AI and robots are not here to take workers’ jobs. In fact, an IT skills gap means many human employees have a bright future
Attention-grabbing headlines about technology laying waste to entire industries can make for concerning reading, backed up by research suggesting people are prone to dramatically exaggerating the rates at which their careers may be ended by technology.

Rather than simply taking over, however, research has found workplaces that integrate employees and robots will generate more value for human labour. What’s more, a report from MIT Sloan Management Review and Boston Consulting Group found that 60% of employees have already welcomed AI as a coworker. Organisations with employees working well with AI are almost six times more likely to see significant financial benefits than organisations that are not using AI.
However organisations looking to embrace the AI revolution and its world of opportunities will have the tech skills crisis to contend with. According to a study by Equinix, 26% of businesses said they had shortages for those with an aptitude for AI and ML, with demand for skilled workers only set to rise in future.
marcus.law@bizclikmedia.com

“According to a study by Equinix, 26% of businesses said they had shortages for those with an aptitude for AI and ML, with demand for skilled workers only set to rise in future”




LivaNova
Transforming lives through MedTech and Procurement

IOT
Make or break: Manufacturing industry’s plans for IoT

AR/VR
Virtual reality healthcare: Treatment rooms in the metaverse
Autonomous vehicles
A self-driving future: The road to level 5 automation Top







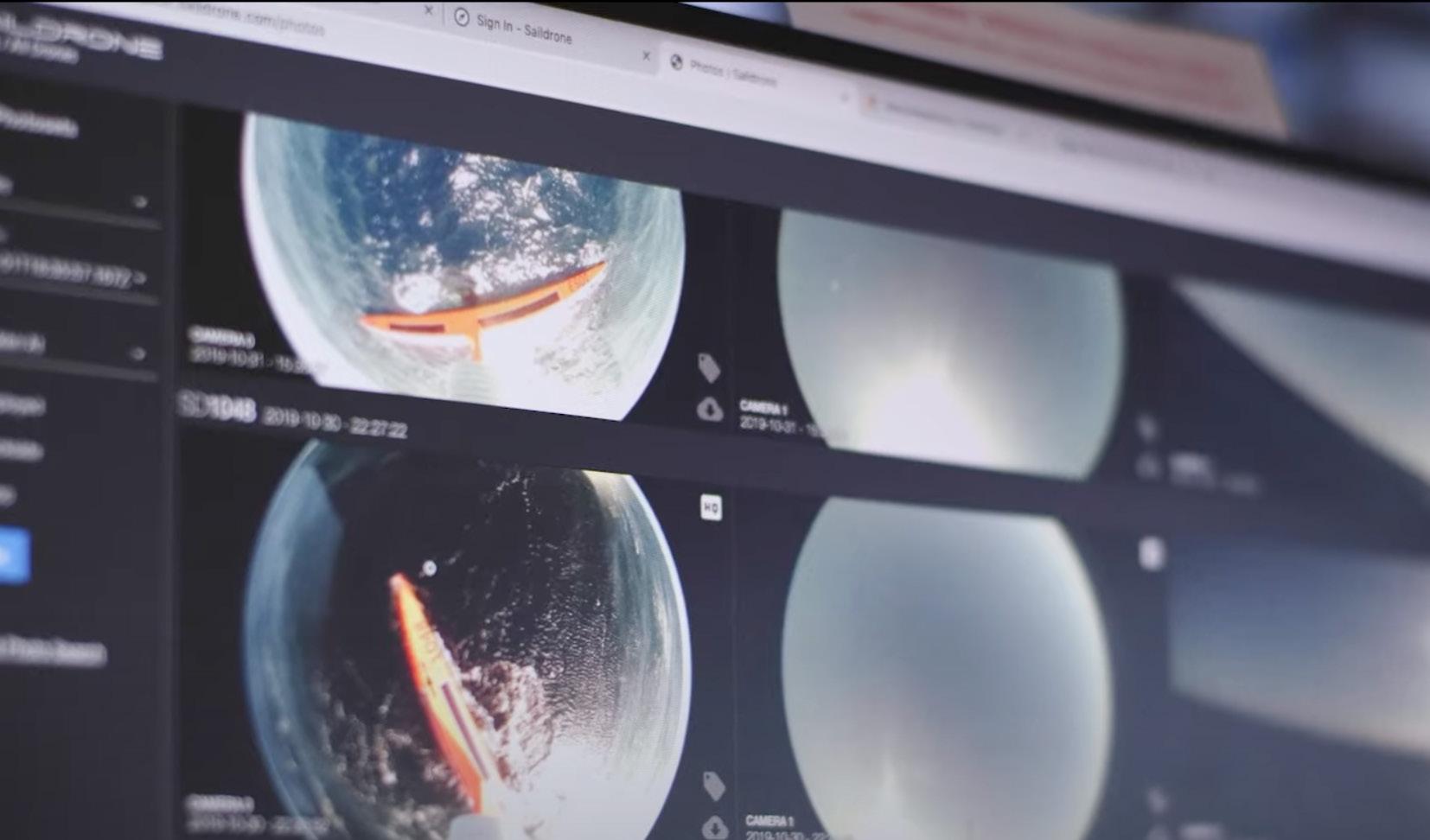
Hokkaido Electric Power Company is using Microsoft’s mixed-reality HoloLens 2 headset to help staff inspect critical equipment at a thermal power plant.
On every inspection patrol, workers navigate a vast labyrinth of boilers, turbines and generators, examining thousands of pieces of equipment for often subtle changes that can help them avoid larger problems.
“I had an image of (mixed reality) as a technology for games, but it was a revelation to find that it can be used as an intuitive and easy-to-understand solution from the perspective of transferring patrol inspection skills,” said Takaharu Umemoto, who works in the company’s IT section of the Thermal Power Department.

9 out of 10 consumers say they are curious about the metaverse, while over half say they are excited by it and would use it when it becomes accessible to them, according to research published by Capgemini.
7 7%
of consumers expect immersive experiences to impact how they interact with people, brands and services
43 %
would like to use the metaverse mainly as a place to interact with their family and friends


A new breed of chatbot is ready to take its place in business, according to new research, but companies will need more than words if this is to be successful. OpenAI’s headline-grabbing generative AI platform, ChatGPT, isn’t just hype; it could, in fact, be used by businesses to help with crucial tasks – including enterprise support, customer interaction and even product development, a new report claims.
US football team the Los Angeles Chargers has partnered with a conversational AI company to take artificial intelligence into the locker room. MeetKai – also based in LA – has been tasked with creating fresh, engaging experiences using conversational AI and other new technologies. As the ‘Official AI partner’ of the Los Angeles Chargers, MeetKai and the team will work together to develop new in-stadium and at-home experiences.
Tech workers are nearly twice as likely as those in other industries to find that distractions make it hard to care about their jobs and are also more than three times as likely to do the bare minimum around security, according to new research. The data emerged in security and privacy company 1Password’s annual State of Access Report, Distraction on overdrive: Security in a time of perma-crisis, based on a survey of 2,000 North American workers.
“We believe that seamless and secure payment solutions can help our clients and their business… to grow, diversify, and thrive”
Christine (Jang) Tan Head of FIG Sales APAC, J.P. Morgan Payments
BEAMERY AI talent lifecycle management platform Beamery has announced it has closed a US$50mn Series D funding round, taking the company to a valuation of over US$1bn – and into unicorn status.

INFINITY AI

Researchers in the US say they have demonstrated how machine learning could predict rare disastrous events, including earthquakes and pandemics Predicting extreme events, including earthquakes, pandemics or ‘rogue waves’, can be problematic as computational modelling often falls short; statistically speaking, these events are so rare that there’s just not enough data to use predictive models to accurately forecast when they’ll happen again.
A team of researchers from Brown University and Massachusetts Institute of Technology say they may have solved this problem and in a new study in Nature Computational Science, the scientists describe how they combined statistical algorithms – which need less data to make accurate, efficient predictions –with a powerful machine learning technique developed at Brown.
Infinity AI, a startup that generates automated synthetic training data, has announced a US$5mn seed round led by Matrix, with participation from founders and operators from companies like Snorkel AI, Tesla, and Google.
CHINESE CHIP INDUSTRY
The US Government has added Chinese memory chipmaker YMTC and 21 ‘major’ Chinese players in the artificial intelligence chip sector to a trade blacklist, broadening its crackdown on China's chip industry.
FAKE FACES
Facebook parent company Meta says more than twothirds of the influence operations it found and took down this year used profile pictures that were generated by a computer.
G O O D T I M E S B A D T I M E S
FEB 23
AIis here to stay. Increasingly capable of generating creative material such as music, art, and writing, AI could be used to disrupt the convention that coding is only performed by humans. In December, AI software system AlphaCode was entered into online coding competitions, and in contests with at least 5,000 participants,
AI can be used to predict the next piece of code that a developer is likely to write, based on the context and the task at hand. This can save time and reduce the likelihood of errors. AI could also be used to analyse code and suggest changes that would make it more readable, maintainable, or efficient, such as renaming variables or extracting functions.
outperformed 45.7% of programmers. Generating code in Python or C++, while filtering out any bad coding, DeepMind says AlphaCode can write computer programs at a level consistent with an average human programmer with about a year of training.
Below, we look at how AI could change how coding works forever.
AI can be used to automatically identify and fix bugs in code. For example, an AI system might be trained to recognise common programming errors and suggest a fix. Based on analysis, an AI system could also suggest possible fixes for identified errors, such as changing a line of code or adding a missing function call.
AI can be used to generate code based on a set of inputs and desired outputs. For example, an AI system might be able to generate code that sorts a list of numbers in ascending order. An AI system could also be used analyse an example of code that solves a particular problem, and then generate new code that solves a similar problem.
AI can be used to optimise code for efficiency and performance. An AI system might be able to identify sections of code that could be rewritten to run faster, or can suggest changes to the code that could improve performance, such as using a different algorithm or optimising loops.
AI can be used to automate the testing process by generating test cases and evaluating the output of a program. According to software company Parasoft, through the application of reasoning, problem solving, and machine learning, AI can be used to help automate and reduce mundane and tedious tasks in development and testing.
Sam Altman is a technology entrepreneur and investor.
Born in St. Louis, Missouri, he is the CEO of OpenAI, a research organisation that aims to advance artificial intelligence in a responsible and safe manner.
After dropping out of Stanford University as a computer science student in 2005, Altman co-founded the location-based social networking company Loopt, which provided a service for smartphone users that allowed them to share their location selectively with other people and was acquired by Green Dot Corporation in 2012.
He then served as the CEO of the technology incubator Y Combinator from 2014 to 2017. During his tenure, Y Combinator funded and supported many successful startups, including Airbnb, Dropbox, and Reddit.
Altman has also been an investor in various technology companies through his investment firm, Altman Ventures. He has served on the boards of directors of companies
such as OpenGov and Optimizely, and has advised numerous other startups.
As an advocate of nuclear energy, Altman is also chairman of the board for Helion and Oklo, two nuclear energy companies.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Altman helped fund and create Project Covalence which aimed to help researchers rapidly launch clinical trials in partnership with TrialSpark a clinical trial startup.
With all his hard work at Y Combinator and YC Group, Altman was recognised as a top investor under 30 by Forbes in 2015.
US$43.4mn
Loopt sold to Green Dot Corporation in 2012
Setting his sights on founding his own company, Altman co-founded OpenAI in 2015 with Elon Musk and other entrepreneurs. To fully focus on his new company. Altman transitioned to Chairman of YC in 2019.
2015:
Formation of OpenAI announced by Altman, Elon Musk, Greg Brockman, Reid Hoffman, Jessica Livingston, Peter Thiel, Amazon Web Services, Infosys, and YC Research
Since OpenAI’s founding, Altman and his team have released GPT-3, a language model trained on trillions of words from the Internet, the image creating tool DALLE 2, and last year released to the public the ultra powerful AI chat bot ChatGPT.
thoughts on the
revolutionary ChatGPT as a ‘preview of progress’ and how artificial general intelligence is the next breakthrough

“[ChatGPT] is a preview of progress; we have lots of work to do on robustness and truthfulness”
GPT-3 (short for "Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3") is one of the largest and most powerful language models currently available, with a capacity of 175 billion parameters. GPT-3 can be fine-tuned for a variety of language tasks, such as translation, summarisation, and question answering, and has been used to generate human-like text in a variety of settings. It has received significant attention in the media and the technology industry due to its impressive performance and potential to revolutionise natural language processing.
Unlike previous iterations of the GPT model, ChatGPT is specifically designed to serve a chatbot function. However, unlike other chatbots or intelligent software assistants, ChatGPT is much more adept at engaging in dialogue with its users and can even respond to feedback, request clarification, and iterate on its answers based on a user's response.

“
There will be scary moments as we move towards AGI- level systems, but the upsides can be so amazing that it’s well worth overcoming the great challenges to get there”
Please provide a creative idea for a magazine cover that would illustrate the huge popularity of ChatGPT at the start of 2023 and how the world needs to be ready for artificial intelligence everywhere.

In a tweet in December, Altman said it would be "a mistake to be relying on it for anything important" and that it's currently merely "a preview of progress" rather than the finished product.
“ChatGPT is incredibly limited but good enough at some things to create a misleading impression of greatness,” he said. “It's a mistake to be relying on it for anything important right now. It’s a preview of progress; we have lots of work to do on robustness and truthfulness.”
Microsoft backed OpenAI with $1bn in investment back in 2019. The two companies formed a multi-year partnership to develop artificial intelligence supercomputing technologies with the help of Microsoft's Azure cloud computing infrastructure.
Following ChatGPT’s launch, Altman said artificial general intelligence (AGI) will be the next major technological breakthrough, offering “amazing” upsides but also major challenges.
“There will be scary moments as we move towards AGI-level systems, and significant disruptions, but the upsides can be so amazing that it’s well worth overcoming the great challenges to get there,” he wrote.
“And we’ll see great benefits all along the way – they will make ChatGPT look like a boring toy. In particular, there are going to be significant problems with the use of OpenAI tech over time; we will do our best but will not successfully anticipate every issue.”

SVP Product, SambaNova
SambaNova Systems SVP of Product
Marshall Choy speaks to AI Magazine about Dataflow-as-a-Service and the key role of AI in digital transformations

An experienced products and solutions leader, Marshall Choy, SVP of Product at SambaNova Systems, is skilled in AI/ ML, cloud, data centre, management, pre-sales, solution architecture, and technical leadership. Having held previous roles at Oracle and Sun Microsystems, he joined SambaNova in 2018.
Q. Tell me about SambaNova, your role and your responsibilities there?
» SambaNova turned five years old last November. We’re a growth-stage start-up, focusing on developing and delivering game-changing deep-learning products and solutions. Our mission is to develop the capabilities that enable businesses and organisations to transform their technology stack and accelerate their business with deep learning.
My responsibility, as Senior VP of Product, is to oversee the definition, development, design, and delivery of our products. I work closely across all organisations – both internally and externally – with our customers and partners. What I find most exciting about my role is being able to touch every aspect of the product development lifestyle. From ideation to deployment at a customer site, I get to know every organisation and person involved in the process.
Q. Why do you think AI is critical for a company’s digital transformation journey?
» AI is critical not just as the enabler, but as the accelerant for a company’s digital transformation journey. It is the driving force for businesses today and in the future. When you look at prior digital transformations in the last couple of decades, two milestones come to mind. More recently, it’s the advent
of mobile computing; before that, the big bang that was the internet. I believe AI will have an even greater magnitude of impact than the last two technology shifts we’ve seen over the last 20 years or so.
AI has the potential to reshape the Fortune 500, just like the internet did. Established, decades-old players could fall away while unknown, disruptive challengers could rise and become the next leaders of industries. The defining factor determining the winners will be their adoption of AI: to ride out the coming wave, or rise to the top, companies need to adopt AI as a key tenet of their digital transformation strategy.
Digital transformation driven by AI has massive implications across three significant areas: first, and most obviously, is the technology stack; second is the way that AI will transform the business processes and operations of the firm; third, and perhaps most importantly, is the transformation that AI will have on the organisation.
AI will change the nature of work. This is because AI-enhanced automation can take over tasks that are mundane, repetitive, and error-prone when performed by a human. This allows humans to operate in a more strategic manner and perform more innovative, creative, or emotional tasks –in short, more innately human activities.
“A key learning we have taken from our customers is that many are moving from model-centric computing to datacentric computing”
How do you structure your organisation to really harness this potential? Such change begins from the top, at the C-level. Engagement, ownership, governance, and investment into centres of excellence. These are the keys to fostering an AI-driven culture throughout the organisation. A means to make the firm not just a user of AI to start off with, but – in the end – a firm that has been totally transformed by AI. In effect, an ‘AI-native’ organisation.
» Dataflow-as-a-Service is an evolution of SambaNova’s product offerings. It supports customers ideally as it has been 100% driven by customer feedback since the first iteration. A key lesson we have taken from our customers is that many are moving from model-centric computing to data-centric computing. Dataflow-as-aService enables end-users to engage with AI computing from a data-centric standpoint. It provides the machine learning model and the underlying infrastructure, right-sized, and made available in an applicationfriendly, accessible way through APIs. Gone are the days when end-users need years of experience developing machine learning models. SambaNova selects and provides the optimal model for the use cases that the customer needs. We make these models
accessible through said APIs and ensure they can be plugged in effortlessly at the application level.
This leaves the end-user customer to focus on their areas of expertise: their dataset and their applications. The rest of AI transformations’ complexity can be left to SambaNova, provided to them as-a-Service.
» There are two trends happening right now that are transforming how AI is being used in organisations, which is ultimately changing how we work.
The first is the growth of multiple model deployments. This is the convergence of different types of AI models within a single pipeline – one well-known example is the combination of natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision that has resulted in OpenAI’s DALL-E 2.
Another more practical multiple model example is in language models pulling out anomalies in a text-log that are subsequently fed into a recommendation algorithm. We all know recommendation engines from the ‘you bought this, perhaps you’d like this’ use case in ecommerce, but in the context of an NLP model, it can be leveraged to provide a recommendation of the next best action to a support analyst when remediating the anomaly seen in the text log.
“AI has the potential to reshape the Fortune 500, just like the internet did. Established, decadesold players could fall away while unknown, disruptive challengers could rise and become the next leaders of industries”
The second trend I’m seeing is the convergence of machine learning models. Go back just three years and there were hundreds of new research papers about machine learning models coming out each week, with there being concerns that model growth was out of control. Now, the trajectory has reversed. There’s less specificity and more generalisation, which is resulting in a more finite number of models.
Q. What is next for SambaNova, what can we expect in the future?
» Stay tuned for the specifics of what’s coming next for SambaNova. However, where we’re seeing the market moving, in terms of customer demand for many companies is, again, more towards data-centric computing driven by AI. As the first movers accelerate past their peers then the rest of the market will naturally want to follow them.

The real challenge in the near future in this industry is the skills crunch. We ran some research recently that found over 80% of enterprise tech managers are struggling to hire AI talent and over half are finding retention a challenge too.
Businesses want to adopt AI models in various aspects of their organisation and this change is coming from the top – the C-suite and leadership team. If you think about it, we’re already very much in an AI-driven world, so AI should be at the heart of business strategy. It's just that not every business realises it yet.


 WRITTEN BY: ALEX CLERE
PRODUCED BY: BEN MALTBY
WRITTEN BY: ALEX CLERE
PRODUCED BY: BEN MALTBY


When Christine (Jang) Tan talks to us from her office in Singapore, she has just returned from Sibos – the landmark financial conference held in Amsterdam. It’s a major event for J.P. Morgan. Indeed, several of the company’s executives participated in panel discussions and debates at the conference, held in person for the first time in three years.
J.P. Morgan showcased Confirm powered by LIINK, a global account validation service designed to enhance the efficiency of crossborder payments. Confirm runs on the ONYX platform, the firm’s blockchain division. Confirm is the world’s first bank-led, production-grade, peer-to-peer blockchain network that has the ability to verify over 2bn bank accounts from over 3,500 financial institutions1,2

“We are propelling solutions that address the demands of customers globally – that means they need to be agile, nimble and frictionless,” says Jang. “We have that ability, as we can leverage global infrastructure and incorporate local best practices to our solutions, customising them to the specific client and industry segments, including strategic partnerships to enable an endto-end payments ecosystem. We also featured our cross-currency proposition customised for banks, fintechs, corporates, and non-bank FIs.”
1 Expected estimates on number of institutions, number of accounts and number of corridors on Confirm are calculated based on projections from market research and incoming clients in Confirm’s pipeline and are subject to change. 2 All estimates on number of institutions, number of accounts and number of corridors include data from J.P. Morgan as a Responder and Inquirer on Confirm.
Example of an image captionJ.P. Morgan, led by the ONYX team, also attended the Fintech Festival in Singapore. As a key foreign bank, the team is working closely with various central banks around the world, including the Monetary Authority of Singapore. The aim of this is to support new areas of innovation leveraging blockchain technology, with the goal of enabling the movement of money to be faster, better, more cost effective, and take place in a secured manner.

 CHRISTINE (JANG) TAN Head of FIG Sales APAC, J.P. Morgan Payments
CHRISTINE (JANG) TAN Head of FIG Sales APAC, J.P. Morgan Payments
“WE BELIEVE THAT SEAMLESS AND SECURE PAYMENT SOLUTIONS CAN HELP OUR CLIENTS AND THEIR BUSINESS… TO GROW, DIVERSIFY, AND THRIVE”
Jang works in J.P. Morgan’s Payments business, heading up Financial Institutions
Group Sales in APAC. Not only is Payments a key part of J.P. Morgan’s push in redefining the future of finance, APAC is also a region that has historically been at the forefront of innovation with real-time payments and continues to be a torchbearer to this day.

“We operate with in-country presence in 16 markets,” Jang says. “We support 18 markets from a client segment standpoint within Asia.”
And then of course they move their flows on a global basis. In APAC alone, the Payments business operates hubs in Manila and Mumbai, which facilitate
some of the treasury services and trade processing that J.P. Morgan carries out on behalf of its clients.
J.P. Morgan is regarded as the number one US dollar clearing bank globally, processing almost US$10tn a day in payments.
With such large volumes at stake, the company is keenly aware of its responsibilities around cybersecurity and protecting clients’ money. “That cybersecurity aspect is very critical and in our connections with all the banks, that's one of their key priorities – to have not just a

trusted partner who innovates, but the ability to execute securely,” Jang says. “That's very critical, particularly in Asia where you've got a lot of central banks as well as regulators and a complex landscape.”
Sheer volume means cyber becomes key focus
That duty of care comes with expected levels of best practice: large financial institutions and emerging fintechs alike expect their partners to act impeccably, particularly when it comes to complying with legal
Christine (Jang) Tan is Managing Director and Head of Asia Pacific – Financial Institutions Group for J.P. Morgan Payments, based in Singapore. In this role, she has leadership responsibility for banks, broker-dealers and non-bank financial institutions portfolios across the region, providing strategic advice and growing the business with both existing and new clients.
Prior to this position, Christine was Head of Treasury Services, ASEAN responsible for embedding the endto-end Treasury Services model across Indonesia, Malaysia, Pakistan, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam, ensuring resilience and robustness in product offering, service model and control environment.

She was also Head of Multinational Corporates (MNCs) for Asia Pacific for five years and has a wealth of MNC experience in the region across multiple key markets.
Christine joined J.P. Morgan from Bank of America Merrill Lynch (BAML), where she was Head of Regional Treasury Sales for South Asia, with responsibility for developing and executing the
sales strategy for pan-Asia subsidiary businesses of multinational clients and for large corporates in the region.
Prior to her time at BAML, Christine spent 12 years at Citi in a number of regional roles, including head of the Hong Kong Global Subsidiaries Group.

Christine also worked as an analyst covering Asian airlines and airports earlier in her career, where she also engaged in aircraft financing through structured trade finance, global cash management and fuel hedging for airlines.
Christine holds a Master of Business Administration and a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration from the

and regulatory obligations or safeguarding systems from attack. “While we do share best practices, we also expect the same in terms of the companies [that we partner with] actually adhering to certain standards. It's really to protect the entire community.”
When she looks at how J.P. Morgan is likely to invest its resources in the future, Jang says: “We have to keep developing, and there has to be a cyber component that we continue to invest in. On blockchain, the use cases will continue and we've leveraged Confirm as one of our applications for banks, non-bank financial institutions, corporates and fintechs to use.
“We also just recently had the announcement with VISA B2B, who will be leveraging Confirm to facilitate their payment flows cross-border as well.”
When you’re working at such an astronomic level, it takes some bright-shining stars to inspire you. Within J.P. Morgan, Jang says she looks up to Takis Georgakopoulos, the Global Head of J.P. Morgan’s Payments division. “He was previously my boss when he ran the MNCs Corporate Banking business, and brings a unique strategic background to his current role. His vision of bringing together four discrete businesses under a single Payments umbrella is what differentiates us today, enabling the bank to provide end-to-end pay-in, pay-out cash management and trade finance capabilities to our clients. Today, we process almost US$10tn in payments daily in more than 120 currencies and over 160+ countries across the world, and we’re only getting started on this journey.”
A Singaporean native, Jang takes inspiration from the country’s late founding father and first prime minister, Lee Kuan Yew, as well.
“Mr. Lee put Singapore on the map, and the financial services industry
 CHRISTINE (JANG) TAN
Head of FIG Sales APAC, J.P. Morgan Payments
CHRISTINE (JANG) TAN
Head of FIG Sales APAC, J.P. Morgan Payments
“WE ARE WORKING GLOBALLY ON OPPORTUNITIES TO LEVERAGE [ BLOCKCHAIN ] TECHNOLOGY AND THEN APPLY THEM TO VARIOUS REQUIREMENTS AND SOLUTIONING”
thrived under his leadership,” Jang says. “It's been growing as a key financial hub globally so I’m really inspired by his journey running the country.”
Within its payments business in APAC, J.P. Morgan takes an approach that Jang calls the ‘three Cs’: client, collaborator and competitor.
On a client side, the firm is obsessively focused on innovating to support its clients with the rollout of new features and functionality. J.P. Morgan is a co-founder – alongside Singaporean bank DBS and sovereign fund Temasek – of an entity called Partior. The vision for Partior is to facilitate multi-bank settlement on the blockchain in multiple currencies. The firm has facilitated live transactions settling Singapore and US Dollars, and is in the process of adding settlement banks to facilitate additional currencies – including Euros, Japanese Yen and Chinese Renminbi.



 CHRISTINE (JANG) TAN Head of FIG Sales APAC, J.P. Morgan Payments
CHRISTINE (JANG) TAN Head of FIG Sales APAC, J.P. Morgan Payments
“THE CYBERSECURITY ASPECT IS VERY CRITICAL AND IN OUR CONNECTIONS WITH ALL THE BANKS, THAT'S ONE OF THEIR KEY PRIORITIES”
For J.P. Morgan, collaboration is key to growth in the Payment business. A prime example is the partnership with European car manufacturer Volkswagen to create Mobility Payments Solutions, focused on the future of cars and how payments can drive innovation through the auto segment. The company continues to look at additional partnerships that it might leverage in Asia – whether that’s with fintechs, aggregators, financial institutions, nonbanks or corporates. The firm also conducted strategic acquisition and alliances with Cleareye.AI, and the latest in-region partnership was with In-Solutions Global (ISG), a leading payment solutions provider.
“Those are collaboration aspects where we would look at whether we want to partner with them, invest in them, and then leverage their technology to support our solutions at the end of the day,” Jang explains.
Finally, on competition, J.P. Morgan does not allow its size or scale to cloud its judgement of rivals in the market. “Clearly we do face competition, with fintechs these days becoming more prevalent,”
Jang elaborates. “But I do think having competition is healthy. Ultimately, it’s about benefitting the consumers who have the ability to choose their payment options – whether it's through banks, wallets or fintechs. And J.P. Morgan wants to be part of partnerships that deliver for clients.”
Jang is a firm believer in the possibilities brought about by blockchain, and expects the decentralised technology to form a key pillar of J.P. Morgan’s strategy as the company prepares for the future of payments. Jang explains: “We are working globally on opportunities to leverage the technology and apply them to various requirements and solutioning
– whether it's on the markets front, tokenisation, real-time movement of money and cross-border payments.”
In addition to using SWIFT and ISO as the payment rails for cross-border transactions, J.P. Morgan is seeking to improve the sharing of data in real-time with Liink – the world’s first bank-led, productiongrade, peer-to-peer blockchain network for information sharing – and Confirm, an application for global account validation. This will reduce timescales for banks, cutting down on laborious tasks that need to be carried out manually while lowering rejection rates at the same time.
The company is working with a lot of different companies to facilitate cross-

border exchange of that data into different corridors, particularly when it comes to demand for remittances associated with overseas workers, who want to send money back home to markets like Indonesia, India, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka to support their family and communities. J.P. Morgan is expanding the service into the Philippines, Vietnam and Thailand.


As she looks ahead to a promising future – one in which J.P. Morgan will play an undoubtedly pivotal role – Jang neatly summarises the pin-sharp focus of its Asia Pacific payments team: “We believe that seamless and secure payment solutions can help our clients and their business to grow, diversify, and thrive by enabling rails for companies, financial institutions, and
consumers to pay anyone by any method or channel from anywhere, anytime.” It’s not a straightforward brief – end-users want everything, and they want it now – but if any company has the track record behind it to make it happen, it’s J.P. Morgan.

AI and robots are not here an IT skills gap means many a bright future – if they
GEORGE HOPKIN
here to take your job. In fact, many human employees have stay ahead of the curve
Despite what you may have heard, the rise of robots and AI in the workplace is no reason to panic. Employees can, in fact, supercharge their career opportunities if they adapt to these new technologies, say experts.
But human resources departments and boardrooms will have to successfully surf the wave of change if they are to introduce and promote a virtuous cycle of technology use and valuation in the workplace.
Attention-grabbing headlines about technology laying waste to entire industries could cause business leaders to work with an inaccurate picture of the reality on the ground, a point supported by a Brigham Young University study in the US discovered people are prone to exaggerate the rate at which their careers may be ended by technology.
“Overall, our perceptions of robots taking over is greatly exaggerated,” says Brigham Sociology Professor Eric Dahlin. “Those who hadn’t lost jobs overestimated by about double, and those who had lost jobs overestimated by about three times.”
These findings are consistent with previous studies, says Dahlin, suggesting that workplaces integrate employees and robots in ways that generate more value for human labour.
“An everyday example is an autonomous, self-propelled machine roaming the aisles and cleaning floors at your local grocery store,” he says. “This robot cleans the floors while employees clean under shelves or other difficult-toreach places.”
The aviation industry offers another example of robots and humans working together, as Dahlin explains: plane manufacturers have used robots to paint
wings at a rate of one coat of paint in 24 minutes, something that would take a human painter hours to accomplish. Humans are nevertheless required to load and unload the paint while the robot does the painting.
A separate report from MIT Sloan Management Review and Boston Consulting Group (BCG) found that 60% of employees
have already welcomed AI as a coworker. Organisations with employees working well with AI are 5.9 times more likely to see significant financial benefits than organisations that are not using AI.
The report, Achieving Individual – and Organisational – Value With AI, indicates individuals derive personal value from AI when using the technology, which improves self-determination.
“When individuals don’t know that they are using AI, they have a harder time recognising its value”
FRANÇOIS CANDELON MANAGING DIRECTOR & SENIOR PARTNER, BOSTON CONSULTING GROUP







"AI use in business is now pervasive,” says Sam Ransbotham, Professor of Analytics at Boston College. “Many technologies have embedded, even hidden, AI components that workers may not even be aware of. When everyone is using AI to some degree – and getting value from it – familiar tropes become problematic. The idea that managers who use AI will replace managers who don't, loses meaning when everyone is using AI."
AI use is so pervasive, in fact, that individual workers may take some of its applications for granted. According to the findings, 66% of individuals report that they do not use AI or use it only minimally. But when prompted with specific examples of AI-enhanced business applications –office productivity applications, calendar schedulers, and customer relationship management software, for example – 43% of respondents acknowledge they regularly or sometimes use business products with AI.
“When individuals don’t know that they are using AI, they naturally have a harder time recognising its value,” says François Candelon, Global Director of the BCG Henderson Institute and coauthor of the report. “But our research shows that employees using AI knowingly are 1.6 times more likely to get individual value, and 1.8 times more likely to be satisfied with their jobs, than those who do not realise they use AI.”
The survey revealed that many respondents think that using AI has improved interactions with their team members (56%), with their managers (47%), and with other people in their departments (52%), in addition to helping them feel more capable in their job performance.
“To obtain the financial and organisational benefits of AI, managers must promote a virtuous cycle of use and value at the individual level by cultivating trust, understanding, agency, and awareness of the technology,” says Shervin Khodabandeh, a Senior Partner and Managing Director at BCG, co-leader of GAMMA in North America, and a co-author of the report. “The relationship between individual and organisational value from AI is additive, not zero-sum.”
“When everyone is using AI to some degree, familiar tropes become problematic”
SAM RANSBOTHAM PROFESSOR AT BOSTON COLLEGE; AI EDITOR AT MIT SLOAN MANAGEMENT REVIEW
Those employees who do get to grips with data analysis, cloud services, AI and machine learning find there is a world of new opportunities as companies scramble to keep up with expansion plans.
Research by digital infrastructure company Equinix discovered 67% of IT decision-makers in the UK view a shortage of personnel with IT skills as one of the main threats to their business, while 61% acknowledged that the skills’ shortage has been exacerbated by the speed at which the tech industry is being transformed.
Equinix’s 2022 Global Tech Trends Survey found that, across the globe, the most in-demand tech employees are IT technicians (27%), cloud computing specialists (26%) and those with an aptitude for AI and machine learning (26%).
Other skills shortages raised in the research include data analysis (21%), data protection (21%), security software development (19%) and security analysis (18%). Globally, IT leaders anticipate that the gaps in tech skills will remain similar in the future, with AI/machine learning becoming even more in demand.
“The skills’ gap is present across the entire tech industry, but is particularly acute in operations roles where the rapid pace of change means the workforce needs to be constantly upskilled and expanded,” says Gary
Aitkenhead, Senior Vice President, EMEA IBX Operationsat Equinix.
“Overall, our perceptions of robots taking over is greatly exaggerated”
ERIC DAHLIN BRIGHAM SOCIOLOGY PROFESSOR

 PRODUCED BY: CRAIG KILLINGBACK
PRODUCED BY: CRAIG KILLINGBACK
LivaNova is a global medical technology company built on decades of experience and a strong commitment to their patients. Their focus is on transforming lives with products and therapies for the head and heart, operating in Cardiopulmonary, Neuromodulation and Advanced Circulatory Support technologies.
For LivaNova, it’s health innovation that truly matters Their diverse product portfolio and pipeline include the following therapeutic areas:
• Advanced Circulatory Support
• Cardiopulmonary
• Difficult-to-Treat Depression
• Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
• Heart Failure
• Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Their Chief Procurement Officer (CPO), Jérôme Lesenechal, has spent his entire career in Procurement, coming from 17 years’ experience in Automotive, through multiple categories, before joining LivaNova in February 2018.
Lesenechal leads the global Procurement team in charge of strategic sourcing activities, both for indirect services and for direct material, as well as new product development.

LivaNova’s CPO, Jérôme Lesenechal, chronicles what it takes to provide life-changing medical services through technology, procurement and innovation

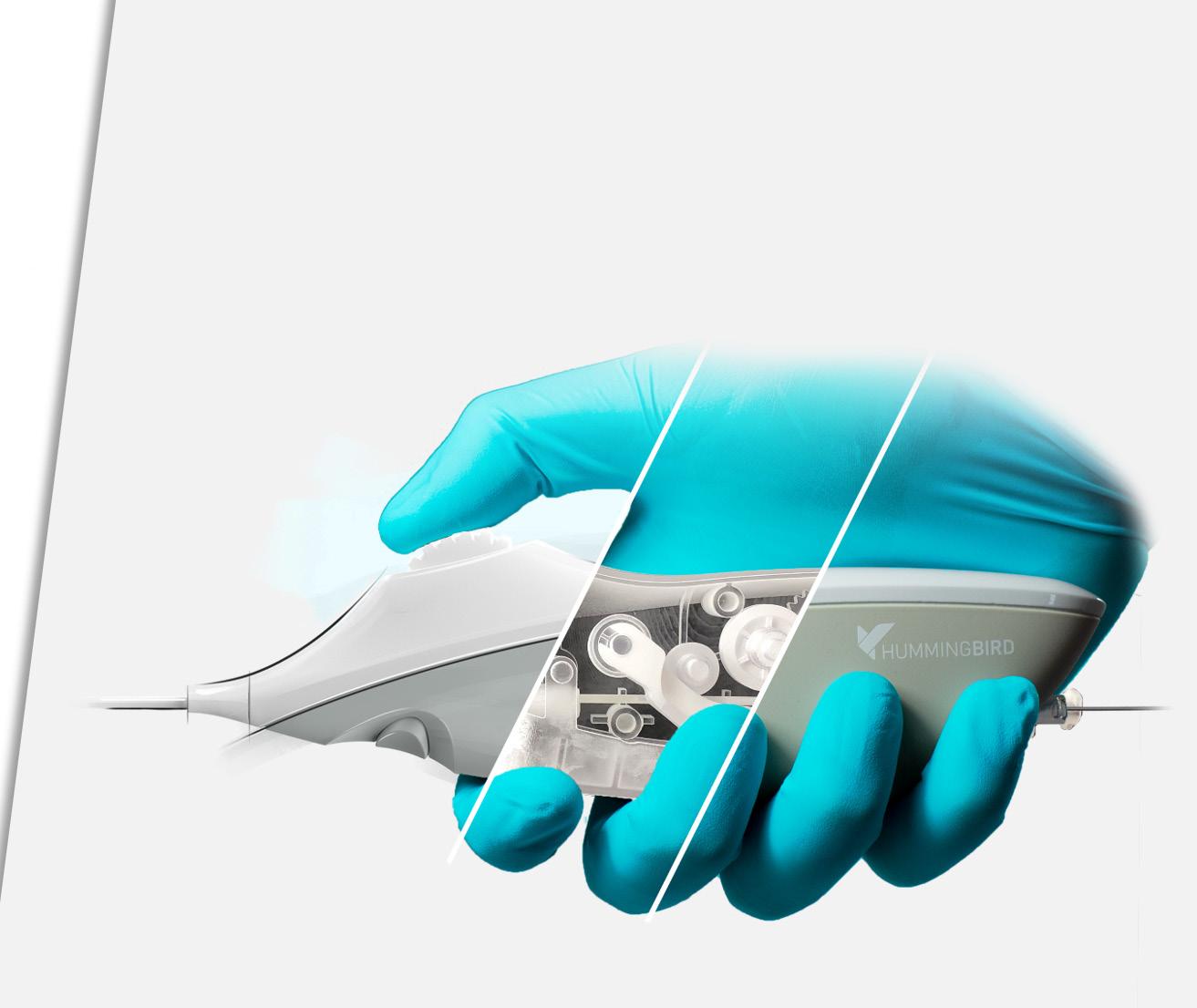
When LivaNova needed a medically certified touchscreen computer to communicate with their new revolutionary perfusion system monitors they turned to Teguar, who assembled a team of product design specialists and developed a custom computer meeting every single requirement of LivaNova’s requests.

Medical computers manufacturer Teguar on why its latest work on LivaNova’s heart & lung machine was so rewarding
It might be said a healthy bottom line is the most gratifying thing for a business leader, yet for organisations working in the medical sector, saving and improving lives offers rewards that are on another level entirely.
Teguar builds medical and industrial computers, and its CEO, Jonathan Staub says one recent project in particular “felt extremely important” – its contribution to the development of the hardware component of the Essenz Patient Monitor, a medical device that is used by clinicians during Cardio-pulmonary bypass procedures.
The project saw Teguar working with LivaNova, a global medical technology company that specialises in products and therapies for the head and heart.
LivaNova tasked Teguar with providing the hardware
component of the Essenz Patient Monitor, a medical device that provides continuous, advanced and insightful data to show the key parameters at all times during a case. “Cardiopulmonary bypass perfusion supports patients during open heart surgical procedures, by taking over the function of the heart and lungs,” Staub explains.
Teguar developed an all-in-one touch-screen PC that met the exacting specifications that all medical electrical equipment have to satisfy, for the performance of highly invasive procedures. But as well as this, Staub says it was hugely important that the PC was also pleasing on the eye. “We pride ourselves on the elegance of our products,” he says. “Elegance is an important part of who we are and what we do.”

Among the important services Teguar provides to customers is long-term availability of computer components – vital for healthcare equipment that customers might not be able to afford to replace for many years. The company also has “an experienced and agile” global team that can meet customers’ needs.

So what was it about the LivaNova opportunity that drew Teguar in?
“LivaNova’s mission is to support perfusionists and their patients during lifesaving procedures,” says Staub. The Essenz Patient Monitor is the realisation of this mission.
“That we could be a crucial part of the development of such a cutting-edge medical computer was an exciting opportunity and a challenge to us.”
“This means our responsibilities go from clinical studies to spare parts management, through serial production and corporate services,” he says.
The relationship between a MedTech company like LivaNova and their suppliers is, of course, crucial: in the end, the quality of those relationships will determine patient outcomes.

“Suppliers share our values,” says Lesenechal, “especially our purpose to improve the lives of patients (which speaks to one of our core values, ‘patients first’).
“I consider myself as accountable for the healthcare supply chain, and our suppliers are doing so, too.”
Supplier relationship management, in MedTech and beyond, has been growing to a level of importance higher than ever before. Contract obligations or Purchase Price Management are not enough to manage ongoing supply chain disruptions anymore, and it’s not only about the power dynamic between the company and its suppliers.
"There is an urgent need to extend the company's borders to external partners,” Lesenechal says, “because together, we are stronger and more creative in anticipating and fixing problems.
“The CPO especially needs to orchestrate brainstorming sessions with suppliers; this can be to get support for a
“I CONSIDER MYSELF AS ACCOUNTABLE FOR THE HEALTHCARE SUPPLY CHAIN, AND MOST OF OUR SUPPLIERS ARE DOING SO, TOO”
LivaNova: Transforming lives through MedTech and Procurement
JÉRÔME LESENECHAL CHIEF PROCUREMENT OFFICER, LIVANOVA
difficult-to-source component, to drive a game-changing design evolution, or to influence business decisions.”
Lesenechal expresses that he has, on several occasions over the last few years, seen that the value coming from that type of co-working is very high, compared to a standard purchase price discussion.
Regarding internal stakeholders, he believes that procurement must play a strong role in Product Lifecycle Management.
From supplier selection in a new product design phase to the phase-out of another one through the proactive management of the obsolescence risk, Lesenechal maintains that procurement’s partnership with R&D and marketing can have a massive impact on the sourcing agility, as well as the profitability per product – and that this is what procurement must drive.
Developing second sources, having a dynamic process of redesign for electronics, and revisiting specifications to make them easier to source are key.
“What we call ‘Sustaining R&D’ must now be fully integrated into procurement´s strategy, as well as to the daily management of supply issues,” he says.
People development ‘beyond resilience’ Resilience is becoming quite a common topic, and not only in business circles.
“Resilience remains super important, and management must keep working on it, but I
TITLE: CHIEF PROCUREMENT OFFICER
INDUSTRY: MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
MANUFACTURING
LOCATION: MUNICH, GERMANY
Jérôme Lesenechal was named CPO of LivaNova in August of 2020. His role includes leading the global team responsible for the success of Liva Nova‘s Material and Services Procurement, ranging from contract negotiations to supply chain remediations, delivering consistent operational results for LivaNova customers.

In January of 2021, his role was expanded to include Replenishment Process transformation to answer to the global disruptions in Supply Chain. With this added responsibility, he works with teams across Production Planning, Tactical Purchasing and Logistics to continue the modernisation of critical supply processes that team members use to deliver a reliable and predictable replenishment.
“Procurement can leverage its new image and influence to move from an ‘instructions-taking’ department to a ’decision-making’ one.”
Before this, Jérôme was Global Director of Procurement for New Product Development at LivaNova, where he led multi-year sourcing projects to increase LivaNova‘s portfolio. He began his career in the automotive industry at Peugeot SA by leading multiple categories, as well as global sourcing activities.
believe the new profile of a strategic buyer must go beyond that, to reach a kind of ‘extreme ownership’,” he says.

Lesenechal understands that, first, procurement needs to realise that its role is now a key to success in troubled times. “Yes, it comes with many responsibilities, but it is also a noble purpose to secure the healthcare supply chain. Procurement must be super proud about that!”

Second, he holds that procurement can leverage this new image and influence to move from an ‘instruction-taking’ department to a ’decision-making’ one.
He says: “For those who were able to navigate across the 2020-2022 period
with success, the gain in credibility to the executive leaders opens new possibilities of challenging the status quo.
“Then, the coaching that procurement can provide to a cross-functional team can be very valuable, for example to speed up the implementation of a new design, giving the supplier a seat in this cross-functional team. The ‘new-gen buyer’ is now a mix of programme manager and marketing influencer, on top of the traditional skills of negotiations and strategic leadership.”
On one side of the value stream, it’s important for procurement executives to leverage the suppliers’ own market intelligence to predict the unexpected. Lesenechal thinks that all these risk assessments and information are very valuable intelligence that can be used at
the highest level of the company to orient the global strategy.
On the other side of the value stream, you have the customer, or ‘the user’. Here, too, there is a need to develop and quickly

“AS LONG AS WE STAY CLOSE TO THE PATIENTS, THE USERS AND THE CLINICIANS TO UNDERSTAND THEIR NEEDS AND TRANSLATE THEM INTO SPECIFICATIONS, THE MEDICAL DEVICE INDUSTRY WILL KEEP ITS HIGHPERFORMANCE STANDARD”
JÉRÔME LESENECHAL CHIEF PROCUREMENT OFFICER, LIVANOVA
reinforce the relationship with the company's sales organisation, and with the final user.

“You will collect amazing data (about competition, about new needs, new market insights etc) that can influence your procurement strategy,” says Lesenechal. “I can tell you that you behave very differently when you know that a hospital has been waiting months for oxygenators for children, or that your main competitor is not predictable with its delivery plan anymore”.
Another layer of complexity is for LivaNova to procure, and thereby provide, these critical medical services, whilst balancing that against its Net-Zero ambitions.

And procurement is not only screening the current state: LivaNova also includes ESG considerations in each decision, in collaboration with corporate leaders.
Suppliers represent a large portion of their products’ bill of materials (BoM), and their customers also rely on them to control supplier engagements.
LivaNova’s next step will be to set up targets together with their suppliers internally, (travel, company cars, etc) for the commodities that are under management by procurement.
Continuous improvement on processes such as logistics can also help considerably. Redesigning the packaging, revisiting the supplier’s footprint to avoid long lead-time logistics – every decision can decrease the carbon emission of their sourcing activities and make their BoM more compliant with new and emerging regulations.
“FOR THOSE WHO WERE ABLE TO NAVIGATE ACROSS THE 2020-2022 PERIOD WITH SUCCESS, THE GAIN IN CREDIBILITY TO THE EXECUTIVE LEADERS OPENS NEW POSSIBILITIES OF CHALLENGING THE STATUS QUO”
Customers are prepared to reward companies that make ESG a central part of their mission.
“Procurement needs to act in a similar way and award business to the best suppliers in ESG,” says Lesenechal. “I believe that selecting a supplier with a very good rating can lead to better business for LivaNova and make us even more competitive in tenders.
“Given the way we need to balance deviations with additional action items to put us back on track, it’s easy to see why procurement needs to develop the right battle plan with stakeholders and suppliers.”
LivaNova’s partnership with Teguar
LivaNova’s partnerships are crucial to helping them achieve their goals. One of their main partners is Teguar, an industrial and medical computer company.
Jonathan Staub (CEO of Teguar) and Lesenechal have been working very closely for many years to drive a new development.
The collaboration keeps LivaNova’s configuration as standard as possible, both to contain costs and to ensure the right design-to-source.
Lesenechal says: “There is no way that LivaNova or Teguar can influence market trends in consumer goods technology like laptops, but, together with the cross-functional team, we were able to limit customisation and other exotic specifications. This leads to better profitability on both sides, as well as better material availability for the sub-components.
“I need here to underline the great collaboration with our marketing and our programme management. Our team always managed the relationship with a dynamic and constructive approach.
“On its side, Teguar always challenged our requirements and design changes in the right way – and this is exactly what I expect from all my suppliers – helping us to bring to the market a product that will be sustainable both in terms of supply and costs of goods.”
Lesenechal is confident that LivaNova´s pipeline will match with customers’ expectations. “As long as we stay close to the patients, to the users and to the clinicians in order to understand their needs and translate it into specifications, the medical device industry will keep its high-performance standard.”
LivaNova’s products and therapies are used worldwide. With a presence in more than 100 countries, their team of approximately 3,000 talented people works to improve and sustain patients’ quality of life each and every single day.


Orienting to the future, Lesenechal says: “I believe the supply chain disruptions will remain my biggest focus in 2023, especially in electronics, costs containment and logistics management.
“We will continue our transformation of the replenishment process, and reinforce our partnerships with our strategic suppliers further. More than ever before, the integration of our suppliers into the company's strategy can make a difference in the design of sustainable products that fit with the market's expectations and in remaining predictable in lead-times despite all the headwinds.
“The last discussion I had some weeks ago with perfusionists and scientists from Belgium convinced me that these are procurement´s main missions for the near future. I am confident that LivaNova´s pipeline will match with customers’ expectations. As long as we stay close to the patients, to the users and to the clinicians in order to understand their needs and translate them into specifications, the medical device industry will keep its highperformance standard.”
Major changes in technology, as well as the industry as a whole, are opening doors for important transformations.

In closing, Lesenechal says: “Areas we expect to grow or continue to grow in importance in the Medical Device industry are: 1) direct-toconsumer engagement, which has been a key for pharmaceuticals for years, but is just starting to gain traction in our market; 2) a continued shift toward less invasive/wearable diagnostics that can be used in the home setting; 3) better connectivity between implantable devices and patients and physicians with apps and the cloud; 4) more effective ways to meet with and train physicians remotely, including the use of AR/ VR technology; and 5) a continued shift toward more investment in clinical evidence to drive awareness, adoption and reimbursement”

“WHAT WE CALL SUSTAINING R&D MUST NOW BE FULLY INTEGRATED INTO PROCUREMENT’S STRATEGY, AS WELL AS TO THE DAILY MANAGEMENT OF SUPPLY ISSUES”
JÉRÔME LESENECHAL CHIEF PROCUREMENT OFFICER, LIVANOVA

Since the introduction of what most would consider to be modern cruise control in the late 1940s, driving has become increasingly automated. Modern vehicles can slow and stop in reaction to other vehicles around them, stay in lane and even drive for short distances without a guiding hand on the steering wheel.
But, up to this point, true automation has eluded a market valued at approximately US$25bn last year, with the holy grail – level 5 automation – still seemingly in the distance.

SAE, the Society of Automotive Engineers, determines vehicles' intelligence level and automation capabilities, ranking from 0 to 5. The most widespread autonomous systems, such as Tesla’s autopilot software, fall into level 2 or 3.
While level 3 vehicles can make informed decisions for themselves such as overtaking slower-moving vehicles, they still require human override when the machine is unable to execute the task at hand or the system fails.
The key difference between level 3 and level 4 automation is that vehicles in the latter category are able to intervene themselves if things go wrong or there is a system failure. In this sense, these cars are left completely to their own devices without any human intervention in the vast majority of situations – although the option to manually override does remain in difficult or preferable circumstances.
This is where level 5 automation comes in. Level 5 autonomous vehicles (AVs) lack typical driving controls such as steering wheels or pedals, with the traditional role of the driver eliminated completely.
Autonomous vehicles are expected to be worth up to US$1.3tn when it comes to cost/timesaving benefits, but the road to full automation may not be smooth


educators. Empowering students. Explore how we accelerate student discovery, learning and innovation with our Digital Education 3D Experience.

The self-driving revolution represents another potential change: the ways in which technology might completely alter the ‘how’ in terms of transportation. Is this the start of the robotaxi rise?
“Just as mobile phones slowly replaced digital cameras, the driverless vehicle is the next inevitable phase of transport,” says Stuart Parker, Head of Future Lab, Goodwood Group. “There are several wellknown companies within this space already, but others are following in their footsteps and creating new and more innovative ways to get people from A to B.”
According to a report by KPMG, AVs may cut travel time by up to 40%, recover up to 80 billion hours lost to commuting and congestion, and reduce fuel consumption by up to 40%. “These cost/time-saving benefits are expected to be worth about US$1.3tn in the country,” the report adds. “Other potential cost-saving domains include reduced manpower – drivers and law enforcers.”
Robotaxis are fully-automated vehicles to take passengers to their intended destinations, on demand. Whether that eventually comes true is yet to be seen; what is certain, however, is that robotaxis are already undergoing limited public trials across the world, from Arizona to China.

Last August, Baidu became the first robotaxi operator in China to obtain permits for selling rides with no human driver or staff member inside the vehicles.
The tech giant’s autonomous ride-hailing service, Apollo Go, is now authorised to
“More connected cars require connected vehicle ecosystems in smart cities to facilitate the shift”
JORDAN
PARK PLACE TECHNOLOGIES
Level 0 – No Automation

Conventional vehicles with no automation features
Level 1 – Driver Assistance
Lowest level of automation, including vehicles that have features to help with steering or braking. Level 1 vehicles have some automated features – adaptive cruise control, for instance.
Level 2 – Partial Automation
Vehicles that have advanced driving assistance systems that can take over steering, acceleration and braking. Level 2 vehicles still require humans to take control.
Level 3 – Conditional Automation
The first stage of automation that has less reliance on a driver to pilot the vehicle. Level 3 automation pairs driver assistance systems with AI to handle more complex situations.
Level 4 – High Automation
Level 4 automated vehicles can drive themselves and are programmed to stop themselves if their systems fail. They are primarily used for services like robotaxis, which are pre-programmed to drive within specific areas.
Level 5 – Full Automation
Level 5 vehicles are fully automated with no need for the driver to do anything but set the destination and ride along. They can drive themselves anywhere, under any conditions, safely.
collect fares for robotaxi rides in Chongqing and Wuhan – two of China's largest cities –across 13sq/km in the Wuhan Economic & Technological Development Zone and 30sq/ km in Chongqing's Yongchuan District.
Nevertheless, it’s Alphabet Inc-owned Waymo that has perhaps the greatest experience with real-world conditions, saying on its website that, since 2009, its
“fully self-driving technology” has clocked up 10 million miles on real-world roads.
The company’s Waymo One robotaxi trial in Phoenix, Arizona relies on users utilising Waymo’s app. Recently, however, the company announced a partnership with ride-hailing company Lyft, making ten of its vehicles available outside of Waymo’s own ecosystem.
“Despite initial reservations, driverless vehicles will be a common sight at the end of this decade,” Parker says. “The next phase of motoring cannot be ignored; instead, it must be embraced. The key to this is understanding it and having the best possible innovations at the heart of it.
“With technology providing an environment where we can push the boundaries of what is possible, the future of driving is set to change forever, and the benefits to extend far beyond a pleasant driving experience.”
Real-time data about the environment –weather, road conditions, other vehicles, pedestrians and street signs – combined with information about the vehicle and the intelligence needed to make instant driving decisions, generates up to four terabytes of data per hour for one test vehicle.
“The bottom line is that more connected cars require connected vehicle ecosystems in smart cities to facilitate the shift – with well-crafted edge infrastructures set up to absorb the data deluge,” explains Jordan MacPherson, Director, Product Operations, Park Place Technologies.
According to a report from CoBank’s Knowledge Exchange, another major challenge alongside social acceptance, safety and regulatory restrictions that is often overlooked is the monumental impact these vehicles will have on the data centre market.

“The next phase of motoring cannot be ignored; instead it must be embraced”
STUART PARKER GOODWOOD GROUP


According to research by Strategic Market Research, the worldwide Autonomous Car Market's value in 2021 was worth US$25.14bn and, by 2030, will reach US$196.97bn at a 25.7% CAGR. North America came out on top of the overall market, with the highest market share of about 45% in 2021.
“Self-driving vehicles are expected to generate unthinkable amounts of data that will have a profound impact on the markets for data centre storage and computation,” said Jeff Johnston, lead communications economist with CoBank. “And there’s an enormous chasm between the existing digital infrastructure and what is needed to support widespread adoption of self-driving vehicles.”
“Governments are already working to build the necessary ecosystems and prepare citizens for the changes ahead,” concludes MacPherson. “In the UK, for example, the first autonomous bus scheme is rolling out and the government has just updated the highway code in preparation for autonomous vehicles. It is the back-end data infrastructure that forms the foundations for these technologies – with autonomous vehicles producing 300TB a year, optimised data management is mission critical.”
“Building networks and ecosystems that can handle this data – as much as 40TB of data an hour from cameras, radar, and other sensors from driverless cars – will determine the success, the safety, and the experience of autonomous driving.”

Manufacturers worldwide are increasing their investment in key technology areas to improve operations, product and service offerings, or keep up with their digitally savvy competitors.

But cybersecurity issues remain – one in four UK manufacturing companies reported they had been hit by a security issue last year, with individual losses of as much as £250,000.
According to an analysis by the McKinsey Global Institute, the installed base for the roughly US$50 billion advanced robotics industry used in the manufacturing industry is expected to grow six per cent per year for the next three years as companies are taking advantage of smarter, more flexible and cost-effective equipment to automate more of their activities. By 2030, Industry 4.0 applications are expected to account for almost half the total sales of 5G-connected IoT devices.
“The old image of manufacturing — which was around factories that were greasy and dirty — doesn’t exist anymore,” says Asutosh Padhi, Managing Partner for McKinsey in North America. “You walk into one of these companies and the places look clean, the machines are new, the people are working together in teams, the place is inviting. You get the sense that there is something happening that is much more modern and oriented around precision manufacturing, whether it’s using new materials, new technologies, or different types of equipment.
The image of manufacturing as a greasy, dirty business is outdated, say experts, but fresh security risks have emerged as new tech enters the industry
HOPKIN






A modern network must be able to respond easily, quickly and flexibly to the growing needs of today’s digital business. Must provide visibility & control of applications, users and devices on and off the network and Intelligently direct traffic across the WAN. Be scalable and automate the process to provide new innovative services. Support IoT devices and utilize state-of-the-art technologies such as real-time analytics, ML and AI. And all these must be provided with maximum security and minimum cost.
This is the power that brings the integration of two cloud managed platforms, Cisco Meraki and Cisco Umbrella. This integration is binding together the best of breed in cloud-managed networking and Security. cisco.com




“You also get a sense of purpose,” says Padhi. “Why are these people so excited to be here? It’s because they believe that they’re driving innovation, that they’re doing things that are important to our future.”
McKinsey’s report suggests that US manufacturers stand to benefit from further waves of digital innovation as capital markets continue to make big investments in nextgeneration technologies. Annual investment in AI has reached roughly US$150bn, with investors pouring US$250bn into IoT technologies and US$300bn into cloud computing every year.

In the UK, nearly half of the nation’s manufacturers (42%) have been victims of cybercrime in 2022, it is believed. This information emerged in the report Cyber Security: UK manufacturing, published by Make UK, the manufacturers’ organisation, in association with BlackBerry.
The report found that, though 74% of manufacturers said the cyber protection processes they had in place prevented any business impact whatsoever, the remaining 26% revealed they had sustained substantial financial loss, with losses ranging from £50,000 to £250,000.
“Digitisation is revolutionising modern manufacturing and becoming increasingly important to drive efficiencies in this incredibly difficult inflationary environment”
STEPHEN PHIPSON
“In my experience, it is possible — indeed, likely — that malware is present in your legacy infrastructure, just waiting for the right time to strike,” says Keiron Holyome, Vice President of UKI, Middle East & Africa at BlackBerry. “Today’s sophisticated threats are not deterred by outdated antivirus and firewall protection. The threat landscape in the sector is expanding — and fast — because of ‘smart’ and connected manufacturing, which economies-of-scale demand. However, this growth of the industrial IoT increases potential cyber risk, as well.”
An added risk for companies has been the need to speed up the adoption of digital processes to boost production in today’s challenging economic climate. This increase in the implementation of tech solutions at the heart of production operations has increased the emphasis on cybersecurity within businesses, with 95% of companies reporting that cybersecurity is a necessary function of their operations.
The Make UK report noted that targeted attacks are the most common, with operational disruption the most frequent result of a cyber incident. Reputational loss is the second most significant issue for companies, with customers looking for evidence of cyber protection.

“No business can afford to ignore this issue — failing to get this right could cost the manufacturing industry billions”
STEPHEN PHIPSON


Supply chain robotics company Gather AI is using autonomous warehouse drones powered by artificial intelligence to address Covid-19’s enormous impact on global supply chains.
The company’s platform includes drones which fly autonomously using software that enables them to navigate warehouses without the aid of GPS or changes to building infrastructure or processes such as lighting, WiFi or labelling.
Gather AI says its drones collect data 15 times faster than human counters, with the ability to read over 95 per cent of labels and barcodes, minimising the work for human counters.
"The supply chain issues making headlines less than a year ago put a spotlight on challenges that the logistics industry has been trying to address for the last two decades - how to effectively manage operations to maximise revenue and efficiency, all while minimising frustrations that come with labour shortages," says Gather AI Co-Founder Sankalp Arora. "The reality is, the majority of warehouses have access to technology that is from before the e-commerce boom, which has exacerbated the struggle to keep up with the changes in both industry demands and customer habits."
Over half of manufacturers have taken no cyber action Legacy IT within a business was found to be the most common risk to manufacturers (45%), followed by a lack of cyber skills. The necessity of providing access to third parties for monitoring and maintenance is the third most frequent reason for a cyber incident among manufacturers.
Despite knowing the risks, most companies (54%) have not taken further cybersecurity action — even after adopting new technologies. Only those who have introduced systems from the IoT appear to have invested heavily in cyber protection.
IoT technologies often lie at the centre of the manufacturing processes and are seen as business critical, driving companies to spend more to protect them. The Make UK report found those businesses that have implemented industrial IoT report it to be the biggest driver in increasing their overall level of organisational cybersecurity.
“Digitisation is revolutionising modern manufacturing and becoming increasingly important to drive efficiencies in this incredibly difficult, inflationary environment,” says Stephen Phipson, CEO of Make UK. “While cost remains the main barrier to companies installing proper cyber protection, the need to increase the use of the latest technology makes mounting a proper defence against cyber threats essential.”
Employee error remains the most common reason for a cyber-attack in the manufacturing industry. To address this issue, 62% of manufacturers now offer cybersecurity training to their staff, in an effort to reduce the risk of cyber attacks. Smaller companies are, however, lagging behind, with only 50% of 0-9-employee companies offering any training at all.
Boardrooms take control of driving cyber protection
The report also found that 62% of manufacturers now have a formal cybersecurity procedure in place in the event of an incident — an increase of 11% from last

“You walk into one of these companies and the places look clean, the machines are new, the place is inviting”
ASUTOSH PADHI
year’s figures. Additionally, 62% of the industry now says that there is a senior manager involved in a cybersecurity committee within the business, while 58% reported that a main board director is responsible for driving cyber protection for the firm.
The report found that 89% of companies are investing heavily in antivirus software and firewalls to secure internet connections. Very few companies — under 1% — reported not having any technical mitigation in place. Regarding perceived threat origin, Russia and China are level-pegging, with 75% of manufacturers perceiving a cyber threat originating from these regions, followed by the EU (25%) and the US (23%).
The report also identified the main barriers to companies increasing their level of cybersecurity: the initial cost of cyber protection products was cited as the main block by just over 40% of manufacturers, while the cost of maintaining these security systems was the second most cited barrier, with 35% of the industry suggesting it is a key obstacle.
“No business can afford to ignore this issue, and failing to get this right could cost the manufacturing industry billions of pounds and put thousands of jobs at risk,” says Phipson. “Every business is vulnerable, and every business needs to take the necessary steps to protect themselves properly.”

The COVID-19 pandemic triggered a massive increase in telehealth services, allowing care providers to connect with patients. The metaverse is the next step
As the metaverse continues to dominate news headlines at the start of 2023 – promising to change workplaces, our social lives, and how we do business – the world of healthcare is already benefitting from advances in technology.
Referred to as the ‘new horizon’ in Accenture’s most recent Digital Health Technology Vision report, the metaverse could have a transformative impact on the healthcare industry. And with that announcement, it’s safe to say that virtual reality (VR) is no longer just for gaming.
As pointed out by the non-profit hospital Cedars-Sinai, scientists have been quietly discovering the health benefits of VR for ailments ranging from burn injuries and strokes to PTSD and schizophrenia.
“Over ten thousand studies reveal that VR has an uncanny ability to calm pain, steady nerves, and boost mental health,” it claims. “VR is helping to deliver babies, enabling soldiers to cope with the mental scars of war, and reminding doctors that patients are not broken machines, but are people whose subjective lives matter.”
VR can even provide a safe practice space for intricate surgery. A study by Seymour et
“Virtual reality also helps with learning how to better communicate with patients and their families by offering them ‘a 360-degree view’ of the experience”
JOÃO BOCAS CEO, DIGITAL SALUTEM
al. into the use of VR surgical simulation for training purposes found that, as well as being faster, VR-trained individuals were five times less likely to injure the tissue, and six times less likely to make other impactful mistakes.
The technology is also emerging as a tool to help with mental health conditions like anxiety, immersing the user in a scenario that would habitually cause them to become anxious while practising therapies like cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT).
“For some chronic condition patients, enhancing telemedicine with AR and VR presented a life-changing experience,” says Liza Dzhezhora, a Healthcare IT Analyst at Itransition. “Delivered with the help of an AR/VR headset, telemedicine helps manage diverse conditions, from psychological and neurological disorders to chronic pain, substance abuse and cancer. Such tools may also assist with recovery after a stroke or a brain injury, PTSD therapies and more.”
Among the use cases for VR in healthcare are improvements in overall telehealth services. “The pandemic triggered a massive increase in telehealth services, and those services aren’t going away any time soon,” explains Bob Zemke, Director of Business Development at Extreme Networks. “In future, patients will see the biggest difference in the fact that they are no longer making trips to see their doctor or GP in person, instead scheduling virtual visits.

“The amount of personalised, in-home healthcare services will continue to increase as patients are able to use more applications and medical devices at home, including outpatient monitoring devices.”
“Telehealth technologies have marked a new era for patients residing in remote or rural areas,” comments Dzhezhora.
“Small rural hospitals have long suffered from the shortage of healthcare
The Metaverse Could Transform Healthcare!
professionals. In a dire situation like the pandemic, telemedicine can become a viable care assistant for patients and clinicians. Patients can schedule a virtual consultation with reputable experts from across the country. For clinicians, virtual meetings with fellow doctors may serve as a powerful means of improving professional skills and bringing their approaches up to speed with the modern trends in their care specialty.”
As Zemke explains, VR is just one component of how technology can be used to create better experiences for patients: “Network infrastructures will increasingly bring all these different elements together as part of a connected, real-time healthcare system that ensures scalability, efficiency, and accuracy.
“This will enhance the quality of care healthcare providers are able to deliver and create a better patient experience,” Zemke says. “For example, sensor data can provide insights into the location and availability of healthcare devices, while analytics from Wi-Fi access points can help determine things like the busiest times in waiting rooms when an in-person visit is necessary. These insights can all be used to support patient care, cut wait times, and ensure more effective asset utilisation.”
states. “If a patient requires an appointment with another doctor for some clarification, the tool may spare them the need to wait for hours or days. Their physician may connect to a colleague via a telemedicine app and ask for a consultation immediately.
“Telemedicine may also streamline care delivery at emergency departments. There are smart hospitals that have introduced telecarts (devices that offer an immediate professional assessment). Moreover, telemedicine may allow providers to increase their on-premises staff, attracting out-ofoffice clinicians to run telecart consultations.”
“For some chronic condition patients, enhancing telemedicine with AR and VR presented a life-changing experience”
LIZA DZHEZHORA HEALTHCARE IT ANALYST, ITRANSITION
Improving the patient experience
“Telemedicine may help improve patient experience on-premises,”
Itransition’s Dzhezhora
“Virtual reality is a great tool for training clinicians,” says João Bocas, CEO at Digital Salutem. “In fact, some experts believe that this form of training will become more important than traditional hands-on training methods. They believe that VR offers a completely different way to learn and practise human relationships, affecting how patients interact with the physicians they see, and how they communicate with each other while they are working in the same room.
“Virtual reality also helps with learning how to better communicate with patients and their families by offering them ‘a 360degree view’ of the experience. This allows them to connect with their family members and understand the context of what’s happening in their lives on an intimate level.
“The use of VR in healthcare is still relatively new, but it has already shown promise as a tool for training clinicians. In fact, some experts believe that this form of
training will become more important than traditional hands-on training methods such as lectures and case studies. One study showed that virtual reality therapy helped reduce stress levels during treatment by 50%. Others have shown promising results when using VR during physical therapy.
“As time goes on, however, we will likely see more use cases outside of healthcare –including gaming, education, legal studies, etc – so it remains to be seen what impact VR will have on such industries over time.”
SALUTEM
“Virtual reality is a great tool for training clinicians”
WITH AI THE ‘IN THING’ FOR MOST BUSINESSES AT THE MINUTE, WE LOOK AT THOSE PLATFORMS OUTSHINING – OR SOON TO OUTSHINE – THE REST IN 2023

In this ever-evolving, data-driven age, AI technologies are being increasingly deployed by the world’s businesses. Across almost every sector, spanning everything from global healthcare to logistics and supply chains, AI platforms are being used by businesses to improve their efficiencies and unlock new capabilities for their services. But which AI platforms are leading the charge? Keep reading to find the top 10 AI platforms that the world’s businesses are depending on.


Infosys Nia is a knowledge-based AI platform, utilising ML and other pioneering automation technologies to help businesses extract greater value from their data. Its main success stories include increasing the productivity of an American bank by 10 times, achieving 90% cost reduction for a Fortune 500 Conglomerate, and identifying a $90mn revenue leakage opportunity for a telecom major.


Rainbird is a no-code intelligent automation platform offering businesses the full breadth of process automation and ML technologies, regardless of their existing experience in the field. Designed for businesses operating in transactional and regulated markets, the platform offers easily implemented intelligent automation solutions for recurrent processes –which are around 100 times faster and 25% more accurate than when they are undertaken manually by humans.


With over 75 years in the digital transformation sphere, few have as much industry experience as Wipro.

Wipro HOLMES – the company’s AI and automation platform – connects users to a suite of intelligent automation solutions.
The platform’s tools include: the Remote Worker suite (a series of selfhelp and self-healing systems for remote workers); the Virtual Health Assistant Prompt (providing accurate healthcare information and adverse event reporting); a remote digital contact centre; and the end-to-end IT compliance suite for remote working.
TensorFlow allows users to create production-grade ML models, with specialist ML solutions available for developers at every skill level.

Through this end-to-end ML platform, users can deploy and accelerate ML tasks at every stage of their workflow, spanning everything from preparing, processing and loading the data to running the models in production.
What’s more, users can either find pre-trained models, undertake research with state-of-the-art models, or use TensorFlow to build their own.


H2O.ai is the trusted AI partner of over 20,000 organisations across the world. The platform has earned a reputation for being an industry leader in autoML, responsible AI, driverless AI and time series forecasting.

Utilising the end-to-end platform, users can accelerate AI results and create a simple, scalable solution that operates seamlessly across on-premises environments, multiclouds and data sources.



Despite only announcing the availability of its AI services in 2021, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure has already asserted itself as one of the market leaders in AI platforms.
The platform is designed to offer an easy solution for developers, allowing them to apply AI services even if they do not have any prior data science experience. Through the OCI platform, developers can either use out-of-the-box models or custom train the services using their own company data.
Watson Studio – IBM’s software platform for data science – is designed for data scientists, developers and analysts. It comprises a workspace of collaboration and open-source frameworks (including PyTorch, TensorFlow and scikit-learn).


The platform allows users to build, develop, manage and scale AI through an open multicloud architecture. Watson Studio users have the option to work with Jupyter notebooks, JupyterLab and CLIs, or use a variety of languages, such as Python, R and Scala.

Azure AI comprises a portfolio of sophisticated and specialised AI services, designed for developers and data scientists to evolve specific business scenarios.

Microsoft offers a range of vision, speech, language, and decisionmaking AI models through simple API calls, alongside the required tools for users to build their own ML models with tools such as Jupyter Notebooks and Visual Studio Code.
Its customer base includes some of the world’s most well-known businesses, such as the NBA, Nestle and the NHS.


With the internet giant’s full wealth of knowledge at its disposal, Google Cloud's AI tools are indisputably among the leaders in the market.
The services available through the platform include data science –replete with a suite of data management, analytics and ML tools – AI infrastructure with deep learning and ML models, and industry-leading value-based, responsible AI.
Google also offers a wealth of educational resources for users of its AI platform. Everything from the highly influential ‘AI for Social Good Guide’ to information and exercises shared by Google’s own ML experts are available to help support businesses.



And securing the number one spot, we (perhaps unsurprisingly) have AWS.
AWS prides itself on having the most complete set of AI and ML business services on the market. And, through Amazon SageMaker, users can build, train, and deploy ML models that fulfil all of their specific requirements.

Its tool base is immensely broad, being deployed across a huge variety of use cases and spanning everything, from Duke University’s use of the AWS platform to diagnose autism earlier to PFF’s work in gathering and interpreting data across global sports. With over 100,000 users, it’s difficult to imagine the sheer global impact AWS’ technology continues to enjoy.