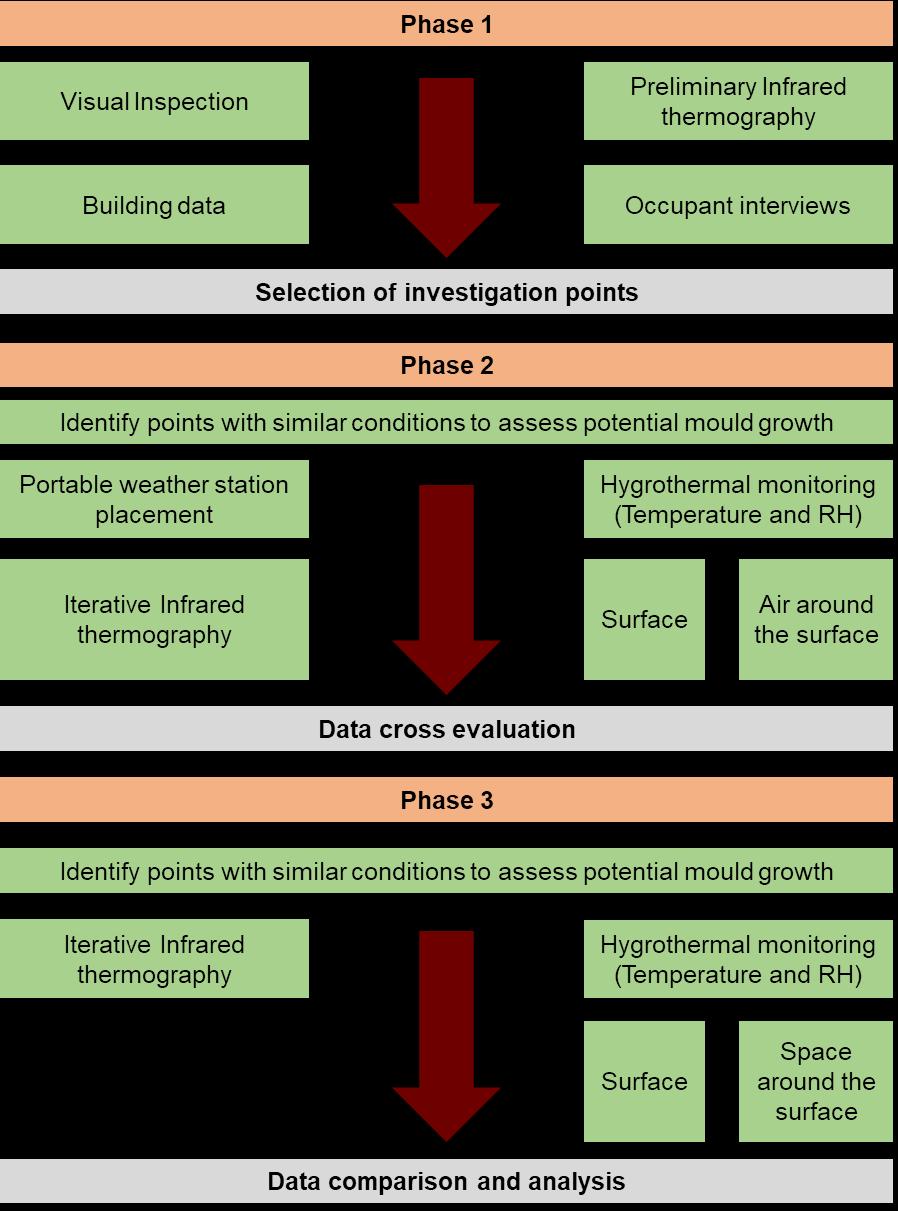
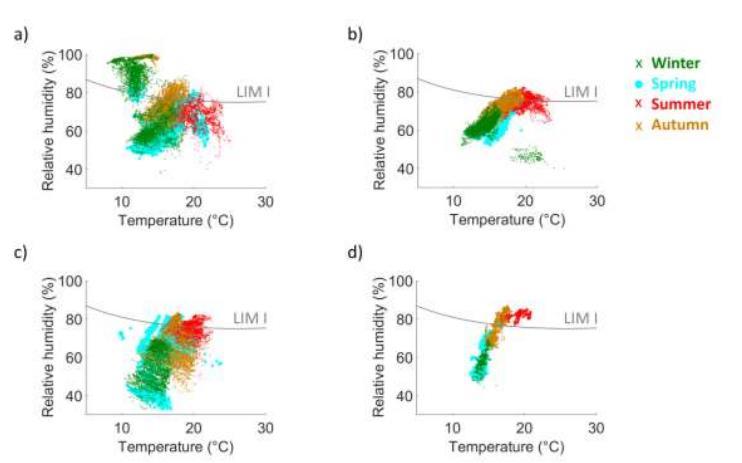
1 minute read
References
[1] Alamdari, F., Arnold, D., Bordass, W., Ho, K., Oughton, R. and Twinn, C., 2000. Mixed Mode Ventilation - CIBSE Applications Manual AM13: 2000. London: CIBSE. [2] Bajno, D., Bednarz, L., Matkowski, Z. and Raszczuk, K., 2020. Monitoring of Thermal and Moisture Processes in Various Types of External Historical Walls. Materials, 13(3), p.505. [3] Bottino-Leone, D., Larcher, M., Troi, A. and Grunewald, J., 2021. Hygrothermal characterization of a fictitious homogenized porous material to describe multiphase heat and moisture transport in massive historic walls. Construction and Building Materials, 266, p.121497. [4] 2013. BS 7913:2013 Guide to the conservation of historic buildings. BSI Standards Publication. [5] 1999. BS EN 13187 Thermal Performance of Buildings - Qualitative Detection of Thermal Irregularities in Building Envelopes - Infrared Method. London: BSI. [6] 2012. BS EN 16242:2012 Conservation of cultural heritage. Procedures and instruments for measuring humidity in the air and moisture exchanges between air and cultural property. London: BSI. [7] Cheshire, D., 2020. CIBSE Guild L Sustainability. Chartered Institution of Building Services Engineers. [8] Diamond, S., 2021. Building Performance Evaluation Guide 2021. 1st ed. Cardiff: Good Homes Alliance. [9] Gradeci, K., Labonnote, N., Time, B. and Köhler, J., 2017. Mould growth criteria and design avoidance approaches in wood-based materials – A systematic review. Construction and Building Materials, 150, pp.77-88. [10] Kubičár, Ľ., Hudec, J. and Dieška, P., 2016. MONITORING THE HYGROTHERMAL REGIME OF THE CHURCH SAINT JAMES IN LEVOČA. European Journal of Science and Theology, 12(1), pp.283291. [11] Litti, G., Khoshdel, S., Audenaert, A. and Braet, J., 2015. Hygrothermal performance evaluation of traditional brick masonry in historic buildings. Energy and Buildings, 105, pp.393-411. [12] Pelsmakers, S., Vereecken, E., Airaksinen, M. and Elwell, C., 2019. Void conditions and potential for mould growth in insulated and uninsulated suspended timber ground floors. International Journal of Building Pathology and Adaptation, 37(4), pp.395-425. [13] Sedlbauer, K., 2002. Prediction of Mould Growth by Hygrothermal Calculation. Journal of Thermal Envelope and Building Science, 25(4), pp.321-336. [14] WELL Standard. 2022. WELL Standard V2. [online] Available at: https://v2.wellcertified.com/en/wellv2/overview
Advertisement