3 minute read
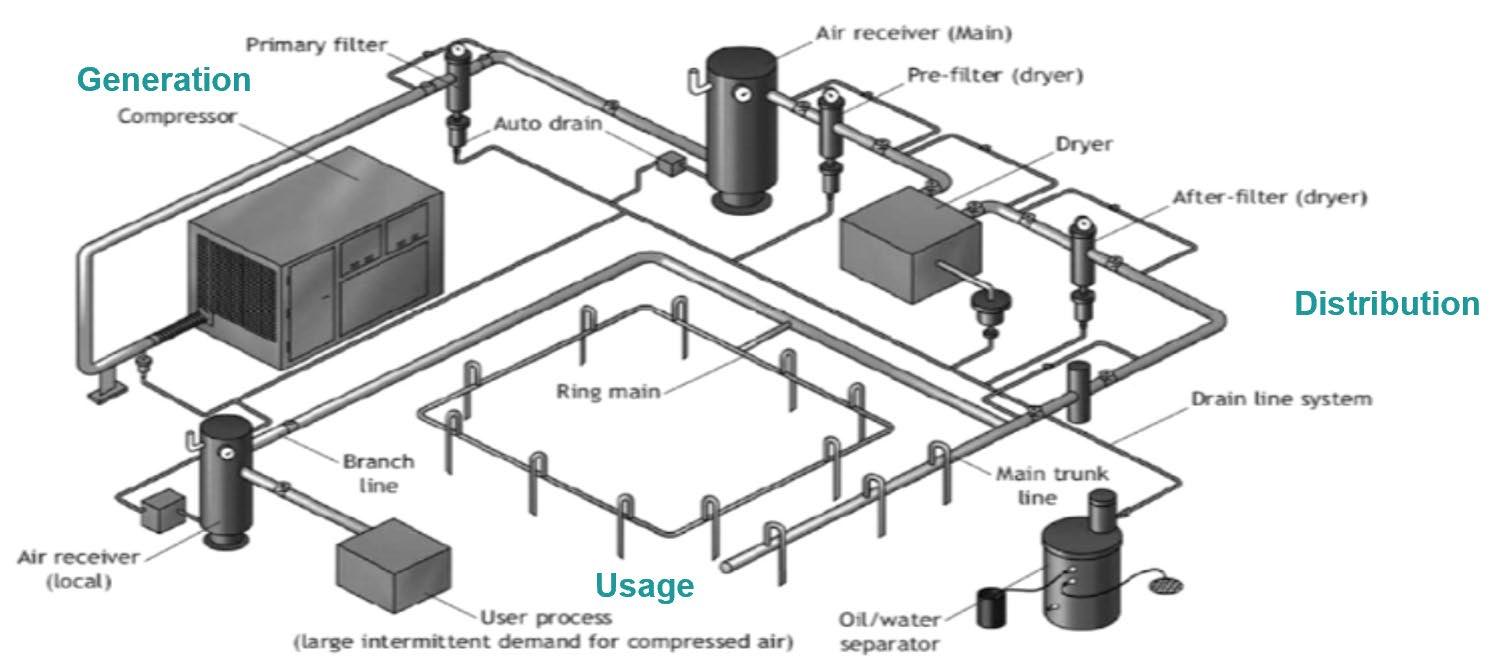
Figure 5: A generic compressed air system
• Recover heat waste from an air compressor. More than 80 percent of the electricity supplied to the compressor can be recovered if the enterprise utilises the heat generated from cooling the compressor.28 For example, hot air can be used to produce hot water, which can be further used for process heating or washing purposes. Water-cooled air compressors can provide hot water, at about 75 degrees Celsius, which can be used in other enterprise processes, thereby saving energy that would be spent heating water. A generic compressed air system is shown in Figure 5.
29
Advertisement
Figure 5: A generic compressed air system
• Utilise colder intake air for an air compressor, as every 4-degree-Celsius rise in inlet air temperature results in increased energy consumption of 1 percent.30 As compressors require less energy to compress cooler and denser air, an enterprise may use inlet air from outside, which is cooler than the air in the compressor room. To provide better ventilation for cool air intake, an enterprise may invest in a separate compressor room or make arrangements for ventilation in the existing room. Typical results are energy savings of about 5 percent, with payback periods of less than a year for compressors under continuous operation.
• Repair compressed air leaks. In a typical industrial plant without a leak detection and repair programme, air leaks contribute to 25 to 40 percent of utilised air.31 A leak detection and repair programme can reduce leaks to only about 10 percent of air compressor demand. Air leaks occur mainly in the following areas:
o Couplings, flexible hoses, rubber and plastic tubes, and fittings
o Pressure regulators
o Pipe joints and thread sealants
28 Moskowitz, Frank. Heat Recovery and Compressed Air Systems. Compressed Air Best Practices. LINK. 29 Source of figure: The Chemical Engineer. LINK. 30 Government of India. Compressed Air System. Bureau of Energy Efficiency. LINK. 31 Marshall, Ron. Protect Profits with Compressed Air Leakage Best Practices. Compressed Air Best Practices. LINK.
• Reduce line pressure to the minimum required. As a rule of thumb, 1 percent savings can be achieved with every 0.1 bar reduction in pressure for screw compressors, 32 which is a common kind of compressor used by industrial enterprises.
• Segregate high- and low-pressure requirements. If several appliances require high-pressure air, but others require low-pressure air, consider using a smaller, separate high-pressure compressor.
• Design for a minimum pressure drop in the distribution line. A properly designed system should have a pressure loss of less than 10 percent of the compressor’s discharge pressure, measured from the receiver tank output to the point-of-use.33
• Start with an energy audit, then make an air compressor efficiency-maintenance program as part of your continuous energy management program.
Boiler and steam pipeline system
Boilers are used in various industrial units to convey heat through steam for different processes such as cooking rice, boiling milk or sterilisation of containers prior to packing. Steam is commonly used as the heating medium due to two main reasons. First, steam is generated from water that is usually readily available and inexpensive. Second, steam can store a large quantity of heat at a temperature that can be conveniently used for heat transfer. Boilers require various types of fuel, namely coal, oil, gas or biomass, to generate steam, depending on the availability of fuel and its cost. A generic steam distribution system is found in Figure 16. 34 Some best practices for energy saving in boiler systems are given below:
• Insulate exposed pipelines, the body of the boiler and its door with tightly wound glass wool fortified with ceramic ribbon and waterproof cladding.
• Regularly check the oxygen content in the boiler’s exhaust gas. To maintain optimum oxygen levels in the exhaust gas, regularly adjust the damper of the FD fan based on exhaust (flue) gas analysis. Best performance is obtained by installing an automatic air control system that will adjust the supplied air volume depending on the residual oxygen content in the exhaust gas.
• Install a condensate recovery system to conserve and recirculate condensate from steam.
• Optimise blowdown (release of hot water) by measuring the boiler water’s conductivity and installing a system that automatically controls blowdown.
• Recover heat from flash steam (which is low pressure and forms from blowdown or returning condensate). A flash tank acts as a separator, allowing the remaining liquid to separate from flash steam. Low-pressure steam can then be used for process applications such as producing hot water.
32 Air Compressor Guide. Why Am I Wasting Money on Compressed Air? LINK. 33 Compressed Air Best Practices. Distribution Piping: Understanding Pressure Drop. LINK. 34 Wermac. Steam Distribution System. LINK.









