Morphogenetic Design Integral Envelope
Ahmed Adel

Ahmed Adel

Bearded Dragon


Alligator

The American Alligator is indigenous only to Southeastern United States, available as both farm raised and harvested from the wild. Its skins are prized for their incredible quality and texture. Along with crocodiles and caimans, the American alligator is part of the Crocodillian family
Alligators have been on earth for more than 65 million years. Alligators were here when dinosaurs roamed the land and have remained almost unchanged since then. Being reptiles, alligators are cold-blooded. They lie motionless for lengthy durations, but move swiftly to hunt both on land and in water. An alligator relies on its large and incredibly strong tail for mobility in water. Like all crocodillians, they also have four short legs with webbed back feet. Alligators have very tough skin, usually a dull gray or deep olive in color. They are often mistaken for logs floating in the water. The bony plates within the skin give the body of alligators an “armored” look.






Defining the pattern using intersection points

Re-creating the pattern using the intersection points

Defining the centroids of the original pattern shapes

Connecting the centroids creating quadilateral shapes

Connecting centroids creating triangular shapes

Defining the centroids of the triangular shapes

Connecting centroids creating new triangular shapes


Creating curves inside the triangular shapes

Connecting centroids creating rhombuses


Creating curves inside the rhombuses

Defining the centroids of the curves inside the rhombuses



Creating perpendicular axes inside the curves

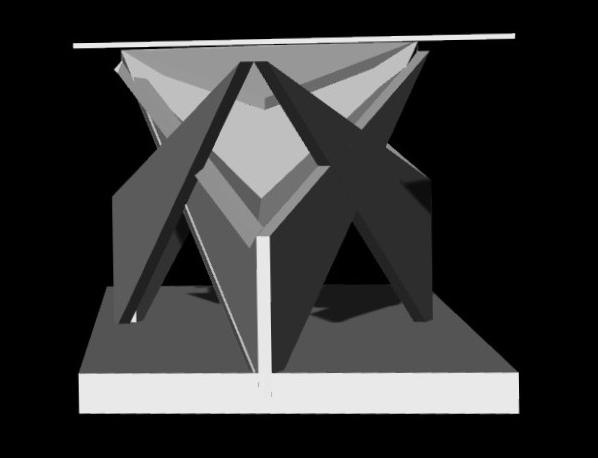
Creating a star shape inside the rhombuses




Creating curves based on the star-shape inside rhombuses


















Moving all the points of the pattern up to define the surface

Joining points using lines to create the surface


Completion
of the 3D compnents generating













Thank You
