
WaterfordPublicSchools




Grades6-8
MathematicsCurriculumRevision
2023
Grades 6-8 Mathematics
MichaelEllis MathematicsDepartmentChair
WaterfordHighSchoolMathematicsTeacher
HeatherJoyner
KellyBarnes
KirstenEident
CristinadeCastro
JayGionet
Grades6-8MathematicsDepartmentCurriculumLeader
ClarkLaneMiddleSchoolMathematicsTeacher
ClarkLaneMiddleSchoolMathematicsTeacher
ClarkLaneMiddleSchoolMathematicsTeacher
ClarkLaneMiddleSchoolMathematicsTeacher
ClarkLaneMiddleSchoolMathematicsTeacher
CourseName:Grade6Unit1Title:AreaandSurfaceAreaEst.#ofLessons:18
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentswilldivemoredeeplyintotheconceptofareabyextendingtheirknowledgeof rectanglestocalculatingtheareaofparallelograms,triangles,andpolygons,includinggeneralizingandusing formulas.Oncethatfoundationisbuilt,wewillextendinto3-dimensionalshapestocalculatesurfacearea.
CSDEContentStandards:
6.EE.A.2.a: Writeexpressionsthatrecord operationswithnumbersandwithlettersstanding fornumbers.
6.EE.A.2.c: Evaluateexpressionsatspecificvalues oftheirvariables.Includeexpressionsthatarise fromformulasusedinreal-worldproblems. Performarithmeticoperations,includingthose involvingwhole-numberexponents,inthe conventionalorderwherethereareno parenthesestospecifyaparticularorder.
6.G.A.1: Findtheareaofrighttriangles,other triangles,specialquadrilaterals,andpolygonsby composingintorectanglesordecomposinginto trianglesandothershapes;applythesetechniques inthecontextofsolvingreal-worldand mathematicalproblems.
6.G.A.4: Representthree-dimensional figuresusing netsmadeupofrectanglesandtriangles,anduse thenetsto findthesurfaceareaofthese figures. Applythesetechniquesinthecontextofsolving real-worldandmathematicalproblems.
● Howtodecomposeashapeandrearrange thepiecestokeeptheareathesame.
● Makingageometricargumentrequires referencingdefinitionsandfacts.
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● COMMUNICATION: Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #3Constructviableargumentsandcritiquethe reasoningofothers;MP#6:Attendtoprecision
● CRITICALTHINKING: Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#1 Makesenseandperseverethroughchallenges; MP#2Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively;MP #4Modelwithmathematics.
● CRITICALTHINKING: Analyzedatainorderto drawconclusions. MP#6:Attendtoprecision;MP #8:Lookforandexpressregularityinrepeated reasoning.
● HowdoIdeterminehowmuchmaterialIneed tocoverthisspace?
● HowdoIjustifymyargumentusingprecise mathlanguageandthestrategyIused?
Knowledge Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Howtodefineandcalculatearea.
● Howtodefineandcalculatesurfacearea.
● Icanexplainwhatareais.
● Icanusedifferentstrategiestodeterminethe areaofaparallelogram.
Grade6Unit1EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanidentifyabaseandheightofatriangle withoutagrid.
● Icancalculatetheareaofanytriangle..
○ Problem1
● Icandescribethefacesofapolyhedron.
● Icancompareandcontrastprismsand pyramids.
● Iknowwhatanetisandhowitisrelatedto apolyhedron.
○ Problem2
● Icanusedifferentstrategiestodetermine theareaofaparallelogram.
● Icanidentifythebaseandheightofa
● Icanidentifythebaseandheightofa parallelogramonagrid.
● Icanexplainhowtocalculatetheareaofany parallelogramusingitsbaseandheight.
● Icanidentifyabaseandheightofatriangle withoutagrid.
● Icancalculatetheareaofanytriangle.
● Icandescribethecharacteristicsofapolygon.
● Icancalculatetheareaofapolygon.
● Icanidentifyandexplaincommonmistakesor misconceptionsrelatedtoarea.
● Icanexplainwhatsurfaceareais.
● Icancalculatethesurfaceareaofa rectangularprismandexplainmystrategy.
● Icandescribethefacesofapolyhedron.
● Icancompareandcontrastprismsand pyramids.
● Iknowwhatanetisandhowitisrelatedtoa polyhedron.
● Icanmatchapolyhedronwithitsnet.
● Icancalculatethesurfaceareaofaprismor pyramidfromadrawinganddescribemy strategy.
● Icandesignanetforathree-dimensional object.
● Icancalculatesurfaceareatoanswer problemsincontext
● Icanidentifyandexplaincommonmistakesor misconceptionsrelatedtosurfacearea.
Grade6Unit1MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● Area
● SurfaceArea
parallelogramonagrid.
● Icanexplainhowtocalculatetheareaof anyparallelogramusingitsbaseandheight.
○ Problem3
● Icandescribethecharacteristicsofa polygon.
● Icancalculatetheareaofapolygon.
○ Problem4
● Icanexplainwhatsurfaceareais.
● Icancalculatethesurfaceareaofa rectangularprismandexplainmystrategy.
○ Problem5
● Icanmatchapolyhedronwithitsnet.
● Icancalculatethesurfaceareaofaprismor pyramidfromadrawinganddescribemy strategy.
○ Problem6
● Icanidentifyabaseandheightofatriangle withoutagrid.
● Icancalculatetheareaofanytriangle.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask
● I’lltakeittogo! Designatake-outfood containergiventheconstraintsthatthe teacherprovidesbasedonthecarryout food.
○ Icandesignanetfora three-dimensionalobject.
○ Icancalculatesurfaceareato answerproblemsincontext
● Lights,Camera,Action! Makeavideotutorial explainingwhatareaorsurfaceareais. Thenshowhowtotakeaneasyproblem andsolveit.Andthenamorecomplex problemandsolveit.Sharesomecommon mistakes/misconceptions.
○ Icanexplainwhatareais.
○ Icanexplainwhatsurfaceareais.
○ Icanidentifyandexplaincommon mistakesormisconceptionsrelated toarea.
○ Icanidentifyandexplaincommon mistakesormisconceptionsrelated tosurfacearea.
Understandings 1&2
LearningTargets 1,9,10,19
TransferSkills: CommunicationandCritical Thinking
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Calculatingareaofrectangles.(3.MD.C, 3.MD.C.6,3.MD.C.7.B,4.MD.A.3, 5.NF.B.4B)
● Classifyingshapessuchasrighttriangles andparallelograms.(4.G.A.2,5.G.B.4)
● Calculatingthevolumeofarectangular prism.(5.MD.C.4)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck
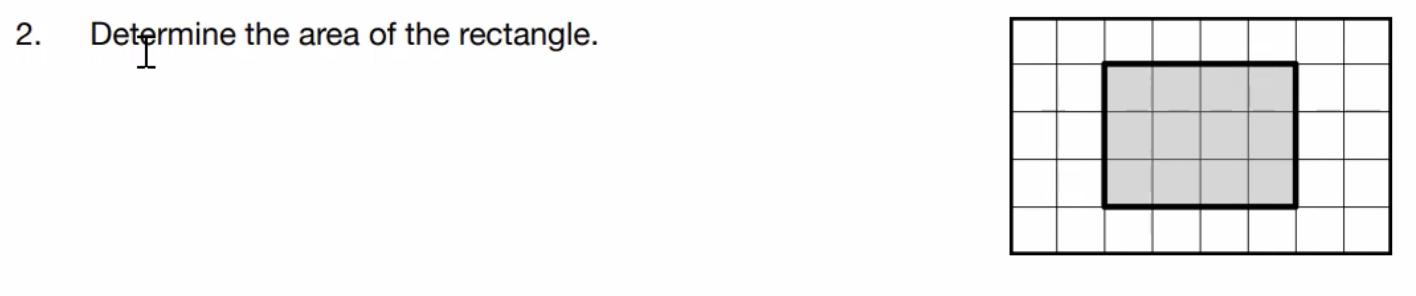
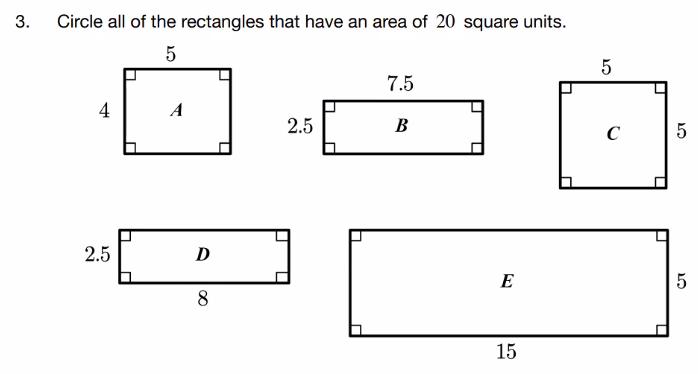
Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbeprepared tosharetheirthinkingwithothers.Studentsthenshare withotherstosolidifytheconceptofareaandbeable explainitintheirownwords.
FirstTopic:Area
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainwhatareais.
● Icanusedifferentstrategiestodetermine theareaofaparallelogram.
● Icanidentifythebaseandheightofa parallelogramonagrid.
● Icanexplainhowtocalculatetheareaof anyparallelogramusingitsbaseandheight.
● Icanidentifyabaseandheightofatriangle withoutagrid.
● Icancalculatetheareaofanytriangle.
● Icandescribethecharacteristicsofa polygon.
● Icancalculatetheareaofapolygon.
● Icanidentifyandexplaincommonmistakes ormisconceptionsrelatedtoarea.
Estimated#ofLessons:10
EssentialQuestions: HowdoIdeterminehowmuchmaterialIneedto coverthisspace?
LearningActivities:
● Studentsdevelopstrategiesfordeterminingtheareaofnot-rectangularshapes.
● Studentsdevelopandnamestrategiesforcalculatingtheareaofmorecomplexshapes.
● Studentsdevelopstrategiesforcalculatingtheareaandapplyaformulafortherelationship betweenthebase,height,andareaofallparallelograms.
● Studentscalculatetheareaofparallelogramswithoutagrid.
● Studentsgenerate,discuss,andapplyseveraldifferentstrategiesforcalculatingtheareaoftriangles onagrid
● Studentsmakeconnectionsbetweentheareasoftrianglesandtheareaofparallelograms
● Studentscalculatetheareasoftriangleswithoutagrid.
● Studentsapplywhattheyhavelearnedaboutcalculatingtheareasofparallelogramsandtrianglesto anewcategoryofshapes:polygons.
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainwhatsurfaceareais.
● Icancalculatethesurfaceareaofa rectangularprismandexplainmystrategy.
● Icandescribethefacesofapolyhedron.
● Icancompareandcontrastprismsand pyramids.
● Iknowwhatanetisandhowitisrelatedto apolyhedron.
● Icanmatchapolyhedronwithitsnet.
● Icancalculatethesurfaceareaofaprismor pyramidfromadrawinganddescribemy strategy.
● Icandesignanetforathree-dimensional object.
● Icancalculatesurfaceareatoanswer problemsincontext
● Icanidentifyandexplaincommonmistakes ormisconceptionsrelatedtosurfacearea.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:8
EssentialQuestions:
HowdoIjustifymyargumentusingprecisemath languageandthestrategyIused?
● Studentsdevelopaconceptualunderstandingofthemeaningofsurfacearea.
● Studentsbegintovisualizethreedimensionalobjectsknownaspolyhedra.
● Studentsareintroducedtothenamesofpolyhedraandpracticeidentifyingpolyhedrafromtheir nets.
● Studentscalculatethesurfaceareasofprismsandpyramids.
● Studentsusetheircreativity,personalexperiences,andtheconceptstheylearnedinthisunitto designatake-outcontainer.
CourseName:Grade6Unit2Title:IntroducingRatios
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentswilllearnwhatratiosare,howtodescribethemandhowtogenerateequivalentratios. Studentsareintroducedtodoublenumberlinesandtablesastoolsforsolvingproblemswithequivalent ratios.Studentswilluseequivalentratiostocompareratiosandsolvemorecomplexproblems.
EstablishedGoals
CSDEContentStandards:
6.RP.A.1: Understandtheconceptofaratioand useratiolanguagetodescribearatiorelationship betweentwoquantities.
6.RP.A.2: Understandtheconceptofaunitrate associatedwitharatiowith,anduse ��/�� ��:�� ��≠0 ratelanguageinthecontextofaratiorelationship.
6.RP.A.3: Useratioandratereasoningtosolve real-worldandmathematicalproblems,e.g.,by reasoningabouttablesofequivalentratios,tape diagrams,doublenumberlinediagramsor equations.
6.RP.A.3.a: Maketablesofequivalentratios relatingquantitieswithwhole-number measurements, findmissingvaluesinthetables, andplotthepairsofvaluesonthecoordinate plane.Usetablestocompareratios.
6.RP.A.3.b: Solveunitrateproblemsincluding thoseinvolvingunitpricingandconstantspeed.
● Alimitedsetofsymbolscanbeusedto representnumericaldescriptionsand relationships.
● Mathematicsisauniversallanguagethat usesassumedandlogicalstatementsto describetheworld.
● Aratioisacomparisonoftwoquantities.
● Tworatiosareequivalentifyoucan multiplyeachofthevaluesinthe firstratio bythesamenumbertogetthevaluesinthe secondratio.
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● CRITICALTHINKING:Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#1 Makesenseandperseverethroughchallenges; MP#2Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively;MP #5Useappropriatetoolsstrategically
● Whatisthisnumber/relationshipexpressing? HowcanIrepresentitindifferentways?
● Howdoweuseratiostrategiestoidentifyand describerelationshipstohelpmesolve problems?
● Icanexplainwhataratioisandidentifythem inthreedifferentrepresentations.
● Icanexplainwhatequivalentratiosareand createthembasedongivenratios.
● Icanexaminewhethertworatiosare equivalentandjustifymyreasoning.
● Icanexplainwhataunitrateisandusethatto interpret,compare,andsolveratioproblems.
● Icandeterminewhichobjectismovingfaster andexplainhowIknow.
● Icanusedifferentstrategies(doublenumber line,tapediagram,tables)tosolveproblems involvingratios.
SummativeAssessment
Grade6Unit2EndUnitAssessment
● Icanexplainwhataratioisandidentify theminthreedifferentrepresentations
Problem1-7
● Icanexplainwhatequivalentratiosareand createthembasedongivenratios.
Problem1,2,3,4,6
● Icanexaminewhethertworatiosare equivalentandjustifymyreasoning.
Problem4,6
● Icanexplainwhataunitrateisandusethat tointerpret,compare,andsolveratio problems.
Problem4,5
● Icandeterminewhichobjectismoving fasterandexplainhowIknow.
Problem5
● Icanusedifferentstrategies(double numberline,tapediagram,tables)tosolve problemsinvolvingratios.
Problem:6,7
PerformanceTask
● Howmuchwaste? Studentsuseratio relationshipstodeterminehowmuchtrash iscreatedataschoolinadayandinayear. Studentsthenmakeaplantoreducethe amountofwastegenerated,
○ Icanusedifferentstrategies (doublenumberline,tapediagram, tables)tosolveproblemsinvolving ratios.
Understanding#1and2
LearningTarget#6
TransferSkills:CriticalThinking
FormativeAssessment
Grade6Unit2MidunitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● Ratio
● UnitRate
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Creatingandinterpretingnumberline diagrams.(2.MD.B.6)
● Recognizingandgeneratingequivalent fractions.(4.NF.A.1)
● Understandingmultiplicativerelationships, includingtherelationshipbetween multiplyingbyaunitfractionanddividing byawholenumber.(4.OA.A.1,4.OA.A.2, 4.NF.B.3,5.NF.B.4,5.NF.B.5)
FirstTopic:IntroducingRatios
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainwhataratioisandidentify theminthreedifferentrepresentations.
● Icanexplainwhatequivalentratiosareand createthembasedongivenratios.
● Icanexaminewhethertworatiosare equivalentandjustifymyreasoning.
● Icanexplainwhataunitrateisandusethat tointerpret,compare,andsolveratio problems.
LearningActivities:
● Studentsinformallyexploreratiosincontext.
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience

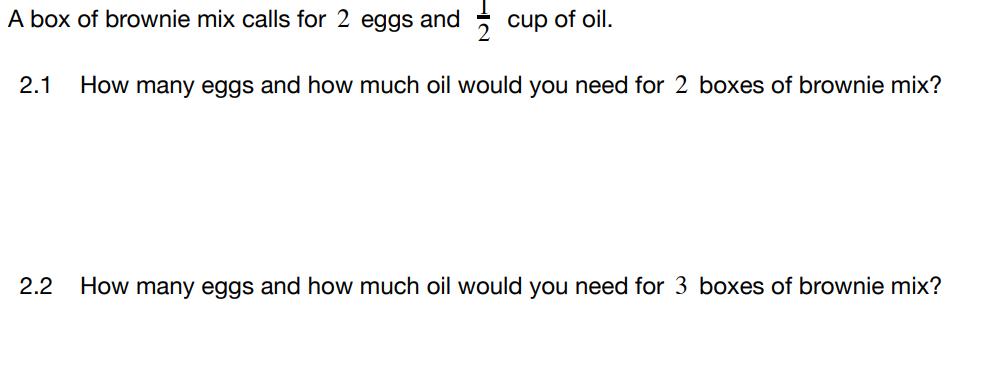
Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptofmultiplicativerelationshipsandscaling recipes.
Estimated#ofLessons:8
EssentialQuestions:
Whatisthisnumber/relationshipexpressing?How canIrepresentitindifferentways?
● Studentsexplainwhataratioisusingmathematicallanguage,
● Studentsexplainwhatequivalentratiosareand findthembydoubling,tripling,andhalvingin context.
● Studentsgenerateequivalentratiosandjustifythattheyareequivalent.
● Studentsuseadoublenumberlinetogenerateequivalentratios.
● Studentsuseunitpricestosolveproblems.
SecondTopic:SolvingProblemswithRatios Estimated#ofLessons:11
RelevantLearningTargets(fromStage1):
● Icanexplainwhataunitrateisandusethat tointerpret,compare,andsolveratio problems.
● Icandeterminewhichobjectismoving fasterandexplainhowIknow.
● Icanusedifferentstrategies(double numberline,tapediagram,tables)tosolve problemsinvolvingratios.
EssentialQuestions: Howdoweuseratiostrategiestoidentifyand describerelationshipstohelpmesolveproblems?
LearningActivities:Studentsdevelopstrategiesforcomparingratiosincontext.
● Studentscalculatethespeedofanobjectasaunitrate.
● Studentsusetablesofequivalentratiostodeterminelargeunknownvaluesincontext.
● Studentssolveproblemsbyreasoningabouttablesofequivalentratiosanddoublenumberline diagrams.
● Studentsusedifferentstrategiestosolveproblemsandtodeterminewhetherornotyoucanuse equivalentratiostosolveaproblem.
● Studentsuseandinterprettapediagramstosolveproblemsinvolvingpart-part-wholeratios.
● Studentscreateandusetapediagramsandtablestohelpsolveproblemsinvolvingpart-part-whole ratios.
● StudentsapplythestrategiestheylearnedinLesson12tosolveproblemsinvolvingpart-part-whole ratiosinthecontextofhousingandgreenspaceinneighborhoods.
● Studentsapplyratioreasoningtoanswerquestionsaboutareal-worldsituation.
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentswilluseratioreasoningtoconvertbetweenunitsofmeasurementbothwithinand acrosssystemsofmeasurement.Studentsrecognizethateachratiorelationshiphastwounitrates,anduse eachofthoseunitratestosolveproblemsinvolvingtablesofequivalentratios.Studentsmakeconnections betweenpercentages,ratios,andrates,thenusethisratioreasoningtodetermineunknownparts,wholes, andpercentages.
CSDEContentStandards:
6.RP.A.2: Understandtheconceptofaunitratea/b associatedwitharatioa:bwithbanduserate ≠0, languageinthecontextofaratiorelationship.
6.RP.A.3: Useratioandratereasoningtosolve ● CRITICALTHINKING:Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#2 Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively;MP#5Use
real-worldandmathematicalproblems,e.g.,by reasoningabouttablesofequivalentratios,tape diagrams,doublenumberlinediagrams,or equations.
6.RP.A.3.b: Solveunitrateproblemsincludingthose involvingunitpricingandconstantspeed.
6.RP.A.3.c: Findapercentofaquantityasarateper 100(e.g.,30%ofaquantitymeans30/100times thequantity);solveproblemsinvolving findingthe whole,givenapartandthepercent.
6.RP.A.3.d: Useratioreasoningtoconvert measurementunits;manipulateandtransform unitsappropriatelywhenmultiplyingordividing quantities. appropriatetoolsstrategically;MP#7Lookfor andmakeuseofstructure.
● Ratioscanbeusedtoconvertbetween differentunitsofmeasurements.
● Unitratescompareto1.
● Percentsareratiosthatcompareto100.
● Findequivalentratiosandpercentages
● Recognizeandcalculatetwounitratesfor thesameratiorelationship.Useunitrates tosolveproblemsinvolvingtablesof equivalentratios.
● Makeconnectionsbetweenpercentages, ratiosandrates.Useratioreasoningto determineunknownparts,wholes,and percentages.
● Howdoweuseratiostrategiestoidentifyand describerelationships?Howdoesthathelp mesolvetheproblem?
● Howdoweuseratiosandpercentagesto solverealworldproblems?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icanconvertmeasurementsfromoneunitto anotherindifferentmeasurementsystems
● Icanusethewordpertodescribeunitrates.
● Icancompareratesthatarewrittenin differentunits.
● Icancalculateandinterpretthetwounitrates forthesamerelationship.
● Icanchoosewhichunitratetousetosolvea problemandexplainmychoice.
● Icanmakecomparisonsandcalculate unknownquantitiesusingunitrates.
● Icanmakeconnectionsbetweenpercentages andratios.
● Icanuseadoublenumberline,tapediagram, ortabletodetermineunknownpartsor wholes.
● Icancreatetapediagrams,doublenumber linediagrams,ortablestodetermineunknown parts,percentages,orwholes.
● Icancalculateanypercentageofanumber.
● Icanexplaintwodifferentexpressionsfor calculatingapercentageofanumber.
● Icancalculateanunknownpercentage.
● Icanexplaindifferentexpressionsfor calculatinganunknownpercentage.
● Icanuseratesandpercentagestoanalyze characteristicsofacountry’spopulation.
SummativeAssessment
Grade6Unit3EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanmakeconnectionsbetween percentagesandratios.
● Icanuseadoublenumberline,tape diagram,ortabletodetermineunknown partsorwholes.
○ Problem1
● Icancalculateandinterpretthetwounit ratesforthesamerelationship.
● Icanchoosewhichunitratetousetosolve aproblemandexplainmychoice.
○ Problem2
● Icanmakecomparisonsandcalculate unknownquantitiesusingunitrates.
○ Problem3
● Icancalculateanypercentageofanumber.
● Icanexplaintwodifferentexpressionsfor calculatingapercentageofanumber.Ican calculateanunknownpercentage.
○ Problem4
● Icanconvertmeasurementsfromoneunit toanotherindifferentmeasurement systems
○ Problem5
● Icanusethewordpertodescribeunit rates.
● Icancompareratesthatarewrittenin differentunits.
● Icancalculateanunknownpercentage.
● Icanexplaindifferentexpressionsfor calculatinganunknownpercentage.
○ Problem6
● Icancreatetapediagrams,doublenumber linediagrams,ortablestodetermine unknownparts,percentages,orwholes.
● Icancalculateanypercentageofanumber.
● Icanexplaintwodifferentexpressionsfor calculatingapercentageofanumber.
FormativeAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blank templateandrationale)
● UnitsandMeasurement
● UnitRates
● Percentages
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask:
● ACountryasaVillage:Studentswillchoose acountryandlookatsomefactsaboutit. Theywillthencreateaposterpretending thatthecountryisavillageof100people. Theywillneedtoconvertallofthe informationtobehowmanyoutof100.
○ Icanuseratesandpercentagesto analyzecharacteristicsofa country’spopulation.
Understanding 3
LearningTarget 14
TransferSkills:CriticalThinking
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesand unitsmaysupportstudentsinmeetinggrade-level standardsinthisunit:
● Measuringandestimatinglengths, volumes,andmasses/weightsinstandard units.(2.MD.A,3.MD.A)
● Multiplicationofwholenumbersby fractionsandfractionsbyfractions. (4.NF.B.4,5.NF.B.4)
● Understandingtheconceptofaratioand usingratioreasoningtosolveproblems. (6.RP.A.1)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:

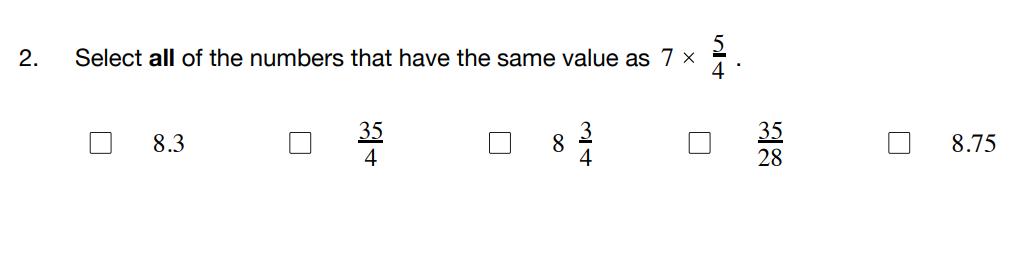
Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofunitsformeasuringlengthandvolumeas wellasmultiplyingawholenumberbyafraction.
FirstTopic:Unitsandmeasurement Estimated#ofLessons:3(1-3)
LearningTargets:
EssentialQuestions:
toanotherindifferentmeasurement systems describerelationships?Howdoesthathelp mesolvetheproblem?
LearningActivities:
● Studentsdescribedifferentunitsofmeasurementandconnectthemwithmeasurementsof everydayobjects,suchasthewidthofa fingerortheweightofasliceofbread.
● Studentsconvertmeasurementsfromoneunittoanother.
● Studentsconvertmeasurementsbasedoninformationfrompenpalsaroundtheworld.
SecondTopic:UnitRates
RelatedLearningTargets:
● Icanusethewordpertodescribeunit rates.
● Icancompareratesthatarewrittenin differentunits.Icancalculateandinterpret thetwounitratesforthesamerelationship.
● Icanchoosewhichunitratetousetosolve aproblemandexplainmychoice.
● Icanmakecomparisonsandcalculate unknownquantitiesusingunitrates.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:7
EssentialQuestions: Howdoweuseratiostrategiestoidentifyand describerelationships?Howdoesthathelpmesolve theproblem?
● Studentscomparethespeedsofmodeltrainsanddiscussunitratesusingtheword per
● Studentslearnthateveryratiorelationshiphastwoassociatedunitratesandthateachunitrateis usefulforsolvingdifferentproblems.
● Studentsrecognizethatinatableofequivalentratios,theycanmultiplybyaunitratetogofromone columntoanother.
● Studentspracticeusingwhatthey’velearnedaboutunitratestomakecomparisonsandcalculate unknowns.
ThirdTopic:Percentages
RelatedLearningTargets:
● Icanmakeconnectionsbetween percentagesandratios.
● Icanuseadoublenumberline,tape diagram,ortabletodetermineunknown partsorwholes.
● Icancreatetapediagrams,doublenumber linediagrams,ortablestodetermine unknownparts,percentages,orwholes.
● Icancalculateanypercentageofanumber.
● Icanexplaintwodifferentexpressionsfor calculatingapercentageofanumber.Ican calculateanunknownpercentage.
● Icanexplaindifferentexpressionsfor calculatinganunknownpercentage.
● Icanuseratesandpercentagestoanalyze
Estimated#ofLessons:9
RelatedEssentialQuestions: Howdoweuseratiosandpercentagestosolvereal worldproblems?
characteristicsofacountry’spopulation.
LearningActivities:
● Studentsbuildontheirexperienceswithpercentagesinordertoreasonaboutthesebenchmark percentages:10%,25%,50%,75%.
● Studentsmakeconnectionsbetweentapediagramsanddoublenumberlinesthatrepresent percentages,andthenusedoublenumberlinesandtablestosolveproblemsinvolvingfriendly percentages.
● Studentscreatetapediagrams,doublenumberlines,andtablestosolveproblemswithpercentages.
● Studentsdevelopandusestrategiesforcalculatinganypercentofanumber.
● Studentsdevelopanduseoneormorestrategiestocalculateunknownpercentages.
● Studentsusewhatthey’velearnedaboutratesandpercentagestoanalyzecharacteristicsof countries’populations.
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsdevelopmultiplestrategiesfordividingfractionsandapplythosestrategiestosolve problemsaboutareasandvolumeswithfractionaldimensions.Studentsreasonaboutwhatitmeansto dividebyafractionandmakeconnectionsbetweencontexts,tapediagrams,andexpressions.Students developstrategiesforcalculatingquotientsoftwofractions,includingtheuseofcommondenominators. Studentsthenusewhattheyknowaboutdividingfractionstosolveproblems.
EstablishedGoals
CSDEContentStandards:
6.NS.A.1: Interpretandcomputequotientsof fractions,andsolvewordproblemsinvolving divisionoffractionsbyfractions(e.g.,byusing visualfractionmodelsandequationstorepresent theproblem).
6.G.A: Solvereal-worldandmathematical problemsinvolvingarea,surfacearea,andvolume.
6.G.A.2: Findthevolumeofarightrectangular prismwithfractionaledgelengthsbypackingit withunitcubesoftheappropriateunitfraction edgelengths,andshowthatthevolumeisthesame aswouldbefoundbymultiplyingtheedgelengths oftheprism.Applytheformulasand ��=����ℎ to findvolumeofrightrectangularprisms ��=��ℎ withfractionaledgelengthsinthecontextof solvingreal-worldandmathematicalproblems.
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● CRITICALTHINKING:Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#2Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively.
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP#6Attendtoprecision;MP#7Lookfor andmakeuseofstructure
Afractionisadivisionproblemthatcanbe manipulatedandrepresentedindifferentways.
● Dividingtwofractionsisthesameas multiplyingthe firstfractionbythe reciprocalofthesecondfraction.
● Areaandvolumewithfractionaldimensions
Howdoweusefractionstosolverealworld problems?
● Icandecideifquotientsofdivisionsituations aregreaterthan1,lessthan1,orequalto1.
● Icanconnectsituations,expressions,andtape diagramsthatrepresentthesamesituation.
● Icanusetapediagramstorepresentandsolve divisionproblemswhentheanswerisa fraction.
● Icandecideifthenumberofgroupsina divisionproblemisgreaterthanorlessthan1.
● Icanusetapediagramswithcommon denominatorstosolvedivisionproblems.
● Icanexplainwhyitisequivalentto. 12 5 ÷ 3 5 =12÷3
● Icanusecommondenominatorstodivide fractions.
● Icancalculatethequotientoftwofractions andexplainmystrategy.
● Icancompareandcontrasttwostrategiesfor dividingfractions.
● Icansolveproblemsinvolvingdivisionof fractionsbyfractionsincontext.
● Icanwritemyownproblemtorepresenta divisionexpression.
● Icanuseadivisionexpressiontorepresenta questionlike“Howmanytimesaslong?”
● Icandividefractionstosolveproblemsabout comparinglengths.
● Icancalculatetheareaofarectanglewith lengthsthatarefractions.
● Icanusedivisionandmultiplicationtosolve problemsaboutareasofrectangleswith lengthsthatarefractions.
● Icancalculatethevolumeofarectangular prismwithlengthsthatarefractions.
● Icanusedivisionandmultiplicationtosolve problemsaboutvolumesofrectangularprisms withlengthsthatarefractions.
● Icanusefractiondivisionandmultiplicationto solveproblemsaboutareaandvolumein context.
SummativeAssessment
Grade6Unit4EndofUnitAssessment
● Icandecideifquotientsofdivision situationsaregreaterthan1,lessthan1,or equalto1.
○ Problem1
● Icandecideifthenumberofgroupsina divisionproblemisgreaterthanorlessthan 1.
● Icanusetapediagramswithcommon denominatorstosolvedivisionproblems
○ Problem2
● Icanexplainwhyitisequivalentto.
● 12 5 ÷ 3 5 =12÷3
● Icanusecommondenominatorstodivide fractions.
● Icancalculatethequotientoftwofractions andexplainmystrategy.
● Icancompareandcontrasttwostrategies fordividingfractions.
○ Problem3
● Icanuseadivisionexpressiontorepresent aquestionlike“Howmanytimesaslong?”
● Icandividefractionstosolveproblems aboutcomparinglengths.
○ Problem4
● Icanconnectsituations,expressions,and tapediagramsthatrepresentthesame situation.
● Icanusetapediagramstorepresentand solvedivisionproblemswhentheansweris afraction.
○ Problem5
● Icancalculatetheareaofarectanglewith lengthsthatarefractions.
● Icanusedivisionandmultiplicationtosolve problemsaboutareasofrectangleswith lengthsthatarefractions.
● Icancalculatethevolumeofarectangular prismwithlengthsthatarefractions.
● Icanusedivisionandmultiplicationtosolve problemsaboutvolumesofrectangular prismswithlengthsthatarefractions.
○ Problem6
FormativeAssessment
Grade6Unit4MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● DividingFractions
● AreaandVolumewithFractions
● Icansolveproblemsinvolvingdivisionof fractionsbyfractionsincontext.
● Icanwritemyownproblemtorepresenta divisionexpression.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask: PlanterPlanner. Studentsare giveninformationregardingareaneededand servingsizeaboutdifferentplantsthattheycan growintheirgarden.Theywillusethisinformation toanswerquestionsandultimatelydesigntheir ownplanter.
● Icanusefractiondivisionandmultiplication tosolveproblemsaboutareaandvolumein context.
Understanding #2 LearningTargets 18 TransferSkills: CommunicationandCritical Thinking
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesand unitsmaysupportstudentsinmeetinggrade-level standardsinthisunit:
● Understandingdivisionasanunknown factorproblem.(3.OA.B.6)
● Explainingwhytwofractionsareequivalent andgeneratingequivalentfractions. (4.NF.A.1)
● Makingconnectionsbetweendivisionand fractions(i.e.,that �� ÷ �� =).(5.NF.B.3) ��
● Multiplyingfractionsbywholenumbersand fractionsbyfractions.(5.NF.B.4)
● Calculatingthevolumeofarectangular prismwithwholenumbersidelengths. (5.MD.C.5.B)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:
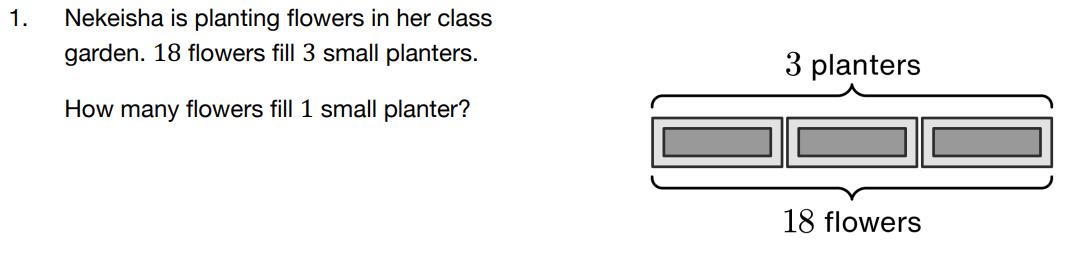
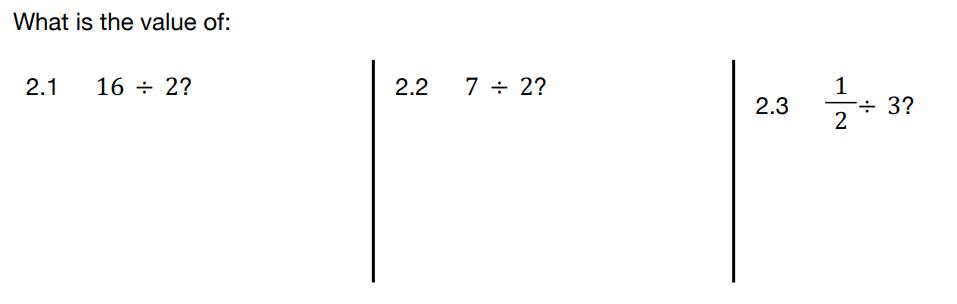
Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptofdivisionincludingdividingfractionsby wholenumbers.
FirstTopic:IntroductiontoDividingFractions Estimated#ofLessons:4
LearningTargets:
● Icandecideifquotientsofdivision situationsaregreaterthan1,lessthan1,or equalto1.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions:
Howcandividingbyafractionbeimplementedina realworldsituation?Exhowmanybatchesofcookies canImakeifIhave3cupsof flourandeachbatch requires ⅔ acup.
● Studentsestimatequotientsbydeterminingiftheyaregreaterthan`1`,lessthan`1`,orequalto`1`.
● Studentsinterpretandcreatetapediagramsthatrepresentdivisionsituationswithwholenumber dividendsanddivisors.
● Studentsmakeconnectionsbetweendrawings,tapediagrams,andmultiplicationanddivision expressionstoanswerthequestion"Howmanygroups?"
● Studentsextendwhattheyknowaboutwholenumberstoanswerthequestion“Howmanyin`1` group?”whenthenumberofgroupsisafraction.
SecondTopic:DividingFractions
LearningTargets:
● Icanconnectsituations,expressions,and tapediagramsthatrepresentthesame situation.
● Icanusetapediagramstorepresentand solvedivisionproblemswhentheansweris afraction.
● Icandecideifthenumberofgroupsina divisionproblemisgreaterthanorlessthan 1.
● Icanusetapediagramswithcommon denominatorstosolvedivisionproblems.
● Icanexplainwhyitisequivalentto.
● 12 5 ÷ 3 5 =12÷3
● Icanusecommondenominatorstodivide fractions.
● Icancalculatethequotientoftwofractions andexplainmystrategy.
● Icancompareandcontrasttwostrategies fordividingfractions.
● Icansolveproblemsinvolvingdivisionof fractionsbyfractionsincontext.
● Icanwritemyownproblemtorepresenta divisionexpression.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:8
EssentialQuestions:
Howcandividingbyafractionbeimplementedina realworldsituation?Exhowmanybatchesofcookies canImakeifIhave3cupsof flourandeachbatch requires ⅔ acup.
● Studentsmakeconnectionsbetweensituations,expressions,andtapediagramsthatrepresentthe samesituation.
● Studentsdeterminewhetherthenumberofgroupsinadivisionproblemisgreaterthanorlessthan `1`.
● Studentsdevelop fluencyinusingcommondenominatorstodividefractions.
● Studentsexploreastrategyfordividingbyaunitfractionbyaskingthequestion“Howmanyin`1` group?”
● Studentsdevelop fluencywithatleastonemethodfordividingfractions.
● Solveproblemsinvolvingdivisionoffractionsbyfractionsincontext.
ThirdTopic:AreaandVolumewithFractions
LearningTargets:
● Icandividefractionstosolveproblems aboutcomparinglengths.
● Icancalculatetheareaofarectanglewith lengthsthatarefractions.
● Icanusedivisionandmultiplicationtosolve problemsaboutareasofrectangleswith lengthsthatarefractions.
● Icancalculatethevolumeofarectangular prismwithlengthsthatarefractions.
● Icanusedivisionandmultiplicationtosolve problemsaboutvolumesofrectangular prismswithlengthsthatarefractions.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:7
EssentialQuestions:
HowdoIdeterminehowmuchmaterialIneedto coverthisspacewhenthedimensionsarenotwhole numbers?
● Studentspracticedividingfractionsbycomparinglengthsandansweringquestionsoftheform “Howmanytimesaslong?”
● Studentsapplywhattheyknowaboutmultiplyinganddividingfractionstoafamiliarcontext: calculatingarea.
● Studentsextendwhattheyhavelearnedtocalculatevolumesofrectangularprismswithfractional dimensions.
● Studentsapplywhattheyhavelearnedaboutfractiondivision,area,andvolumetosolveproblems aboutbuildingagarden.
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsdevelopanduseavarietyofstrategiesforadding,subtracting,multiplying,anddividing decimals.Theyalsoexploretheleastcommonmultipleandgreatestcommonfactoroftwonumbers.
CSDEContentStandards:
6.RP.A.3.B: Solveunitrateproblemsincluding thoseinvolvingunitpricingandconstantspeed.
6.RP.A.3.C: Findapercentofaquantityasarate per100;solveproblemsinvolving findingthe whole,givenapartandthepercent.
6.NS.B: Compute fluentlywithmulti-digitnumbers and findcommonfactorsandmultiples.
6.NS.B.2: Fluentlydividemulti-digitnumbersusing thestandardalgorithm.
6.NS.B.3: Fluentlyadd,subtract,multiply,and dividemulti-digitdecimalsusingthestandard algorithmforeachoperation.
6.NS.B.4: Findthegreatestcommonfactoroftwo wholenumberslessthanorequalto100andthe leastcommonmultipleoftwowholenumbersless thanorequalto12.Usethedistributiveproperty toexpressasumoftwowholenumbers1-100with acommonfactorasamultipleofasumoftwo wholenumberswithnocommonfactor.For example,expressas 36+8 4(9+2).
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #3Constructviableargumentsandcritiquethe reasoningofothers;MP#6:Attendtoprecision
● CRITICALTHINKING:Analyzedatainorderto drawconclusions. MP#6:Attendtoprecision;MP #8:Lookforandexpressregularityinrepeated reasoning.
● Estimationcanhelpyoudetermineifyour answertoamultiplication/divisionproblem isreasonable.
● Determiningthegreatestcommonfactor andleastcommonmultiplemakesyoua moreefficientproblemsolver.
● Howtocomputeoperationswithdecimals.
● Howtoidentifytheleastcommonmultiple andgreatestcommonfactor.
● HowdoIuseestimationtoseeifmy calculationsmakesense?
● HowdoIbuildonmypriormathknowledgeto findcommonfactorsandmultiples?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icanusediagrams,verticalcalculations,and placevaluetoaddandsubtractdecimals.
● Icanaddandsubtractdecimalsusingdifferent strategies.
● Icanuseareatoreasonaboutdecimal multiplication.
● Icanusefractionstomultiplydecimals.
● Icanusetheproductofwholenumbersto calculatetheproductofdecimals.
● Icanmultiplydecimalsusingdifferent strategies.
● Icanuseahundredthschartandreasoningto dividedecimals.
● Icanmakeconnectionsbetweendecimal divisionanddividingfractionswithcommon Denominators.
● Icanuselongdivisionorotherstrategiesto dividedecimalswithnoremainders.
● Icanwriteanequivalentdivisionexpressionin ordertodividedecimals.
● Icandividedecimalstosolveproblemsabout moviespeedsanddurations.
● Icanadd,subtract,multiply,anddivide decimalstosolveproblemsincontext.
● Icanexplainwhattheleastcommonmultiple oftwonumbersmeans.
● Icandeterminetheleastcommonmultipleof twonumbers
● Icanexplainwhatthegreatestcommonfactor oftwonumbersmeans.
● Icandeterminethegreatestcommonfactor oftwonumbers.
SummativeAssessment
Grade6Unit5EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanexplainwhattheleastcommon multipleoftwonumbersmeans.
● Icandeterminetheleastcommonmultiple oftwonumbers
○ Problem1
● Icanuseahundredthschartandreasoning todividedecimals.
● Icanmakeconnectionsbetweendecimal divisionanddividingfractionswithcommon Denominators.
○ Problem2
● Icanaddandsubtractdecimalsusing differentstrategies.
● Icanusetheproductofwholenumbersto calculatetheproductofdecimals.
● Icanmultiplydecimalsusingdifferent strategies.
● Icanuselongdivisionorotherstrategiesto dividedecimalswithnoremainders.
● Icanwriteanequivalentdivision expressioninordertodividedecimals.
FormativeAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● AddingandsubtractingDecimals
● Multiplyinganddividingdecimals
● Solvingproblemswithdecima;s
● Leastcommonmultipleandgreatestcommon factor
○ Problem3
● Icanusediagrams,verticalcalculations,and placevaluetoaddandsubtractdecimals.
○ Problem4
● Icanuseareatoreasonaboutdecimal multiplication.
● Icanusefractionstomultiplydecimals.
○ Problem5
● Icanexplainwhatthegreatestcommon factoroftwonumbersmeans.
● Icandeterminethegreatestcommon factoroftwonumbers.
○ Problem6
● Icandividedecimalstosolveproblems aboutmoviespeedsanddurations.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTasks: BudgetVehicles Studentsare giveninformationaboutdifferenttypesofcars. Theyneedtodecidewhichtypeofcarwouldbe besttopurchasebasedoncost,gasefficiencyor electricityuse.
● Icanadd,subtract,multiply,anddivide decimalstosolveproblemsincontext.
Understanding: 1
LearningTarget: 13
TransferSkills: CommunicationandCritical Thinking
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Representingdecimalsusingtenthsand hundredths.(5.NBT.A.3.A)
● Adding,subtracting,multiplying,and dividingwholenumbers.(3.NBT.A.2, 4.NBT.B.6, 5.NBT.B.5, 5.NBT.B.7)
● Determiningfactorsandmultiplesofa number.(4.OA.B, 4.OA.B.4)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:

FirstTopic:AddingandSubtractingDecimals
LearningTargets:
● Icanusediagrams,verticalcalculations,and placevaluetoaddandsubtractdecimals.
● Icanaddandsubtractdecimalsusing differentstrategies.
LearningActivities:
Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptofworkingwithdecimalsinregardtoplace value(tenthsandhundredths)andmoney.
Estimated#ofLessons:5
EssentialQuestions:
● HowdoIuseestimationtoseeifmy calculationsmakesense?
● Studentsmakeestimatesandroughcalculationsabouttheamountitwillcosttomakevarious dishesandcreateadishoftheirown.
● Studentsrevisitwhattheyhavelearnedaboutplacevalueinpreviousgradesandmakeconnections betweenplacevalueandthedecimalrepresentationofnumbers.Studentsthenusethese relationshipstoaddandsubtractdecimals.
● Studentsaddandsubtractdecimalsbymakingconnectionsbetweenplacevaluethinking,diagrams, andverticalcalculations.
● Studentsdevelop fluencywithaddingandsubtractingdecimalsusingverticalcalculations.They practiceaddingandsubtractingmulti-digitdecimalsbycompletingaseriesofmissingdigitpuzzles.
SecondTopic:MultiplyingandDividingDecimals
LearningTargets:
● Icanuseareatoreasonaboutdecimal multiplication.
● Icanusefractionstomultiplydecimals.
● Icanusetheproductofwholenumbersto calculatetheproductofdecimals.
● Icanmultiplydecimalsusingdifferent strategies.
● Icanuseahundredthschartandreasoning todividedecimals.
● Icanmakeconnectionsbetweendecimal divisionanddividingfractionswithcommon Denominators.
● Icanuselongdivisionorotherstrategiesto dividedecimalswithnoremainders.
● Icanwriteanequivalentdivision expressioninordertodividedecimals.
● Icandividedecimalstosolveproblems aboutmoviespeedsanddurations.
Estimated#ofLessons:9
EssentialQuestions: HowdoIuseestimationtoseeifmycalculations makesense?
LearningActivities:
● Studentsusewhattheyknowaboutahundredthscharttoreasonaboutplacevaluewhen multiplyingdecimals.
● Studentsuseareamodelstohelpthemmultiplydecimalsthathavemorethanonenon-zerodigit.
● Studentsareintroducedtoonemorestrategyformultiplyingdecimalsandhavetheopportunityto develop fluencybycompletingascavengerhuntactivity.
● Studentsmakesenseofdividingdecimalsusingahundredthschart.Studentswilluseastrategy similartowhattheylearnedfordividingfractions:writinganequivalentdivisionproblem.
● Inthislesson,studentsbeginbydividingwholenumberswithnoremainders,makingconnectionsto astrategytheymayhaveseeninearliergrades:longdivision.Laterinthelesson,studentswilldivide decimalsbywritingequivalentdivisionexpressionswithwholenumbers.
● Inthislesson,studentsuselongdivisionandvisualmodelstodividedecimalswhenthereisa remainder.Studentscontinuetobuild fluencywithdividingdecimalsbywritingequivalent expressionsandusinglongdivision.
● Studentspracticedividingdecimalstosolveproblemsandanswerthequestion“Howlongwillthis movietakeifIplayitatadifferentspeed?”
ThirdTopic:SolvingProblemswithDecimals
LearningTargets:
● Icanadd,subtract,multiply,anddivide decimalstosolveproblemsincontext.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:2
EssentialQuestions: HowdoIuseestimationtoseeifmycalculations makesense?
● Studentspracticetheskillstheyhavelearnedaroundoperationswithdecimalstohelpthemmake decisionsaboutpurchasingacar.
● Inthislesson,studentsusewhattheyhavelearnedaboutpercentagesandoperationswithdecimals tocomparethepricesofgroceriesindifferentplacesaroundtheU.S.
FourthTopic:LeastCommonMultipleandGreatest CommonFactor
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainwhattheleastcommon multipleoftwonumbersmeans.
● Icandeterminetheleastcommonmultiple oftwonumbers
● Icanexplainwhatthegreatestcommon factoroftwonumbersmeans.
● Icandeterminethegreatestcommon factoroftwonumbers.
Estimated#ofLessons:4
EssentialQuestions: HowdoIbuildonmypriormathknowledgeto find commonfactorsandmultiples?
LearningActivities:
● Studentslearnhowtodeterminetheleastcommonmultiple(LCM)oftwonumbers.
● Studentslearnhowtodeterminethegreatestcommonfactor(GCF)oftwonumbers.
CourseName:Grade6Unit6Title:ExpressionsandEquationsEst.#ofLessons:21
UnitOverview:
Inthisunitstudentswriteandsolveequationsoftheform andinandoutofcontext. ��+��=�� ����=�� Studentsexplorewhatequivalentexpressionswithvariablesareandusethedistributivepropertytowrite equivalentexpressions.Studentsextendtheirworkwithexpressionstoevaluatenumericalandvariable expressionswithwholenumberexponents.Studentsareintroducedtodifferentwaysofrepresenting relationships:usingtables,equations,andgraphs.
EstablishedGoals
CSDEContentStandards:
6.RP.A.1: Understandtheconceptofaratioanduse ratiolanguagetodescribearatiorelationship betweentwoquantities.
6.RP.A.2: Understandtheconceptofaunitrate �� �� associatedwitharatioa:bwith,anduserate ��≠0 languageinthecontextofaratiorelationship.
6.RP.A.3: Useratioandratereasoningtosolve real-worldandmathematicalproblems,e.g.,by reasoningabouttablesofequivalentratios,tape diagrams,doublenumberlinediagrams,or equations.
6.RP.A.3.A: Maketablesofequivalentratios relatingquantitieswithwhole-number measurements, findmissingvaluesinthetables, andplotthepairsofvaluesonthecoordinate plane.Usetablestocompareratios.
6.NS.B.2: Fluentlydividemulti-digitnumbersusing thestandardalgorithm.
6.EE.A.1: Writeandevaluatenumerical expressionsinvolvingwhole-numberexponents.
6.EE.A.2: Write,read,andevaluateexpressionsin
● CRITICALTHINKING:Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#2 Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively;MP#7Look forandmakeuseofstructure.
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #3Constructviableargumentsandcritiquethe reasoningofothers.
whichlettersstandfornumbers.
6.EE.A.2.A: Writeexpressionsthatrecord operationswithnumbersandwithlettersstanding fornumbers.
6.EE.A.2.B: Identifypartsofanexpressionusing mathematicalterms(sum,term,product,factor, quotient,coefficient);viewoneormorepartsofan expressionasasingleentity.
6.EE.A.2.C: Evaluateexpressionsatspecificvalues oftheirvariables.Includeexpressionsthatarise fromformulasusedinreal-worldproblems. Performarithmeticoperations,includingthose involvingwhole-numberexponents,inthe conventionalorderwhentherearenoparentheses tospecifyaparticularorder(Orderofoperations).
6.EE.A.3: Applythepropertiesofoperationto generateequivalentexpressions.
6.EE.A.4: Identifywhentwoexpressionsare equivalent.
6.EE.B.5: Understandsolvinganequationor inequalityasaprocessofansweringaquestion: whichvaluesfromaspecifiedset,ifany,makethe equationorinequalitytrue?USesubstitutionto determinewhetheragivennumberinaspecified setmakesanequationorinequalitytrue.
6.EE.B.6: Usevariablestorepresentnumbersand writeexpressionswhensolvingareal-worldor mathematicalproblem;understandthatavariable canrepresentanunknownnumber,or,depending onthepurposeathand,anynumberinaspecified set.
6.EE.B.7: Solvereal-worldandmathematical problemsbywritingandsolvingequationsofthe form andforcasesinwhichp,q ��+��=�� ����=�� andxareallnonnegativerationalnumbers.
6.EE.C.9: Usevariablestorepresenttwoquantities inareal-worldproblemthatchangeinrelationship tooneanother;writeanequationtoexpressone quantity,thoughtofasthedependentvariable,in termsoftheotherquantity,thoughtofasthe independentvariable.Analyzetherelationship betweenthedependentandindependentvariables usinggraphsandtables,andrelatethesetothe equation.
6.G.A.1: Findtheareaofrighttriangles,other triangles,specialquadrilaterals,andpolygonsby composingintorectanglesordecomposinginto trianglesandothershapes;applythesetechniques
inthecontextofsolvingreal-worldand mathematicalproblems.
6.G.A.2: Findthevolumeofarightrectangular prismwithfractionaledgelengthsbypackingit withunitcubesoftheappropriateunitfraction edgelengths,andshowthatthevolumeisthesame aswouldbefoundbymultiplyingtheedgelengthof theprism.Applytheformulasand ��=����ℎ ��=��ℎ to findvolumesofrightrectangularprismswith fractionaledgelengthsinthecontextofsolving real-worldandmathematicalproblems.
● Inanequation,avariablerepresentsone number,andanygivensolutionmaybe checkedforprecision.
● Equationsmaybeusedasmodelstosolve real-worldproblems.
● Howtowriteandsolveexpressionsand equationsinvolvingrationalnumbersand exponents.
● Howtorepresentrelationshipsintable, graph,andequationform.
● Howcanwesolvemultistepequationsand checkthatsolutionsarecorrect?
● Howcanrepresentingthesamemathematical relationshipindifferentwaysallowusto modelreal-worldscenariosandsolve problems?
● Icansolveequationsthatincludewhole numbers,decimals,andfractions.
● Icanexplainwhatthesolutiontoanequation meansinasituation.
● Icanjustifywhethertwoexpressionsare equivalent.
● Icanuseanareamodeltowriteequivalent expressions.
● Icandecidewhethertwoexpressionsthat includeexponentsareequivalent.
● Icandeterminethevalueofanexpression thathasanexponentandaddition, subtraction,multiplication,ordivision.
● Icandeterminethevalueofanexpression thathasavariable,anexponent,andaddition, subtraction,multiplication,ordivisionfora specificvalueofthevariable.
● Icanuseatableoranequationtorepresenta relationship.
● Icanconnecttables,graphs,andequations thatrepresentthesamerelationship.
● Icanusetables,graphs,andequationsto analyzeanissueinsociety.
SummativeAssessment
Grade6Unit6EndofUnitAssessment
● Icansolveequationsthatincludewhole numbers,decimals,andfractions.
○ Problem3
● Icanexplainwhatthesolutiontoan equationmeansinasituation.
○ Problem1
● Icanjustifywhethertwoexpressionsare equivalent.
○ Problem2
● Icanuseanareamodeltowriteequivalent expressions.
○ Problem7
● Icandecidewhethertwoexpressionsthat includeexponentsareequivalent.
○ Problem4
● Icandeterminethevalueofanexpression thathasanexponentandaddition, subtraction,multiplication,ordivision.
○ Problem7
● Icandeterminethevalueofanexpression thathasavariable,anexponent,and addition,subtraction,multiplication,or divisionforaspecificvalueofthevariable.
○ Problem7
● Icanuseatableoranequationtorepresent arelationship.
○ Problem5,6
● Icanconnecttables,graphs,andequations thatrepresentthesamerelationship.
○ Problem5,6
● Icanusetables,graphs,andequationsto analyzeanissueinsociety.
○ Problem6
PerformanceTask: SubwayFares Studentsare giveninformationaboutsubwaytransportation. Theyrepresenttheinformationingraphs,tables andequationsandusethemtomakedecisions aboutthebestchoicesoftickettopurchase.
● Icanusetables,graphs,andequationsto analyzeanissueinsociety.
FormativeAssessment
Grade6Unit6MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● SolvingEquations
● Equivalentexpressions
● Exponents
Understanding 2 LearningTargets 13
TransferSkills: CommunicationandCritical Thinking
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesor earlierinGrade6maysupportstudentsinmeeting grade-levelstandardsinthisunit:
● Adding,subtracting,multiplying,and dividingdecimalsandfractions.(6.NS.A.1, 6.NS.B.3)
● Usingwholenumberexponentsto representpowersof10.(5.NBT.A.2)
● Evaluatingexpressionswithaddition, subtraction,multiplication,division,and parenthesesorbrackets.(5.OA.A.1)
● Graphingpointsinthe firstquadrantofthe coordinateplane.(5.G.A.2)
FirstTopic:SolvingEquations
LearningTargets:
● Icansolveequationsthatincludewhole numbers,decimals,andfractions.
● Icanexplainwhatthesolutiontoan equationmeansinasituation.
LearningActivities:
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:

Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofusingtapediagramstorepresent relationshipsbetweenwholenumbersand determiningunknownnumbersinadditionand multiplicationequations.
Estimated#ofLessons:5
EssentialQuestions:
Howcanwesolvemultistepequationsandcheckthat solutionsarecorrect?
● Studentsusereasoning,equations,andtapediagramstodetermineunknownweightsonasee-saw.
● Thislessonintroducessituationsdescribedinwords.Studentsconnecttapediagrams,equations, andsituations,andusethemastoolstoanswerquestionsincontext.
● Studentsusehangerstorepresentequationsandthendetermineunknownvaluesthatbalanceeach hanger.
● Studentsdevelop fluencywithsolvingequations,particularlywithequationsthatincludedecimals andfractions.
● Studentsconnectequationstosituationsbywritingtheirownsituationstomatchequationsand
thentradesituationswithclassmates.
SecondTopic:EquivalentExpressions
LearningTargets:
● Icanjustifywhethertwoexpressionsare equivalent.
● Icanuseanareamodeltowriteequivalent expressions.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:6
EssentialQuestions: Howcanwesolvemultistepequationsandcheckthat solutionsarecorrect?
● Studentsuseexpressionswithvariablestorepresentsituations(inthiscase,thecostofsome numberofpoundsoffruit).
● Studentsexploretheconceptof equivalentexpressions (twodifferentexpressionsthatdescribethe samething)inthecontextofthenumberoftilesthatborderasquare.
● Studentsusevariableexpressionstorepresentareasofrectanglesintwodifferentways:asthesum oftwoareasandastheproductofthetwosidelengths.
● Studentsstrengthentheworktheydidinthepreviouslessonaswellasextendtheirthinkingto expressionsthatinvolvesubtractionorexpressionsinwhichthecommonfactorisavariable.
ThirdTopic:Exponents
LearningTargets:
● Icandecidewhethertwoexpressionsthat includeexponentsareequivalent.
● Icandeterminethevalueofanexpression thathasanexponentandaddition, subtraction,multiplication,ordivision.
● Icandeterminethevalueofanexpression thathasavariable,anexponent,and addition,subtraction,multiplication,or divisionforaspecificvalueofthevariable.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:3
EssentialQuestions: Howcanwesolvemultistepequationsandcheckthat solutionsarecorrect?
● Studentsmakesenseofexponents,bothwhenthebaseisawholenumberandwhenitisafraction.
● Studentsuseareastomakesenseofmorecomplexexpressionswithexponents,particularly evaluatingexpressionsthatincludeanexponentandoneotheroperation.
● Studentsextendwhattheyhavelearnedaboutnumericalexpressionswithexponentstoevaluate variableexpressionsthatinvolveexponentsandotheroperations.
FourthTopic:Relationships
LearningTargets:
● Icanuseatableoranequationtorepresent
Estimated#ofLessons:7
EssentialQuestions:
● Howcanrepresentingthesamemathematical
arelationship.
● Icanconnecttables,graphs,andequations thatrepresentthesamerelationship.
● Icanusetables,graphs,andequationsto analyzeanissueinsociety.
LearningActivities:
relationshipindifferentwaysallowusto modelreal-worldscenariosandsolve problems?
● Studentsextendtheirworkwithvariableexpressionsinearlierlessonstoexplorerelationships betweentwovariables.Studentsusebothtablesandequationstorepresentrelationshipsandlearn theterms independentvariable and dependentvariable todescribeeachpartofarelationship.
● Studentsareintroducedtographsasawayofrepresentingrelationshipsbetweentwovariables.
● Studentsfocusonmakingconnectionsbetweendifferentrepresentationsofthesamerelationship.
● Studentsusetables,graphs,andequationstohelpcustomersmakedecisionsaboutwhattypeof transportationtickettobuy.
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsexplorepositiveandnegativenumbersinseveralcontexts:onanumberline, representedasinequalities,andinthecoordinateplane.Studentsdescribelocationsonthenumberline andsituationsincontextusingpositiveandnegativenumbers.Theyalsocompareandorderpositiveand negativenumbersandtheirabsolutevalues.Studentsrepresentinequalities,suchas , usingsymbols, ��>3 words,andgraphs,andidentifysomeoftheirsolutions.Studentssolvereal-worldandmathematical problemsbygraphingpoints,anddrawpolygonsgivencoordinatesforthevertices.
EstablishedGoals
CSDEContentStandards:
6.NS.C.5: Understandthatpositiveandnegative numbersareusedtogethertodescribequantities havingoppositedirectionsorvalues;usepositive andnegativenumberstorepresentquantitiesin real-worldcontexts,explainingthemeaningof0in eachsituation.
6.NS.C.6: Understandarationalnumberasapoint onthenumberline.Extendnumberlinediagrams andcoordinateaxestorepresentpointsontheline andintheplanewithnegativenumbercoordinates.
6.NS.C.6.A: Recognizeoppositesignsofnumbersas indicatinglocationsonoppositesidesof0onthe numberline;recognizethattheoppositeofthe oppositeofanumberisthenumberitself,andthat 0isitsownopposite.
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #3Constructviableargumentsandcritiquethe reasoningofothers;MP#6:Attendtoprecision
● CRITICALTHINKING:Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#2 Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively.
6.NS.C.6.B: Understandsignsofnumbersin orderedpairsasindicatinglocationsinquadrants ofthecoordinateplane;recognizethatwhentwo orderedpairsdifferonlybysigns,thelocationsof thepointsarerelatedbyreflectionsacrossoneor bothaxes.
6.NS.C.6.C: Findandpositionintegersandother rationalnumbersonahorizontalorvertical numberlinediagram; findandpositionpairsof integersandotherrationalnumbersona coordinateplane.
6.NS.C.7: Understandorderingandabsolutevalue ofrationalnumbers.
6.NS.C.7.A: Interpretstatementsofinequalityas statementsabouttherelativepositionoftwo numbersonanumberlinediagram.
6.NS.C.7.B: Write,interpret,andexplain statementsoforderforrationalnumbersin real-worldcontexts.
6.NS.C.7.C: Understandtheabsolutevalueofa rationalnumberasitsdistancefrom0onthe numberline;interpretabsolutevalueasmagnitude forapositiveornegativequantityinareal-world situation.
6.NS.C.7.D: Distinguishcomparisonsofabsolute valuefromstatementsaboutorder.
6.NS.C.8: Solvereal-worldandmathematical problemsbygraphingpointsinallfourquadrantsof thecoordinateplane.Includeuseofcoordinates andabsolutevalueto finddistancesbetween pointswiththesame firstcoordinateorthesame secondcoordinate.
6.EE.B.5: Understandsolvinganequationor inequalityasaprocessofansweringaquestion: whichvaluesfromaspecifiedset,ifany,makethe equationorinequalitytrue?Usesubstitutionto determinewhetheragivennumberinaspecified setmakesanequationorinequalitytrue.
6.EE.B.6: Usevariablestorepresentnumbersand writeexpressionswhensolvingareal-worldor mathematicalproblem;understandthatavariable canrepresentanunknownnumber,or,depending onthepurposeathand,anynumberinaspecified set.
6.EE.B.8: Writeaninequalityoftheformor ��>�� torepresentaconstraintorconditionina ��<�� real-worldormathematicalproblem.Recognize thatinequalitiesoftheformorhave ��>�� ��<��
infinitelymanysolutions;representsolutionsof suchinequalitiesonnumberlinediagrams.
6.G.A.3: Drawpolygonsinthecoordinateplane givencoordinatesforthevertices;usecoordinates to findthelengthofasidejoiningpointswiththe same firstcoordinateorthesamesecond coordinate.Applythesetechniquesinthecontext ofsolvingreal-worldandmathematicalproblems.
● Signednumberscanbeusedinreal-world situations.
● Equationsandinequalitiesusesymbolsto representquantitiesandtheirrelationships.
● Howtocompareandordersignednumbers.
● Howtoreadandinterpretorderedpairson thecoordinateplane.
Whatdosignednumbers(positiveandnegative) meaninrealworldcontexts?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icanidentifyandplotpositiveandnegative numbersonthenumberline.
● Icancomparepositiveandnegativenumbers usingwordsandsymbols.
● Icanuseanumberlinetoorderpositiveand negativenumbers.
● Iunderstandwhattheabsolutevalueisand howtowriteitinsymbols.
● Icanshowthesameinformationaboutan inequalityusingwords,symbols,andanumber line.
● Icanwriteandinterpretinequalitiesto describeunbalancedhangers.
● Icandrawandlabelanumberlinediagram thatrepresentsthesolutiontoaninequality.
● Icanexplainhowmanysolutionsaninequality canhave.
● Icanjustifywhetherornotavalueisa solutiontoagiveninequality.
● Icanexplainwhatthecoordinateplanelooks likewithpositiveandnegativenumbers.
● Icanwritecoordinatesforpointsinthe coordinateplane.
● Icanplotpointsincoordinateplanes.
● Icandrawapolygoninthecoordinateplane.
● Icandeterminehorizontalandverticalside lengthsofapolygoninthecoordinateplane.
● Icanuseagraphtotellastoryabouta solution. ●
SummativeAssessment
Grade6Unit7EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanidentifyandplotpositiveandnegative numbersonthenumberline.
○ Problem1
● Icandrawandlabelanumberlinediagram thatrepresentsthesolutiontoan inequality.
● Icanjustifywhetherornotavalueisa solutiontoagiveninequality.
● Icanexplainhowmanysolutionsan inequalitycanhave.
○ Problem2
● Icancomparepositiveandnegative numbersusingwordsandsymbols.
● Icanuseanumberlinetoorderpositive andnegativenumbers.
○ Problem3
● Iunderstandwhattheabsolutevalueisand howtowriteitinsymbols.
○ Problem4
● Icanshowthesameinformationaboutan inequalityusingwords,symbols,anda numberline.
● Icanwriteandinterpretinequalitiesto describeunbalancedhangers.
○ Problem5
● Icanplotpointsincoordinateplanes.
● Icandrawapolygoninthecoordinate plane.
● Icandeterminehorizontalandverticalside lengthsofapolygoninthecoordinate plane.
○ Problem6
● Icanexplainwhatthecoordinateplane lookslikewithpositiveandnegative numbers.
● Icanwritecoordinatesforpointsinthe coordinateplane.
● Icanuseagraphtotellastoryabouta solution.
○ Problem7
FormativeAssessment
Grade6Unit7MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● NegativenumbersandAbsoluteValue
● Inequalities
● TheCoordinateplane
PerformanceTask: GraphTelephone:Studentsplot andinterpretcoordinatestomakesenseof situationsincontext.Theythencreategraphsthat representsituationsandtellstoriesbasedonthe graphs.
● Icanuseagraphtotellastoryabouta solution.
Understanding 2 LearningTargets 15
TransferSkills: CommunicationandCritical Thinking
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Representingfractionsanddecimalsonthe numberlineandcomparingfractionsand decimals.(3.NF.A.2.b, 4.NF.A.2, 4.NF.C.6)
● Identifyingandplottingpointswithpositive coordinatesonthecoordinateplane. (5.G.A.1, 5.G.A.2)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:


Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofmeasuringdistancesinopposite directionsandestimatingthelocationsoffractions anddecimalsonanumberline.
FirstTopic:NegativeNumbers
Estimated#ofLessons:7
LearningTargets: EssentialQuestions:
● Icanidentifyandplotpositiveandnegative numbersonthenumberline.
● Icancomparepositiveandnegative numbersusingwordsandsymbols.
● Icanuseanumberlinetoorderpositive andnegativenumbers.
● Iunderstandwhattheabsolutevalueisand howtowriteitinsymbols.
LearningActivities:
Whatdosignednumbers(positiveandnegative) meaninrealworldcontexts?
● Studentsareintroducedtonumberslessthan`0`onthenumberline.
● Studentsdescribeandusestrategiesforidentifyingandplottingnegativerationalnumbersonthe numberline.Thislessonalsointroduceswhatitmeansfortwonumberstobeoppositeswhenthey arethesamedistancefromzeroonanumberline.
● Studentspracticecomparingpositiveandnegativenumbersinasocialway.
● Studentsapplywhattheyhavelearnedaboutpositiveandnegativenumbersinthecontextsof elevationsandtemperaturesaroundtheworld.
● Thislessonintroducestheconceptofabsolutevalue.Itisalsoanopportunityforstudentsto practicewhatthey'velearnedsofarinthisunitbysolvingaseriesofpuzzles.
SecondTopic:Inequalities
LearningTargets:
● Icanshowthesameinformationaboutan inequalityusingwords,symbols,anda numberline.
● Icanwriteandinterpretinequalitiesto describeunbalancedhangers.
● Icandrawandlabelanumberlinediagram thatrepresentsthesolutiontoan inequality.
● Icanexplainhowmanysolutionsan inequalitycanhave.
● Icanjustifywhetherornotavalueisa solutiontoagiveninequality.
●
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:3
EssentialQuestions: Whatdosignednumbers(positiveandnegative) meaninrealworldcontexts?
● Thepurposeofthislessonistointroduceinequalitieswithvariablesandconnectverbal descriptions,symbols,andnumberlinerepresentationsofinequalities.
● Studentsdevelopadeeperunderstandingofusinginequalitysymbolstodescribeunknownvalues. Studentsusethehangerrepresentationtointerpretandwriteinequalitiesthatinvolveonevariable andmorethanonevariable.
● Studentsconsolidateandapplywhattheyhavelearnedaboutinequalitiesonthenumberlineand
learntheterm solutiontoaninequality.
ThirdTopic:TheCoordinatePlane
LearningTargets:Icanexplainwhatthecoordinate planelookslikewithpositiveandnegative numbers.
● Icanexplainwhatthecoordinateplane lookslikewithpositiveandnegative numbers.
● Icanwritecoordinatesforpointsinthe coordinateplane.
● Icanplotpointsincoordinateplanes.
● Icandrawapolygoninthecoordinate plane.
● Icandeterminehorizontalandverticalside lengthsofapolygoninthecoordinate plane.
● Icanuseagraphtotellastoryabouta solution.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:7
EssentialQuestions: Whatdosignednumbers(positiveandnegative) meaninrealworldcontexts?
● Studentsdevelopanunderstandingofnegativenumbersinthecoordinateplane.
● StudentspracticewhattheylearnedaboutcoordinatesinLesson9inthecontextofsolvingmazes. Thislessonalsointroducesgridsthatusedifferentscalesfortheaxesandpatternsincoordinates thatdifferonlybythesign.
● Studentsapplywhatthey'velearnedaboutcoordinateswithpositiveandnegativenumbersto createpolygonsanddeterminedistancesinthecoordinateplane.
● Studentsplotandinterpretcoordinatesinordertomakesenseofsituationsincontext.
CourseName:Grade6
UnitOverview: Inthisunit,studentswillbeintroducedtostatisticsbyvisualizingdata,usingdotplots,histograms,andbox plots,aswellascalculatingmeasuresofcenterandspread.
CSDEContentStandards:
6.SP.A.1: Recognizeastatisticalquestionasone thatanticipatesvariabilityinthedatarelatedtothe questionandaccountsforitintheanswers.
6.SP.A.2: Understandthatasetofdatacollectedto answerastatisticalquestionhasadistribution whichcanbedescribedbyitscenter,spread,and overallshape.
6.SP.A.3: Recognizethatameasureofcenterfora numericaldatasetsummarizesallofitsvalueswith asinglenumber,whileameasureofvariation describeshowitsvaluesvarywithasinglenumber.
6.SP.B.4: Displaynumericaldatainplotsona numberline,includingdotplots,histograms,and boxplots.
6.SP.B.5: Summarizenumericaldatasetsinrelation totheircontext.
6.SP.B.5.A: Reportthenumberofobservations.
6.SP.B.5.B: Describethenatureoftheattribute underinvestigation,includinghowitwasmeasured anditsunitsofmeasurement.
6.SP.B.5.C: Givingquantitativemeasuresofcenter (medianand/ormean)andvariability(interquartile rangeand/ormeanabsolutedeviation),aswellas describinganyoverallpatternandanystriking deviationsfromtheoverallpatternwithreference tothecontextinwhichthedataweregathered.
6.SP.B.5.D: Relatingthechoiceofmeasuresof centerandvariabilitytotheshapeofthedata distributionandthecontextinwhichthedatawere gathered.
● CRITICALTHINKING:Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#2 Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively.
● COMMUNICATION: Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #3Constructviableargumentsandcritiquethe reasoningofothers.
● CRITICALTHINKING: Analyzedatainorderto drawconclusions. MP#6:Attendtoprecision
● Graphicalrepresentationsandstatistics allowustoidentifyandrepresentkey featuresofdata.
● Identifyandappropriatelyutilizemeasures ofcentraltendencies.
Howcanstatisticsbecollected,displayed,and analyzed?
● Howtorepresenttwovariabledatain multipleways(graphically,frequency tables,lists)
● Howtocalculatemeasuresofcentral tendencies.
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icandescribeandinterpretadotplottohelp answerastatisticalquestion.
● Icancreateadotplottovisualizedata.
● Icanusedotplotstocompareandcontrast datasets.
● Icandescribeandinterpretahistogramthat representsadataset.
● Icancalculatethemeanofadataset.
● Icancalculatethemeanabsolutedeviation (MAD)ofadataset.
● Icandetermineandinterpretthemedianofa dataset.
● Icandetermineandinterpretthequartilesof adataset.
● Icandeterminetherangeandinterquartile range(IQR)ofadataset.
● Icanuseboxplotstocompareandcontrast datasets.
● Icancreateadotplot,histogram,orboxplot tovisualizeadataset.
● Icanchooseandcalculateeitherthemeanand MADormedianandIQRforadataset.
● IcanusemeanandMADormedianandIQR tocomparereal-worlddatasets.
SummativeAssessment
Grade6Unit8EndofUnitAssessment
● Icandescribeandinterpretadotplotto helpanswerastatisticalquestion.
● Icandetermineandinterpretthemedianof adataset.
○ Problem1
● Icandescribeandinterpretahistogram thatrepresentsadataset.
○ Problem2
● Icancalculatethemeanofadataset.
○ Problem3
● Icancreateadotplottovisualizedata.
● Icanusedotplotstocompareandcontrast datasets.
● Icandetermineandinterpretthequartiles ofadataset.
○ Problem4
Grade6Unit8MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● VisualizingData
● MeasuringData:MeanandMAD
● MeasuringData:MedianandIQR
● Icandeterminetherangeandinterquartile range(IQR)ofadataset.
○ Problems4&5
● Icancalculatethemeanabsolutedeviation ofadataset.
○ Problem5
● Icanuseboxplotstocompareandcontrast datasets.
○ Problem6
● Icancreateadotplot,histogram,orbox plottovisualizeadataset.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask: Hollywood(Part3) Studentsuse whattheyhavelearnedaboutmeasuresofcenter andspreadtocomparethepercentageofwords spokenbywomenandmenintop-grossingmovies. Inparticular,studentsconsiderwhetherornotthe differencesaregettinglargerorsmallerovertime. Studentswillcreateavisualrepresentation includingagraph,ameasureofcenterandtheir analysisoftheinformationthattheychoose.
● Icancreateadotplot,histogram,orbox plottovisualizeadataset.
● Icanchooseandcalculateeitherthemean andMADormedianandIQRforadataset.
● IcanusemeanandMADormedianandIQR tocomparereal-worlddatasets.
Understanding 2 LearningTargets 11,12,13
TransferSkills: CommunicationandCritical Thinking
STAGE3:LEARNINGPLAN
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesor earlierinGrade6maysupportstudentsinmeeting grade-levelstandardsinthisunit:
● Positioningfractionsanddecimalsona numberline.(3.NF.A.2, 4.MD.B.4)
● Visualizingdatausinglineplots(another namefordotplots).(5.MD.B.2)
● Calculatingdistancesonanumberline. (4.MD.A.2)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:
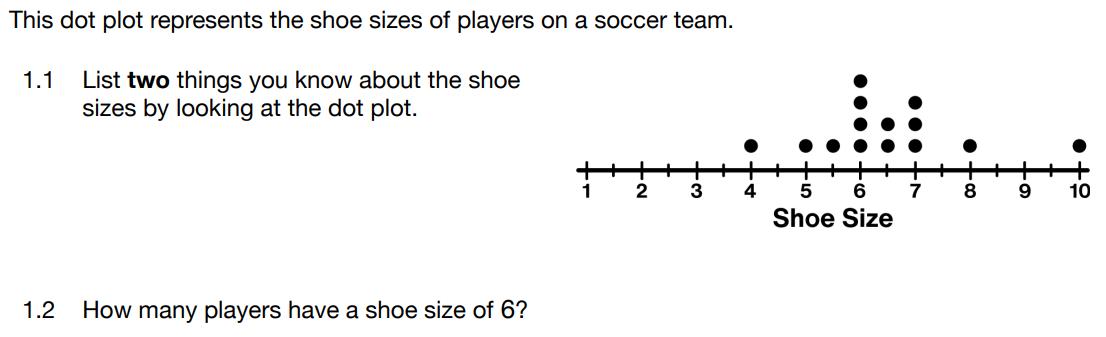
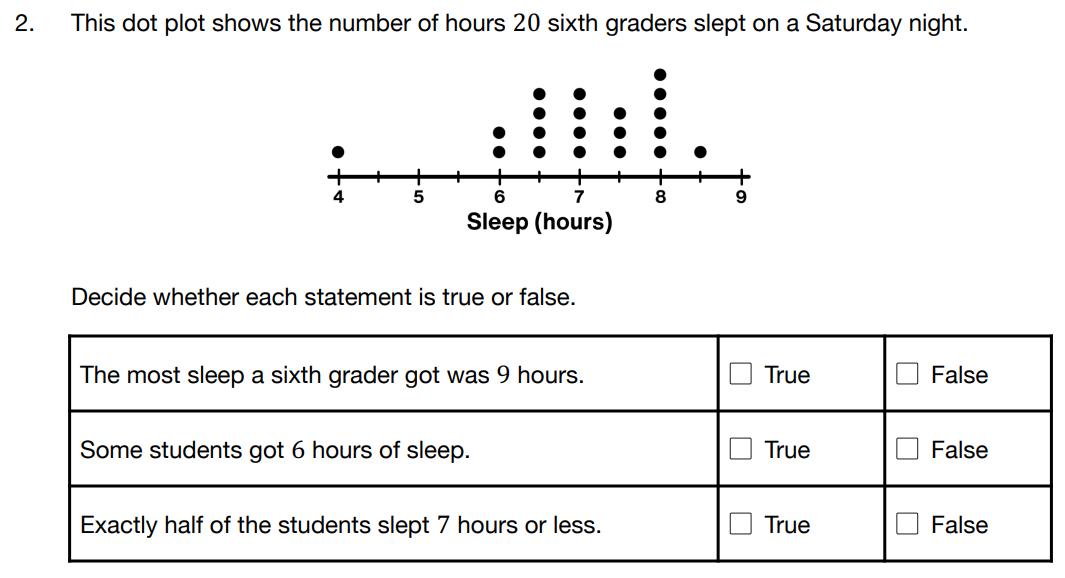
Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifytheir abilitytomakesenseofinformationpresentedina dotplot(calledalineplotinGrades4–5).
FirstTopic:VisualizingData Estimated#ofLessons:6
LearningTargets:
● Icandescribeandinterpretadotplotto helpanswerastatisticalquestion.
● Icancreateadotplottovisualizedata.
● Icanusedotplotstocompareandcontrast datasets.
● Icandescribeandinterpretahistogram thatrepresentsadataset.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions: Howcanstatisticsbecollected,displayed,and analyzed?
● Studentsmakeconnectionsbetweenquestions,claims,anddataastheybegintheunit.
● Studentsmakesenseofdotplotsandlearntheterm statisticalquestion.
● Studentsfocusoncreatingdotplotstovisualizedatasets.
● Studentslearnabout center and spread aswaystodescribeadatasetandusethosetermsto comparedataaboutminimumhourlywages.
● Studentslearnanotherwaytovisualizedata:inahistogram.
● Studentspracticecreatinghistogramsbyhandandusehistogramstocomparedatasets.
SecondTopic:MeasuringData:MeanandMAD Estimated#ofLessons:7
LearningTargets:
● Icancalculatethemeanofadataset.
● Icancalculatethemeanabsolutedeviation ofadataset.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions: Howcanstatisticsbecollected,displayed,and analyzed?
● Studentslearnabout mean asanequalshareandasanumberthatcanbeusedtodescribethe centerofadataset.
● Studentslearnapropertyofthemean:thesumsofthedistancesfromeachpointtothemean (absolutedeviations)areequalontheleftandontheright.
● Studentslearnwhatmeanabsolutedeviation(MAD)isandhowtocalculatetheMADofadataset.
● Studentsusewhattheyhavelearnedaboutmeanandmeanabsolutedeviation(MAD)tocompare thesalariesofthe fivetop-earningactorsofdifferentgendersindifferentyears.
ThirdTopic:MeasuringData:MedianandIQR Estimated#ofLessons:9
LearningTargets:
● Icandetermineandinterpretthemedianof adataset.
● Icandetermineandinterpretthequartiles ofadataset.
● Icandeterminetherangeandinterquartile range(IQR)ofadataset.
● Icanuseboxplotstocompareandcontrast datasets.
● Icancreateadotplot,histogram,orbox plottovisualizeadataset.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions: Howcanstatisticsbecollected,displayed,and analyzed?
● Studentslearnhowtodetermineanewmeasureofcenter:themedian.
● Studentsconsiderhowtheshapeofadatasetaffectsthemeanandmedian,andthendecidewhich measureofcentermoreaccuratelydescribesthedata.
● Studentslearnwhat quartiles areandwhytheymaybeusefulwhendescribingdata.
● Studentsareintroducedtoanewwaytovisualizedata(asaboxplot)andtwonewwaystomeasure spread(rangeandIQR).Studentsalsomakeconnectionsbetweendatasets,boxplots,interquartile range,andrange.
● Studentsinterpretandcompareboxplotsinordertomakeandevaluateclaimsaboutoriginal animatedmoviesandsequels.
● Studentsusewhattheyhavelearnedaboutmeasuresofcenterandspreadtocomparethe percentageofwordsspokenbywomenandmenintop-grossingmovies.
CourseName:Grade7Unit1Title:ScaleDrawings
UnitOverview:
Est.#ofLessons:18
Inthisunit,studentsexaminethescalefactor(theamountitisenlargedorreduced)ofpicturesandplane figures,thenapplywhattheyhavelearnedtoverify/createscaledrawings,e.g.,mapsand floorplans.
STAGE1:DESIREDRESULTS
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
7.G.A.1: Solveproblemsinvolvingscaledrawings ofgeometric figures,includingcomputingactual lengthsandareasfromascaledrawingand reproducingascaledrawingatadifferentscale.
7.G.B.6: Solvereal-worldandmathematical problemsinvolvingarea,volume,andsurfacearea oftwo-andthreedimensionalobjectscomposedof triangles,quadrilaterals,polygons,cubes,andright prisms.
Scalefactorsmaintainproportionalitywhen creatingdesignsforobjectswhicharetobe manufactured.
Knowledge
● Objectsarescalecopiesofeachotherwhen alldimensionsusethesamescalefactor.
● Scaleisusedtorepresentthecommonratio betweentwodrawings.
● CRITICALTHINKING: Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#2Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively; MP#4Modelwithmathematics.
● COMMUNICATION: Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP#3Constructviableargumentsandcritique thereasoningofothers;MP#6Attendto precision.
Howisscalefactorusedinrealworldscenarios?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icantellwhetherornota figureisascaledcopy ofanother figureanddescribesomeofthe characteristics
● Icandrawascaledcopyofa figureusingagiven scalefactor.
● Icandescribehowscalefactorimpactsthearea ofascaledcopyandcalculatetheareaofa scaledcopy.
● Icanexplainandinterpretthescaleofa drawing.
● Icanuseascaledrawingandascaletocalculate actualandscaleddistances.
● Icancreateascaledrawinggivenascale.
● Icancalculateadistanceononescaledrawing
basedonanotherdrawingwithadifferent scale.
● Icanchooseanappropriatescaletomakea scaledrawing.
SummativeAssessment
Grade7Unit1EndUnitAssessment:
● Icantellwhetherornota figureisascaled copyofanother figureanddescribesomeof thecharacteristics
○ Problem1
● Icandescribehowscalefactorimpactsthe areaofascaledcopyandcalculatethearea ofascaledcopy.
○ Problems2,3
● Icandrawascaledcopyofa figureusinga givenscalefactor.
○ Problem4
● Icanuseascaledrawingandascaleto calculateactualandscaleddistances.
○ Problem5
● Icancalculateadistanceononescale drawingbasedonanotherdrawingwitha differentscale.
○ Problem6
PerformanceTask
RoomRedesign:Studentspracticechoosingan appropriatescaleforascaledrawingandcreatinga drawingusingthatscale.
Understanding#1 LearningTargets
● Icanexplainandinterpretthescaleofa drawing.
● Icanchooseanappropriatescaletomakea scaledrawing.
● Icanuseascaledrawingandascaleto calculateactualandscaleddistances.
FormativeAssessment
Grade7Unit1MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● ScaledCopies
● ScaleDrawings
● Icancreateascaledrawinggivenascale TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Measuringandestimatinglengthsand anglesingeometric figures.(4.MD.C.5)
● Relativesizesofmeasurementunitswithin onesystemofunits,suchasinchesandfeet, orgramsandkilograms.(4.MD.A.1)
● Multiplicationanddivisionoffractions. (6.NS.A.1)
● Findingtheareaofpolygonsby decomposingintorectanglesandtriangles. (6.G.A.1)
FirstTopic:ScaledCopies
LearningTargets:
● Icantellwhetherornota figureisascaled copyofanother figureanddescribesomeof thecharacteristics
● Icandrawascaledcopyofa figureusinga givenscalefactor.
● Icandescribehowscalefactorimpactsthe areaofascaledcopyandcalculatethearea ofascaledcopy.
LearningActivities:
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:
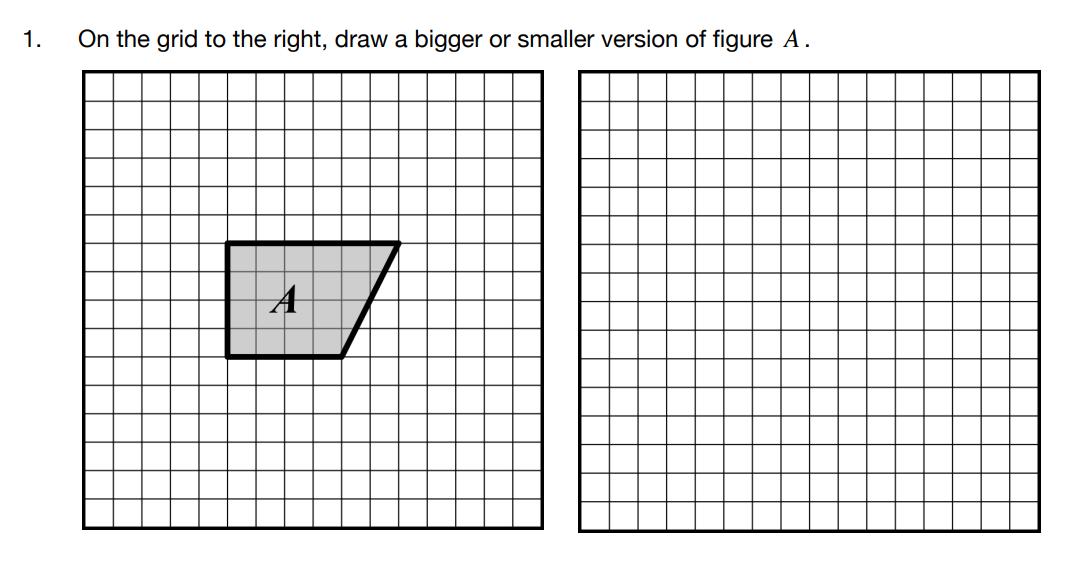
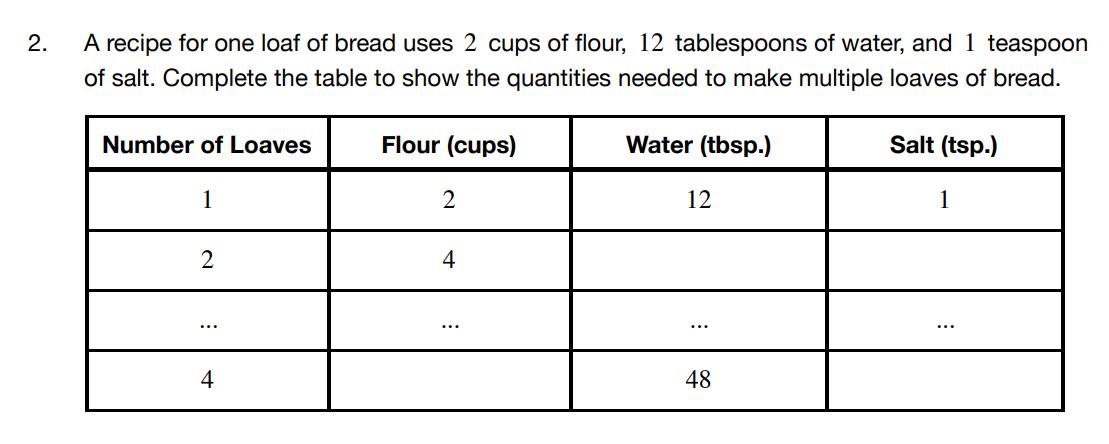
Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptofscalingusingbothgridpaperandtables.
Estimated#ofLessons:9
EssentialQuestions
● Howisscalefactorusedinrealworld scenarios?
● Studentsdevelopanunderstandingofwhatscaledcopiesareanddescribecharacteristicsofscaled copiesusinginformallanguage.
● Studentsunderstandhowlengthsinanoriginal figureandinascaledcopyarerelatedandlearna newphrase:scalefactor.
● Studentsdrawscaledcopiesofshapesonandoffagridandstrengthentheirunderstandingthatthe samescalemustbeappliedtoalllengthsinascaledcopy.
● Studentsunderstandhowscalefactorsaffectthesizeofscaledcopies.
● Studentsusepatternsandstructuretomakesenseofhowscalefactorimpactstheareaofascaled copy.
SecondTopic:ScaleDrawings
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainandinterpretthescaleofa drawing.
● Icanuseascaledrawingandascaleto calculateactualandscaleddistances.
● Icancreateascaledrawinggivenascale.
● Icancalculateadistanceononescale drawingbasedonanotherdrawingwitha differentscale.
● Icanchooseanappropriatescaletomakea scaledrawing.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:9
EssentialQuestions: Howisscalefactorusedinrealworldscenarios?
● Studentstransitionfromthinkingaboutscalingusingscalefactortothinkingaboutscalingusing scale.Studentsusescalestoreasonaboutscaledrawingsfortheremainderoftheunit.
● Studentsanalyzescaledrawings(scaledtwo-dimensionalrepresentationsofactualobjectsor places).
● Studentsusereal-worlddistancestocalculatescaleddistancesandcreatetheirownscaledrawings.
● Studentsreasonaboutmultiplescaledrawingsofthesameobjectusingdifferentscales.
● Studentschooseanappropriatescaleforascaledrawingandcreatingadrawingusingthatscale.
CourseName:Grade7Unit2Title:IntroducingProportionalRelationshipEst.#ofLessons:19
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsbuildontheirknowledgeofscalefactorandunitratestodeveloptheideaofa proportionalrelationship.Studentswillexaminearangeofrealworldscenariostosetupequationsand determinesolutions.
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
7.RP.A.2: Recognizeandrepresentproportional relationshipsbetweenquantities.
7.RP.A.2.A: Decidewhethertwoquantitiesareina proportionalrelationship(e.g.,bytestingfor equivalentratiosinatableorbygraphingona coordinateplaneandobservingwhetherthegraphis astraightlinethroughtheorigin).
7.RP.A.2.B:Identifytheconstantofproportionality (unitrate)intables,graphs,equations,diagrams,and verbaldescriptionsofproportionalrelationships.
7.RP.A.2.C: Representproportionalrelationships withequations.
7.RP.A.2.D: Explainwhatpoint(x,y)onthegraphof aproportionalrelationshipmeansintermsofthe situation,withspecialattentiontothepoints(0,0) and(1, r)where r istheunitrate.
Thecorrectratioinagivensituationisbasedonan understandingofproportionality.
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● CRITICALTHINKING: Demonstrate flexibilityanddeterminationwhensolving problems. MP#2Reasonabstractlyand quantitatively;MP#4Modelwith mathematics.
● COMMUNICATION: Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP#3Constructviableargumentsand critiquethereasoningofothers;MP#6 Attendtoprecision.
HowcanIuseproportionalityinanauthentic contexttodetermineaprecisesolution?
Knowledge Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Howcanaproportionalrelationshipbe representedusingatable,equation,or graph?
● HowcanIcalculateandapplytheconstantof proportionality?
● Icanuseatabletocalculateunknown quantitiesinaproportionalrelationship.
● Icanexplainwhyarelationshipis proportionalornotbylookingatthe equation.
● Icanexplainwhataproportional relationshiplookslikewhenrepresented withagraph.
● Icaninterpretpointsonthegraphofa proportionalrelationshipandidentifythe constantofproportionality.
● Icanwriteanequationofaproportional relationshipfromapointonagraph.
● Icancomparerelatedproportional relationshipsbasedontheirgraphs.
● Icanmodelareal-worldsituationby
decidingwhatinformationisimportantand makingassumptions.
● Icanuseproportionalrelationshipsto answeraquestionaboutareal-world situation.
SummativeAssessment
Grade7Unit2EndUnitAssessment:
● Icanexplainwhataproportional relationshiplookslikewhenrepresented withagraph.
○ Problem1
● Icaninterpretpointsonthegraphofa proportionalrelationshipandidentifythe constantofproportionality.
○ Problem2
● Icanwriteanequationofaproportional relationshipfromapointonagraph.
○ Problem3
● Icancomparerelatedproportional relationshipsbasedontheirgraphs.
○ Problem4
● Icanuseatabletocalculateunknown quantitiesinaproportionalrelationship.
○ Problem5
● Icanexplainwhyarelationshipis proportionalornotbylookingatthe equation.
○ Problem6
● Icanwriteanequationofaproportional relationshipfromapointonagraph.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask
WaterEfficiency:Studentsusetheirunderstanding ofproportionalrelationshipstoexplorewhether bathsorshowersusemorewater.
Understanding#1
LearningTargets:
● Icanmodelareal-worldsituationby decidingwhatinformationisimportantand makingassumptions.
● Icanuseproportionalrelationshipsto answeraquestionaboutareal-world
FormativeAssessment
Grade7Unit2MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● Proportionalrelationshipsintables
● Proportionalrelationshipsinequations
● Proportionalrelationshipsinequations
● Usingproportionalrelationships
TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
PreviousMathConnections
● Understandingandusingratioandrate languageinavarietyofcontexts.(6.RP.A.1, 6.RP.A.2)
● Findingequivalentratiosusingascalefactor. (6.RP.A.2,6.RP.A.3)
● Findingunitratesincontext.(6.RP.A.3.band 6.RP.A.2)
● Givenonevalueofaratio,usetheunitrate to findtheother.(6.RP.A.3.b)
● Representingequivalentratiosinatable. (6.RP.A.1,6.RP.A.3.a)
● Graphingpointsinthecoordinateplane. (6.RP.A.3.a)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbased onpriorgradelevelexperience
From ReadinessCheck:


Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptofUnitRateandProportionalRelationships.
FirstTopic:ProportionalRelationshipsinTables Estimated#ofLessons:4
LearningTargets:
● Icanuseatabletocalculateunknown quantitiesinaproportionalrelationship.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions: HowcanIuseproportionalityinanauthentic contexttodetermineaprecisesolution?
● Studentssurfaceinitial,informalthinkingaboutthekeyideasinproportionalrelationships.
● Studentsareintroducedtotheconceptofaproportionalrelationshipbylookingattablesof equivalentratios
● Studentsdetermine,interpret,anduseconstantsofproportionalitytomakesenseofproportional relationships.
SecondTopic:ProportionalRelationshipsin Estimated#ofLessons:6
Equations
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainwhyarelationshipis proportionalornotbylookingatthe equation.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions: HowcanIuseproportionalityinanauthentic contexttodetermineaprecisesolution?
● Studentsaresupportedinwritingequationsforproportionalrelationships.Thismaybeoneofthe firsttimesthatstudentsencounterequationswithtwovariables.
● Studentsdevelop fluencywritingandusingequationstomakesenseofproportionalrelationshipsin avarietyofcontexts.
● Students findthetwoconstantsofproportionalityforaproportionalrelationship,andexplainhow thoseconstantsarerelated.
● Studentsdevelopstrategiesfordecidingwhetherarelationshipisproportionalornotbasedonthe structureofitsequation.
ThirdTopic:ProportionalRelationshipsinGraphs Estimated#ofLessons:4
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainwhataproportional relationshiplookslikewhenrepresented withagraph.
● Icaninterpretpointsonthegraphofa proportionalrelationshipandidentifythe constantofproportionality.
● Icanwriteanequationofaproportional relationshipfromapointonagraph.
● Icancomparerelatedproportional relationshipsbasedontheirgraphs.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions: HowcanIuseproportionalityinanauthentic contexttodetermineaprecisesolution?
● Studentsexplorewhataproportionalrelationshiplookslikegraphically.
● Studentsdevelop fluencyworkingwithgraphsofaproportionalrelationshipandidentifythe constantofproportionalityusingagraph.
● Studentsusegraphsandequationstocompareproportionalrelationships.
FourthTopic:UsingProportionalRelationships Estimated#ofLessons:5
LearningTargets:
● Icanmodelareal-worldsituationby
EssentialQuestions: HowcanIuseproportionalityinanauthentic contexttodetermineaprecisesolution?
decidingwhatinformationisimportantand makingassumptions.
● Icanuseproportionalrelationshipsto answeraquestionaboutareal-world situation.
LearningActivities:
● Studentscreateandconnectdescriptions,tables,equations,andgraphsofproportional relationships.
● Studentsusetheirunderstandingofproportionalrelationshipstoexplorewhetherbathsorshowers usemorewater.
CourseName:Grade7Unit3Title:MeasuringCircles
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsexplorepropertiesofcirclesbyapplyingtheirknowledgeofproportionalrelationships. Studentswilluseradius,diameter,andpitodevelopformulasforareaandcircumference.Theyapplythese formulastosolverealworldproblems.
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
7.RP.A.2.A: Decidewhethertwoquantitiesareina proportionalrelationship(e.g.,bytestingfor equivalentratiosinatableorbygraphingona coordinateplaneandobservingwhetherthegraph isastraightlinethroughtheorigin).
7.G.B.4: Knowtheformulasfortheareaand circumferenceofacircle,andusethemtosolve problems.Giveaninformalderivationofthe relationshipbetweenthecircumferenceandarea ofacircle.
7.G.B.6: Solvereal-worldandmathematical problemsinvolvingarea,volume,andsurfacearea oftwo-andthree-dimensionalobjectscomposedof triangles,quadrilaterals,polygons,cubes,andright prisms.
● Circumferenceandareaofacircleare
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● CRITICALTHINKING: Identifyaproblem,ask keyquestions,andmakepredictions. MP#2 Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively;MP#4 Modelwithmathematics.
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP#3Constructviableargumentsand critiquethereasoningofothers;MP#6 Attendtoprecision.
● Whatmakesacircleacircle?
dependentontheradiusofthecircle.
● Howtocalculatecircumferenceandareaof acirclegivenadimensionofacircle,orvice versa.
● HowcanIusecircumferenceandareaofa circletosolvereal-worldproblems?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icandescribetherelationshipbetweenthe radius,diameter,andcircumferenceofacircle.
● Giventheradius,diameter,orcircumference ofacircle,Icancalculatetheothertwo measurements.
● Icancalculatetheperimeterofacomplex shapethatincludespartsofcircles.
● Icanwriteperimeterasanexpressionthat includesπ,suchas20π+50.
● Icancalculatetheareaofacircle.
● Icancalculatetheareaofacomplexshape thatincludespartsofcircles.
● Icanexpressthevalueofareaasan expressionthatincludesπ,suchas20π+50.
● Icancalculatetheareaofacirclegivenits circumference.
● Icanevaluateasituationanddetermineifit involvescircumferenceorareaofacircle.
SummativeAssessment
Grade7Unit3EndUnitAssessment
● Icancalculatetheareaofacircle.
○ Problem1
● Icandescribetherelationshipbetweenthe radius,diameter,andcircumferenceofa circle.
○ Problems2,3
● Giventheradius,diameter,or circumferenceofacircle,Icancalculatethe othertwomeasurements.
○ Problems2,3
● Icanevaluateasituationanddetermineifit involvescircumferenceorareaofacircle.
○ Problem4
● Icancalculatetheareaofacomplexshape thatincludespartsofcircles.
○ Problem5
● Icanexpressthevalueofareaasan expressionthatincludesπ,suchas20π+ 50.
FormativeAssessment
MidUnitAssessmentGrade7Unit3Quiz
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● Circumferenceofacircle
● Areaofacircle
○ Problem5
● Icancalculatetheperimeterofacomplex shapethatincludespartsofcircles.
○ Problem5
● Icanwriteperimeterasanexpressionthat includesπ,suchas20π+50.
○ Problem5
● Icancalculatetheareaofacirclegivenits circumference.
○ Problem6
PerformanceTask
● Stained-GlassWindows-Students determinethecircumferenceandareaof partsofcirclesinastainedglasswindowto determinetheamountandcostofmaterials needed.(OpenUpResourceslink)
Understanding#1 LearningTargets:
○ Icancalculatetheperimeterofa complexshapethatincludesparts ofcircles.
○ Icanwriteperimeterasan expressionthatincludesπ,suchas 20π+50.
○ Icancalculatetheareaofacomplex shapethatincludespartsofcircles.
○ Icanexpressthevalueofareaasan expressionthatincludesπ,suchas 20π+50.
TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
PreviousMathConnections
● Writingandusingequationsofproportional relationships.(7.RP.A.2.C)
● Calculatingtheareaofrectanglesand triangles,includingtheareaofcomplex polygons.(6.G.A.1)
● Evaluatingexpressionsforspecificvaluesof theirvariables,(e.g.,evaluatingπ·4). (6.EE.A.2.C)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:

FirstTopic:CircumferenceofaCircle
LearningTargets:
● Icandescribetherelationshipbetweenthe radius,diameter,andcircumferenceofa circle.
● Giventheradius,diameter,or circumferenceofacircle,Icancalculatethe othertwomeasurements.
● Icancalculatetheperimeterofacomplex shapethatincludespartsofcircles.
● Icanwriteperimeterasanexpressionthat includesπ,suchas20π+50.
LearningActivities:

Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptofwritingandusingequationsof proportionalrelationshipsandbeabletoexplainitin theirownwords.
Estimated#ofLessons:8
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatmakesacircleacircle?
● Studentsexaminetherelationshipbetweenthesidelengthofasquareanditsperimeter,aswellas therelationshipbetweenthediagonalofasquareanditsperimeter,bothofwhichareproportional.
● Studentsgeneratecharacteristicsthatdefineacirclebeforeexploringthecircumferenceandareaof circleslaterintheunit.
● Studentsmakesenseoftherelationshipbetweenthediameterofacircleanditscircumference.
● Studentspracticecalculatingtheperimeterofshapescomposedofsquaresandpartsofcircles.
SecondTopic:AreaofaCircle
LearningTargets:
● Icancalculatetheareaofacircle.
● Icancalculatetheareaofacomplexshape thatincludespartsofcircles.
Estimated#ofLessons:8
EssentialQuestions:
● HowcanIusecircumferenceandareaofa circletosolvereal-worldproblems?
● Icanexpressthevalueofareaasan expressionthatincludesπ,suchas20π+ 50.
● Icancalculatetheareaofacirclegivenits circumference.
● Icanevaluateasituationanddetermineifit involvescircumferenceorareaofacircle.
LearningActivities:
● Studentssurfaceandusestrategiesforreasoningabouttheareaofcomplexshapesandestimate theareaofshapeswithcurvededges.
● Studentsestimateanduserepeatedreasoningtomakesenseoftherelationshipbetweentheradius ofacircle,thesquareoftheradius,andtheareaofthecircle.
● Studentsunderstandwhytheformulafortheareaofacirclemakessensebyconnectingittothe formulaforthecircumferenceofacircle.
● Studentspracticecalculatingtheareaofshapescomposedofsquaresandpartsofcircles.
● Studentsusewhatthey’velearnedaboutcircumferenceandareatosolvechallengeslikecalculating theareaofasquareandacirclebasedontheirperimeters.
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsextendtheirgrade6knowledgeofequivalentratios(tapediagrams,tables,anddouble numberlines)andtheirUnit2knowledgeofproportionalrelationshipstosolveproblemsinvolving fractionalquantitiesandpercentchange.Studentsinterpretandsolveproblemsaboutdailysituations involvingproportionalrelationshipsandpercentchange.
ContentMathStateStandards:
7.RP.A.1: Computeunitratesassociatedwithratios offractions,includingratiosoflengths,areas,and otherquantitiesmeasuredinlikeordifferentunits.
7.RP.A.2: Recognizeandrepresentproportional relationshipsbetweenquantities.
7.RP.A.3: Useproportionalrelationshipstosolve multistepratioandpercentproblems(e.g.,simple interest,tax,markupsandmarkdowns,gratuities andcommissions,fees,percentincreaseand decrease,andpercenterror).
● CRITICALTHINKING: Identifyaproblem,ask keyquestions,andmakepredictions. MP#2 Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively;MP#4 Modelwithmathematics.
● COMMUNICATION: Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP#3Constructviableargumentsand critiquethereasoningofothers.
● CRITICALTHINKING: Analyzedatainorder todrawconclusions. MP#6Attendto
7.EE.A.2: Understandthatrewritinganexpression indifferentformsinaproblemcontextcanshed lightontheproblemandhowthequantitiesinit arerelated.
7.EE.B.4: Usevariablestorepresentquantitiesina real-worldormathematicalproblem,andconstruct simpleequationsandinequalitiestosolveproblems byreasoningaboutthequantities.
precision;MP#8Lookforandexpress regularityinrepeatedreasoning.
Aconsumer,user,orwageearnerexpectsavalueto increaseordecreasebasedontheadvertised percentchange.
● Howtodevelopapercentequationandits solution
● Howtoevaluatesituationsforwhich percentagescanbeusedtodescribea changerelativetoaninitialamount
HowcanIuseproportionalrelationshipsandpercent ofchangetoanalyzeasituationinarealworld setting?
● Icanusetheconstantofproportionalityto solveproblemsthatinvolvefractions
● Icanuseatabletodetermineanunknown valueinaproportionalrelationship.
● Icanusetapediagramsandtablesto representaddingorsubtractingapercentage from100%.
● IcandeterminethenewamountifIknowthe originalamountandthepercentchange
● Icanwriteanequationtorepresentaddingor subtractingapercentagefrom100%.
● Icanusedoublenumberlinestorepresent addingorsubtractingapercentagefrom 100%.
● IcandeterminetheoriginalamountifIknow thenewamountandthepercentchange.
● IcandeterminetheoriginalamountifIknow thenewamountandthepercentchangefor one-stepandmultistepproblems.
● Icansolvemultistepproblemsaboutsalestax andtip.
● Icanwriteequationstorepresentthecostof collegeovertime.
● Icansolveproblemsaboutthecostofcollege overtime.
● Icanexplainwhatpercenterrorisandhowto calculateit.
● Icandecidewhetheravalueiswithinan acceptablepercenterror.
SummativeAssessment
Grade7Unit4EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanusetapediagramsandtablesto representaddingorsubtractinga percentagefrom100%.
○ Problems1,5,6
● IcandeterminethenewamountifIknow theoriginalamountandthepercentchange
○ Problems1,5,6
● Icanusetheconstantofproportionalityto solveproblemsthatinvolvefractions
○ Problem2
● Icanuseatabletodetermineanunknown valueinaproportionalrelationship.
○ Problem2
● Icanexplainwhatpercenterrorisandhow tocalculateit.
○ Problem3
● Icandecidewhetheravalueiswithinan acceptablepercenterror.
○ Problem3
● IcandeterminetheoriginalamountifI knowthenewamountandthepercent changeforone-stepandmultistep problems.
○ Problem4
● Icanwriteanequationtorepresentadding orsubtractingapercentagefrom100%.
○ Problem6
● Icanwriteequationstorepresentthecost ofcollegeovertime.
○ Problem7
● Icansolveproblemsaboutthecostof collegeovertime.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask
● RestaurantPercentProject-Studentswill explorehowpercentagesareusedina restaurantsettinginregardstopricing, taxesandtips.
Understanding#1 LearningTargets:
FormativeAssessment
Grade7Unit4MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● PercentagesasProportionalrelationships
● Applyingpercentages
○ Icansolvemultistepproblems aboutsalestaxandtip.
○ IcandeterminethenewamountifI knowtheoriginalamountandthe percentchange
○ Icandeterminetheoriginalamount ifIknowthenewamountandthe percentchange.
○ Icandeterminetheoriginalamount ifIknowthenewamountandthe percentchangeforone-stepand multistepproblems.
TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
PreviousMathConnections
● Usingunitratestosolveaproblem, includingratesthatinvolvefractions. (6.RP.A.2,6.RP.A.3)
● Recognizingrelationshipsbetween fractions,percentages,anddecimals. (6.RP.A.3.C)
● Calculatingapercentageofanumber. (6.RP.A.3.C)
● Recognizingequivalentexpressionsandthe distributiveproperty. (6.EE.A.3)
● Representingrelationshipsusingdouble numberlines. (6.RP.A.3)
FirstTopic:PercentagesasProportional Relationships
LearningTargets:
● Icanusetheconstantofproportionalityto solveproblemsthatinvolvefractions
● Icanuseatabletodetermineanunknown valueinaproportionalrelationship.
● Icanusetapediagramsandtablesto representaddingorsubtractinga
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck

Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithothersjtosolidifythe conceptofunitratesandratiosandbeabletoexplain itintheirownwords.
Estimated#ofLessons:9
EssentialQuestions:
● HowcanIuseproportionalrelationshipsand percentofchangetoanalyzeasituationina realworldsetting?
percentagefrom100%.
● IcandeterminethenewamountifIknow theoriginalamountandthepercentchange
● Icanwriteanequationtorepresentadding orsubtractingapercentagefrom100%.
● Icanusedoublenumberlinestorepresent addingorsubtractingapercentagefrom 100%.
● IcandeterminetheoriginalamountifI knowthenewamountandthepercent change.
● IcandeterminetheoriginalamountifI knowthenewamountandthepercent changeforone-stepandmultistep problems.
LearningActivities:
● Studentsdiscoverwhattheyalreadyknowabouttherelationshipsbetweenpercentsandfractions.
● StudentsusestrategiesfromUnit2tocomparerelationshipsthatinvolvefractionalquantities.
● Studentsuseconstantsofproportionalitytodetermineunknownvaluesinproportional relationships,someofwhichinvolvefractionalquantities
● Studentsvisualizewhatitmeanstoincreaseordecreasebyapercentage,andusethatvisualtohelp themcalculateunknownvalues.
● Studentsrepresentsituationsinvolvingpercentincreaseordecreaseusingequationsandmake connectionsbetweendifferentwaystowritethatequation.
● Studentspracticecalculatingtheoriginalamount,thenewamount,orthepercentchangegiventhe othertwoquantities.
● Studentspracticecalculatingtheoriginalvalue,thenewvalue,orthepercentchangegiventheother twoquantities.
SecondTopic:ApplyingPercentages Estimated#ofLessons:11
LearningTargets:
● Icansolvemultistepproblemsaboutsales taxandtip.
● Icanwriteequationstorepresentthecost ofcollegeovertime.
● Icansolveproblemsaboutthecostof collegeovertime.
● Icanexplainwhatpercenterrorisandhow tocalculateit.
● Icandecidewhetheravalueiswithinan acceptablepercenterror.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions:
● HowcanIuseproportionalrelationshipsand percentofchangetoanalyzeasituationina realworldsetting?
● Studentsapplywhatthey'velearnedinthe firstsectionoftheunittosolvemultisteppercent problemsinacommoncontext:salestaxandtip.
● Studentsusewhatthey’velearnedaboutproportionalrelationshipsandpercentchangetoanalyze anissueinsociety.
● Studentsusewhatthey’velearnedaboutcalculatingpercentincreasetosolveproblemsabout increasesinminimumwageandthecostofcollegeovertime.
● Studentsareintroducedtoreal-worldcontextsinwhicherroroccurs.Theyconsiderwhypercent errorisuseful,andtheypracticecalculatingpercenterroranddecidingwhetherornota measurementiswithinanacceptablerange.
● Studentsapplywhatthey'velearnedaboutincreasinganddecreasingbyapercentagetogenerate andanswerquestionsaboutthesocietyinwhichwelive.
● Studentsconvertfractionstodecimalsusinglongdivision. CourseName:Grade7Unit5Title:RationalNumberArithmetic
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsinterpretsignednumbersincontexts(e.g.,temperature,elevation,depositand withdrawal,position,direction,speedandvelocity,percentchange)togetherwiththeirsums,differences, products,andquotients.
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
7.NS.A.1 Applyandextendprevious understandingsofadditionandsubtractiontoadd andsubtractrationalnumbers.Representaddition andsubtractiononahorizontalorverticalnumber linediagram.
7.NS.A.1.A Describesituationsinwhichopposite quantitiescombinetomake0.
7.NS.A.1.B Understand p+q asthenumberlocated adistanceof|q|from p inthepositiveornegative directiondependingonwhether q ispositiveor negative.Showthatanumberanditsoppositehave asumof0(areadditiveinverses).Interpretsumsof rationalnumbersbydescribingreal-world contexts.
7.NS.A.1.C Understandsubtractionofrational numbersasaddingtheadditiveinverse, p-q=p+(-q). Showthatthedistancebetweentworational
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● CRITICALTHINKING: Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#2Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively; MP#4Modelwithmathematics.
● COMMUNICATION: Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP#3Constructviableargumentsand critiquethereasoningofothers.
● CRITICALTHINKING: Analyzedatainorder todrawconclusions. MP#6Attendto precision;MP#8Lookforandexpress regularityinrepeatedreasoning.
numbersonthenumberlineistheabsolutevalue oftheirdifference,andapplythisprinciplein real-worldcontexts.
7.NS.A.1.D Applypropertiesofoperationsas strategiestoaddandsubtractrationalnumbers.
7.NS.A.2 Applyandextendprevious understandingsofmultiplicationanddivisionof fractionstomultiplyanddividerationalnumbers.
7.NS.A.2.A Understandthatmultiplicationis extendedfromfractionstorationalnumbersby requiringthatoperationscontinuetosatisfythe propertiesofoperations,particularlythe distributiveproperty,leadingtoproductssuchas (-1)(-1)=1andtherulesformultiplyingsigned numbers.Interpretproductsofrationalnumbers bydescribingreal-worldcontexts.
7.NS.A.2.B Understandthatintegerscanbe divided,providedthatthedivisorisnotzeroand everyquotientofintegers(withanon-zerodivisor) isarationalnumber.If p and q areintegers,then -(p/q)=(-p)/q=p/(-q).Interpretquotientsofrational numbersbydescribingreal-worldcontexts.
7.NS.A.2.C Applypropertiesofoperationsas strategiestomultiplyanddividerationalnumbers.
7.NS.A.2.D Convertarationalnumbertoadecimal usinglongdivision.Knowthatthedecimalformofa rationalnumberterminatesinzerosoreventually repeats.
7.NS.A.3 Solvereal-worldandmathematical problemsinvolvingthefouroperationswith rationalnumbers.
7.EE.B.3 Solvemultistep,real-life,and mathematicalproblemsposedwithpositiveand negativerationalnumbersinanyform(whole numbers,fractions,anddecimals)usingtools strategically.Applypropertiesofoperationsto calculatenumbersinanyform.Convertbetween formsasappropriate,andassessthe reasonablenessofanswersusingmental computationandestimationstrategies.
● Computationswithsignednumbersfollow thesamefractionanddecimalrulesthat youhavebeenusingsince4thgrade.
● Calculationsandsolutionswithsigned numbersfollowtheintegerrules.
● “Signednumbers”includeallrational numbers,writtenasdecimalsorintheform
● Howtoapplytheintegerruleswhen computingwithintegers,fractionsand decimals.
● HowdoIuseprecisemathematicalnumbers andsymbolstodescribegivensituations?
● Howcantheuseofoperationswithpositive andnegativenumbersbeusedinrealworld situations?
● Icanconnectaddingandremoving floatsand anchorstoaddingandsubtractingintegers.
● Icanidentifydifferentexpressionsthathave thesamevalue.
● Icanaddandsubtractintegers,decimals,and fractionsonanumberline.
● Icandeterminethevalueofavariablethat makesanequationtrue.
● Icandrawanumberlinetoaddandsubtract positiveandnegativenumbers.
● Icancompareandcontrastsimilar expressions(e.g.,2.5−3.5and3.5−2.5).
● Icanmakeargumentsaboutadditionand subtractionwithvariables.
● Icanuseposition,rate,andtimetorepresent multiplyingpositiveandnegativenumbers.
● Icanexplainwhymultiplyingtwonegative numbershasapositivevalue.
● Icanmultiplyanddividepositiveandnegative numbers.
● Icanidentifydifferentexpressionsthathave thesamevalue.
● Icanreasonaboutexpressionsthatinvolve variables.
● Icanadd,subtract,multiply,anddivide integersincomplicatedexpressions.
● Icansolveproblemsandmakepredictions usingpositiveandnegativerates.
● Icancomparechangesinthevalueof differentstocks,includingthedollaramount andthepercentageofthepreviousvalue.
● Icaninterprettablesthatrepresentthe valuesofdifferentstocksinthestockmarket.
Grade7Unit5EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanaddandsubtractintegers,decimals, andfractionsonanumberline.
○ Problems1,2,6
● Icandeterminethevalueofavariablethat makesanequationtrue.
○ Problems1,2,6
● Icanconnectaddingandremoving floats andanchorstoaddingandsubtracting integers.
○ Problem2
● Icanidentifydifferentexpressionsthat havethesamevalue.
○ Problem2
● Icandrawanumberlinetoaddand subtractpositiveandnegativenumbers.
○ Problem3
● Icancompareandcontrastsimilar expressions(e.g.,2.5−3.5and3.5−2.5).
○ Problem3
● Icanmakeargumentsaboutadditionand subtractionwithvariables.
○ Problem3
● Icanreasonaboutexpressionsthatinvolve variables.
○ Problem3
● Icanadd,subtract,multiply,anddivide integersincomplicatedexpressions.
○ Problem4
● Icanmultiplyanddividepositiveand negativenumbers.
○ Problems5,6
● Icanidentifydifferentexpressionsthat havethesamevalue.
○ Problems5,6
● Icanuseposition,rate,andtimeto representmultiplyingpositiveandnegative numbers.
○ Problem7
● Icanexplainwhymultiplyingtwonegative numbershasapositivevalue.
○ Problem7
● Icansolveproblemsandmakepredictions usingpositiveandnegativerates.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask:
TheStockMarket-
Grade7Unit5MidUnitAssessments (2)
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
FrayerModel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● AddingandSubtractingrationalnumbers
● MultiplyingandDividingrationalnumbers
● Applyingoperations
Studentsapplytheirknowledgeofoperationswith rationalnumberstocalculateastock’snewvalue, changeinvalue,orchangeexpressedasasigned percentageofthepreviousvalue.(OpenUp Resourceslink)
Understanding#1 LearningTargets:
● Icancomparechangesinthevalueof differentstocks,includingthedollar amountandthepercentageoftheprevious value.
● Icaninterprettablesthatrepresentthe valuesofdifferentstocksinthestock market.
TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
PreviousMathConnections
● Usingpositiveandnegativenumbersto representquantitiesinreal-worldcontexts. (6.NS.C.5)
● Plottingpositiveandnegativenumbersona numberline. (6.NS.C.6)
● Identifyingwhentwoexpressionsor equationshavethesamevalue. (6.EE.A.4)
● Determiningthevalueofavariableinan equationoftheformx+p=qandpx=q. (6.EE.B.7)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:


Studentswill preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifytheir abilitytoreasonwithnegativenumbersandcompare signednumbers.
FirstTopic:AddingandSubtracting
LearningTargets:
● Icanconnectaddingandremoving floats andanchorstoaddingandsubtracting integers.
● Icanidentifydifferentexpressionsthat havethesamevalue.
● Icanaddandsubtractintegers,decimals, andfractionsonanumberline.
● Icandeterminethevalueofavariablethat makesanequationtrue.
● Icandrawanumberlinetoaddand subtractpositiveandnegativenumbers.
● Icancompareandcontrastsimilar expressions(e.g.,2.5−3.5and3.5−2.5).
● Icanmakeargumentsaboutadditionand subtractionwithvariables.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:8
EssentialQuestions:
● HowdoIuseprecisemathematicalnumbers andsymbolstodescribegivensituations?
● Studentsdevelopamodelforaddingandsubtractingpositiveandnegativeintegers.
● Studentstransitionfrommanipulating floatsandanchorstousing floatsandanchorstoreason aboutaddingandsubtractingintegers.
● Studentsextendwhattheylearnedaboutrepresentingaddingandsubtractingintegersonanumber linetoaddingandsubtractingdecimalsandfractions.
● Studentsreasonaboutrepresentingsubtractionofsignednumbersonanumberlineandpractice drawingtheirownnumberlines.
● Studentspracticereasoningaboutthesignsandvaluesofexpressions.
SecondTopic:MultiplyingandDividing
LearningTargets:
● Icanuseposition,rate,andtimeto representmultiplyingpositiveandnegative numbers.
● Icanexplainwhymultiplyingtwonegative numbershasapositivevalue.
● Icanmultiplyanddividepositiveand negativenumbers.
● Icanidentifydifferentexpressionsthat havethesamevalue.
● Icanreasonaboutexpressionsthatinvolve variables.
● Icanadd,subtract,multiply,anddivide integersincomplicatedexpressions.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:7
EssentialQuestions:
● HowdoIuseprecisemathematicalnumbers andsymbolstodescribegivensituations?
● Studentsextendthe floatsandanchorsmodeltomakesenseofmultiplyingpositiveandnegative integers.
● Studentsmakesenseofadifferentmodelformultiplyingpositiveandnegativenumbers(rateof change·time=position).
● Studentsmakesenseofdivisionofsignednumbersusingthecontextofposition,rate,andtimeasa model.
● Studentsreasonaboutvariableexpressionsinvolvingadding,subtracting,multiplying,anddividing signednumbers.Studentsalsogeneralizepatternsforthevalueofvariableexpressions.
● Studentspracticereasoningaboutthesignsandvaluesofexpressionsthatincludeallfour operationsandpositiveandnegativenumbers.
ThirdTopic:ApplyingOperations
LearningTargets:
● Icansolveproblemsandmakepredictions usingpositiveandnegativerates.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:5
EssentialQuestions:
● Howcantheuseofoperationswithpositive andnegativenumbersbeusedinrealworld situations?
● Studentsusewhattheyhavelearnedabouttheadditionandsubtractionofpositiveandnegative numberstomakesenseofchangingtemperaturesaroundtheworldandseaicemelt.
● Studentsusewhattheyhavelearnedaboutpositiveandnegativeratestounderstandtheeffectsof climatechangeonArcticseaiceandrisingsealevels.
● Studentsusewhattheyhavelearnedaboutallfouroperationswithpositiveandnegativenumbers tounderstandsolarpanelsandcarbonfootprints.
CourseName:Grade7Unit6Title:Expressions,Equations,andInequalitiesEst.#ofLessons:24
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsextendwhattheylearnedinGrade6aboutsolvingone-stepequationstosolve multi-stepequationsthatincludeexpanding,factoring,oraddingtermsto findasolution.Sometimesa situationhasmanysolutionswhichcanberepresentedasinequalities.
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
7.EE.A.1 Applypropertiesofoperationsas strategiestoadd,subtract,factor,andexpand linearexpressionswithrationalcoefficients.
7.EE.B.3 Solvemultistep,real-life,and mathematicalproblemsposedwithpositiveand negativerationalnumbersinanyform(whole
Blue toverifysignificance
● COMMUNICATION: Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP#3Constructviableargumentsand critiquethereasoningofothers.
● CRITICALTHINKING: Analyzedatainorder todrawconclusions. MP#6Attendto
numbers,fractions,anddecimals)usingtools strategically.Applypropertiesofoperationsto calculatewithnumbersinanyform.Convert betweenformsasappropriate,andassessthe reasonablenessofanswersusingmental computationandestimationstrategies.
7.EE.B.4 Usevariablestorepresentquantitiesina real-worldormathematicalproblem,andconstruct simpleequationsandinequalitiestosolveproblems byreasoningaboutthequantities.
7.EE.B.4.A Solvewordproblemsleadingto equationsoftheform`px+q=r`and`p(x+q)=r`, where`p`,`q`,and`r`arespecificrationalnumbers. Solveequationsoftheseforms fluently.Compare analgebraicsolutiontoanarithmeticsolution, identifyingthesequenceoftheoperationsusedin eachapproach.
7.EE.B.4.B Solvewordproblemsleadingto inequalitiesoftheform`px+q>r`or`px+q<r`, where`p`,`q`,and`r`arespecificrationalnumbers. Graphthesolutionsetoftheinequalityand interpretitinthecontextoftheproblem.
● Realisticsolutionstoequationsorinequalities requireunderstandingofwhatthereal-world scenariolookslikeregardlessoftheform(i.e., table,graph,oralgebraically)
● Leveragingtechnologytodemonstratethe relationshipbetweenequationsand inequalitiescreatesadynamicrepresentation ofthereal-worldscenarioforfurther possibilities.
● Howtoconstructandsolveequationsto modelreallifeproblems.
precision;MP#8Lookforandexpress regularityinrepeatedreasoning.
● Howdowewriteandsolveequationsand inequalitiestomakesenseofreal-world problems?
● Whatdoestheequationorinequalitylooklikeon thegraph?Howdoesthatrevealpossible solutionstothereal-worldproblem?
● Icandrawtapediagramstorepresent situationsinwhichthevariablerepresenting
● Howtoconstructinequalitiestomodelreal lifeproblems.
theunknownisspecified.(Foundational)
● Icansolveequationsthatinvolveexpanding.
● Icancomparedifferentstrategiesforsolving thesameequation.
● Icanwriteequivalentexpressions.
● Icanexplainwhetherornottwoexpressions areequivalent.
● Icanconnectbalancingmovesonhangersto solvingequations.
● Icansolveequationswithpositivenumbers.
● Icanwriteequivalentexpressionswithfewer terms.
● Icanexpandandfactorexpressions.
● Icanexplainwhetherornotfractionsor negativenumbersmakesenseassolutionsto aninequality.
● Icanwriteandsolveaninequalitytoanswera questionaboutasituation.
● Ican figureoutthesolutionstoaninequality.
● Icanexplainthedifferencebetweenthe solutiontoanequationandthesolutionstoan inequality.
● Icanwriteaninequalitytorepresenta context.
● Icansolveaninequalityincontextbyusinga relatedequation. STAGE2:DETERMINEACCEPTABLEEVIDENCE SummativeAssessment
Grade7Unit6EndofUnitAssessment
● Ican figureoutthesolutionstoan inequality.
○ Problem1
● Icanexplainthedifferencebetweenthe solutiontoanequationandthesolutionsto aninequality.
○ Problem1
● Icanwriteaninequalitytorepresenta context.
○ Problems2,6
● Icansolveaninequalityincontextbyusing arelatedequation.
○ Problems2,6
● Icanexpandandfactorexpressions.
Grade7Unit6MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
FrayerModel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● EquationsandTapeDiagrams
● SolvingEquations
● Inequalities
○ Problem3
● Icansolveequationsthatinvolve expanding.
○ Problem3
● Icancomparedifferentstrategiesfor solvingthesameequation.
○ Problem3
● Icanwriteequivalentexpressions.
○ Problem3
● Icanexplainwhetherornottwo expressionsareequivalent.
○ Problem3
● Icanconnectbalancingmovesonhangers tosolvingequations.
○ Problem4
● Icansolveequationswithpositive numbers.
○ Problem4
● Icanwriteequivalentexpressionswith fewerterms.
○ Problem5
● Icanexplainwhetherornotfractionsor negativenumbersmakesenseassolutions toaninequality.
○ Problem6
● Icanwriteandsolveaninequalityto answeraquestionaboutasituation.
○ Problem6
PreviousMathConnections
● Generatingequivalentexpressionsbyusing thedistributivepropertyandbyadding terms.(6.EE.A.3)
● Usingsubstitutiontodetermineifavalueis asolutiontoanequationoraninequality. (6.EE.B.5)
● Writingandsolvingone-stepequationsof theform �� + �� = �� and ���� = ��.(6.EE.B.7)
● Writingandgraphinginequalitiesofthe form �� > �� and �� < ��.(6.EE.B.8)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience.
FirstTopic:EquationsandTapeDiagrams
LearningTargets:
● Icandrawtapediagramstorepresent situationsinwhichthevariable representingtheunknownisspecified. (Foundational)
LearningActivities:

Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptoftapediagramsandwritingandsolving equationsrelatingtotherealworld.
Estimated#ofLessons:6
EssentialQuestions:
● Howdowewriteandsolveequationsand inequalitiestomakesenseofreal-world problems?
● Studentsextendwhattheyknowaboutproportionalrelationshipstoexplorepatternsinothertypes ofrelationships.
● Studentsrevisittapediagramsandsurfacestrategiesforusingtapediagramstodetermineunknown valuesinsituations.
● Studentsusewhattheyknowabouttapediagramsandsituationstomakesenseofequationsof nonproportionalrelationships.Studentsbothconnectdifferentrepresentationsofthesame situationandcreatetheirownrepresentations.
● Studentsusestructuretoanalyzeandsolveaquestionincontextandinterpretthemeaningofits solution.
SecondTopic:SolvingEquations
LearningTargets:
● Icanexpandandfactorexpressions.
● Icansolveequationsthatinvolve expanding.
● Icancomparedifferentstrategiesfor solvingthesameequation.
● Icanwriteequivalentexpressions.
● Icanexplainwhetherornottwo expressionsareequivalent.
● Icanconnectbalancingmovesonhangers tosolvingequations.
Estimated#ofLessons:11
EssentialQuestions:
● Howdowewriteandsolveequationsand inequalitiestomakesenseofreal-world problems??
● Icansolveequationswithpositive numbers.
● Icanwriteequivalentexpressionswith fewerterms.
LearningActivities:
● Studentsdevelopstrategiesfor figuringoutanunknownweightbycreatingbalancedhangerswith fewerobjects.
● Studentsunderstandstrategiesforsolvinganequationandconnectthosetobalancedmovesona hanger.
● Studentsdescribeandusestrategiesforsolvingequationsoftheforms
and
)= �� that involvepositiveandnegativenumbers.
● Studentsextendwhattheyknowaboutdistributingandsolvingtofactorandexpandexpressions, andthensolveequationsinmultiplewaysandcomparetheresults.
● Studentsunderstandthatequivalentexpressionshavethesamevalueforanyvalueofthevariable. Studentswillreasonaboutequivalentexpressionsthatinvolvefactoring,expanding,andreordering terms
● Studentspracticewritingexpressionswithfewertermsbyaddingandexpandingterms.
● Studentspracticesolvingequationsthatinvolveaddingtermsandexpandingexpressions.
● Studentsuseeverythingthey’velearnedsofarintheunittorepresentandanswerquestionsabout situationsincontext.
ThirdTopic:Inequalities
LearningTargets:
● Ican figureoutthesolutionstoan inequality.
● Icanexplainthedifferencebetweenthe solutiontoanequationandthesolutionsto aninequality.
● Icanwriteaninequalitytorepresenta context.
● Icansolveaninequalityincontextbyusing arelatedequation.
● Icanexplainwhetherornotfractionsor negativenumbersmakesenseassolutions toaninequality.
● Icanwriteandsolveaninequalityto answeraquestionaboutasituation.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:7
● Whatdoestheequationorinequalitylook likeonthegraph?Howdoesthatreveal possiblesolutionstothereal-worldproblem?
● StudentsbuildontheirknowledgefromGrade6aboutgraphinginequalitiesandareintroducedto twonewsymbols:≥and≤.
● Studentsmakesenseofsolvinginequalitiesusinghangerdiagrams.
● Studentsusewhattheyhavelearnedtowriteandsolveinequalitiesrelatedtosituationsabout budgetingandspendingmoney.
● Studentspracticesolvinginequalitieswithbothpositiveandnegativecoefficients,andconnectthe solutionsofinequalitiestotheirgraphs.
● Studentspracticewritingandsolvinginequalitiesandcriticallyexaminewhatthesolutionstothose inequalitiesmeanincontext.
CourseName:Grade7Unit7Title:Angles,Triangles,andPrismsEst.#ofLessons:19
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsextendtheir6thgradeworkonrectangularsurfaceareaandvolumetotriangular prisms.Studentssolveequationsbasedongeometricproperties(complementary,supplementary,vertical). Studentsalsoexplorewhetheritispossibletodrawnotriangles,onetriangle,ormorethanonetriangle giventhreemeasuresofsidesorangles.
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
7.G.A.2 Draw(byhand,witharulerandprotractor, andwithtechnology)geometricshapeswithgiven conditions.Focusonconstructingtrianglesfrom threemeasuresofanglesorsidesandnoticewhen theconditionsdetermineauniquetriangle,more thanonetriangle,ornotriangle.
7.G.A.3 Describethetwo-dimensional figuresthat resultfromslicingthree-dimensional figures,asin planesectionsofrightrectangularprismsandright rectangularpyramids.
7.G.B.5 Usefactsaboutsupplementary, complementary,vertical,andadjacentanglesina multistepproblemtowriteandsolvesimple equationsforanunknownangleina figure.
7.G.B.6 Solvereal-worldandmathematical problemsinvolvingarea,volume,andsurfacearea oftwo-andthree-dimensionalobjectscomposedof triangles,quadrilaterals,polygons,cubes,andright prisms.
7.EE.A.2 Understandthatrewritinganexpression indifferentformsinaproblemcontextcanshed lightontheproblemandhowthequantitiesinit arerelated.
7.EE.B.4 Usevariablestorepresentquantitiesina
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● CRITICALTHINKING: Identifyaproblem,ask keyquestions,andmakepredictions. MP#2 Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively;MP#4 Modelwithmathematics.
real-worldormathematicalproblem,andconstruct simpleequationsandinequalitiestosolveproblems byreasoningaboutthequantities.
● Recognizingdifferentrelationsbetween anglescanassistin findinganunknown angle.
● Thechangeindimensionsofaprismaffects thesurfaceareaandvolumeofanobject.
● Howtodifferentiateandapplydifferent anglerelationships.
● Howtoconstructatriangleusinggivenside lengthsandangles.
● Howtoevaluatetheeffectsonvolume givenchangestoanydimension.
● Whatanglerelationshipsareformedwith intersectinglines?
● Howdoesmypriorknowledgeofrectangles helpmedeterminethepropertiesoftriangles?
● Icandescribewhatcomplementaryand supplementaryanglesare.
● IcandetermineunknownanglesusingwhatI knowaboutcomplementaryand supplementaryangles.
● Icanconnectananglediagramwithan equationthatrepresentsit.
● Icandescribewhatverticalanglesare.
● Icanwriteanduseequationstodetermine unknownangles.
● IcansolvemultistepproblemsusingwhatI knowaboutcomplementary,supplementary, andverticalangles.
● Icandecidewhetherornotthreesidelengths willmakeatriangle.
● Icanbuildtrianglesgiventhree measurements.
● Icanexplainwhythereissometimesmore thanonepossibletrianglegiventhree measurements.
● Icandescribecrosssectionsofasolid.
● Icancompareandcontrastcrosssectionsof prismsandpyramids.
● Icanexplainhowthevolumeofaprismis relatedtotheareaofitsbaseanditsheight.
● Icancalculatethevolumeofrectangularand triangularprisms.
● Icancalculatethesurfaceareaofaprism.
● Icancompareandcontrastdifferent strategiesforcalculatingsurfacearea.
● Icandecidewhethervolumeorsurfaceareais moreusefultoansweraquestionabouta situation.
● Icanansweraquestionaboutareal-world situationusingmyknowledgeofsurfacearea andvolume.
SummativeAssessment
Grade7Unit7EndofUnitAssessment
● Icandescribewhatcomplementaryand supplementaryanglesare.
○ Problem3
● Icandetermineunknownanglesusingwhat Iknowaboutcomplementaryand supplementaryangles.
○ Problem3
● Icanconnectananglediagramwithan equationthatrepresentsit
○ Problem3
● Icandescribewhatverticalanglesare.
○ Problem3
● Icanwriteanduseequationstodetermine unknownangles
○ Problem3
● Icandecidewhetherornotthreeside lengthswillmakeatriangle.
○ Problem1
● Icandescribecrosssectionsofasolid.
○ Problem2
● Icancompareandcontrastcrosssections ofprismsandpyramids.
○ Problem2
● Icanbuildtrianglesgiventhree measurements.
○ Problem4
● Icanexplainwhythereissometimesmore thanonepossibletrianglegiventhree measurements.
○ Problem4
● Icanexplainhowthevolumeofaprismis relatedtotheareaofitsbaseanditsheight.
○ Problem5
● Icancalculatethevolumeofrectangular andtriangularprisms.
○ Problem5
● Icancalculatethesurfaceareaofaprism.
○ Problem5
FormativeAssessment
Grade7Unit7MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● AngleRelationships
● DrawingTriangles
● SolidGeometry
● Icancompareandcontrastdifferent strategiesforcalculatingsurfacearea.
○ Problem5
● IcansolvemultistepproblemsusingwhatI knowaboutcomplementary, supplementary,andverticalangles.
○ Problem6
● Icandecidewhethervolumeorsurface areaismoreusefultoansweraquestion aboutasituation.
○ Problem7
● Icanansweraquestionaboutareal-world situationusingmyknowledgeofsurface areaandvolume.
○ Problem7
FirstTopic:AngleRelationships
LearningTargets:
● Icandescribewhatcomplementaryand supplementaryanglesare.
● Icandetermineunknownanglesusingwhat Iknowaboutcomplementaryand supplementaryangles.
● Icanconnectananglediagramwithan equationthatrepresentsit.
● Icandescribewhatverticalanglesare.
● Icanwriteanduseequationstodetermine unknownangles.
● IcansolvemultistepproblemsusingwhatI knowaboutcomplementary, supplementary,andverticalangles.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:6
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatanglerelationshipsareformedwith intersectinglines?
● Studentsrecallwhattheyknowaboutanglesandhowtoestimatethemeasure.Thentheyusewhat theyknowaboutangleslike90°and360°toreasonaboutanglemeasurementsaroundacircle.
● Studentscontinuetoexploreanglemeasurementsandtheirrelationships.Theylearnformalwaysto describetwospecificanglerelationships:complementaryanglesandsupplementaryangles.They alsorevisitwhattheylearnedinUnit6astheyconnectanglediagramstoequations.
● Studentsapplywhatthey’velearnedsofartounderstandtherelationshipbetweenverticalangles. Theywritetheirownequationstorepresentcomplexdiagramsandusethoseequationsto determineunknownanglemeasures.
● Thislessonconcludesstudents’explorationofanglerelationshipsinGrade7.Studentssolve multistepproblemsanddeterminemissinganglemeasuresonpaper.Theyalsocreatetheirown
challengestotradewiththeirclassmates.
SecondTopic:DrawingTriangles
LearningTargets:
● Icandecidewhetherornotthreeside lengthswillmakeatriangle.
● Icanbuildtrianglesgiventhree measurements.
● Icanexplainwhythereissometimesmore thanonepossibletrianglegiventhree measurements.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:6
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatanglerelationshipsareformedwith intersectinglines?
● Thislessoninvitesstudentstonoticethatnotallcombinationsofthreesidescreateatriangleandto reasonaboutcharacteristicsofsidelengthsthatdoanddonotcreatetriangles.
● Studentscontinuetostudythesidelengthsofpolygons.Studentsmakeconnectionsbetweenside lengthsandcircles,andusethosecirclestocreatetriangleswithspecificsidelengths.Thislesson alsointroducestheideathatalltriangleswiththesamesidelengthsareidenticalcopies,butall quadrilateralswiththesamesidelengthsarenot.
● Studentsareaskedtoconsiderboththelengthsandtheanglesoftriangles.Theyrecognizethattwo triangleswithtwoanglemeasuresandonesidelengthincommon(ortwosidelengthsandoneangle measureincommon)arenotnecessarilyidenticalcopies.Studentsalsocometounderstandthat knowingtheorderofthemeasurementscanhelpcreateidenticaltriangles.
● Studentsareinvitedtotakethethinkingtheyweredoingindigitallessons5–7andapplyittopaper. Theyuserulersandprotractorstodrawtrianglesgiventhreemeasurementsandcontinuetoanswer questionslike: Isitpossibletodrawatrianglewiththesemeasurements?Isitpossibletodrawmorethan one?
ThirdTopic:SolidGeometry
LearningTargets:
● Icandescribecrosssectionsofasolid.
● Icancompareandcontrastcrosssections ofprismsandpyramids.
● Icanexplainhowthevolumeofaprismis relatedtotheareaofitsbaseanditsheight.
● Icancalculatethevolumeofrectangular andtriangularprisms.
● Icancalculatethesurfaceareaofaprism.
● Icancompareandcontrastdifferent strategiesforcalculatingsurfacearea.
● Icandecidewhethervolumeorsurface areaismoreusefultoansweraquestion
Estimated#ofLessons:7
EssentialQuestions:
● Howdoesmypriorknowledgeofrectangles helpmedeterminethepropertiesoftriangles?
aboutasituation.
● Icanansweraquestionaboutareal-world situationusingmyknowledgeofsurface areaandvolume.
LearningActivities:
● Studentsexploreanddescribepossiblecrosssectionsofsolids.Theyalsoexploreideasaboutcross sectionsofprismsandpyramids.
● Studentsusepriorknowledgeaboutvolumeofrectangularprismstohelpthemcalculatethevolume oftriangularprismsusingthebaseareaandheight.
● Studentsextendthisworktocalculatethevolumeofmorecomplicatedprisms.Studentsusea varietyofstrategiestodeterminetheareasofcomplicatedbases,includingdecomposingintomore familiarshapesorsurroundingandsubtracting.
● StudentsbuildontheworktheyhavedonecalculatingsurfaceareaofrectangularprismsinGrade6 inordertocalculatethesurfaceareaofmorecomplicatedprisms.
● Studentswrapupthisunitbyapplyingtheirknowledgeofsurfaceareaandvolumetosolvea complexprobleminvolvingfoldingan8.5-by-11-inchsheetofpaper.Studentsdeterminewhetheror notfoldingthepaperinonedirectionortheotheraffectstheamountofpopcornaboxcanholdor theamountofmaterialneededtocreatethebox. CourseName:Grade7Unit8Title:ProbabilityandSamplingEst.#ofLessons:22
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsexploretheconceptofprobabilitytodescribethelikelihoodofunknowneventsand usesimulationstoestimatetheprobabilityofreal-worldsituations.Astheybecomemoresophisticated, studentsusesamplestocalculateprobabilitiesandmakepredictionsaboutthepopulation(ex.peopleor things).
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
7.SP.A.1 Understandthatstatisticscanbeusedto gaininformationaboutapopulationbyexamininga sampleofthepopulation.Generalizationsabouta populationfromasamplearevalidonlyifthe sampleisrepresentativeofthatpopulation. Understandthatrandomsamplingtendsto producerepresentativesamplesandsupportvalid inferences.
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● CRITICALTHINKING: Identifyaproblem,ask keyquestions,andmakepredictions. MP#2 Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively;MP#4 Modelwithmathematics.
● CRITICALTHINKING: Analyzedatainorder todrawconclusions. MP#6Attendto
7.SP.A.2 Usedatafromarandomsampletodraw inferencesaboutapopulationwithanunknown characteristicofinterest.Generatemultiple samples(orsimulatedsamples)ofthesamesizeto gaugethevariationinestimatesorpredictions.
7.SP.B.3 Informallyassessthedegreeofvisual overlapoftwonumericaldatadistributionswith similarvariabilities,measuringthedifference betweenthecentersbyexpressingitasamultiple ofameasureofvariability.
7.SP.B.4 Usemeasuresofcenterandmeasuresof variabilityfornumericaldatafromrandomsamples todrawinformalcomparativeinferencesabouttwo populations.
7.SP.C.5 Understandthattheprobabilityofa chanceeventisanumberbetween0and1that expressesthelikelihoodoftheeventoccurring. Largernumbersindicategreaterlikelihood.A probabilitynear0indicatesanunlikelyevent,a probabilityaround1/2indicatesaneventthatis neitherunlikelynorlikely,andaprobabilitynear1 indicatesalikelyevent.
7.SP.C.6 Approximatetheprobabilityofachance eventbycollectingdataonthechanceprocessthat producesitandobservingitslong-runrelative frequency,andpredicttheapproximaterelative frequencygiventheprobability.
7.SP.C.7 Developaprobabilitymodelanduseitto findprobabilitiesofevents.Compareprobabilities fromamodeltoobservedfrequencies.Ifthe agreementisnotgood,explainpossiblesourcesof thediscrepancy.
7.SP.C.7.A Developauniformprobabilitymodelby assigningequalprobabilitytoalloutcomes,anduse themodeltodetermineprobabilitiesofevents.
7.SP.C.7.B Developaprobabilitymodel(whichmay notbeuniform)byobservingfrequenciesindata generatedfromachanceprocess.
7.SP.C.8 Findprobabilitiesofcompoundevents
precision;MP#8Lookforandexpress regularityinrepeatedreasoning.
usingorganizedlists,tables,treediagrams,and simulation.
7.SP.C.8.A Understandthat,justaswithsimple events,theprobabilityofacompoundeventisthe fractionofoutcomesinthesamplespaceforwhich thecompoundeventoccurs.
7.SP.C.8.B Representsamplespacesforcompound eventsusingmethodssuchasorganizedlists, tables,andtreediagrams.Foraneventdescribedin everydaylanguage(e.g.,"rollingdoublesixes"), identifytheoutcomesinthesamplespacewhich composetheevent.
7.SP.8.C Designanduseasimulationtogenerate frequenciesforcompoundevents.
Theaccuracy/effectivenessofasampleiscentralto thevalidityofaprediction.
● Howtodeterminetheprobabilityofan event.
● Howtodecidethepropersamplingmethod andanalysisofagivensituation.
● HowcanIuseprobabilitytounderstandor predictanoutcome?
● Isthisagoodsample?
● Icandeterminetheprobabilityofanevent usingitssamplespace.
● Icancompareprobabilitieswrittenas fractions,decimals,andpercentages.
● Icanexplainwhytheresultsofarepeated experimentmaynotexactlymatchthe probabilityoftheevent.
● Icanexplainhowtheresultsofarepeated experimentarerelatedtotheprobabilityof theevent.
● Icancalculatetheprobabilityofamultistep event.
● Icanwriteoutthesamplespacefora multistepexperimentusingalist,table,ortree diagram.
● Icancalculatethemeanandmeanabsolute deviation(MAD)foradataset.
● Icancompareandcontrastpopulationsusing meanandMAD.
● Icanexplainwhyasamplingmethodisoris notlikelytoproduceabiasedsample.
● Icanusemeasuresofcenterandthe variabilityoftwosamplestodecideiftwo populationsareverydifferent.
● Icanuseameasureofvariabilitytoexplain thedifferencebetweenmeasuresofcenter.
● Icancomparetwogroupsbytakingrandom samples,thencalculatingandinterpretingthe statistics.
● Icanuseproportionalreasoningandasample toestimateinformationaboutapopulation.
Grade7Unit8EndofUnitAssessment
● Icandeterminetheprobabilityofanevent usingitssamplespace.
○ Problem1
● Icancompareprobabilitieswrittenas fractions,decimals,andpercentages.
○ Problem1
● Icanexplainwhyasamplingmethodisoris notlikelytoproduceabiasedsample.
○ Problem2
● Icancalculatethemeanandmeanabsolute deviation(MAD)foradataset.
○ Problem3
● Icancompareandcontrastpopulations usingmeanandMAD.
○ Problem3
● Icanexplainhowtheresultsofarepeated experimentarerelatedtotheprobabilityof theevent.
○ Problem4
● Icanexplainwhytheresultsofarepeated experimentmaynotexactlymatchthe probabilityoftheevent.
○ Problem4
● Icanwriteoutthesamplespacefora multistepexperimentusingalist,table,or treediagram.
○ Problem5
● Icancalculatetheprobabilityofamultistep event.
○ Problem5
Grade7Unit8MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
FrayerModel(blanktemplateandrationale)
● Probability
● Sampling
● Icanuseproportionalreasoninganda sampletoestimateinformationabouta population.
○ Problem6
● Icanusemeasuresofcenterandthe variabilityoftwosamplestodecideiftwo populationsareverydifferent.
○ Problem7
● Icanuseameasureofvariabilitytoexplain thedifferencebetweenmeasuresofcenter.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask:
AsthmaRates-Studentsanalyzerealdataabout asthmaratesbygeneratingrandomsamplesand usingthesamplestocompareasthmaratesin differentplacesinNewYork.
Understanding#2 LearningTargets:
● Icancomparetwogroupsbytakingrandom samples,thencalculatingandinterpreting thestatistics.
TransferSkill:CriticalThinking
PreviousMathConnections
Writingequivalentfractions,decimals,and percentages.(6.RP.A.3.C)
● Understandingwhatthecenter,variability,and shapedescribeaboutasetofdata.(6.SP.A.2, 6.SP.A.3)
● Calculatingquantitativemeasuresofcenter (meanandmedian)andvariability(meanabsolute deviationandinterquartilerange). (6.SP.B.5.c)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck

Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifytheir understandingofconceptsofchance,benchmark fractions,anddecimalsbetween0and1.
FirstTopic:Probability
LearningTargets:
● Icandeterminetheprobabilityofanevent usingitssamplespace.
● Icancompareprobabilitieswrittenas fractions,decimals,andpercentages.
● Icanexplainwhytheresultsofarepeated experimentmaynotexactlymatchthe probabilityoftheevent.
● Icanexplainhowtheresultsofarepeated experimentarerelatedtotheprobabilityof theevent.
● Icancalculatetheprobabilityofa multistepevent.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:12
● HowcanIuseprobabilitytounderstandor predictanoutcome?
● Studentsconductexperimentsandusephrasessuchas“likely”and“equallylikelyasnot”todescribe thelikelihoodofdifferentevents.
● Studentsconnecttheconceptoflikelihoodwithprobabilityusingnumbersbetween0and1.They alsousesamplespacestohelpdeterminetheseprobabilities.
● Studentsuserepeatedexperimentsandproportionalitytopredictthecontentsofamysterybag, recognizingthatthenumberofrepeatedexperimentsaffectstheaccuracyofyourprediction.
● Studentsrecognizethatifyouperformanexperimentrepeatedly,theresultswillapproach,butmay notexactlymatch,theprobabilityoftheevent.
● Studentschallengetheirassumptionsaboutprobabilitytoolssuchascoinsandnumbercubes.They decidewhetherornotanobjectisfairbycomparingprobabilitiesfromamodeltotheresultsofa repeatedexperiment.
● Studentsmakesenseofprobabilitiesofmultistepevents.Theylearnaboutanduselists,tables,and treediagramstorepresentthesamplespaceofeventswithmultiplepenniesorspinners.Theythen usethesetoolstodeterminetheprobabilitiesofmultistepeventsandconsiderwhetherornot different
● Studentsusespinnersandblocksinbagstosimulatethechancesthatitrainsbasedonprobabilities fromaweatherforecast.gamesarefair.
● Studentsdesignandperformsimulationstoestimatetheprobabilitiesofmultistepreal-world situations.
SecondTopic:Sampling
LearningTargets:
● Icanwriteoutthesamplespacefora multistepexperimentusingalist,table,or treediagram.
● Icancalculatethemeanandmeanabsolute deviation(MAD)foradataset.
● Icancompareandcontrastpopulations usingmeanandMAD.
● Icanexplainwhyasamplingmethodisoris
Estimated#ofLessons:10
EssentialQuestions: ● Isthisagoodsample?
notlikelytoproduceabiasedsample.
● Icanusemeasuresofcenterandthe variabilityoftwosamplestodecideiftwo populationsareverydifferent.
● Icanuseameasureofvariabilitytoexplain thedifferencebetweenmeasuresofcenter.
● Icancomparetwogroupsbytakingrandom samples,thencalculatingandinterpreting thestatistics.
● Icanuseproportionalreasoninganda sampletoestimateinformationabouta population.
● Studentscalculatethemeanandmeanabsolutedeviation(MAD),andusethesemeasuresto compareandcontrastdatarepresentedbydotplots.
● Studentslearnthetermssampleandpopulation,andexploretheadvantagesanddisadvantagesof usingsamplestoansweraquestionaboutapopulation.
● Studentsreviewheadlinesproducedfromdifferentsamplesofdataandexplainwhetherornota givensamplingmethodislikelytoproducedatathatisrepresentativeofthepopulation.
● Studentsrevisitproportionalrelationshipsandpercentagesusingdatafromasampletoestimate thenumberofmarigoldsinalarge flowergarden.
● Studentsestimateameasureofcenterofapopulationbasedononeormoresamplesofthe population.Theyalsoexplainwhyanestimateforthecenterofapopulationismorelikelytobe accuratewhenitisbasedonarandomsamplewithlessvariability.
● Studentscomparetwopopulationsbasedonsamples.Thislessonintroducestheideathatyoucan determineifthereisabigdifferencebetweentwopopulationsbylookingatthedifferencebetween thecentersofsamplesandcomparingthedifferencetothemeasureofvariability.
● Studentsanalyzerealdataaboutasthmarates.Theygeneraterandomsamplesandusethemto comparetheasthmaratesofdifferentplacesinNewYork.
CourseName:Grade8Unit1Title:RigidTransformationsandCongruenceEst.#ofLessons:20
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentswillinvestigate translations, rotations,and reflections,andusethesetransformationsto makeinformalargumentsaboutcongruence.Theyalsoexploreanglerelationshipsonparallellinesandthe trianglesumtheorem.
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
8.G.A Understandcongruenceandsimilarityusing physicalmodels,transparencies,orgeometry software.
8.G.A.1: Verifyexperimentallythepropertiesof rotations,reflections,andtranslations.
8.G.A.1.A Linesaretakentolines,andline segmentstolinesegmentsofthesamelength.
8.G.A.1.B Anglesaretakentoanglesofthesame measure.
8.G.A.1.C Parallellinesaretakentoparallellines.
8.G.A.2 Understandthatatwo-dimensional figure iscongruenttoanotherifthesecondcanbe obtainedfromthe firstbyasequenceofrotations, reflections,andtranslations;giventwocongruent figures,describeasequencethatexhibitsthe congruencebetweenthem.
8.G.A.3: Describetheeffectofdilations, translations,rotations,andreflectionson two-dimensional figuresusingcoordinates.
8.G.A.5 Useinformalargumentstoestablishfacts abouttheanglesumandexteriorangleoftriangles, abouttheanglescreatedwhenparallellinesarecut byatransversal,andtheangle-anglecriterionfor similarityoftriangles.
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #3Constructviableargumentsandcritiquethe reasoningofothers;MP#5:Useappropriatetools strategically;MP#6:Attendtoprecision.
● CRITICALTHINKING:Analyzedatainorderto drawconclusions. MP#:1Makesenseofproblems andpersevereinsolvingthem;MP#5:Use appropriatetoolsstrategically;MP#6:Attendto precision;MP#7:Lookforandmakeuseof structure.
● Partsofcongruent figuresdonotchangeno matterthetransformationapplied.
Knowledge
● Howtotranslate,reflect,androtatea congruent figurefromonepositionto another.
● Howtodeterminewhethertwo figuresare congruent.
Howcanyouusetranslations,rotations,and reflectionstoprovecongruence?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icandescribehowtomoveonepartofa figure toanotherusingarigidtransformation.
(Foundational)
● Icandecidewhichtypeoftransformations willworktomoveone figuretoanother.
● Icanusegridstocarryouttransformationsof figures.
● Icanapplytransformationstopointsonagrid ifIknowtheircoordinates.
● Icandescribetheeffectsofarigid transformationonapairofparallellines.
● IfIhaveapairofverticalanglesandknowthe anglemeasureofoneofthem,Ican findthe anglemeasureoftheother.
● Ican findmissingsidelengthsorangle measuresusingpropertiesofrigid transformations.
● Icanuseprecisemathematicalknowledgein communicatingthetransformation.
● Icandecidevisuallywhetherornottwo figuresarecongruent.
● Icandecideusingrigidtransformations whetherornottwo figuresarecongruent.
SummativeAssessment
EndUnitAssessment
● Icandecidewhichtypeoftransformations willworktomoveone figuretoanother.
○ Problem2
● Icanusegridstocarryouttransformations of figures.
○ Problem2
● Icanapplytransformationstopointsona gridifIknowtheircoordinates.
○ Problem1
● Icandescribetheeffectsofarigid transformationonapairofparallellines.
○ Problem3,4,5
● IfIhaveapairofverticalanglesandknow
FormativeAssessment
MidunitGradeAssessment 8Unit7Quizzes1and2
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesis,cooldownsand practicedaysasappropriate.
Frayermodel(rationale)
● Transformations
● DefiningCongruence
● ApplyingCongruence
theanglemeasureofoneofthemIcan find theanglemeasureoftheother.
○ Problem3,4,5
● Ican findmissingsidelengthsorangle measuresusingpropertiesofrigid transformations.
○ Problem7
● Icandecidevisuallywhetherornottwo figuresarecongruent.
○ Problem7
● Icandecideusingrigidtransformations whetherornottwo figuresarecongruent.
○ Problem6,7
PerformanceTask TransformationGolf:
● Studentsidentifyanddescribesequences oftransformationsthattakeone figureto anotherinthecontextofseveral TransformationGolfchallenges.
Understanding#1
LearningTargets#1&2 TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
AretheyCongruent?
● Studentsuserigidtransformationstomake argumentsforwhytwo figuresareorare notcongruent.Theylearnthattwo figures withcommonalities,suchashavingthe sameareaorhavingcorrespondingside lengthsthatareequal,doesnotguarantee congruence.
Understanding#2
LearningTargets#8,9,10 TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Identifyingparallelandperpendicularlines. (4.G.A.1)
● Graphingpointsanddrawingpolygonsin thecoordinateplane.(5.G.A.1,6.G.A.3)
● Identifyingverticalandadjacentangles. (7.G.B.5)
● Drawinggeometricshapeswithgiven conditions,payingspecialattentiontothe anglesoftriangles.(7.G.A.2)
● Calculatingtheareaoftrianglesand quadrilaterals.(6.G.A.1)


Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofrigidmotionsintheplaneaswellas parallelandperpendicularlines.
FirstTopic:Transformations
LearningTargets:
● Icandecidewhichtypeoftransformations willworktomoveone figuretoanother.
● Icanusegridstocarryouttransformations of figures.
● Icanapplytransformationstopointsona gridifIknowtheircoordinates.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:8
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatarecongruent figuresandhowarethey translated,rotated,andreflectedaboutthe coordinateplane?
● Studentsareintroducedtotransformationsof figuresanddescribethesemovementsusing everydaylanguage.
● Studentsbegintodescribeagiventranslation,rotation,orreflectionwithgreaterprecision.
● Studentsidentifyanddescribesequencesoftransformationsthattakeone figuretoanotherinthe contextofseveralTransformationGolfchallenges.
● Studentsusethetermstranslation,rotation,andreflectiontodescribeanddrawtransformationson agrid.
● Studentsusecoordinatestodescribe figuresandtheirimagesundertransformationsinthe coordinateplane.
● Studentscommunicatepreciselyabouttransformationsofpolygonsonacoordinategrid.
SecondTopic:DefiningCongruence
LearningTargets:
● Icandescribetheeffectsofarigid transformationonapairofparallellines.
● IfIhaveapairofverticalanglesandknow theanglemeasureofoneofthem,Ican find theanglemeasureoftheother.
● Ican findmissingsidelengthsorangle measuresusingpropertiesofrigid transformations.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:6
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatarecongruent figuresandhowarethey translated,rotated,andreflectedaboutthe coordinateplane?
● Studentsexplorewhatitmeansforshapestobe“thesame”andtolearnthetermcongruent.
● Studentsbegintoseethattranslations,rotations,andreflectionspreservelengthsandangle measures,andusethetermrigidtransformationsforthe firsttime.
● Studentsuserigidtransformationstomakeargumentsforwhytwo figuresareorarenotcongruent.
ThirdTopic:ApplyingCongruence
LearningTargets:
● Icandecidevisuallywhetherornottwo figuresarecongruent.
● Icandecideusingrigidtransformations whetherornottwo figuresarecongruent.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:6
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatarecongruent figuresandhowarethey translated,rotated,andreflectedaboutthe coordinateplane?
● Studentsseethatparallellinesaretakentoparallellinesunderanyrigidtransformations.They justifythatpairsofverticalanglesandalternateinterioranglesonparallellinesarecongruent.
● Studentsobservethatthesumoftheinterioranglesofanytriangleisalways180degrees.
● Studentsapplywhatthey'velearnedaboutanglerelationshipsinpreviouslessonsandinformally establishthetrianglesumtheorem.
● Studentsexamineandcreatedifferentpatternsofshapes,includingtessellationsandcomplex designsthatexhibitrotationalsymmetry.
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentswillinvestigatetheconceptsofdilation,similarity,andslopeinorderinorderto discoverhowtoenlargeorreducethesizeofaplane figure.Thisdiscoverywillallowthestudentstowork with“slopetriangles”andusethesimilarityofslopetrianglesonthesamelinetounderstandthatanytwo distinctpointsonalinedeterminethesameslope.
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
8.G.A: Understandcongruenceandsimilarityusing physicalmodels,transparencies,orgeometry software.
8.G.A.2: Understandthatatwo-dimensional figure iscongruenttoanotherifthesecondcanbe obtainedfromthe firstbyasequenceofrotations, reflections,andtranslations;giventwocongruent figures,describeasequencethatexhibitsthe congruencebetweenthem.
8.G.A.3: Describetheeffectofdilations, translations,rotations,andreflectionson two-dimensional figuresusingcoordinates.
8.G.A.4: Understandthatatwo-dimensional figure issimilartoanotherifthesecondcanbeobtained fromthe firstbyasequenceofrotations, reflections,translations,anddilations.Giventwo similartwo-dimensional figures,describea sequencethatexhibitsthesimilaritybetween them.
8.G.A.5: Useinformalargumentstoestablishfacts abouttheanglesumandexteriorangleoftriangles, abouttheanglescreatedwhenparallellinesarecut byatransversal,andtheangle-anglecriterionfor similarityoftriangles
8.EE.B.6: Usesimilartrianglestoexplainwhythe slope`m`isthesamebetweenanytwodistinct pointsonanon-verticallineinthecoordinate plane.Derivetheequation`y=mx`foraline throughtheoriginandtheequation`y=mx+b`fora lineinterceptingtheverticalaxisat`b`.
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #3Constructviableargumentsandcritiquethe reasoningofothers;MP#5:Useappropriatetools strategically.
● CRITICALTHINKING:Analyzedatainorderto drawconclusions. MP#5:Useappropriatetools strategically;MP#8Lookforandexpress regularityinrepeatedreasoning.
● Whenyoushrinkorenlargea figure,the anglesstaythesamebutthesidelengths change.
● Theslopeofalineisfoundthroughthe
● Howdo figureschangewhentheyarereduced orenlarged?
● Howdosimilartriangleshelprevealtheslope ofaline?
explorationofthepropertiesofsimilar triangles.
● Howtoreduceorenlargeaplane figure throughdilationsinordertoconstruct similar figures.
● Howtodeterminetheslopeofalineusing theconceptofsimilartriangles.
● Icanapplyadilationtoapolygonusingagrid.
● Icanapplydilationstopolygonsona rectangulargridifIknowthecoordinatesof theverticesandofthecenterofdilation.
● Icanapplyasequenceoftransformationsto one figuretogetasimilar figure.
● Icanuseasequenceoftransformationsto explainwhytwo figuresaresimilar.
● Icanuseanglemeasuresandsidelengthsto concludethattwopolygonsarenotsimilar.
● Iknowtherelationshipbetweenangle measuresandsidelengthsinsimilarpolygons.
● Iknowhowtodecideiftwotrianglesare similarjustbylookingattheiranglemeasures.
● Icandecideiftwotrianglesaresimilarby lookingatquotientsoflengthsof correspondingsides.
● Ican findmissingsidelengthsinapairof similartrianglesusingquotientsofside lengths.
● Icandrawalineonagridwithagivenslope.
● Ican findtheslopeofalineonagrid.
SummativeAssessment
EndofUnitAssessment
● 1.Icanapplyadilationtoapolygonusinga grid.
○ Problem4
● 2.Icanapplydilationstopolygonsona rectangulargridifIknowthecoordinatesof theverticesandofthecenterofdilation.I knowhowtodecideiftwotrianglesare similarjustbylookingattheirangle measures.
○ Problem7
● 3.Icanapplyasequenceof transformationstoone figuretogeta similar figure.
○ Problem2,4
● 4.Icanuseasequenceoftransformations
FormativeAssessment
MidunitassessmentsGrade8Unit2
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate.
Frayermodel(rationale)
● Dilations
● Similarity
● Slope
toexplainwhytwo figuresaresimilar.
○ Problem2,4
● 5.Icanuseanglemeasuresandside lengthstoconcludethattwopolygonsare notsimilar.
○ Problem3
● 6.Iknowtherelationshipbetweenangle measuresandsidelengthsinsimilar polygons.
○ Problem3
● 7.Iknowhowtodecideiftwotrianglesare similarjustbylookingattheirangle measures.
○ Problem5
● 8.Icandecideiftwotrianglesaresimilarby lookingatquotientsoflengthsof correspondingsides.
○ Problem1
● 9.Ican findmissingsidelengthsinapairof similartrianglesusingquotientsofside lengths.
○ Problem1
● 10.Icandrawalineonagridwithagiven slope.
○ Problem7
● 11.Ican findtheslopeofalineonagrid
○ Problem7
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Graphingpointsinallfourquadrantsofthe coordinateplane.(6.NS.C.8)
● Usingproportionalrelationshipsto determineunknownvalues.(7.RP.A.2)
● Graphingproportionalrelationships. (7.RP.A.2.d)
● Dividingvaluesintofractionalparts. (6.NS.A.1)
● Computinglengthsandscalefactorsof scaledcopies.(7.G.A.1)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:
FirstTopic:Dilations
LearningTargets:
● Icanapplyadilationtoapolygonusinga grid.
● Icanapplydilationstopolygonsona rectangulargridifIknowthecoordinatesof theverticesandofthecenterofdilation.I knowhowtodecideiftwotrianglesare similarjustbylookingattheirangle measures.
LearningActivities:

Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofplottingpointsonthecoordinateplane, locatingthey-axis,and findingdistancesonaplane.
Estimated#ofLessons:6
EssentialQuestions:
● Whataresimilar figuresandhowarethey usedtohelpdeterminetheslopeofaline?
● Studentsareinformallyintroducedtotheconceptsofdilationandsimilarityandexploredilationas aprocessthatproducesscaledcopies.
● Studentsperformdilations,movingfrominformaltoformalwaysofmeasuringtodeterminethe distancesbetweenthecenter,pre-image,andimageinadilation.
● Studentsapplydilationstopolygonsonagridandexploretheimpactofscalefactorsbetween0and 1.Studentsdiscoverthatdilationsmaplinesegmentstolinesegments,andpolygonstopolygons.
● Studentsworkonacoordinategridtopreciselycommunicatetheinformationneededtoperform dilations.
SecondTopic:Similarity
LearningTargets:
● Icanapplyasequenceoftransformations toone figuretogetasimilar figure.
● Icanuseasequenceoftransformationsto
Estimated#ofLessons:5
EssentialQuestions:
● Whataresimilar figuresandhowarethey usedtohelpdeterminetheslopeofaline?
explainwhytwo figuresaresimilar.
● Icanuseanglemeasuresandsidelengthsto concludethattwopolygonsarenotsimilar.
● Iknowtherelationshipbetweenangle measuresandsidelengthsinsimilar polygons.
● Iknowhowtodecideiftwotrianglesare similarjustbylookingattheirangle measures.
● Icandecideiftwotrianglesaresimilarby lookingatquotientsoflengthsof correspondingsides.
● Ican findmissingsidelengthsinapairof similartrianglesusingquotientsofside lengths.
LearningActivities:
● Studentsidentifyanddescribesequencesoftransformations,includingdilations,thattakeone figuretoanotherinthecontextofTransformationGolf.
● Studentsexaminethesidelengthsandanglemeasuresofpolygonsinordertounderstandsimilarity.
● Studentsexamineanglemeasurementsintrianglestodeterminewhetherornottwotrianglesare similar.
● Studentsdiscoverthatthequotientoftwosidelengthsinonetriangleisequaltothequotientofthe correspondingsidelengthsinasimilartriangle.
ThirdTopic:Slope Estimated#ofLessons:5
LearningTargets:
● Icandrawalineonagridwithagivenslope.
● Ican findtheslopeofalineonagrid.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions
● Whataresimilar figuresandhowarethey usedtohelpdeterminetheslopeofaline?
● Studentsareintroducedtotheslopeofthelineasthequotientoftheverticalsidelengthandthe horizontalsidelength.
● Studentsuseslopetohelpdetermineifpointslieonaparticularline.
CourseName:Grade8Unit3Title:LinearRelationships Est.#ofLessons:16
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentswilldeepentheirunderstandingofslopeaslinearequationstranslateverticallyalong they-axis.Theymakeconnectionsamongrateofchange,slope,andconstantofproportionality,and betweenlinearandproportionalrelationships.
EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
8.EE.B: Understandtheconnectionsbetween proportionalrelationships,lines,andlinear equations.
8.EE.B.5: Graphproportionalrelationships, interpretingtheunitrateastheslopeofthegraph. Comparetwodifferentproportionalrelationships representedindifferentways.Forexample, compareadistance-timegraphtoadistance-time equationtodeterminewhichoftwomoving objectshasgreaterspeed.
8.EE.B.6: Usesimilartrianglestoexplainwhythe slopemisthesamebetweenanytwodistinct pointsonanon-verticallineinthecoordinate plane;derivetheequationy=mxforalinethrough theoriginandtheequationy=mx+bforaline interceptingtheverticalaxisatb.
8.EE.C: Analyzeandsolvelinearequationsand pairsofsimultaneouslinearequations.
8.EE.C.8.A: Understandthatsolutionstoasystem oftwolinearequationsintwovariablescorrespond topointsofintersectionoftheirgraphs,because pointsofintersectionsatisfybothequations simultaneously.
8.F.A.2: Comparepropertiesoftwofunctionseach representedinadifferentway(algebraically, graphically,numericallyintables,orbyverbal descriptions).Forexample,givenalinearfunction representedbyatableofvaluesandalinear functionrepresentedbyanalgebraicexpression, determinewhichfunctionhasthegreaterrateof change.
8.G.A.1: Linesaretakentolines,andlinesegments tolinesegmentsofthesamelength
● Understandingthatslopeisarateof changebetweenthexandyvariableshelps
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas.MP #3:Constructviableargumentsandcritiquethe reasoningofothers;MP#4:Modelwith Mathematics.
● CRITICALTHINKING:Analyzedatainorderto drawconclusions. MP#2:Reasonabstractlyand quantitatively;MP#6:Attendtoprecision.
● Howdoesthegraphofalineconnecttoreal worldscenarios?
initsapplicationinrealworldscenarios.
● Alineismadeupofallthepossible solutionstoanequationintwovariables whichcanberepresentedintable, equation,orgraphform.
● They-interceptadjustsasthecontextof therealworldscenariochanges.
● Howtocalculatearateofchangefora linearrelationshipgivenitsgraph,pointson thegraph,oratableofitsvalues.
● Howtographaline,onthecoordinate plane,givenitsslopeandy-intercept.
● Keyvocabulary:
a.rateofchange
b.linearrelationship
c.verticalintercept
● Howtoidentifythesolutionofatwo variableequation.
● WhatinformationdoIneedtodetermine whetherit’salinearrelationship?HowcanI representthatusingprecisemathlanguage?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icanidentifythemeaningofslope.
● Ican findtherateofchangeofalinear relationshipfromatable,graphorequationby figuringouttheslopeofthelinerepresenting therelationship.
● Icanscaleandlabelacoordinategridinorder tography=mx+b.
● Icanexplainwhereto findtheslopeand verticalinterceptinbothanequationandits graph.
● Icangiveanexampleofasituationthatwould haveanegativeslopewhengraphed.
● Icanwriteequationsoflinesusingy=mx+b.
● Icanwritelinearequationstoreasonabout real-worldsituations.
● Iunderstandwhatthesolutiontoanequation intwovariablesis. STAGE2:DETERMINEACCEPTABLEEVIDENCE
SummativeAssessment
EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanidentifythemeaningofslope.
○ Problem3
● Ican findtherateofchangeofalinear relationshipfromatable,graphorequation by figuringouttheslopeoftheline representingtherelationship.
○ Problem5,7
● Icanscaleandlabelacoordinateaxesin ordertography=mx+b.
○ Problem7
● Icanexplainwhereto findtheslopeand verticalinterceptinbothanequationand itsgraph.
○ Problem2
FormativeAssessment
MidunitGrade8Unit3Quiz
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesisandcooldowns asappropriate
Frayermodel(rationale)
● Proportionalityrevisited
● SlopeInterceptform
● SolutioninStandardform
● Icangiveanexampleofasituationthat wouldhaveanegativeslopewhengraphed
○ Problem2
● Icanwriteequationsoflinesusingy=mx+b.
○ Problem4
● Icanwritelinearequationstoreasonabout real-worldsituations.
○ Problem7
● Iunderstandwhatthesolutiontoan equationintwovariablesis.
○ Problem1,6,7
PerformanceTask
● Lesson3-Posters-Comparing ProportionalRelationships-Inthislesson onproportionalrelationships,students expandontheworkofthepreviouslessons bycomparingtwosituationsrepresentedin differentways.
Understanding#1 LearningTargets#1&2 TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Decidingwhetherornotquantitiesareina proportionalrelationship.(7.RP.A.2.a)
● Usingproportionalrelationshipstosolve problems.(7.RP.A.3)
● Writingequationstodescribeproportional relationships.(7.RP.A.2.c)
● Solvingproblemswithpositiveand negativenumbers.(7.EE.B.3)
● Applyingtransformationstolines. (8.G.A.1.aand8.G.A.1.c)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:
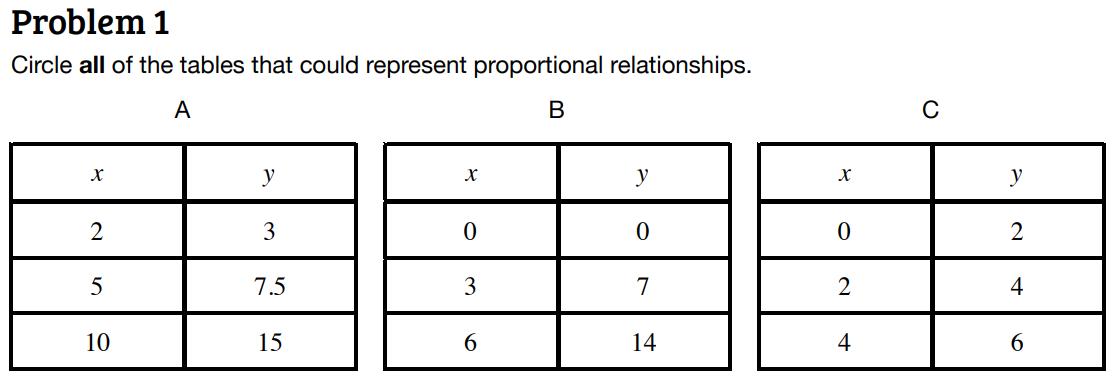

Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptofproportionalrelationships.
FirstTopic:ProportionalityRevisited
LearningTargets:
● Icanidentifythemeaningofslope.
● Ican findtherateofchangeofalinear relationshipfromatable,graphorequation by figuringouttheslopeoftheline representingtherelationship.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:4
EssentialQuestions:
● Howdoesthegraphofalineconnecttoreal worldscenarios?
● WhatinformationdoIneedtodetermine whetherit’salinearrelationship?HowcanI representthatusingprecisemathlanguage?
● Studentsmakeconnectionsbetweenthedifferentrepresentationsofproportionalrelationships.
● Studentsscaleaxesinmultiplewaysinordertographproportionalrelationships.
● Studentscomparetwodifferentproportionalrelationshipsgivendifferentrepresentationsofthem.
SecondTopic:SlopeInterceptForm
LearningTargets:
● Icanscaleandlabelacoordinategridin ordertography=mx+b.
● Icanexplainwhereto findtheslopeand verticalinterceptinbothanequationand itsgraph.
● Icangiveanexampleofasituationthat wouldhaveanegativeslopewhengraphed.
● Iunderstandwhatthesolutiontoan equationintwovariablesis.
● Icanwriteequationsoflinesusingy=mx+b.
● Icanwritelinearequationstoreasonabout real-worldsituations.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:7
EssentialQuestions:
● Howdoesthegraphofalineconnecttoreal worldscenarios?
● WhatinformationdoIneedtodetermine whetherit’salinearrelationship?HowcanI representthatusingprecisemathlanguage?
● Studentsmovefromproportionalrelationshipstolinearrelationshipswithpositiveratesofchange.
● Studentswriteandinterpretequationsoflinesbyconsideringtheslopeandverticalintercept.
● Studentswriteequationsoflinesusingtheideathatanylineinaplaneisaverticaltranslationofa linethroughtheorigin.
● Studentsreflectonsimilaritiesanddifferencesbetweenlineswithpositiveandnegativeslopes.
● Studentsdevelopamethodforcalculatingtheslopeofanylinegiventhecoordinatesoftwopoints ontheline.
● Studentswriteequationsofhorizontalandverticallinesinadditiontolineswithpositiveand negativeslopes.
ThirdTopic:SolutionsandStandardForm
LearningTargets:
● Iunderstandwhatthesolutiontoan equationintwovariablesis.
Estimated#ofLessons:5
EssentialQuestions:
● Howdoesthegraphofalineconnecttoreal worldscenarios?
● WhatinformationdoIneedtodetermine whetherit’salinearrelationship?HowcanI representthatusingprecisemathlanguage?
LearningActivities:
● Studentscometounderstandthatthegraphofanequationisavisualrepresentationofallsolutions totheequation.
● Studentsinterpretmultiplerepresentationsofnon-proportionallinearrelationshipsincontext, includingslopes,intercepts,andsolutions.
CourseName:Grade8Unit4Title:LinearEquationsandLinearSystemsEst.#ofLessons:20
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsbuilduponUnit3wheretheyarenowusingmultiplelinearequationsonacoordinate plane.Theylookattheintersections(orlackthereof)tosolvelinearequationswithrationalcoefficients (decimals,fractions,andintegers)anddeterminethenumberofpossiblesolutions.Studentsalsolearnto recognizethatsolutionscanbefoundbysolvingasystemofequationsalgebraically.
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
ContentMathStateStandards:
8.EE.C: Analyzeandsolvelinearequationsand pairsofsimultaneouslinearequations.
8.EE.C.7: Solvelinearequationsinonevariable.
8.EE.C.7.A: Giveexamplesoflinearequationsin onevariablewithonesolution,infinitelymany solutions,ornosolutions.Showwhichofthese possibilitiesisthecasebysuccessively transformingthegivenequationintosimplerforms untilanequivalentequationoftheform`x=a`, `a=a`,or`a=b`results(where`a`and`b`are differentnumbers).
8.EE.C.7.B: Solvelinearequationswithrational numbercoefficients,includingequationswhose solutionsrequireexpandingexpressionsusingthe distributivepropertyandcollectingliketerms.
8.EE.C.8: Analyzeandsolvepairsofsimultaneous
● CRITICALTHINKING:Analyzedatainorderto drawconclusions. MP#2:Reasonabstractlyand quantitatively;MP#5:UseAppropriatetools strategically;MP#7:Lookforandmakeuseof structure.
linearequations.
8.EE.C.8.A: Understandthatsolutionstoasystem oftwolinearequationsintwovariablescorrespond topointsofintersectionoftheirgraphsbecause pointsofintersectionsatisfybothequations simultaneously.
8.EE.C.8.B: Solvesystemsoftwolinearequationsin twovariablesalgebraically,andestimatesolutions bygraphingtheequations.Solvesimplecasesby inspection.
8.EE.C.8.C: Solvereal-worldandmathematical problemsleadingtotwolinearequationsintwo variables.
● Realisticsolutionstoequationsorsystems ofequationsrequireunderstandingofwhat real-worldscenariolookslikeregardlessof theform(i.e.,table,graph,oralgebraically)
● Leveragingtechnologytodemonstratethe relationshipbetweenequationsand systemsofequationscreatesadynamic representationofthereal-worldscenario forfurtherpossibilities.
Knowledge
● Howtoconstructandsolveequationsand systemsofequationstomodelreallife problems.
● Howdoweconstructandsolvelinear equationsorsystemsoflinearequationsto makesenseofreal-worldproblems?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icanvisuallybalanceanequation.
● Icanmakesenseofmultiplewaystosolvean equation.
● Icansolveanequationwherethevariable appearsonbothsides.
● Icanuseanexpressionto findwhentwo things,likeheight,arethesameinareal-world situation.
● Icanexplainthesolutiontoasystemof equationsinareal-worldcontext.
● Icanexplainwhatasystemofequationsis.
● Icanmakegraphsto findanorderedpairthat tworeal-worldsituationshaveincommon.
● Icangraphasystemofequations.
● Icansolvesystemsofequationsusingalgebra.
● Icancalculateasolutiontoasystemof equationsincontext.
● Icanusethestructureofequationstohelpme figureouthowmanysolutionsasystemof equationshas.
● Icanidentifyandinterpretpointsthatsatisfy tworelationshipsatthesametimeusing graphs.
SummativeAssessment
EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanvisuallybalanceanequation.
○ Problem1
● Icanmakesenseofmultiplewaystosolve anequation.
○ Problem4
● Icansolveanequationwherethevariable appearsonbothsides.
○ Problem4
● Icanuseanexpressionto findwhentwo things,likeheight,arethesameina real-worldsituation.
○ Problem6
● Icanexplainthesolutiontoasystemof equationsinareal-worldcontext.
○ Problem6
● Icanexplainwhatasystemofequationsis.
○ Problem2
● Icanmakegraphsto findanorderedpair thattworeal-worldsituationshavein common.
○ Problem6
● Icangraphasystemofequations.
○ Problem3
● Icansolvesystemsofequationsusing algebra
○ Problem3
● Icancalculateasolutiontoasystemof equationsincontext.
○ Problem7
● Icanusethestructureofequationstohelp me figureouthowmanysolutionsasystem ofequationshas.
○ Problem3
FormativeAssessment
Grade8Unit4MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesis,cooldownsand practicedaysasappropriate.
Frayermodel(rationale)
● SolvingLinearequations
● SystemsofLinearEquations
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Applyingthedistributivepropertyto generateequivalentexpressions.(6.EE.A.3)
● Combiningliketermstogenerate equivalentexpressions.(6.EE.A.3,7.EE.A.1)
● Solvingproblemsbywritingandsolving equationswithvariablesononesideofthe equation.(6.EE.B.7,7.EE.B.4.a)
● Understandingwhatitmeansforavalueto beasolutiontoanequation.(6.EE.B.5)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:

Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofdistributivepropertyandnegative numbers.
FirstTopic:SolvingLinearEquations
LearningTargets:
● Icanvisuallybalanceanequation..
● Icanmakesenseofmultiplewaystosolve anequation.
● Icansolveanequationwherethevariable appearsonbothsides.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:12
EssentialQuestions:
● Howdoweconstructandsolvelinear equationsorsystemsoflinearequationsto makesenseofreal-worldproblems?
● Studentscreateandsolvenumberpuzzlesthatcanberepresentedbylinearequationsinone variable.
● Studentsusehangerdiagramstocalculateunknownweightsofobjectsbyaddingandremoving equalitemsfromeachside.
● Studentsmovefromusinghangerstousingequationstorepresentaproblem.
● Studentsreviewandcritiquesolvingstrategiesbeforesolvingcomplexequationsindependently.
● Studentsmovetowardgeneralmethodsforsolvinglinearequations.
● Studentscategorizelinearequationsinonevariablebasedontheirstructure,andsolveequations fromeachcategory.
● Studentsencounterequationsthathavenosolutionsandequationsforwhicheverynumberisa
solution.
● Studentsencounterequationsthathavenosolutionsandequationsforwhicheverynumberisa solution.
SecondTopic:SystemsofLinearEquations Estimated#ofLessons:8
LearningTargets:
● Icanuseanexpressionto findwhentwo things,likeheight,arethesameina real-worldsituation.
● Icanexplainthesolutiontoasystemof equationsinareal-worldcontext.
● Icanexplainwhatasystemofequationsis.
● Icanmakegraphsto findanorderedpair thattworeal-worldsituationshavein common.
● Icangraphasystemofequations.
● Icansolvesystemsofequationsusing algebra.
● Icancalculateasolutiontoasystemof equationsincontext.
● Icanusethestructureofequationstohelp me figureouthowmanysolutionsasystem ofequationshas.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions:
● Howdoweconstructandsolvelinear equationsorsystemsoflinearequationsto makesenseofreal-worldproblems?
● Studentsinterpretpointsthatlieonone,both,orneitherlineonagraphoftwosimultaneous equationsincontext.
● Studentscreateandinterpretagraphoftwolinesincontext.
● Studentsunderstandthatsolvingasystemofequationsmeans findingvaluesofthevariablesthat makebothequationstrue.
● Studentssolveasystemofequationsusingalgebraicmethods.
● Studentsconsidertherelationshipbetweenthestructureoftheequationsinasystemandthe numberofsolutions.
● Studentsidentify,describe,andemploystrategiesforsolvinglinearsystemsofequationswith differentfeaturesorstructures.
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsareintroducedtotheconceptofafunctionasarelationshipbetweeninputsand outputs.ThistakesthembacktotheirGrade6explorationofindependentanddependentvariablesand asksthemtomakeconnectionstoinputsandoutputsofafunction.Studentsthenmanipulateequationsto isolatetheoutputtosolveformissingpartsoftheformula.
Thisfoundationalknowledgewillbedeepenedthroughoutmostoftheirhighschoolmathcurriculum.for
the firsttime,analyzerepresentationsoffunctions,andexaminefunctionsinthecontextofthevolumeof cylinders,cones,andspheres.
ContentMathStateStandards:
8.F.A.1: Understandthatafunctionisarulethat assignstoeachinputexactlyoneoutput.Thegraph ofafunctionisthesetoforderedpairsconsisting ofaninputandthecorrespondingoutput.
8.F.A.2: Comparepropertiesoftwofunctionseach representedinadifferentway(algebraically, graphically,numericallyintables,orbyverbal descriptions).
8.F.A.3: Interprettheequation`y=mx+b`as definingalinearfunctionwhosegraphisastraight line.Giveexamplesoffunctionsthatarenotlinear.
8.F.B.4: Constructafunctiontomodelalinear relationshipbetweentwoquantities.Determine therateofchangeandinitialvalueofthefunction fromadescriptionofarelationshiporfromtwo`(x, y)`values,includingreadingthesefromatableor fromagraph.Interprettherateofchangeand initialvalueofalinearfunctionintermsofthe situationitmodels,andintermsofitsgraphora tableofvalues.
8.F.B.5: Describequalitativelythefunctional relationshipbetweentwoquantitiesbyanalyzinga graph(e.g.,wherethefunctionisincreasingor decreasing,linearornonlinear).Sketchagraphthat exhibitsthequalitativefeaturesofafunctionthat hasbeendescribedverbally.
8.G.C.9: Describequalitativelythefunctional relationshipbetweentwoquantitiesbyanalyzinga graph(e.g.,wherethefunctionisincreasingor decreasing,linearornonlinear).Sketchagraphthat exhibitsthequalitativefeaturesofafunctionthat hasbeendescribedverbally.
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #3Constructviableargumentsandcritiquethe reasoningofothers;MP#4Modelwith Mathematics;MP#6:Attendtoprecision.
● CRITICALTHINKING:Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#1 Makesenseofproblemsandpersevereinsolving them;MP#2ReasonAbstractlyand Quantitatively;MP#5Useappropriatetools strategically.
Modelingofreal-worldscenarios,withtheuseofa function,allowsforpredictionstobemadeinthe pastorinthefuture.
Knowledge
● Howtoconstructthemodelofafunction sothatpredictionscanbemadeby evaluatingthefunction.
● Howtousefunctionstodeterminevolume orgiventhevolumedetermineamissing dimension.
Howarefunctionsdefinedtomodelandpredict behaviorofreal-worldscenarios?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icanexplainthestrengthsandweaknessesof differentrepresentations.
● Icancompareinputsandoutputsoffunctions thatarerepresentedindifferentways.
● Icanusedatapointstomodelalinear function.
● Icandecidewhenalinearfunctionisagood modelfordataandwhenitisnot.
● Icanexplainthestorytoldbythegraphofa function.
● Ican findandinterpretpointsonthegraphof afunction.
● Icandeterminewhetherafunctionis increasingordecreasingbasedonwhetherits rateofchangeispositiveornegative.
● Icanexplainwhyagraphdoesordoesnot representafunction.
● Icanusepreciselanguagetodescribe functions(e.g.,“isafunctionof”or “determines”).
● Icanusedatapointstomodelalinear function.
● Icandecidewhenalinearfunctionisagood modelfordataandwhenitisnot.
● Icanexplainthestrengthsandweaknessesof differentrepresentations.
● Icancompareinputsandoutputsoffunctions thatarerepresentedindifferentways.
● Icanexplaintherelationshipbetweenthe volumeofaconeandthevolumeofacylinder.
● Icanusetheformulaforthevolumeofacone.
● Ican findmissinginformationaboutacylinder orconeifIknowitsvolumeandother information.
● Icancompareandcontraststrategiesfor findinginformationaboutaconeorcylinder.
● Icananalyzetherelationshipbetweenthe heightorradiusofacylinderanditsvolume.
● Icanexplainwhytherelationshipbetween heightandvolumeislinearbutthe relationshipbetweenradiusandvolumeis not.
SummativeAssessment
EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanexplainthestrengthsandweaknesses ofdifferentrepresentations.
○ Problem1
● Icancompareinputsandoutputsof functionsthatarerepresentedindifferent ways.
○ Problem1
● Icanusedatapointstomodelalinear function.
○ Problem1
● Icandecidewhenalinearfunctionisagood modelfordataandwhenitisnot.
○ Problem1
● Icanexplainthestorytoldbythegraphofa function.
○ Problem3
● Ican findandinterpretpointsonthegraph ofafunction.
○ Problem3
● Icandeterminewhetherafunctionis increasingordecreasingbasedonwhether itsrateofchangeispositiveornegative.
○ Problem3
● Icanexplainwhyagraphdoesordoesnot representafunction.
○ Problem5
● Icanusepreciselanguagetodescribe functions(e.g.,“isafunctionof”or “determines”).
○ Problem5
● Icanusedatapointstomodelalinear function.
○ Problem5
● Icandecidewhenalinearfunctionisagood modelfordataandwhenitisnot.
○ Problem5
● Icanexplainthestrengthsandweaknesses ofdifferentrepresentations.
○ Problem7
● Icancompareinputsandoutputsof functionsthatarerepresentedindifferent ways.
○ Problem7
FormativeAssessment
Grade8Unit5MidUnitAssessments(2)
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesis,cooldownsand practicedaysasappropriate.
Frayermodel(rationale)
● IntroductiontoFunctions
● RepresentingandInterpretingFunctions
● Volume
● Icanexplaintherelationshipbetweenthe volumeofaconeandthevolumeofa cylinder.
○ Problem2
● Icanusetheformulaforthevolumeofa cone.
○ Problem2
● Ican findmissinginformationabouta cylinderorconeifIknowitsvolumeand otherinformation.
○ Problem4
● Icancompareandcontraststrategiesfor findinginformationaboutaconeor cylinder.
○ Problem4
● Icananalyzetherelationshipbetweenthe heightorradiusofacylinderandits volume.
○ Problem6
● Icanexplainwhytherelationshipbetween heightandvolumeislinearbutthe relationshipbetweenradiusandvolumeis not.
○ Problem6
PerformanceTask Charge!:
● Studentsuselinearfunctionstomodela real-worldsituation(MP4).Theyaregiven dataforarelationshipthatisalmostlinear, andfromthat,theydevelopalinearmodel. Theyusetheirmodeltomakepredictions andtodeterminewhetheralinear approximationisreasonableandforwhich valuesitwouldbereasonable.Students begintoseeboththevalueandthe limitationsoflinearmodels.Onesuch limitation—thatsomedatasetscannotbe modeledwellbyasingleline—leadsintothe nextlessonwherestudentsmodel nonlinearscenarioswithpiecewiselinear functions.
Understanding#1
LearningTarget#1
TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Readingandplottingcoordinatepointson graphs.(6.NS.C.6.c)
● Calculatingtherateofchangeoflines. (7.RP.A.2.b,8.EE.B.5)
● Orderofoperationsandcalculation techniques(e.g.,evaluatingπ·42 ·7). (4.OA.A.3,6.EE.A.2.c)
● Workingwithdecimalsorfractions(e.g., usingtheequation ).(5.NF.B.4, ��= 4 3 π�� 3 5.NBT.B.5)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:


Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofwritingequationstorepresentthe relationshipbetweenquantitiesaswellas representationsofproportionalandnon-proportional relationships.
FirstTopic:IntroductiontoFunctions Estimated#ofLessons:6
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainwhyagraphdoesordoesnot representafunction.
● Icanusepreciselanguagetodescribe functions(e.g.,“isafunctionof”or “determines”).
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions:
● Howarefunctionsdefinedtomodeland predictbehaviorofreal-worldscenarios?
● Studentsbegintomakeconnectionsbetweenscenariosandgraphsthatrepresentthem.
● Studentswriterulesbasedoninput-outputpairsrepresentedintables,andareintroducedtothe conceptoffunction.
● Studentsdeterminewhetherornotagraphrepresentsafunctionandexplaintheirreasoning.
● Studentsexploretherelationshipbetweenequationsandfunctions,andunderstandthatan equationmaylookdifferentdependingonhowtheindependentanddependentvariablesare defined.
SecondTopic:RepresentingandInterpreting Functions
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainthestrengthsandweaknesses ofdifferentrepresentations.
● Icancompareinputsandoutputsof functionsthatarerepresentedindifferent ways.
● Icanusedatapointstomodelalinear function.
● Icandecidewhenalinearfunctionisagood modelfordataandwhenitisnot.
● Icanexplainthestorytoldbythegraphofa function.
● Ican findandinterpretpointsonthegraph ofafunction.
● Icandeterminewhetherafunctionis increasingordecreasingbasedonwhether itsrateofchangeispositiveornegative.
● Icanusedatapointstomodelalinear function.
● Icandecidewhenalinearfunctionisagood modelfordataandwhenitisnot.
● Icanexplainthestrengthsandweaknesses ofdifferentrepresentations.
● Icancompareinputsandoutputsof functionsthatarerepresentedindifferent ways.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:7
EssentialQuestions:
● Howarefunctionsdefinedtomodeland predictbehaviorofreal-worldscenarios?
● Studentsinterpretqualitativefeaturesofafunctionandspecificpointsincontext.Studentsalso considerthemeaningofrateofchangeovergivenintervals.
● Studentsdrawthegraphofafunctionthatrepresentsareal-worldsituation.
● Studentscompareandcontrastthreecalorie-burningrelationshipsrepresentedindifferentways.
● Studentsusedatapointstomodelalinearfunctionanddecidewhenitisreasonabletomodelthe relationshipwithalinearfunction.
● Studentsusepiecewisefunctionstomodelreal-worlddatasetspresentedasgraphs.
ThirdTopic:Volume
Estimated#ofLessons:9
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplaintherelationshipbetweenthe volumeofaconeandthevolumeofa cylinder.
● Icanusetheformulaforthevolumeofa cone.
● Ican findmissinginformationabouta cylinderorconeifIknowitsvolumeand otherinformation.
● Icancompareandcontraststrategiesfor findinginformationaboutaconeor cylinder.
● Icananalyzetherelationshipbetweenthe heightorradiusofacylinderandits volume.
● Icanexplainwhytherelationshipbetween heightandvolumeislinearbutthe relationshipbetweenradiusandvolumeis not.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions:
● Howarefunctionsdefinedtomodeland predictbehaviorofreal-worldscenarios?
● Studentsestimatethevolumesofcylinders,cones,cubes,andspheres.
● Studentsexploreanduseastrategytocalculatethevolumeofacylinder.
● Studentsusefunctionstoexplorehowchangingacylinder’sradiusorheightimpactsitsvolume.
● Studentsrecognizethatthevolumeofaconeisthevolumeofacylinderwiththesameradiusand 1 3 thesameheight.
● Studentscalculatemissingdimensionsofcylindersandconesgiventheirvolumeandanother dimension.
● Studentsdevelopanduseaformulaforthevolumeofasphere.
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsbuildontheirpreviousexperienceinearlierunitswiththecoordinateplaneandlinear functionstofocusondataintwovariables.Theyusescatterplotsand fittedlinestoanalyzenumericaldata. Theyalsousetwo-waytables,bargraphsandsegmentedbargraphstoanalyzecategoricaldata.
ContentMathStateStandards:
8.SP.A.1: Constructandinterpretscatterplotsfor bivariatemeasurementdatatoinvestigatepatterns ofassociationbetweentwoquantities.Describe patternssuchasclustering,outliers,positiveor negativeassociation,andlinearassociationor nonlinearassociation.
8.SP.A.2: Knowthatstraightlinesarewidelyused tomodelrelationshipsbetweentwoquantitative variables.Forscatterplotsthatsuggestalinear association,informally fitastraightlineandassess themodel fitbyjudgingtheclosenessofthedata pointstotheline.
8.SP.A.3: Usetheequationofalinearmodelto solveproblemsinthecontextofbivariate measurementdata,interpretingtheslopeand intercept.
8.SP.A.4: Understandthatpatternsofassociation canalsobeseeninbivariatecategoricaldataby displayingfrequenciesandrelativefrequenciesina two-waytable.Constructandinterpretatwo-way tablesummarizingdataontwocategorical variablescollectedfromthesamesubjects.Use relativefrequenciescalculatedforrowsorcolumns todescribepossibleassociationbetweenthetwo variables.
● Graphicalrepresentationsandstatistics allowustoidentifyandrepresentkey featuresofdata.
● Modelsmayallowustopredictresponses tochangesinavariable.
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #4ModelwithMathematics;MP#7Lookforand makeuseofstructure.
● CRITICALTHINKING:MP#1Makesenseof problemsandpersevereinsolvingthem; MP#2 ReasonAbstractlyandQuantitatively;MP#5Use appropriatetoolsstrategically.
● HowdoIusemypriormathematical knowledgetodeepenmyconnectionsin statistics?
● Howcanyoudeterminetheeffectivenessofa linearmodel?
Knowledge Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Howtorepresenttwovariabledatain multipleways(graphically,frequencytable, lists)
● Howtodescribetwovariabledata (direction,outliers,strength)
● Icanorganizedatatonoticepatternsmore clearly.(Foundational)
● Icancompareandcontrasttwodifferent waystodisplaydata(adotplotandascatter plot)(Foundational)
● Icanuserelativefrequenciesintablesandin segmentedbargraphstodecideifthereisan associationbetweentwovariables.
● Icanidentifyandrepresentthesamedatain bargraphsandintwo-wayfrequencytables.
● Icanuserelativefrequenciesintablesandin segmentedbargraphstodecideifthereisan associationbetweentwovariables.
● Icanexplainwhetherdatainascatterplothas apositiveassociation,anegativeassociation, orneither.
● Icaninterprettheslopeofaline fittodataina real-worldsituation.
● Icanuseascatterplottodecideiftwo variableshavealinearassociationandmake connectionstowhatthedatarepresents.
● Icanpickoutclustersindataandmake connectionstowhatthedatarepresents.
● Icanusealineof fittopredictvaluesnotin thedata.
● Icanidentifyoutliersonascatterplot.
● Icandrawalineto fitdatainascatterplot.
● Icandescribefeaturesofalinethat fitsdata well.
SummativeAssessment
EndofUnitAssessment
● Icanuserelativefrequenciesintablesand insegmentedbargraphstodecideifthere isanassociationbetweentwovariables.
○ Problem2
● Icanidentifyandrepresentthesamedata inbargraphsandintwo-wayfrequency tables.
○ Problem5
● Icanuserelativefrequenciesintablesand insegmentedbargraphstodecideifthere isanassociationbetweentwovariables.
○ Problem6
● Icanexplainwhetherdatainascatterplot hasapositiveassociation,anegative association,orneither.
○ Problem1
● Icaninterprettheslopeofaline fittodata inareal-worldsituation.
○ Problem1
● Icanuseascatterplottodecideiftwo variableshavealinearassociationand
FormativeAssessment
Grade8Unit6MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesis,cooldownsand practicedaysasappropriate.
Frayermodel(rationale)
● Organizingnumericaldata
● Analyzingnumericaldata
● Categoricaldata
makeconnectionstowhatthedata represents.
○ Problem3,4
● Icanpickoutclustersindataandmake connectionstowhatthedatarepresents.
○ Problem3,4
● Icanusealineof fittopredictvaluesnotin thedata.
○ Problem7
● Icanidentifyoutliersonascatterplot.
○ Problem7
● Icandrawalineto fitdatainascatterplot.
○ Problem7
● Icandescribefeaturesofalinethat fits datawell.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask FindingAssociations
UsingDataDisplaystoFindAssociations
● Studentsuserelativefrequenciesdisplayed intablesandinsegmentedbargraphsto identifypossibleassociationsbetween variablesindatarelatedtothesinkingof theRMSTitanic.TransformationGolf:
Understanding#2 LearningTarget#3
TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication STAGE3:LEARNINGPLAN
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Determiningtherateofchangeofalinear functiongiventwopoints.(8.F.B.4)
● Makingconnectionsbetweenalinear relationshipandacontext,including calculatingaunitrate.(6.RP.A.3.b,8.EE.B.6)
● Drawingbargraphsandinterpreting informationpresentedinabargraph. (2.MD.D.10,3.MD.B.3)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:
FirstTopic:OrganizingNumericalData
LearningTargets:
● Icanorganizedatatonoticepatternsmore clearly.(Foundational)
● Icancompareandcontrasttwodifferent waystodisplaydata(adotplotanda scatterplot)(Foundational)
LearningActivities:

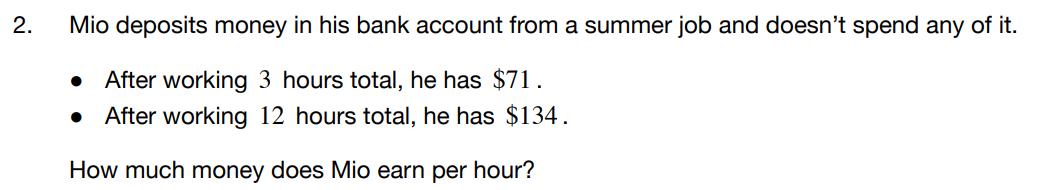
Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofslopeofalinewhengiventwopointsand calculatingarateusingcontext.
Estimated#ofLessons:3
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatstatisticalmeasurementscouldbeused todescribeadataset?
● Howcanyoudeterminetheeffectivenessofa linearmodel?
● Studentsparticipateina"clicking"challengetogeneratedatathattheywillorganizeandthenuseto recognizepatternsandmakepredictions.
● Studentscompareandcontrastthesamedatarepresentedbyadotplotandbyascatterplot.
SecondTopic:AnalyzingNumericalData
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainwhetherdatainascatterplot hasapositiveassociation,anegative association,orneither.
● Icaninterprettheslopeofaline fittodata inareal-worldsituation.
● Icanuseascatterplottodecideiftwo variableshavealinearassociationand makeconnectionstowhatthedata represents.
Estimated#ofLessons:8
EssentialQuestions:
● Howcanyoudeterminetheeffectivenessofa linearmodel?
● Icanpickoutclustersindataandmake connectionstowhatthedatarepresents.
● Icanusealineof fittopredictvaluesnotin thedata.
● Icanidentifyoutliersonascatterplot.
● Icandrawalineto fitdatainascatterplot.
● Icandescribefeaturesofalinethat fits datawell.
LearningActivities:
● Studentsinterpretpointsonascatterplotintermsofacontextandaddpointstoascatterplotgiven informationaboutanindividualinthepopulation.
● Studentsbegintoseeasetofdatapointsasasinglethingthatcanbeanalyzed,notjustabunchof disconnectedpoints.
● Studentspracticecreatinglinearmodelsthatmatchtheassociationofsetsofdata.
● Studentsinterprettheslopeofalineof fitincontext.
● Studentsvisualizeclusteringandassociationsindata.
● Studentsanalyzeandinterpretbivariatedataincontext.
ThirdTopic:CategoricalData
LearningTargets:
● Icanuserelativefrequenciesintablesand insegmentedbargraphstodecideifthere isanassociationbetweentwovariables.
● Icanidentifyandrepresentthesamedata inbargraphsandintwo-wayfrequency tables.
● Icanuserelativefrequenciesintablesand insegmentedbargraphstodecideifthere isanassociationbetweentwovariables.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:6
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatstatisticalmeasurementscouldbeused todescribeadataset?
● Studentsstudycategoricaldatadisplayedintwo-waytablesandinbargraphs.Thedifferent graphicalrepresentationshelpstudentsvisualizethefrequencies.
● Studentsuserelativefrequenciesdisplayedintablesandinsegmentedbargraphstoidentify possibleassociationsbetweenvariablesindatarelatedtothesinkingoftheRMSTitanic.
● Studentsusetwo-waytables,bargraphs,andsegmentedbargraphstodecidewhetherthereis evidenceofanassociationincategoricaldata.
UnitOverview: Inthisunit,studentsgain fluencywithexpressionsinvolvingexponents(anextensionof6thgrade)andnow
extendtopowersof`10`andscientificnotation.Then,theyperformoperationsonnumberswrittenin scientificnotation.Finally,theyapplytheseconceptstothebase-tensystemlearningaboutordersof magnitudeandscientificnotationtorepresentandcomputewithverylargeandverysmallquantities.
ContentMathStateStandards:
8.EE.A.1: Knowandapplythepropertiesofinteger exponentstogenerateequivalentnumerical expressions.
8.EE.A.3: Usenumbersexpressedintheformofa singledigittimesanintegerpowerof`10`to estimateverylargeorverysmallquantities,andto expresshowmanytimesasmuchoneisasthe other.
8.EE.A.4: Performoperationswithnumbers expressedinscientificnotation,includingproblems wherebothdecimalandscientificnotationare used.Usescientificnotationandchooseunitsof appropriatesizeformeasurementsofverylargeor verysmallquantities.Interpretscientificnotation thathasbeengeneratedbytechnology.
● Rulesofexponentsallowustosimplify complexexpressions.
● ScientificNotationallowsustoworkwith verylargeorverysmallnumbersina manageablefashion.
● Howtouseexponentsandscientific notationtosolvereal-worldscenarios involvinglargeorsmallnumbers.
TransferGoals
CSDEMathPractices(MP)in Blue toverifysignificance
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #4ModelwithMathematics.
● CRITICALTHINKING:Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#1 Makesenseofproblemsandpersevereinsolving them;MP#2ReasonAbstractlyand Quantitatively.
● CRITICALTHINKING:Identifyaproblem,askkey questions,andmakepredictions. MP#5Use appropriatetoolsstrategically;MP#6Attendto precision;MP#7Lookforandmakeuseof structure;MP#8Lookforandexpressregularity inrepeatedreasoning.
● Howcanrepresentingthesamemathematical relationshipindifferentwaysallowusto modelreal-worldscenariosandsolve problems?
● Icandescribewhatitmeansfortwo expressionswithexponentstobeequivalent.
● Icancreateequivalentexpressionswith exponents.
● Icanrewriteexpressionswithpositive exponentsasasinglepower.
● Icanexplainwhatitmeansforanumbertobe raisedtoazerooranegativeexponent.
● Icandetermineiftwoexpressionswith positive,zero,andnegativeexponentsare equivalent.
● Icandivideexpressionswithexponentsthat havethesamebase.
● IcanapplywhatIlearnedaboutpowersof10 toanswerquestionsaboutreal-world situations
● Icanrepresentlargeandsmallnumbersas multiplesofpowersof10usingnumberlines.
● Icanaddandsubtractnumbersgivenin scientificnotation.
● Icanusescientificnotationandestimationto compareverylargeorverysmallnumbers
● Icanmultiplyanddividenumbersgivenin scientificnotation.
● Icanusescientificnotationtocompare differentquantitiesandanswerquestions aboutreal-worldsituations.
SummativeAssessment
EndofUnitAssessment
● Icandescribewhatitmeansfortwo expressionswithexponentstobe equivalent.
○ Problem1
● Icancreateequivalentexpressionswith exponents.
○ Problem1
● Icanrewriteexpressionswithpositive exponentsasasinglepower.
○ Problem6
● Icanexplainwhatitmeansforanumberto beraisedtoazerooranegativeexponent.
○ Problem6
● Icandetermineiftwoexpressionswith positive,zero,andnegativeexponentsare equivalent.
○ Problem6
● Icandivideexpressionswithexponents thathavethesamebase.
○ Problem6
● IcanapplywhatIlearnedaboutpowersof 10toanswerquestionsaboutreal-world situations
○ Problem2
● Icanrepresentlargeandsmallnumbersas multiplesofpowersof10usingnumber
FormativeAssessment
Grade8Unit7MidUnitAssessment
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesis,cooldownsand practicedaysasappropriate.
Frayermodel(rationale)
● ExponentRules
● ScientificNotation
lines.
○ Problem4
● Icanaddandsubtractnumbersgivenin scientificnotation.
○ Problem3
● Icanusescientificnotationandestimation tocompareverylargeorverysmall numbers
○ Problem5
● Icanmultiplyanddividenumbersgivenin scientificnotation.
○ Problem5
● Icanusescientificnotationtocompare differentquantitiesandanswerquestions aboutreal-worldsituations.
○ Problem7
PerformanceTask
WriteaRule:
● Studentswriterulesforsimplifying exponentialexpressions.
Understanding#1
LearningTargets#8
TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
StarPower:
● Inthisunit-culminatinglesson,studentsuse scientificnotationasatoolforcomparing, combining,andoperatingonthenetworth ofdifferentcelebrities.Studentsidentify theessentialfeaturesofthequestionsand reasonquantitativelyandabstractlyin ordertoanswerthemincontext(MP2, MP4).
Understanding#1
LearningTargets#9,10,11,12
TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Writingandevaluatingnumerical expressionsinvolvingwhole-number exponents.(6.EE.A.1)
● Multiplyinganddividingmulti-digitwhole numbersanddecimals.(6.NS.B.2,6.NS.B.3)
● Reading,writing,andcomparingdecimals. (5.NBT.A.3)
FromReadinessCheck:


Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofestimation,placevalue,decimalsand quotients.
FirstTopic:ExponentRules
LearningTargets:
● Icandescribewhatitmeansfortwo expressionswithexponentstobe equivalent.
● Icancreateequivalentexpressionswith exponentsthathavethesamebase.
● Icanrewriteexpressionswithpositive exponentsasasinglepower.
● Icanexplainwhatitmeansforanumberto beraisedtoazerooranegativeexponent.
● Icandetermineiftwoexpressionswith
Estimated#ofLessons:9
EssentialQuestions:
● Howcanrepresentingthesamemathematical relationshipindifferentwaysallowusto modelreal-worldscenariosandsolve problems?
positive,zero,andnegativeexponentsare equivalent.
LearningActivities:
● Studentsreviewtheconceptsofwholenumberexponents
● Studentsdiscoverwaystowriteequivalentexponentialexpressionsinvolvingtheproductofpowers andpowersofpowers.
● Studentslookforandmakeuseofstructuretoidentifyequivalentexponentexpressionsthatuse powersofpowersandproductsofpowers.
● Studentsrewriteproductsofpowers,quotientsofpowers,andpowersofpowersassinglepowers.
● Studentsdevelopanunderstandingofthemeaningofzeroandnegativeexponents.
● Studentswriterulesforsimplifyingexponentialexpressions.
SecondTopic:ScientificNotation
LearningTargets:
● Icandivideexpressionswithexponents thathavethesamebase.
● IcanapplywhatIlearnedaboutpowersof 10toanswerquestionsaboutreal-world situations
● Icanrepresentlargeandsmallnumbersas multiplesofpowersof10usingnumber lines.
● Icanaddandsubtractnumbersgivenin scientificnotation.
● Icanusescientificnotationandestimation tocompareverylargeorverysmall numbers.
● Icanmultiplyanddividenumbersgivenin scientificnotation.
● Icanusescientificnotationtocompare differentquantitiesandanswerquestions aboutreal-worldsituations.
LearningActivities:
Estimated#ofLessons:10
EssentialQuestions:
● Howcanrepresentingthesamemathematical relationshipindifferentwaysallowusto modelreal-worldscenariosandsolve problems?
● Studentsrepresentlargeandsmallnumbersusingmultiplesofpowersof10.
● Studentsusenumberlinestorepresentlargeandsmallnumbersasmultiplesofpowersof10.
● Studentsapplypowersof10andexponentrulestosolveproblemsincontext.
● Studentsusescientificnotationtoexpressverylargenumbersandverysmallnumbers.
● Studentsmultiplyanddividenumbersexpressedinscientificnotation,andexpresshowmanytimes asmuchonequantityisastheother.
● Studentsaddandsubtractnumbersexpressedinscientificnotationandexpresstheresultingsums anddifferencesinscientificnotation.
● Studentsusescientificnotationasatoolforcomparing,combining,andoperatingonthenetworth ofdifferentcelebrities.
CourseName:Grade8Unit8Title:PythagoreanTheoremandIrrationalNumbers Est.#ofLessons:20
UnitOverview:
Inthisunit,studentsexplorethePythagoreantheoremanddifferenttypesofnumbers(squarerootsand cuberoots,rationalandirrationalnumbers).Thisdeepenstheirmathematicalunderstandingthatthereare irrationalsolutionstoproblemsandhowthatimpactsrealworldscenarios. STAGE1:DESIREDRESULTS EstablishedGoals
ContentMathStateStandards:
8.EE.A.2: Usesquarerootandcuberootsymbolsto representsolutionstoequationsoftheform �� 2 =�� and,where`p`isapositiverationalnumber. �� 3 =�� Evaluatesquarerootsofsmallperfectsquaresand cuberootsofsmallperfectcubes.Knowthatis 2 irrational.
8.G.B: UnderstandandapplythePythagorean theorem.
8.G.B.6: ExplainaproofofthePythagorean theoremanditsconverse.
8.G.B.7: ApplythePythagoreantheoremto determineunknownsidelengthsinrighttriangles inreal-worldandmathematicalproblemsintwo andthreedimensions.
8.G.B.8: ApplythePythagoreantheoremto findthe distancebetweentwopointsinacoordinate system.
8.NS.A: Knowthattherearenumbersthatarenot rationalandapproximatethembyrational numbers.
8.NS.A.1: Knowthatnumbersthatarenotrational arecalledirrational.Understandinformallythat everynumberhasadecimalexpansion.Forrational numbers,showthatthedecimalexpansionrepeats eventually,andconvertadecimalexpansionwhich repeatseventuallyintoarationalnumber.
● COMMUNICATION:Createalogicaland evidence-basedargumenttosupportideas. MP #4ModelwithMathematics;MP#7Lookforand makeuseofstructure.
● CRITICALTHINKING:Identifyaproblem,askkey questions,andmakepredictions. MP#2Reason AbstractlyandQuantitatively;MP#3Construct viableargumentsandcritiquethereasoningof others;MP#5Useappropriatetoolsstrategically.
● CRITICALTHINKING:Demonstrate flexibility anddeterminationwhensolvingproblems. MP#1 Makesenseofproblemsandpersevereinsolving them;MP#2Reasonabstractlyandquantitatively; MP#4Modelwithmathematics.
8.NS.A.2: Userationalapproximationsofirrational numberstocomparethesizeofirrationalnumbers, locatethemapproximatelyonanumberline diagram,andestimatethevalueofexpressions.
Irrationalnumbersallowustosolvereal-world problemsinvolvingroots.
Knowledge
● Howtosolvereal-worldproblemsinvolving squareandcuberoots.
● HowtousethePythagoreanTheoremto solveformissingsidelengthsinright triangles.
Whatroledoirrationalnumbersplayassolutionsto real-worldscenarios?
Skills(FramedasLearningTargets)
● Icanexplainthemeaningofacuberoot,like ,intermsofitsedgelengthandvolume. 35
● Icanidentifythetwowholenumbersacube rootisbetweenandexplainwhy.
● Icanwritearepeatingdecimalasafraction.
● Iunderstandthateverynumberhasadecimal expansion.
● Iknowwhatarationalnumberisandcangive anexample.
● Iknowwhatanirrationalnumberisandcan giveanexample.
● Icanplotsquarerootsonanumberline.
● Icanidentifythetwowholenumbersasquare rootisbetweenandexplainwhy.
● Icanexplainwhyitistruethatiftheside lengthsofatrianglesatisfytheequation thenitmustbearighttriangle �� 2 +��2 =�� 2
● Icandeterminewhetheratriangleisaright triangleifIknowitssidelengths.
● Icanidentifywhichsideisthehypotenuseand whichsidesarethelegsinarighttriangle.
● IcanusethePythagoreantheoremto find unknownsidelengthsinrighttriangles.
● Icancalculatethedistancebetweentwo pointsinthecoordinateplane.
● Icancalculatethelengthofadiagonalline segmentinthecoordinateplane.
● IcanusethePythagoreantheoremtosolve problems.
● Icanexplainthemeaningofacuberoot,like ,intermsofitsedgelengthandvolume.
35
○ Problem1
● Icanidentifythetwowholenumbersacube rootisbetweenandexplainwhy.
○ Problem1
● Icanwritearepeatingdecimalasafraction.
○ Problem3
● Iunderstandthateverynumberhasa decimalexpansion.
○ Problem3
● Iknowwhatarationalnumberisandcan giveanexample.
○ Problem3
● Iknowwhatanirrationalnumberisandcan giveanexample.
○ Problem3
● Icanplotsquarerootsonanumberline.
○ Problem5
● Icanidentifythetwowholenumbersa squarerootisbetweenandexplainwhy.
○ Problem5
● Icanexplainwhyitistruethatiftheside lengthsofatrianglesatisfytheequation thenitmustbearight �� 2 +��2 =�� 2 triangle.
○ Problem2
● Icandeterminewhetheratriangleisaright triangleifIknowitssidelengths.
○ Problem2
● Icanidentifywhichsideisthehypotenuse andwhichsidesarethelegsinaright triangle.
○ Problem4
● IcanusethePythagoreantheoremto find unknownsidelengthsinrighttriangles.
○ Problem4
● Icancalculatethedistancebetweentwo pointsinthecoordinateplane.
○ Problem6
● Icancalculatethelengthofadiagonalline segmentinthecoordinateplane.
○ Problem6
● IcanusethePythagoreantheoremtosolve problems.
○ Problem7
Ongoingassessments:IMsynthesis,cooldownsand practicedaysasappropriate. Frayermodel(rationale)
● Squarerootsandcuberoots
● ThePythagoreanTheorem
● Rationalandirrationalnumbers
PerformanceTask
PondHopperFindingDistancesintheCoordinate Plane StudentscontinuetoapplythePythagorean theoremto finddistancesbetweenpointsinthe coordinateplane:
● Studentsidentifyanddescribesequences oftransformationsthattakeone figureto anotherinthecontextofseveral TransformationGolfchallenges.
Understanding:
● Irrationalnumbersallowustosolve real-worldproblemsinvolvingroots. LearningTargets
● Icancalculatethedistancebetweentwo pointsinthecoordinateplane.
● Icancalculatethelengthofadiagonalline segmentinthecoordinateplane.
● IcanusethePythagoreantheoremtosolve problems.
TransferSkills:CriticalThinkingand Communication
Previousmathconnections
Thefollowingconceptsfrompreviousgradesmay supportstudentsinmeetinggrade-levelstandards inthisunit:
● Writingandevaluatingnumerical expressionsinvolvingwhole-number exponents.(6.EE.A.1)
● Reading,writing,andcomparingdecimals. (5.NBT.A.3)
● Calculatingtheareasofrighttrianglesand otherpolygons.(6.G.A.1)
● Determiningdistancesinthecoordinate plane.(6.G.A.3)
Diagnosticassessmentquestions/problemsbasedon priorgradelevelexperience
FromReadinessCheck:


FirstTopic:SquareRootsandCubeRoots
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainthemeaningofacuberoot,like ,intermsofitsedgelengthandvolume. 35
Problem1
● Icanidentifythetwowholenumbersacube rootisbetweenandexplainwhy.Problem1
● Icanplotsquarerootsonanumberline. Problem5
● Icanidentifythetwowholenumbersa squarerootisbetweenandexplainwhy. Problem5
LearningActivities:
Studentswill firstsolvethetwoproblemsandbe preparedtosharetheirthinkingwithothers. Studentsthensharewithotherstosolidifythe conceptsofcalculatingdistancebetweentwopoints andcalculatingsquaresandcubesofrational numbers.
Estimated#ofLessons:8
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatroledoirrationalnumbersplayinthe solutionstoreal-worldscenarios?
● Studentsestimatesidelengthsofsquareswithknownareasandreviewstrategiesforcalculating areas.
● Studentsdevelopanunderstandingofsquarerootsandsquarerootnotation.
● Studentsapproximatethevalueofsquarerootsbydeterminingthetwointegervaluesitlies betweenandbydrawingasquare.
● Studentslearnaboutrepresentingasquarerootasapointonanumberline.
● Studentsexploretherelationshipbetweentheedgelengthandthevolumeofacube.
SecondTopic:ThePythagoreanTheorem
LearningTargets:
● Icanexplainwhyitistruethatiftheside lengthsofatrianglesatisfytheequation
● thenitmustbearight �� 2 +��2 =�� 2 triangle.Problem2
● Icandeterminewhetheratriangleisaright triangleifIknowitssidelengths. Problem2
● Icanidentifywhichsideisthehypotenuse andwhichsidesarethelegsinaright triangle. Problem4
● IcanusethePythagoreantheoremto find unknownsidelengthsinrighttriangles. Problem4
● Icancalculatethedistancebetweentwo
Estimated#ofLessons:7
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatroledoirrationalnumbersplayinthe solutionstoreal-worldscenarios?
pointsinthecoordinateplane. Problem6
● Icancalculatethelengthofadiagonalline segmentinthecoordinateplane. Problem6
● IcanusethePythagoreantheoremtosolve problems. Problem7
LearningActivities:
● Studentsidentifypatternsintherelationshipbetweenthesquaresofsidelengthsoftrianglesand learnthattherelationshipbetweenthesidelengthsofarighttriangleisthePythagoreantheorem.
● StudentsstudyadiagramthattheywillusetoprovethePythagoreantheoremandthenapplythe Pythagoreantheoremintherestofthelesson.
● StudentspracticeusingthePythagoreantheoremtocalculatesidelengthsofrighttriangles.
● StudentsdevelopandapplytheirunderstandingoftheconverseofthePythagoreantheorem.
● StudentsusethePythagoreantheoremasatooltosolveproblemsinvolvingdiagonaldistances.
● StudentsapplythePythagoreantheoremto finddistancesbetweenpointsinthecoordinateplane.
ThirdTopic:RationalandIrrationalNumbers Estimated#ofLessons:5
LearningTargets:
● Icanwritearepeatingdecimalasafraction.
● Iunderstandthateverynumberhasa decimalexpansion.
● Iknowwhatarationalnumberisandcan giveanexample.
LearningActivities:
EssentialQuestions:
● Whatroledoirrationalnumbersplayinthe solutionstoreal-worldscenarios?
● Studentsexploreconnectionsbetweenunitfractionsandtheirdecimalrepresentationsusinglong divisiontoconvertfractionstodecimals.
● Studentsdevelopastrategyforrewritingrepeatingdecimalsasfractions.
● Studentsbuildontheirworkwithsquareroots,fractions,anddecimalrepresentationsto understandirrationalnumbers.