
28 minute read
Machinery Repairs
Wärtsilä’s comprehensive thruster solution will enable an existing hull to become Boskalis’ crane vessel Bokalift 2
Boskalis contract for Wärtsilä
Advertisement
A comprehensive thruster solution from Finland’s Wärtsilä will enable Holland’s Boskalis to convert an existing hull to create the crane vessel Bokalift 2. In addition to addressing the technical challenges imposed by the project, Wärtsilä has also committed to meeting a demanding delivery schedule for the equipment. Wärtsilä will supply four retractable steerable thrusters and thruster controls, as well as two tunnel thrusters. The proven retraction system, combined with the energy efficient 8 o tilted thruster, is a key factor in enabling effective station-keeping performance. Wärtsilä is a market leader in large-scale retractable thrusters, which are essential to solving operational challenges of this type. The thrusters’ retractability also enables shallow draft operations. “Wärtsilä’s thruster solutions enable this kind of high specification vessel to operate successfully in sustainable energy installation projects. Furthermore, the energy efficiency of our thrusters reduces fuel consumption, which at the same time limits emission levels,” says Stefan Wiik, Vice President, Asset Management Services, Wärtsilä Marine. Wärtsilä’s extensive in-house capabilities across multiple disciplines were cited as being critical to addressing this complex conversion project.
Kongsberg completes first adaptive ferry transit
Norway’s Kongsberg Maritime has announced the world’s first adaptive ferry transit conducted during normal service. This landmark event, which took place recently on a vessel fully loaded with passengers and vehicles and demonstrated fully automatic control from dock to dock, is a key step forward in the integration of autonomous technology into everyday shipping operations. It was made possible by close collaboration between shipping company Bastø Fosen, KONGSBERG and the Norwegian Maritime Authority (NMA). The Bastø Fosen VI will now use adaptive transit functions developed from Kongsberg Maritime’s advanced systems to enhance the daily operation of its Horten-Moss service, while continuing to carry a full complement of crew. The technology introduces new potential for the sustainability of diverse marine operations by providing a platform for optimised fuel consumption and reduced GHG emissions. While supporting key elements of the UN sustainability targets for climate change, ferry owners and operators adopting the technology can experience tangible operational cost savings. The fully-integrated digital system on Bastø Fosen VI automatically performs all docking and crossing functions to a high and repeatable level of accuracy, ensuring that best practice is followed to the smallest detail on every transit. The result is more exact timekeeping and improved customer satisfaction - during trials in December - Bastø Fosen VI consistently arrived within two seconds of the scheduled time. Øyvind Lund, CEO, Bastø Fosen, commented, “Today, at the press of a button, one of our vessels left the quay in Horten, crossed the Oslo fjord and docked in Moss, all completely automatically. This leaves the crew more time to focus on monitoring the vessel and ensuring passenger safety, which for us are the main motivations for adopting this technology. “Co-operation with KONGSBERG and the NMA has been crucial to the success of this venture, as has consultation with our captains and crew,” he continued. “We have included them in this project from the start and have been delighted with how engaged they have been in its delivery. This is an aid, not a replacement. Greater accuracy permits better logistics - for example, we can now preprogram the time allowed for the crossing and thus reduce energy consumption. Digitalisation and automation are the future, and we are proud to be prime movers.” National and international regulatory bodies are still in the early stages of developing legislation to accommodate automatic marine operations, but through its work with Bastø Fosen and KONGSBERG on Bastø Fosen VI, the NMA have shown the world a clear path forward.

The Basto Fosen V1
Bastø Fosen VI now enters a six-month trial period during which the automatic system – called ‘adaptive transit’ – is expected to control the vessel for most services, but the captain will remain in charge and the bridge will be fully staffed. At present, the installed equipment is not fully autonomous – if vessels or objects are detected on a collision course an alarm will sound and the captain will take control. An anti-collision system, comprising radar and electro-optical sensors, is expected to be fitted to Bastø Fosen VI this summer and be under test by autumn, but crew will remain on the bridge even as the level of autonomy increases. To maintain manoeuvring skills, Bastø Fosen’s procedures will require their staff to perform manual transits on a regular basis. This historic event consolidates Norway and the Norwegian maritime industry’s leading position in the development and implementation of autonomous maritime solutions. Speaking from on-board Bastø Fosen VI, Gunnar Pedersen, EVP Integrated Solutions, Kongsberg Maritime, said, “Leaving the quay, crossing and docking again, all at the press of a button – this is a world first. It’s super-smooth too, as we saw today. But without collaboration between a forward-leaning ferry operator like Bastø Fosen, the support of the Norwegian Maritime Authorities and a technology provider like KONGSBERG, none of this would have been possible. This is a big day for everyone involved – this is the future.” New virtualisation and visualisation platform from Alewijnse

virtualisation and visualisation platform for use on trailing suction hopper dredgers as well as many other types of ships. The solution can also be applied to all types of vessels and brings numerous advantages. The AIViVi system has already been successfully installed on several Trailing Suction Hopper Dredgers (TSHDs), and Alewijnse is already discussing possibilities with other dredging contractors on a world-wide basis, including from the US. The innovative platform acts as a central hub, centralising and integrating all the dredging process systems, and distributing the visualisation of the data to all networked screens on-board. Alewijnse has achieved this first and is the only company currently able to offer a fully digitalised platform to the maritime market. The system dramatically reduces the equipment required to see all data from throughout the ship, reducing computer storage from some five cabinets to one, which has a definite effect upon reducing costs. For a life-time of a ship, up to 30 years, this system reduces the need for renewal of the system from five/six times (some 15 computers/ systems) to just four, giving a pay-back time of some 10 years. Having a ‘super server’ gives obvious advantages to the overall operation of any ship. The innovative AlViVi is a unique, fast and flexible platform, comprising several virtualised dredging process-related systems. It replaces the computers and keyboard, Video and Mouse (KVM) equipment and reduces cabling on-board the vessel. The platform can visualise multiple ship’s systems on individual screens. Alternatively, a single system can also be selected for display on multiple screens around the vessel. This makes it a highly flexible solution for operators on-board. Rikxoort outlines the many benefits, “The platform is fast, user-friendly and extremely reliable, resulting in maximum uptime and optimal operational safety. By bringing together multiple systems in one environment, the maintenance and management becomes much easier and efficient. Updates are better and faster to test or roll back. In addition, the life-time of the software is extended by the independence of the platform and the system is also extremely secure from intruders. “An additional benefit considered highly important by Alewijnse for this project is the significant reduction on space and costs of hardware and software maintenance. The solution saves enormously on physical components - the platform takes up 75% less space through much reduced requirements for cabling, computer hardware and cabinets.” Alewijnse has been working with DEME for more than three years in the field of automation on-board dredgers. Previously completed projects are the hopper control systems such as the Alewijnse Draught and Loading System (ADLS) and Alewijnse Suction Tube System (ASTS) with complementary

Alewijnse’s unique, fast and flexible platform - AlViVi
automatic functions.DEME’s TSHDs are part of the large fleet of dredgers operated by DEME. It is one of the most modern and versatile fleets in the dredging industry and the vessels can be found operating all over the world. The system can also be utilised on-board many other types of ship, including offshore, commercial and Navy vessels.
OSV refit contract for Thordon
Capital expenditure is always a key consideration during the system procurement process but when low cost components result in an increase in unbudgeted operational costs, then any savings quickly diminish. That was the experience of Saudi Arabiabased ship operator Hadi Hamad AlHammam when the original shaft seals fitted to Hadi 37, a 2013-built twin-screw offshore tug supply vessel (OTSV), began to leak and vibrate, resulting in regular visits to drydock for costly repairs. “Reducing the maintenance spend associated with the original seal installation was the driving factor behind the decision to retrofit Thordon Bearings’ TG100 seals,” said Rafid Qureshi, Managing Director, Ocean Power International, the Dubai-based engineering and technical services company. “The vessel’s existing arrangement did not perform as expected and for a vessel under charter to Saudi Arabian oil major Aramco, finding a system capable of reducing off-hire time was crucial. The company approached us to source a more cost-effective solution,” explained Qureshi. “Hadi Hamad preferred the maintenancefree seal over other known brands. The costs of pulling a shaft and replacing a seal every 2.5 - 3 years can go upwards of US$35,000 – $50,000 over the life of a vessel, which is well above the acquisition cost of a maintenance free alternative,” said Qureshi. “The owner already had experience with Thordon products on-board the 200 m long OTSV – water lubricated XL propeller shaft and SXL rudder bearings fitted in 2013 as newbuild installations – so retrofitting the TG100 was an easy decision to make. We installed and commissioned a pair of 165 mm (6.5 in) diameter seals at the Dubai Maritime City (DMC) shiplift, in 2016.” During Hadi 37’s most recent classification survey, Hadi Hamad Al-Hammam, which The Hadi 37 up on DMC’s shiplift
operates a fleet of over 40 vessels, found the seals to be in ‘excellent working order’. Khalid Zahran, Engineering Manager for Hadi Hamad, said, “We recently inspected the seals in drydock and they were in perfect condition. We are highly satisfied with their performance.” Since the installation, Ocean Power International says it has witnessed increased interest for Thordon’s bearings and seals for installation to newbuild projects. “They say bad news spreads like wildfire, but so too does good news,” said Qureshi. “By word of mouth, there is a lot of interest in the region for Thordon products.” The TG100 is a mechanical seal specially developed for 86 mm to 305 mm water lubricated propeller shafts typical of workboats, dredgers, tugs, yachts, patrol crafts and other coastal vessels operating in either clean or dirty, abrasive waters. The primary seal uses hard wearing, silicon carbide faces and Thordon’s proprietary elastomeric bellows to provide an unlimited
Fjord1’s ferry Moldefjord

shelf life compared to rubber-based bellows, which need periodic replacement. It also features a unique secondary seal with “Return to Port” capability. In the unlikely event that the primary sealing surface is damaged, this emergency function allows the shaft to turn at reduced speed enabling the ship’s safe return to port for repairs.
Electrical installations from NES
Norway’s Norwegian Electric Systems (NES) will deliver battery systems, integrated electrical and automation packages for the conversion of three 125-car ferries for the ferry link between the Norwegian ports of Halsa - Kanestraum. The conversion of the ferries in the Moldefjord series is scheduled to start during the last half of 2020, and both ferry berths are being rebuilt with a complete land based

MITSUBISHI


● MARINE MACHINERY ● ENERGY SOLUTION ● TURBOCHARGER


www.mhi-mme.com

charging system. This will be NES` delivery numbers 16, 17 and 18 of hybrid electric ferries to Fjord1. “NES is humble and proud that Fjord1 once again has chosen NES as partner for its remodelling projects. Through good dialogue, we ensure sustainable and safe solutions for the future zero-emission ferries, stated Stein Ruben Larsen, Sales Manager at NES. The ferries that will be converted were designed by LMG Marin in Bergen, and were built by Remontowa in Poland in 2009/2010. After having their gas engines replaced with batteries and charging systems, they will become zero-emission ferries. NES has previously converted ferries from diesel-mechanical to both diesel-electric propulsion and hybrid propulsion. The deliveries in these contracts mainly comprise: • QUEST II charging system that will be integrated into the existing ship’s propulsion systems • Battery systems • Charging plugs and transformers • Upgrading of the ship’s IAS and PMS systems • Integration of the environmental reporting system SPM (Ship Performance Monitoring)
On land, the following must be delivered: • Charging plug • Power and charging systems
NES is a supplier of zero emission systems. Its extensive experience in design, construction, commissioning and operation assures customers that the delivery is optimised and of high quality.
ShipFC project by NCE Maritime CleanTech
A maritime innovation project looking to install the world’s first ammonia-powered fuel cell on a vessel has been awarded €10m funding from the EU. The ShipFC project is being run by a consortium of 14 European companies and institutions, co-ordinated by the Norwegian cluster organisation NCE Maritime CleanTech, and has been awarded backing from the EU’s Research and Innovation programme Horizon 2020 under its Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Joint Undertaking (FCH JU). The project will see an offshore vessel, Viking The Viking Energy
Energy, which is owned and operated by Eidesvik and on charter to Equinor, have a large 2 MW ammonia fuel cell retrofitted, allowing it to sail solely on the clean fuel for up to 3,000 hours annually. As such the project will demonstrate that long-range zero-emission voyages with high power on larger ships is possible. The goal is also to ensure that a large fuel cell can deliver total electric power to shipboards systems safely and effectively. This is the first time an ammonia-powered fuel-cell will be installed on a vessel. A significant part of the project will be the scale up of a 100 kW fuel cell to 2 MW. The fuel cell is tested on land in a parallel project and development and construction will be undertaken by Prototech. Testing will be executed at the Sustainable Energy Norwegian Catapult Centre. The ship-side ammonia system will be supplied by Wärtsilä. The ammonia fuel cell system will be installed in Viking Energy in late 2023. The project represents the latest stage in the long running collaboration between Equinor, Eidesvik and Wärtsilä. The three companies successfully collaborated on a number of environmental and Cleantech projects over the years. Viking Energy was the first LNG powered ocean-going vessel in 2003, and Eidesvik and Wärtsilä also collaborated on the 2009-built Viking Lady, another LNG-fuelled vessel that was seen as a milestone in the transition of shipping with its installation of fuel cells and marine batteries. As an energy major and charterer of offshore vessels, energy group Equinor has set itself a high standard when it comes to investing in the future. “We see projects such as the ShipFC conversion to use ammonia on a high-powered marine fuel cell as an important step in finding the right sustainable and clean solutions in the future. Our on

going collaboration with Eidesvik is testament to a long- standing belief that we can achieve our goals by working constructively towards that vision,” says Senior Vice President for Joint Operations Support in Equinor, Cecilie Rønning. Norwegian crop nutrition company Yara has been contracted to supply the green ammonia which will be produced by electrolysis and delivered to Viking Energy containerised to enable easy and safe refuelling. Another part of the ShipFC project will perform studies on three other vessel types, namely offshore construction vessels and two cargo vessel types, to illustrate the ability to transfer this technology to other segments of the shipping industry.
Condition monitoring by SKF
A condition-based monitoring program, devised for the marine industry by SKF, enables ship operators control costs and avoid damaging equipment breakdown. One leading operator, Capital Ship Management, has been investigating condition monitoring strategies since 2006, in order to reduce the maintenance costs and minimise the unexpected machinery & equipment breakdown. Together with SKF, Capital came up with an effective strategy by utilising a new handheld device, launched recently by SKF - the SKF Quick Collect. The company has implemented the solution across a fleet of 30 vessels, with a plan to extend the program for the whole fleet of 56 vessels. SKF helped the company to determine which on-board machines should be regularly monitored.
One of the Capital Ship Management fleet
SKF’s equipment supports ship operators such as Capital to improve the reliability of operations. On-board engineers use the handheld device to collect vibration data from critical machinery including cargo pumps, engine room fans, compressors, purifiers and electric motors.

George Ioannidis, Technical Fleet Director at Capital says, “The SKF QuickCollect portable vibration measuring instrument helps to have quick and reliable results for immediate action and reduces the cost of repairs dramatically. Furthermore, the on-board engineers now using this vibration device may collect vibration data from all critical and non-critical machinery, including cargo pumps, engine room fans, compressors, purifiers, electric motors etc. and present detailed vibrations reports to class surveyors during periodical machinery survey (CMS).” The device is small, portable and offers a fast, convenient way of monitoring the condition of critical machinery. The quick and accurate vibration data analysis and its ease of use, makes it a powerful diagnostic tool, not only for all Chief Engineers but also for office technical superintendents. It provides vibration data in real time, allowing engineers to carry out maintenance and replace components immediately if required. It collects velocity, acceleration enveloping and temperature data and connects with mobile apps such as QuickCollect and ProCollect, accessed via a tablet or smartphone. It is easy-to-understand interface means that even a non-trained user can understand its principle of operation and validate results of the vibration. The system can be customised for different marine customers,
Alewijnse Marine, your global partner in electrical installations and automation for the maritime industry.
Expertise:
• Engineering & contracting • System design • Marine automation • Integrated bridge systems • Electrical & ICT solutions • Switchboard & console solutions • Power & energy distribution • Propulsion & energy storage • Infotainment systems • Navigation & communication equipment • Service & maintenance (24/7)
CONTACT DETAILS:
HEAD OFFICE
Alewijnse Marine Energieweg 46 Nijmegen The Netherlands +31 (0)24 3716 100 info@alewijnse.co
INTERNATIONAL OFFICES
Please check our website for contact details of all other business units. www.alewijnse.com



depending on their specific needs. Vibration data can be viewed in real-time through the app or downloaded and reviewed using Analysis and Reporting Manager (ARM) software on any accessible PC. Data can also be uploaded to the cloud, allowing SKF’s onshore vibration analysts to make a more detailed assessment and prepare a report if needed. Capital’s fleet includes 48 tankers (10 VLCCs, four suezmaxes, seven aframaxes, 26 MR/handy product tankers and one small tanker), seven LNG tankers, and a modern capesize bulk carrier with a total of approximately 6.50m dwt.
Sales of FuelOpt up for Lean Marine
Sweden’s Lean Marine has revealed that sales of FuelOpt in 2019 far surpassed sales achieved in previous years, indicating a sharp uptake in demand for the propulsion optimisation technology based on repeat orders and new customers, particularly in the ro/pax sector. Since the launch of FuelOpt, a smart hardware system that automatically and directly optimises a vessel’s propulsion system based on the commands from the bridge, more than 175 individual systems have been contracted for more than 40 different ship owners. A strong final quarter brought total sales in 2019 to 59 systems, representing over a third of all systems sold since the technology’s launch in 2014. By the end of 2019, FuelOpt was contracted for over 20 ro/pax vessels, with installations undertaken on the two largest ro/pax vessels in the world - Color Lines’ Color Fantasy and Color Magic. Companies, including Stena Line, Viking Line and Bohai, are also investing in the technology as an effective fuel saving solution that achieves actual CO 2 emission reductions in order to take action for the future of our planet and in response to demand from authorities and passengers alike. FuelOpt achieves real time fuel savings by controlling a vessel’s propulsion and making sure that the propulsive power is optimised automatically based on the command set on power or fuel consumption and/or speed from the bridge. This removes costly variations in speed and power caused by human operational factors, allowing the vessel to achieve optimal fuel consumption at every given point throughout a voyage. For vessels with controllable pitch propellers, FuelOpt acts as a dynamic tuning system for the propulsion machinery to assure the engine and propeller operate at optimal conditions. In addition to FuelOpt, Lean Marine also offers the smart fleet monitoring software Fleet Analytics which turns vessel data into knowledge, empowering organisations to be ‘lean’ and take fact-based decisions for more efficient vessel operation. By offering automatic environmental and voyage reports, Fleet Analytics can help to reduce reporting workload on-board. The software system’s performance management features, with aggregated fleet views and status information, also allow onshore personnel to gain insight about the operational performance.
Fuel research by WinGD
Switzerland’s WinGD has bolstered its investment in fuel research with the development of a flexible injection system. In a whitepaper released today, ‘Flexible Injector to Advance Alternative Fuels Research’, the engine designers describe how the concept will play a crucial role in its investigations into low-carbon liquid fuels and engine injection concepts to harness them. The system was developed as part of HERCULES 2 - the collaborative European engine research project which concluded in 2018. It features an adjustable needle to allow for the injection of lower density liquid fuels, including promising alcohol fuels like methanol and ethanol, as well as conventional fuels including heavy fuel oil and marine diesel oil. At present there is great uncertainty around the fuels that shipping will use to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions. Several of the candidates are unconventional liquid fuels including alcohols and synthetic diesel produced from biomass or renewable electricity. These will require different injection strategies to LNG, for example, which is already used in WinGD’s X-DF engines. WinGD installed the fuel flexible injector on its RTX-6 engines in order to test ethanol combustion. Among other findings - detailed in the whitepaper - the company confirmed that ethanol fuel (with a small amount of diesel injected as a pilot fuel) reduces the formation of NOx and smoke emissions. WinGD’s fuel flexible injector installation on RTX-6 Test

WinGD is currently involved in several projects investigating new liquid fuels, including the FALCON project to develop a carbon-neutral alternative to HFO from lignin, a component of sap found in trees and plants. The fuel-flexible injection system will now become part of the company’s toolbox for validating low-carbon alternatives to help shipping meet its greenhouse gas reduction objectives.
SCHOTTEL’s CFD system
In order to ensure that products are always state-of-the-art, detailed knowledge of their flow behaviour is a basic requirement. Thanks to Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) these complex physical processes can be investigated. SCHOTTEL’s investments in the six-digit euro range are currently being made once again to ensure that the high level of the CFD calculations is also maintained in the future. The findings obtained during such a CFD simulation are then used for optimising the propulsion solutions. Manfred Heer, Vice President Technology at SCHOTTEL, said, “At SCHOTTEL, CFD simulations have been an integral part of the hydrodynamic design process for years. CFD calculations can be used to simulate and analyse a wide range of different applications, such as open-water propeller performance, vessel resistance and towing power, manoeuvrability, risk of cavitation or noise development. In addition, this method enables us to obtain valuable load data for the mechanical components of our propulsion systems. By this means, for example, it is possible to simulate extreme operating conditions which would not be tested in real ship operation for safety reasons. “By increasing our capacities, we can ensure CFD calculations of the highest possible quality. The degree of detail in the calculations
The SCHOTTEL CFD system
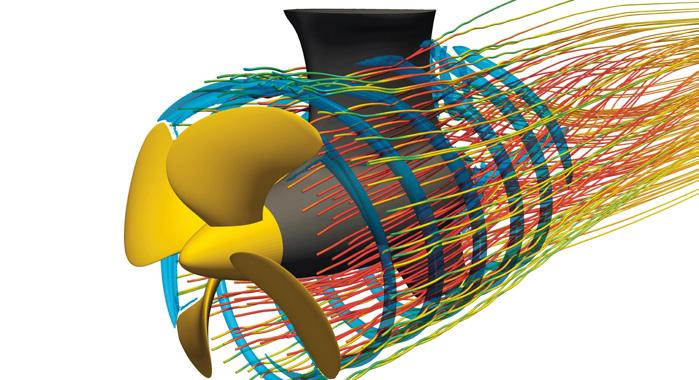
can be enhanced to practically any level required by the task at hand. It is measured against the relevance of the results and is carefully adjusted while taking into account the predicted computing time and the available computing capacity. This means that we can calculate everything that is relevant to fluid dynamics. Beyond this, we are able to support every development project with CFD and make even more precise assertions about the flow behaviour,” adds Manfred Heer. Improved understanding of the phenomenon Even if CFD simulations are still associated with above-average expertise, high time requirements and powerful computers, they are generally considered to be the less expensive and faster alternative to complex model trials. CFD calculations benefit from the fact that the model can be freely expanded, scaled and modified at any time and with minimal effort. In this way, the simulations can also be applied to flows for which experiments are difficult to implement or empirical measurements cannot be determined. Conservation equations (i.e. equations in which the value of a variable does not change in certain physical processes) for physical variables, such as mass, momentum and energy, are used to describe the flow properties around the complex geometries in the flow space. At the end of the calculation, the computational solution of these equations provides exact information about the threedimensional flow field throughout the entire area under investigation. The procedure during a CFD simulation can be divided into three steps - pre-processing, the actual calculation during the solving phase and post-processing in the latter step, the results are validated and visualised. First of all, a 3D model is mapped - geometry details that are not, or only partially, relevant for the simulation are completely removed or represented in a simplified form. Following geometric preparation of the model, its so-called mesh is generated, in which the flow area is divided into a finite number of cells. A mesh of poor quality – for example one for which too few cells were generated, resulting in a mesh that is too coarse or contains greatly deformed cells – can lead to significant errors in the result or even to termination of the calculation. Preprocessing also includes definition of the initial and boundary conditions, such as velocity, volume flow, pressure or speed. Correct definition of these parameters has considerable influence on the computing time as well as on the quality and accuracy of the results. Pre-processing is followed by the actual calculation – the solving phase. This requires appropriate hardware and software that solves the conservation equations in the calculated volume cell by cell. The actual solving process is an iterative calculation procedure which, in the case of a successful outcome, approaches a clear solution step by step. Depending on the complexity of the task, CFD calculations can take several hours or days. Following successful calculation, the results of computational simulations are checked for plausibility. The validation process includes comparisons with empirical values, basic equations or values from model trials. In the final step, the results are visualised and presented in graphics, diagrams or animations. The intermeshing application of CFD simulations and Finite Element Methods (FEM) brings together state-of-the-art technologies for flow calculation with mechanics. When combined with know-how acquired over many years, these techniques make a significant contribution to the successful development and production of efficient and reliable propulsion solutions.
Diesel engine overhaul by Royston

Work to overhaul a high-speed diesel engine on a Pritchard Gordon Tankers-operated oil products tanker has been completed by diesel power specialist Royston. Engineers undertook the 51,000 running hour service on the No.2 generator on-board the 10,005 dwt 2001-built product tanker Henrietta PG in Trinidad as part of a planned refurbishment and maintenance programme of essential power plant. The work carried out by Royston saw the Cummins KTA19 G3 power unit stripped down and critical parts serviced before being fully reassembled onsite. This involved work on all six camshafts sections, replacing main bearing shells and thrust bearings, rebuilding cylinder head valves and springs, and fitting new piston rings and conrod bolts. New STC valves and fuel rails, turbo, piston cooling jets, fuel pump and associated pipework were also fitted.
The Henrietta PG

After the work was completed, the engine was run at idle for several minutes to check for leaks, before being successfully tested at various loads. Rob Middlemiss, technical superintendent at Pritchard Gordon Tankers Ltd, said, “Royston’s professionalism, work ethic and engineering skills are of the highest order, enabling the work on the Henrietta PG to be completed quickly and efficiently, minimising disruptions to our operational schedule.” The Henrietta PG is one of 10 purpose-built shallow draft, double hull tankers from 6,200 dwt to 10,600 dwt in the Pritchard Gordon Tankers’ fleet. The company specialises in the transportation of crude oil, refined petroleum products, chemicals and biofuels in environmentally sensitive regions.
ABS and P&O Maritime collaborate in condition-based systems
ABS and P&O Maritime Logistics (POML) have agreed to a pioneering condition-based class (CBC) pilot project for the 2,740 dwt PSV, DMS Courageous. The historic agreement will see the vessel become the first to utilise ABS Nautical Systems as the computerised maintenance management system to transmit planned maintenance data and conditionbased maintenance activities to ABS, for the purpose of potentially crediting class survey requirements. ABS CBC will enable less intrusive surveys of hull and machinery systems through alternative means of verification of compliance to specific survey requirements. Delivered in three progressive phases, the project focuses initially on improving alternative means of compliance verification, then expanding and evolving to apply remote survey techniques, and ultimately leveraging predictive capabilities to transform the Class process and create efficiencies in on-board surveys. Martin Helweg, Chief Operating Officer of P&O Maritime Logistics, said, “A cardinal element to our future is our continued disruption of the segments in which we operate – pushing ourselves to implement solutions which challenge conventional thinking methods. Our customer demands are increasingly shifting towards advanced services, and in response we began to digitise aspects of our service offering to optimise the supply chain. Through partnerships with companies like ABS, we continue to offer and deliver a difference which drives value for our customers.”
The DMS Courageous

The technology will not only allow POML to further streamline its maintenance and management organisation to reduce OPEX, but will also improve processes through leveraging new technologies. The DMS Courageous project builds on the longstanding relationship between ABS and POML. The project utilises ABS’ Remote Survey offerings and the ABS Guide on Smart Function for Marine Vessels and Offshore Units which introduced the industry’s first notations on Smart technology applications. This, in turn, supports the development of condition-based approaches to enhance safety and increase vessel operating time. Recently, the Caspian Voyager, POML’s largest modern PSV in the Caspian Sea, entered into an ABS extended drydocking scheme, intended to begin the CBC process, with the goal of enrolling the entire fleet into the ABS CBC program within the next five years.
MJP increases its service network
Sweden’s Marine Jet Power (MJP), is further strengthening its world-wide sales and service network with the appointment of Firstbreak, as an official sales and service agent, based in Christchurch, New Zealand. This expansion of the sales and service network will extend current coverage, allowing MJP to offer a more hands-on and localised customer experience, with unmatched support and quicker response times for new and existing customers. Under the terms of the new agreement, Firstbreak will offer MJP customers in-region support, including parts fulfilment and local service for builders and operators in New Zealand and other parts of Southeast Asia. With a long, successful history in the marine, oil and gas industries Firstbreak, led by Brent Paulsen, specialise in sales, marketing, manufacturing and supply chain with offices in Christchurch, Auckland, Sydney and Singapore. Paul Hague, MJP Regional Director of APAC, says, “Installing a sales and service agent in New Zealand, in addition to opening an office in Western Australia in early 2019, will further strengthen our service capabilities in the fast-growing APAC market. “We are extremely pleased for the opportunity to be working with Firstbreak, and its dedicated sales team. As a company, they are extremely well suited to the needs of MJP as we continue to grow in the APAC region.” The Asia Pacific (APAC) sales office, opened in early 2019, is strategically located in Perth Henderson, Western Australia in the Henderson Industrial area, offering close proximity to a number of shipyards and fleet operators in the area. SORJ

Brent Paulsen and team pictured outside Firstbreak’s Christchurch facility






