





















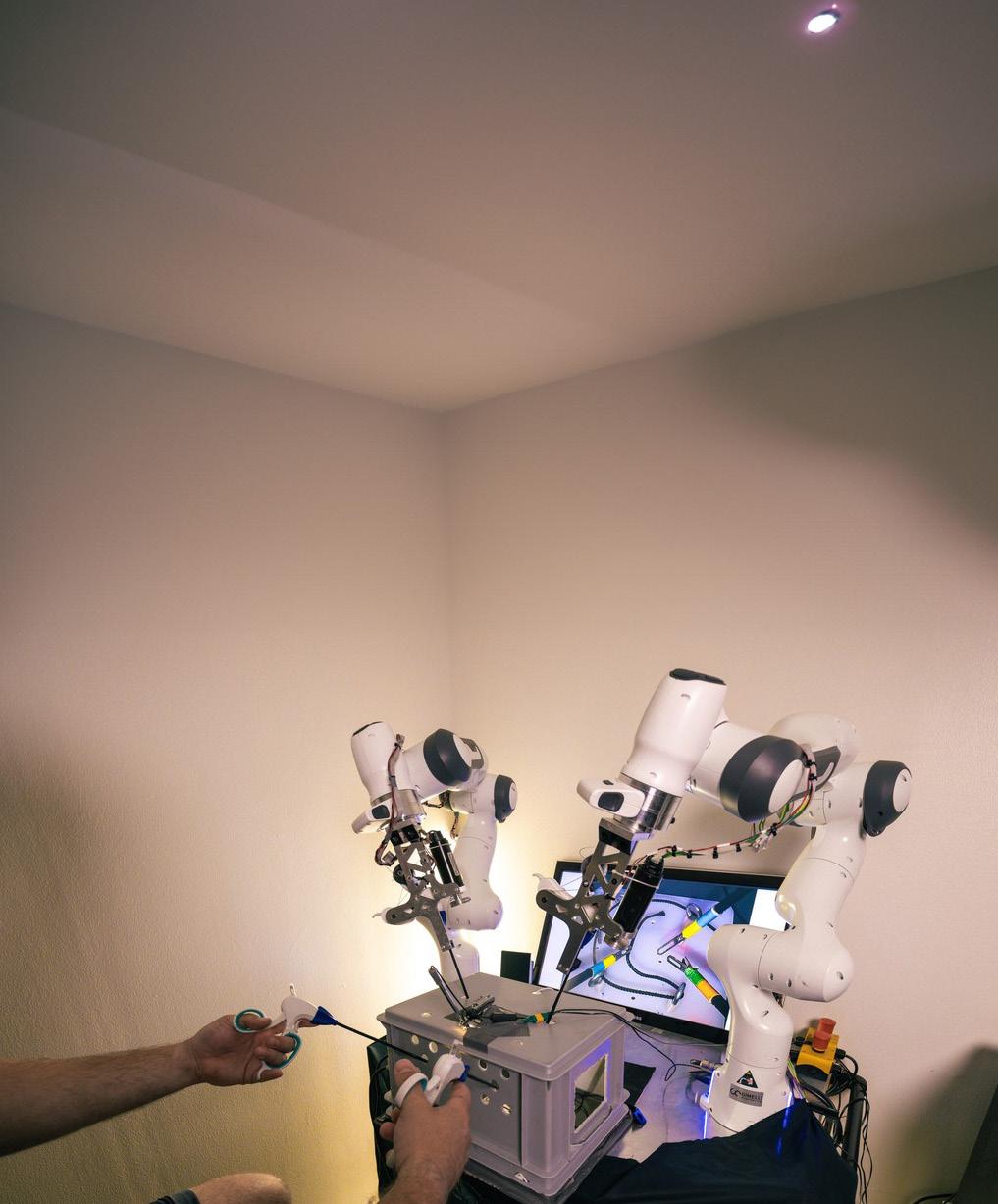
Researchers at EPFL have developed the first system that enables four-arm laparoscopic surgery by controlling two additional robotic arms via haptic foot interfaces.























Researchers at EPFL have developed the first system that enables four-arm laparoscopic surgery by controlling two additional robotic arms via haptic foot interfaces.
Researchers at EPFL, a public research university in Lausanne, Switzerland, have developed a robotic system that allows surgeons to perform laparoscopic surgeries with four arms by controlling two robotic arms using haptic foot interfaces.
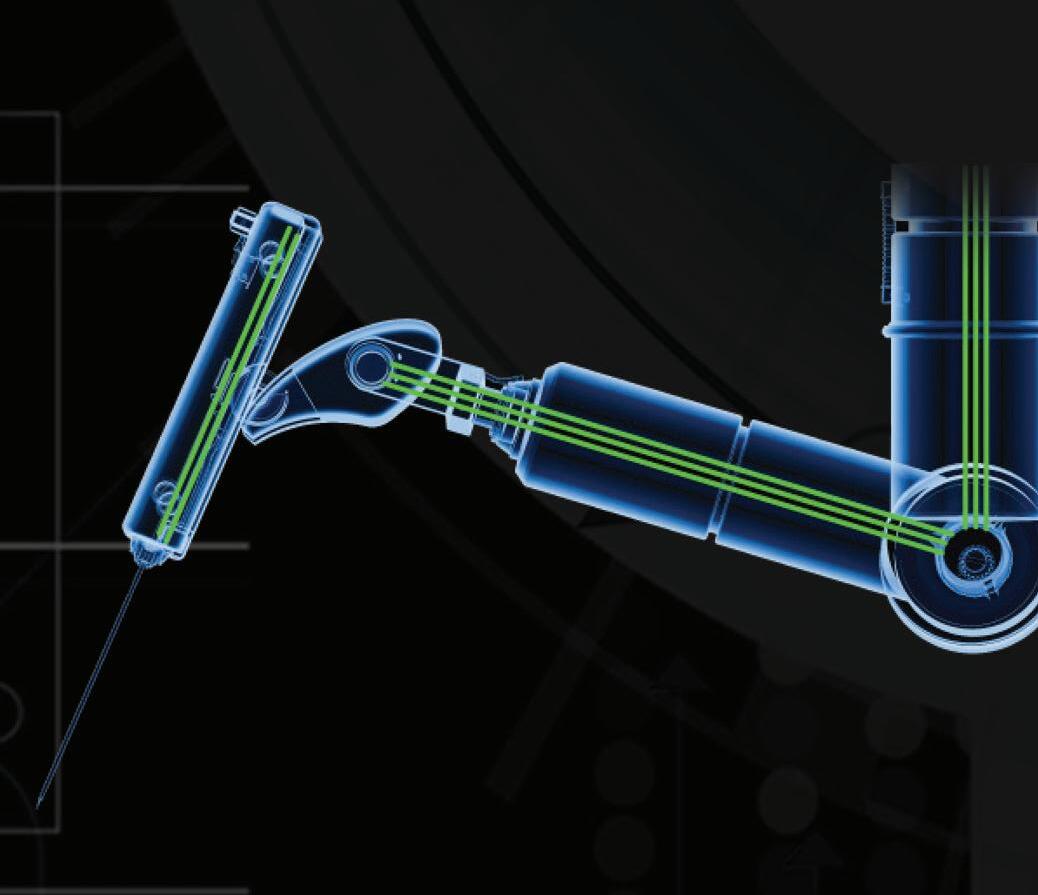
The research was a collaboration between the research group REHAssist and the Learning Algorithms and Systems Laboratory (LASA). It was led by EPFL Ph.D. students Jacob Hernandez and Walid Amanhoud, who developed a system that allows surgeons to control two robotic arms using haptic foot interfaces with five degrees of freedom. In this setup, each of the surgeon’s hands controls a manipulative instrument, while one foot controls an actuated gripper while the other controls an endoscope or camera.
“Actuators in the foot pedals give haptic feedback to the user, guiding the foot towards the target as if following an invisible field-of-forces, and also limit force and movement to ensure that erroneous feet movements do not endanger the patient,” Mohamed Bouri,
head of REHAssist, said. “Our system opens up new possibilities for surgeons to perform 4-handed laparoscopic procedures, allowing a single person to do a task that is usually performed by two, sometimes three people.”
One key aspect of the system is that control is shared between the surgeon and robotic assistants. The researchers designed a control framework that ensures the surgeon and robots can work collaboratively within a concurrent workspace while still
meeting the precision and demands of laparoscopic surgery. This feature helps to minimize fatigue for surgeons, as the robots can sometimes lead the surgeon’s control of an instrument as it predicts where the surgeon wants to move.
Haptic pedals with force feedback allow the control of two robotic arms using feet to manipulate instruments such as an endoscope or a grasper.

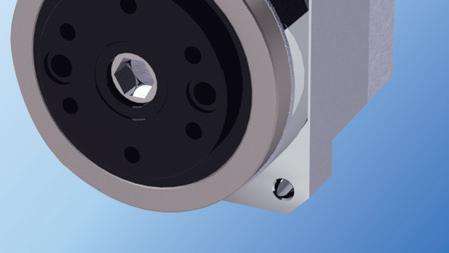


The IDT Series is a family of compact actuators with an integrated servo drive with CANopen® communication. They deliver high torque with exceptional accuracy and repeatability, and feature Harmonic Drive® precision strain wave gears combined with a brushless servomotor. Some models are available with a brake and two magnetic absolute encoders with the second providing output position sensing. This revolutionary product line eliminates the need for an external drive and greatly simplifies cabling, yet delivers high-positional accuracy and torsional stiffness with a compact form factor.
• Actuator with Integrated Servo Drive utilizing CANopen®

• 24 or 48 VDC nominal supply voltage
• A single cable with only 4 conductors is needed: CANH, CANL, +VDC, 0VDC


• Zero Backlash Harmonic Drive® Gearing

• Panel Mount Connectors or Pigtail Cables Available with Radial and Axial Options













• Control Modes include: Torque, Velocity, and Position Control, CSP, CSV, CST

“Controlling four arms simultaneously, moreover with one’s feet, is far from routine and can be quite tiring. To reduce the complexity of the control, the robots actively assist the surgeon by coordinating their movements with the surgeons through active prediction of the surgeon’s intent and adaptive visual tracking of laparoscopic instruments with the camera. Additionally, assistance is offered for more accurate grasping of the tissues,” Professor Aude Billard, head of LASA, said.
Specialists have already been trained on the system and clinical trials are currently ongoing in Geneva. The research team conducted a comprehensive user study with practicing surgeons.
According to Dr. Enrico Broennimann, who has participated in the trials in collaboration with the Swiss Foundation for Innovation and Training in Surgery (SFITS), “The idea to actively use one’s feet to perform robotic-assisted surgery is a good idea, and it’s definitely a learnable skill. I’d like to see it implemented in the operating room, perhaps as a cockpit well away from the patient to increase ergonomics.” RR
Intuitive Surgical president Dave Rosa recently discussed two technological opportunities that will advance surgical robotics and minimally invasive surgery in a major way: improved visualization for surgeons and focal therapy.
“How can we help surgeons see more about what they’re doing? … That, to me, is a huge piece of the puzzle going forward that I’m really excited about,” Rosa said in an interview with DeviceTalks Editorial Director Tom Salemi for our IntuitiveTalks podcast.
The difference between the best and worst surgeons isn’t who can manipulate the instrument better, Rosa said, but rather who has better anatomical knowledge with regard to tissue planes, the subtleties of where bleeding might or might not happen, and the location of nerves or structures like the ureter.
The question is how can device developers help surgeons so they don’t need 1,000 cases to learn that sort of anatomical variation, Rosa said.
“Fluorescence-guided surgery is a big piece of this puzzle, where you can inject a fluorescing marker into the body and using infrared lasers in the system, it lights up. It’s pretty amazing,” Rosa said. “We have a molecule in development that’s specific to prostate cancer, for example. You can inject the drug, turn on the infrared laser, and see the prostate cancer. And if the surgeon has resected the prostate but happens to leave some behind, they can go back and resect that and work for a negative margin. That’s not possible in white light imaging.”
The second area Rosa highlighted is focal therapy, a less invasive treatment for prostate cancer. Focal therapy uses real-time imaging and ablation to destroy small tumors, minimizing the occurrence or severity of side effects from more traditional oncology therapies.
“As work is being done outside of Intuitive for liquid biopsy, better imaging, you see that cancer might be detected earlier, when it’s smaller and not symptomatic,” Rosa said. “If that’s true and you buy that as a thesis — I don’t think we’d argue that — it should be possible to treat it earlier, too, if we can localize it.”



Contactless, no wear and maintenance-free
High positioning accuracy and resolution
Economical, small, compact designs and custom solutions
Flexiblering diameters and measuring lengths






Local stock of absolute and incremental encoders
Lead times as low as 6 weeks on custom encoders





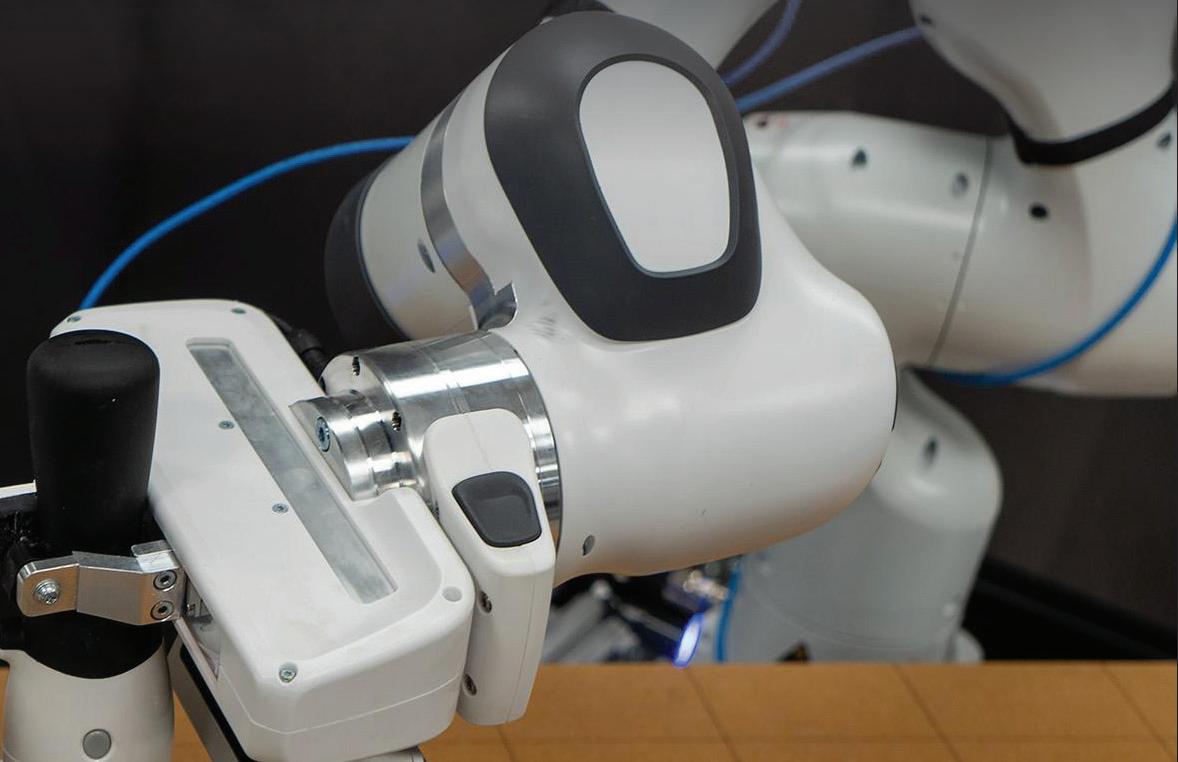
Using its Generative AI approach, TRI has already taught robots more than 60 dexterous behaviors like peeling vegetables, using hand mixers, preparing snacks, and flipping pancakes. TRI said the goal is to teach robots hundreds by the end of 2023 and 1,000 by the end of 2024.

 | Toyota Research Institute
| Toyota Research Institute





 Steve Crowe | Executive Editor | Robotics
Steve Crowe | Executive Editor | Robotics

New approach is a step towards building Large Behavior Models for robots, analogous to Large Language wwModels for conversational AI.
Toyota Research Institute
(TRI) recently unveiled how it is using Generative AI to help robots learn new dexterous behaviors om demonstration. TRI said this new approach “is a step towards building ‘Large Behavior Models (LBMs)’ for robots, analogous to the Large Language Models (LLMs) that have recently revolutionized conversational AI.”


TRI said it has already taught robots more than 60 di cult, dexterous skills using the new approach. Some of these skills include pouring liquids, using tools and manipulating deformable objects. These were all realized, according to TRI, without writing a single line of new code; the only change was supplying the robot with new data.


Whether you’re storing, conveying, picking or handling, there’s not a corner of the warehouse that our robots and solutions will not fit.
Sereact, a German-based AI and robotics developer, recently announced PickGPT, a robotics transformer that combines large language models (LLMs) with the company’s computer vision technology.
PickGPT allows robot operators to instruct robots using natural language by enabling robots to process natural language and visual information and correlate multimode data. PickGPT allows robots to perceive their environment with unprecedented intelligence and accuracy and understand and execute instructions in natural language.
“PickGPT enables straightforward communication between humans and robots via voice commands and intuitive interfaces. This simplifies the link with other warehouse systems and enables employees to instruct the robot in a simple way – for example, to define pick points or to blacklist certain items,” Ralf Gulde, CoFounder and CEO of Sereact, said.
The robotics developer is a software-based robotics system that doesn’t require programming or training. Because of this, PickGPT reduces the time needed to set up and customize robots and allows employees to spend that time focusing on other essential tasks. It also expands the range of people who can work with robots as they don’t need a coding background to work with the system.
Along with faster setup, PickGPT offers more flexibility and quality control. With the robotics transformer, robots can respond quickly and easily to new tasks or changing environmental conditions, which are common in warehouse settings.
PickGPT can also recognize and identify objects and products in real time based on their visual characteristics. The transformer automatically analyzes product images and matches them with items in any real-world scenario.
It can also understand and interpret product titles, descriptions, and other textual information to automatically identify and assign related products to regions in an image. This means that PickGPT has a high potential for quality control processes.
The robotics transformer can also simplify the return process for e-commerce companies. PickGPT has the ability to distinguish between packaging material and products in the first step of the return process, and it can then sort the items automatically based on a description or product image, meaning there is no need for barcode scanning.
Sereact was founded in 2021 by Marc Tuscher and Ralf Gulde, who both researched the combination of robotics and AI at the University of Stuttgart. The company is based in StuttgartVaihingen, Germany.
“The tasks that I’m watching these robots perform are simply amazing – even one year ago, I would not have predicted that we were close to this level of diverse dexterity,” said Russ Tedrake, vice president of robotics research at TRI and the Toyota professor of electrical engineering and computer science, aeronautics and astronautics, and mechanical engineering at MIT.
“What is so exciting about this new approach is the rate and reliability with which we can add new skills. Because these skills work directly from camera images and tactile sensing, using only learned representations, they are able to perform well even on tasks that involve deformable objects, cloth, and liquids — all of which have traditionally been extremely difficult for robots.”
“Our research in robotics is aimed at amplifying people rather than replacing them,” said Gill Pratt, CEO of TRI and Chief Scientist for Toyota Motor Corporation. “This new teaching technique is both very efficient and produces very high performing behaviors, enabling robots to much more effectively amplify people in many ways.”
TRI’s robot behavior model learns from haptic demonstrations from a teacher, combined with a language description of the goal. It then uses an AI-based diffusion policy to learn the demonstrated skill. This process allows a new behavior to be deployed autonomously from dozens of demonstrations.
TRI’s approach to robot learning is agnostic to the choice of teleoperation device, and it said it has used a variety of low-cost interfaces such as joysticks. For more dexterous behaviors, it taught via bimanual haptic devices with position-position coupling between the teleoperation device and the robot. Position-position coupling means the input device sends measured pose as commands to the robot and the robot tracks these pose commands using torque-based Operational Space Control. The robot’s pose-tracking error is then converted to a force and sent back to the input device for the teacher to feel. This allows teachers to close the feedback loop with the robot through force and has been critical for many of the most difficult skills we have taught.
When the robot holds a tool with both arms, it creates a closed kinematic chain. For any given configuration of the robot and tool, there is a large range of possible
“Our research in robotics is aimed at amplifying people rather than replacing them”
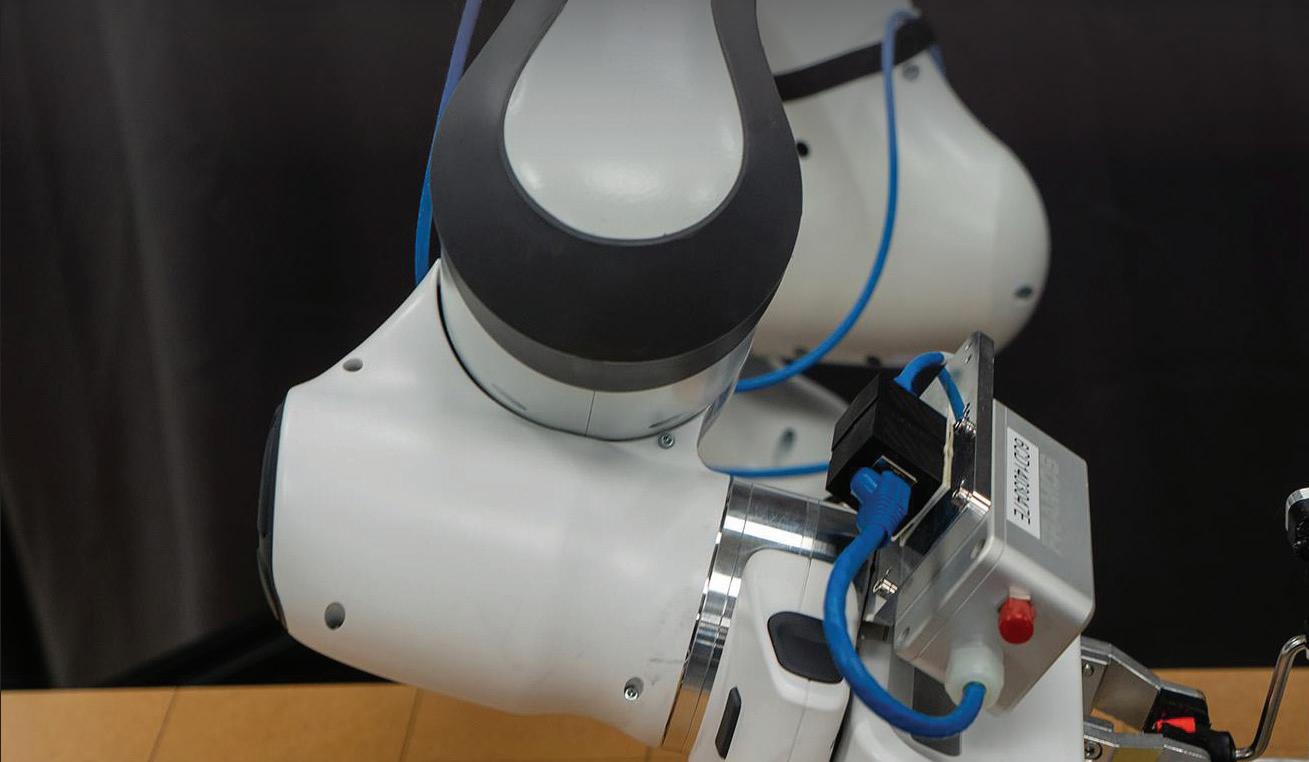
Introducing Northwire, your ultimate partner for custom cable and interconnect solutions for Test & Measurement applications.






With our cutting-edge technology and expertise, we deliver high-quality, reliable cables tailored to your specific needs. Trust us to provide innovative solutions, exceptional performance, and superior customer service.
Experience the Northwire advantage today!
BENEFITS:
• Superior Access to Engineering services and technical support
• UL/CSA certification




• Ruggedized cable solutions
• High-quality custom products built on proven solid cable solutions platforms

• Vertical integrated supply chain

internal forces that are unobservable visually. Certain force configurations, such as pulling the grippers apart, are inherently unstable and make it likely the robot’s grasp will slip. If human demonstrators do not have access to haptic feedback, they won’t be able to sense or teach proper control of force.
So TRI employs its Soft-Bubble sensors on many of its platforms. These sensors consist of an internal camera observing an inflated deformable outer membrane. They go beyond measuring sparse force signals and allow the robot to perceive spatially dense information about contact patterns, geometry, slip, and force.
Making good use of the information from these sensors has historically been a challenge. But TRI said diffusion provides a natural way for robots to use the full richness these visuotactile sensors afford that allows them to apply them to arbitrary dexterous tasks.
In one test, a human teacher attempted 10 egg-beating demonstrations. With haptic force feedback, the operator succeeded every time. Without this feedback, they failed every time.
Instead of image generation conditioned on natural language, TRI uses diffusion to generate robot actions conditioned on sensor observations and, optionally, natural language. TRI said using diffusion to generate robot behavior provides three benefits over previous approaches:
1. Applicability to multi-modal demonstrations. This means human demonstrators can teach behaviors naturally and not worry about confusing the robot.
2. Suitability to high-dimensional action spaces. This means it’s possible for the robot to plan forward in time which helps avoid
myopic, inconsistent, or erratic behavior.
3. Stable and reliable training. This means it’s possible to train robots at scale and have confidence they will work, without laborious hand-tuning or hunting for golden checkpoints.

According to TRI, Diffusion is well suited for high dimensional output spaces. Generating images, for example, requires predicting hundreds of thousands of individual pixels. For robotics, this is a key advantage and allows diffusion-based behavior models to scale to complex robots with multiple limbs. It also gave TRI the ability to predict intended trajectories of actions instead of single timesteps.
TRI said this Diffusion Policy is “embarrassingly simple” to train; new behaviors can be taught without requiring numerous costly and laborious real-world evaluations to hunt for the
To teach new behaviors, TRI’s approach requires a human operator to teleoperate the robot through demonstrations of the desired task. This usually requires an hour or two of teaching which generally equates to anywhere from a couple dozen to a hundred or so demonstrations.
| Toyota Research Institute









best-performing checkpoints and hyperparameters. Unlike computer vision or natural language applications, AI-based closed-loop systems can not be accurately evaluated with o ine metrics — they must be evaluated in a closed-loop setting which, in robotics, generally requires evaluation on physical hardware.
This means any learning pipeline that requires extensive tuning or hyperparameter optimization becomes impractical due to this bottleneck in real-life evaluation. Because Diffusion Policy works out of the box so consistently, it allowed TRI to bypass this di culty.
Next steps
TRI admitted that “when we teach a robot a new skill, it is brittle.” Skills will work well in circumstances that are similar to those used in teaching, but
the robot will struggle when they differ. TRI said the most common causes of failure cases we observe are:
• States where no recovery has been demonstrated. This can be the result of demonstrations that are too clean.
• Camera viewpoint or background significant changes.
• Test time manipulands that were not encountered during training.
• Distractor objects, for example, significant clutter that was not present during training.
Part of TRI’s technology stack is Drake, a model-based design for robotics that includes a toolbox and simulation platform. Drake’s degree of realism allows TRI to develop in both simulation and in reality and could help overcome these shortcomings going forward.
The SHA-IDT Series is a family of compact actuators that deliver high torque with exceptional accuracy and repeatability. These hollow shaft servo actuators feature Harmonic Drive® precision strain wave gears combined with a brushless servomotor, a brake, two magnetic absolute encoders and an integrated servo drive with CANopen® communication. This revolutionary product eliminates the need for an external drive and greatly simplifies cabling yet delivers high-positional accuracy and torsional stiffness in a compact housing.

TRI’s robots have learned 60 dexterous skills already, with a target of hundreds by the end of 2023 and 1,000 by the end of 2024.
“Existing Large Language Models possess the powerful ability to compose concepts in novel ways and learn om single examples,” TRI said. “In the past year, we’ve seen this enable robots to generalize semantically (for example, pick and place with novel objects). The next big milestone is the creation of equivalently powerful Large Behavior Models that fuse this semantic capability with a high level of physical intelligence and creativity. These models will be critical for generalpurpose robots that are able to richly engage with the world around them and spontaneously create new dexterous behaviors when needed.” RR
Today’s AGVs must be compact and functional robots which are able to move vertically and carry heavy loads. These AGVs cannot fail, and so the choice of their motorization is crucial. There are 5 key points to consider when motorizing an AGV.

1. Choose compact motorization where possible - Drives must fit into restricted spaces, as they are sometimes integrated into existing trucks. A small footprint is critical for applications in logistics.
2. Focus on ease of use – select a plug-and-play solution.
3. Opt for fast delivery of your motor solution
4. Base the design on modularity - Not all AGVs do the same job and therefore having the flexibility to select a solution to match needed specifications is essential.
5. Prioritize safety – select motor options with integrated sensors.
maxon’s IDX motor has a diameter of only 56 mm, its performance is equivalent to that of a motor with a footprint 25% larger. The IDX motorization thus combines performance in a compact size and ideal for AGVs.

Go to Drive.tech for more details. Visit www.maxongroup.us for more maxon solutions.
Advancing innovation for over 100 years

Why accept a standard product for your custom application?
NEWT is committed to being the premier manufacturer of choice for customers requiring specialty wire, cable and extruded tubing to meet existing and emerging worldwide markets. Our custom products and solutions are not only engineered to the exacting specifications of our customers, but designed to perform under the harsh conditions of today’s advanced manufacturing processes. Cables we specialize in are LITZ, multi-conductor cables, hybrid configurations, coaxial, twin axial, miniature and micro-miniature coaxial cables, ultra flexible, high flex life, low/high temperature cables, braids, and a variety of proprietary cable designs. Contact us today and let us help you dream beyond today’s technology and achieve the impossible.

At Northwire, we understand the importance of having the right cable and interconnect solutions for your Test & Measurement applications. With over 50 years of experience, we have the expertise and knowledge to provide you with the highest quality products that are both reliable and durable.

Our team of skilled engineers and technicians work closely with you to ensure that your custom cable and interconnect solutions meet your requirements and exceed expectations. We use only the highest quality materials and advanced manufacturing techniques to deliver products that are built to last.
Whether you need a custom cable for data transfer, power transmission, or any other applications, we have the capabilities to deliver the solution you need. Trust Northwire for excellence and reliability.
Robots are flexible and adaptable. Quickly re-tasking robots for job variety can be challenging.
Some common solutions: Changing workpieces – Quick-change gripper fingers and gripper changeouts are easily automated for workpiece variety or changing workpiece characteristics during manufacturing.

Flexible machine table fixtures – Robots are widely identified for their ability to handle workpieces. They also excel at automatically replacing fixtures and other peripheral tooling.
Automating multiple tasks – Use the robot to accomplish a secondary task. Instead of remaining idle during machining, the robot can automatically deburr workpieces.
Adjustable custom tooling – Use dove tails and adjustable mountings in EOATs to expand tools for changing conditions or reach requirements.
Many standard solutions are available - make the most of your investment with automation expert support today!
Northwire, Inc. 110 Prospect Way
Osceola, WI 540 (715) 294-2121
customercare_northwire@lemo.com
www.northwire.com
SCHUNK: 211 Kitty Hawk Drive, Morrisville, NC 27560

919-572-2705
info@us.schunk.com