ISSUE 112 | DISPLAY TO 30 JUNE 2024 | www.asian-power.com | A Charlton Media Group publication US$360P.A. Issue No. 112 Asian Power
Darmawan Prasodjo PT PLN President Director





ISSUE 112 | DISPLAY TO 30 JUNE 2024 | www.asian-power.com | A Charlton Media Group publication US$360P.A. PLN LIGHTS UP INDONESIA’S MOST REMOTE CORNERS
INDONESIA’S CARBON CREDIT MARKET MOMENTUM WHY JAPANESE UTILITY FIRMS ARE INTO THE SERIOUS BUSINESS OF RESELLING
REALITY
INDIA’S
SUMMIT POWER’S
OFFSET
DECLINE
REGULATORY DELAYS DAMPEN
LNG SURPLUS EASIER GRID ACCESS IS NOW A
FOR
ENERGY BULK CONSUMERS
LNG PLANS
GAS
INDO’S RURAL POWER PUSH
Founder
Summit Power International p. 22 Issue No. 112 Asian Power
Muhammed Aziz Khan, PBM
and Chairman,

PUBLISHER & EDITOR-IN-CHIEF Tim Charlton
EDITORIAL MANAGER Tessa Distor
PRINT PRODUCTION EDITOR Eleennae Ayson
LEAD JOURNALIST Vann Villegas
JOURNALISTS Paolo Alfar
Lady Jo-An Llorin
Aulia Pandamsari
Ibnu Prabowo
Jaleen Ramos
Joanne Christine Ramos
EDITORIAL RESEARCHER Angelica Rodulfo
GRAPHIC ARTIST Emilia Claudio
COMMERCIAL TEAM Janine Ballesteros
Jenelle Samantila Cristina Mae Posadas
ADVERTISING Shairah Lambat shairah@charltonmediamail.com +65 3105 1200 ext. 402
AWARDS Julie Anne Nuñez awards@charltonmediamail.com
ADMINISTRATION Eucel Balala accounts@charltonmediamail.com
EDITORIAL ap@charltonmediamail.com
SINGAPORE
101 Cecil St., #17-09 Tong Eng Building, Singapore 069533 +65 3158 1386
HONG KONG
Room 1006, 10th Floor, 299 QRC, 287-299 Queen’s Road Central, Sheung Wan, Hong Kong +852 3972 7166
MIDDLE EAST
FDRK4467,Compass Building,Al Shohada Road, AL Hamra Industrial Zone-FZ,Ras Al Khaimah, United Arab Emirates
www.charltonmedia.com

FROM THE EDITOR
Indonesia is well on its way to achieving the 100% electrification ratio with the help of state-owned provider PT PLN. We sit down with President Director Darmawan Prasodjo as he shares the company’s achievements in implementing digital processes for equitable electricity distribution. Know more about his thoughts on page 20.
In India, consumers who operate their own power plants or energy storage systems no longer have to secure licences to connect their transmission lines to the power grid. Read more about the new regulation on page 14.
Dubbed the “Oscars” of the power industry, the Asian Power Awards lauds top leaders in the power and energy sector for their exceptional projects. In addition, the Asian Oil & Gas Awards recognises excellent initiatives and transformations in the industry. Lastly, the inaugural Asian Water Awards spotlights innovative and sustainable water solutions. Turn to pages 26 to 33 to know more about the award recipients and their projects. Congratulations to all the winners!
Read on and enjoy.
 Tim Charlton
Tim Charlton
Asian Power is a proud media partner and/or host of the following events and expos:

Can we help?
Editorial Enquiries: If you have a story idea or press release, please email our news editor at ap@charltonmedia.com. To send a personal message to the editor, include the word “Tim” in the subject line.
Media Partnerships: Please email ap@charltonmedia.com with “partnership” in the subject line.
Subscriptions: Please email subscriptions@charltonmedia.com.
Asian Power is published by Charlton Media Group. All editorials are copyrighted and may not be reproduced without consent. Contributions are invited but copies of all work should be kept as Asian Power can accept no responsibility for loss. We will, however, take the gains.

ASIAN POWER 1
*If
reading the small print you may be missing the big picture
you’re




2 ASIAN POWER CONTENTS Published Quarterly by Singapore: Charlton Media Group 101 Cecil St. #17-09 Tong Eng Building Singapore 069533 For the latest news on Asian power and energy, visit the website www.asian-power.com Hong Kong: Room 1006, 10th Floor, 299QRC, 287-299 Queen’s Road Central, Sheung Wan, Hong Kong FIRSTS 10 Asia struggles to match Europe in wind tech 11 India's hybrid approach spurs surge in fossil fuel subsidies 12 SIPG launches the first power plant simulator training program EVENT NEWS EXCEPTIONAL PROJECTS LAUDED AT ASIAN POWER, ASIAN WATER, AND ASIAN OIL & GAS AWARDS 2023 28 14 REGULATION WATCH EASIER GRID ACCESS IS NOW A REALITY FOR INDIA'S ENERGY BULK CONSUMERS 20 CEO INTERVIEW PLN LIGHTS UP INDONESIA'S MOST REMOTE CORNERS COMMENTARY COUNTRY REPORT INTERVIEW EVENT COVERAGE 48 Three reasons the US LNG pause does not threaten South Korea's energy security and transition 16 Regulatory delays dampen Indonesia’s carbon credit market momentum 18 Why Japanese utility firms are into the serious business of reselling LNG surplus 22 Summit Power's LNG plans offset gas decline 24 How Japan plans to accelerate its clean energy transformation

News from asian-power.com
Daily news from Asia
MOST READ


PLN IP leads in next-generation plant efficiency

Philippines must be ‘more aggressive’ on RE targets
Homeowners, businesses, and institutions can now integrate energy from photovoltaic (PV) rooftop solar panels into the power grid and enjoy smart home features using one app dashboard, a move by PLN Icon Plus to merge digital solutions with a sustainability ethos. The electricity company plans to maximise the use

Biomass, RE boost Tuas Power's green energy mix
As Singapore embarks on its energy transition, Tuas Power, one of the leading power and utility firms in the country, faces a tall order to decarbonise its operations as it runs fossil fuel-power generating facilities, including the sole coal/ biomass power plant in the market. Some of the measures are increasing the share of biomass use for power.
PT PLN Indonesia Power (PLN IP) is reducing production costs through specialised platforms that provide real-time predictive feedback on power plant efficiency. This ensures power plants always operate at their optimal conditions. Annually, the primary energy efficiency achieved by PLN IP is equivalent to IDR52.5b (US$3.36m).

Safety, supply concern gloom over ammonia co-firing adoption
Ammonia co-firing is touted as one of the solutions to transition coal-fired power plants, however, there are still concerns over its effectiveness in supporting decarbonisation drives, safety, and supply challenges. One challenge of co-firing ammonia in coal plants is delivering ammonia and ensuring that it is properly handled.
A leading renewable energy finance analyst has warned the Philippines should be “more aggressive” on its renewable energy targets. Despite renewable energy accounting for 22% of current electricity production and a target of 35% by 2030 and 50% by 2040, the country is full of natural resources and these targets should be higher.

Singapore faces cost, investment hurdles in hydrogen push
Natural gas-reliant Singapore is putting a premium on low-carbon hydrogen for its energy transition as it faces land scarcity to accommodate other forms of renewable energy. However, the hydrogen sector is still nascent, posing significant challenges in achieving the national target due to cost and investment woes.
 App connects PV rooftop solar panels to grid
App connects PV rooftop solar panels to grid
POWER PLANT RENEWABLE ENERGY GENERATION GENERATION SOLAR
RENEWABLE ENERGY

MWM 25H2-Kit for TCG 3016, TCG 3020 & TCG 2032 Operation with hydrogen. New variants of the TCG 3016, TCG 3020 and TCG 2032 series enable natural gas operation with hydrogen admixture of up to 25 vol.%. Retrofit solutions for existing plants are also available. www.mwm.net/25H2-Kits
Gentrack gains ground on SAP and other legacy solutions
High demand for Gentrack: Utility-specific software is leading the digital revolution towards Net Zero.

years.
The world is currently facing a climate crisis that cannot be overstated. Countries could have anywhere from 20 to 100 power stations, typically powered by coal or gas—both of which have detrimental impacts on the planet. It is an existential global threat that requires a significant reduction in carbon emissions. So, transitioning to clean energy is no longer an option; it is now an urgent imperative as the planet demands immediate action.
The time for action is now, and the stakes are high. Every decision made today will echo for generations to come, shaping the destiny of our planet. The world owes it to itself, to future generations, and to the countless species that share this planet to rise above and act to address climate change.
With that, the transition to renewable energy is also no longer a distant prospect; it is a crucial step to take. Embracing renewable energy technologies holds promise not only in combating climate change but also in economic growth and innovation.
From harnessing solar energy to tapping into wind power, the many renewable energy options present vast opportunities for sustainable development. It empowers communities to participate in decentralised energy production and rectifies inequities in the current energy systems.
Amongst those leading the charge in this shift to renewables is Gentrack, a force in energy retail technology. “We're passionate. We live and breathe energy and water. We live and breathe saving the planet,” stressed Geoff Childs, Gentrack’s General Manager for Asia.
Asian Power had the opportunity to talk to Gentrack to discuss the latest trends and innovations shaping the energy sector, gaining valuable insights into the company's vision and its role in driving sustainable solutions for the future.
What is the secret of Gentrack's success? Gentrack, with over 35 years of specialisation in
energy and water retail, brings unparalleled expertise and insight to its solutions. It is a pioneer in missioncritical energy retail technology, equipping retailers with the tools to navigate this changing landscape.
The company focusses solely on utilities, which allows it to better understand the unique challenges and requirements of these sectors. Unlike other solutions that have been dominating the market for the past decades with generic solutions, Gentrack's technology is tailored specifically for the needs of utilities dealing with electricity, gas, and water management.
The technological transformation is instrumental to achieve Net Zero by 2050 and we need all the governments in Asia to support this and set regulatory frameworks that favours renewable energies
Gentrack's technology boasts an impressive 80% out-of-the-box functionality tailored to meet the diverse needs of utility providers. The remaining 5% to 15% of these features are tailored to specific countries, whilst 5% to 10% cater to individual customer needs.
This streamlined approach translates to substantial cost savings and a significantly faster implementation timeline.
Gentrack's technology also empowers utility companies to drive innovation and launch new products and promotions swiftly. With a low-code, no code approach, billing teams can integrate new offerings within minutes to days, depending on
complexity. In contrast, legacy systems not designed for innovation often need lengthy customisations and the need for new code to be introduced by system integrators, consuming both time and resources.
Furthermore, from legacy meters bringing data once a month to once a year, today’s smart meters can ping data as quickly as once every five minutes. With this huge shift in data, utilities require effective data management.
Gentrack’s technology is capable of supporting the increasing complexity and volume of data that is generated by these advancements. It can process and manage large volumes of data in real-time. This way, homeowners and businesses also receive data immediately and are given the information they need on how they are using their energy, where their energy is coming from, and what they can do to be more efficient.
“Prosumers (consumers that also produce energy) are becoming more proactive in engaging with their energy solar panels, battery or electric vehicle. Our technology supports this”, said Childs. As markets shift towards renewable energy sources and decentralised energy systems, Gentrack's specialised solutions are in high demand. Utilities need to adapt quickly to changing regulations, and Gentrack provides the technology to support this rapid adaptation.
Traditional solutions struggle to keep up with the technological advancements and data requirements of the energy industry. Gentrack's technology offers a modern alternative that is better suited to the current and future needs of utilities.
Gentrack's meteoric rise—a staggering 700% growth in just four years—speaks volumes about its unique approach. It also serves as a testament to the company’s core values: “respect for each other, respect for our customers, and respect for our planet.”
Notably, Gentrack also has a flawless record of 100% transformation success, instilling confidence
6 ASIAN POWER
CO-PUBLISHED CORPORATE PROFILE
Gentrack share price has grown over 800% in the last 4
in utility providers that they are in capable hands. With Gentrack at the helm, utilities can navigate the complexities of the modern landscape with ease, driving efficiency, innovation, and ultimately success.
The unveiling of Gentrack's latest offering, Gentrack g2.0, marks a significant milestone in utility technology. Integrated with Salesforce CRM, the leading CRM platform, and hosted on AWS cloud, the premier cloud infrastructure, Gentrack g2.0 harnesses the power of industry-leading technologies.
Integrated with Salesforce CRM, users can now manage the entire utility lifecycle within a single interface, whilst also leveraging the AI capabilities of Salesforce CRM and Gentrack's own AI and machine learning solutions.
The future for energy providers
Demand for electricity continues to rise, yet intermittent renewable sources create challenges. Tackling these complex concerns whilst achieving Net Zero emissions is a defining challenge for the current generation. In this pivotal time, utility companies find themselves at the centre of this transformation.
Governments across Asia are sprinting towards green energy goals, each setting ambitious Net Zero targets. With this, coal- and gas-fired power plants are being replaced with large-scale industrial-size renewable energy. Amidst this transition comes the rise of off- and onshore wind farms, off- and onshore solar farms, and hydro plants, amongst others.
Utility companies are also expected to upgrade their software in the next decade. They are bound to embrace technological innovation to keep up with these advancements. Evidently, experts predict a rise in technology transformations amongst 200 of the world’s top utilities by 2025.
According to Childs, over the last 10 years, the world has doubled the amount of renewable energy that it can generate. This may seem like a big stride forward at first but Childs highlighted
that due to our expanding global population and advancing economies the world’s electricity usage has also doubled.
“It doesn't look like it's going to be enough to build all this large-scale industrial renewable energy... We're not getting very far,” he said.
Energy suppliers have come to the realisation that Net Zero cannot be reached by simply replacing old fossil fuel capacity with renewables and large-scale generation. Instead, energy
companies can make use of millions of other assets through homes and businesses’ roof space.
At the heart of hitting Net Zero lies a crucial task for energy retailers: changing consumer behaviour. By leveraging innovative technology, they can empower consumers to participate in the energy transition, shifting how they use and manage energy.
“If we're going to win this fight as people's energy is doubled, as well as the renewable energies doubled, we've got to change consumer behaviour,” Childs said. “So who owns the customer relationship? The energy companies own the consumer relationship, to an area that they're in a position to help change, motivate, and get people to shift and become more energy efficient.”
Amidst the ongoing call for cleaner energy, consumers worldwide have been adopting technologies such as solar PV, battery storage, heat pumps, and electric vehicles, and this trend is only set to pick up pace.
For Childs, encouraging the shift to cleaner energy options in Asia has to start with the government, especially since many energy companies in the region are government-owned. He further illustrated: “The technological transformation is instrumental to achieve Net Zero by 2050 and we need all the governments in Asia to support this and set regulatory frameworks that favours renewable energies. I think it's important.”
Energy retailers can provide a Distributed Energy Resource Management System (DERMS) and establish new revenue streams. Meanwhile, many governments can offer subsidies to customers who are investing in clean tech.
Whilst support from the private sector is welcome in the transition, it is through regulatory frameworks that incentivise the generation of renewable

ASIAN POWER 7
Elenita voluptas
CO-PUBLISHED CORPORATE PROFILE
Geoff Childs, Gentrack’s General Manager for Asia

energy that make it worthwhile for consumers. Through such frameworks, consumers can even get paid if they put solar energy into the grid for their energy production.
Accelerating progress by embracing potential solutions
To further stress the potential of renewable energy in Asia, Childs put forward Australia as an example of a country that was able to fulfil its energy needs with the help of rooftop solar panels. Being one of the leading energy markets in the world, Australia is predicting to get over 50% in the next few years of its energy from renewables, mainly rooftop solar, according to data from Gentrack.
Building on this point, Childs noted that Malaysia could enjoy similar benefits. Per Gentrack, 75% of Malaysia’s total energy requirements could be generated if there were solar panels installed on every single roof space in the country.
Childs acknowledged that the shift would not be a quick and easy feat, especially with the amount of time it takes to conduct planning, permissions, and large-scale construction, amongst others. However, he remains optimistic about the potential of a similar framework in other parts of Asia.
“They could shut down all of their coal-fired and gas-fired power plants if they just put solar panels on every single roof in the country. It's not that easy, don’t get me wrong. It'll take you probably five to seven years,” he said.
Given what has already been achieved in Australia, Childs believes this move could help propel the shift to clean energy and help meet governments’ Net Zero goals by 2050.
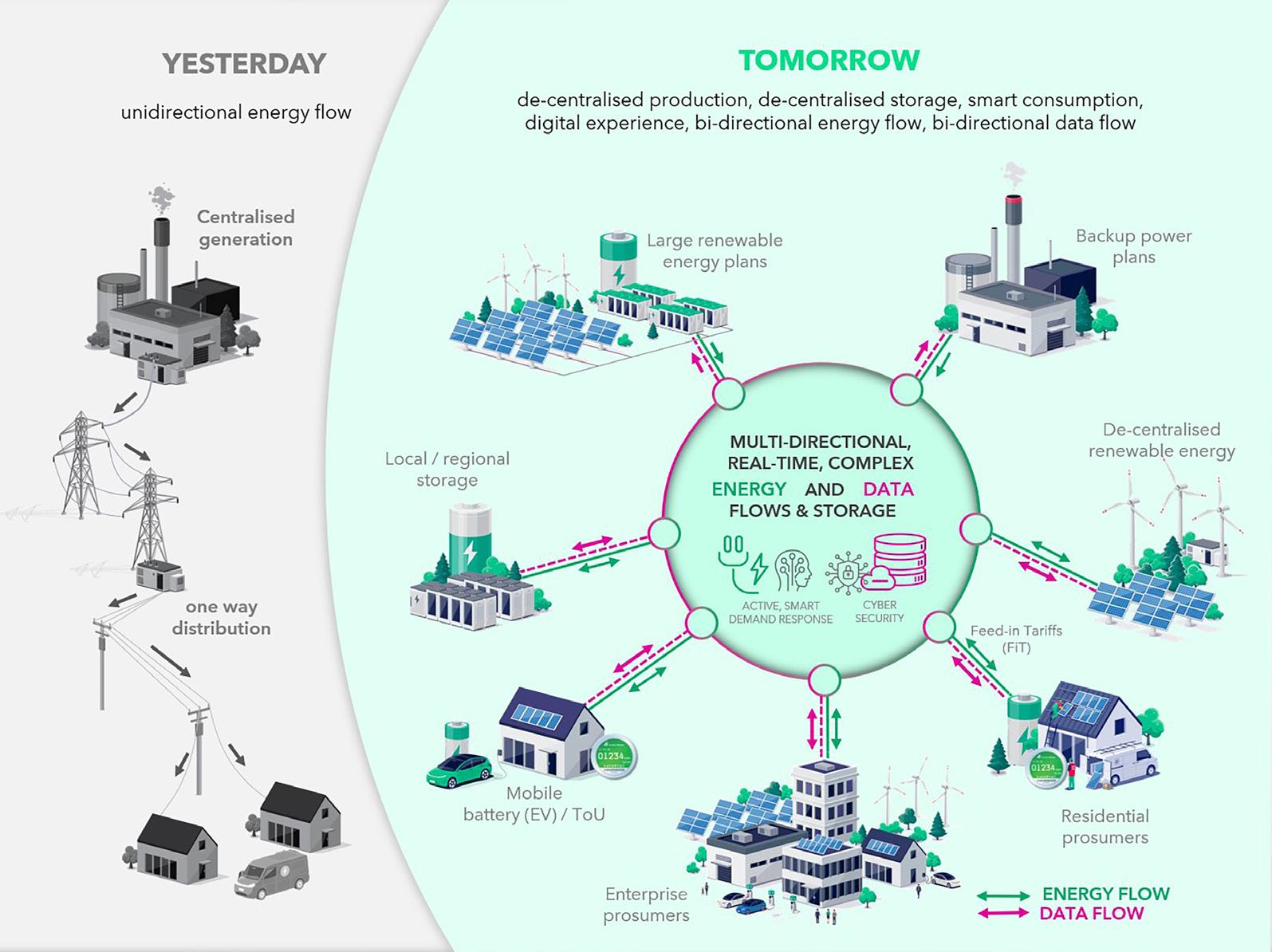
Green initiatives taken by Gentrack customers Gentrack has been introducing world-leading technology to enable innovative Distributed Energy Management (DEM) business models. This enables decentralised production and storage of energy, smart consumption, and digital experiences.
The company’s DEM ecosystem empowers energy suppliers to seamlessly and fully integrate with multiple partners, allowing them the flexibility to collaborate with those suited to their needs, resulting in faster time-to-market, enhanced customer relationship management, and reduced customer churn.
The company takes pride in serving the majority of its customers within some of the most mature energy markets globally, such as Australia, New Zealand, and
the UK. “We have some customers that are living in the future,” noted Childs. These companies include EnergyAustralia and Amber.
EnergyAustralia's Solar Home Bundle
A prominent player in the Australian energy market, EnergyAustraila unveiled its Solar Home Bundle initiative in mid-2022, offering tier-one rooftop solar panels to Australians. This signalled a disruptive shift towards renewable energy adoption, allowing customers to embrace renewable energy solutions without the initial financial burden as the solar and battery are provided to homeowners with no upfront investment and a flat fee over a 7-year energy plan.
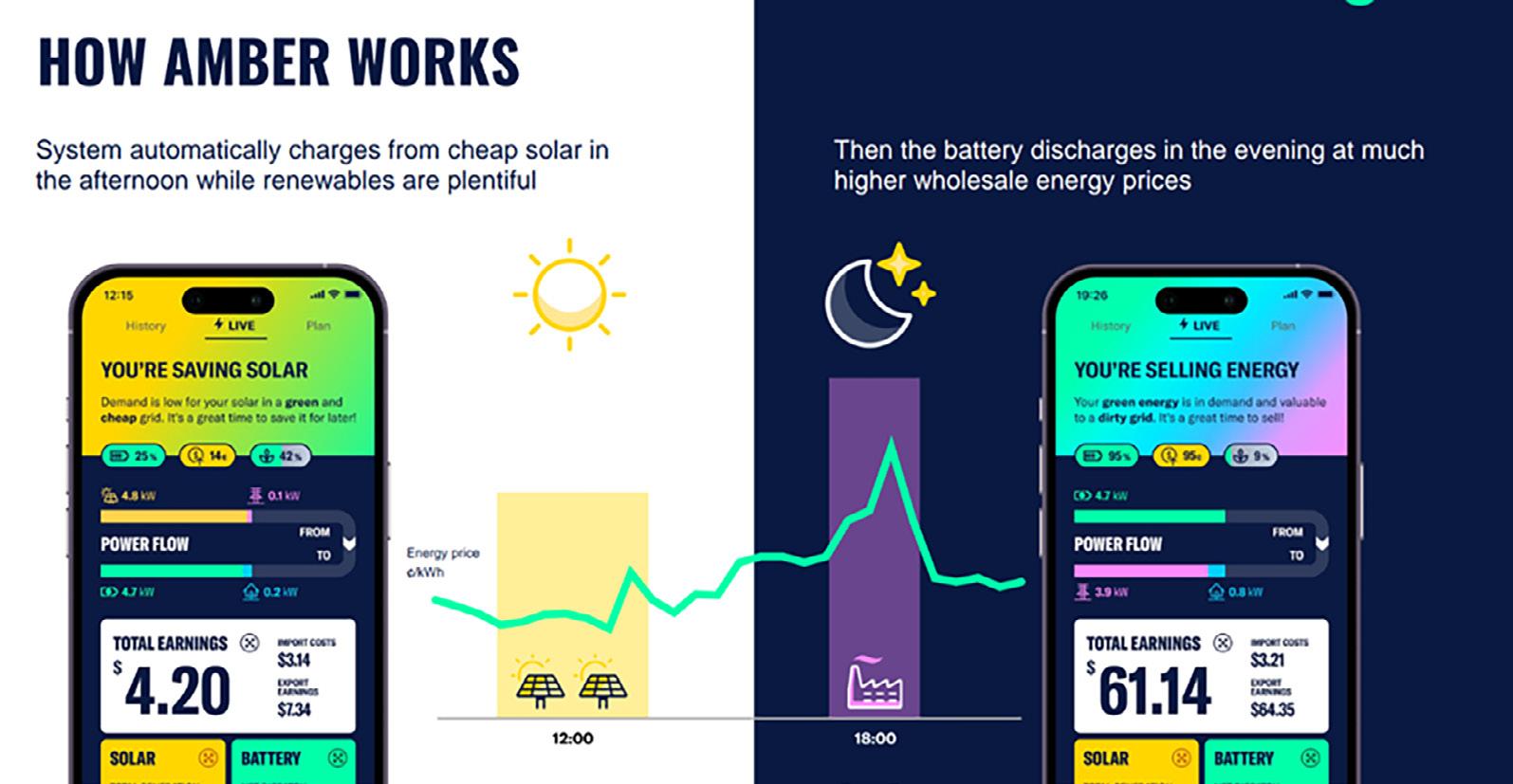
Amber’s Customer-Centric Approach
Meanwhile, technology company and energy retailer Amber prioritised customer-centricity in its approach to the renewable energy transition. This is done through real-time wholesale electricity pricing, smart home automation, selling excess renewable energy to the grid, and maximising the value of household batteries and electric vehicles.
Shaping a Sustainable Future through Innovation and Collaboration
EnergyAustralia and Amber are two examples of Energy Retail companies with innovative offerings in the new era of energy providers. Empowered by Gentrack, they are changing the traditional business model of energy and finding different ways to market renewable energy.
Gentrack is not just leading a future powered by clean energy; it is building a movement and inspiring individuals and companies to join the fight for a healthy, sustainable planet. Environmental stewardship is embedded in it, from technology choices to business practices.
However, the fight against climate change demands collaboration, innovation, and determination. Embrace the power of the future: invest in renewable energy today and secure a cleaner, healthier tomorrow.
8 ASIAN POWER
CO-PUBLISHED CORPORATE PROFILE
A catalogue showcasing innovative offerings that energy utilities around the world are bringing to market.


For over 35 years Gentrack has been partnering with the world’s leading utilities, and more than 60 energy and water companies rely on us.
Gentrack, with our partners Salesforce and AWS, are leading today’s transformation with g2.0, an end-to-end product-to-profit solution. Using low code / no code, and composable technology, g2.0 allows utilities to launch new propositions in days, reduce cost-to-serve and lead in total experience. www.gentrack.com
request your access

ASIAN POWER 9
FIRMS BID FAREWELL TO CLASSICAL APP DEVELOPMENTS

Driven by the need to meet regulatory standards and boost cybersecurity, more businesses are turning to technologies like low code/no code platforms and cybersecurity systems. This shift is paying off, with 72% of companies reporting increased profits due to these innovations, according to KPMG.
Sushant Rabra, Partner, NDT-Digital Advisory, KPMGI in India, said low-code/no-code platforms, which are used to improve customer experience, service quality, ESG compliance and overall collaboration, can fast-track processes.
“Compared with classic platform buildout, lowcode/no-code platforms make processes up to five times faster, which expedites time-to-market, timeto-value and time-to-change,” Rabra said.
Because of this, KPMG found that 74% of the respondents from the energy sector firms said that their business leaders are confident in the resilience of the applications built by the platforms, higher than the 59% average across all sectors surveyed.
Low-code/no-code platforms enable companies to create, design, and launch entire web-based applications with the need for complex coding and development experience, according to KMPG.
“Energy organisations are aware that this is the way forward,” Rabra said. “They have seen the value of these systems first-hand, so they are not going to go back to classical application development factory models.”
KPMG said that regulatory obligations and security concerns are the "top triggers" of digital transformation, adding that stronger data privacy or cybersecurity are the user expectations that compel them to pursue digital transformation projects.
“It’s often repeated that a chain is as strong as its weakest link, so energy firms hold ecosystem partners to a very high standard,” Rabra said. “Energy companies often create governance models for the entire ecosystem to adhere to, helping ensure a clear and strict security baseline.”
Investing in employee capabilities
Due to this, KPMG found that 52% of energy companies are planning to invest more in enhancing the capabilities of their employees.
It noted that energy firms’ investments in technology will only be successful when they have the right talent.
“The roles of tomorrow will likely be a combination of domain skills, such as those of a reservoir engineer, digital skills and professional skills, such as stakeholder or change management,” Rabra said.

Asia struggles to match Europe in wind tech
Asian countries, particularly China and Japan, are driving offshore wind energy with almost 60% cost cuts and tech breakthroughs. Whilst they lead in patents and innovation, they struggle to keep up with Europe's floating wind tech and need to enhance their manufacturing and supply chains. With global offshore wind capacity set to rise to 500 Gigawatts by 2030, overcoming these challenges is key to harnessing its full potential and meeting the world's future energy needs.
"Patents filed in China account for 6% of the first patent office choices, with Japan at 4% and South Korea at 3%, totalling almost a quarter of these choices in Asia," Roland Roesch, Director of Innovation and Technology Center at the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) said.
"Continuous research and innovation have led to a stunning 59% reduction in the levelized costs of offshore wind over the past decade," Roesch stated, emphasising the impact of technological advancements.
IRENA forecasts that by 2030, the global offshore wind capacity will rise to 500 Gigawatts, with a substantial contribution coming from Asia, particularly China.
Whilst the dominance of China in patent filings is marked by a domestic focus with a majority of patents filed related to utility models, China holds a
significant place in international patent families.
He added that the challenges faced by these leading countries, particularly China, include closing the technology gap with Europe in floating offshore wind, improving manufacturing techniques, and enhancing the supply chain's completeness.
Roesch highlighted the correlation between market trends and patent assessments, noting, "Europe remains the dominating region, but Asia and the US are emerging as future markets."
According to an IRENA report with the European Patent Office, three dominant technology trends are shaping this sector: floating foundations, absorbing logistics, and the production of green hydrogen.
"Floating offshore wind is expected to rapidly bring down costs and open new markets," Roesch explained. This innovation is particularly crucial in regions where fixed foundations are not feasible, presenting new opportunities for offshore wind energy.
He emphasised three main principles for an effective regulatory framework: maintaining or increasing installed capacity targets, ensuring market competition, and facilitating the permitting process.

"These elements are essential for reducing costs and promoting competition in offshore wind," he explained.
Cost-competitive technology
The study by IRENA and the European Patent Office (EPO) said offshore wind projects are cost-competitive as it is able to generate high energy output per square metre due to their location.
Aside from this, the global weighted average total installed costs of offshore wind fell from $5,217 per kilowatt (kW) in 2010 to $3,461 per kW in 2022, peaking at $5,975 per kW in 2022.
As such offshore wind deployment increased by twentyfold to 63.2 GW in 2022 from 3.1 GW in 2010.
"Given its potential, offshore wind is expected to play a key role in the energy transition towards 2050," the report read.
IRENA and EPO added that offshore wind-related technologies are improving leading to higher estimated lifetime capacity factors for newlycommissioned projects, increasing from 38% in 2010 to 45% in 2017. It slightly declined to 42% in 2022.
Europe remains the dominating region, but Asia and the US are emerging as future markets
These improvements include larger turbines with longer blades, higher hub heights, and locations farther from shorelines where there are more wind resources.
"Initially, offshore wind farms were situated closer to shore and at shallow depths," the report read.
10 ASIAN POWER
POWER UTILITY
Floating offshore wind, like in Akita, Japan, is expected to bring down costs (Photo from Marubeni)
TECHNOLOGY
FIRST
Roland Roesch
India's energy subsidies
Source: MappingIndia'sEnergyPolicy2023,InternationalInstituteforSustainableDevelopment
Fossil fuels dominate as India's clean energy lags
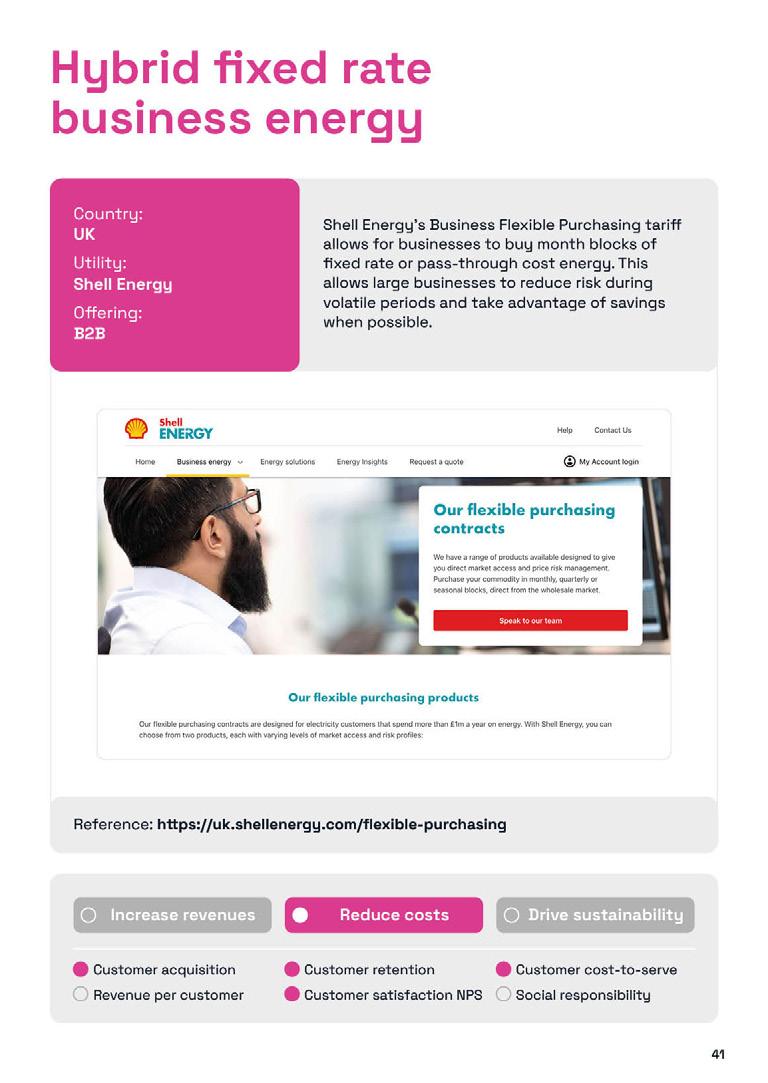
Despite India's adoption of a hybrid approach to funding its energy mix, traditional sources like coal, gas, and oil still received the lion's share of subsidies.
40% of government financial support went to fossil fuels, while emerging sectors such as green hydrogen, battery storage, and offshore wind received less than 10%.
According to a report by the International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD), this supply strategy has propelled India's overall energy subsidies to reach a nine-year high of $39.3b (INR3.2 lakh crore) for the fiscal year ending in 2023 (FY 2023).
India is aiming to grow its economy to $5t within the next three years, up from $3.7t in FY 2024, as per the Mapping India's Energy Policy 2023 report.
In the Union Budget 2023–2024, the government allocated $4.4b (INR35,000 crore) towards priority capital investments for energy transition and achieving net-zero objectives. The nation has also been advocating for a tripling of global renewable energy capacity by 2030.
“However, the country’s rapidly increasing energy demand has also led it to adopt a hybrid approach, bolstering all forms of energy supplies in 2023,” the experts from IISD stated.
The majority of remaining subsidies were allocated to electricity consumption, particularly in agriculture.
Support for fossil fuels
The surge in energy demand, compounded by the repercussions of the international energy price crisis post-Russia's invasion
Whilst fossil fuel subsidies have reduced by 59% since their peak in 2013/2014, without further targeting and a return to a market-based pricing regime, they could mount again, resulting in budgetary impacts
of Ukraine, prompted India to implement measures such as capping retail prices of petrol, diesel, and domestic liquefied petroleum gas, tax reductions, direct budgetary transfers to businesses and consumers, and reinforcement of existing energy supplies to bolster support for fossil fuels in 2023.
Swasti Raizada, policy advisor at IISD and co-author of the report, cautioned against the potential adverse impacts of untargeted fossil fuel subsidies.
“Whilst fossil fuel subsidies have reduced by 59% since their peak in 2013/2014, without further targeting and a return to a market-based pricing regime, they could mount again, resulting in budgetary impacts,” she said.
“This is undesirable, as untargeted fossil fuel subsidies are an inefficient way of supporting low-income households, and they shrink the fiscal space available for supporting clean energy technologies," the expert added.


Raizada also pointed out that the current approach perpetuates dependence on volatile fossil fuels and delays India's clean energy goals for 2030. Moreover, the IISD report also proposed the allocation of a portion of fossil fuel tax revenues to facilitate a just transition toward clean energy.
Deepak Sharma, policy analyst at IISD, stressed the necessity of significant investments to ensure India's energy transition is equitable, sustainable, and inclusive, particularly within state-owned enterprises.
“India’s state-owned enterprises will be a critical part of this shift,” he said. As their majority shareholder, the government should ensure that all fresh capital going to these entities is linked to India’s net zero commitments.”
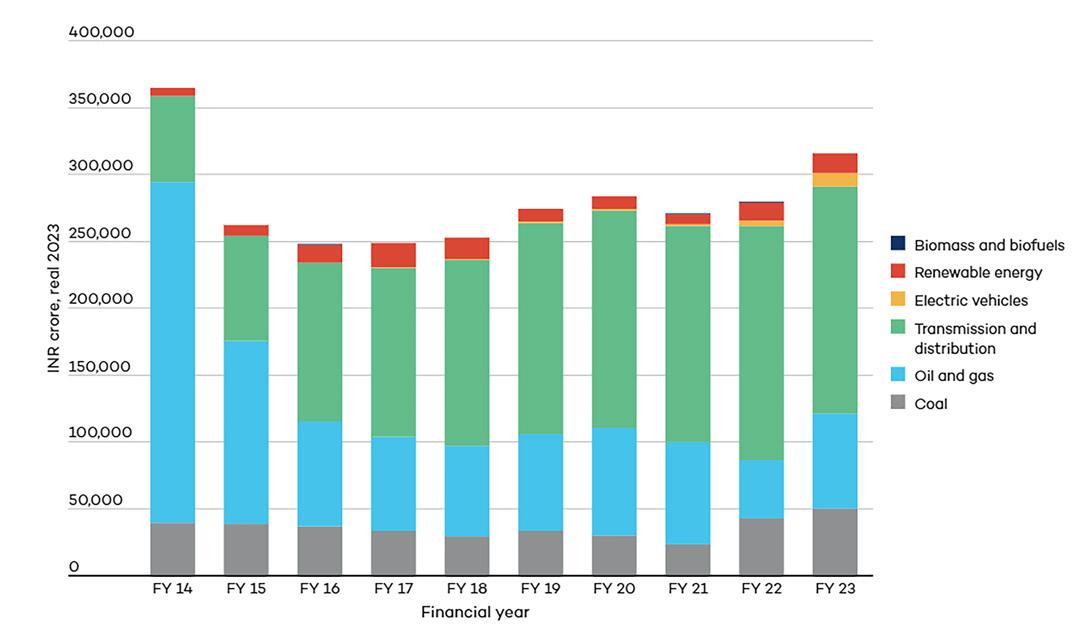
ENR EXECUTIVES CONCERNED ABOUT ENERGY TRANSITION PROJECTS’ ECONOMIC VIABILITY
Executives from the energy and natural resources (ENR) sector are concerned about the financial viability of energy transition projects due to difficulty in looking for customers who are willing to pay higher prices.
In a report, Bain & Company noted that 70% of executives in the sector cited this concern as a major roadblock in their energy transition, significantly higher than the 56% last year.
“In our view, the direct impact of higher interest rates on the cost of transition projects is one of the most important stories of 2023 and is likely shaping executives’ perspective on this issue,” the report read in part.
Bain added that a 500-basis-points raise in the cost of capital can boost the total annual revenue needed for a project by as much as 50%. Aside from
this, 54% also considered as a barrier the government policy and regulators, increasing from 50% in 2023.
Other barriers
The survey also found that 30% of the executives cited the lack of organisational capability for scaling at speed as a barrier, declining from 34% last year. Supply chain constraints are also a barrier for 30% of the executives, a slight uptick from 29% from the previous survey.
Meanwhile, those who identified the lack of cash or capital as a problem increased to 29% from 23% in 2023.
Lack of experience/talent in new business areas remains a problem for 28% of the executives, a slight decline from 31% last year.
Taxes, carbon pricing, and subsidies were top influences on customer behaviour.
viability is still a major roadblock for the energy transition
Source: Bain&CompanyEnergyandNaturalResourceExecutivePulse2024
ASIAN POWER 11
REGULATION FIRST
Financial
Swasti Raizada
Deepak Sharma
70% OF CONSUMERS RELUCTANT TO INVEST IN SUSTAINABLE ENERGY

Sustainability in energy has remained a critical driver in the sector, but 70% of energy consumers have revealed that they are unwilling to invest time or money in sustainable energy, experts from EY said.
According to the report “Energy Transition Consumer Insights” by EY, 65% of consumers are aware of making sustainable energy choices, but they are inundated by consumer fatigue, stalling confidence, and stagnating progress for energy transition.
“Consumer apprehension comes as we enter a new — more difficult — phase of the energy transition, all while dealing with higher energy prices, geopolitical volatility, and growing concerns around energy equity. While efforts on the supply side are gaining momentum, we need an even more fundamental shift in how we engage and encourage sustainable consumer behaviour,” Greg Guthridge, Global Energy & Resources Customer Experience Transformation Leader at EY, stated.
“Energy consumers want a clean energy future but need a broad range of support to make personal energy choices. Closing the gap between their interest and action will depend on energy providers, government, and the broader energy ecosystem working together to pull every lever available,” he added.
Respondents in the report which involved over 100,000 residential energy consumers in 21 markets claimed that the energy sector has failed to deliver on three important factors: affordability, access, and appeal.
Only 30% are optimistic that energy consumption will remain affordable and 72% reveal that they cannot absorb bill increases of 10%. This is despite 26% of consumers having a good understanding of renewable energy and sustainability, reflecting a lack of improvement.
However, a significant 77% of respondents hope for energy providers to offer low-cost energy products and services. It aligns with 67% seeking personalised energy solutions and 18% of consumers wanting to adopt new energy products and services if they are convenient to buy and install.
The lack of urgency in sustainable energy will depend on the energy companies seizing the opportunity to engage with consumers and initiate action.
Consumer confidence
Chinese consumers are the most confident in the energy market and the energy transition with a score of 77.6, according to the EY Energy Consumer Confidence Index.
This is followed by Malaysia with an index of 70.6 and Hong Kong with a figure at 66.2
SIPG launches the first power plant simulator training programme
To address gaps in the skilled workforce and develop competencies, the Singapore Institute of Power and Gas launched the country's first centralized power plant simulator training program, aiming to standardize practices across the energy sector.
Introduced in collaboration with the Energy Market Authority (EMA) and several Singaporean power generation companies, the CPPS aims to centralise and standardise training standards for the energy sector in Singapore to ensure that the workforce can be prepared for rare but critical scenarios for Singapore’s power sector.
“As the energy landscape continues its dynamic and transformative journey, SIPG is focused on cultivating competencies and technological know-how needed for the industry to keep pace with change. The Gencos’ collaborative and structured approach promotes sharing and adoption of best practices,” Chia Soo Ping, Principal of SIPG, said.
Coursework
The six courses integrated with CPPS will establish a consistent standard for skills training, from power plant operations to process controls, from the management of equipment alarms to the safety of plant operators.
First dual-fuel plant opens in NSW

EnergyAustralia opens Tallawarra B Power Station, the first dual-fuel gas and green hydrogen plant in New South Wales (NSW).
Located next to an existing 435 MW gas plant, the AU$300m facility can deliver up to 320 MW of dispatchable power.
It is expected to operate on a blend of 5% (by volume) green hydrogen and natural gas in 2025 subject to the development of a hydrogen manufacturing industry of an appropriate size and scale.

These courses were co-developed with Gencos including Keppel Merlimau Cogen O&M, PacificLight Power, Sembcorp Cogen, Senoko Energy, Tuas Power and YTL PowerSeraya.


Invenergy starts Japan wind farm
Aside from this, SIPG also launched a structured training programme which includes two new Power Generation Certificate Programmes. Upon completion of the courses, certificates recognised by all gencos will be issued, as well as other Power Generation courses offered by the Institute.
Preparing the workforce
Minister of State Low Yen Ling lauded the simulator training programme, adding that there is a need to continue investing in the power grid’s maintenance and upgrade, as well as inspecting electricity-related infrastructure.

US-based Invenergy started the commercial operations of Rusutsu Wind Energy Center with a total capacity of 63 megawatts (MW).
As the company’s first wind farm in Japan, the project consists of 15 wind turbines with a capacity of 4.2 MW each. It could power around 35,000 Japanese households and offset 64,000 tonnes of carbon emissions annually.
It is located in Rusutsu Village in Abuda District, southwest of Sapporo in Hokkaido Prefecture, and situated at an elevation of 800m to maximise energy generation capacity.

Adani Green Energy Limited (AGEL) completed the operation of its 300-megawatt (MW) wind power project in Gujarat with the operation of the remaining 126 MW capacity. This is on top of the 174 MW capacity that started operations earlier. It will produce around 1,091 million electricity units, abating around 0.8 million tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions annually. This makes AGEL the company with the largest renewable energy portfolio in India with a total capacity of 9,604 MW.
12 ASIAN POWER
POWER UTILITY
Adani Green wraps 300 MW wind farm PLANT WATCH AUSTRALIA JAPAN INDIA
Courses include power plant operations and process controls (Photo from EMA)
FIRST
POWER UTILITY
Low Yen Ling
Chia Soo Ping




Easier grid access is now a reality for India's energy bulk consumers
As India boosts its adoption of renewables, the government has removed a bottleneck for consumers operating their own power plants or energy storage systems. New policies state that such consumers no longer have to secure a licence to establish, operate and maintain transmission lines to connect to the grid, a move that also supports the country’s energy security.
The Ministry of Power said this rule would apply only to “bulk consumers” or those with a load of not less than 25 megawatts (MW) if they plan to connect to the Inter-State Transmission System and at least 10 MW if they want to connect to the Intra-State Transmission System.
“By allowing such a facility, a new category of Bulk Consumers would emerge in the country, benefitting from more affordable electricity and enhanced grid reliability,” the ministry said.
Charith Konda, energy specialist for India Mobility and New Energy at the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), said this new policy enhances the ease of doing business.
Konda cited how a green hydrogen producer would no longer have to wait for the government to establish the transmission lines to connect to the grid.
“[A consumer can now just] get approval from the State Government to go ahead and acquire the land or the right of way, design a compensation pay for it, and get my power delivered rather than facing all the delays that could happen if [the] State has to build the grid,” he told Asian Power
“Earlier, state utilities had a monopoly in a particular region for establishing transmission lines. But now even private players can establish their lines. So, probably it improves the overall industry, competitiveness and efficiency,” he said.
Removing bottlenecks
Konda said that prior to this policy, a project operator would have to negotiate with the state to connect their power project to the nearest state-owned substation to build the transmission line.
If the government is taking too long to complete the task, they build the project themselves but would need to secure a licence first. On top of that, they would have to pay additional wheeling charges, transmission charges, and open-access charges to the state to get their power delivered.
Konda said that state distribution utilities usually discourage bulk consumers from procuring from their own generating companies or any other private power-



generating companies through the state grid through the Open Access mechanism.
As the state loses revenue or has no direct interest in the mechanisms, they impose additional surcharges on the Open Access that put an additional burden on the bulk consumers.
“What the federal government is trying to do is to remove that bottleneck,” Konda said.
Aside from the policy on transmission lines for bulk consumers, the government also rolled out a new rule mandating that Open Access charges “must be reasonable and uniform throughout the country,” noting the prohibitive charges imposed by some state regulators.
This policy is not new and was only applicable to generating companies. However, the energy landscape is evolving and the line between a consumer and a generator starts to blur.
“Therefore, it was but natural that the same benefit is extended to consumers because a lot of consumers are at their corporate level trying to achieve net zero and decarbonise their organisations,”
Akhilesh Awasthy, partner at The Lantau Group, told Asian Power
“[It is] bringing parity between a generator and a consumer in terms of how they can build their own transmission line connecting to the grid substation, and to promote these forms to avail open access, get the green energy supplied to them from different sources using this transmission line,” he added.
Energy transition
Removing the state-level barrier will boost the integration of renewable energy (RE) into the grid, as well as the uptake of green hydrogen and energy storage projects, Konda said.
With more power available, this policy creates options for the industry, facilitating energy transition, Awasthy said, adding that corporate power purchase agreements demand with large corporations is growing.
“The consumer can wheel power, maybe, through the regional grid directly and reduce the cost and therefore would encourage energy transition,” he said.
Awasthy also noted that whilst Open Access is also available to conventional power sources, the government has rolled out a rule specifically for green energy.
The Indian government issued the Green Open Access rules in 2022 which aim to promote the generation and consumption of green energy, allowing the procurement of green energy through the Open Access mechanism.
The minimum transaction limit for noncaptive consumers is 100 kilowatts, whilst no limit is imposed for captive consumers.
Under the rule, the concerned nodal agency should approve applications for Green Energy Open Access within 15 days from filing of the application. Failure to do so automatically deems the application approved, but subject to compliance with the technical requirements.
14 ASIAN POWER REGULATION
WATCH: INDIA
The government lifts licence requirements to build, operate, and maintain transmission lines.
A new category of bulk consumers would emerge in the country, benefitting from more affordable electricity and enhanced grid reliability
Consumers no longer have to secure a licence to establish, operate, and maintain transmission lines to connect to the grid
Charith Konda
Akhilesh Awasthy


Regulatory delays dampen Indonesia’s carbon credit market momentum
The new carbon market has as much as 71.95% of carbon credits unsold at the end of 2023.
Despite Indonesia’s robust potential in the burgeoning carbon market, highlighted by a potential worth of $192m (IDR3,000t), industry leaders voice concerns over the lack of regulatory framework for foreign trade.
This absence threatens to squander a significant opportunity in carbon credit demand, against the backdrop of the government’s commitment to climate action, energy experts warned.
“With a minimum of 30 billion tons of carbon credits, while the baseline set by the government is 2.8 billion tons, it is far from enough, so Indonesia has significant potential to achieve emission reduction targets through these carbon credit projects,”
Riza Suarga, who chairs the Indonesia Carbon Trade Association (IDCTA), told Asian Power.
Furthermore, the sluggish start to carbon trading since its opening in September 2023, marked by low transaction volumes and a majority of carbon credits remaining unsold, underscores the challenges facing Indonesia in capitalizing on its environmental and economic goals.
Not optimal yet
Although the carbon market has been open since September 26th 2023, trading transactions on the market are still considered low. From that date up to the end of December 2023, the trading value on the Indonesian Carbon Market reached IDR 30.9 billion with a trading volume of 494,000 tons of carbon dioxide. Until the end of 2023, as much as 71.95% of carbon credits remain unsold.
With a minimum of 30 billion tons of carbon credits, while the baseline set by the government is 2.8 billion tons, it is far from enough
According to the Indonesian Financial Services Authority (Otoritas Jasa Keuangan or OJK), which is the regulatory authority overseeing carbon trading in the Indonesian carbon market, the demand is still minimal. One reason for this is the lack of obligation for corporations to have carbon credits, so transactions in the carbon market tend to be voluntary.
Globally, there are two types of carbon trading mechanisms: the voluntary market and the mandatory market. In the voluntary market, emission producers compensate for the CO2 produced by purchasing carbon credits from projects aimed at reducing or eliminating CO2 emissions. The voluntary market is not regulated by the government, and transactions take place directly between the seller and the buyer.
In the mandatory market or cap-andtrade system, authorities set emission limits for participants, and carbon credits are sold to entities that exceed the government’s limits.

Riza said that whilst optimising carbon credit trading mechanisms and imposing carbon taxes are expected to attract demand for purchasing carbon credits, it is also important to regulate the realisation of trading for foreign investors. “Liquidity comes not only from domestic sources but also from foreign buyers, and if there are no foreign buyers entering, our market is not attractive,” he explained.
He added that the government should regulate foreign trade soon. If the obstacle to foreign trade is due to national emission reduction targets, Riza believes there is no
Carbon offset market process
need to worry about it. “If the issue is about recording, it’s not a problem because there is no obligation to transfer credits, so there is no obligation for buyers, especially from the private sector, to take emission reduction records to their country. Moreover, the projects or forests are in the country,” he said.
Riza acknowledged that one issue regarding carbon trading is verification and data monitoring, where in order to be traded, stored carbon must be registered and then validated. In Indonesia, the validation process is carried out by the Ministry of Forestry and Environment (KLHK). If verified, KLHK will issue emission reduction certification that can be traded on the carbon market.
However, this issue does not need to be a major problem because of current technological advancements, such as the existence of blockchain. “Integrating this data is important to help better understand the market,” he said.
Riza also mentioned Japan as a potential buyer in the Indonesian carbon market as many Japanese companies have growing interest.
Short-term steps
The IDCTA, consisting of carbon project developers, has actually initiated carbon trading even before the existence of the carbon market in Indonesia. The association currently has 40 members, with 20 active members from various sectors, including forestry and energy. One of the association’s members is Pertamina NRE.
Riza noted that the IDCTA has shortterm and long-term steps to support the carbon trading ecosystem in Indonesia. The first involves environmental issues, with the primary goal of supporting the achievement of a 1.5-degree Celsius temperature reduction as targeted by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
“Our contribution here is related to technical issues and research and development for the methodology of carbon credit certification before being traded again, as well as co-benefits for community development and biodiversity,” he said.
Furthermore, the IDCTA supports the carbon trading ecosystem in Indonesia through legal programs and advocates for the government on carbon trading regulations, promoting carbon trading in Indonesia on the global stage.
In addition, the association focuses on providing training to enable its members to trade carbon smoothly and attempts to provide financial solutions between investors and project owners.
16 ASIAN POWER COUNTRY REPORT: INDONESIA
Source: Indonesia Carbon Exchange (IDXCarbon)
Riza Suarga


Why Japanese utility firms are into the serious business of reselling LNG surplus
Declining local demand for LNG directs Japanese companies to the South and Southeast Asian markets.
Japanese utility firms are facing an oversupply of liquefied natural gas (LNG) as demand for the resource declines with the country’s accelerating shift to nuclear and renewables for power generation. Due to the surplus, these utility firms are creating a business, reselling their LNG to other markets.
The country’s LNG imports surged after the 2011 earthquake which resulted in the Fukushima nuclear disaster, peaking at 89 million tonnes in 2014.
However, under Japan’s long-term decarbonisation plan, LNG-fired electricity generation is targeted to decline by 53% by 2030 to 187 terawatt-hours. The LNG demand could fall between 25.7 and 31.6 million tonnes per annum or around a third of 2019 levels, according to the Institute of Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA).
As LNG demand is projected to decline, the country’s largest utilities such as JERA, Tokyo Gas, Osaka Gas, and Kansai Electric will have an over-contracted position of around 11 million tonnes per annum over the decade.
“This means that they will have a surplus that they have to find something to do with. Because of declining opportunities domestically, they are looking to resell that LNG to other countries,” Sam Reynolds, Research Lead for LNG/Gas in Asia at IEEFA, told Asian Power
“A lot of their corporate strategies suggest an outward push rather than looking for domestic opportunities,” he said.
Reynolds said these utility firms are trying to create a new business. For example, they are developing LNG infrastructure in South Asia and Southeast Asian countries such as Bangladesh, the Philippines, and Vietnam.“They’re trying to cultivate demand by investing in, for example, power plants and city gas distribution companies to develop a market where they can offload their surplus LNG volumes,” he added.
Decline in LNG demand
Nuclear energy generation increased by 54% and renewable energy (RE) rose by 7% through November 2023, but LNG imports declined by 8% — higher than the average 3% rate decline over the past decade, according to IEEFA.
In 2022, the country restarted 10 reactors with a total capacity of 9.9 gigawatts (GW), with two more reactors restarting in the summer of 2023, bringing its total nuclear capacity to 11.5 GW by end-2023. This year, nuclear availability could rise to 14 reactors with a total capacity of 13.7 GW and 16 reactors in 2025, it said.
Because of this, LNG demand could decline further by up to 6 million tonnes or 9% of 2023 levels, IEEFA said.
Meanwhile, Japan’s RE growth would further cut LNG demand. Solar capacity rose by over threefold since 2014, whilst wind capacity rose by 60%. In 2023, the two sectors made up 14% of the country’s power requirements, increasing from 1.7% a decade ago.
IEEFA also noted that the country will be launching offshore wind licence tenders which will deploy 10 GW of offshore wind by 2030.
“A third reason is that Japan is facing declining demographic fundamentals. Energy demand and population are expected to decrease over the next decade,” Reynolds said.
“Finally, there’s a restructuring going on in Japan’s gas and power markets. Japan is opening up competition for other suppliers of gas and power and allowing end users to choose their own suppliers. And that’s effectively broken up the monopolies of Japan’s largest utilities,” he said.
Reynolds foresees this would result in the four largest utilities having an LNG oversupply in the next decade.

Japan is opening up competition for other suppliers of gas and power and allowing end users to choose their own suppliers
Addressing LNG surplus
The four utility firms accounted for almost 75% of Japan’s historical activity, with JERA comprising 40% of the total, which includes contracts it took over from its parent firms Tokyo Electric and Chubu Electric. Tokyo Gas, Kansai Electric, and Osaka Gas were responsible for 14%, 9%, and 8%, respectively, of the country’s contracting activity.
JERA, for example, has reduced its gas consumption at a rate of 5.7% since 2017 due to the rise in nuclear generators, new coal capacity and greater efficiency, with the decline rate expected to be at 4.9% this decade.
The company has an over-contracted LNG of 2.2 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) in 2022. The country announced in 2017 aims to be a major global LNG trader. Since then, its LNG sales rose to 6 mtpa in 2023 from 0.6 mtpa.
It also invested in LNG assets abroad to stimulate demand, including LNG-fired power plants, regasification terminals and distribution companies in Bangladesh, Indonesia, the Philippines, Vietnam, Singapore and Thailand.
Tokyo Gas, Japan’s largest city gas utility and second largest LNG buyer, saw its domestic gas sales declining at an average of 4.5% since 2017, with IEEFA expecting the decline rate to accelerate between 5.5% and 6%.
It aims to form a Southeast Asia value chain by investing in assets that will also stimulate demand, which include two 1.5 gigawatts LNG-fired power plants in Vietnam. It also launched an LNG trading unit in September 2020, with its LNG sales increasing by nearly fourfold since 2017.
Meanwhile, Osaka Gas, the second largest city gas utility, saw its gas sales decline at an average annual rate of nearly 4% since 2017, which IEEFA expects to increase to 5% through 2030, as Kansai gas customers switch providers due to market liberalisation.
18 ASIAN POWER
SCAN FOR FULL STORY
Sam Reynolds, Research Lead for LNG/Gas in Asia at the Institute of Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA)
INTERVIEW
Transforming the way we power our world
Fluence is a global market leader in energy storage products and services, and cloud-based software for renewables and storage. With a presence in APAC since 2018, the Fluence team has more than 16 years of global energy storage deployment experience, including the deployment of the industry’s first utility-scale system in 2008.
225+
7.6+ GW ENERGY STORAGE PROJECTS
OF ENERGY STORAGE
22.3+ GW
Blog | Three reasons to avoid self-Integration of battery-based energy storage systems

Blog | Why large-scale fire testing is needed for battery energy storage safety
COMMITMENT TO ASIA PACIFIC
Fluence has delivered battery-based energy storage systems in four major energy markets: Australia, the Philippines, India, and Taiwan. We continue to support our customers in achieving their business goals, and accelerating the region’s clean energy transition with advanced technology and industry-leading safety.



ASIAN POWER 19
MARKETS 47 AI-OPTIMIZED RENEWABLES AND STORAGE
https://fluenceenergy.com/
INTERVIEW
PLN lights up Indonesia's most remote corners
State-run firm’s president succeeded in electrifying 76,900 villages and sub-districts.
Indonesia's state-owned electricity company, PT PLN, is committed to driving the nation towards full electrification with a particular focus on reaching remote and underserved communities.
Guided by a mandate to ensure fair access to electricity in the so-called 3T areas — the disadvantaged, the frontier, and the outermost regions — PLN is dedicated to making sure that no community is left in the dark.
At present, PLN has connected an impressive 76,900 villages to its grid out of a total of 83,637 nationwide, marking significant progress toward universal electrification through its village electricity programme or LISDES.
Meanwhile, the remainder comes from non-PLN electricity in 3,885 villages and energy-saving solar lamps (LTSHE) in 2,852 villages – bringing the national electrified village ratio (RDB) to 99.85% in 2023.
In this exclusive interview with Asian Power, PT PLN President Director Darmawan Prasodjo shares the company’s progress in illuminating Indonesia’s most remote corners.
Village electricity programme
Darmawan said that promoting the LISDES programme is also in line with national steps to achieve a 100% Electrification Ratio.
Through the New Electricity Installation Assistance (BPBL) programme, PLN is working together with the Indonesian government to equalise community access to electricity.
The BPBL is a new electricity installation assistance programme for underprivileged households, including the installation of electricity installations, the cost of certification for proper operation (SLO), the costs of new connections to PLN and even topping up the initial electricity token.
“To be able to complete this mandate is not an easy thing,” Darmawan said. “Various distance obstacles, weather, [and] extreme topography are challenges that do not make PLN afraid to provide access to electricity to the entire community.”
Throughout 2023, PLN has succeeded in implementing this programme for 131,600 households or exceeding the target of 125,000 households.
BPBL recipients are households registered in the Ministry of Social Affairs’ Integrated Social Welfare Data (DTKS) domiciled in the 3T area, and/or based on validation from village/sub-district heads or officials of the same level as eligible to receive BPBL.
“Electricity is the heart of the Indonesian economy, and for this reason we are committed to continuing to increase the ratio of villages with electricity and the electrification ratio,” said Darmawan. “Armed with the digital transformation that we have successfully carried out, in 2024, we are sure it will be even more significant.
Digital approach
PLN embarked on an ambitious initiative to digitalise its endto-end business process from power generation, transmission, distribution, financial systems, procurement, payment systems, and customer services.
The previous mobile app provided no real-time outage alerts and other vital information for monitoring consumption and availability since it was initially developed as software. It was also inefficient in connecting with branch offices for timely and muchneeded assistance.
“In the past, PLN's customer service faced significant challenges

Electricity is the heart of the Indonesian economy, and for this reason we are committed to continuing to increase the ratio of villages with electricity and the electrification ratio
due to manual processes, resulting in issues such as unattended work orders, misplaced requests, and scattered customer inquiries. This often led to slow response times and inaccurate reports, causing customer dissatisfaction and tarnishing the company's reputation,” Darmawan said.
To solve the problem with transparency and lack of visibility, PLN built the Virtual Command Center (VCC), a back-end dashboard that allows management, C-suite, and customer experience representatives to manage queues and service level agreements (SLAs). By tagging tickets as green, yellow, or red, representatives are able to quickly identify services that require immediate attention and to respond accordingly.
The VCC also enables PLN to maximise the data it gathers to identify patterns and insights in behaviors, preferences, and demographics. For example, after seeing that customers prefer live chats to call-center services, PLN made recent updates and included an AI-assisted chat bot.
The results speak for themselves: faster and more satisfying customer service; enhanced efficiency in financial and procurement systems; and significantly improved electrical operational reliability.
“Thankfully, the public has warmly embraced these changes. In just two years, the number of registered Customer ID users on the hashtag#PLNMOBILE app has surged from tens of thousands to an impressive 69.55 million registered PLN customers, with an outstanding rating, up from only 2.6 to 4.9 out of 5.0,” Darmawan said.
“This clearly demonstrates that customers highly value the convenience of accessing PLN's services, such as paying electricity bills, marketplace, EV charging, and other services, through this digital platform,” he added.
20 ASIAN POWER
Darmawan Prasodjo, PT PLN President Director



Summit Power's LNG plans offset gas decline
Other sources like hydro or solar are inaccessible due to geographic constraints
Bangladesh, a country with a small land mass and a dense population of approximately 170 million, struggles with deploying renewable sources due to scarcity of available land for development, and lack of strong irradiance and wind to generate electricity. As such, liquefied natural gas (LNG) will be key in driving the country’s energy transition and security as its accessible gas reserve dwindles.
To support the drive for LNG adoption, Summit Power International, the largest independent power producer in Bangladesh which accounts for 17% of the private installed capacity and 7% of the country’s total capacity, operates the second floating storage regasification unit (FSRU) for LNG with a storage capacity of 138,000 cubic metres and regasification capacity of 500 million cubic feet per day.
At present, Summit Power is developing the company's second and Bangladesh's third FSRU, which is expected to begin construction in 2025. Given the company's ownership and operation 2, 255 megawatts (MW) of power stations across 18 plants, founder and chairman Muhammad Aziz Khan, PBM, carries much optimism with Summit Power's progress toward cleaner energy in this exclusive interview with Asian Power.
How vital would you say is the role of liquefied natural gas for Bangladesh’s energy transition?
[LNG] is a transitional fuel. Bangladesh requires a lot of energy and natural gas continues to be its main energy source. Therefore, the gas pipeline and other supporting infrastructure are already existing. People also know how to manage natural gas. LNG, fortunately, has come at a time when Bangladesh’s almost double-digit growth is requiring a lot of energy. LNG will play a major part as we try to move towards more climate-friendly energy like solar, offshore wind, cross-border electricity or nuclear.
How important is LNG for Summit Power as the largest IPP?
For Bangladesh’s operations, LNG is vital at this point. The country has been facing a severe shortage of natural gas as we were constrained and unable to [purchase] LNG when it hit $25 to $30 per metric million British thermal units (MMBtu) in 2022. It is currently at a more reasonable rate of about $10-$12 per MMBtu, enabling Bangladesh to restart LNG imports.
During the first six months of 2023, Bangladesh imported about 12 cargoes from the spot market. This year, it is projected to be about 25 cargoes along with the long-term contracts that Bangladesh has. This helps to provide ample LNG to generate electricity. The people of Bangladesh know how to use natural gas as we have domestic gas production of about 2,500 Million cubic feet per day (MMcf/d).
The gas supply can be further augmented if we can provide for the enhancement of imported LNG and the exploration of new offshore gas resources. Many companies are working towards that along with the Government of Bangladesh. I hope that we get some natural gas from there as well so that the combination of imported natural gas LNG and domestically produced natural gas is balanced and the people of Bangladesh can afford the per MMBtu cost.
Please share with us how the company performed in 2023 and the challenges it needed to overcome.
In 2023, we concluded two agreements for the supply of 1.5 million tonnes of LNG per annum to Bangladesh and for the development of

LNG fortunately has come at a time when Bangladesh’s almost doubledigit growth is requiring a lot of energy
a floating storage regasification unit of 600 million cubic feet per day guaranteed send-out capacity.
The challenges were global, as we saw more wars in the world diverting our attention from climate change, which is the biggest problem in the world. The empowerment of the poor people and energy have not been looked into as it should have been during 2023.
It’s challenging because Bangladesh, with its 170 million people, requires a lot of electricity. Currently, its per capita income is the lowest and we need to enhance it at a reasonable cost price.
So, we are happy to see that LNG prices are coming down to a more realistic level. But in 2023, because of the focus of the world moving towards the Ukraine-Russia war and then subsequently to the Middle East wars, there have been challenges, alongside the rapid increase of interest rates. We have been able to manage during this tough period because of the substantial financial resources that our companies have gradually built up over the years.
Several Summit Power power plants run on heavy fuel oil. What initiatives are you taking for the energy transition?
I feel that cross-border electricity for green energy is a necessity. In Bangladesh, we can access electricity from the Himalayas’ hydroelectricity.
We’re working with Denmark's [Copenhagen Offshore Partners] to develop 500 megawatts of offshore wind farm in Bangladesh. Also, we are working towards supplying solar power to hard-toreach villages, where there is no electricity at the moment, in order to provide marginalised people with electricity, more as a corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiative than as a commercial venture. Having said that, the huge enhancement would have to come from the cross-border import of green energy, as well as nuclear, if we want to become fully green. The round-the-clock electricity or the intermittency of weather for solar has to be addressed in some way. That intermittency can be resolved through nuclear power, such as small modular reactors. That is where we need to focus. Unfortunately, I haven’t seen that focus.
22 ASIAN POWER
INTERVIEW SCAN FOR FULL
Muhammed Aziz Khan, PBM, founder and chairman of Summit Power International
STORY


ASIAN POWER 23
EVENT NEWS: SMART ENERGY WEEK
How Japan plans to accelerate its clean energy transformation
It targets to raise renewable energy share to up to 38% by 2030.

As Japan is amongst the top contributors to carbon emissions in the world, the country is targeting over $1t (JPY150t) of investment over the next 10 years from both the private and public sectors to drive the country’s green transformation (GX).
Japan ranked fifth in the world for carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in 2017, accounting for 3.4% of the total 32.8 billion tonnes of CO2 emissions.
“The public and private [sectors] should cooperate for green transformation,” Hiro Inoue, director-general of Energy Conservation and Renewable Energy Department Agency for Natural Resources and Energy Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), said at the World Smart Energy Week held in Tokyo, Japan. Since the energy sector is responsible for 93% of the country’s emissions, totalling 1.14 billion tonnes, Japan is allocating around $405.8b (JPY60t) to ramp up its renewable energy (RE) capacity, and develop nuclear power and hydrogen/ ammonia over the next 10 years.
On top of that, about $541.1b (JPY80t) will be allotted for energy saving and fuel conversion in the manufacturing industry, digital investment for decarbonisation, support for the battery industry and the
The government also aims to introduce growth-oriented carbon pricing to boost the added value of greentransformationrelated products and businesses
transformation of the aircraft industry, and next-generation vehicles, houses, and buildings, Inoue said.
Another $67.6b (JPY10t) will be made available for the resource recycling industry, biomanufacturing, and carbon capture and storage, he added.
GX Promotion Act
Under the GX Promotion Act, the Japanese government plans to employ five strategies, starting with formulating and implementing a promotion strategy for GX that considers the status of the economy.
It will also offer GX Economic Transition Bonds with around (JPY20t) targeted over the 10-year period, which will support technological development that will make decarbonisation as well as its raw components more profitable, Inoue said.
The government also aims to introduce growth-oriented carbon pricing to boost the added value of green-transformation-related products and businesses. One component of this strategy is the introduction of a fossil fuel surcharge for importers, based on the amount of CO2 emissions, starting in 2028.
By 2033, Japan shall introduce CO2 emission allowances (volumes) to power generation businesses for a partial fee.
A GX Promotion Organisation will also be established to support the investment of private companies, whilst the government will be on the lookout for progress evaluation. This will ensure that investments, both locally and abroad, are meeting its targets and implementing necessary revisions based on the evaluation.
Renewable targets
As of financial year 2022, the share of RE in Japan’s energy mix stood at 21.7%, up from 10.4% in 2011. Inoue said they aim to reach a renewable energy mix of 36%-38%.
Per sector, solar is projected to reach a 14%-16% share by 2030 from 9.2% in 2022, wind energy will increase to 5% from 0.9%, hydropower will reach 11% from 7.6%, geothermal will rise to 1% from 0.3%, whilst biomass will be at 5% from 3.7%.
Inoue added that as part of the strategy to boost the country’s renewables, they plan to introduce them in coexistence with local communities.
He said they will promote rooftop solar installation to promote solar in communities. To install offshore wind farms, they will improve the local communities such as the ports, amongst others.
For hydropower, they will also use artificial intelligence to improve operations to enhance power generation as well as flood control. He noted in the presentation that they will promote cost reduction of domestically-produced biomass fuel by developing other sources such as fastgrowing trees and broad-leaved trees.
According to data from METI, to make RE a “mainstay power source” and to achieve its target, the government would have to augment its power grid system by over eight times more than the previous decade. So, Japan will be building an undersea transmission line from Hokkaido Prefecture which will be completed by 2030.
METI added that Japan plans to use nuclear power but there is a need to build next-generation advanced reactors within the existing nuclear power plants site that will be decommissioned.
It added that the operation period for power plants, which is limited to 40 years but could be extended for another 20 years, “will be approved to be additionally extended for a certain length of outage periods.”
“In addition, we will promote the nuclear fuel cycle, develop a mechanism for sharing knowledge and securing funds for steady and efficient decommissioning, encourage country-led understanding by citizens to realise final disposal and drastically strengthen proactive work for local municipalities,” it said.
Japan in 2011 was struck by a magnitude 9 earthquake followed by a tsunami, damaging the nuclear power plant in Fukushima.
World Smart Energy Week, held from 28 February to 1 March, is the largest-scale energy show and exhibit for the latest technologies across various sectors, drawing over 1,400 exhibitors and 69,000 attendees.
24 ASIAN POWER
Hiro Inoue, director-general of Energy, Conservation, and Renewable Energy Department Agency for Natural Resources
Dhaka Power Distribution Company Limited (DPDC) is one of the largest power distribution companies in Bangladesh. DPDC had been incorporated on 25th October, 2005 under the Companies Act 1994. DPDC is now serving approximately 1.7 million customers.
CORPORATE MOTTO:
Dependable Power - Delighted Customer.
COMMITMENTS:
Quality power supply to all customers.
Quickest response to customers need.
Initiatives to match the changing needs of the customers.
Digitalization of Distribution System.

www.facebook.com/dpdcbd
Dhaka Power Distribution Company Limited
(An Enterprise of the Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh)
www.
ASIAN POWER 25
(DPDC)
dpdc.gov.bd NET ZERO: TOUGH BUT DOABLE. That’s True Power™
Exceptional projects lauded at Asian Power, Asian Water, and Asian Oil & Gas Awards 2023
The power, oil & gas, and water industries in Asia have witnessed significant transformation in recent years, driven by economic growth and growing demand. This is amidst various challenges and the growing trend to shift to sustainable energy sources and environmentally-friendly practices.
As an expression of appreciation and recognition for the key players within these industries, Asian Power Magazine proudly presented the Asian Power Awards, Asian Oil & Gas Awards, and Asian Water Awards to celebrate the innovative and groundbreaking projects and initiatives in the region.
Dubbed as the “Oscars” of the power industry, and now in its 19th year, the Asian Power Awards provides industry players with an opportunity to be acknowledged for their exceptional power projects and share their experiences with one another.
The inaugural Asian Water Awards, on the other hand, celebrates excellence in Asia’s water sector, whilst the Asian Oil & Gas Awards is in its third year and lauds top oil and gas companies in the region.
Winners for all three award programmes were celebrated at an awards dinner in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, on 8 November 2023.
This year's entries to the Asian Power Awards were judged by an elite panel
ASIAN OIL & GAS AWARDS
AGP International Holdings Pte. Ltd. (AG&P)
• Downstream Project of the Year - Singapore
• LNG Project of the Year - Singapore
Alaa For Industry (AFI)
• Innovation Award - Saudi Arabia
APSCO
• Net-Zero Initiative of the Year - Saudi Arabia
• Water Management Initiative - Saudi Arabia
Aramco
• Digital Transformation Initiative of the Year - Saudi Arabia
Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited
• Net-Zero Initiative of the Year - India
• New Product of the Year - India
• Operations and Maintenance Initiative of the Year - India
Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited-Kochi Refinery
• Innovative Technology Initiative of the Year - India
• Plant/Facilities Upgrade of the Year - India
BPCL, India and Aspen Technology Inc. USA
• Digital Transformation Initiative of the Year - India
GAIL (India) Limited
• Innovation Award - India
• Midstream Project of the Year - India
Gasco Engineering Pvt Limited
• Operations and Maintenance Initiative of the Year - Pakistan
Magellan X Pte. Ltd.
• Health and Safety Initiative of the Year - Singapore
• Innovative Technology Initiative of the Year - Singapore
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Ltd.
• Offshore Initiative of the Year - India

of experts in the field consisting of Petteri Härkki, Managing Director at AFRY South-East Asia and AFRY (Thailand); Mike Thomas, Managing Director at The Lantau Group; John Yeap, Senior Advisor - Energy Transition at Pinsent Masons; Rajneesh Sharma, Partner, Consulting - Energy & Resources at Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu India LLP; Gervasius Samosir, Partner, Regulated & Infrastructure at Roland Berger Southeast Asia at Roland Berger; and Sean Purdie, Managing Director - Asia Pacific Sustainability, Energy Transition at PwC Hong Kong.
The judges of the Asian Oil & Gas Awards were: Sanjeev Gupta, Partner, Strategy and Transactions at Ernst & Young; Tim Rockell, Managing Director at Energy Strat Asia Pte. Ltd.; and Gervasius Samosir, Partner, Regulated Infrastructure at Roland Berger South East Asia.
Meanwhile, the panel of judges for the Asian Water Awards consists of Josette Soh, Sustainability & Climate Audit & Assurance Partner at Deloitte Singapore; Gregory Poussardin, Partner, Power & Utilities, ASEAN, Transformation Consulting at EY; and Dieter Billen, Partner, Lead of Roland Berger's Energy & Sustainability Practice in Southeast Asia at Roland Berger.
Congratulations to this year’s winners! See the full list of award recipients below:
Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS)
• Digital Transformation Initiative of the Year - Malaysia
Polish Oil and Gas Company - Pakistan Branch
• People Development Initiative of the Year - Pakistan
PTT Exploration and Production Public Company Limited
• ESG Initiative of the Year - Thailand
Shell APAC Lubricants
• Digital Transformation Initiative of the Year - Singapore
• ESG Initiative of the Year - Singapore
Shell Indonesia Lubricants
• New Product of the Year - Singapore
Yanbu Aramco Sinopec Refining Company (YASREF) LTD
• Operations and Maintenance Initiative of the Year - Saudi Arabia
• People Development Initiative of the Year - Saudi Arabia
ASIAN WATER AWARDS
Abu Dhabi Sustainable Water Solutions
• Water Company Excellence Award - UAE
• Water Sanitation Initiative of the Year - UAE
Agthia Group PJSC
• Environmental Conservation Excellence Award - UAE
• Innovation of the Year - UAE
Coca-Cola Pinya Beverages Myanmar Limited
• Water Access Initiative of the Year - Myanmar
• Water Company Excellence Award - Myanmar
Ever-Clear Environment Engg. Corp.
• Water Technology Excellence Award (Research & Development) - Taiwan
Global Water Consultants Sdn Bhd
• Water Company Excellence Award - Malaysia
• Community-Based Water Project of the Year - Malaysia
Kirloskar Brothers Limited
• Community-Based Water Project of the Year - India
ASIAN POWER, WATER, OIL & GAS AWARDS 2023 26 ASIAN POWER
EVENT:

San Miguel Global Power - Limay Power Inc.
• Water Conservation Initiative of the Year - Philippines
MANHAT
• Net Zero Carbon Project of the Year - UAE
Marafiq
• Water Company Excellence Award - Saudi Arabia
• Water Quality Improvement Project of the Year - Saudi Arabia
Mawongpa Water Solutions Private Limited
• Clean Drinking Water Initiative of the Year - Bhutan
Metro Pacific Iloilo Water
• Water Technology Excellence Award (Industrial) - Philippines
• Water Governance Initiative of the Year - Philippines
MTI Water Technologies, Inc.
• Water Innovation Hub of the Year - Philippines
Nanoplus Tech
• Innovation of the Year - China
Pengurusan Aset Air Berhad
• Collaborative Water Initiative of the Year - Malaysia
• Water Technology Excellence Award (Water Resource Management) - Malaysia
POWER 4 ALL
• Water Reuse and Recycling Project of the Year - Philippines
PrimeWater Infrastructure Corporation
• Outstanding Water Treatment Plant Design Award - Philippines
• Water Company Excellence Award - Philippines
• Water Education and Awareness Initiative of the Year - Philippines
PT Sarana Multi Infrastruktur (Persero)
• Engineering Excellence of the Year - Indonesia
• Outstanding Water Treatment Plant Design Award - Indonesia
Rayyan Mineral Water Company
• Environmental Conservation Excellence Award - Qatar
Syarikat Air Terengganu Sdn. Bhd.
• Water Quality Improvement Project of the Year - Malaysia
• Water Technology Excellence Award (Digital Technology) - Malaysia
Sydney Water
• Water Education and Awareness Initiative of the Year - Australia
VEOLIA WATER TECHNOLOGIES AND SOLUTIONS (INDIA) PRIVATE LIMITED
• Water Technology Excellence Award (Water Resource Management) - India
WOG TECHNOLOGIES PTE LTD
• Water Technology Excellence Award (Industrial) - Singapore
ASIAN POWER AWARDS
Battery Storage Project of the Year
• Gold - Hazelwood Battery Energy Storage System (HBESS) by Fluence Energy Pty Ltd
• Silver - San Miguel Global Power Portfolio of Battery Energy Storage System Projects by San Miguel Global Power Holdings Corp.
• Bronze - Tibet Gangba Photovoltaic and Chemical Energy Storage Power Station by Tibet Development and Investment Group Co., Ltd
Coal Power Project of the Year
• Gold - Empower and Ignite: GNPD strengthens performance towards a better future today by GNPower Dinginin Ltd. Co.



• Silver - Coal Power Plant of the Year - DangJin Power Complex Unit 7&8 Turbine Retrofit by DangJin Power Complex, Korea East-West Power Co., Ltd
• Bronze - Zhejiang Zheneng JiaHua Power Generation Co., LTD. U8 (1X1000MW) by EmersonZhejiang Zheneng Jiahua Power Generation Co., LTD
Diesel-Fired Power Project of the Year
• Gold - 2 x 28MW TM2500 Aeroderivative Gas Turbine Project, Zamboanga Philippines by Malita Power Inc. (San Miguel Global Power)
District Cooling Initiative of the Year
• Qatar - Qatar Cool - GDCP by Qatar Cool
Environmental Upgrade of the Year
• China - Heze Plant-wide Zero-wastewater Discharge Project: Leader of the Industry by China Resources Power (Heze) Co., Ltd.
• India - OMC Power
ESG Programme of the Year
• Australia - ESG Enabled Enterprise Value Uplift by Zenith Energy
• Indonesia - Desa Harapan (Village of Hope) Scale Up by PT Shenhua Guohua Pembangkitan Jawa Bali
• Pakistan - 1180 MW Combined Cycle Power Plant, Bhikki, District Sheikhupura, Pakistan by Quaid-e-Azam Thermal Power (Pvt) Limited
• Philippines - AGROSOLAR by CITICORE RENEWABLE ENERGY CORPORATION
Gas Engine Combined Cycle Power Project of the Year
• Gold - Bang Pakong Combined Cycle (Units 1-2 Replacement) Project by EGAT
• Silver - Huizhou Fengda Phase II CCGT Power Plant by Huizhou Shenzhen-Energy Fengda Power Co., Ltd
Gas Power Project of the Year
• Afghanistan - 40MW Siemens (SGT-A45) Mobile Gas-Fired Power Plant - Sheberghan Afghanistan by Bayat Power and Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS)
• China - Huizhou Fengda Phase II CCGT Power Plant by Huizhou Shenzhen-Energy Fengda Power Co.,Ltd
• Taiwan - The Hsinta Power Plant Combined Cycle Renewal Project by Taiwan Power Company
• Vietnam - TNPower- Solar Initiative by TNPower Energy Joint Stock Company
Hydro Power Project of the Year
• Gold - UPPER Chameliya Hydropower Project - 40 MW by API Power Company Limited
• Silver - Sustainable Hydropower Operation Through Dynamic Water Dispatch Management by Bakun Hydro Power Generation Sdn Bhd
Independent Power Producer of the Year
• Australia - Zenith Energy
• India - Greenko
• Indonesia - PT Shenhua Guohua Pembangkitan Jawa Bali
• Pakistan - Quaid-e-Azam Thermal Power (Pvt) Limited
Information Technology Project of the Year
• India - DigiGrid- Digital Transformation Project by India Grid Trust
• Malaysia - TNB Genco - Hydro Catchment Area Surveillance (THyCAS) - Using Space Technologies by TNB Genco
• Philippines - Enhancing Operational Efficiency and accuracy through eDNA Historian, RTD Dashboard and CEMS Real-time Monitoring by Malita Power Inc. (San Miguel Global Power)
Innovative Power Technology of the Year
• Bangladesh - GIS ( Geographical Information System) mapping project under DPDC) by Dhaka Power Distribution Company Limited
• China - Huizhou Fengda Phase II CCGT Power Plant by Huizhou Shenzhen-Energy Fengda Power Co., Ltd
• India - Revolutionizing Customer Services - V-Assist & Genius Pay Kiosks by Adani Electricity Mumbai Ltd. (AEML)
• Indonesia - BOSF Samboja Micro-grid by Solar Power Indonesia
• Japan - ULTY-V plus, system to optimise boiler fuel control by NYK Idemitsu Green Solutions Co., Ltd.
• Malaysia - TNB Genco - Leveraging Innovative IT Applications by IIOT, Wireless Vibration and
ASIAN POWER 27
EVENT: ASIAN POWER, WATER, OIL & GAS AWARDS 2023

Temperature Monitoring System for Continuous Ship Unloader (CSU) by TNB Genco
• Pakistan - 1180 MW Combined Cycle Power Plant Bhikki Sheikhupura, Pakistan by Harbin Electric International Co. Ltd
• Philippines - San Miguel Global Power Portfolio of BESS Facilities by San Miguel Global Power Holdings Corp.
Power Plant Upgrade of the Year
• China - Wenergy Maanshan Power Generation Co., Ltd. U2 (1x660MW) DCS Retrofit Project by Emerson - Wenergy Group Ma'anshan Power Generation Co., Ltd.
• India - Solar Assets Performance Improvement by Greenko
• Korea - Power Plant Upgrade of the Year - DangJin Power Complex Unit 7&8 Turbine Retrofit by DangJin Power Complex, Korea East-West Power Co., Ltd
• Philippines - Value in Waste: Fly Ash Reuse by Malita Power Inc. (San Miguel Global Power)
• Taiwan - The Taichung Power Plant’s Unit 5 to 10 Air Quality Control System Retrofit Project by Taiwan Power Company
Power Project Finance House of the Year
• Gold - KASIKORNBANK PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
Power Utility of the Year
• Bangladesh - Dhaka Power Distribution Company Limited
• Malaysia - Bakun Hydro Power Generation Sdn Bhd
• Pakistan - K- Electric Limited
• Thailand - CK Power Public Company Limited - Bangpa-in Cogeneration Power Plant
• UAE - Emirates Water & Electricity Company (EWEC)
• Vietnam - TNPower Energy Joint Stock Company
Power Utility of the Year for Transmission and Distribution
• India - Adani Electricity Mumbai Ltd. (AEML)
Smart Grid Project of the Year
• Hong Kong - CLP Power demand response system leverages smart grid technology through deep customer engagement by CLP Power Hong Kong Ltd.
• Philippines - San Miguel Global Power Portfolio of Battery Energy Storage System Projects by San Miguel Global Power Holdings Corp.
• Taiwan - A New Milestone in the Journey to Become a Smart Grid Equipped, Zero-Carbon Island — Kinmen ESS III & IV by Taiwan Power Company
• Thailand - KASIKORNBANK PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
Solar Power Project of the Year
• Afghanistan - Kandahar 15 megawatt (MW) Solar Power Plant by 77 Construction Company, Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS), and Zularistan Ltd.
• Australia - Chichester Solar Gas Hybrid Project by Alinta Energy
• Bangladesh - IDCOL Solar Irrigation Pump by Infrastructure Development Company Limited (IDCOL)
• China - Tibet Gangba Photovoltaic and Chemical Energy Storage Power Station by Tibet Development and Investment Group Co., Ltd
• India - OMC Power
• Indonesia - Cirata 145MWac Floating Solar Plant by Abu Dhabi Future Energy Company PJSC - Masdar
• Malaysia - 98MWp Floating Solar, Danau Tok Uban, Pasir Mas, Kelantan, Malaysia by Cypark Resources Berhad
• UAE - Al Dhafra Solar PV - The world's largest single-site solar power plant by Emirates Water & Electricity Company (EWEC)
• Vietnam - PROINSO Group, strengthen our position in Vietnam by installing the NGU LONG Solar Rooftop Project by PROINSO
Standby Power Plant of the Year
• Gold - 125 Mw power plant of the Year Supporting the Saudi National Grid by Altaaqa Alternative Solutions Co. (A Zahid Group of Company)
• Silver - Panjin Boiler Combustion System Optimisation and Transformation: Improving unit flexibility for better peak demand management by China Resources Power (Panjin) Co., Ltd.
Transmission & Distribution Project of the Year
• Gold - Energy Integrated Platform (EIP) as an Enabler Towards Energy Transition of TNB Distribution Network by TENAGA NASIONAL BERHAD
• Silver - The Modern and Sustainable Power Supply Solution - CLP Power Kwu Tung North
132kV Substation by CLP Power Hong Kong Ltd.
• Bronze - Replacing Transmission Towers with a Novel "Tower Wrapping replacement Method" by Taiwan Power Company
Wind Power Project of the Year
• China - Suixian Longxiang Wind Farm: Introducing unmanned operation to boost efficiency and safety by China Resources New Energy (Suixian Tianhekou) Wind Power Co., Ltd.
• India - Wind Assets Performance Improvement by Greenko
CEO of the Year
• Othman Juma Al Ali of Emirates Water & Electricity Company (EWEC)



28 ASIAN POWER
GAIL (India) Limited Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Ltd.
APSCO












ASIAN POWER 29
PTT Exploration and Production Public Company Limited
Yanbu Aramco Sinopec Refining Company (YASREF) LTD
77 Construction Company, Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS)
Abu Dhabi Future Energy Company PJSC - Masdar
Alinta Energy
Altaaqa Alternative Solutions Co. (A Zahid Group of Company)
CITICORE RENEWABLE ENERGY CORPORATION
Bayat Power and Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS)
EVENT: ASIAN POWER, WATER, OIL & GAS AWARDS 2023







30 ASIAN POWER
Bakun Hydro Power Generation Sdn Bhd
CLP Power Hong Kong Ltd.
Cypark Resources Berhad
Dhaka Power Distribution Company Limited
Emirates Water & Electricity Company (EWEC)
GNPower Dinginin Ltd. Co.











ASIAN POWER 31
Greenko Harbin Electric International Co. Ltd
San Miguel Global Power Holdings Corp.
Huizhou Shenzhen-Energy Fengda Power Co.,Ltd
India Grid Trust
Malita Power Inc. (San Miguel Global Power)
NYK Idemitsu Green Solutions Co., Ltd.
EVENT: ASIAN POWER, WATER, OIL & GAS AWARDS 2023








32 ASIAN POWER
Quaid-e-Azam Thermal Power (Pvt) Limited
Taiwan Power Company
TENAGA NASIONAL BERHAD
Zenith Energy
Abu Dhabi Sustainable Water Solutions
Kirloskar Brothers Limited
Global Water Consultants Sdn Bhd











ASIAN POWER 33
Metro Pacific Iloilo Water
POWER 4 ALL PrimeWater Infrastructure Corporation
Pengurusan Aset Air Berhad
PT Sarana Multi Infrastruktur (Persero)
San Miguel Global Power - Limay Power Inc.
Syarikat Air Terengganu Sdn. Bhd.

Collaborative Water Initiative of the Year - Malaysia Water Technology Excellence Award (Water Resource Management) - Malaysia
PENGURUSAN ASET AIR BERHAD: Bringing The Nation’s Water Security to The Fore
PAAB is revolutionising Malaysia's water landscape with innovative financial and operational methodologies, achieving significant milestones underscored by prestigious recognitions at the Asian Water Awards 2023.

Through its unique methodologies, comprehensive projects, and dedication to sustainable solutions, PAAB continues to play a pivotal role in elevating Malaysia's water infrastructure and security
Malaysia's water landscape is undergoing a transformative journey, thanks to the groundbreaking achievements of Pengurusan Aset Air Berhad (PAAB). Its recent accolades at the Asian Water Awards in 2023, where PAAB clinched two prestigious wins, underscore the company's commitment to a multi-faceted business model. This model, encompassing three distinctive methodologies, stands as a beacon for sustainable water infrastructure development across the nation.
Seamless Transition: The Migration Approach
At the core of PAAB's success lies the Migration methodology, orchestrating the seamless transition of financial obligations. PAAB assumes the mantle of federal government water infrastructure loans previously held by state governments. This transition is complemented by PAAB's strategic acquisition of State Government's water assets, equivalent in value to federal loans owed by state governments. This innovative approach not only streamlines financial processes but also ensures a clear settlement of federal loan obligations directly with the Ministry of Finance. PAAB emerges as a conduit for fostering financial clarity and efficiency, setting a new standard in responsible financial management.
Empowering Progress: Develop Water Asset Methodology
The Development of Water Assets methodology empowers state water operators (SWO) to leverage migrated loans for infrastructure development. PAAB's role as a facilitator enables SWOs to utilise funds and execute pre-approved business plans aligning with the community's needs. This strategic
collaboration allows SWOs to focus on providing exemplary services whilst PAAB spearheads the progression of water infrastructure development nationwide.
Bridging Financial Gaps: NRW Financing
Addressing the critical issue of Non-Revenue Water (NRW), PAAB introduces a short-term loan scheme under the NRW financing methodology. This initiative empowers SWOs to undertake NRW reduction programmes, providing essential financial resources to minimise water losses, optimise operational efficiency, and bridge the gap between operational expenses and capital expenditures.
As of December 2022, PAAB's methodologies have culminated in the completion of water treatment plants boasting a capacity of 1846 million litres per day. This remarkable feat signifies a significant enhancement in water treatment capacity, ensuring access to clean and safe water for Malaysia's growing population.
A shining example of PAAB's commitment to innovation and sustainability is the Langat 2 Water Treatment Plant Phase 1 Project. Delivering an impressive 1130 million litres per day of treated water, this project addresses water disruption challenges faced by approximately 8.3 million consumers, particularly in the Klang Valley. PAAB's dedication to engineering excellence, technological innovation, and environmental sustainability shines through in this monumental endeavour.
As of December 2022, PAAB's contributions to water infrastructure projects are noteworthy, with completed projects valued at RM4.25 billion. The commitment to progress is ongoing, with RM2.31
billion worth of projects currently under construction and an additional MYR3.64 billion worth of projects in various design and tendering stages.
The recent wins at the Asian Water AwardsCollaborative Water Initiative of the Year - Malaysia and the Water Technology Excellence Award (Water Resource Management) Malaysia - further solidify PAAB's position as a leader in water management innovation.
As the Asian Water Awards continue to celebrate groundbreaking innovations in water management throughout Asia, PAAB stands as a testament to Malaysia's commitment to shaping a water-secure and sustainable future. The company's dedication to innovation, collaboration, and sustainability is not only elevating Malaysia's water infrastructure but also inspiring change on a regional and global scale. PAAB's triumphs are not just awards; they are a pledge towards a future where water is not just a resource but a right for all.
In its journey towards a water-secure future, PAAB recognises that the challenges ahead are multifaceted and evolving. With a steadfast commitment to innovation, collaboration, and sustainability, PAAB remains poised to tackle these challenges headon. The company's relentless pursuit of excellence, coupled with its unwavering dedication to serving communities and safeguarding the environment, serves as a guiding light for the water industry not just in Malaysia but globally. As PAAB continues to push the boundaries of what's possible in water management, it reaffirms its pledge to ensure that every drop counts and that the legacy of responsible water stewardship endures for generations to come.

34 ASIAN POWER
PAAB's methodologies have culminated in the completion of water treatment plants
Ir. Zulkiflee Omar, CEO of Pengurusan Aset Air Berhad (PAAB)


Deploying innovative technologies for active demand management and greener substation design
CLP Power Hong Kong Limited (CLP Power) has effectively managed peak demand and integrated sustainable concepts in substation design whilst continuing to supply its customers with world-class reliability.

The continuous development of Hong Kong and the wider adoption of electric vehicles (EV) call for increasing electricity demand. This steady rise in peak demand has brought substantial challenges to electricity service provider CLP Power. On the system-wide level, peak demands stress generation capacity. On the local level, it becomes challenging for the company to manage the growing distribution demands whilst upholding power quality standards.
Enhancing demand management with smart grid technology
To address rising peak demand and distribution grid congestion, traditional reinforcement like building additional power plants and substations is costly and limited by Hong Kong's space constraints, leading to low asset utilisation. CLP Power's Demand Response (DR) offers a scalable, cost-effective alternative, leveraging customer load flexibility for system-wide and local demand reduction through targeted DR programmes and a dynamic Distributed Energy Resource Management System (DERMS).
In the first project stage, CLP Power introduced innovative DR programmes for various customer groups. In summer 2022, 600,000 residential and business customers with smart metres contributed over 130 MW of load flexibility. Additionally, Localised Demand Response identifies an area with potential network constraints and addresses a targeted group of customers within the area to provide demand flexibility.
The second stage evolves DR programmes into a smarter, more efficient, automated system. Leveraging advanced digital technologies, a cloud-based DERMS uses AI to forecast and manage network constraints by identifying and automatically activating the most suitable flexibility resources based on price and location.
“The developed DR system enables CLP Power to achieve better operational efficiency and system reliability. Through integrating customer resources
into active power network management, we can effectively manage peak demand whilst continuing to supply our customers with world-class reliability,” said Eric Cheung, CLP Power's Senior Director of Power Systems.
CLP Power has demonstrated the possibility of customer engagement and integrated it with its flexibility for localised demand management. This effort has been lauded by the Asian Power Awards as it received the Smart Grid Project of the YearHong Kong category win.
Developing environmentally-friendly substation
CLP Power also earned the Transmission & Distribution Project of the Year - Silver Award with its Kwu Tung North Substation, designed for the emerging Kwu Tung North New Development Area. This project aligns with the company's
sustainability goals, featuring green, intelligent designs like a grid-connected solar panel system, rainwater harvesting for irrigation, energyefficient installations such as LED lighting, and water-efficient fixtures. Its low-rise architecture and vertical greenery integrate well with the environment, whilst low-noise equipment minimises community disturbance, showcasing CLP Power's dedication to decarbonising infrastructure and enhancing sustainability.
The project team at CLP Power utilised cuttingedge technologies like building information modelling, virtual reality, and computational fluid dynamics for the Kwu Tung North Substation. A 3D simulation model created early in the design phase facilitated stakeholder communication, significantly enhancing construction safety, buildability, and future operation efficiency. Additionally, environmental sustainability was a key focus in its design, with the substation achieving a provisional platinum rating in Hong Kong's BEAM Plus assessment, the top tier for green building standards.
Cheung said the company was honoured to receive the two awards as they recognised the power expertise and exceptional performance of the project teams. “As one of the leading power utilities, CLP Power is committed to integrating green and sustainable features in our new substations, and adopting innovative technologies to enhance power network efficiency, providing greener, smarter and highly reliable electricity supply to our customers, and supporting the city’s continuous development,” he said.
The Asian Power Awards, celebrating its 19th year, acknowledges companies and projects pioneering innovative solutions to address climate change and meet increasing energy demands.
Through integrating customer resources into active power network management, we can effectively manage peak demand whilst continuing to supply our customers with world-class reliability

36 ASIAN POWER
The Kwu Tung North Substation, designed with sustainability in mind, will provide a highly reliable and safe power supply to the city's New Development Area.
Smart Grid Project of the Year - Hong Kong Transmission
Distribution Project of the Year - Silver
CLP Power Senior Director Eric Cheung (fourth from left), Director of Transmission Alex Wong (fourth from right), Director of Smartgrid & Innovation Bruce Chan (third from left), and the project teams receive the award for the two winning projects.
&

Pioneering the future of comprehensive energy and environmental services globally

Shenzhen Energy Group Co., Ltd. (000027), founded in June 1991 and listed in September 1993, is the first major power industry joint-stock enterprise on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. In December 2007, it was listed as a whole, setting the precedent for China Electric Power Company to go public as a whole.
Shenzhen Energy Group, headquartered in Shenzhen within the Pearl River Delta, boasts a nationwide presence and international expansion, evolving from a regional to a global multinational enterprise. Pioneering in power management and
a leader in waste-to-energy, the company seizes energy transformation opportunities to develop a diversified industrial system. Transitioning from solely power generation to a comprehensive energy service provider, it operates across 27 provinces in China and in countries like Ghana, Vietnam, and Papua New Guinea, marking its status as an international comprehensive energy enterprise.
Decades of Energy Excellence
Over 30 years, Shenzhen Energy Group has achieved significant milestones: establishing
Shenzhen's first large-scale thermal power plant (Mawan Power Plant), receiving the first BOT project (Shajiao B Power Plant), launching South China's first ultra-supercritical coal-fired plant (Heyuan Power Plant), creating the first EU standard waste-to-energy plant in China (Nanshan Environmental Protection Power Plant), and building China's inaugural power plant in Africa (Ghana Gas Turbine Power Plant).
In 2023, its Huizhou Fengda Power Plant Phase II project won three Asian Power Awards, amongst other honours for quality, sustainability, and contributions to poverty alleviation and environmental protection in Guangdong Province and beyond.
Shenzhen Energy Group, actively engaged in the power, environmental protection, gas, comprehensive energy, and overseas sectors, is poised for a new era and journey. With a steadfast commitment, the group aims to expand its reach across China and globally, embodying a robust determination to evolve into a globally influential comprehensive energy and environmental protection service provider.

ASIAN POWER 37 Indigrid Magazine Ad 200mm X 130mm final Q.pdf 1 09-02-2024 12:47:45
Gas
Engine Combined Cycle Power Project of the Year - Silver Gas Power Project of the Year - China Innovative Power Technology of the Year - China
Huizhou Fengda Power Plant



















ASIAN POWER









Zenith Energy is one of Australia’s leading independent power producers (IPP’s), unique for its vertically integrated business model and in-house capability. It specialises in tailored off grid hybrid power and innovative grid connected solutions with a Build, Own, Operate (BOO) service model that allows clients to deploy their capital more effectively within their business.
Zenith Energy is committed to net zero by 2035 for its scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions. While this is an ambitious target, it is realistic and achievable with innovative commercial and technical solutions when working with
clients.

ASIAN POWER 39 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION VISIT
likeminded
Providing
Clean Coal Technology (CCT), ensuring its operations are safe, economical, and clean with high efficiency to secure energy supply for high quality economic and social development based on ESG Principles & Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to achieve highest acknowledgement in the power generation industry.
our clients a glide path to achieve net zero.
Independent Power Producer of the Year - Indonesia PT Shenhua
Pembangkitan
ESG Programme of the YearIndonesia PT
Gold Award for Fast Track Power Plant of the Year PT Shenhua
Award for Coal
PT Shenhua Guohua Pembangkitan Jawa Bali @ptsgpjb @ptsgpjb PT SGPJB
Guohua
Jawa Bali
Shenhua Guohua Pembangkitan Jawa Bali
Guohua Pembangkitan Jawa Bali Gold
Power Project of the Year
JAWA 7 COAL-FIRED POWER PLANT THE MOST ENVIRONMENTAL FRIENDLY CFPP IN INDONESIA
PT Shenhua Guohua Pembangkitan Jawa Bali

Solar Power Project of the Year - China Battery Storage Project of the Year - Bronze
Tibet Development and Investment Group Leads the Charge in Clean Energy Transformation

Tibet Development and Investment Group (Xizang Development Investment Group Co., Ltd.) was established on November 13, 2013. As the sole energy industry group amongst the seven major industries in the Xizang Autonomous Region and a key state-owned enterprise, it is based in Lhasa. The company adheres to a development strategy and goal of "strategic guidance, benefit first, rooted in Xizang, serving the whole country, and striving to build a clean energy industry group with significant domestic influence." Focusing on energy investment, development, construction,
operation, and management, it also extends its reach into upstream and downstream industrial chains, including engineering consulting, real estate, and building materials logistics. This strategy aims to establish a pivotal role in enabling Xizang to develop a new pattern of clean energy.
Aligned with Xizang's natural resources and the actual development needs of enterprises, Xizang Development Investment Group has set clear medium and long-term strategic objectives to accelerate the formation of a clean energy industry group with notable domestic influence, following a "three-step" development strategy.
Strategic Growth Milestones
By 2025, the group intends to independently install and initiate equity production with an installed capacity exceeding 3 million kilowatts, becoming the largest power generation enterprise group in the region with assets over 50 billion yuan. By 2030, it expects its self-installed capacity and equity production capacity to surpass 12 million kilowatts, with the asset scale exceeding 100 billion yuan. By 2035, the goal is for the installed capacity to exceed 30 million kilowatts, establishing itself as a leading clean energy industry group in China with assets over 200 billion yuan.
In 2023, the Gangba PV project of Xizang Development Investment Group received two Asian power awards, symbolising the group's steadfast commitment to innovation, excellence, and a pioneering spirit. Its achievements in highaltitude photovoltaic power generation, coupled with advanced energy storage solutions, have redefined the renewable energy landscape's potential. With a resilient approach and unparalleled achievements, the group is eager to contribute to the future of sustainable power generation.
 Gangba PV project
Gangba PV project

To Achieve Low Carbon Transition In Innovative Ways
As a green energy and integrated energy service provider based in Mainland China and Hong Kong, China Resources Power has always adhered to the concept of sustainable development and integrated the implementation of environmental, social and governance responsibilities into the Company’s strategies and operations.


Persisting in the transformation to green and low -carbon energy
Dedicating to key original technology research, such as CCUS, and striving to become the vanguard of the digital transformation of the energy industry
Focusing on different energy -saving and carbon reduction scenarios to provide systematic and customised integrated energy solutions






Bringing clean energy to you. www.agpglobal.com
Clean Power Generation
Technological Innovation
Integrated Energy



CKPOWER: INNOVATING FOR A SUSTAINABLE FUTURE
At Bangpa-in Cogeneration, Commitment Meets Achievement - Net Zero GHG by 2050
CKPower is redefining sustainable energy leadership. At Bangpa-in Cogeneration, our vision for a carbon-neutral future is becoming a reality. Our drive for Net Zero GHG emissions by 2050 reflects our dedication to innovation and efficiency. We're not just in the business of electricity, we're forging a path to a greener, more sustainable tomorrow.











About Bangpa-in Cogeneration Power Plant Bangpa-in Cogeneration Company Limited (BIC) a subsidiary of CKPower Public Company Limited, one of the largest renewables-based electricity producers with one of the lowest carbon footprints in the region, BIC is a Small Power Producer (SPP) Cogeneration that collaborates with business partners and the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand (EGAT). BIC is a producer and distributor of electricity and steam from the natural gas-fired cogeneration power which consists of two projects: Bangpa-in Cogeneration Power Plant 1 and 2 with 238 MW installed capacity. Both projects are located in Bang Pa-in Industrial Estate, Amphoe Bang Pa-in, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya Province Thailand. บริษัท บางปะอิน โคเจนเนอเรชั่น จำกัด BANGPA-IN COGENERATION LIMITED
With honorable awards from Asian Power Awards for Bangpa-in Cogeneration power plant for 4 consecutive years

PIONEERING ENERGY
Since 2006, Masdar has been a pioneer in advancing the clean energy sector and a key enabler of the UAE’s vision as a global leader in sustainability and climate action. As one of the world’s fastest-growing clean energy companies, we are advancing the development and deployment of renewable energy and green hydrogen technologies to address global sustainability challenges. If you want to help create a more sustainable future for all, find out more at www.masdar.ae.
Our project portfolio has a combined capacity of over 20 GW
Projects expected to displace 30 million tonnes of CO2 per year
We have invested in projects worth more than US$30 billion
Developed & partnered projects in over 40 countries
























Accelerating Indonesia's Development
PT Sarana Multi Infrastruktur (Persero) is a Special Mission Vehicle (SMV) of the Ministry of Finance with a role and mandate to act as a catalyst for the acceleration of national development.


&


A reliable connection with the newly commissioned 120 MLD Bukit Berapit Water Treatment Plant. A 350 mm treated water pipe, tapped from the main pipeline, provides treated water to the Losong Treatment Plant. This innovative solution ensures a consistent supply of safe water, mitigating the impact of salinity intrusion
The AMS improved operational efficiency, enabling the engineering team to prioritise maintenance based on asset risk rating, and reducing consumer impact during maintenance. It provided insights during budget preparation, allowing for the allocation of priority to high replacement priority assets. This improved financial control and provided management with an overview of asset status.

ASIAN POWER 45
Care For Life and Beyond 1-300-88-2111 www.satuwater.com.my Terengganu, Malaysia 01.
Financing
Investment Advisory Services Project Development
Asset Management System (AMS) 02. PROGRESSIVE TRANSFORMATION Syarikat Air Terengganu Sdn Bhd #satuwater
Combat Salinity Intrusion













SWS: At the forefront of circular economy
Dedicated to building a greener future and protecting natural water resources, SWS boasts a daily wastewater recycling capacity of over 1.3 million m3
Committed to fostering sustainability and building a greener future.
To learn more about SWS, visit sws.ae.



















MICHELLE CHAEWON KIM
Three reasons the US LNG pause does not threaten South Korea's energy security and transition
Since the United States (US) Biden Administration announced the temporary pause on new liquefied natural gas (LNG) export approvals early this year, many Asian countries expressed concern about the potential disruption in energy security and decarbonization goals.
South Korea, the largest US LNG importer in Asia until 2022, is one of them. SK gas and KOSPO were identified as potential buyers for new LNG projects that could be affected. However, IEEFA found that the US LNG export pause does not threaten South Korea’s energy security and transition goals for the following three reasons.
US LNG imports have largely been prompted by geopolitical reasons South Korea began importing US LNG in 2017, driven more by political motives than by concerns for energy security.
Despite the Korea-US Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in 2012 and the U.S. Obama Administration labelling LNG as a ‘bridge fuel’ in 2014 to promote the role of US LNG in global energy security, there has been no significant discussion of US LNG as a major energy source in South Korea until 2017. That year, South Korea’s U.S. LNG intake spiked 70 times year-on-year after the first US. LNG export project, Sabine Pass, started in 2016 and South Korea’s state-run gas utility, KOGAS, signed a long-term contract with them.
There were other stronger reasons behind the U.S. LNG imports, such as trade disputes. During the U.S. Trump Administration in 2017, they addressed the mounting trade deficit caused by the Korea-US FTA. LNG has been frequently mentioned as one of the remedies to mitigate this arguable deficit and alleviate potential risks of FTA cancellation by the U.S.
At the 2017 G20 Summit, South Korea’s Moon Administration declared the 'Coal and Nuclear-free Economy' policy, supporting the narrative that LNG is a ‘green energy’ in the energy transition pathway. In December 2017, the country’s Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy increased the targeted share of LNG in the power mix from 16.9% in 2017 to 18.8% in 2030.
In 2017, the US LNG imports by South Korea more than doubled year-onyear, coinciding with the start of the Korea-US FTA renegotiation.
In December 2020, the targeted share of LNG in South Korea’s power mix by 2030 further rose to 23.3%, and the US LNG imports hit a historic high in 2021.
US LNG showcased insecurity, unreliability, and unaffordability
The belief that US LNG will bolster South Korea’s energy security with abundant supply and affordable price has been questioned since the outages at the US Freeport LNG export facility in 2022, which lasted more than a year.
In 2022, South Korea's US LNG imports plummeted by 31.84% year-on-year due to the outage at the US Freeport facility, which accounts for 17% of total US LNG export capacity. Despite the promotion of US LNG as a ‘saviour’ to stabilize global energy security, US LNG showcased insecurity and unreliability when South Korea required a stable supply in the wake of the Russia-Ukraine war.
The disrupted supply of US LNG reduced the power output from one of South Korea’s fleet of LNG-fired power plants. For example, SK E&S, an offtaker from the US Freeport LNG export facility, lowered the operating rates of its LNG-fired power plants from 79% in 2021 to 71% in 2022 due to a lack of LNG supply. This prompted the company and KOGAS to purchase more expensive spot LNG to make up for the losses due to the outages. The US LNG cargoes purchased by South Korea were also costly, as prices were 16% higher than cargoes sold to neighbouring Japan in 2022.
LNG’s role in the energy transition is diminishing
Despite less carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, LNG's role in greenhouse gas reduction is controversial due to its high methane emissions, as methane has a

more significant warming effect than CO2 over a relatively short time frame. The South Korean government aims to decrease LNG's share in the power mix from 26.82% in 2023 to 9.3% by 2036.
South Korea’s LNG imports have already decreased by 4.9% in 2023 amid increased nuclear and renewable energy generation. This trend is likely to continue with the country’s strengthened decarbonization targets.
The predicted annual reduction rate of LNG demand in South Korea, at 3.6%, could offset the portion of US LNG in total LNG imports, currently at 11%, by the end of this decade. It is also essential to recognize LNG as a fossil fuel that must be phased out by 2050. Prolonging its use by increasing US LNG exports should not be justified for energy security or energy transition rhetoric.
The real energy security and transition for South Korea is reducing heavy reliance on imported fossil fuel and rapidly shifting to domestically produced renewable energy, as the country promised at the recent COP28.
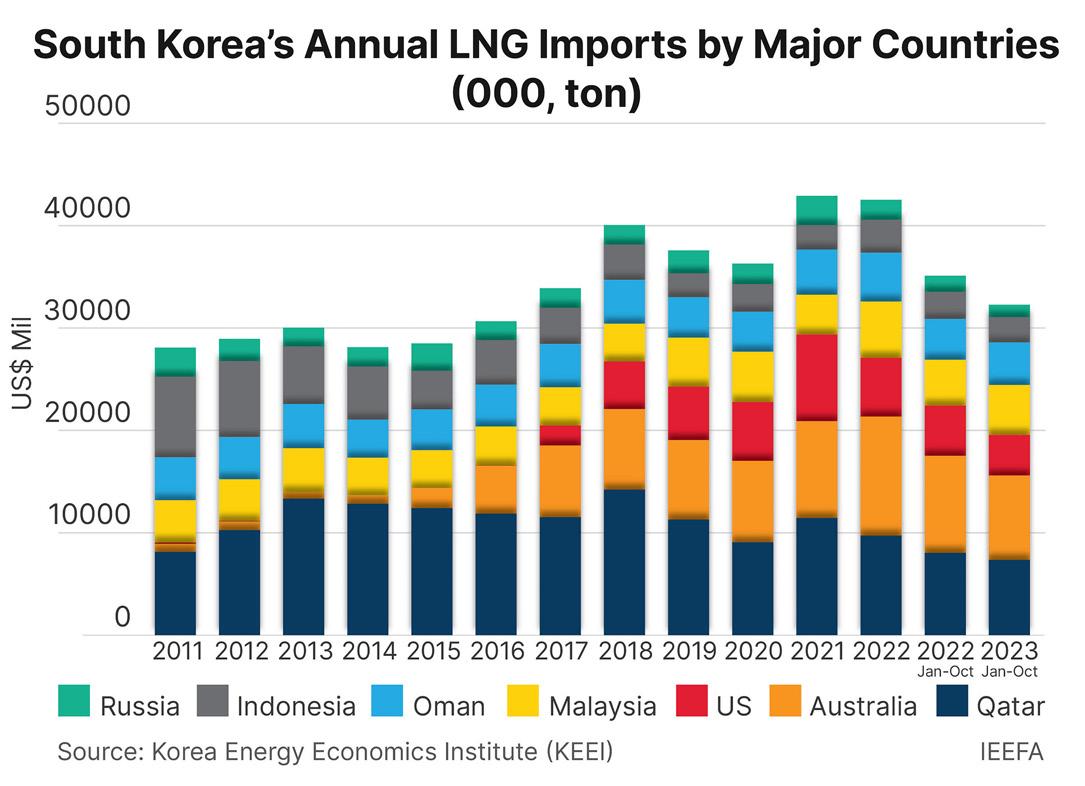
48 ASIAN POWER OPINION
Michelle Chaewon Kim Energy Finance Specialist, South Korea, IEEFA












 Tim Charlton
Tim Charlton













 App connects PV rooftop solar panels to grid
App connects PV rooftop solar panels to grid



































































































































 Gangba PV project
Gangba PV project