
11 minute read
Chapter 1: What is Long Covid?
CHAPTER 1
What is Long Covid?
What is Long Covid?
LongCovidisabroadrangeofsymptomsfollowingresolution oftheacutephaseofthedisease.ThosewithLongCovidare nolongertestingpositivefortracesoftheSARS-CoV-2virusbut exhibitlong-termsymptomsthatpersistforweeksorevenmany monthsafterinitialinfection.
Between 10 and 30% of Covid-19 patients are estimated to experience Long Covid symptoms.1 For more debilitating symptomsthatlastmorethanayear,theestimateisbetween2 and 5%. The likelihood of full or partial recovery from Long Covidvariesfrompersontoperson. Thisdefinitionexcludeslong-termconsequencesattributableto organdamagethatcanoccurasaresultofCovid-19infection.
Can Long Covid affect people of all ages?
Long Covid can affect people of all ages who are otherwise healthy,includingchildren.
Can Long Covid affect people who are healthy?
LongCovidaffectspeopleofallmedicalbackgrounds,eventhose whoarecompletelyhealthy.
1 GAO-22-105666, Science & Tech Spotlight: Long COVID
Can asymptomatic individuals develop Long Covid?
LongCovidisseeninthosewhowerehospitalizedwithCovid19 and people who experienced very mild symptoms or were asymptomatic.
Are there other names for Long Covid?
LongCovidisalsodescribedasLong-haulCovid,ChronicCovid, and Post-acute sequelae of Covid-19 (PASC). Long Covid was officially recognizedby the US Centers forDisease Control and Prevention(CDC)withadiagnosticICD-10codeinOctober2021 knownasU09.9PostCovidCondition.
ThereisalsoanICD-11code:RA02forPostCOVIDdefinition.It isbasedontheWorldHealthOrganization(WHO)definitionof LongCovidestablishedinOctober21:2 “PostCovid-19conditionoccursinindividualswithahistoryof probable orconfirmedSARSCoV-2infection,usually3months fromtheonsetofCovid-19withsymptomsthatlastforatleast2 months and cannot be explained by an alternative diagnosis. Common symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, cognitive dysfunction but also others and generally have an impact on everyday functioning. Symptoms may be new-onset following initial recovery from an acute Covid-19 episode or persistfromtheinitialillness.Symptomsmayalsofluctuateor relapseovertime.” TheWHOdidnotrestricttheirdefinitiontoconfirmedinfections only. Unequal access to Covid-19 testing, particularly at the
2 A clinical case definition of post COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus, 6 October 2021
beginningofthepandemic,entailsthatmanypeoplewithLong CoviddonothaveserologicalproofofSARS-CoV-2infection.
How does this book define Long Covid?
Definitions of Long Covid vary. This book defines Long Covid broadlyinordertoemphasize post Covidconditionsandlongtermcomplicationsofacutedisease(seeChapterSeven). Thefollowingcriteria,basedonarecentpaperpublishedin The Lancet,arewhatconstitutetheparametersofthisconditionin A Family Guide to Long Covid:34 Survival Fatigueorexhaustion Pain
Post-exertionsymptoms Cardiovascularfunctioning Respiratoryfunctioning Nervoussystemfunctioning Cognitivefunctioning Mentalfunctioning Overallphysicalfunctioning
What is the cause of Long Covid?
ThecauseofLongCovidremainsunclear.Researchsuggeststhat thesymptomsexperiencedbyLongCovidpatientscouldbethe
3 A core outcome set for post-COVID-19 condition in adults for use in clinical practice and research: an international Delphi consensus study - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 4 Key outcomes of Long COVID identified in international consensus study
resultofuptofourdifferentsyndromes:permanentdamageto vital organs; post-intensive-care syndrome; post-viral fatigue syndrome;andcontinuedCovid-19syndrome.5 LongCovidmaybetheresultoflowlevelsofcompleteorpartial viral persistence. It might also arise due to an autoimmune response caused by the initial Covid-19 infection. Long Covid may also result from chronic inflammation triggered by the initialinfection.Formoreonthishypothesis,seethequestion“Is LongCovidanautoimmunedisease?”inChapterTwo.
How is Long Covid different from Covid-19?
Covid-19iscausedbytheactivereplicationofSARS-CoV-2virus inthebody,whileLongCoviddevelopsoncereplicationduring theacutephaseofinfectionhasceased. Covid-19 is easy to diagnose with rapid antigen or PCR tests. ThereisnoonetesttodiagnoseLongCovidandthesymptoms arewide-ranging. ThesymptomsofaCovid-19infectionaretemporary,normally lasting anywhere from a few days to one to two weeks. In contrast,LongCovidsymptomscanlastformonthsoryears.6
5 Long covid could be four different syndromes, review suggests 6 Health outcomes in people 2 years after surviving hospitalisation with COVID19: a longitudinal cohort study
Source:ACCESSHealthInternational;Long-termcomplicationsof COVID-19
How is Long Covid different from Chronic Covid?
ChronicCovidandLongCovidareoftenusedinterchangeablyto describethelong-termeffectsofCovid-19.Technically,thereis adistinctionbetweenthetwo.
ChronicCovidisdefinedbythepersistentinfectionofSARS-CoV2, while Long Covid symptoms occur after SARS-CoV-2 infection.7 PeoplewithChronicCovidtestpositiveforCovid-19 forlongperiodsoftime.8
What are the symptoms of Long Covid?
The list of Long Covid symptoms continues to evolve as new researchemerges.Arecentstudyidentifiedupto200symptoms
7 Longest Covid infection lasted more than 16 months, tests show -BBC News 8 The man who tested positive for Covid 43 times -BBC News
that could be associated with Long Covid.9 The five most commonsymptomsfoundwerefatigue(58%),headache(44%), attentiondisorder(27%),hairloss(25%),anddyspnea(24%).10 ThesymptomsofLongCovidaremanyanddiverse.Symptoms ofLongCoviddefinedbytheCDCinclude: fatiguethatinterfereswithdailyactivities difficultybreathing heartpalpitations memory,concentrationorsleepproblems depression anxiety lightheadedness stomachpain alteredsenseoftasteorsmell changeinmenstrualcycles jointpain rash lingeringcough
LongCovidcanalsodamagemanyotherorgans,includingbrain, heart,kidney,liver,bloodvesselsandbone.Organdamagemay leadtolastinghealthcomplications,including: long-termbreathingproblems
9 Characterizing long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact 10 More than 50 long-term effects of COVID-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis
heartcomplications chronickidneyimpairment stroke Guillain-Barré syndrome, a condition that causes temporaryparalysis
Chapter Seven of this book details how Long Covid can affect eachorgan.
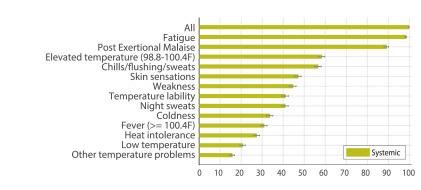

Source:CharacterizinglongCOVIDinaninternationalcohort:7 monthsofsymptomsandtheirimpact
When does Long Covid begin?
The majority of people recover from the acute phase of SARSCoV-2infectionwithintwotothreeweeks.Ifsymptomspersist formorethanfourweeksafterinitialinfection,apersoncanbe classified as having Long Covid.11 These symptoms may continuetopresentformonthsorevenyears. Long Covid can also manifest in those who did not develop symptoms during Covid-19 infection. It is estimated that up to one in five Covid-19 patients with no symptoms end up presenting at least one Long Covid symptom.12 In such cases, symptomsusuallyappearwithinthreemonthsofrecoveryfrom acuteinfection.13 Wedonotknowifthereisanupperlimitfor theonsetofLongCovid.Ifyouoralovedoneisexperiencinga sudden onset of symptoms that mirror those commonly associatedwithLongCovid,evenifithasbeenweeksormonths sinceinitialinfection,don’truleoutthepossibilityfromtheget go.
What are the psychological symptoms associated with Long Covid?
The most common psychological symptoms associated with Long Covid are anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Covid-19 PTSD (CV-PTSD) is a trauma that develops as a result of the threat of Covd-19 to one’s life and lovedones,includingwitnessingunexpecteddeathandphysical
11 Long COVID or Post-COVID Conditions | CDC. 12 FAIR HEALTH white paper –A Detailed Study of Patients with Long-Haul COVID 13 A clinical case definition of post COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus, 6 October 2021
injurytoanotherperson.14 MoreonCV-PTSDcanbereadinthe book CV-PTSD: What It Is and What To Do About It. Altered smell/taste, brain fog, and sleep disorders also impact mental health.
There is no singular cause for these psychological symptoms. SARS-CoV-2 infection likely causes unknown neurological impactsonthebrainandimmunesystem.Itcouldbearesponse to the unpredictable loss of physical ability or permanent disability caused by Long Covid, especially for those with persistent brain fog, difficulty breathing, or fatigue.15 People hospitalized for Covid-19 may develop post-intensive care syndrome,thuscompoundingPTSDordepression.16 Moreover, LongCovidisnotwidelyrecognized;thedismissalofsymptoms from medical practitioners, one’s workplace or family can worsenfrustrationandanxiety.17 Theculminationofpsychologicalandphysicalsymptomscanbe overwhelming for people with Long Covid and their families. TherearenostandardtreatmentsforLongCovid’spsychological symptoms. At this time, the best practice is to find support— physically, cognitively, and emotionally. Consider some of the following: Medical advice for physical symptoms can help identify underlying causes (although this may not alleviate psychologicalsymptoms).
14 Posttraumatic Stress Disorder during COVID-19 | Psychiatry | Michigan Medicine
15 COVID-19 Impact on the Brain and Psyche | Northwestern Medicine 16 What is Long COVID? The Physical and Psychological Symptoms and Management | UCSF Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences 17 Impact of post-COVID conditions on mental health: a cross-sectional study in Japan and Sweden | BMC Psychiatry
A psychiatrist may screen your mental health and prescribe medication or nonpharmacological interventionstomanagedepressionand/oranxiety. Psychotherapy—and cognitive behavior therapy in particular— may help people with Long Covid adjust to newcognitiveandphysicallimitations.18 Cognitive Rehabilitation Therapy (CRT) is a customized treatment plan which focuses on improving one’s memory, attention processing, and emotional regulation.19Aneuropsychologistcanscreenifthisnewly developedtherapyisrightforyou. Long Covid advocacy groups update frequently with useful resources and self-management tools, and the community can bridge the loneliness and isolation that comeswithLongCovid. Confide in loved ones who sympathize with the Long
Covidexperience.
If you or someone you know is experiencing a mental health crisis,pleaseuseanyofthefollowing24/7resourcesatanytime: Forpotentiallylife-threateningsituations,call911 Forsomeonewhoissuicidalorinemotionaldiscress,call 988 to reach the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline (alternative:1-800-273-8255) For those who need immediate help of all kinds, text HOME to741741toreachacrisiscounselor
18 We need to talk about Long-Covid | The Psychologist 19 Clinical Guidelines: Long COVID-19
What are the neurological symptoms associated with Long Covid?
Neurologicalsymptomsformwhenthebrain,spinalcordand/or nerves that connect them experience dysfunction.20 Long Covid’s most common neurological symptoms include fatigue, difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, sleep disturbances, limb weakness, and headaches.21 22 A minority of people display symptoms of PASC-TAC, a newly identified Long Covid syndrome consisting of the following neurological symptoms: tremor, ataxia, and cognitive dysfunction.23 People with PASCTAC can experience tremors; difficulty with coordination, balance and speech; memory impairment and decreased concentration.
How long do PASC neurological symptoms last for?
Preliminary data suggests that neurological symptoms can resolvewithin6months;studyparticipantswhodidnotrecover at that mark still saw some improvement. The results suggest that many, but not all, recover from Long Covid neurological symptoms,butalsothattheroadtoneuro-normalcyisnotquick oreasy.Thosewithpersistentsymptomshadnohistoryofpreexistingneurologicalconditionspriortoinfectionandreported mild/moderate Covid-19 infections, emphasizing the jarring impactofLongCovid’sneurologicalsymptoms.
20 5 neurological disorders: Symptoms explained 21 Neurological outcomes 1 year after COVID‐19 diagnosis: A prospective longitudinal cohort study 22 Longitudinal evaluation of neurologic-post acute sequelae SARS-CoV2 infection symptoms
23 Longitudinal evaluation of neurologic‐post acute sequelae SARS‐CoV‐2 infection symptoms -Shanley
If I had severe Covid-19, am I more likely to develop Long Covid?
PatientswithsevereCovid-19areatahigherriskofdeveloping Long Covid.24 Those who require hospitalization, and in particularthosewhorequireintubationinintensivecareunits, are especially at risk.25 But studies also show that Long Covid remainsathreatevenifinfectionismild.26 27 MildCovid-19can stillyieldsevereLongCovidsymptoms.28 Further reading Incidence, co-occurrence, and evolution of long-COVID features: A 6-month retrospective cohort study of 273,618survivorsofCOVID-19|PLOSMedicine Multiple early factors anticipate post-acute COVID-19 sequelae:Cell
What are the risk factors for Long Covid?
Asfarasweknow,noadditionalriskfactorsbeyondthosethat predisposesomeoneforsevereCovid-19.RiskfactorsforLong Covidcaneitherbedirectorindirect.Directriskfactorsincrease riskforLongCovid once you have already been infected by SARSCoV-2. Indirect risk factors increase your chances of being infected in the first place.
24 Post COVID-19 condition diagnosis: A population-based cohort study of its occurrence, risk factors and healthcare use by severity of acute infection 25 COVID Symptoms, Symptom Clusters, and Predictors for Becoming a LongHauler: Looking for Clarity in the Haze of the Pandemic 26 Post COVID-19 Syndrome in Patients with Asymptomatic/Mild Form 27 COVID Symptoms, Symptom Clusters, and Predictors for Becoming a LongHauler:Looking for Clarity in the Haze of the Pandemic 28 Delayed catastrophic thrombotic events in young and asymptomatic post COVID-19 patients
Indirectriskfactorsincludeobesity,beingmale,beingolder,and high blood pressure.29 Individuals with compromised immune systems—organ transplant recipients on immunosuppressive medication, cancer patients receiving chemo- or immunotherapy, individuals suffering from autoimmune diseases,andindividualswithhumanimmunodeficiencyviruses (HIV)—arealsomorepronetoinfections. ThedataonthedirectriskfactorsofLongCovidislessclear,but there are a few factors that stand out. Many studies show that womenaremorelikelytodevelopLongCovidthanmen.30 31 32 Thisechoeswhatweknowaboutgenderbiasandautoimmune diseases—which overlap symptomatically with Long Covid— moregenerally. Type 2 diabetes is another risk factor for developing Long Covid.33
What are the non biological risk factors for Long Covid?
Once again, risk factors that determine Covid-19 infection are the same for Long Covid. In addition to biological and medical factors,socialandeconomicfactorsdeterminewhoisathigher risk of developing Long Covid. These include factors such as socioeconomic status, access to education, food insecurity,
29 Risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 among patients in the Oxford Royal College of General Practitioners Research and Surveillance Centre primary care network: a cross-sectional study 30 Female gender is associated with long COVID syndrome: a prospective cohort study 31 Clinical characteristics with inflammation profiling of long COVID and association with 1-year recovery following hospitalisation in the UK: a prospective observational study 32 Incidence and risk factors for persistent symptoms in adults previously hospitalized for COVID-19 33 Multiple early factors anticipate post-acute COVID-19 sequelae
working conditions, and housing. Working class communities, forexample,hadasignificantlyhigherriskofcontractingCovid19earlyinthepandemic,adisparitythatlikelypersiststoday.34 In the United States social and economic disparities are intimately linked to race and ethnicity. Since the pandemic began, prevalence of Covid-19 infections and severe Covid-19 has been higher in black and other minority communities.35 36 The same is likely true of Long Covid, creating an impetus to includethesepopulationsinLongCovidstudies.37
Does breakthrough infection (Covid-19 infection after vaccination) increase my long term chance of severe Covid19 and death?
Some people with breakthrough infections do suffer adverse consequenceslikeseverediseaseanddeath.Thepositivenews is vaccination reduces the probability of severe consequences very substantially. Breakthrough infections also increase the chances of Long Covid, particularly outcomes associated with organfailure.38
Are certain SARS-CoV-2 variants associated with an increased chance of getting Long Covid?
Covid-19infectionscausedbytheOmicronvariantmaybeless likely to result in Long Covid, regardless of age or vaccination
34 When lockdown policies amplify social inequalities in COVID-19 infections: evidence from a cross-sectional population-based survey in France 35 Assessing differential impacts of COVID-19 on black communities 36 COVID-19 Cases and Deaths by Race/Ethnicity: Current Data and Changes Over Time 37 Researchers fear people of color may be disproportionately affected by long Covid 38 Long COVID after breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection
status.Recentdataestimates4.5%ofOmicroncasesledtoLong Covid,comparedto10.8%ofDeltacases.39

Source:RiskoflongCOVIDassociatedwithdeltaversusomicron variantsofSARS-CoV-2
There are currently five known Omicron sub variants in circulation—BA.1,BA.2,BA.2.12.1,BA.4andBA.5—whichhave distincttransmissionratesandacutediseasepresentations.The LongCovidriskforeachOmicronsubvariantisunknown.
How does Long Covid impact my chances of Covid-19 reinfection?
LongCovidhasnoeffectonreinfection.Ingeneral,reinfections can occur within three months or less of the last infection.40 Protection acquired from previous infection(s) and vaccines wanes over time.41 The best protection against reinfection is
39 Risk of long COVID associated with delta versus omicron variants of SARSCoV-2 -The Lancet 40 For unvaccinated, reinfection by COVID-19 is likely, study finds | NSF 41 How Often Can I Be Infected With Covid-19? -The New York Times
using preventative measures—wearing masks, handwashing, andgettingvaccinesandboosters.
Are there biomarkers for Long Covid?
A clinical biomarker is a measurable indication of a biological process, condition, or disease. No definitive biomarkers have been established for Long Covid, which makes it difficult for physicianstodiagnose. Atleastonepreprintstudyhasdocumentedthepresenceofthe SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the majority of its Long Covid patientcohort,meaningitmightmakeapromisingcandidatefor a Long Covid biomarker.42 Researchers offered two possible explanationsforthelingeringspikeprotein.Oneisthatverylow levels of virus replication persist in a privileged cellular compartment. Another is the persistence of subgenomic viral RNAsthatproducethespikeprotein.
What is Long Covid Fatigue?
Fatigue that can last from weeks to months afflicts approximately half of patients with Covid-19. The term fatigue doesnotsimplydenotebeingtiredduringorafteraninfection, but being persistently and excessively tired after resting or havingagoodsleepevenaftertheinfectionresolves. Following Infection, 13 to 33% of participants in most Long Covidstudieshadpersistentfatigueat16to20weeksafterthe beginning of their Covid-19 symptoms.43 This is also seen in many acute systemic infections, such as infectious
42 Persistent circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike is associated with post-acute COVID19 sequelae 43 Long COVID and Post-infective Fatigue Syndrome: A Review
mononucleosis. Fatigue has physical, mental, and psychosocial dimensions and usually is accompanied by other symptoms, demandingacomprehensiveapproachtoassessingandtreating it.
What is the difference between Long Covid and chronic fatigue syndrome?
It is true that notable overlap exists between Long Covid and myalgicencephalomyelitis/chronicfatiguesyndrome.44 Fatigue consistently ranks as one of the most common Long Covid symptoms,inhibitingmanylonghaulersfromreturningtowork and resuming their usual routines. So do brain fog and postexertionalmalaise,twoothersymptomsfrequentlyreportedby patientswithchronicfatiguesyndrome.Nottomentionchronic fatiguesyndrome,likeLongCovid,isalsonotoriouslydifficultto diagnose and treat due to conflation with psychosomatic conditionsand/orclinicalbiases. While the emergence of Long Covid can be traced back to the Covid-19 pandemic, no such genesis has been confirmed for chronic fatigue syndrome, though plausible causes abound, amongthemviralinfection.Furtherresearchcomparingthetwo is needed to determine with greater accuracy the extent of convergence. This has promise to yield breakthroughs in treatments for not only Long Covid and chronic fatigue syndrome,butcomplexpost-infectiousillnessesmorebroadly.
44 Long COVID and Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)—A Systemic Review and Comparison of Clinical Presentation and Symptomatology




