2 minute read
6. CONCLUSION
This dissertation aimed to identify a workflow for ML techniques application on BIM models. The literature review performed allowed to conclude that BIM plays a crucial role in the data management process in the construction industry. BIM models contain a rich dataset of information about many parameters of objects relating to different disciplines and simulating the lifecycle of the built environment. Therefore, this research suggests that there is an opportunity to apply data science techniques to learn from BIM models. Literature shows that data science techniques are also key factors to facilitate the digital transition of the industry towards the concept of Construction 4.0.
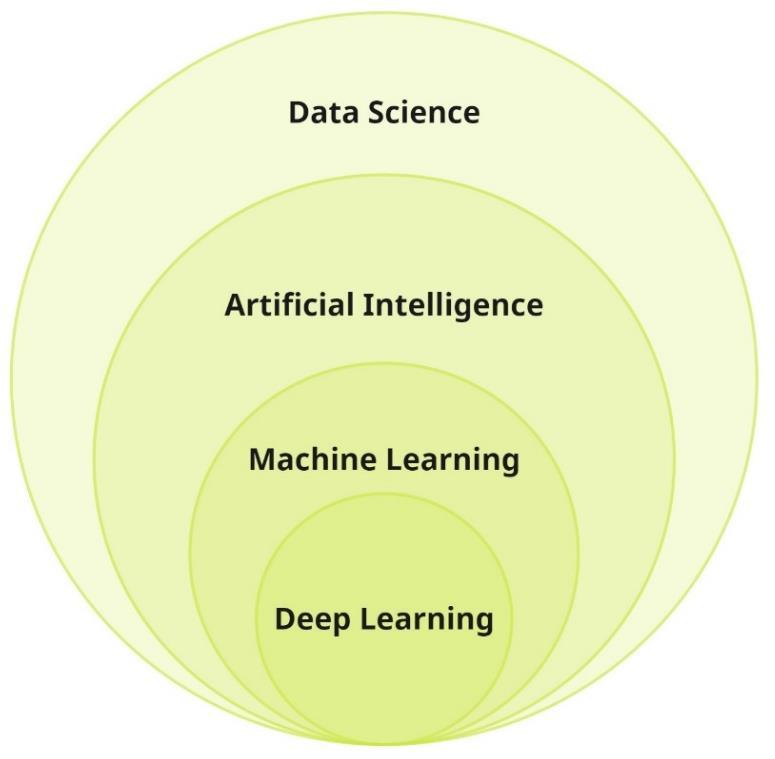
Machine Learning is one of those techniques which can be used to learn from BIM models. ML algorithms are constantly improving, highly dependent on the amount of available data; thus, the dissertation proposed taking advantage of a large amount of data in BIM models and identifying and discussing challenges related to it. Space Syntax theory was presented in this study as a tool for analysing spaces in a mathematical way that can be an input for ML tasks.
Advertisement
To achieve these objectives, this work presented a general framework for the implementation of ML techniques in BIM models: (i) understanding of the current situation with the digitalisation, data exploitation, application of ML techniques with or without the use of BIM models within the review of performed case studies; (ii) experimental case study that explores a working framework from BIM to ML within the architectural layout design concept.
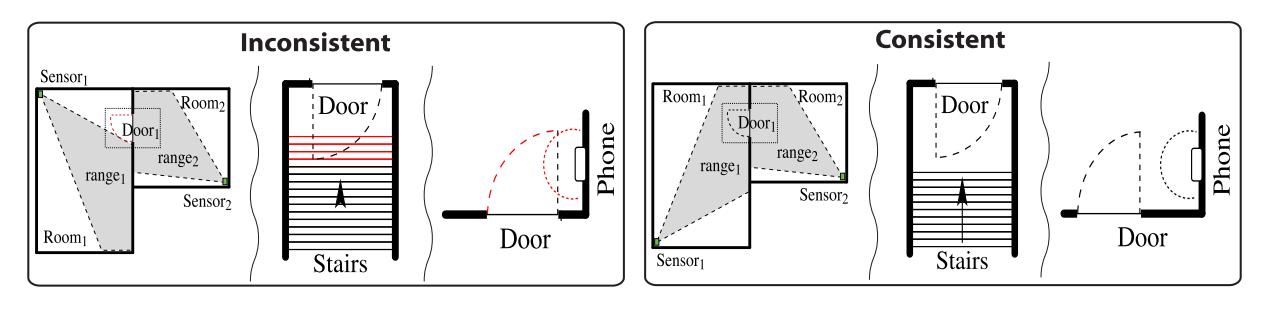
The BIM2GNN experimental framework developed revealed the importance of data acquisition and management from the outset of any project. The case study is based on the rooms (spaces) and their connectivity data exported from the native software. CNN and GNN algorithms were tested for learning and labelling from the group data. Both algorithms presented similar results. Despite the low accuracy of trained algorithms' results, the implementation opens new opportunities for further research development. Due to the current maturity level of digitalisation in the industry, the results naturally posed more questions for future research on this topic.
Future implementation of learning methodologies by using ML with BIM models require overcoming, at the industry level, several challenges. This work prioritises two major issues: data fragmentation and the limited amount of open-source BIM model data, which constraints interoperability, hence data integrity at scale. Addressing such hurdles could improve not only the overall performance of AEC but also the general individual and collective knowledge management by making use of the already large digital repositories of information.
To conclude, this dissertation proposed a new approach to research on layout design beyond the applications reviewed in the academic literature. The proposed use of data from the BIM model (as a fundamental enabler of the Construction 4.0 industry) helped test fundamental assumptions of data availability at the practical level for the academic and industry user. For this, this study also developed a substantial review of the challenges that can be faced in the implementation of ML on BIM. It is believed that this work can create insight for further implementations and applications that can benefit the design process in the industry and the general industry data management.
This page is intentionally left blank