforce. This chapter will delve deeper into strategies and practices to protect health and safety at the workplace, empowering learners with the knowledge to thrive in their careers while safeguarding their physical and mental health.
Evacuation during a hazard refers to the systematic and organised process of moving individuals, employees, and occupants out of a workplace to a safer area around it when there is a potential threat to their health and safety. This is a critical aspect of ensuring the well-being of employees and visitors in any workplace, as it helps mitigate serious risks and minimise the harm caused by various types of hazards.
General evacuation procedures are essential to ensure the safety of employees when a workplace hazard or an emergency situation occurs. These procedures provide a structured and organised way for everyone to leave the workplace quickly and safely. Here are the general steps involved in evacuation procedures:
Alert Everyone When a hazard is detected, the first step is to alert everyone in the workplace. This can be done through fire alarms, sirens, or other audible signals. In some cases, verbal announcements or messages through the intercom system may also be used to inform employees about the emergency.
Stay Calm It’s crucial for everyone to stay calm and avoid panic. Panic can lead to chaos and make the situation more dangerous.
Follow Designated Evacuation Routes Workplaces typically have designated evacuation routes marked with clear signs and illuminated exit signs. Employees should familiarise themselves with these routes in advance and follow them during an evacuation. These routes are chosen to minimise exposure to hazards and provide the safest path to exits.
Do Not Use Elevators Elevators can be dangerous during emergencies, as they may malfunction or become non-operational. It’s a standard practice to avoid using elevators and use stairs instead.
Assist Others If possible, help colleagues or visitors who may have mobility issues or need assistance in evacuating. However, prioritise your own safety and do not put yourself at risk.
Gather at Assembly Points Once outside the building, employees should gather at predetermined assembly points that are a safe distance away from the place of hazard. These assembly points are typically located in open areas where emergency personnel can account for everyone and provide further instructions.
Do Not Re-enter the Building Under no circumstances should employees re-enter the building until it has been declared safe by authorised personnel. Re-entering too soon can expose individuals to ongoing situations.
Follow Instructions During the evacuation, employees should listen to instructions from designated personnel, such as fire wardens or emergency responders. These individuals are trained to manage emergencies and will provide guidance on what to do next.
Account for Everyone Employers are responsible to account for all the employees and visitors following an evacuation. They will often have procedures in place to track who were safely evacuated and who may still be inside the building.
Wait for the All-clear Instruction Once the hazard is resolved or the situation is deemed safe, employees will be allowed back into the building. Until then, it’s essential to remain at the assembly point.
Activity 1: Role Play on Accident Management (Group Work)
Divide the class into six groups. Each group will be allotted different types of accidents that can occur in a workplace, as listed below. They will perform a role-play and illustrate the appropriate ways to deal with the particular accident.
Group 1 — Fire or explosion at the workplace
Group 2 — Any electrical incident at the workplace
Group 3 — Falling or tripping at the workplace
Group 4 — Structural collapse at the workplace
Group 5 — Machine-related accidents at the workplace
Group 6 — Vehicle-related accidents at the workplace
Activity 2: School Evacuation Drill (Group Work)
Conduct a simulated evacuation drill at your school. Follow the designated evacuation routes and gather at the assembly point on the school grounds. Afterwards, discuss the experience of the evacuation and suggest any improvements for a safer evacuation process.

A Select the correct option.
1 What is an unplanned or unintended event called that results in injury or damage?
a Emergency
c Accident
b Sickness
d Safety
2 Which of the following can be a cause of a fire emergency?
a Uneven stairs
c Water spilled on the floor
b Faulty electrical equipment
d Roof collapse
3 Which of the following steps should not be followed while handling an accident?
a Call for medical assistance
c Secure the accident scene
B Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
b Notify the concerned authorities
d Do not give first aid to the injured
1 is a box that contains all the necessary supplies to provide initial treatment for injuries, illnesses, and emergencies.
2 is a widespread outbreak of an infectious disease.
3 An accident where the infrastructure of any organisation is disrupted is known as
4 Foster open regarding safety concerns and encourage employees to voice their ideas.
C State whether the following is True or False. Correct the statements that are false.
1 A workplace emergency can be anticipated by everyone.
2 An employee can get injured by slipping on a wet or slippery floor.
3 Accidents should be adequately documented with all the details in place.
4 Emergency drills should not be taken seriously.
D Answer the following questions.
Q1. What are the different types of accidents that may occur in an organisation?
A1. Various types of accidents that may occur in a workplace are:
• Slips, trips and falls
• Structural collapse
• Machine-related accidents
• Fire and explosions
• Vehicle-related accidents
• Electrical incidents
Q2. What do you understand by natural disasters? Give a few examples.
A2. Natural disasters include accidents or events that are caused by nature and are often uncontrollable. They pose a threat to human life, property, and the environment. They can have devastating consequences but can be mitigated through preparedness, mitigation efforts, and effective responsive strategies. For example, earthquake, droughts, tsunami, or floods.
Q3. Reena works for a multinational organisation. One day, she was running late, and unfortunately, the elevator was also not working. In a hurry, she failed to notice that the stairs were wet and sprained her ankle while tripping on them. What measures can be taken by the organisation to handle Reena’s case and avoid such scenarios in the future?
A3. Various steps can be taken by the organisation to help Reena and avoid such instances in the future:
• Medical assistance should be called immediately so that the doctor could ensure that there was no serious injury.
• Any trained employee should give first aid to Reena immediately to stabilise her condition until medical help arrives.
• The housekeeping staff should be given strict instructions by the authorities to place precautionary signs at necessary places to avoid such accidents in the future.
Q4. Imagine you are a Safety Officer in a manufacturing company. During a routine safety drill, you notice that some employees hesitate to follow the designated evacuation routes and instead try to retrieve their personal belongings. How would you address this situation, and what steps would you take to ensure a safer evacuation in the future?
A4. In addressing this situation, my primary concern is the safety of all employees. I would take the following steps:
• Immediate action: During the drill, I would immediately remind employees that safety is the top priority and that they should leave personal belongings behind.
• Feedback and education: After the drill, I would gather feedback from employees to understand their concerns and reasons for hesitating. This would help identify any specific issues that need to be addressed.
• Training and awareness: I would conduct additional training sessions to emphasise the importance of following evacuation procedures, including leaving personal items behind. Visual aids and real-life examples can help prove this point.
• Regular drills: To reinforce the importance of following designated routes, we would conduct more frequent and surprise evacuation drills. This practice helps employees become more familiar with the process and reduces hesitation during real emergencies.
• Individual support: For employees who may have mobility issues or other concerns about leaving personal items behind, I would work with them individually to develop a plan that ensures their safety while still following evacuation procedures.
• Communication: Continuous communication about the importance of safety and adherence to procedures, both within the workplace and through safety campaigns, would be essential.
By taking these steps, we can create a safer work environment where employees can understand the significance of following evacuation procedures and prioritise their well-being during emergencies.
Q5. What equipment/items should a first-aid kit contain?
A5. A first-aid kit is a box that contains all the necessary supplies to provide initial treatment for injuries, illnesses, and emergencies. A well-stocked first-aid kit helps to respond effectively and quickly to situations ranging from minor injuries to serious medical conditions.
A basic first-aid kit should contain the following items:
• Bandage
• A bottle of antiseptic liquid
• Instant heat and cold pack
• Cotton
• Tweezers
• Surgical gloves
• 10 adhesive cloth tapes
• A thermometer
• An antibiotic ointment
• Scissors
• A packet of pain reliever tablets
False. A workplace emergency cannot be anticipated by anyone. 2. True.
3. True.
4. False. Emergency drills should be taken very seriously.

First Aid: It is the first and immediate care or assistance given to an injured person right after an accident or until hospital assistance arrives.
Accident: An accident is an unplanned, unexpected, and unintended event that typically results in damage or injury.
Emergency: An emergency is a sudden and often unforeseen situation or event that needs immediate attention and action.
Ergonomics: It is the science of designing and arranging workplaces, products, and systems to fit the people who use them.
Occupational overuse syndrome: Also known as repetition strain injury (RSI), is defined as performing the same movement repeatedly—such as typing, clicking a mouse, or using a touchscreen.
• Workplace safety is defined as a safe and healthy office environment in which each and every person feels comfortable.
• Good air quality and clean water enhance the capabilities of all workers to be focused and effective in their assignments.
• There are three kinds of pollution monitoring analyses used for air and water: physical analysis, chemical analysis, biological analysis.
• Good and ergonomic workstation design prevents discomfort, fatigue, and the development of long-term health problems.
• Handling accidents effectively at an office is extremely important because they can occur anytime, despite safety measures or regulations in place.
• Fire safety refers to the steps used to control and prevent a fire. It includes measures to prevent the initiation and spread of fire, as well as providing secure means for individuals to evacuate during fire emergencies.
• Hazards, in the context of office safety, are conditions or situations that have the potential to cause harm to employees, ranging from minor injuries to life-threatening incidents.
• Evacuation during a hazard refers to the systematic and organised process of moving individuals, employees, and occupants out of an office to a safer area around it when there is a potential threat to their health and safety.
A. Select the correct option.
1. Which of the following does not fall under the category of fire and electrical hazard?
a. Faulty wiring
c. Excessive workload
2. Evacuation procedures involves
a. Alert system
c. Buddy system
3. Which item should be a part of any first-aid kit?
a. Stethoscope
c. X-ray machine
b. Inadequate fire safety measures
d. Improper handling of electrical equipment
b. Immediate shutdown
d. All of these
b. Water
d. Bandages
4. What is an unplanned or unintended event called that results in injury or damage?
a. Emergency
c. Accident
b. Sickness
d. Safety
5. emergencies have the potential to cause significant harm to the environment, wildlife, and human health.
a. Security
c. Fire
B. Fill in the blanks with the most suitable words.
b. Safety
d. Environmental
1. The quickest and simplest way to raise awareness among people is to use
2. clothes should not be worn by workers in firecracker factories.
3. Fire safety is a that everyone should learn.
4. Poor conditions can lead to musculoskeletal disorders among workers.
5. Absorbing certain chemicals can lead to , resulting in symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
C. State whether the following is True or False. Correct the statements that are false.
1. A basic first-aid kit should contain cotton.
2. Contact with chemicals can cause irritation in the eyes, redness, tearing, and potential eye injuries.
3. One of the parameter of emotional health is stress management.
4. Risk assessment is an integral part of the safety measures required to prevent accidents.
5. Emergency drills should not be taken seriously.
D. Short answer-type questions.
1. Name any two types of emergencies that may occur at home, school, or the office.
2. What do you understand by natural disasters?
3. What is a chemical spillage?

E. Long answer-type questions.
1. What are the dos and don’ts during an evacuation process?
2. What are public health emergencies?
3. List any five causes of electrical hazards.
F. Competency-based questions.
1. Why is it important to keep the office clean and organised?
2. Rohan works at a construction company. What measures can his office take to prevent falls on construction sites?
A. Select the correct option.
1. What is workplace safety defined as?
a. A healthy workplace environment
c. A place with minimal supervision
b. An environment where employees can take breaks
d. An area without any hazards
2. What can happen if a company does not follow government safety rules?
a. They receive a reward
c. They can ignore the rules
3. Why is proper clothing important at the workplace?
a. It enhances fashion
c. It distracts employees
4. What is a key measure to prevent fire hazards in a workplace?
a. Ignoring safety protocols
c. Increasing the number of employees
5. Which of the following is a common cause of slips and falls?
a. Well-lit areas
c. Proper footwear
6. What is an accident defined as?
a. A planned event
c. A natural disaster
7. Which of the following is NOT a type of workplace accident?
a. Vehicle-related accidents
c. Machine-related accidents
b. They can get into serious trouble
d. They might be praised by employees
b. It contributes to the safety of the environment
d. It makes employees look professional
b. Installing sprinklers and fire alarms
d. Keeping flammable materials nearby
b. Wet or slippery floors
d. Clear pathways
b. An unplanned, unexpected event
d. A medical emergency
b. Weather-related emergencies
d. Electrical incidents
8. Which type of emergency involves uncontrollable events caused by nature?
a. Medical Emergencies
c. Security and Safety Emergencies
9. What should be the first priority when handling an accident?
a. Document the accident
c. Ensure immediate safety
b. Natural Disasters
d. Fire Emergencies
b. Call for medical assistance
d. Notify relevant authorities
10. What is a key component of preventing accidents in the workplace?
a. Ignoring safety concerns
c. Disregarding feedback
11. What are hazards in the context of workplace safety?
a. Risks that can be completely eliminated
b. Conditions or situations that can cause harm to employees
c. Safety measures implemented in the workplace
d. Workplace accidents
b. Risk assessment
d. Delaying training

12. Which of the following does not fall under the category of fire and electrical hazard?
a. Faulty wiring
c. Excessive workload
b. Inadequate fire safety measures
d. Improper handling of electrical equipment
13. What is the undeniable link between health and professional success?
a. Good health is only relevant for physical well-being.
b. Good health impacts every aspect of life, including career performance.
c. Career success can be achieved without considering one’s health.
d. Professional success relies solely on qualifications and skills.
14. Which of the following is a common chemical hazard in agriculture?
a. Poor ergonomics b. Pesticides c. Stress d. Faulty wiring
15. What should employees do if they encounter a hazard?
a. Ignore it
c. Handle it themselves
b. Report it immediately
d. Evacuate without alerting others
16. Which of the following is an example of good ergonomic practice?
a. Keeping the monitor at eye level
c. Typing with bent wrists
b. Sitting in the same position for long hours
d. Using chairs without back support
17. Which safety measure helps prevent Occupational Overuse Syndrome (OOS)?
a. Reducing break times
c. Using an ergonomic keyboard and mouse
B. Fill in the blanks with the most suitable words.
b. Encouraging repetitive tasks
d. Increasing screen brightness to the maximum
1. Workplace safety helps in reducing the risk of costly and legal liabilities.
2. Employees should be aware of their and watch out for potentially hazardous scenarios.
3. First aid is the immediate assistance provided to a person before help arrives.
4. should be installed to warn employees about electrical hazards.
5. Proper such as a good-quality ladder decreases the chances of slipping and falling.
6. An emergency is a sudden and often unforeseen situation that needs attention and action.
7. Slips, trips, and falls can occur when an employee slips on a wet or floor.
8. accidents can happen due to inadequate training and malfunctioning equipment.
9. Natural disasters pose a threat to human life, property, and the
10. Effective accident management involves a timely response to minimise the caused.
11. Physical hazards arise from the of the workplace and the materials used.
12. In industries involving the use of , employees may encounter hazardous substances that can cause skin irritations, respiratory problems, etc.
13. refers to the systematic process of moving individuals out of a workplace due to a potential threat to safety.
14. Express for all the good things in your life regularly.
15. Poor ergonomic conditions can lead to disorders among workers.
16. analysis checks for bacteria and microorganisms in air and water.
17. The rule suggests taking a break every 20 minutes to rest the eyes.
C. State whether the following is True or False. Correct the statements that are false.
1. Workplace safety is the sole responsibility of the employer.
2. Fire drills should be conducted every six months.
3. Employees feel happy when they know they’re safe.
4. Chemical hazards can only occur if chemicals are improperly stored.
5. Slips and falls can only happen in poorly lit areas.
6. An accident can be anticipated by anyone.
7. Medical emergencies do not require immediate attention.
8. Employees should be involved in safety programs and their feedback should be recognised.
9. Fire emergencies are critical situations involving the uncontrolled outbreak of fire.
10. Risk assessments are not necessary for preventing accidents at the workplace.
11. It’s recommended to use elevators during a fire evacuation for a quicker exit.
12. During an evacuation, employees should prioritise their personal belongings over their safety.
13. Physical health, mental, and emotional health are all equally important for career success.
14. Re-entering a building immediately after an evacuation is generally safe.
15. Stress, harassment, and excessive workload are examples of physical hazards.
16. Employees should take frequent breaks and maintain proper posture to avoid musculoskeletal issues.
17. The best way to dispose of industrial waste is by dumping it into nearby water bodies.
D. Short answer-type questions.
1. What is the primary goal of workplace safety?
2. Why is it important to have a first-aid kit at the workplace?
3. What should be done if an employee notices a hazardous situation?
4. How can proper signage help in workplace safety?
5. What role does employee training play in electrical safety?
6. What is the main purpose of safety plans in organisations?
7. Name one type of accident that can happen due to the malfunctioning of equipment.
8. What does an emergency response plan involve?
9. How can accidents due to slips and trips be prevented?
10. What should be done immediately after an accident occurs?
11. What is the main purpose of evacuation procedures during hazards?
12. Name two types of hazards found in workplaces.
13. Why should employees avoid using elevators during emergencies?
14. How can workplaces encourage healthy living among employees?
15. What is the significance of the buddy system during evacuations?
16. List two ways organisations can reduce air pollution in office environments.
17. How does improper workstation setup contribute to eye strain?

1. Explain the importance of implementing safety measures in the workplace.
2. Discuss the common causes of fire in a workplace and how to prevent them.
3. What are some key safety rules to follow to prevent slips and falls in the workplace?
4. Describe the steps involved in conducting a risk assessment for workplace safety.
5. What measures should be taken to ensure electrical safety in the workplace?
6. Explain the types of emergencies that can occur at a workplace.
7. Describe the steps that should be followed to handle an accident at the workplace.
8. Describe the importance of conducting regular risk assessments in the workplace.
9. Explain the different types of workplace accidents and their potential impacts.
10. Discuss the steps to effectively handle an accident at the workplace.
11. What role do safety drills play in accident prevention at the workplace?
12. How can organisations foster a culture of safety among employees?
13. Describe the steps involved in general evacuation procedures during a workplace hazard.
14. Explain the potential health issues caused by chemical hazards in the workplace.
15. What measures can workplaces take to improve employee mental health?
16. Discuss the importance of conducting regular evacuation drills in workplaces.
17. Why is it essential for employers to account for all employees following an evacuation?
1. Arjun noticed a spark coming from a wire in his office. What should he do?
2. Priya is responsible for ensuring that the first-aid kit is well-stocked. What should she regularly check?
3. Rohan works in a construction site where there are often slips and falls. What safety measure should he be aware of?
4. Neha is training her colleagues on fire safety protocols. How often should fire drills be conducted?
5. When Ravi sees trailing cables on the floor, what action should he take?
6. If Riya is injured in a vehicle-related accident while coming to work, what immediate actions should be taken?
7. During a fire emergency drill, if Arjun notices the emergency exit is blocked, what should he do?
8. When Priya is exposed to hazardous chemicals due to a spillage, what precautions should be taken to protect her?
9. If Ayaan sees someone slip on a wet floor, what should be his first action?
10. During a natural disaster, how can Anisha ensure her safety at work?
11. Aman saw a fire break out in the office kitchen. What should he do first?
12. Priya is helping a colleague with mobility issues during an evacuation. What should she prioritise?
13. During a flood evacuation drill, Ravi did not know the evacuation route. What should he do?
14. Nisha is feeling overwhelmed with work. How can she maintain her mental health?
15. During a safety meeting, Akash learned about the importance of good health. How can he apply this knowledge?
16. A manufacturing company produces excessive industrial waste, which is affecting the environment. Suggest ways to handle and dispose of waste responsibly.
17. A new IT company wants to ensure proper workstation setup for its employees. What ergonomic principles should they follow?
Education is constantly evolving, and CBSE regularly updates its curriculum to keep learning relevant. With recent changes in the Information Technology (Subject Code 402) syllabus, we have revised our book accordingly. While the main structure remains unchanged, some chapters have been updated to meet new requirements.
To ensure a smooth transition, this Supplementary Booklet has been created, which includes the revised content. It maintains the clarity and practical approach of the main textbook, helping students stay updated and confidently prepare for their assessments. We hope this supplement supports your learning and keeps you aligned with the latest curriculum.
• Remember: Important points to aid memory and recall.
• Did You Know?: Fun facts related to the topic, included to captivate students' interest.
• Points to Remember: Chapter-end point-wise summary to consolidate concepts.
• Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end exercises containing objective and subjective questions to enable comprehensive practice of concepts.
• Activity Time: Classroom and laboratory-based group and individual activities for an enhanced learning experience.
• Additional Practice Questions: Additional practice questions to reinforce learning and ensure mastery of the concepts covered
• Answers Key: Solutions to unsolved questions to support independent practice and learning.
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East.
