
13 minute read
A brief tour of the Toyota Camry fuel and P

from Auto Service Professional - July/August 2015
by EndeavorBusinessMedia-VehicleRepairGroup
Camry generations fve and six
A brief tour of the Toyota Camry fuel and EVAP systems
By Jacques Gordon
Jacques Gordon has worked in the automotive industry for 40 years as a service technician, lab technician, trainer and technical writer. His began his writing career writing service manuals at Chilton Book Co. He currently holds ASE Master Technician and L1 certifcations and has participated in ASE test writing workshops.
Since the day it was introduced to the U.S. market, the Toyota Camry has been one of the most reliable cars on the road. With normal maintenance or even a fair amount of neglect, it seems these cars almost never break down. When problems do arise, the diagnosis is rarely a challenge. But diagnosis is always faster and more accurate when you know more about the vehicle. If you don’t normally work on Toyotas, or if you simply haven’t had the opportunity to look into a Toyota fuel system lately, here’s a quick overview of the two most common models.
The 2002-2006 model is the Camry’s ffth generation and the frst year for the 2.4-liter 2AZ-FE engine with an electronic mass airfow sensor, electronic throttle and a returnless fuel injection system. That system architecture became the model for Toyota port fuel injected engines right up through current generation, including the other engines used in that car, the 3.0-liter 1MZ-FE and the 3.3-liter 3MZ-FE.
Returnless fuel systems were developed to reduce evaporative emissions. The main difference is the fuel pressure regulator is inside the fuel tank instead of under the hood. The fuel rail may have something that looks like a pressure regulator, but it’s actually a pulse damper to reduce pressure pulsation and fuel pump noise. The mechanical pressure regulator is part of the fuel pump module that includes the pump, a reservoir, the gauge sending unit and a fuel flter.
The fuel pump module is usually sold as a complete assembly, but according to the service manual each of those components can be replaced separately once the module is removed. That includes the only fuel flter in the whole system, the strainer or “sock” on the inlet side of the pump. Turbine pumps are not particularly strong on the suction side, so if there’s a no-start or driveability issue that’s caused by lack of fuel, the problem just might be nothing more than a clogged fuel flter.
Specs for this fuel system are the same for all three engines: fuel pressure with the engine running or not running is 44 to 50 psi, hold pressure is 21 psi and fuel injector resistance is 11.6 to 12.4 ohms at 68 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius).
There is no fuel pump fow rate specifcation, and there’s no pressure tap on the fuel rail either. One way to check fuel volume is to monitor fuel pressure during full-throttle acceleration. If fuel pressure falls below specifcation during a full-throttle acceleration, that means the fuel pump can’t keep up with the demand.
The fuel injection system’s electrical circuit design is the same on all three engines, but it is uniquely Toyota. Power for the fuel pump is supplied by what they call the circuit-opening relay (C/OPN), which any
Fortunately that’s Fuel suction plate easily reached sub-assembly through the access panel under the rear Fuel pump harness seat. By the way, Toyota OEM wiring diagrams
Fuel sender gauge are some of the most assembly informative and Fuel flter assembly user-friendly, and they often include notes about voltage, resistance and signal specs at the terminal connections. O-ring Despite the CamFuel pump ry’s reputation for
Fuel pressure regulator reliability, this was assembly the frst generation designed to meet Fuel pump flter LEV II evaporative emissions regulaClip tions. That means EVAP codes are Cushion rubber common on these models because the Fuel suction EVAP system is relasupport No. 2 tively complicated: It includes the charFigure 1: Retainer clips are used on fuel pump module components. coal canister with a pressure sensor, two other manufacturer would simply call the solenoid valves and some sophisticated softfuel pump relay. Like other cars, power for ware. The purge valve is under the hood, the relay coil comes from the ignition switch but the vent valve and pressure sensor are (through a 10-amp fuse), and the ground part of the canister assembly, and that’s circuit is provided by the PCM when the ignimounted underneath right next to the fuel tion switch is in the START position or when tank. This makes it easier to food the canengine speed is above cranking speed. ister if the tank is overflled.
What’s different here is that power for A complete and detailed service bay the C/OPN relay contacts is supplied by the test is available in Toyota Service Bulletin main electronic fuel injection (EFI) relay, EG048-04. and power for this relay coil is provided We’ll describe how the onboard EVAP by the PCM. Depending on the model, the monitors work here. EFI relay provides power to the fuel pump The PCM runs two different EVAP purge (through the C/OPN relay) the EVAP purge monitors to test the vacuum switching valve valve (VSV) and/or an oxygen sensor (VSV). That’s what Toyota calls the purge heater. This means you can’t really detervalve because it’s switched on and off in a mine fuel pump voltage or current draw duty cycle to control how much vacuum is at the C/OPN relay socket, you’ll need to applied to the canister. When the engine check it at the fuel pump connector itself. is running and all the normal drive-cycle

criteria are met, the PCM turns on the canand the VSV and CCV both closed. If ister closed valve (CCV), commonly called pressure inside the canister goes below the vent valve. The CCV is normally open, so atmospheric pressure, the PCM decides the turning it on closes it. With the CCV closed, VSV is stuck open. A pending code will be the PCM cycles the VSV and monitors the recorded in memory, and if this happens on pressure sensor in the canister. If canister two consecutive trips, the PCM will illumipressure doesn’t decrease during this test, nate the MIL and set code P0441 (purge the CCV is turned off (opened) and the PCM fow incorrect). looks for a pressure increase of at least two The CCV is tested the same way. With the inches of water (3.75 mmHg). If pressure CCV commanded closed (turned on) and still doesn’t change, the PCM decides the the VSV commanded open, the PCM expects VSV is not opening and a pending code will to see high vacuum in the canister. If not, be recorded in memory. If this happens on the CCV is not closing. When the canister two consecutive trips, the PCM will illumiis at atmospheric pressure and both valves nate the MIL and set code P0441 (purge are commanded open, the PCM expects to fow incorrect). see no pressure change in the canister. If
In the other test, the PCM reads atmothe canister develops negative pressure spheric pressure (there’s a “baro” sensor for more than four seconds, the CCV is not inside the PCM) with the engine running opening. A pending code will be recorded, and if this happens on Air cleaner case two consecutive trips, Intake air Throttle valve Intake manifold the PCM will illuminate the MIL and set code P0446 (vent valve circuit
Charcoal flter malfunction). Air cleaner flter When EVAP VSV is open, partial vacuum is created The vent passage goes through a flter and terPurge minates in the fuel fller line Leak detection area tube. Toyota says the flter can become clogged, but EVAP codes have also
ECM EVAP VSV been caused by spider nests in that passage. Vapor To leak-test the fuel pressure Diaphram tank and EVAP system, sensor (Atmospheric pressure) the PCM simply closes the Fuel tank cap EVAP line Small hole CCV and opens the VSV to draw a vacuum on the system with the engine running. After closing EVAP service port Air inlet line Fuel tank Purge line Trap canister Charcoal canister the VSV, it measures the time required for the vacuum to decay. If there is a leak, the rate of pressure rise determines When CCV is opened, air is drawn or Charcoal canister flter CCV which fault code will be set: P0442 (large leak) released or P0456 (small leak) or Air inlet line P0455 (gross leak). This is also a two-trip test Figure 3: (A76844) EVAP schematic for the 2002-2006 Camry. that sets a pending code
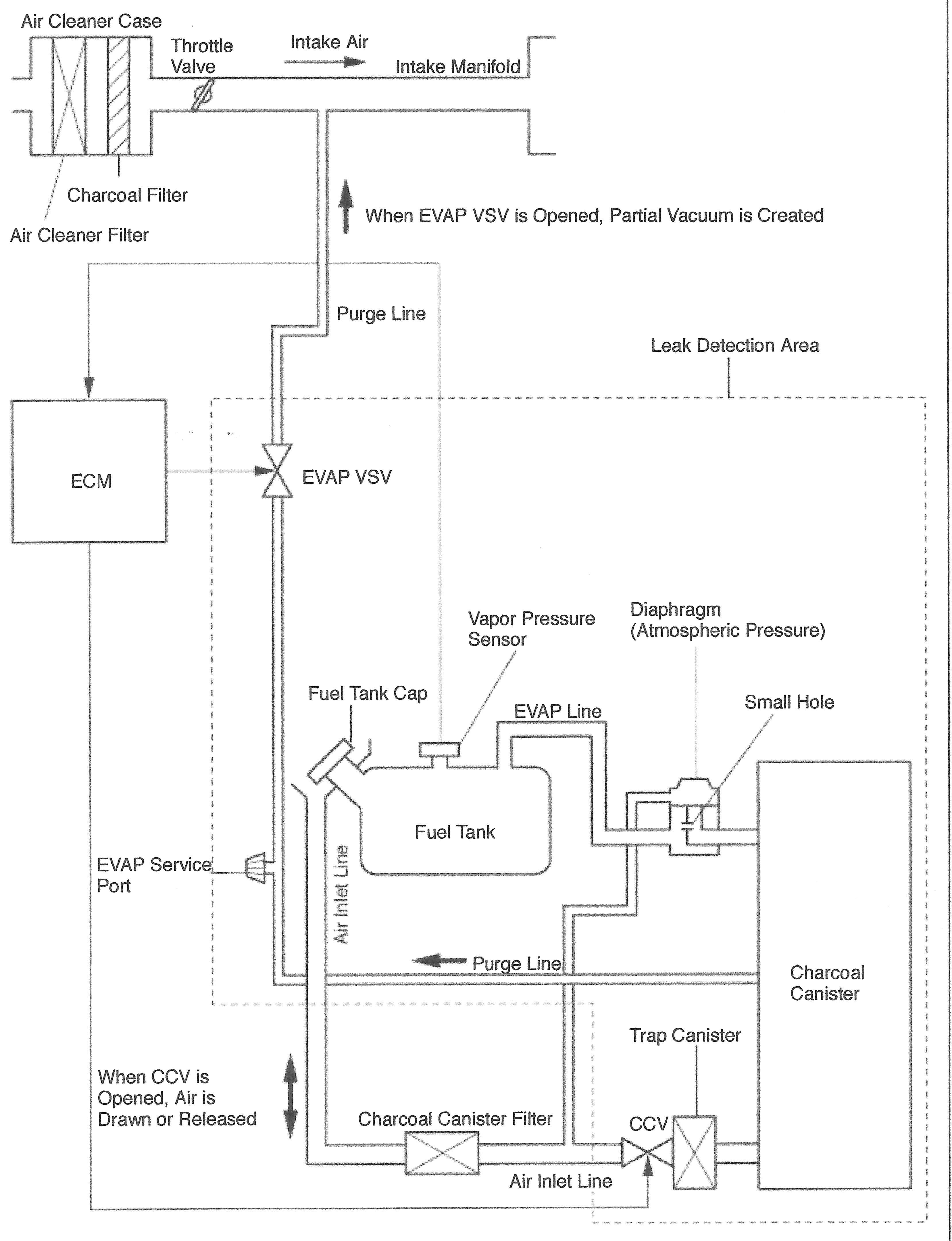
on the frst failure and a hard code on the P0453) plus a number of Toyota-specifc second consecutive failure. codes for the valves and pump. Sixth generation to run with a scan tool, which is good
The next (sixth) generation Camry is the because it’s possible for local conditions to 2007-2011 model. The 2AZ-FE engine carries prevent it from running automatically. If over with the same fuel injection system, battery voltage falls below 10.5, the test but now the C/OPN relay coil shares a power will be aborted. If coolant temperature is circuit with the injectors. There’s also a new not between 40 and 95 degrees F (4 – 35 3.5-liter 2GR-FE six-cylinder engine. degrees C) within fve hours after shut
This is the frst year that the EVAP system down, the PCM will wait two more hours has a dedicated Leak Detection Pump (LDP). and try again. A third attempt will be made All of the other components and most of after another 2.5 hours. If pressure altitude the operating strategy remain the same, is greater than 8,000 feet, the monitor will except for the leak test. not run.
The EVAP system leak test runs only if Incidentally, the LDP makes noise when it there are no codes or pending codes for the runs, which sometimes causes customers to valves. After the engine has been turned ask why their car is making strange noises off for fve hours (to let fuel tank pressure while parked in the garage overnight. stabilize), the PCM wakes up, reads ambiThe EVAP monitors can be commanded ent pressure, turns on the CCV to close the Smart key vent, then operates the LDP. Remember, The sixth generation Camry is the frst the purge valve is normally closed, but in available with an optional Smart Key system this system, closing the CCV doesn’t actuthat has an Engine Start button in place of ally seal the system; it connects the LDP an ignition key. to a 0.020-inch reference orifce. Air fows The Smart Key system adds a major layer of out of the canister through the reference complexity because some engine operations orifce while the PCM monitors the decrease are controlled by what Toyota calls the main in canister pressure. If it decides there is a body ECU (aka body control module or BCM). leak, it sets a pending code. If the test is The fuel pump is still operated by the C/ failed again after the next drive/rest cycle, OPN relay, and power for that relay’s contacts the PCM will illuminate the MIL and store still comes from the main EFI relay. However, the appropriate leak code(s). There are also power for the C/OPN relay coil comes from a sensor failure codes (P0450, P0451, P0452, third relay labeled IG2 (ignition 2) that also provides power to the Reference orifce (0.02 inch) injectors. Power for Fuel cap Refueling valve the IG2 coil comes Canister pressure sensor from the BCM when To atmosphere the Smart Key is detected. Purge VSV On the Smart Key (ON) Fuel tank Canister system, the BCM and the PCM control the starter together. When the Engine
To intake Start button is manifold ECM Canister flter Vent valve (OFF) pushed, various onLeak detection pump (OFF) board control units Canister pump module verify that the correct
Soak timer key has been detected Figure 4: EVAP schematic for the 2007-2011 Camry. in the vehicle, and
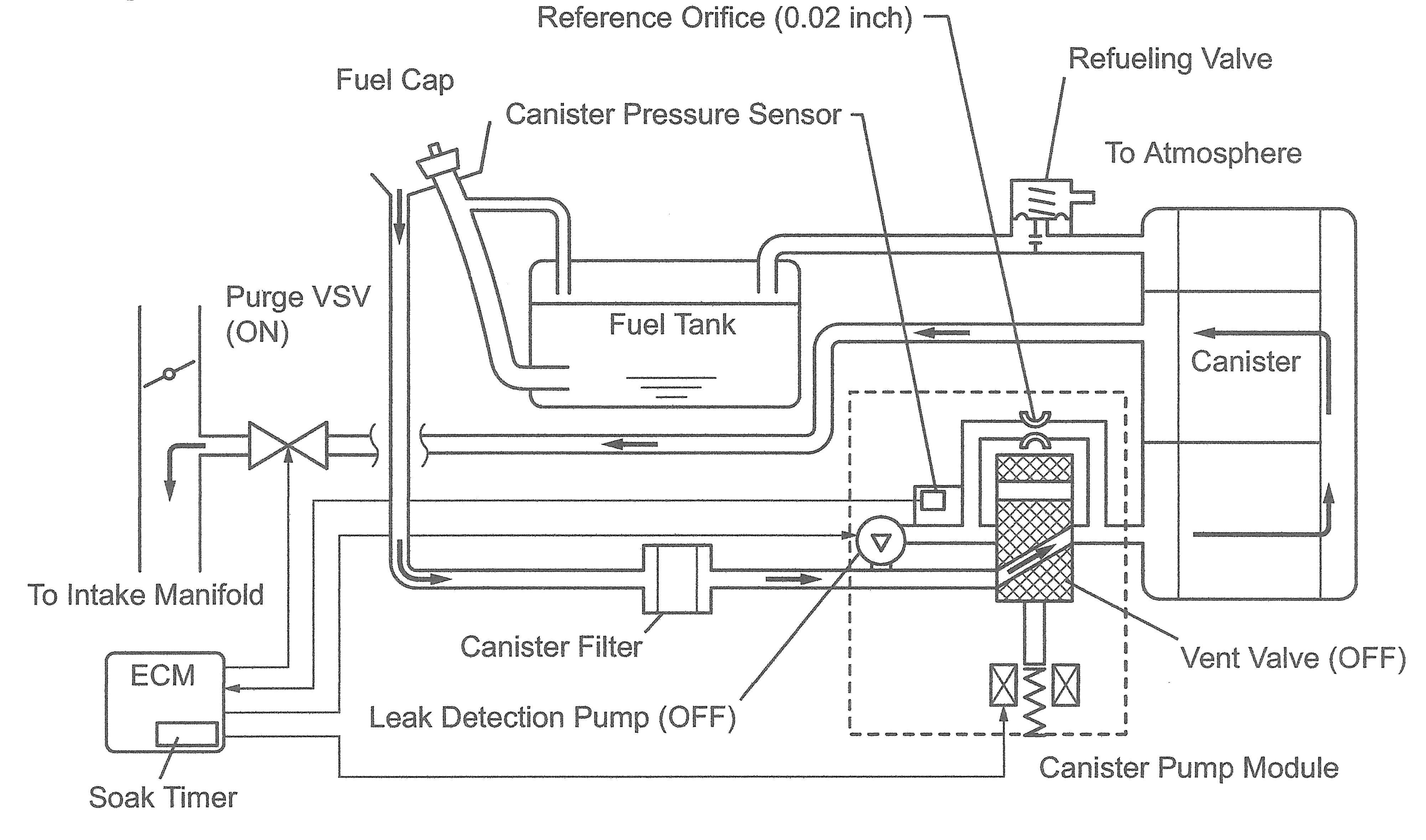

then accessory power is turned on by the BCM. When the Start button is pressed with the gear selector in Park or Neutral and the brake pedal depressed, the BCM activates both ignition relays, unlocks the steering and sends a “start” request to the PCM. The PCM will then request a cut in accessory power (from the BCM) while it activates the starter relay. Once engine speed reaches 1,200 rpm, it will release the starter relay and terminate the accessory-cut request.
If the brake light switch or circuit fails, the engine can still be started by pressing the engine Start button once to turn on accessory power, then pressing it again and holding it for 15 seconds. If there is no fuel in the tank (or if the fuel gauge sending unit fails), the start sequence will not be initiated.
Registering (programming) new keys is the most common issue with this system. It’s usually easy and it can be done with aftermarket pass-through tools. Once you’re in the right section of the Toyota Information System (TIS) website, the process is menu-driven and takes only a few minutes. You can register new keys or keys that had previously been used in another vehicle. However, if you only have a valet key and not a master key, you’ll need a locksmith identifcation number (LSID). It’s also easy for key registration to fail. Toyota notes that only one key should be in the car during key registration: If there’s more than one, they will interfere with each other and prevent the process from running to completion.
The key registration process was updated last year (July 2014). Toyota Service Bulletin 0043-14 describes new security requirements to obtain a smart key reset pass-code, and the instructions for this new process must be reviewed before attempting to get the passcode. The TSB also describes how to reset a vehicle immobilizer and/or smart key system.
Service bulletins
Since we’re on the subject of TSBs, don’t forget there were many bulletins and recalls to address accelerator pedal issues on all Toyota models. Here are some of the other important service bulletins covering the ffth and sixth generation Camry.
TSB-0122-08 describes why some smart keys tend to use up their battery quickly. The smart key “wakes up” upon receiving a “ping” or query signal from the BCM, but other electronic devices also emit signals that may activate the smart key. These include certain video devices, computers and monitors, cell phones and cordless telephones, microwave ovens and even some light fxtures. The only fx is to keep the smart key at least three feet away from other electronic devices.
TSB-0003-09 says a faulty “Engine Start” button may cause intermittent no crank/no start on vehicles with smart key. The bulletin describes a diagnostic procedure and includes part numbers for replacement buttons.
Service Campaign SC90K was launched to replace the oil supply line for the camshaft actuator on the six-cylinder engine. The rubber part of that line can develop a leak big enough to turn on the oil pressure light. Parts or repairs are free if the work is performed at a Toyota dealer before the end of 2021(no mention of reimbursement for work done elsewhere).
Safety Recall SC-C0M130213-007 was issued to cover all 2007–2009 Toyota models, but not all VINs (the National Highway Traffc Safety Administration (NHTSA) recall number is 12V491000). The master power window switch tends to stick or develop a “notchy” feeling over time. If that switch is lubricated with “commercially available” lubricants, it may overheat and melt or even catch fre (evidently there were lubrication “irregularities” at the factory). The recall bulletin describes how to disassemble, lube and reassemble the switch using the special grease (04002-18242) and applicator syringe. You’ll need some new one-way screws (04002- 18342) to reassemble the switch.
The next generation Camry has even more changes, including a new 2.5-liter engine and lots of new electronic features on the control screen. It will be a while before these models appear in your service bay, but it’s never too early to start learning about them. ●
Thank you to the technicians at MotoLOGIC for their help in preparing this article. –Ed.




