1 minute read
www.usgbc.org/resources/case-study-rmz- ecoworld
it is possible to ensure that all aspects constantly run at their optimal levels, thereby decreasing water consumption.
5.3.2.3. Waste 5.3.2.3.1. Innovation When the project team began to work towards LEED Gold certification for RMZ Ecoworld, the site already had a fairly robust recycling program in place. Since its opening, RMZ Ecoworld has been partnered with external vendors that pick up recyclable waste on site and transport it to various recycling facilities. These vendors have also worked directly with tenants to ensure that waste is well sorted, preventing contamination of recycling loads.
Advertisement
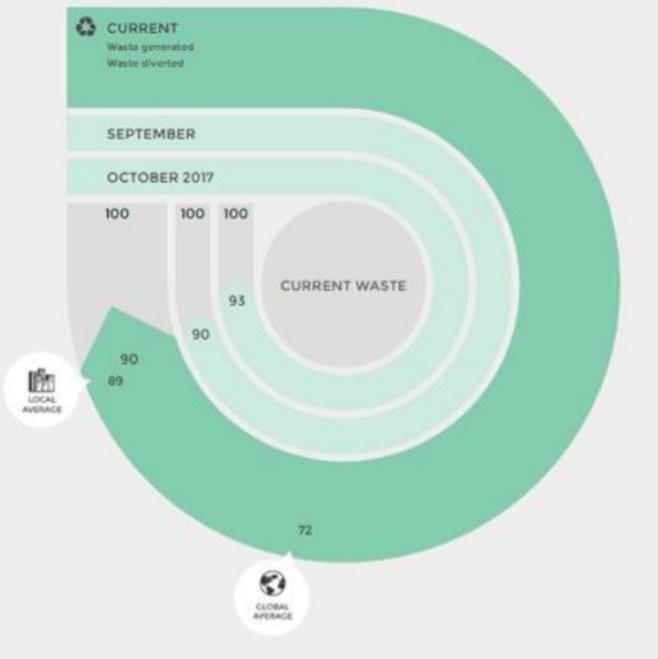
Fig 29: Waste Score
Source :www.usgbc.org/resources/case-study-rmz-ecoworld
The primary change to the existing system has simply been more awareness of the waste stream and a closer monitoring of waste diversion. Through more conscious monitoring practices, waste sorting issues can become more visible and be tackled if necessary. Additionally, the management had begun to integrate an organic waste management system into offices. This has helped to manage food waste, diverting it from landfill and converting it into compost offsite.
5.3.2.3.2. Arc Integration Using the Arc platform, the project team input monthly data regarding RMZ Ecoworld’s generated waste and diverted waste. Through this, it was possible to see monthly fluctuations in the waste diversion ratio and an average success rate of waste diversion. After inputting the data, it was found that the project was significantly more successful than both the global and local average in the category of waste, earning a weighted Waste performance score of 7/8.










