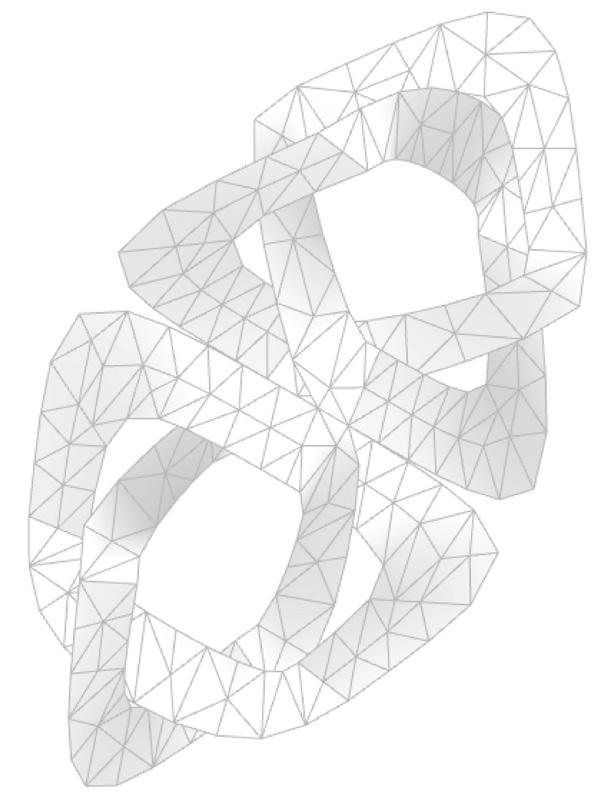
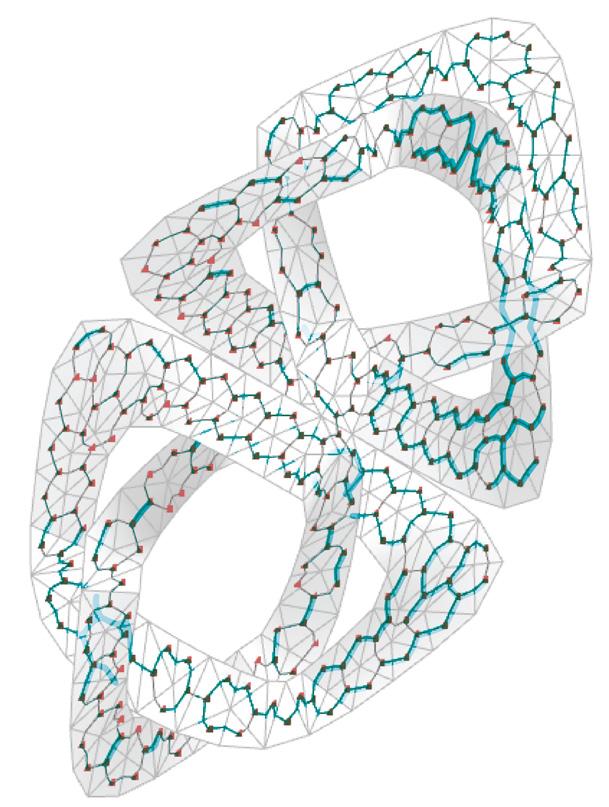
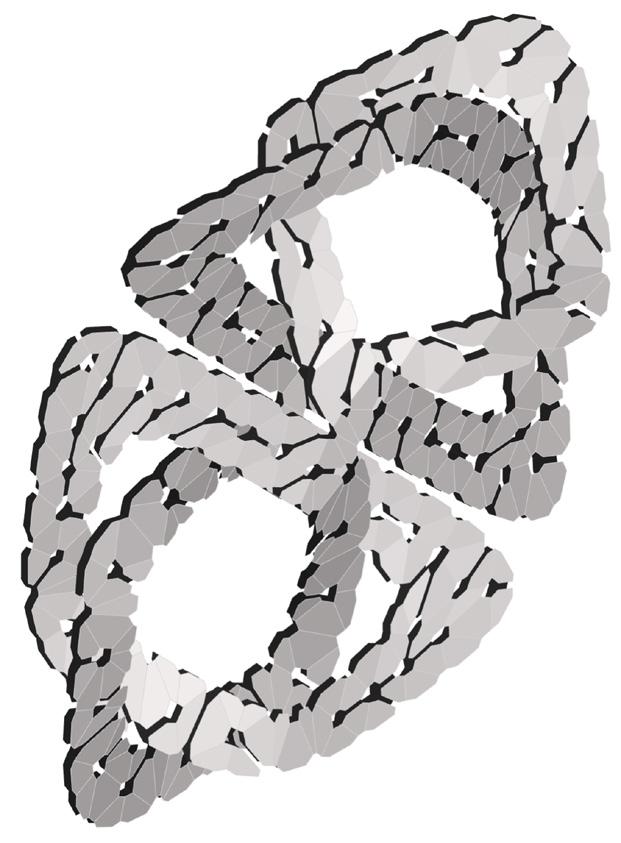
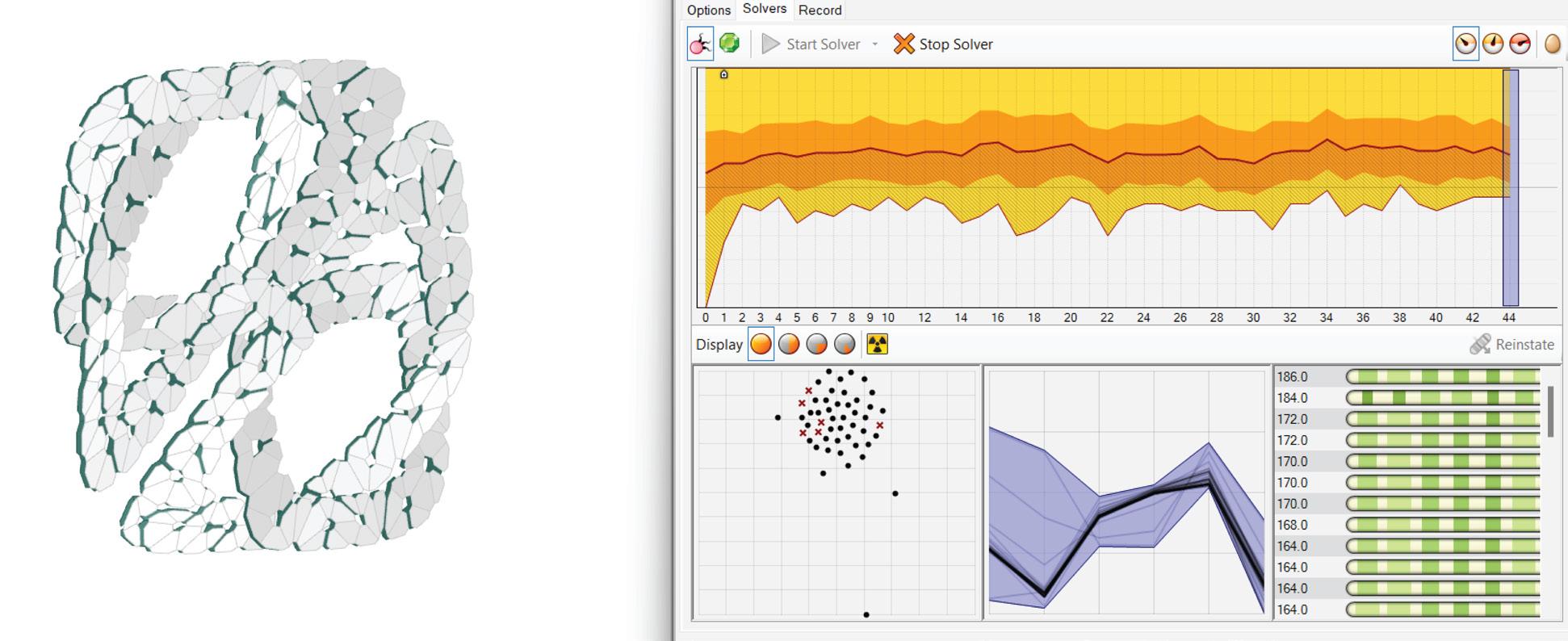
Building Engineering Portfolio 2021-2024
Zahra Cheragh Nia
Zahra.Cheraghnia@mail.polimi.it
I am a computational designer with a background in architecture and experience in digital fabrication, additive manufacturing, and robotic fabrication. Utilizing advanced design and fabrication techniques, I develop innovative solutions for a wide range of projects.
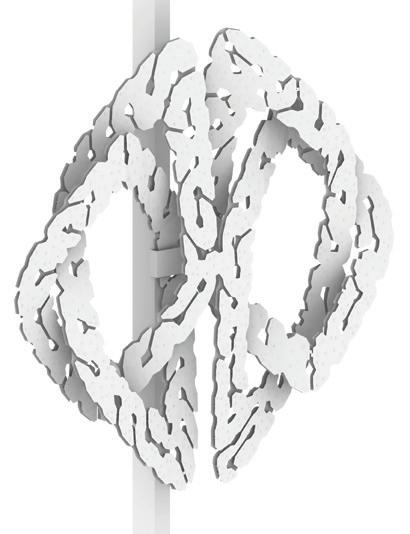
Exploring Advanced Design and Fabrication Methodologies for a Free-form Shading Element through Algorithmic Programming, Robotics and Augmented Reality
Soft Robotic Solar Facade
Table of Content
Designing a nZEB Building Using Passive and Active Strategies
Exploring Advanced Design and Fabrication Methodologies for a Free-form Shading Element through Algorithmic Programming, Robotics and Augmented Reality
Final Project
Supervisor: Pierpaolo Ruttico
Software: Rhino - Grasshopper
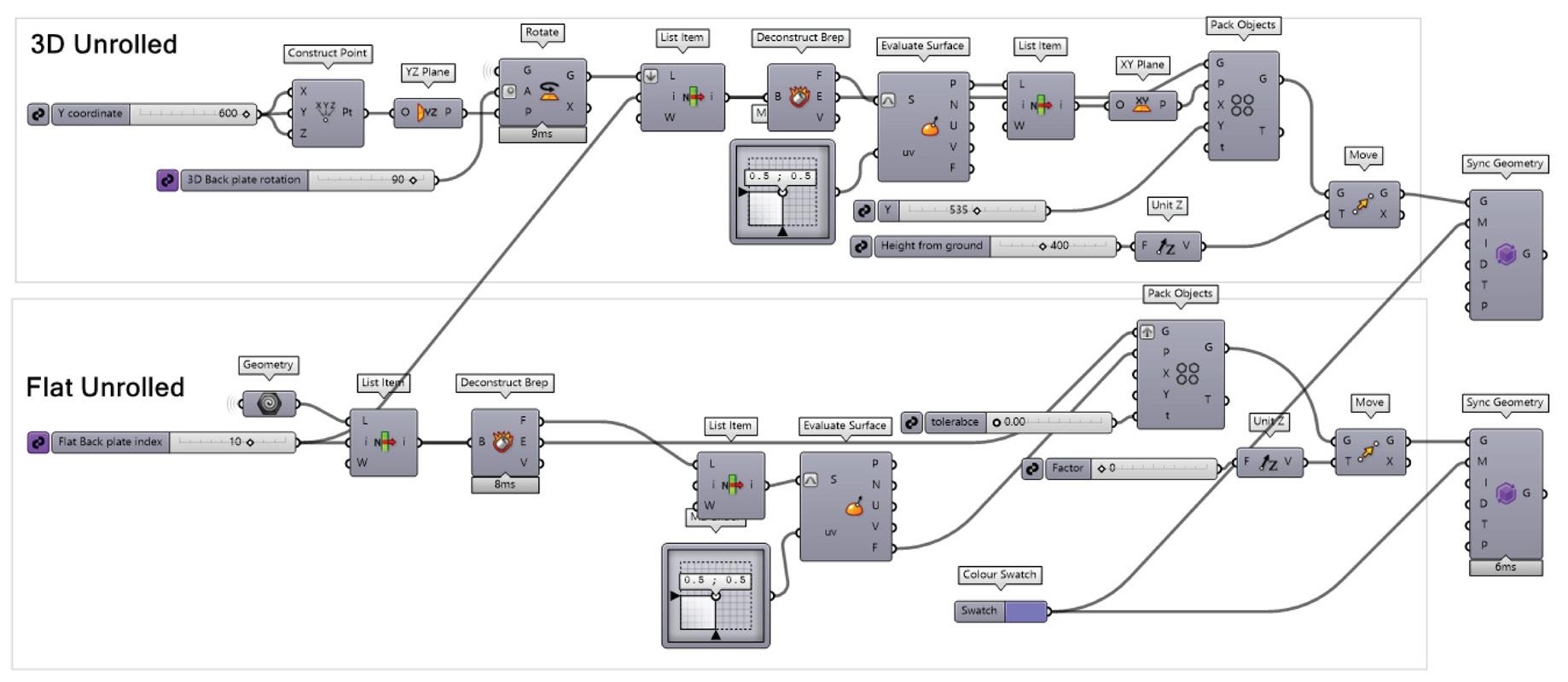
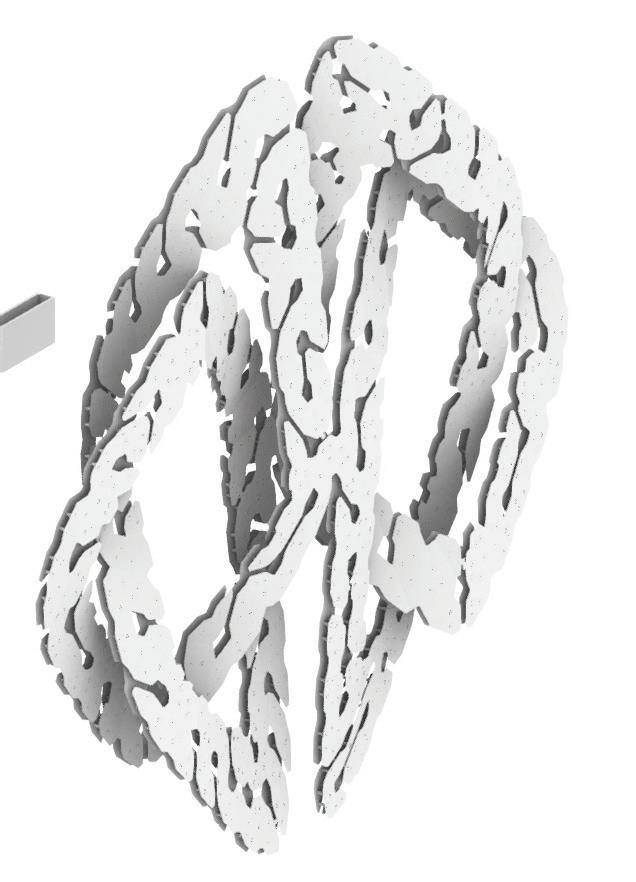
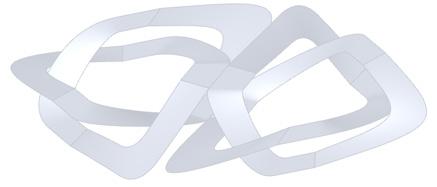
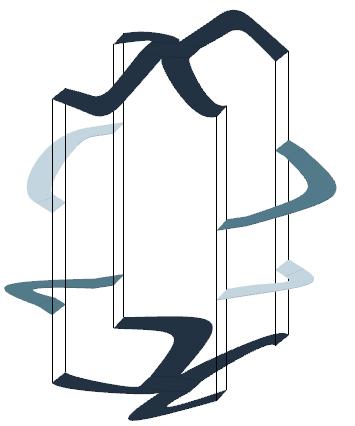
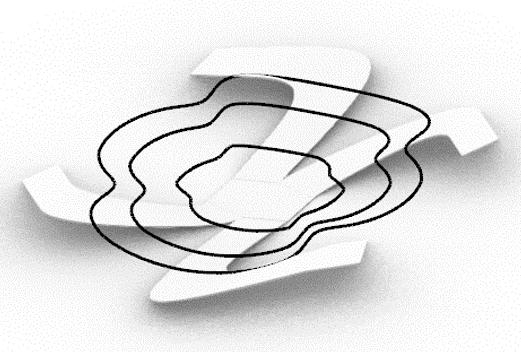
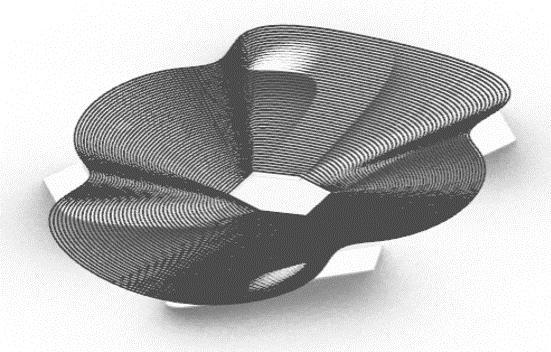
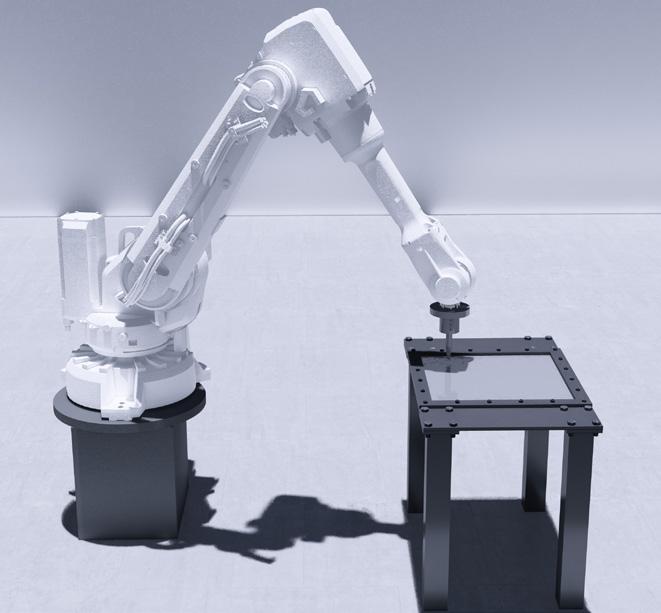
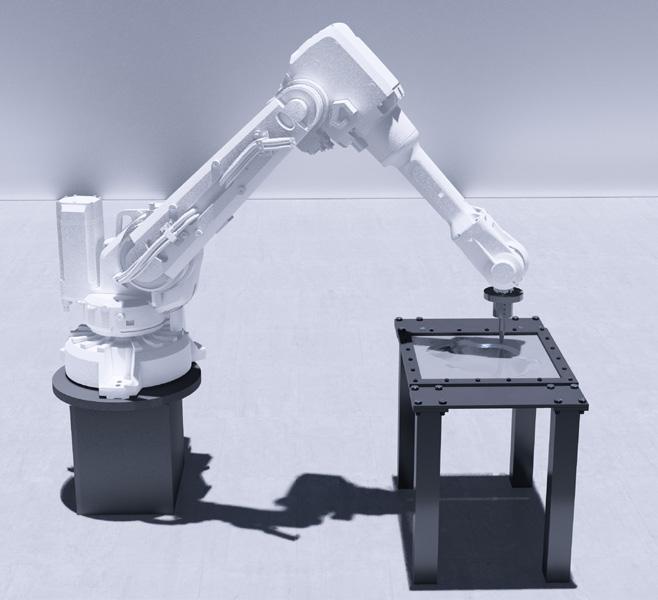
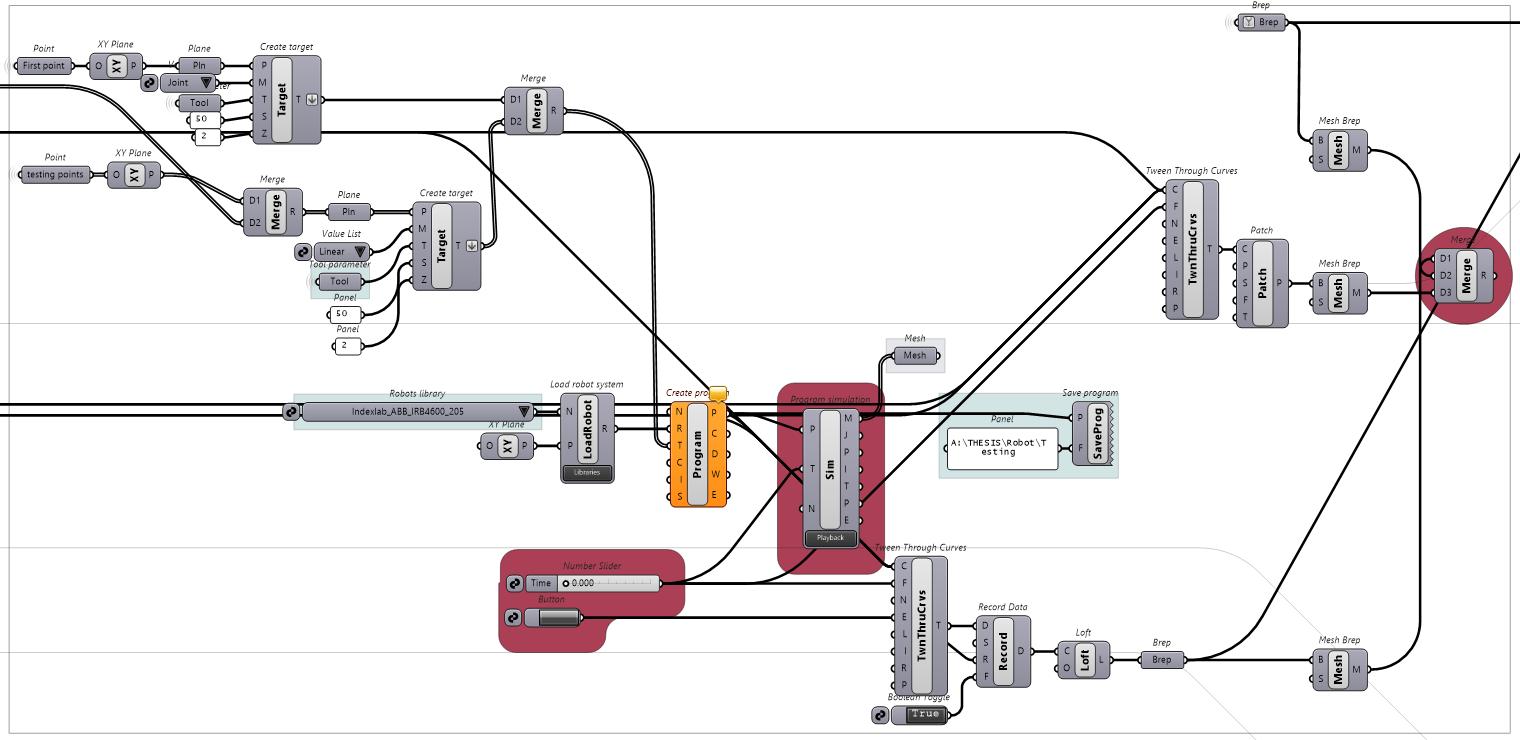
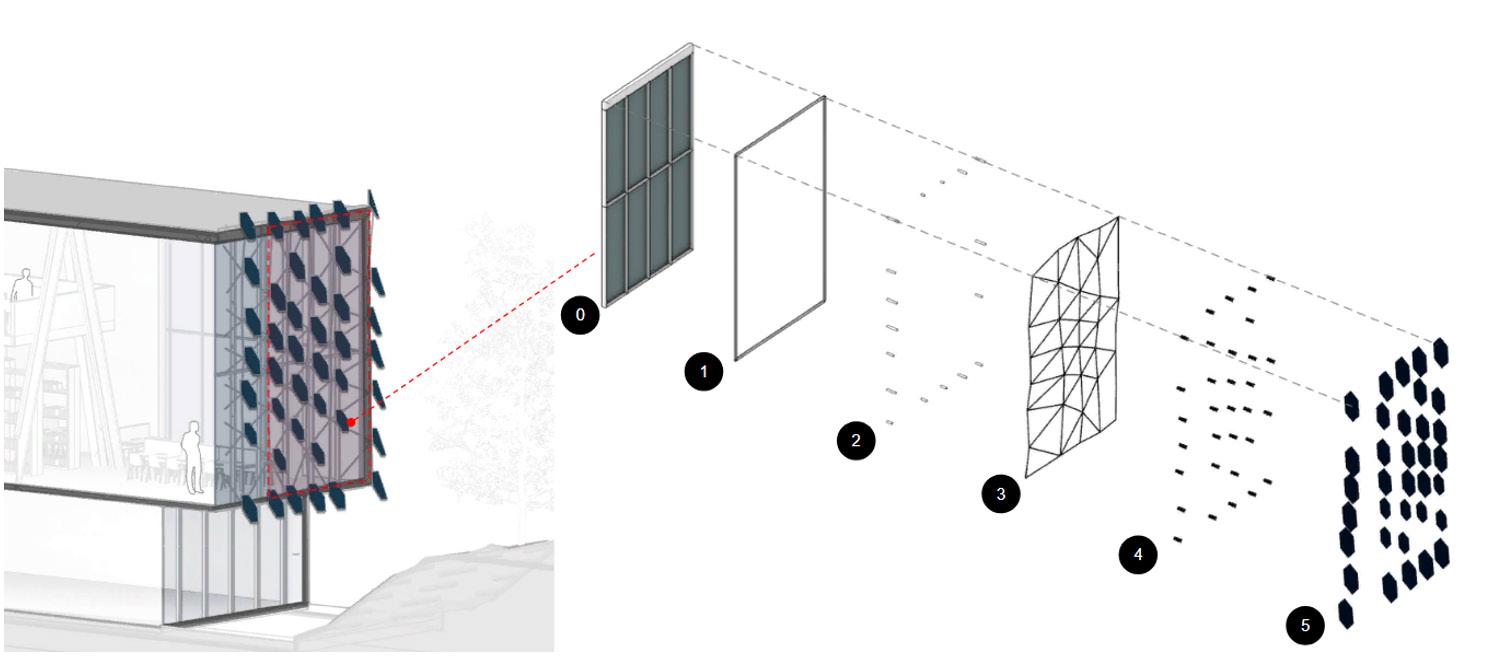
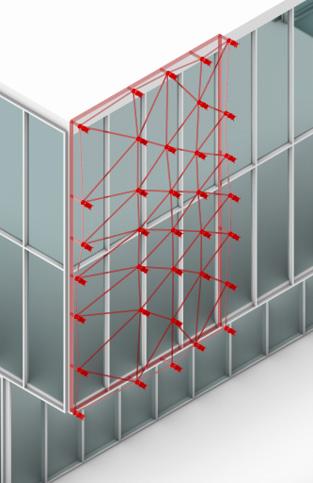
This project explores advanced fabrication methods for complex shading elements on building facades, integrating algorithmic programming, robotics, and augmented reality (AR). By developing a digital workflow that unifies design, fabrication, and performance analysis, the research demonstrates how robotic fabrication and AR can enhance precision, efficiency, and sustainability.
Through a case study, the project shows that these technologies streamline the design-to-fabrication process and improve the adaptability and performance of architectural facades, laying the groundwork for future innovation in complex architectural systems.
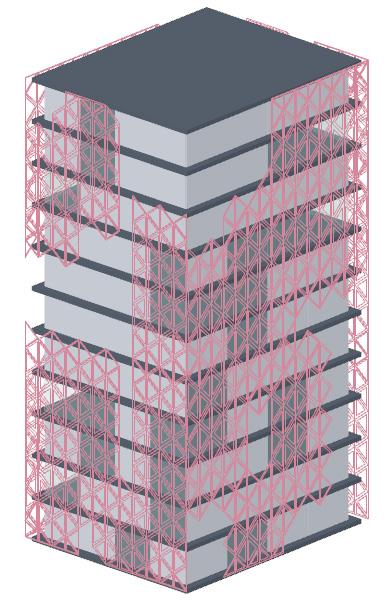
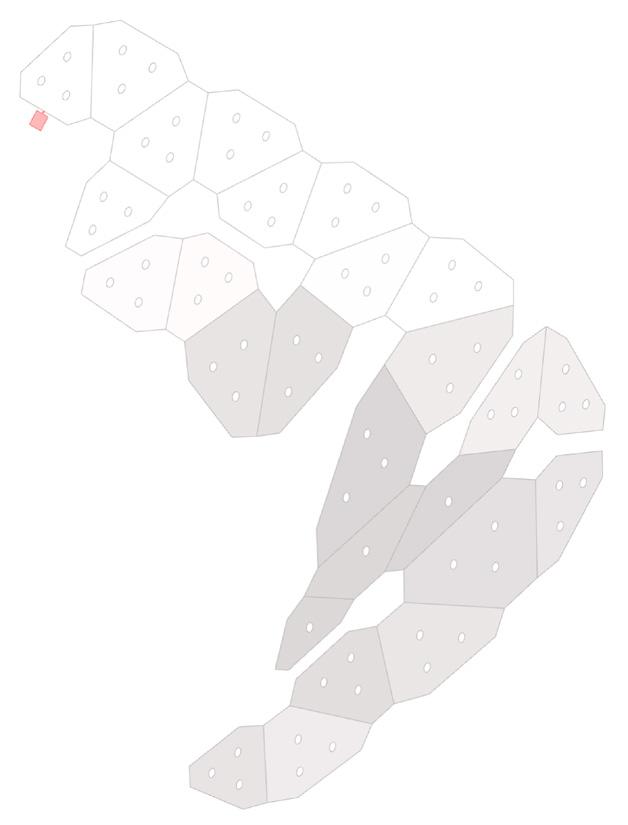
1.Generic Building Model
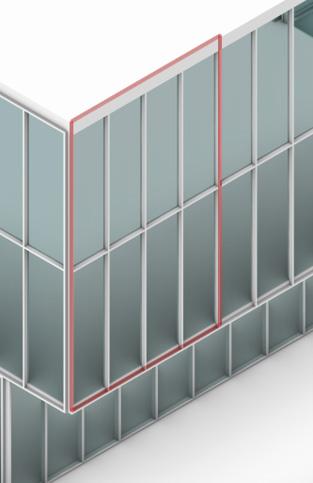
2.Base Façade Skin
3.Panelizing the Base Skin
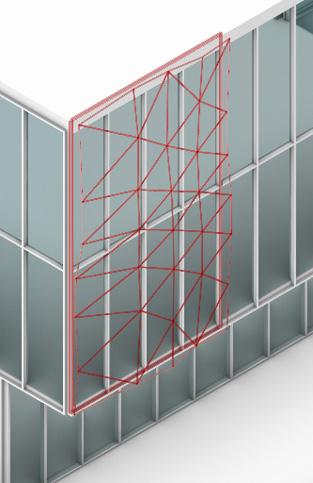
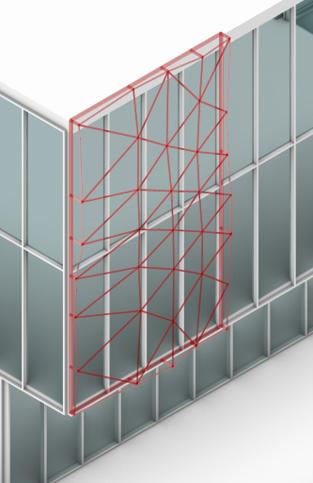
4.Generating a Base for the Pattern
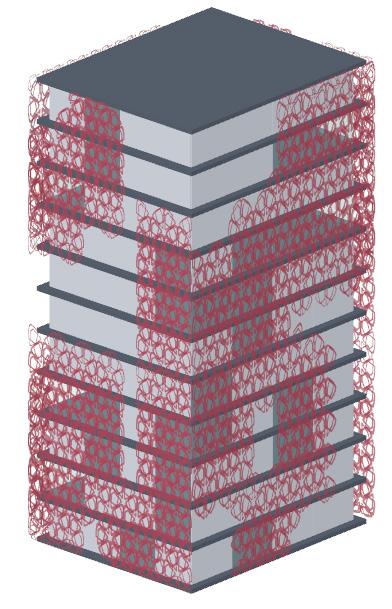
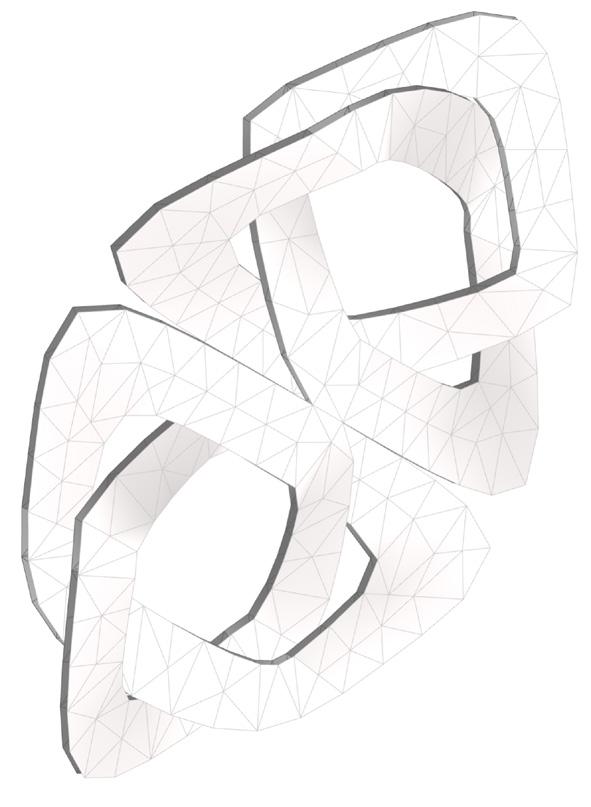
5.Generating the Pattern from the Base
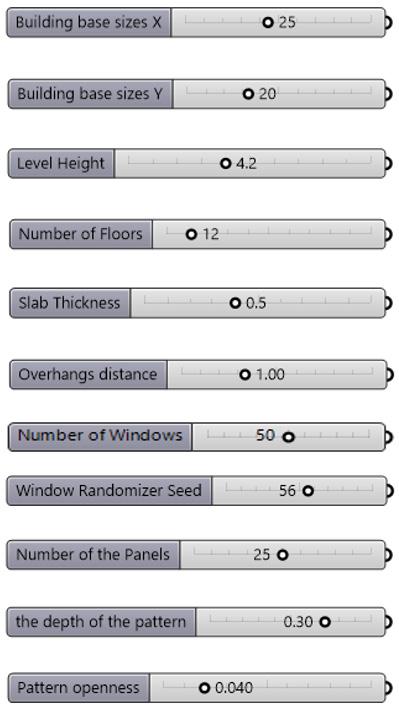
Controllable Parameters
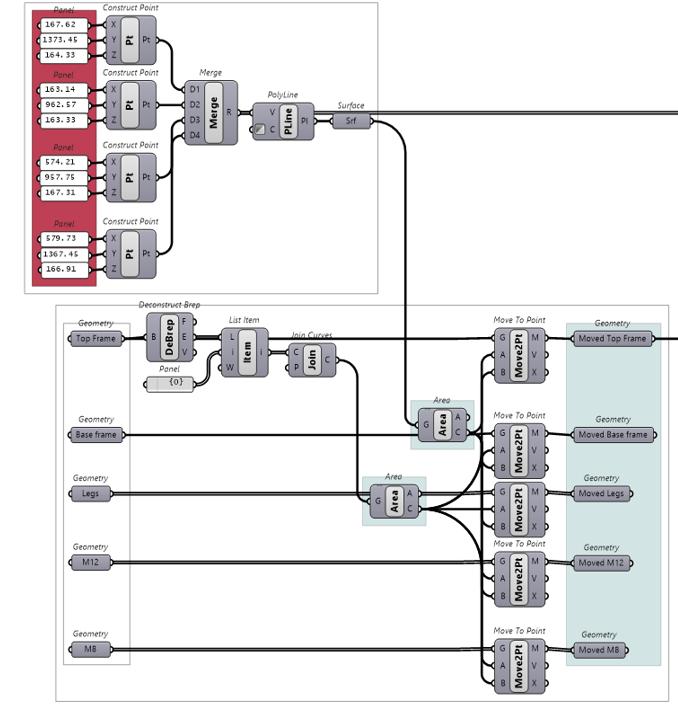
Graph-Based Mesh Panelization
Find
1. Base Surface
5. Panelization
6. Optimization to
Maximized Stiffness and Overlap Between the Two Layers 2. Rationalization
Offsetting
Clustering
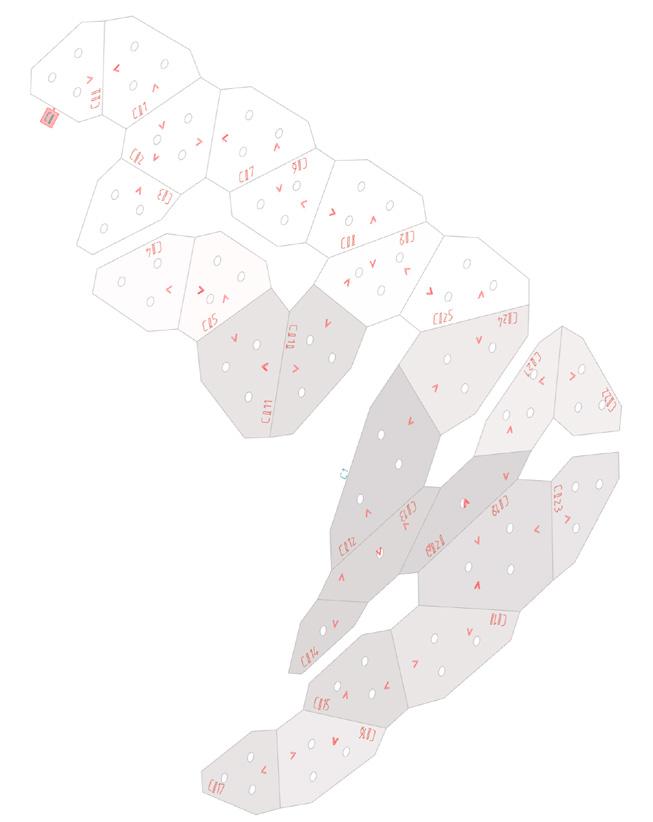
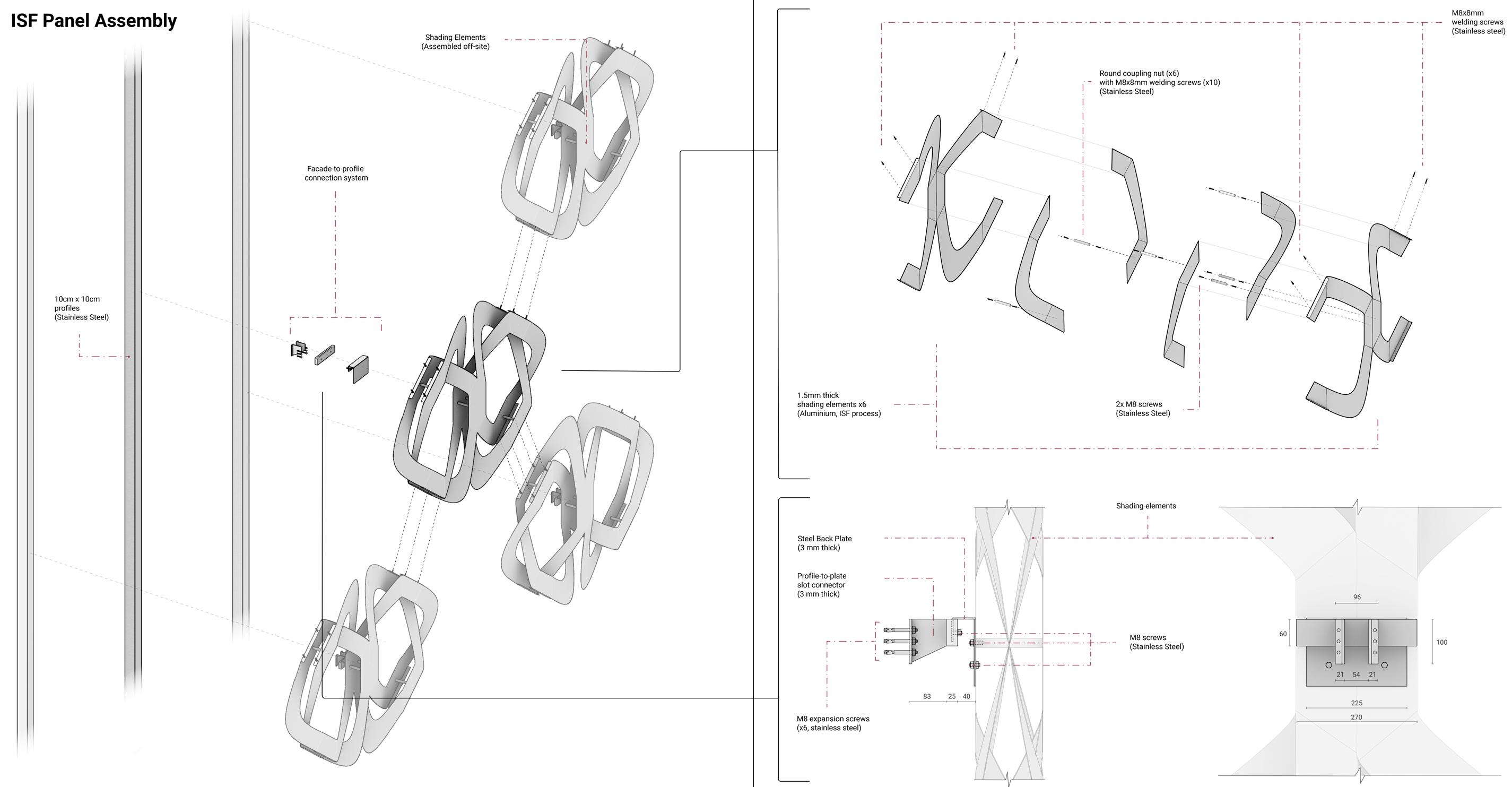
1.Folding Lines of the panels
connection Between Layers
connected module
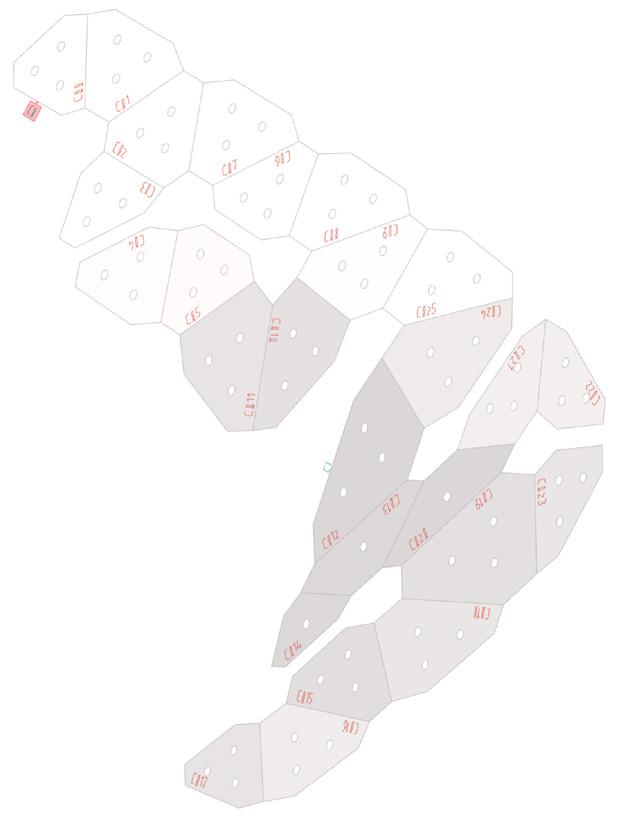
1.Base Panel
2.Panel Labelling
3.Surface Labelling
4.Angle Labelling 1.Outline of the Panel 2.Rivet Holes 3.Fold Lines
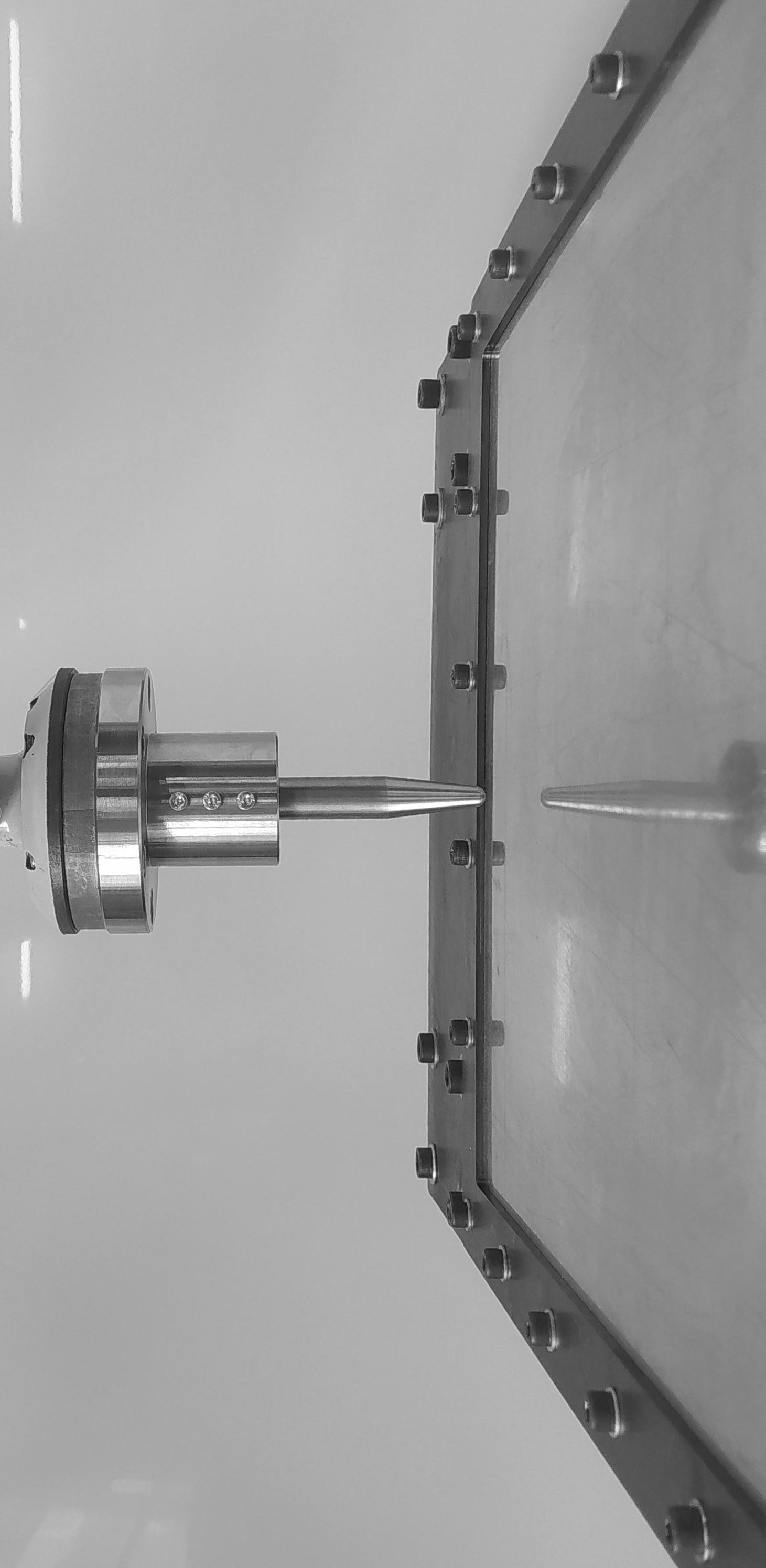
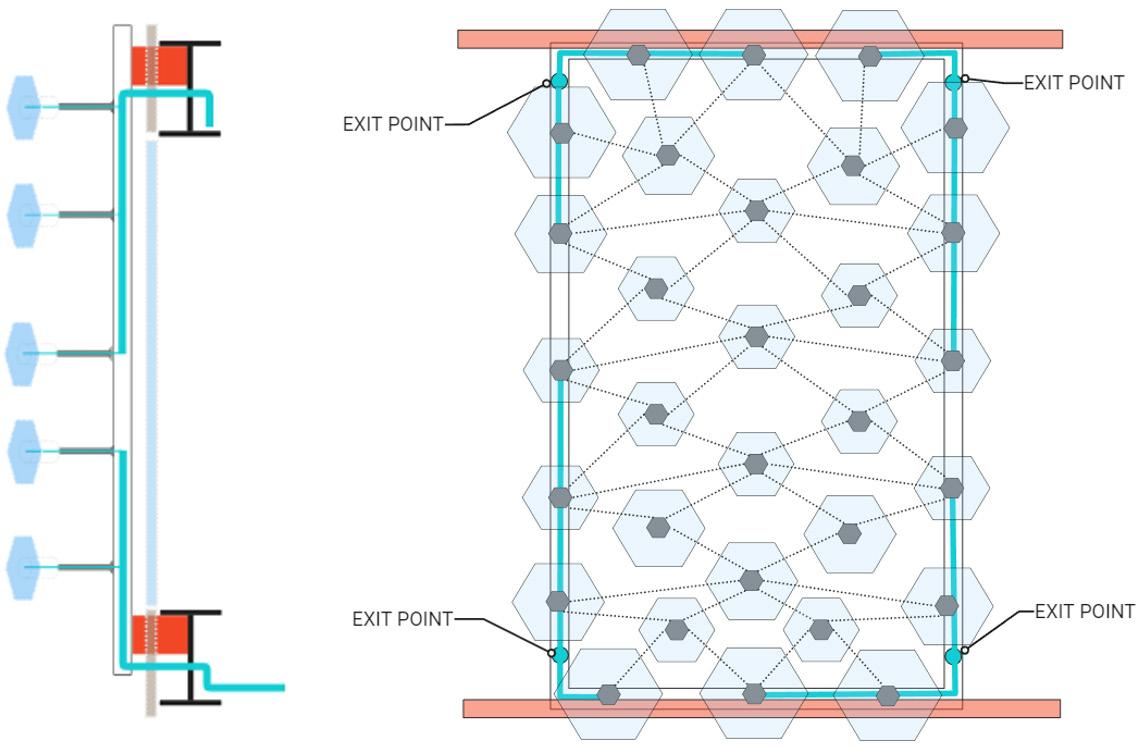
Connections Documentation Labelling Setting Up Augmented Reality Using Fologram
Documentation
On-site Assembly
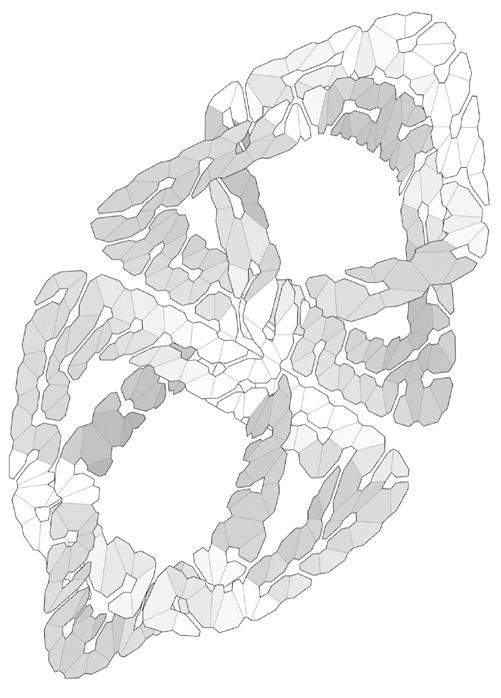
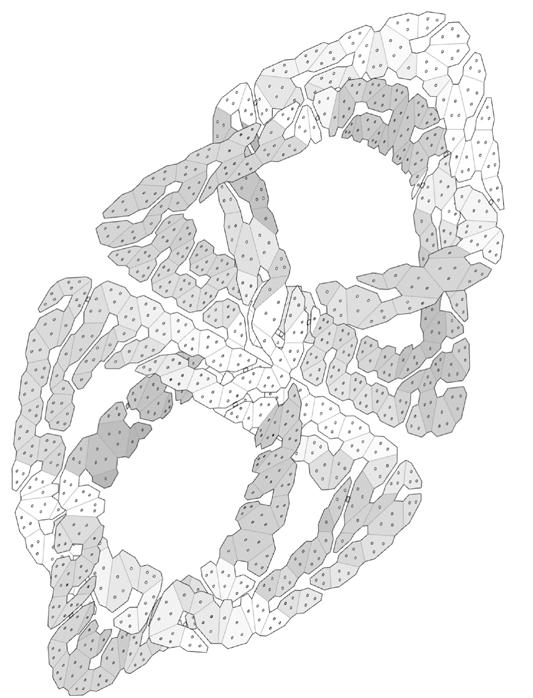
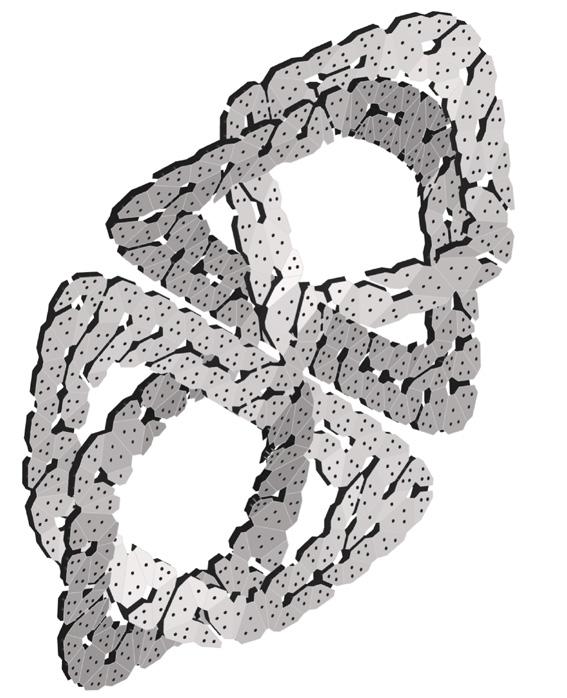
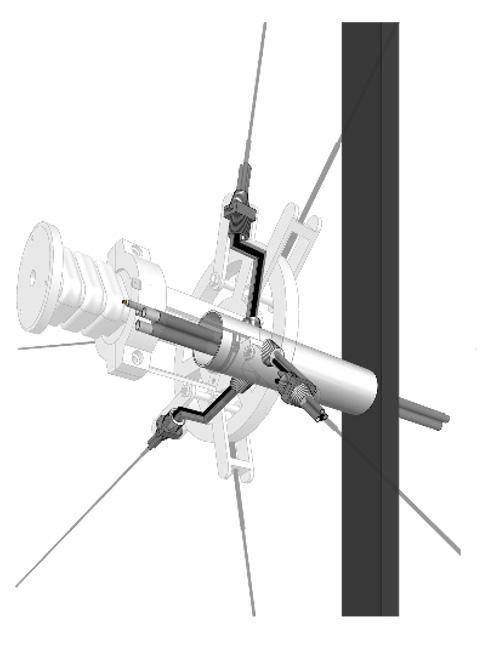
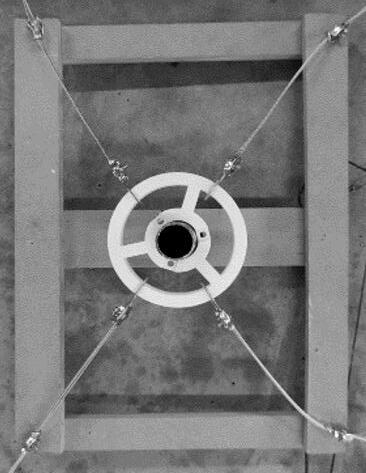
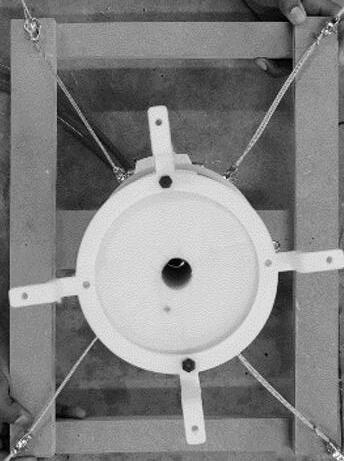
Soft Robotic Solar Facade
Adaptive Facade Studio - Teamwork
Supervisor: Pierpaolo Ruttico
Software: Rhino - Grasshopper
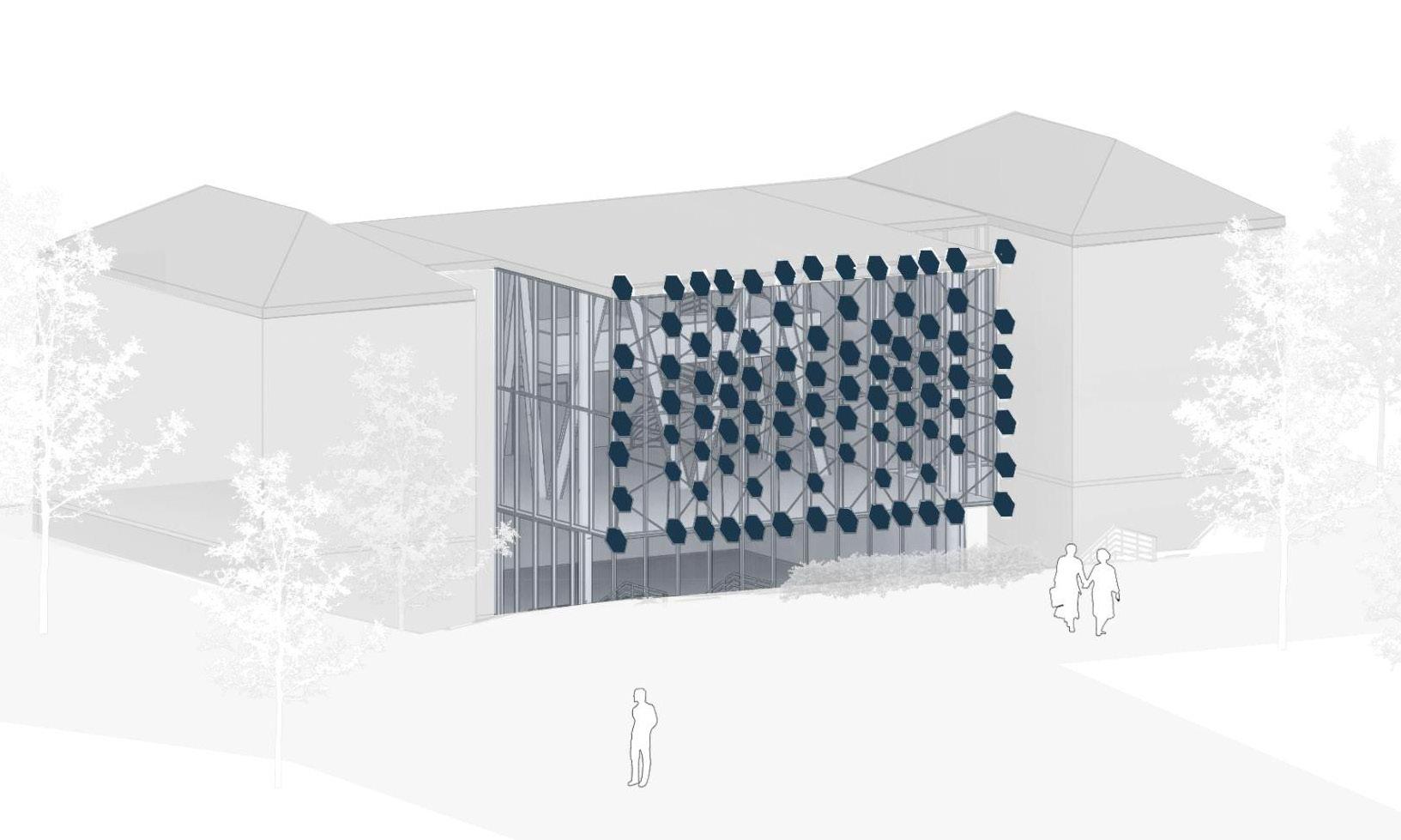
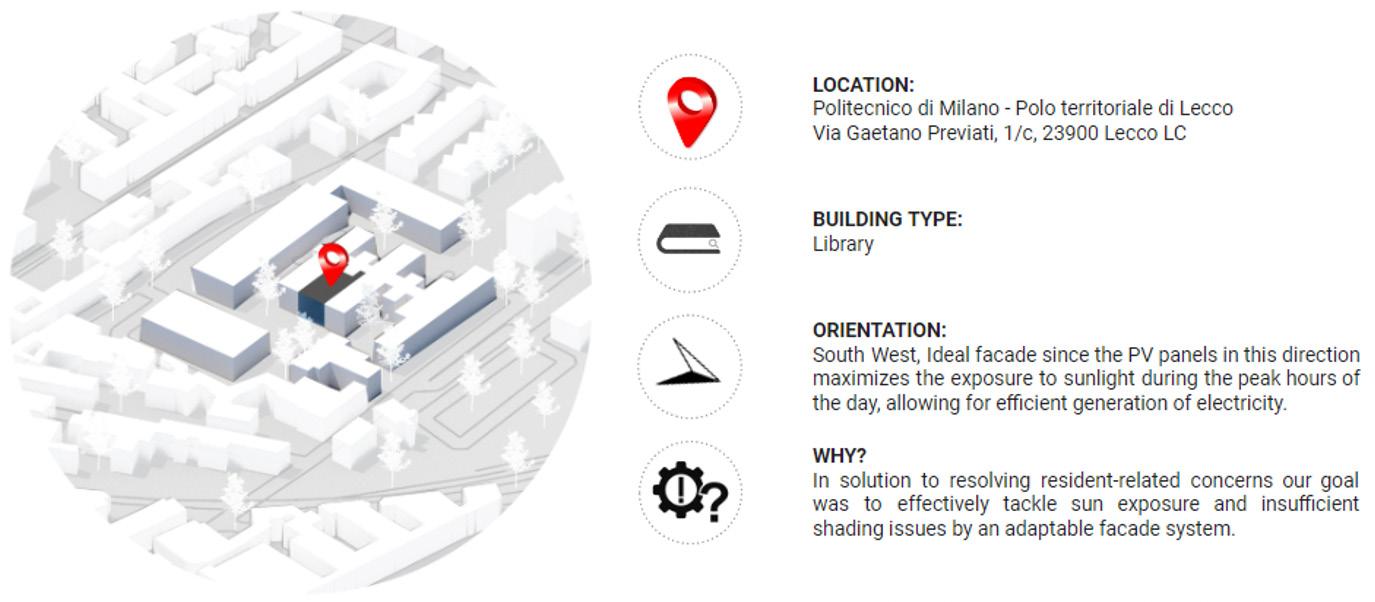
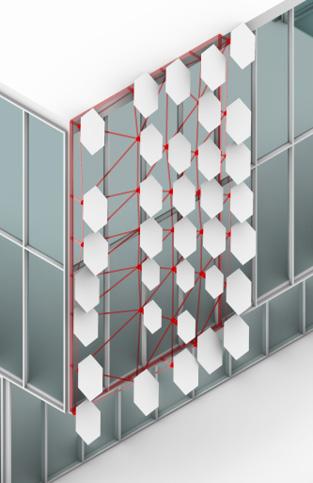
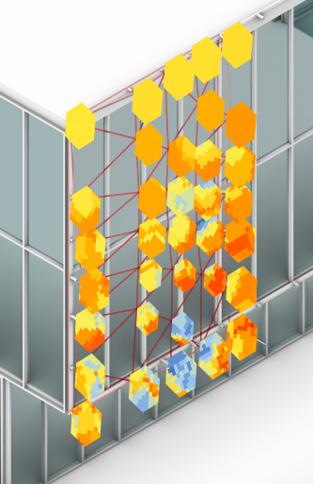
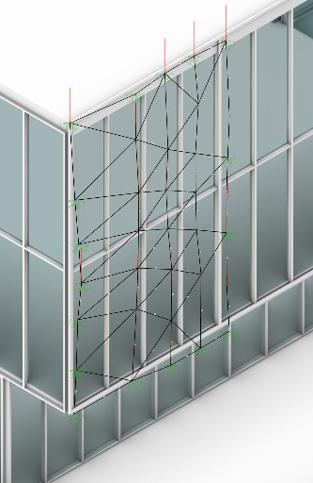
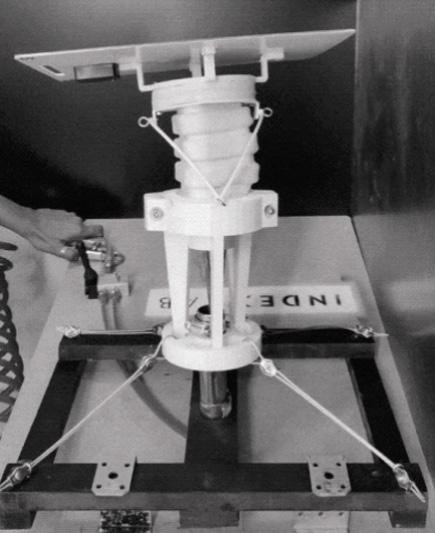
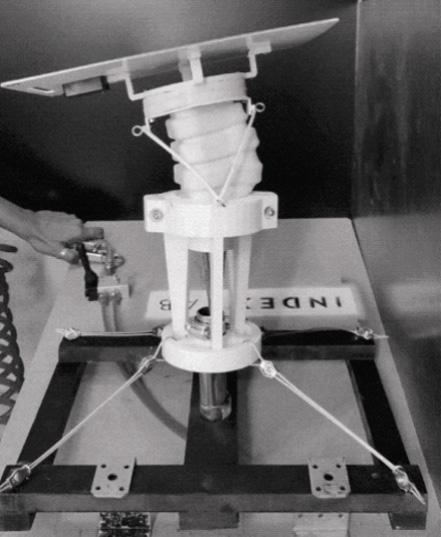
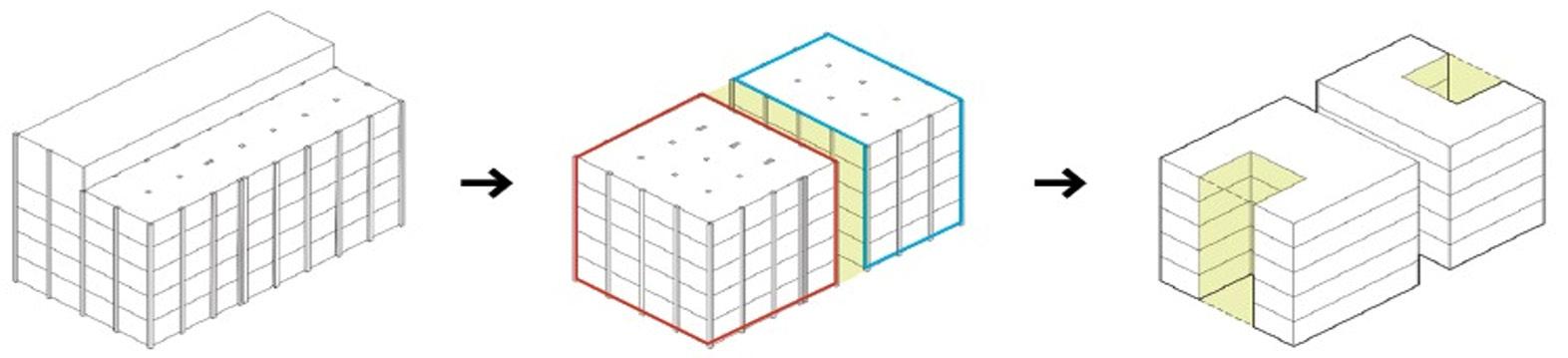
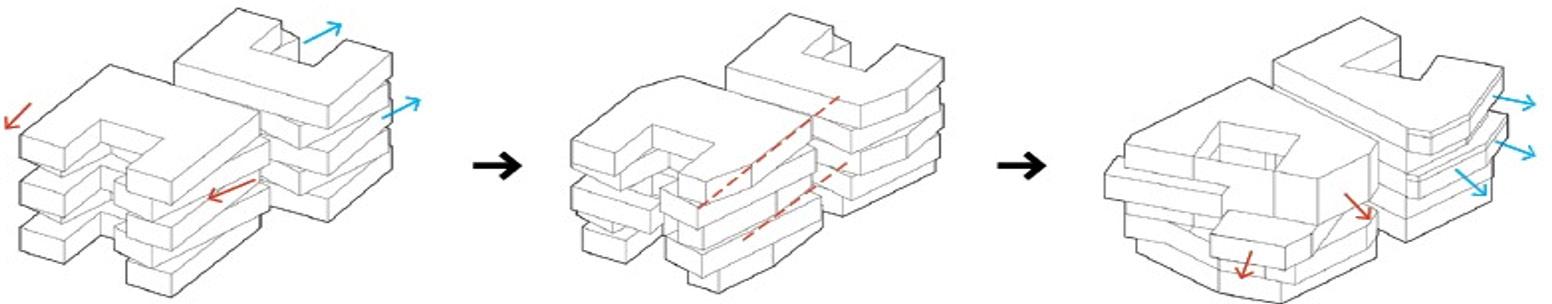
Solymorph is an integrated kinematic building facade designed to optimize energetic behavior and architectural expression through individual modules. Installed on an existing library facade at Politecnico di Milano, Lecco, this case study demonstrates significant improvements in electricity generation compared to static photovoltaic systems.
The project highlights the potential for energy savings in various climates and aims to drive advancements in sustainable building design by leveraging soft robotics and artificial intelligence. This innovative approach contributes to developing energy-efficient facade solutions for both new constructions and existing buildings.
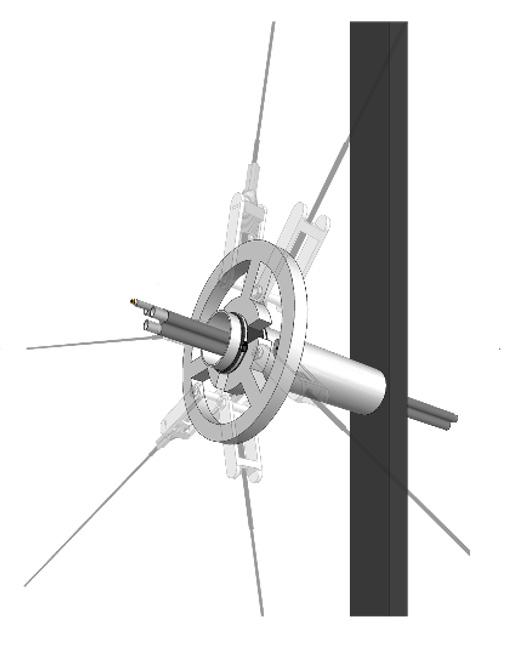
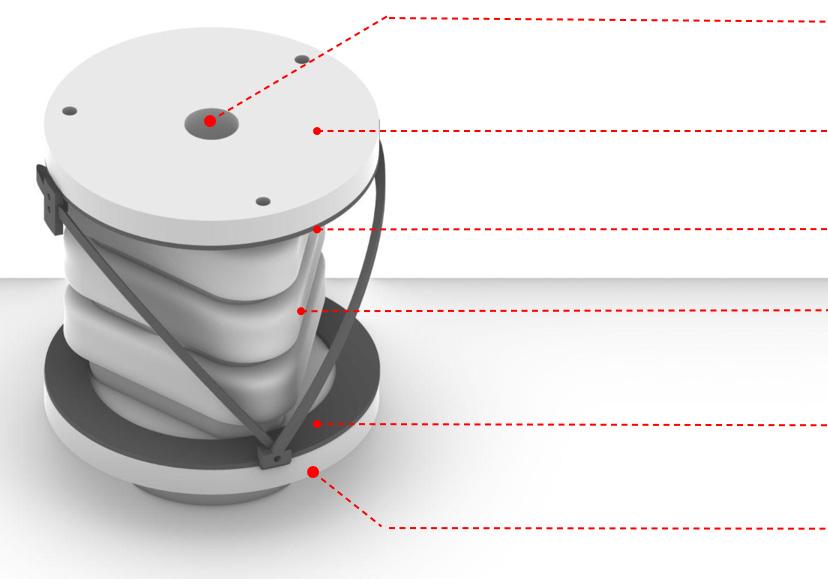
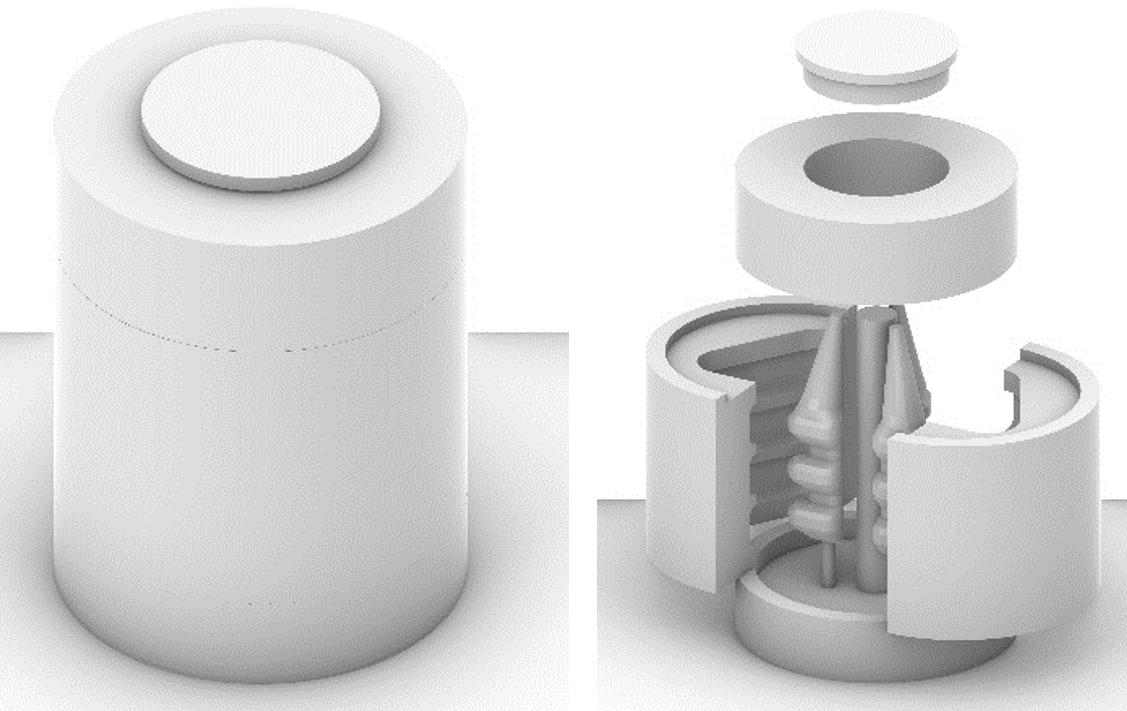
0. Existing building façade 1. Main steel frame
2. Steel anchor rods
3. Cable net structure 4. Soft robot assembly
5. Hexagonal PV-panels
System Breakdown
Supporting Frame
Surface Generation
Cable Structure Edge Anchors
Soft Robots at Nodes Solar Panels
Solar Radiattion Analysis
Structural Analysis
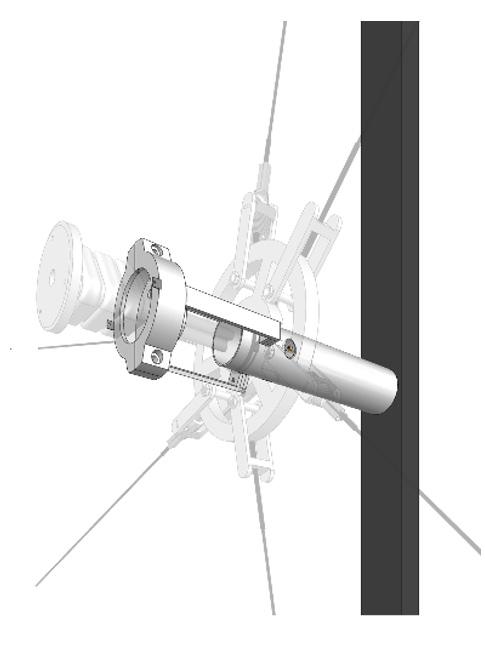
Cable Connection To The Building
Assembly
1. Support rod node 73mm with 3 20mmø holes
2. 20mm thick 242mmø steel connecting ring node 73mmø internal diameter
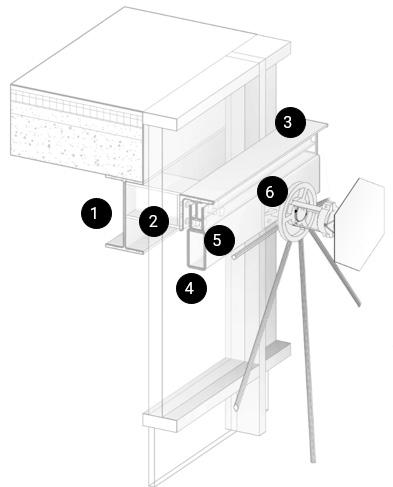
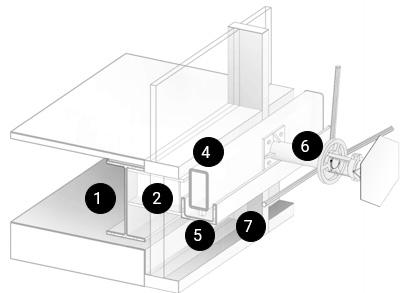
1. Existing Structure I-Beam
2.Main Support Beam Heb160
3. L-Section 150x12 Top Sliding Beam
4. Module Steel Frame Hss 160x80x5
5. Rollers
6. Steel Rod Od73
7. U-Section 150x80 Bottom Sliding Beam
Connection to The Structure
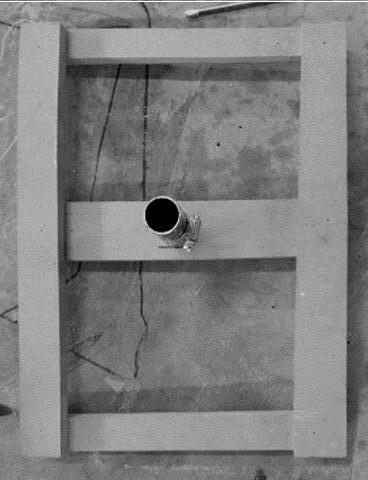
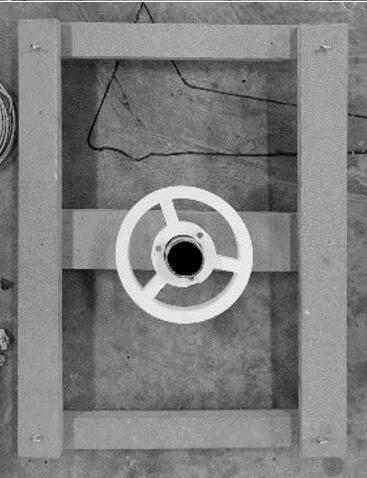
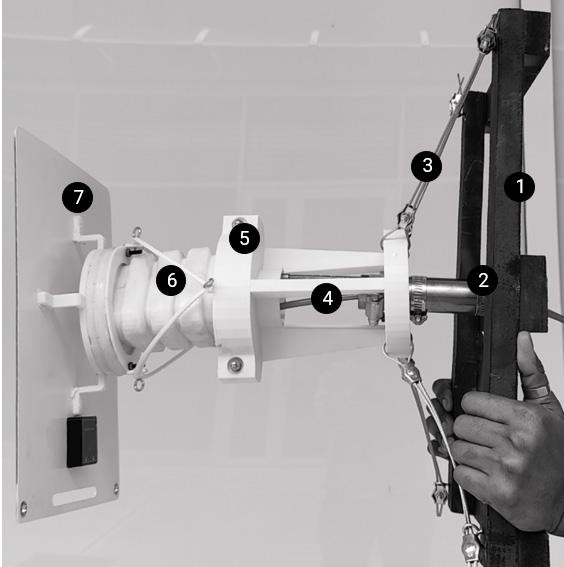
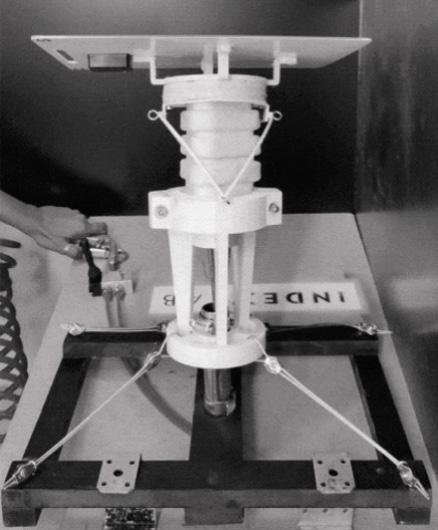
Robot Unit Assembly
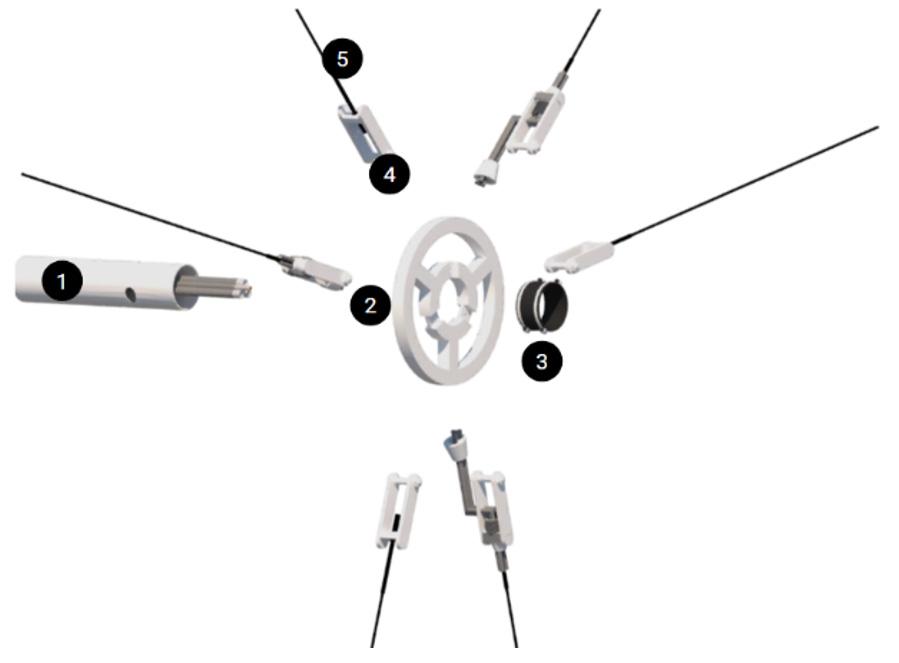
3. Steel no hub coupling 73 mmø 4. Cable connector 5. Combined cable 1. 10mm thick, 100mm long steel support legs 2. 2mm thick aluminum universal joint with aluminium plate
3. Silicon actuator 4. Steel connector 5. Junction box 6. 1mm aluminum sheet
7. Hexagonal PV panel
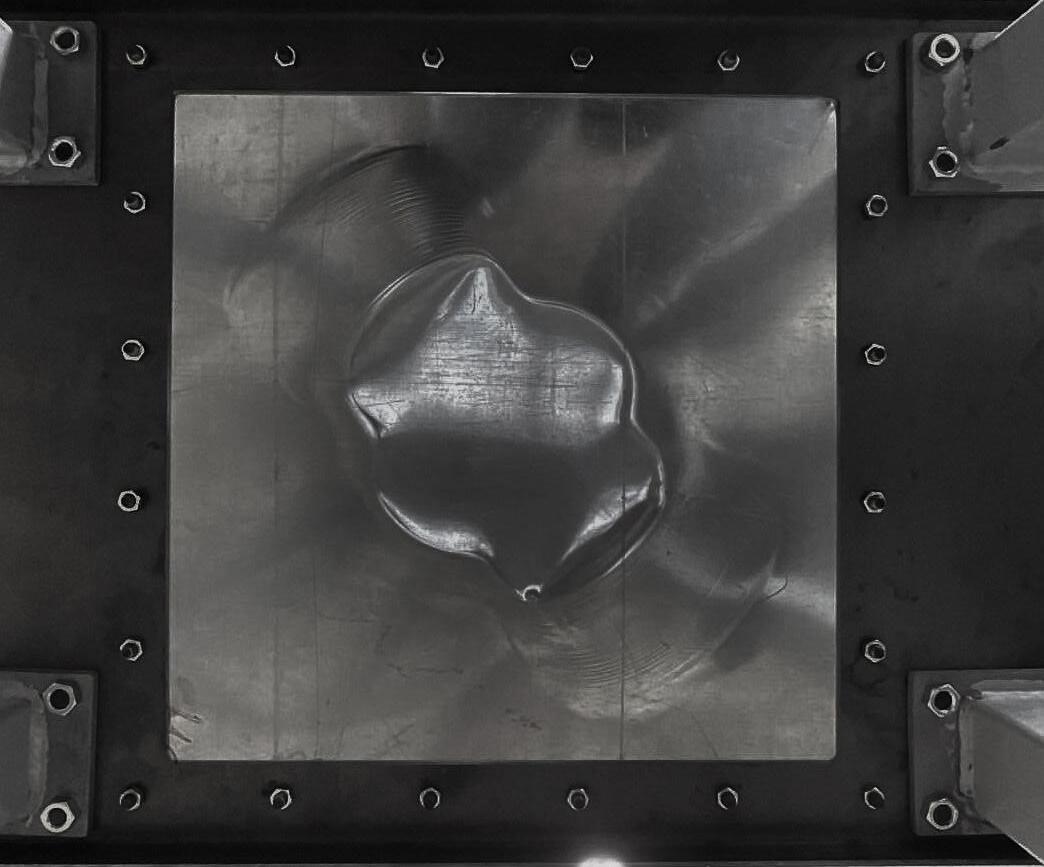
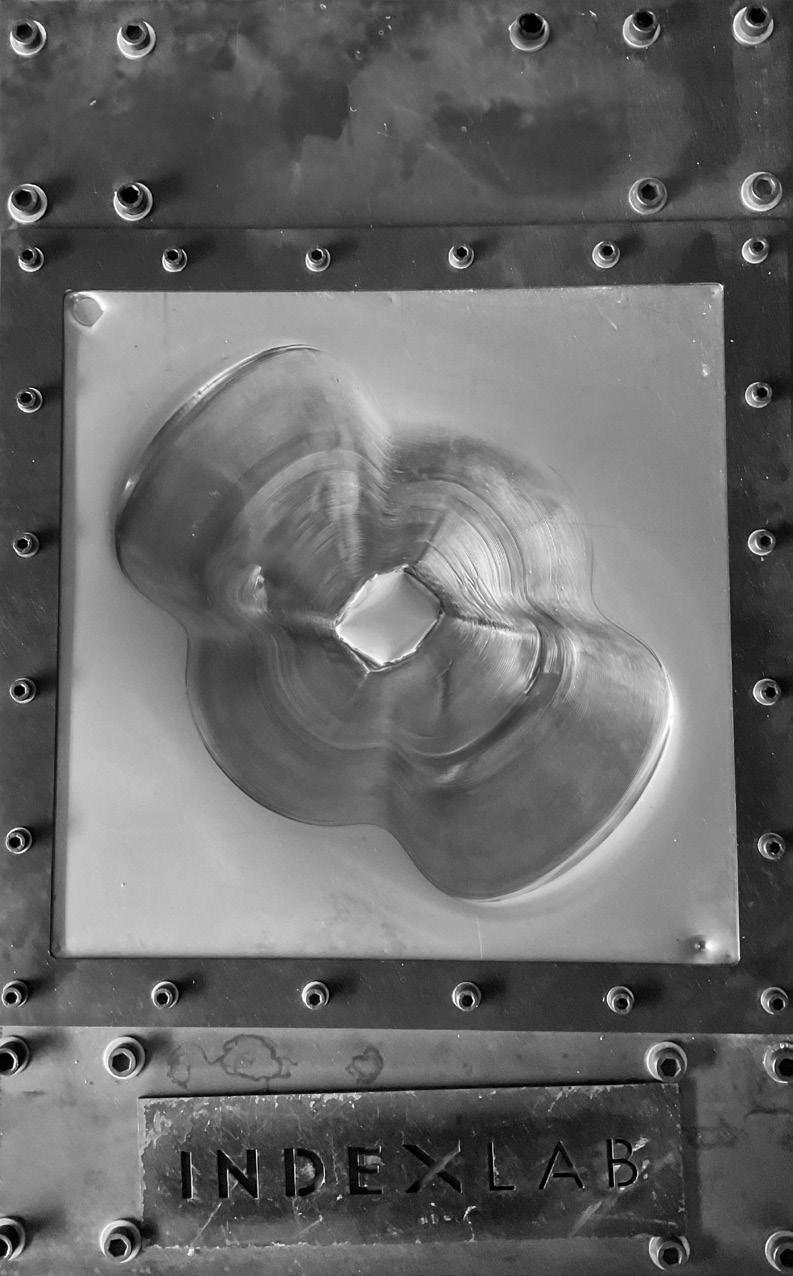
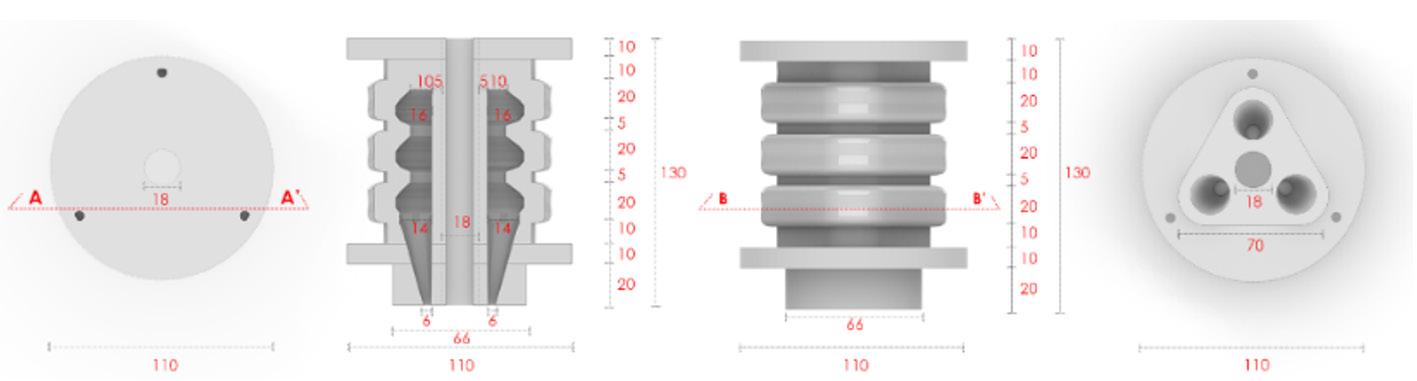
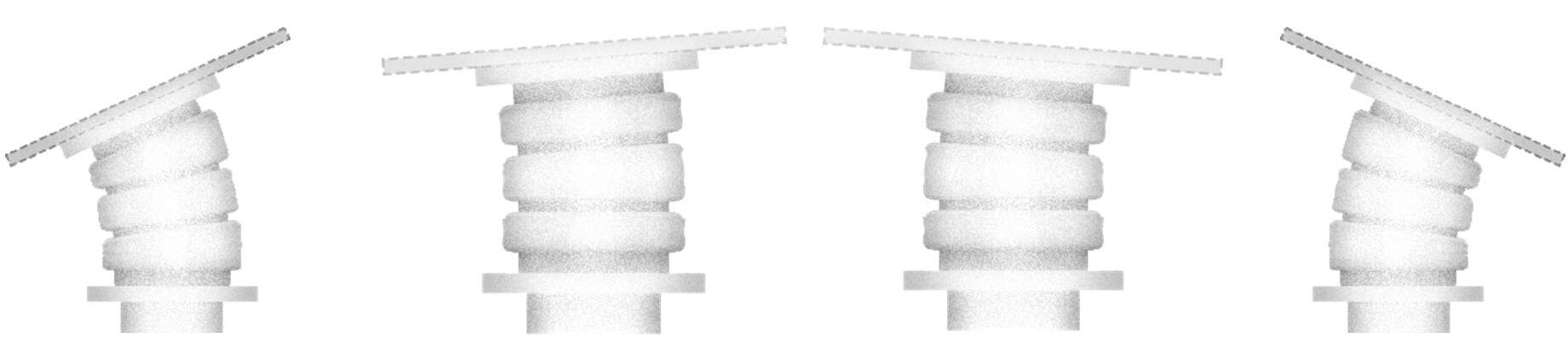
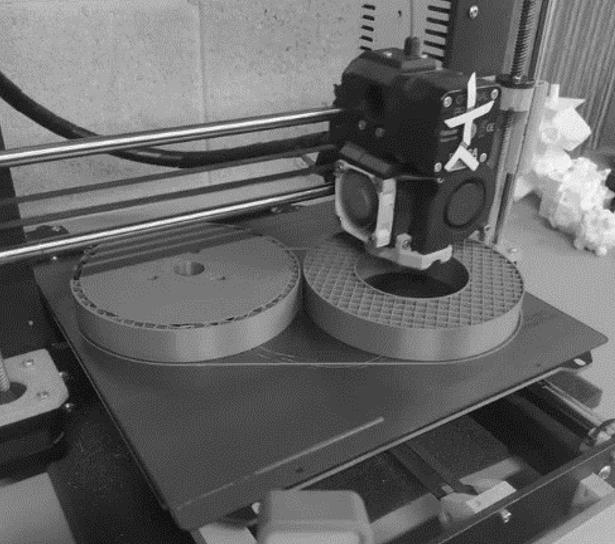
Silicon Actuator
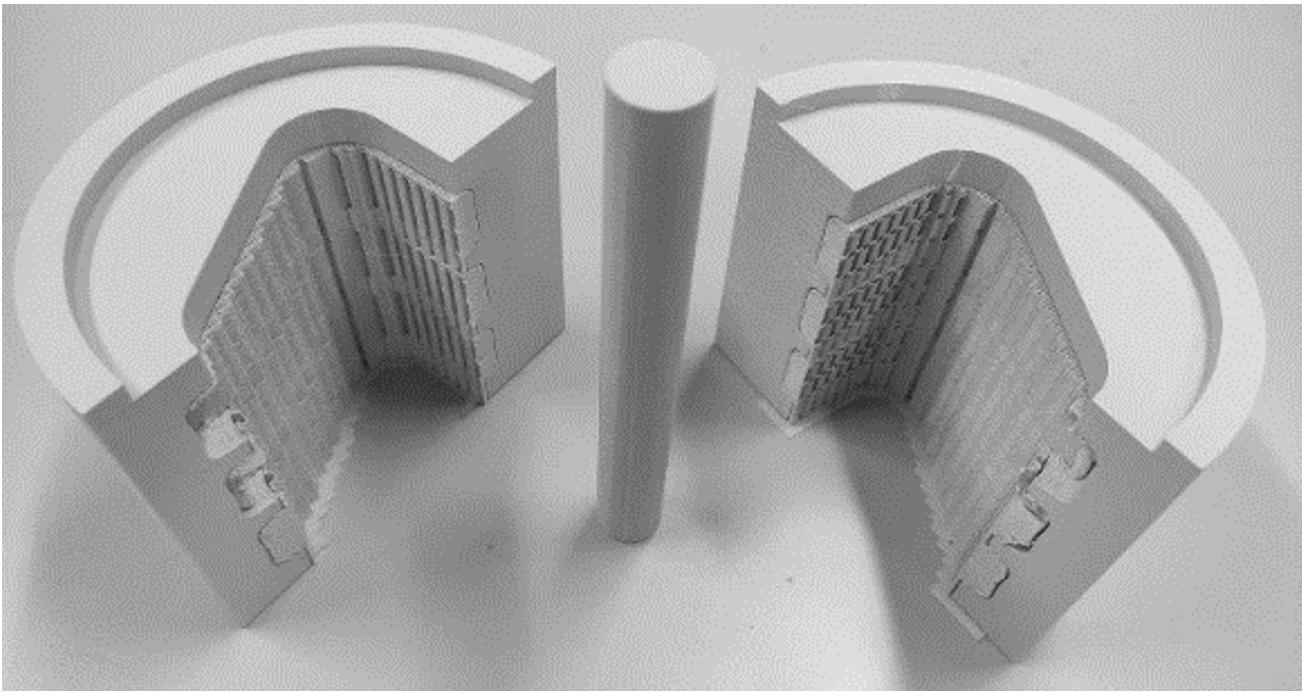
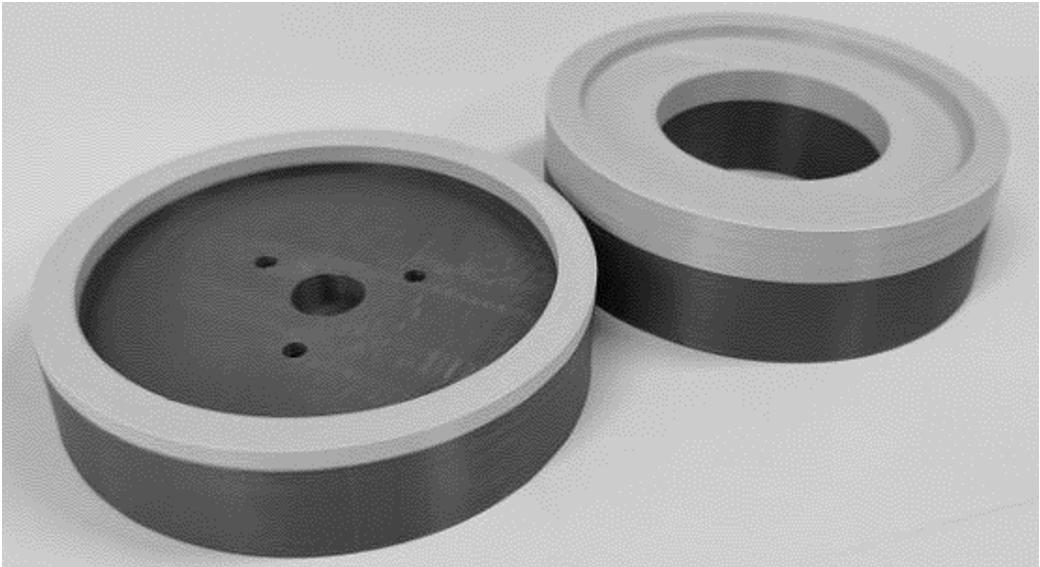
Silicon Actuator Rotation Designed Mold for the Physical Prototype
Designing a nZEB Building Using Passive and Active Strategies
Sustainable Building Technologies Studio - Teamwork
Supervisors: Gabriele Masera, Matteo Brasca
Software: Revit - Rhino - Grasshopper
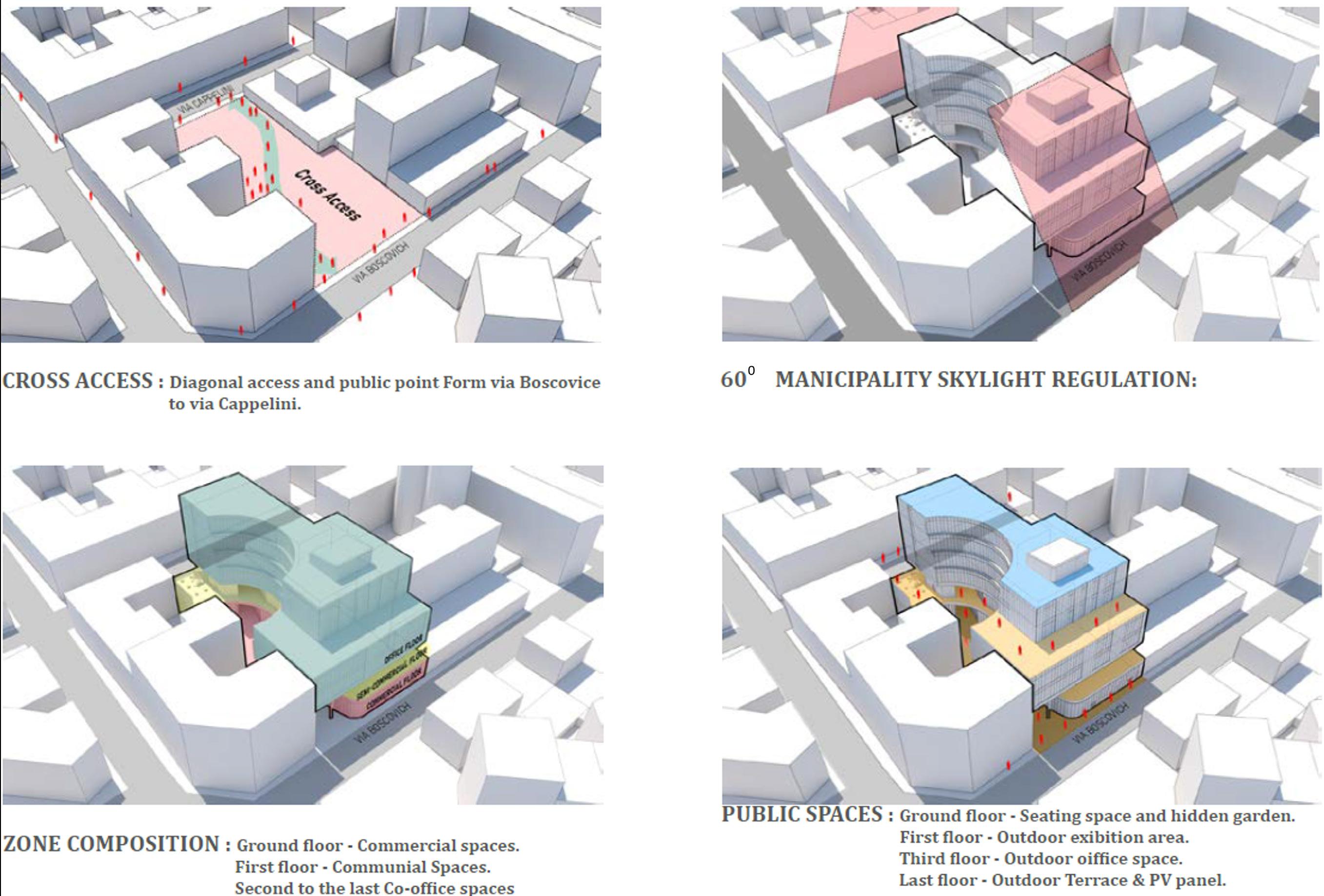
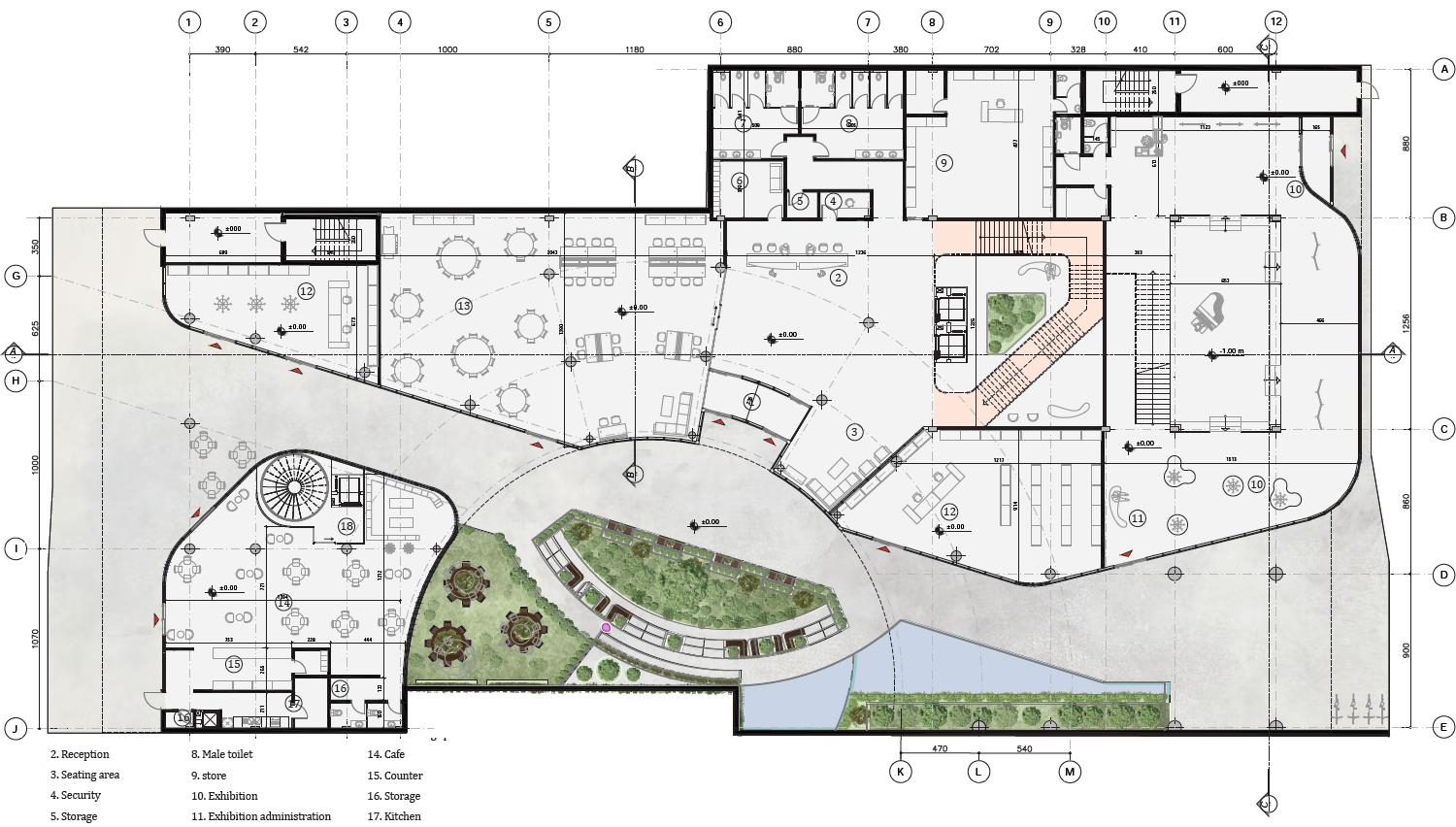
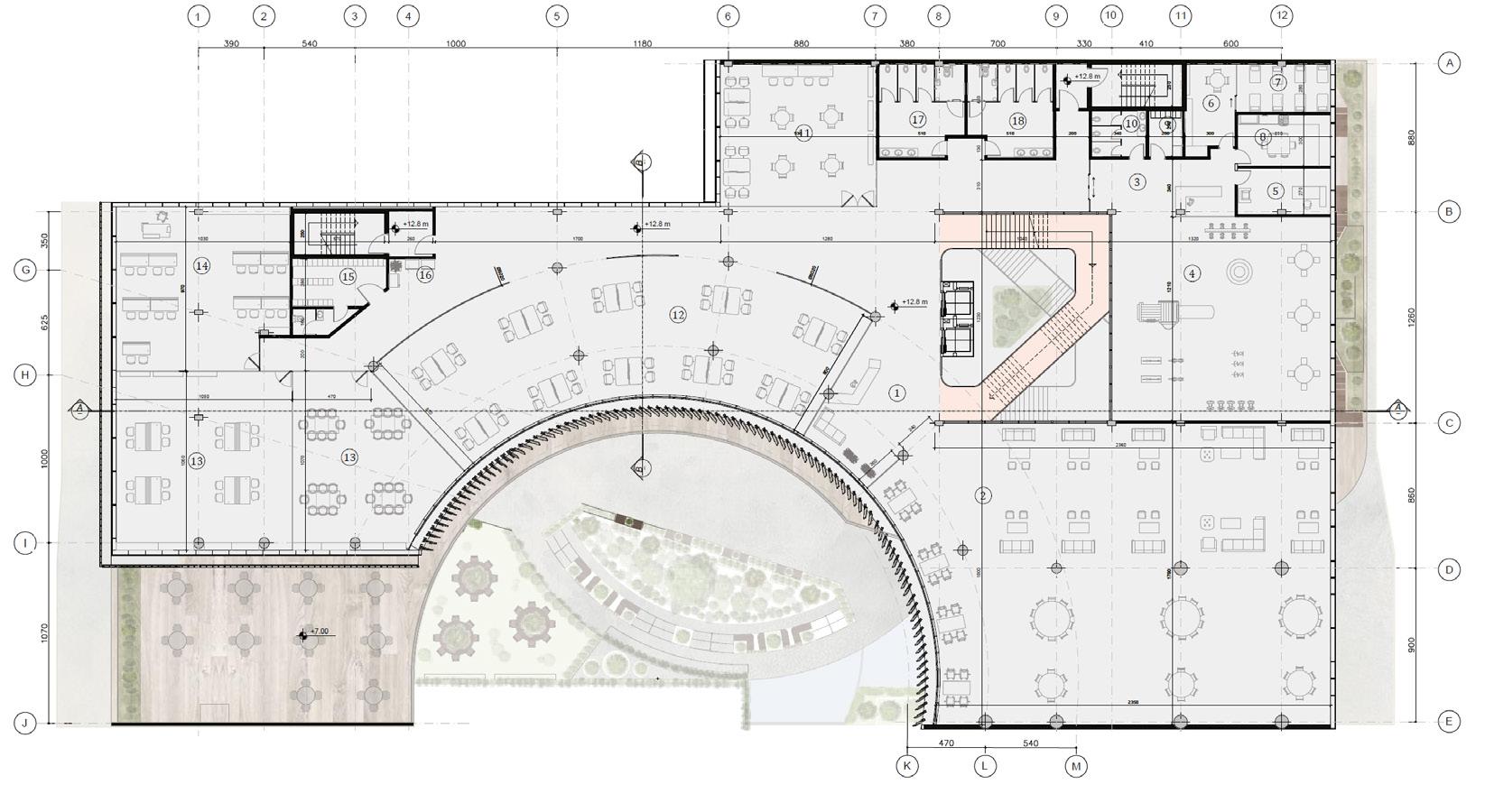
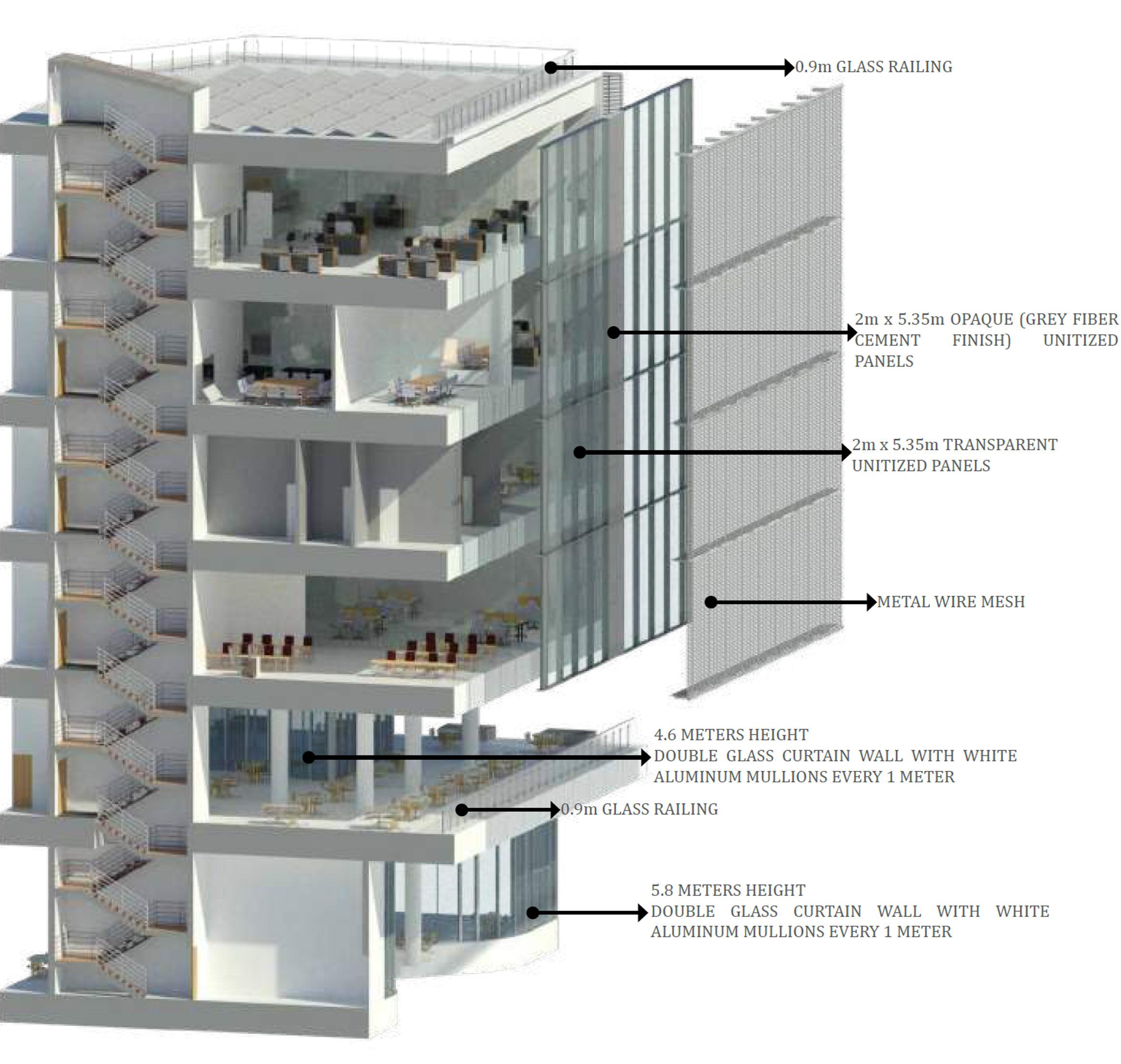
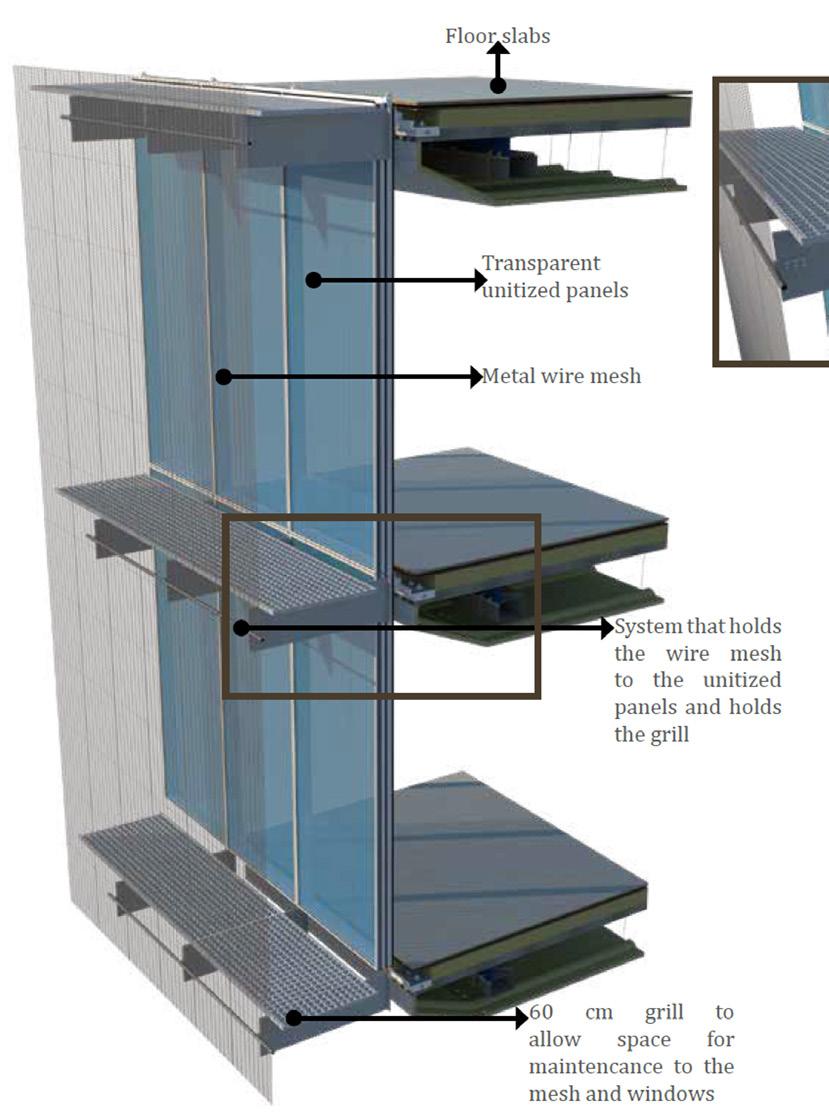
In this project, we focused on integrating design methodology with energy efficiency and advanced building technologies. By applying a holistic approach to sustainability, we optimized the building design, achieving a 62% reduction in energy consumption and significantly enhancing daylighting performance. Our comprehensive simulation and analysis framework streamlined the design process, enabling faster iteration and optimization of strategies. This project exemplifies the application of Nearly Zero Energy Building standards and showcases best practices in sustainable architecture, informed by European and Italian examples.
2. Courtyard - Communities
To enhance site permeability, two main nodes were connected via a central path: the historical Sanctuary of San Camillo de Lellis with its adjacent plaza, and the expansive, socially active area of Porta Nuova.
4. Inside - Out Views
The ground floor courtyard serves as the site’s focal point, providing a stopping point between A and B, and offering a relaxing or meeting space. It also introduces greenery, enhancing the site’s natural feel and promoting a sustainable mindset.
A green network follows the path between points A and B, with increasingly lush greenery as pedestrians approach the courtyard area, enhancing the path’s appeal.
The building’s design integrates visual connections between internal and external spaces through a transparent facade, linking the courtyard with the street. The atrium enhances vertical movement, connecting the courtyard with dynamic visual lines.
6. Transparency - Active Street Frontage
The ground floor’s curved edges invite pedestrians from both streets, promoting interaction along the path from A to B. This openness also creates flexible social zones that connect users with passersby.
The ground floor’s fully transparent facade creates an active connection between both streets and the courtyard, allowing users inside to engage with the outside environment and inviting passersby into the building.
S/V Optioneering
Adding terraces
- Courtyard And Retail Area
Section
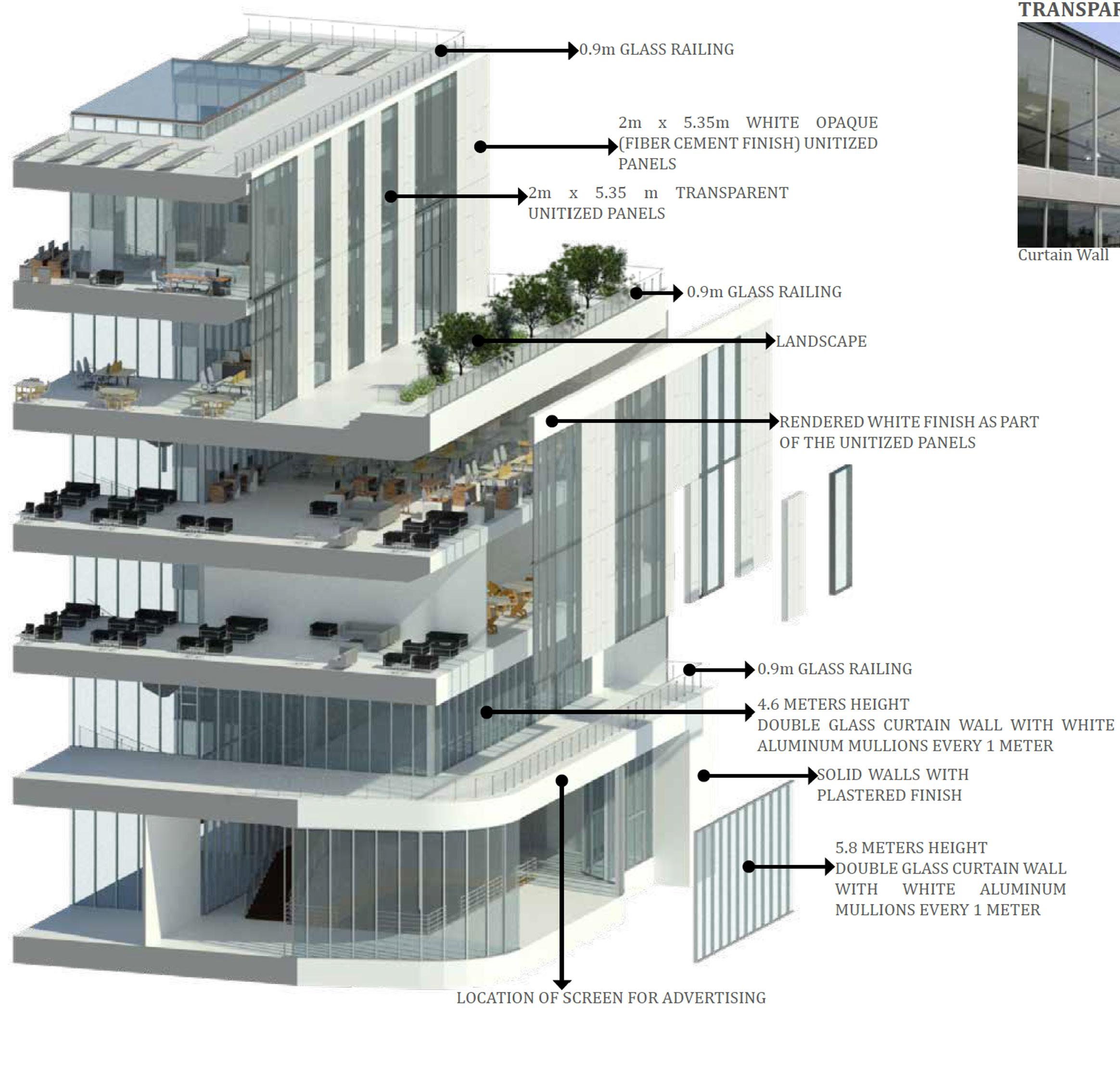
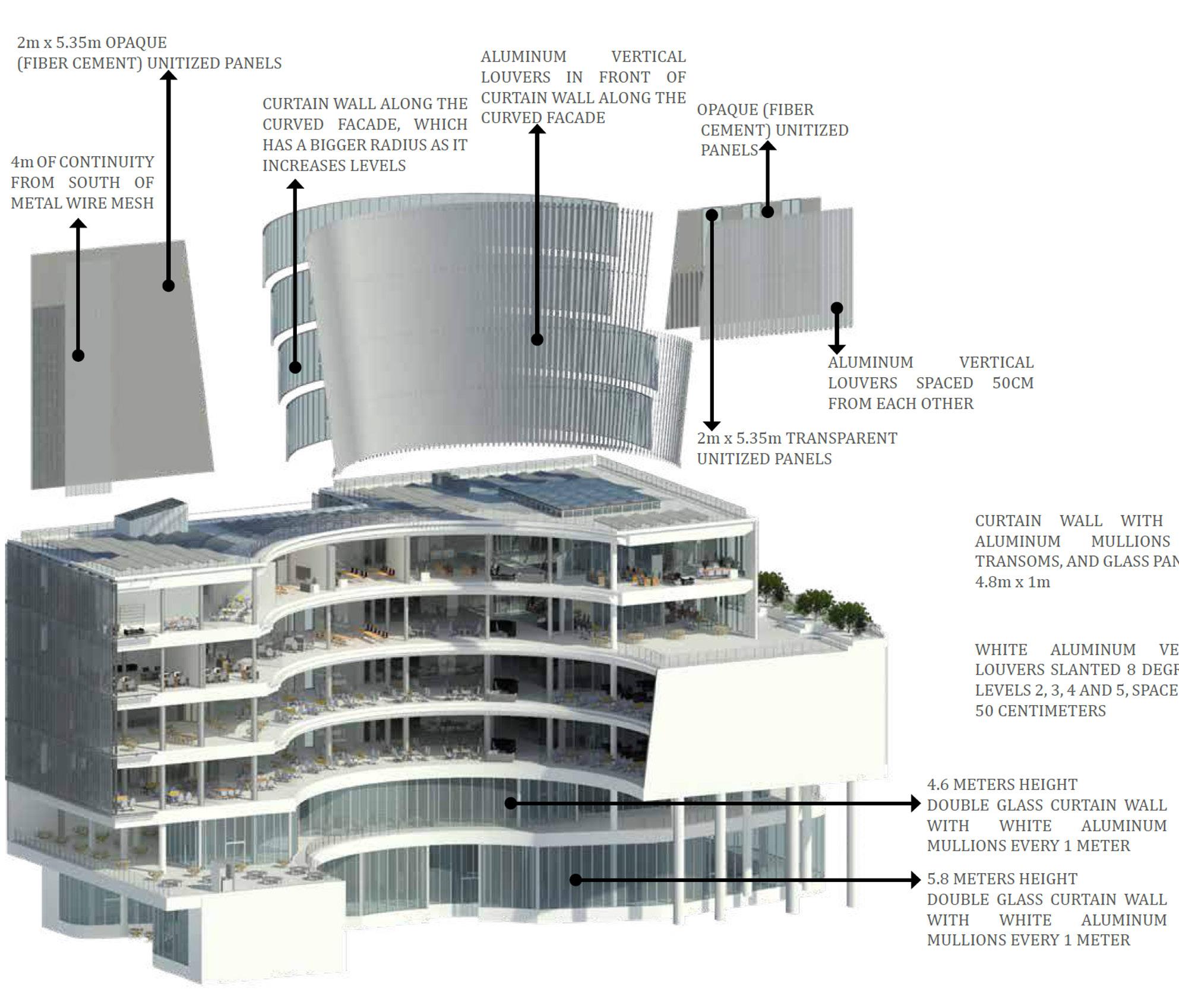
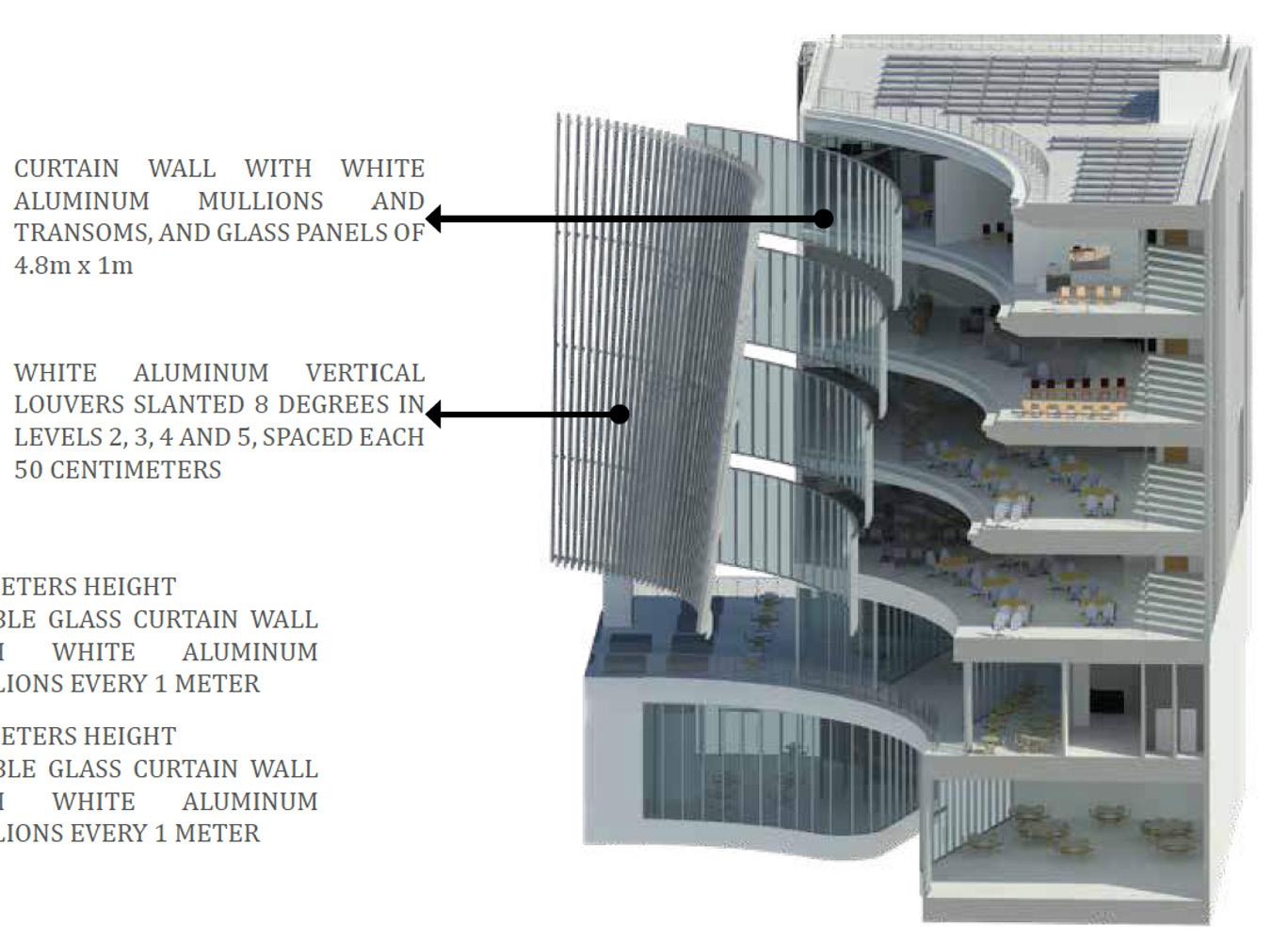
North Facing Facade
East Facing Facade
South Facing Facade
ECO-SUSTAINABLE CAVA VAIOLO
Building Renovation - Teamwork
Supervisor: Manuela Grecchi
Software: Revit - Rhino
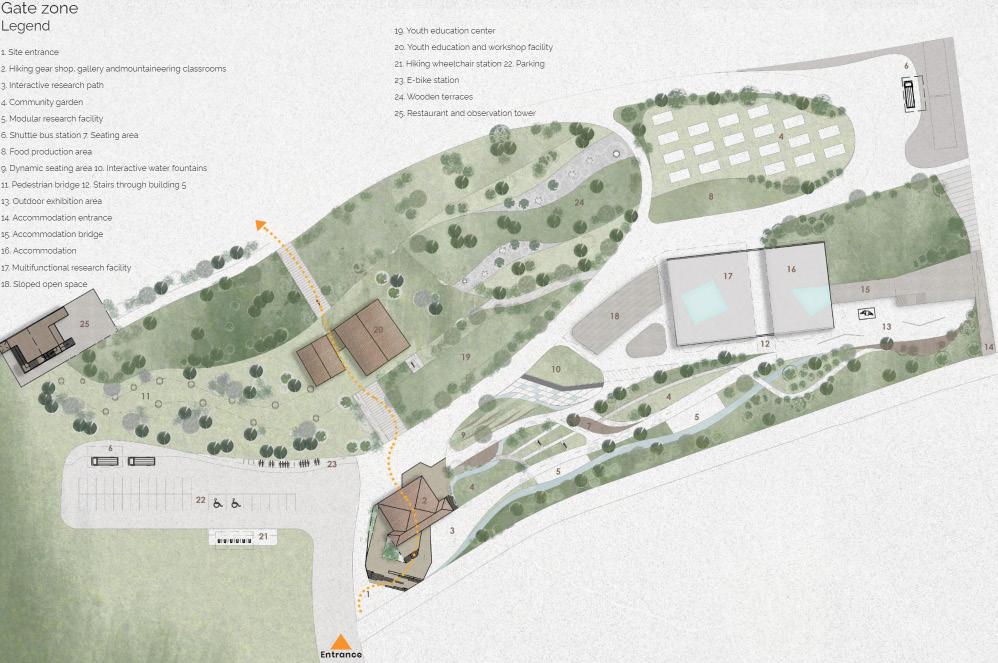
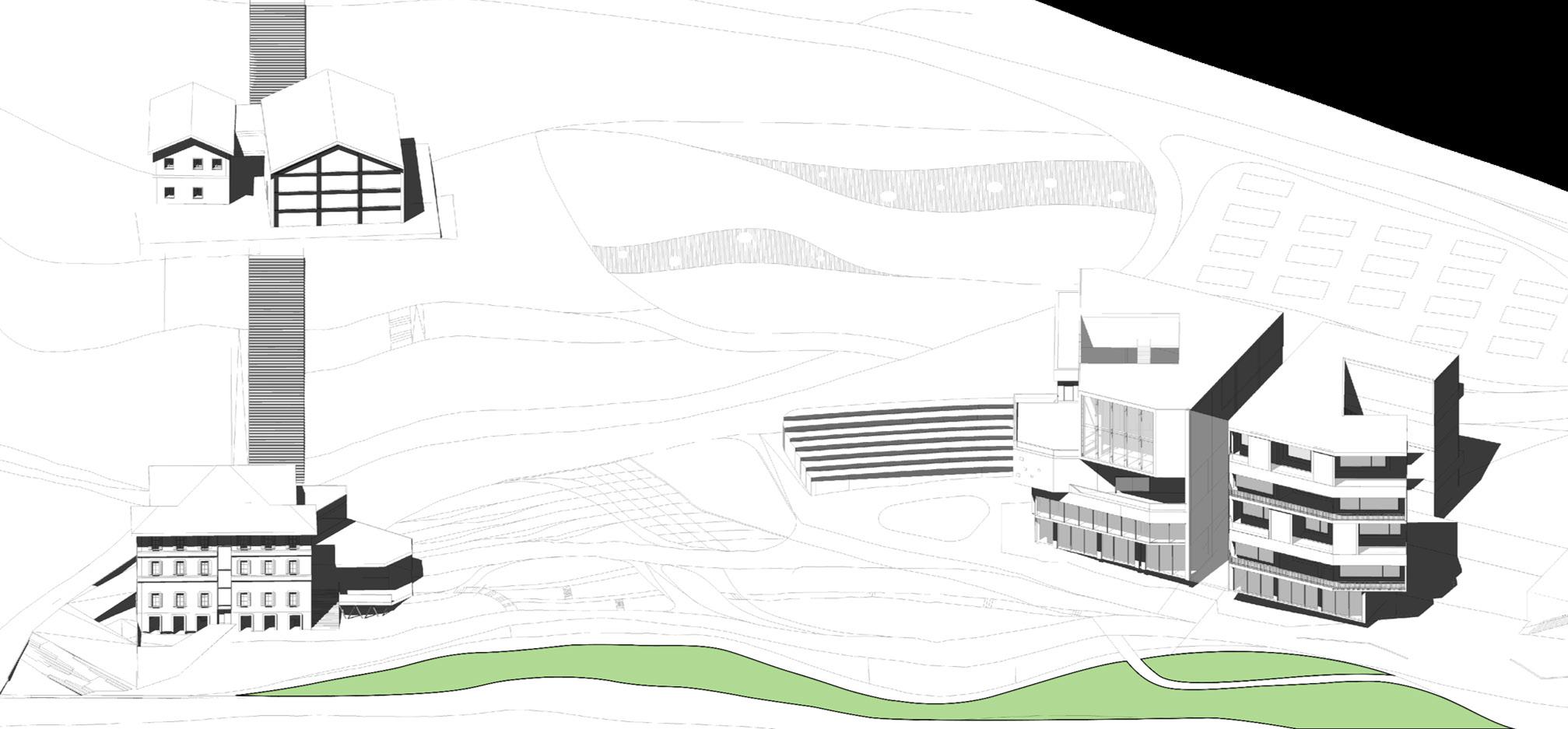
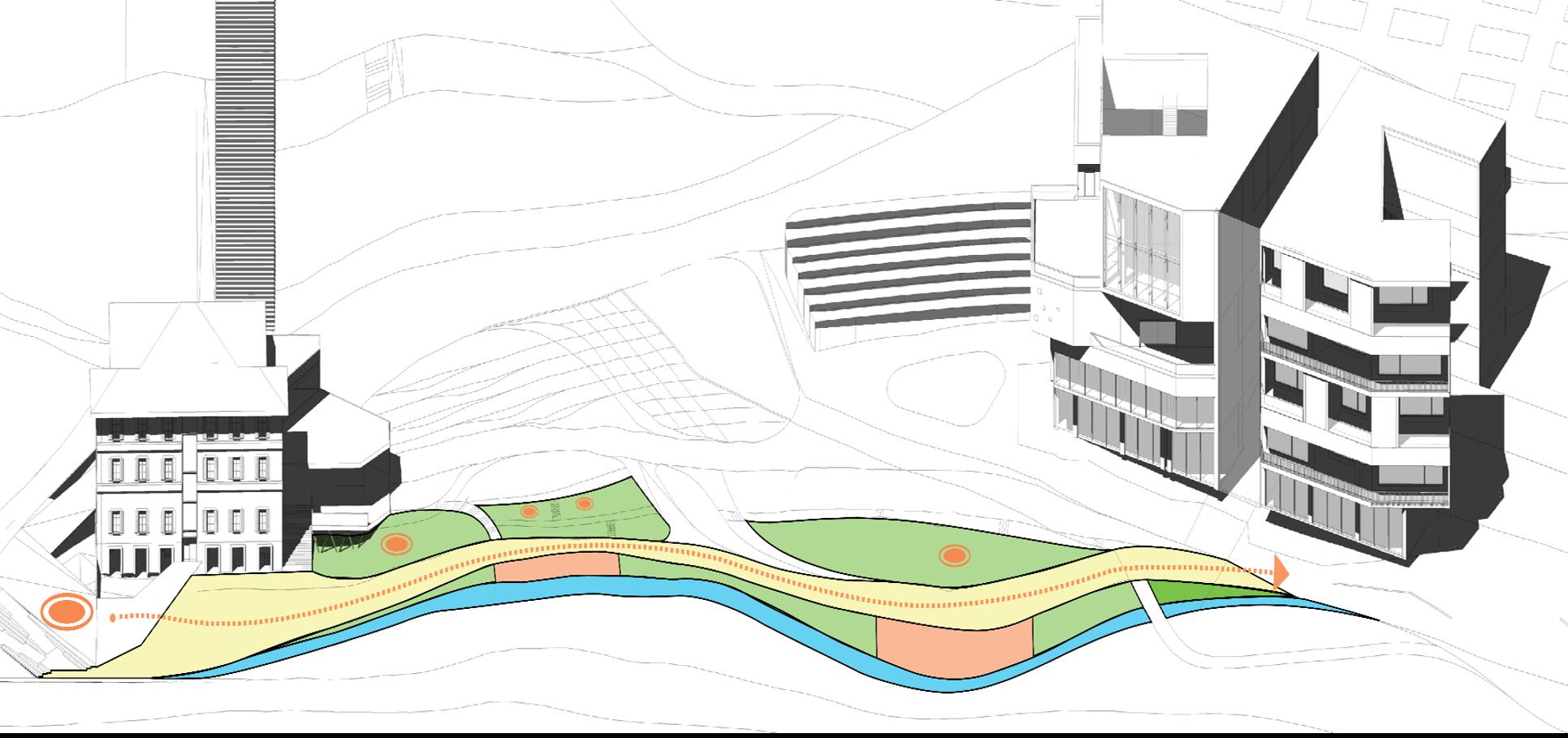
The project focuses on repurposing existing buildings and enhancing the urban spaces between them, creating a gateway from the city to nature, specifically connecting to Cava Vaiolo of Lecco. The design connects five buildings through urban design, promoting resilience and serving as an access point to the Alps. It includes research labs, commercial functions, and prioritizes pedestrian access with shuttle buses to the mountain. The first building serves as an indooroutdoor passage guiding people to nature or interactive urban spaces.
2. Green Barrier
A green barrier of trees and vegetation acts as a buffer, providing acoustic and visual separation from industrial areas near the gate zone.
The community axis encourages participation in research activities through “learning by doing.”
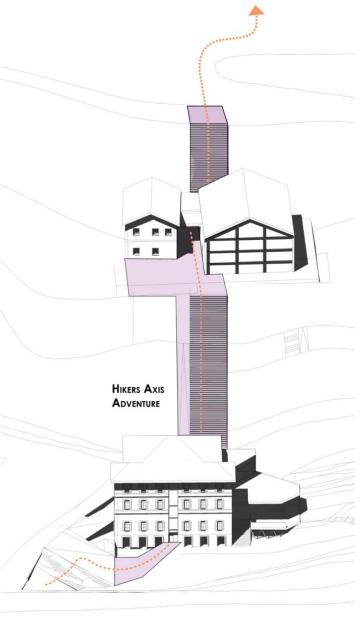
3. Hiking Axis
The hiking axis connects the entrance directly to the hiking routes.
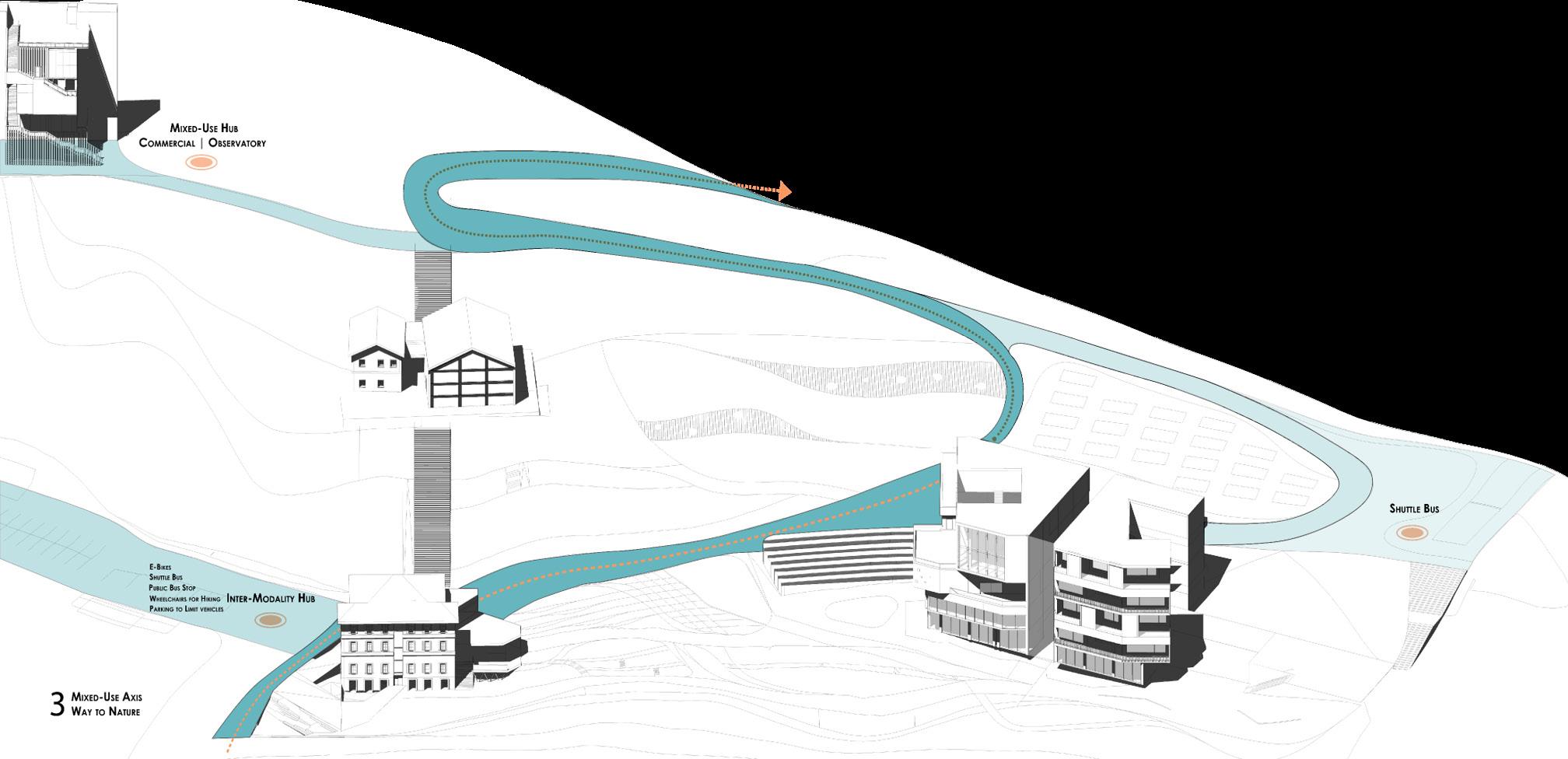
4.Intermodality Hub
Mixed-use facilities and shuttle bus stations support the flow of people through the gate zone towards higher mountain areas.
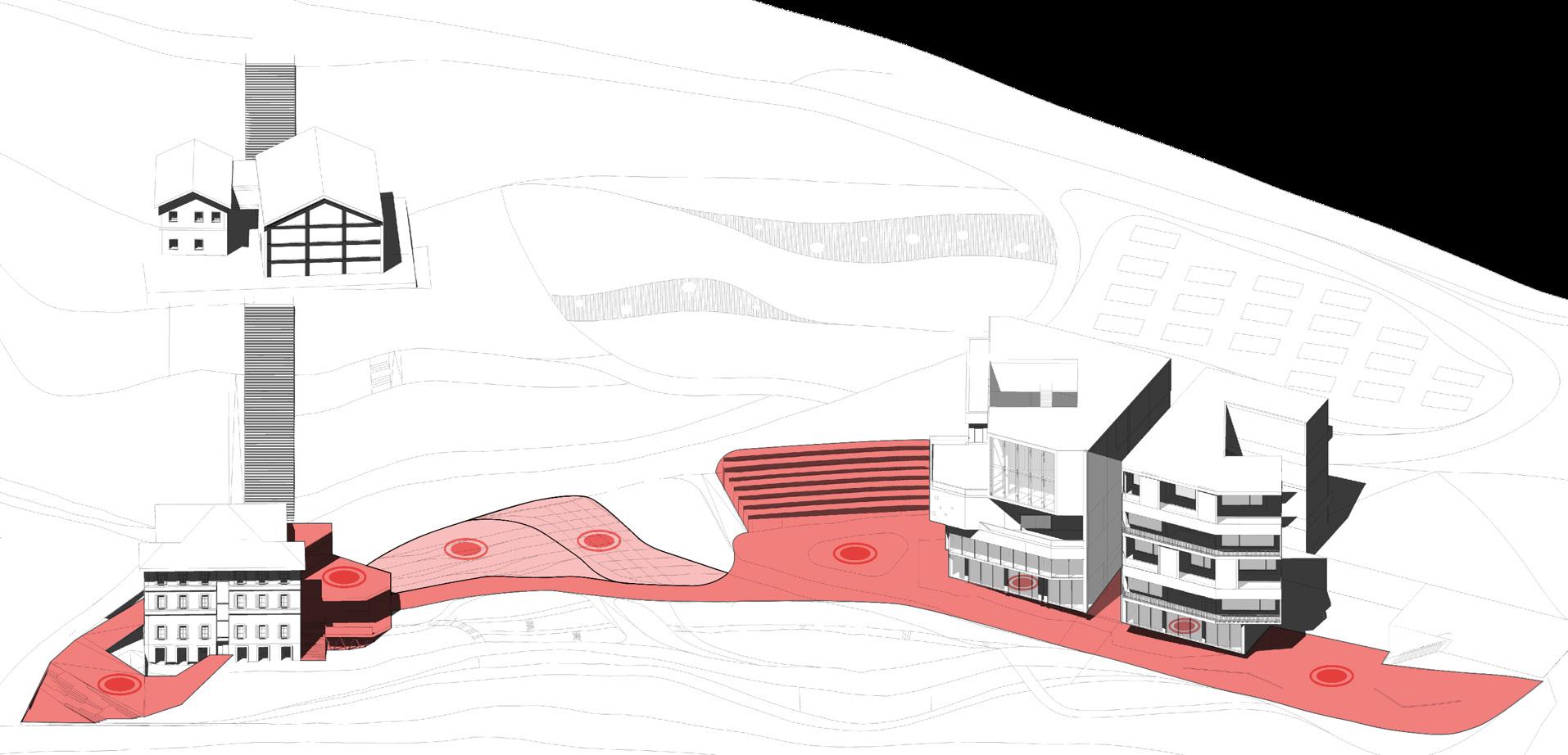
5.Social Engagement Axis
The social engagement axis between buildings 1 and 5 fosters interaction and recreation, blending indoor and outdoor spaces seamlessly.
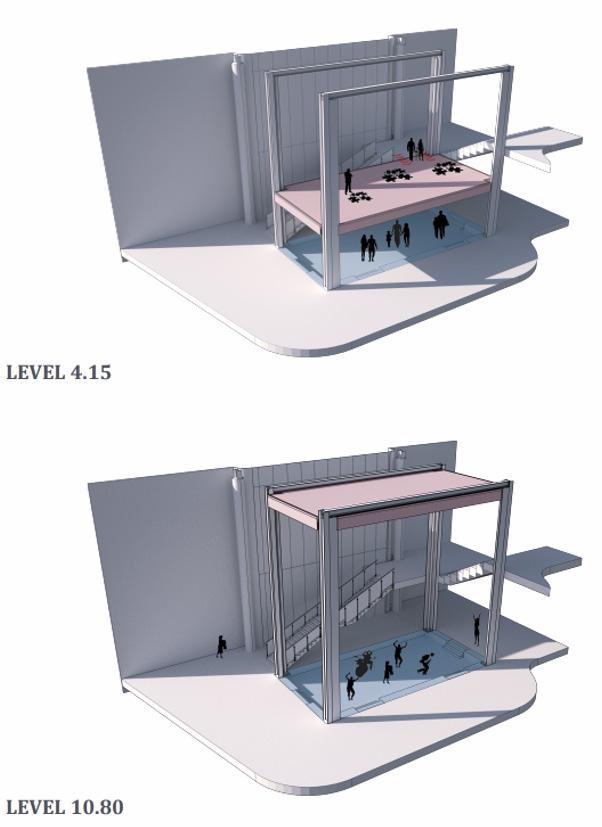
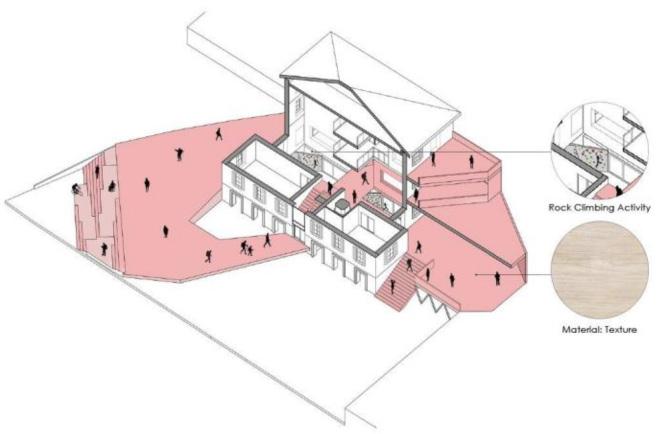
1. Interactive Research Facilities
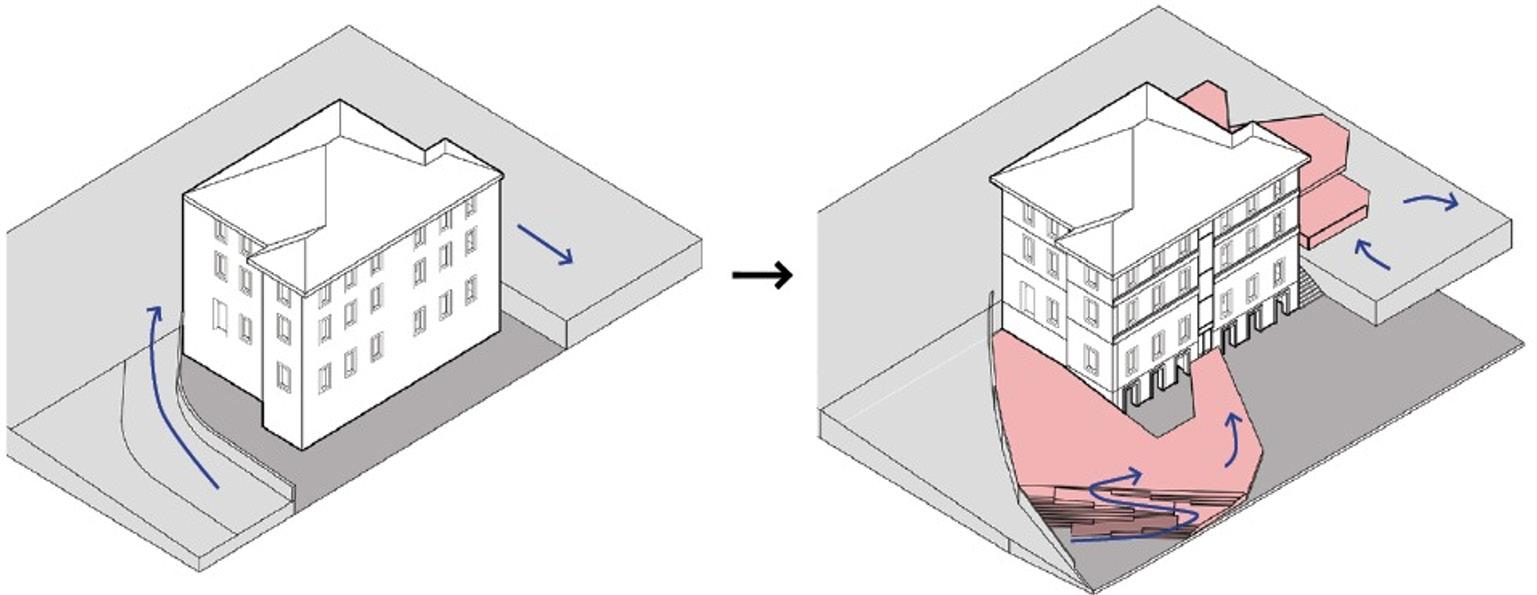
Existing: Building 1 and the site’s level differences.
Addition: A new platform is added to Building 1 to create more accessible circulation.
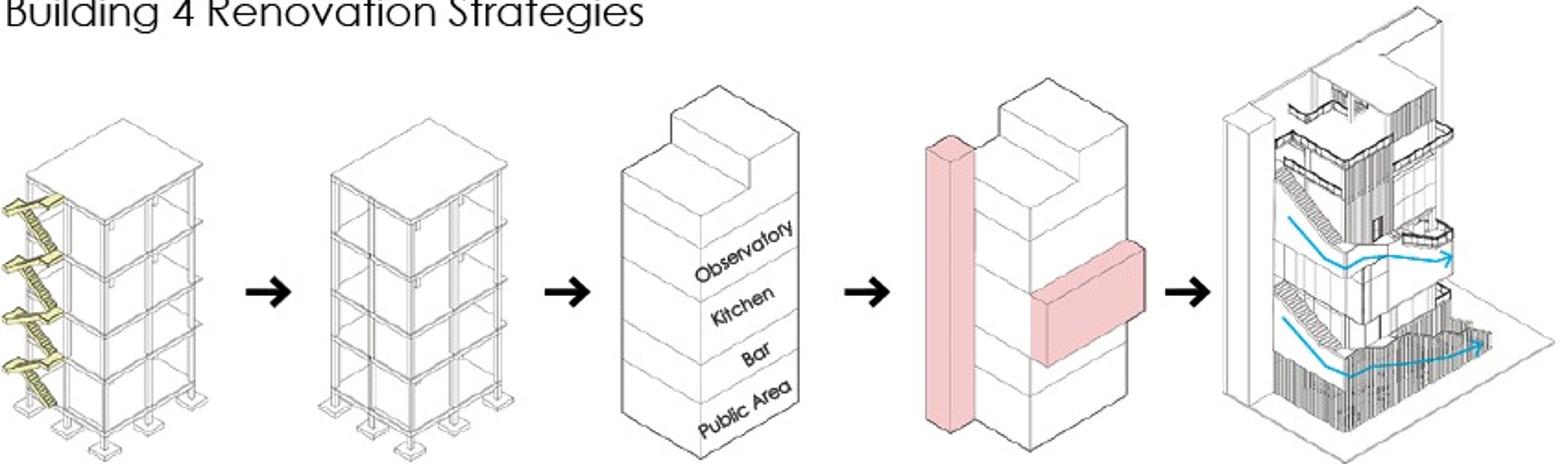
Commercial Zone and Observatory
Existing: Building 4 Subtraction: Removing the original staircase. Organizing different uses (restaurants and observatory).
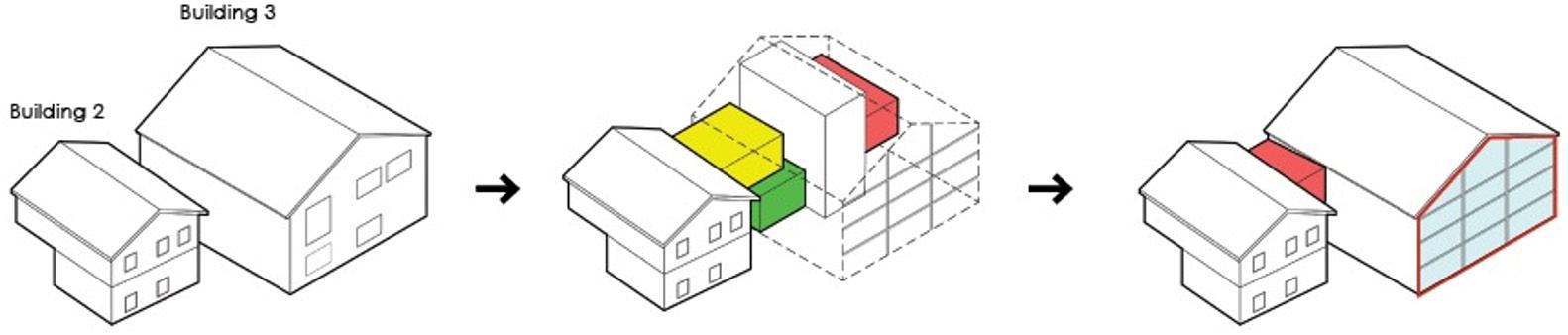
Existing: Building 2 and 3
Addition: Adding volumes and elevators.
Creating a new staircase with decorative elements on the facade.
Addition (Internal + External): Boxes are added to the buildings to introduce new functions.
Research center and accommodation facility
Transformation: The original facade of Building 3 is transformed into a curtain wall
Existing: Building 5 Dividing into 2 Parts: Research Centre and Accommodation.
Subtraction: Adding atriums and Courtyard.
Floors are arranged according to the new grid system provided by the site
Inclined edges are tapered A new massing of push and pull is formed according to the functions.
Site Approach
Educational Hub for the Youth