SINGAPORE THE ENGINEER


August 2023 |

Research initiative launched for developing next generation photovoltaics


































August 2023 |

Research initiative launched for developing next generation photovoltaics































11 Research ini a ve launched for developing next genera on photovoltaics
It is expected to drive innova on in ultra-high-efficiency solar cell technologies in Singapore.

14 Perovskite solar cells invented by NUS scien sts set new world record
The achievement marks a major milestone in photovoltaic technology.
15 The important connec on between water and energy Embracing it will offer environmental benefits.
18 NTU Singapore scien sts invent spray cooling method to lower the carbon footprint of data centres


The technology uses non-conduc ve fluids.
20 Why data centre infrastructure must be at the forefront of sustainability efforts
Crea ng more data centre capacity, while using less energy, is a challenge.

22 Experimental inves ga on of the cooling capacity and thermal performance of the passive displacement dual cooling coil system in tropical climates

Impressive results were obtained from the studies conducted in a laboratory and under a commercial se ng.
President Mr Dalson Chung
Chief Editor
T Bhaskaran
t_b_n8@yahoo.com
Publica ons Manager Desmond Teo desmond@iesnet.org.sg
Publica ons Execu ve Nuraini Ahmad nuraini@iesnet.org.sg
Editorial Panel Dr Chandra Segaran
Dr Ang Keng Been Mr Jaime Vega Bau sta Jr Dr Victor Sim

Mr Soon Ren Jun Dr Alexander Wiegand Media Representa ve Mul media Communica ons (2000) Pte Ltd sales@mul mediacomms.sg
Design & layout by 2EZ Asia Pte Ltd
Cover designed by Irin Kuah
Cover images by REC@NUS Corporate R&D Lab
6467 1108
www.ies.org.sg

24 Three transforma on projects for greater rail sustainability

They are said to be a first for Singapore’s MRT networks.
28 Strengthening Singapore’s compe veness as a hub port and interna onal mari me centre
The various ini a ves undertaken include digitalisa on, decarbonisa on and talent development.

32 Finalists of the ‘2023 Going Digital Awards in Infrastructure’ announced
The winners will be selected and honoured at an event which will be held in Singapore, in October.
34 Char ng a new course for robo c process automa on in highly secured environments
Organisa ons will be able to safely do more with less.


36 Reducing a vehicle’s emissions
The ar cle explains why lighter and closer-cu ng shoulder milling and face milling is the answer.
38 Targeted surface finishing of femur components with high process stability and increased produc vity
For proper func oning and durability, orthopedic implants in the human body require precisely defined finishes.
The Singapore Engineer is published monthly by The Ins tu on of Engineers, Singapore (IES). The publica on is distributed free-of-charge to IES members and affiliates. Views expressed in this publica on do not necessarily reflect those of the Editor or IES. All rights reserved. No part of this magazine shall be reproduced, mechanically or electronically, without the prior consent of IES. Whilst every care is taken to ensure accuracy of the content at press me, IES will not be liable for any discrepancies. Unsolicited contribu ons are welcome but their inclusion in the magazine is at the discre on of the Editor.



On 18 August 2023, over 250 representa ves from Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) a ended the inaugural SkillsFuture SME Conference 2023, held at the Lifelong Learning Ins tute.

The event was graced by Minister of State for Educa on and Manpower, Ms Gan Siow Huang.


Themed ‘By Industry, For Industry’, the SkillsFuture SME Conference 2023 aimed to inspire and empower SMEs to take charge of their workforce skills development across the three priority growth pillars – Digital Economy, Care Economy, and Green Economy.


At the event, IES launched the Engineering Chartership in Sustainability framework to promote and recognise competencies across the sub-sectors of Sustainability, as part of the IES Green Plan 2030.

Engineers applying to be cer fied are required to complete core course modules and selected elecves, and these will be followed by a panel interview. This chartership will promote engineers’ competencies in Sustainability, allowing them to navigate the expanding green sector with confidence.
During the IES Breakout Session, industry partners from AECOM Singapore and LTA enlightened attendees on how the IES Engineering Chartership has benefi ed employees and their organisa ons.
IES was appointed as a Skills Development Partner (SDP) in April 2023 by SkillsFuture Singapore (SSG), to advance the skills development agenda for Engineering professionals and sectors, through the development of engineering standards, cer -


IES is delighted to announce the appointment of Dr Boh Jaw Woei as the Execu ve Director of The Ins tu on of Engineers, Singapore (IES), from 1st August 2023.

Dr Boh graduated from the University of Liverpool with a 1st Class Honors in Civil Engineering and also holds a diploma in Civil & Environmental Engineering with Merits from Ngee Ann Polytechnic.
He was awarded the Shell Gold Medal in 1998, obtained the NUS President Research Fellowship for his work on Blast Barriers Against Hydrocarbon Explosion, which was part of a large-scale industrial project conducted by Imperial College London, and has wri en over 20 papers for interna onal journals and conferences, and industry-funded reports, including one which was awarded

the James Wa Medal by the Ins tu on of Civil Engineers.
In his professional career, Dr Boh is well-versed in the areas of structural design and analysis, finite element analysis, project management, tender preparaon and business development, for both local and interna onal projects.
He is the Non-Execu ve Director of several en es, with the businesses spanning across trading and service companies suppor ng the construc on sector, natural resource stewardship, enhanced environmental performance and sustainable development.
With his extensive experience and leadership, Dr Boh is well-posi oned to launch into this new role, having served as IES Council Member from 2010 to 2018 and 2020 to 2023, as

well as Chairman of the Qualificaon and Membership Commi ee, Honorary Treasurer and Honorary Secretary, of the Ins tu on. He took on the role of Ac ng Chief Execu ve in 2017.
Dr Boh became a Fellow of IES in 2016 and Honorary Fellow of the ASEAN Federa on of Engineering Organisa ons (AFEO) in 2017. He is also a cer fied APEC Engineer, Chartered Engineer (Singapore) and ASEAN Engineer.
As the Execu ve Director of IES, Dr Boh will lead the Ins tu on in its day-to-day opera ons and spearhead strategic ini a ves aimed at cul va ng stronger synergy and coopera on among staff and the network of stakeholders and partners.
TEMBUSU Asia Consul ng (TAC), formed by a group of Singapore Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), recently celebrated its fi h anniversary, since commencing opera ons in July 2018. The local sustainability and environmental consul ng company was set up in response to the urgent need for climate ac on and to contribute towards mee ng the United Na ons’ (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).

TAC provides one-stop solu ons that integrate management consul ng, science and engineering exper se, to support the Singapore Green Plan 2030, and help companies in their sustainability journey. The company embraces the UN SDGs at the heart of its services.
The anniversary celebra on was a ended by more than 100 guests, including partners and clients of TAC, government agencies, IHLs, associa ons, private sectors organisa ons and NGOs.
TAC is said to be the only Singaporean company accredited by the Na onal Environmental Agency (NEA) as a Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions Verifier under the Carbon Pricing Act (CPA). It is also the first Singaporean company accredited under the Singapore Accreditaon Council’s (SAC) Accredita on Scheme for GHG Valida on and Verifica on Bodies. These achievements recognise TAC’s GHG validaon and verifica on exper se in suppor ng the industry’s decarbonisa on efforts. TAC’s members have also obtained the Singapore Business Advisors & Consultants Council’s (SBACC) cer fica on as Prac cing Management Consultant (PMC) for Sustainability, which allows TAC to be er assist SMEs in obtaining grants to support their own sustainability journeys.
“TEMBUSU Asia Consul ng leverages on our local SMEs’ exper se and

builds local competency in the field of sustainability and the environment. Over the past five years, our work has created jobs in Singapore and created opportuni es for local SMEs to expand into the global market,” said Er. Tan Seng Chuan, Managing Director of TAC.
To-date, TAC has verified over 2.5 million tonnes of CO equivalent GHG emissions, carried out biodiversity surveys in over 385 hectares of land in Singapore, trained more than 320 sustainability professionals and completed projects in China, Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, the Philippines, Cambodia and Malaysia.
TAC signed two MoUs to explore collabora ve opportuni es during the anniversary event. The first MoU is with the Singapore Ins tute of Technology (SIT), which aims to foster the growth of future engineers in climate ac on, by bridging the gap between theore cal knowledge and prac cal industry experience.


The second MoU is with S ch ng Deltares, a Dutch knowledge instute for water, to explore new business and research opportuni es in areas such as flood management and nature-based solu ons.
“We are happy to extend our longterm coopera on with TAC, an excellent local environmental consultant. As Deltares, the Dutch Na onal Research Ins tute for water and the subsurface, we share our knowledge with local, na onal knowledge partners, like NUS, TCOMS, and TMSI, and with local private partners like TAC. We congratulate TAC on their fi h anniversary and look forward to an excellent coopera on,” said Mr JanJaap Brinkman, Director of Deltares Singapore.
This collabora on will allow both companies to work together to address the climate challenges faced in Southeast Asia.
Engineering Good (EG) and Kaplan Singapore (KSG) recently formalised a partnership which will see the two organisa ons doing good for vulnerable communi es in Singapore as well as the environment.

Themed ‘Revive, Reconnect, Reimagine: Empowering Communi es, Sustaining the Environment’, the comprehensive partnership will see coopera on in the form of donaons, volunteering opportuni es and collabora on possibili es, to benefit low-income families and the disabled, and to ensure that electronic waste is responsibly recycled.
KSG staff, students and alumni will be ac vely encouraged to donate their used electronic devices at a collec on point which has been set up on its campus. In addi on to dona ng devices, KSG staff, students and alumni can also volunteer to support ac vi es or events conducted by EG in various capaci es, such as assis ng with collec on, sor ng or refurbishing devices. The partnership will also explore possible collabora ons such as sustainability projects to reduce e-waste in corporate organisa ons, and involving KSG students in addressing real-world problems, through solu on-based projects under the Kaplan Industry Project.
Mr Eric Chua, Senior Parliamentary Secretary, Ministry of Culture, Community and Youth and Ministry of Social and Family Development, graced the event as Guest-of-Honour. Mr Chua witnessed the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding between EG and KSG. To kickstart the ini a ve, Mr Chua together with EG CEO, Mr Patrick Hee, and KSG President, Dr Susie Khoo, donated used electronic devices at the event.
At the event, Mr Chua lauded the partnership between EG and KSG as a commendable effort which not only helps save the environment, but also helps segments of the community to harness technology to improve their lives. He also highlighted
the importance of such partnerships in upli ing those in need.
“At Engineering Good, our main thrusts include bridging the digital divide, reducing carbon and e-waste, and helping persons with disabili es live a life of independence and opportunity via technology and engineering solu ons. We see that Kaplan’s CSR goals, as an established private educa on ins tute in Singapore, are aligned to ours and this heartens us,” said Mr Patrick Hee.
“Today, Engineering Good supports over 200 social service agencies in Singapore and our collec ve efforts with our volunteers and partners have seen nearly 8,000 laptops and devices being distributed to various beneficiaries. By working together with Kaplan, we hope to increase these numbers to benefit even more people,” he added.
“The Kaplan Ini a ve for Nurturing Development or KIND Programme is Kaplan’s integrated CSR effort which brings together the various ac vi es and good work done by different groups in Kaplan, such as our staff, students and alumni. KIND reflects Kaplan’s commitment to create shared value for society by suppor ng growth and development of individuals and communies,” said Dr Susie Khoo.
“We therefore hope that by partnering with Engineering Good, our staff, students and alumni will also get to do good for the individuals and
communi es that we serve as well as the environment,” she added. For this partnership, EG and KSG target to salvage an es mated 220 kg worth of electronic devices comprising laptops, mobile phones, tablets, and wired keyboards and mice. Those found suitable for reuse or refurbishing could benefit some of the social service agencies EG supports. Those found unsuitable will be harvested for parts and then responsibly recycled.
Engineering Good
Engineering Good is a Singaporebased non-profit organisa on that empowers vulnerable groups through humanitarian engineering and technology. Engineering Good has served over 200 social service agencies in Singapore, focusing on persons with disabili es and low-income communi es, serving them through Assis ve Technology (AT) and Digital Inclusion (DI), respec vely.
Kaplan Singapore
Kaplan Singapore is part of Kaplan Inc, one of the world’s most diverse educa on providers. To-date, Kaplan Singapore has students from over 35 countries and regions, and has served over 95,000 graduates. With over 450 academic programmes for higher learning and professional cer fica on courses available for skills development, Kaplan provides opportuni es for individuals to pursue lifelong learning.
DeburringEXPO 2023, the 5th Leading Trade Fair for Deburring Technology and Precision Surface Finishing will be held from 10 to 12 October 2023 at the Karlsruhe Exhibi on Centre in Germany.
Market and technology leaders, hidden champions, start-ups and research ins tutes will present innova ve and further developed solu ons and services for current and future challenges in manufacturing processes. The interna onal spectrum of exhibitor offerings will be rounded off with an a rac ve supplementary programme, including theme parks and a bilingual expert forum.
The exhibits will highlight the methods to op mise produc on processes such as deburring, edge rounding, component cleaning and surface finishing.
As an interna onal informa on and procurement pla orm for these disciplines, DeburringEXPO iden fies opportuni es targeted at improvement, streamlining and enhanced resource efficiency in the relevant processes, for investment decision-makers, developers, design engineers and technical purchasing agents, as well as manufacturing and produc on managers.
“This is reflected, on the one hand, by the numerous innova ons and further developments presented by the exhibitors at the leading trade fair for deburring technologies and precision surface finishing. Furthermore, solu ons are also provided for dealing with the current shortage of skilled personnel. On the other hand, the supplementary programme with its various theme parks and the expert forum is also geared towards offering companies inspira on and sugges ons for opmising processes, reducing costs and increasing sustainability,” said Hartmut Herdin, Managing Director of fairXperts GmbH & Co KG, organisers of DeburringEXPO.
DeburringEXPO 2023 will feature several innova ons and further developments. These include:
• Self-learning deburring robots for toothed parts and the chamfering cu er with a V-shaped cu ng edge, which prevent secondary burrs and thus the need for addi onal, downstream deburring processes.
• New systems and methods for fully automated deburring and cleaning of components in a single process, using high-pressure water jet techniques, as well as ultrasound or dry processes with CO

• New and further developed products, technologies, processes and services in the field of micromachining, as well as for energy- and resource-efficient produc on of applica on-oriented surfaces.
The three theme parks at DeburringEXPO 2023 will also provide inspira on for mastering current and future challenges.
The theme park for ‘Quality Assurance in the Deburring Process’ will provide targeted informa on on various measuring methods, as well as their strengths and limita ons, in order to verify compliance with ever stricter specifica ons in the areas of deburring, edge rounding and surface finishing.
The special show on ‘Automated Deburring’ will present up-to-date op ons for automated polishing, grinding and deburring of components with robots, and will also address the current shortage of skilled personnel.
The ‘Cleaning A er Deburring’ theme park will address methods and processes to achieve technical cleanliness, before and a er deburring, in accordance with specified requirements – essen al for ensuring the high quality of downstream processes and components.
As a supplement to the exhibitors’ cross-technology, mul -material and inter-industry spectrum of solu ons, DeburringEXPO will facilitate effecve transfer of knowledge, via the integrated, three-day expert forum. The programme, featuring a total of 23 simultaneously interpreted presenta ons (German to English and English to German) by experts from industry and science, is divided into five thema c blocks – mechanical deburring, quality assurance, automated deburring with industrial robots, cleaning a er deburring, and non-mechanical deburring. Presenta on focal points include fundamentals, approaches to process and cost op misa on, reports on best prac ce applica ons and current trends.
It is expected to drive innova on in ultra-high-efficiency solar cell technologies in Singapore.
Jointly set up by the Solar Energy Research Ins tute of Singapore (SERIS) at the Na onal University of Singapore (NUS), and REC Solar (REC), the REC@NUS Corporate R&D Laboratory for Next Generaon Photovoltaics (REC@NUS Corp Lab), a new SGD 77 million research ini a ve, was recently launched at NUS to boost innova on and research on advanced solar cell technologies in Singapore.
Deputy Prime Minister and Coordina ng Minister for Economic Policies, Mr Heng Swee Keat, who is also Chairman of the Na onal Research Founda on (NRF), was the Guest-of-Honour at the event.

Over the next five years, the REC@ NUS Corp Lab will research, develop, and commercialise disrup ve solar photovoltaic (PV) technologies based on perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells.

Supported by Singapore’s Research, Innova on and Enterprise (RIE) 2025 Plan, this strategic investment in high-power clean energy solu ons
is crucial in accelera ng Singapore’s transi on to renewable energy for a greener future and maintaining the na on’s leading posi on in PV R&D and manufacturing.
By bringing together NUS-SERIS’ world-class research exper se in PV technologies and REC’s deep experience in upscaling innova ve solar PV technology, the new corporate laboratory aims to champion bold technology innova ons for more powerful, more efficient, more
sustainable and less costly solar energy. Successful outcomes from the corporate laboratory could transform the solar industry globally and, in turn, accelerate global energy transi ons.
NUS President, Professor Tan Eng Chye said, “NUS’ strong research capabili es and technology leadership, coupled with ac ve industry collabora ons, have enabled the university to make significant advances in PV technologies. We have
been collabora ng with REC on solar PV research for around 14 years, and I am heartened that this strategic industry-academia partnership has now blossomed into the REC@ NUS Corporate R&D Laboratory for Next Genera on Photovoltaics, which will further consolidate and integrate our complementary strengths to make a quantum leap in solar power. I have every confidence that REC and NUS will achieve technical breakthroughs to cross the 30% conversion efficiency barrier for large-area, low-cost solar cells that would accelerate solar PV deployment in urbanised and space-constrained Singapore.”
“REC has been pushing the boundaries of solar energy technology since its founding, and is committed to con nuously improving efficiencies and costs, crea ng novel products and driving global transions. With our in-depth exper se and cu ng-edge technology, REC is known for its many ‘world’s first’ achievements and is the one and only solar panel brand in the market with three pres gious Intersolar Awards. By con nuously increasing the power density of solar panels and their longevity, more clean energy can be generated at lower cost, more emissions can be offset and more resources can be saved,” explained Dr Shankar G Sridhara, Chief Technology Officer of REC. NRF’s Chief Execu ve Officer, Mr Beh Kian Teik, said, “The REC@ NUS Corporate R&D Laboratory is a showcase of partnership between our academia and industry, in support of Singapore’s decarbonisa on efforts. As one of the leading solar laboratories in the world, SERIS had provided novel solar solu ons unique to Singapore’s urban environment, such as floa ng solar PV on our reservoirs and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). These innova ve technologies enabled valuable solar deployment opportuni es in our land-scarce na on as Singapore strives to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050.”
The REC@NUS Corp Lab will be led by two Co-Directors – Professor Armin Aberle, CEO of SERIS, and Dr Shankar G Sridhara, Chief Technology Officer of REC.

Crossing the conversion
efficiency barrier
Singapore has iden fied solar energy as one of the na on’s ‘Four Energy Switches’. However, its widespread global adop on will require further improvements in the efficiency of energy conversion, while keeping manufacturing costs under control.
The energy conversion efficiency (i.e. the percentage of solar energy that is converted into usable electrical energy) of the best-in-class, commercially available solar cells is around 24% to 25% today. Research communi es around the world are currently finding ways to further improve the efficiency of large-area solar cells (> 400 cm ) to reach the milestone level of 30% or more.
Developing such cost-effec ve, ultra-high-efficiency solar cells requires a technological transi on from today’s single-junc on solar cell technology (which uses one layer of photovoltaic absorber
material, typically made of silicon) to a two-junc on tandem solar cell technology.

A two-junc on tandem solar cell uses two layers of photovoltaic material stacked on top of each other to absorb and convert solar radia on more efficiently into electricity. The sun-facing top cell is designed to op mally convert the visible wavelengths of the solar spectrum (from blue to red), while allowing the invisible wavelengths (near-infrared light) to pass through to the bo om cell. A promising top cell absorber material is perovskite, which is a family of crystalline compounds that has been gaining a en on for next-genera on solar cells due to its low produc on cost and high energy conversion efficiency.
“The REC@NUS Corp Lab will address the technological efficiency-cost dilemma of the PV industry by demonstra ng large-area perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell
technology with an energy conversion efficiency of 30%. It will also develop one-of-its-kind capabili es to manufacture these advanced solar cells cost-effec vely to facilitate industry adop on,” said Prof Aberle. The corporate lab will bring together complementary research experse and talent from NUS and REC, in partnership with the Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore), to facilitate Singapore’s manufacturing of cost-effec ve high-performance tandem solar cells. The project will comprise about 40 researchers and aims to train up to 20 PhD students over the next five years.
The Na onal University of Singapore (NUS) is Singapore’s flagship university, which offers a global approach to educa on, research and entrepreneurship, with a focus on Asian perspec ves and exper se. NUS has 16 colleges, facul es and schools across three campuses in Singapore, with more than 40,000 students from 100 countries. The NUS Overseas Colleges programme has also been established in more than 15 ci es around the world.
Researchers in the university’s facul es, research centres of excellence, corporate labs and more than 30 university-level research ins tutes focus on themes that include energy; environmental and urban sustainability; treatment and preven on of diseases; ac ve ageing; advanced materials; risk management and resilience of financial systems; Asian studies; and Smart Na on capabili es such as ar ficial intelligence, data science, operaons research and cybersecurity.
The Solar Energy Research Ins tute of Singapore (SERIS) at the Na onal University of Singapore (NUS) is the city-state’s na onal ins tute for applied solar energy research. Since its incep on in 2008, the ins tute has emerged as one of the leading solar energy laboratories in the world. SERIS is supported by NUS, the Na onal Research Founda on
Singapore (NRF), the Energy Market Authority of Singapore (EMA) and the Singapore Economic Development Board (EDB).
SERIS conducts research, development, deployment, tes ng and consul ng on solar energy technologies and their integra on into urban infrastructures, buildings, and power systems. The ins tute’s R&D spectrum covers industrially relevant materials, components, processes, systems and services, with an emphasis on solar photovoltaic (PV) cells, modules and systems.
This serves the na on’s need for solar adop on and industry development, and also supports the government’s pledge to reduce the na on’s carbon emissions. SERIS is globally ac ve but focuses on technologies and services for tropical regions, in par cular for Singapore and Southeast Asia. SERIS collaborates closely with universi es, research organisa ons, government
agencies and industry, both locally and globally.
REC Group is an interna onal solar energy company dedicated to empowering consumers with clean, affordable solar power through high-quality solar panels with high power density. REC is known for its patented innova ons and mul ple award-winning products with reliable long-term performance.
Founded in 1996 in Norway, REC is commi ed to a low carbon footprint in its solar materials and panels. REC is headquartered in Norway with opera onal headquarters in Singapore and regional hubs in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. As of December 2021, REC is part of Reliance Industries Limited, India’s largest private sector company.
Allimages by
REC@NUS Corporate R&D LabThe global solar industry is ready for a revolu on, with all signs poin ng to growth. Recently, at the Intersolar Europe Conference 2023, the European industry associa on, SolarPower Europe, presented the latest edi on of its Global Market Outlook for Solar Power 2023-2027. The market study shows that in 2022, the worldwide PV market hit a new growth record with a deployment of 239 gigawa s (GW) of newly installed capacity.
At 239 GW, global installed capacity grew by 45% in 2022, compared to 2021. This solar boom is set to con nue in 2023 – SolarPower Europe’s forecast sees the deployment of another 341 GW, which translates to a growth of 43%. In total, photovoltaics (PV) accounted for two-thirds of all power generaon capaci es from renewable sources installed last year.
But even beyond that, the outlook is posi ve. While global
solar surpassed 1 terawa (TW) mark of cumula ve capacity last year, it is set to reach the 2 TW mark in 2025 and the 3 TW mark in 2027. The driving forces behind this dynamic global growth are diverse –from the flexible range of applica ons to the desire for a more independent energy supply using renewable energies and large-scale projects that can be implemented quickly and at compe ve costs.
With an installed capacity of around 95 GW and an annual growth of 72%, China is at the very top of the global markets, followed by the USA (21.9 GW), India (17.4 GW) and Brazil (10.9 GW). The European market is led by Spain (8.4 GW), Germany (7.4 GW), Poland (4.5 GW) and the Netherlands (4.1 GW). Compared to the global market, Europe con nues to have the largest number of installa ons per capita.

The achievement marks a major milestone in photovoltaic technology.
Perovskite solar cells designed by a team of scien sts from the Na onal University of Singapore (NUS) have a ained a world record efficiency of 24.35% with an ac ve area of 1 cm . This achievement paves the way for cheaper, more efficient and durable solar cells.

To facilitate consistent comparisons and benchmarking of different solar cell technologies, the photovoltaic (PV) community uses a standard size of at least 1 cm to report the efficiency of one-sun solar cells in the ‘Solar Cell Efficiency Tables’. Prior to the record-breaking feat by the NUS team, the best 1 cm perovskite solar cell recorded a power conversion efficiency of 23.7%.
This ground-breaking achievement in maximising power genera on from next-genera on renewable energy sources will be crucial to securing the world’s energy future. Perovskites are a class of materials that exhibit high light absorp on efficiency and ease of fabricaon, making them promising for solar cell applica ons. In the past decade, perovskite solar cell technology has achieved several breakthroughs, and the technology con nues to evolve.
“To address this challenge, we undertook a dedicated effort to develop innova ve and scalable technologies aimed at improving the efficiency of 1 cm perovskite solar cells. Our objec ve was to bridge the efficiency gap and unlock the full poten al of larger-sized devices,” said Assistant Professor Hou Yi, leader of the NUS research team comprising scien sts from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering under the NUS College of Design and Engineering as well as the Solar Energy Research Ins tute of Singapore (SERIS).
He added, “Building on more than
14 years of perovskite solar cell development, this work represents the first instance of an invertedstructure perovskite solar cell exceeding the normal structured perovskite solar cells with an ac ve area of 1 cm , and this is mainly a ributed to the innova ve charge transpor ng material incorporated in our perovskite solar cells. Since inverted-structure perovskite solar cells always offer excellent stability and scalability, achieving a higher efficiency than for normalstructured perovskite cells represents a significant milestone in commercialising this cu ng-edge technology.”
This milestone achievement by Asst Prof Hou Yi and his team has been included in the Solar Cell Efficiency Tables (Version 62) in 2023. Published by scien fic journal, Progress in Photovoltaics, on 21 June 2023, these consolidated tables show an extensive lis ng of the highest independently confirmed efficiencies for solar cells and modules.
solar cell technology
The record-breaking accomplishment was made by successfully incorpora ng a novel interface material into perovskite solar cells.
The promising results mark a milestone in advancing the commercialisa on of a low-cost, efficient, stable perovskite solar cell technology.
Building upon this exci ng development, Asst Prof Hou and his team aim to push the boundaries of perovskite solar cell technology even further.
Asst Prof Hou commented, “We are developing a customised accelera ng ageing methodology to bring this technology from the lab to the fab. One of our next goals is to deliver perovskite solar cells with 25 years of opera onal stability.”
The team is also working to scale up the solar cells to modules by expanding the dimensions of the perovskite solar cells and demonstra ng their viability and effec veness on a larger scale.
The Singapore Engineer (TSE): How can an understanding of the water-energy nexus assist in ensuring greater sustainability?
Truls Lystang (TL): The water-energy nexus refers to the inextricable rela onship between water and energy. It takes energy to move water at every stage of the water cycle, from withdrawal to transporta on, recycling and discharge. Similarly, the process of energy genera on relies heavily on water resources. The increased demand for one can significantly affect the security of the other. Therefore, to ensure greater sustainability of our resources, we must take a holis c approach that considers both water and energy.
Embracing the water-energy nexus in the transi on to more sustainable opera ons offers clear environmental benefits. By adopting more energy-efficient water, we can reduce both water and energy consump on, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. There is also a strong business case for considering the water-energy nexus. For manufacturers, adop ng water- and energy-efficient solu ons can achieve significant savings in both resources, thus cu ng down opera ng costs. The use of intelligent solu ons also allows manufacturers to monitor the condi on of their equipment in real- me and remotely, and gain preven ve maintenance insights to reduce unplanned outages and losses, while achieving be er energy efficiency and system op misa on.
A good example is our work with Arla Foods [1]. As part of their 2050 net zero targets, one of their milestones is to lower their carbon emissions, by 63%, at 60 dairies worldwide, by 2030. We were ap-
pointed in 2022 to support this, by audi ng the water systems across Arla’s global dairy sites to iden fy energy-saving opportuni es, and upgrading their exis ng pumping systems for be er energy efficiency, with state-of-the-art motors, pumps and controls.
We have since assessed two thirds of their sites and iden fied annual savings of 7 GWh (gigawa -hours), with total expected savings around 10 GWh. We have replaced the old pumps with our new intelligent pumps for chilled and iced water applica ons, at Arla Westbury dairy in the UK, leading to savings per year of 481,800 kWh of energy and 194 tons of CO , with a return on investment of less than two years.
TSE: Could you elaborate on the importance of sustainable and intelligent water management solu ons in a aining the net-zero transi on?
TL: As the world popula on con nues to grow, the demand for water also rises significantly, resul ng in higher energy consump on at every stage of the water cycle. According to the Interna onal Energy Agency (IEA), the global energy consumpon of the water sector is projected to more than double by 2040 [2].
A concerning outcome of this escalated energy usage is the substanal carbon emissions associated with water usage. On average, every cubic metre of water consumed currently generates 10.6 kg of carbon emissions [3]. To contribute to the global transi on towards a net-zero future, it is crucial to embrace sustainable and intelligent water management solu ons. By doing so, we can reduce the average carbon emissions associated with water usage, while simultaneously mee ng the surging demand
for this precious resource.
Through digitalisa on and the use of efficient technology, we can approach water use more strategically. Tradi onally, our rela onship with the water system has been a one-way process, simply moving water from supply to demand.
Now, new digital innova ons are able to turn this rela onship into a dialogue – by retrieving feedback throughout the process. At Grundfos, we are innova ng across the water cycle and applying digital technologies to improve water circularity and efficiency.
Across the region and globally, real- me sensors and data analy cs are increasingly used to conduct pre-emp ve and predic ve maintenance of the en re water system. These intui ve technologies help to enhance sustainable opera ons and resiliency of infrastructure, ensuring that water is used and managed efficiently and op mally, as well as preven ng resource and energy wastage.
TSE: How can a circular economy be created, with regard to water?









TL: In a tradi onal linear economy, water is o en used once and then discarded as wastewater a er it has served its ini al purpose. This wasteful approach is not sustainable, par cularly for regions facing water scarcity and increased demand due to popula on growth, industrial expansion and urbanisa on.
In contrast, a circular water economy takes a sustainable approach to managing water resources, focusing on reducing waste and maximising the reuse and recycling of water.
In the context of industries, a circular approach to managing water begins with the design phase. Engineers can focus on incorporat-
ing water-efficient prac ces and technologies into the layout and industrial processes of manufacturing sites. This includes designing the site to capture and u lise rainwater for non-potable uses such as irriga on, installing water-saving technologies in water-intensive areas, and implemen ng closed-loop water systems to minimise water losses and enhance overall water efficiency. Water reuse is another crucial element. There are a number of technologies available for water treatment and reuse, such as reverse osmosis, a technology that is used to remove a large majority of contaminants from water by pushing the water under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane. Such technologies are cri cal in water treatment and water reuse, but they are also energy-intensive and thus come with a significant carbon footprint.
Intelligent technology offers a soluon to improve the energy efficiency of water treatment processes like reverse osmosis. Grundfos worked with a water treatment supplier in the UK, Industrial Water Equipment (IWE), to provide intelligent reverse osmosis solu ons which provide greater control via variable-speed pumps powered by IE5 motors. Notably, the pump opera on will vary, moving up and down in speed, according to demand, which reduces the energy ra ng of the pumps used, massively. In this specific case, intelligent reverse osmosis demonstrated the ability to save up to 70% energy per m water produced.
Another example is our work with one of the world’s top cider producers to improve its industrial cooling processes [4]. Industrial cooling, which involves moving large amounts of water, is an energy-intensive process. Recognising this, they worked with us to integrate Grundfos iSOLUTIONS intelligent pumps and controls with their cooling system. Variable speed, conven onal end suc on pumps are combined with intelligent mul -pump controllers, external Grundfos sensors and communicaon. This enabled them to control
and refine their cooling produc on to op mum levels, while adap ng to changes in process demands through Grundfos technologies and communica on capabili es. Thanks to Grundfos iSOLUTIONS, the factory now has be er control of its cooling processes. Compared to a compe tor’s proposed solu on, the newly implemented Grundfos system is es mated to save an impressive 30% energy on pumps and chillers. In addi on, the improved condensing system reduces the need for water replacement in the cooling towers.
This not only leads to substan al energy- and water-savings compared to conven onal systems, it also provides valuable insights into key data points. They can see how efficiently the system is opera ng and they can make adjustments quickly if they have process changes. And the intelligence is also fed into the building management system for full and transparent control and visibility. The cider company achieves its goals in manufacturing quality cider for its customers while contribu ng to global sustainability.
TSE: What are the ini a ves that Grundfos has taken to ensure the sustainability of its own operaons?
TL: As a global leader in water technologies for over 75 years, we recognise that water solu ons play a key role in securing a sustainable future for all, and in 2022, we unveiled our new brand promise to respect, protect and advance the flow of water.
In November 2022, Grundfos took a step further, to become the first organisa on in the water solu ons sector to receive full valida on of our sustainability targets from the Science-Based Targets ini a ve (SBTi). We have commi ed to reducing, by 2030, absolute Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 50%, and reducing absolute Scope 3 GHG emissions 25%, from a 2020 base year. For our 2050 goal, we have commi ed to reducing absolute Scope 1, Scope 2 and Scope 3 GHG emissions by 90%, and reaching net-zero GHG
across our value chain, from a 2020 base year.
Our SBTi Net-Zero targets are testament to our commitment and guide our sustainability ambi ons which include saving energy and saving water, as well as ensuring a circular business and water access.
To achieve these ambi ous goals, we need to con nue innova ng our products to deliver the world’s most energy-efficient and digitally enabled product por olio, while walking the talk by embedding sustainability into our own opera ons.
In line with our sustainability ambi ons, we have set clear targets and taken diverse ini a ves to save energy and water, and implement circular business prac ces in our opera ons.
Firstly, saving energy. Key ini aves to reduce emissions include procuring renewable energy sources, advancing manufacturing and re-manufacturing ac vi es, enabling energy-efficient buildings and transi oning to electric vehicles. In 2022, we have invested in alterna ve energy sources in our facili es in Hungary and Serbia, in accordance with Gold Leadership in Energy & Environmental Design (LEED) cer fica on.
Secondly, saving water. We aim to reduce our water withdrawal by 50%, by 2025, compared to 2008. And we will apply the 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) principle to preserve water at every stage of the water cycle. Highlights in 2022 included a xeriscaping project at our Fresno Plant in the US, which is expected to reduce the usage of water for irriga on by 77%. In our new Serbian facility, an extended underground rainwater pond allows approximately 3.5 million litres of rainwater collec on annually. All sanita on at the plant is now connected to our own water treatment/water reuse facility, which increases the water re-use capacity by nearly 50%.
Lastly, adop ng a circular business approach. By 2025, we aim to reduce waste to landfill by 50%, based on our 2018 baseline of 1260 tonnes. We deliver on it through promo ng the 3Rs principle
across all our sites and focusing on packaging and pallet re-use, wood mulching, and be er waste segregaon among others. We have already reduced by 32%, the total waste to landfill since 2020.
TSE: Any other informa on that you would like to provide?
TL: The key challenge for industries to transi on to net zero and a circular model for water has shi ed beyond being convinced on the ‘why’ to now understanding the ‘how’.
To kickstart that process, businesses need to first understand the scale of the issue, including resource use in their opera ons. They can then understand the poten al areas for op misa on and assess various op ons.
At Grundfos, we support our customers in gaining this understanding through audits such as Grundfos Energy Check Advanced, where they receive an overview of the life-cycle costs (LCC) of their pumps. This informa on can then help them consider the necessary changes in their opera ons to reduce energy consump on.

Going green is undeniably a big task. For businesses that do not know where to start, tapping on rela onships with aligned partners not only within the industry, but also with others in both the public and private sectors, can expedite the net zero transi on.
Such strategic partnerships can help businesses understand the complexity of the transi on, come up with and deploy solu ons more quickly and effec vely, and capture the best value out of the transi on.
For example, we formed a partnership with Singapore Polytechnic, back in 2021, with the aim of helping businesses effec vely adopt sustainable solu ons and enabling solu on providers like Grundfos to develop tailored solu ons that can create real value.

References
[1] Grundfos: ‘Grundfos helps Arla reduce its energy consump on and carbon emissions across its global produc on facili es’.
The Charles Rudd Dis nguished Public Lectures 2023 concluded with a series of green-centric learning journeys for the benefit of par cipants. This included the opportunity to explore the first Grundfos APAC Industry Demo Truck featuring a range of world-class sustainable water technologies. Jointly organised by the Ins tu on of Engineers, Singapore (IES), Singapore Polytechnic (SP), and the World Federa on of Engineering Organiza ons (WFEO), the Charles Rudd Dis nguished Public Lectures 2023 was held on 25 May 2023, at the Singapore Polytechnic Conven on Centre.

[2] IEA: ‘Introduc on to the water-energy nexus’.
[3] WINT Water Intelligence (February
2022): ‘The carbon footprint of water’.
[4] Grundfos: ‘Pump intelligence opmises processes, saving 30% energy’.

Scien sts from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have invented a more sustainable method for cooling down servers in data centres, poten ally reducing both energy costs and the carbon footprint, by up to 26%.
Currently, data centres in Singapore accounts for 7% the na on’s total electricity consump on. With demand for cloud compu ng increasing, it is cri cal to find a sustainable solu on that reduces energy consump on and the carbon footprint of data centres.
In a data centre, the ho est component in a server is the CPU (central processing unit) which requires a dedicated air-cooled heatsink for heat dissipa on.
When servers are stacked together in a rack, ver cally, they produce a substan al amount of heat. Therefore, cold air has to be drawn in to cool the server, a er which, the hot air is expelled to the surroundings. This air-cooling method is the reason why data centres have to run on energy-intensive air-condi oning systems to lower the air temperatures.
In comparison, this new method developed by NTU scien sts uses a special spray of non-conduc ve fluids to cool the CPU directly without a heatsink, by u lising a combinaon of highly efficient heat removal mechanisms such as evapora on and boiling.
The gases and excess fluids are then collected in an enclosed
system, condensed into a liquid at tropical ambient temperatures (around 30°C) and recirculated back into the system to be reused. More importantly, spray cooling has the poten al to carry away more heat than air cooling, which will allow for CPUs to run faster and perform be er than at today’s speeds which are limited by air cooling, since faster speeds will lead to higher temperatures.
With power being consumed by the servers in a rack, waste heat is generated, which is es mated to be around 7 kW/m in conven onal air-cooled racks [1]. In comparison, it has been shown that the spray-cooling prototype is able to dissipate signi ficantly more heat and is therefore capable of
handling rack densi es as high as 23 kW/m
If spray cooling is adopted industrially, it can allow for higher compu ng power servers to be packed into a smaller space than in current data centres. The NTU team es mates that this could translate into space savings of 30% when compared to conven onal data centres that use air-cooling systems, which would be a significant advantage for land-scarce countries like Singapore.
The leader of the project, Associate Professor Wong Teck Neng from NTU’s School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, believes the main benefits of the new method are its high energy efficiency and targeted approach.
“Instead of cooling the en re data centre conven onally, we designed special sprays to aim directly at the CPU, the cri cal component, which is the key source of heat in a data centre,” said Assoc Prof Wong, who is also the Assistant Chair (Faculty) at the school.
“The inspira on for our innova on is simple. If there is a fire breaking out on a piece of wood, we are taught to point the fire ex nguisher at the base of the fire to put it out, not spray at the flames or around the fire to cool it down, since the fire will con nue to burn at the source. Similarly, why are we spending an immense amount of energy cooling down the air around the heat source, when we should be cooling it directly?”, he added.
Assoc Prof Wong explained that their targeted approach is a smarter approach, especially in tropical environments, where the high humidity and heat can put a significant strain on tradi onal air-cooling systems. For instance, a conven onal data centre has to be cooled down to about 18°C, which accounts for about 40% of its total energy usage.
In contrast, using spray cooling, CPUs can maintain their op mal temperature at about 55°C, without the need for energy-intensive air-condi oning units. The power
usage effec veness (PUE) of the new prototype, which is the ra o of total amount of power used by the data centre to the actual power delivered to the servers, can go to as low as 1.08. This can result in significant savings in cooling energy when compared to tradi onal air-cooled data centres which are usually at 1.8 PUE.
Studies by the team also showed that, based on a data centre IT load of 1 MW, its spray cooled system can save up to 1550 t of CO emission annually, when compared to conven onal air-cooling systems.
This will be a signi ficant reduc on in the carbon footprint, given that most data centres consume 1000 kWh/m of energy [2]. Energy-efficient opera on of spray cooled data centres can also lead to a 26% cent savings in annual energy costs.
It can also pave the way for faster and more efficient data centres in future, as demand for cloud compu ng con nues to rise annually by some 15% [3].
A spokesperson from AFTERSHOCK PC, which is Singapore’s largest, high performance, custom, personal computer builder and which is collabora ng with Assoc Prof Wong on another sustainability project, said, “Spray cooling technology offers superior cooling capability and this certainly helps to unlock the full poten al of compu ng chips and graphics cards currently in market, by overclocking beyond its normal opera ng range. This directly leads to the future and the poten al of seamless compu ng and video rendering performance for our high-performance computers”.
The prototype system consists of an enclosed spray-cooled server rack, capable of opera ng near atmospheric pressure, a water pump, sprays with mul ple nozzles over each CPU, a collec on system to collect the vapourised liquid, and an energy-efficient room-temperature condenser to convert the gases back into liquid again. Unlike conven onal air-condi oning systems, no chiller system is required.
It was developed by a mul -disciplinary team which included former Assoc Prof Toh Kok Chuan, Asst Prof Ho Jin Yao from NTU’s School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, and research fellows, Ranjith Kandasamy and Liu Pengfei.
This project is supported by the Na onal Research Founda on, Singapore, under its Green Data Centre Programme. The NTU team took three years to design, build, test and commission their working prototype.
Patent applica ons for the technology have been filed through NTUi ve, NTU’s innova on and enterprise company. One patent has already been granted in the US, in July last year.
Sustainability and innova on are two key pillars of NTU’s 2025 Strategic Plan which aims to tackle some of humanity’s greatest challenges, such as climate change and to support Singapore’s ambi on of achieving long-term, net zero emissions, by 2050.
Accelera ng the transla on of research breakthroughs into prototypes, ready for commercialisa on or adop on by industry, is also one of the university’s objec ves, under its new NTU Innova on and Entrepreneurship ini a ve.
Moving forward, Prof Wong and his team will seek to work with industry partners to develop a larger pilot plant system which can demonstrate the poten al of spray cooling in an industrial se ng.
[1] Gowen L (2022, January 17): ‘The future is liquid’, Data Center Dynamics. Retrieved April 4, 2023, from h ps:// www.datacenterdynamics.com/en/ opinions/the-future-is-liquid/
[2] Mahan J (2023, January 27): ‘Understanding Data Center Energy Consumpon’, C&C Technology Group.
[3] GLOBE NEWSWIRE (2022, June 22): ‘Cloud Compu ng Market - Global & Regional Industry Perspec ve, Comprehensive Analysis, Size & Share, Growth, Trends, Sta s cal Research, and Forecast 2022 – 2028. Facts and Factors.
 by Tony Gaunt, Vice President, Hyperscale and Coloca on, ASI, Ver v Crea ng more data centre capacity, while using less energy is a challenge.
by Tony Gaunt, Vice President, Hyperscale and Coloca on, ASI, Ver v Crea ng more data centre capacity, while using less energy is a challenge.
Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) ac vism and investment is reshaping the business world.
Although ESG efforts have been championed for many years, there is a sense of urgency for decisive ac on from all stakeholders, now, especially in the corporate sector.
The impact of the global pandemic, climate-change disasters, and bolder reforms signalled at COP26 have changed how employees, consumers, investors, suppliers, regulators, communi es and trade associa ons perceive value, risk, growth, cost, produc vity and more.
While Europe and North America are ESG first-movers, Asia is set to catch up fast, on the back of regulatory changes and investor demand, according to research released by Accenture.
Progressive ESG policies are more than good op cs – they are good for the environment, employees, customers and our business, because consumers and the general public have much higher expectaons for companies, around ESG responsibility, today.
While Ver v is eleva ng its focus on many important ESG topics, we are uniquely posi oned to help our customers meet the environmental part of this strategy. Regardless of the ver cal that organisa ons operate in, environmental goals, which support efficiency and sustainability strategies, must con nually keep pace with the demands of the market.
Certainly, in today’s business climate, sustainability and resilience are inseparable. According to EY,
businesses in emerging markets with robust ESG ra ngs reaped a 1% reduc on in capital costs, compared to laggards, highlighting that sustainability may be as important as risk management and site reliability.
Mee ng sustainability targets is not without challenges, however.
Demand for data is ramping up rapidly and we saw this during the height of the pandemic. In Spain, internet traffic increased 40%, when shutdowns were enforced. And in the US, Microso teams were deployed to work and sleep in data centres, to ensure a smooth 24/7 opera on of systems at peak periods.
The insa able demand for compu ng power and digital services means bigger data centres. While 10 MW or 20 MW centres were
‘the norm’ five years ago, they range between 100 MW to 200 MW today, and will get bigger as energy-intensive technologies such as 5G mobile networks, ar ficial intelligence, and high-performance compu ng become mainstream. This points to a bright and exci ng future for the data industry. It also points to change because we cannot scale up like we used to. According to MIT, a single data centre can consume the equivalent electricity of 50,000 homes today, and the electricity u lised by data centres accounts for about 0.3% percent of overall carbon emissions.
Providing more capacity, while using less energy and shrinking our carbon footprint, is a challenge we take in our stride, and our commitment starts at the top.
Ver v’s senior leaders are driving change and our first public ESG report, released recently, profiles current energy and water efficiency; diversity; equity and inclusion; employee health and safety ini aves; and plans in the pipeline.
Serving as a founda on, or baseline, upon which we can build, the report spotlights more efficient resource u lisa on and the use of renewable energy as top priori es on our sustainability ‘to-do list’, for both Ver v opera ons and our solu ons por olio.
Solid progress is being made on the technologies we offer our customers, to help them meet their efficiency goals, with a new uninterrup ble power supply (UPS) opera ng mode that safely and dynamically adapts to changes in power quality, enabling opera ng efficiency up to 99%.
Energy-efficient and water-free economisa on systems (an alternave to water-intensive cooling systems) have also been introduced, as well as the integra on of solar energy solu ons into telecommunica ons access sites.
We believe reducing dependence on the grid is another big step in the data centre path to net-zero for Ver v and our customers. While carbon-based energy sources will power our sites in the foreseeable future, we expect that fuel cells and long-dura on energy storage as well as intelligent power management systems will enable the transi on to locally generated renewable power, to happen sooner rather than later.
As climate change impacts everyone, we believe collabora on is another vital driver of success in
achieving sustainability. We are truly ‘in this together’ and should learn from one another. That is why we currently partner with thought leadership groups – EcoEdge Prime Power, Open Compute Project, European Data Centre Associa on and others – to share research and best prac ces to enable future-ready digital infrastructures.
We want to reset the digital infrastructure playing field (and many current rules) with a holis c and collabora ve game plan to build a cleaner, greener, brighter future for our industry. The vision is of a future in which data centres con nue to fuel scien fic advances, improve business processes, provide home entertainment, and support new ways to shop and connect with the world, while minimising their impact on the planet and the communi es in which they operate.
Ver v, a global provider of cri cal digital infrastructure and con nuity solu ons, recently unveiled the Ver v EnerSav, a data centre op misa on service that helps operators benefit from cost-saving measures that reduce energy consump on within their crical facili es, without the need for a major infrastructure overhaul. The service is available throughout Asia Pacific, including Southeast Asia, Australia and New Zealand.
The Ver v EnerSav op misa on service is a low-risk, economical and environmentally-efficient service offering for data centres and server rooms. It is done with the help and guidance of trained Ver v service engineers who will conduct a detailed on-site assessment and gap analysis report of the data centre’s cooling infrastructure, highligh ng poten al energy savings and return on investment calcula ons.
A er comprehensive analysis of collected data, Ver v engineers will recommend the appropriate thermal management strategy –either computer room air condioning (CRAC) unit op misa on, or hotspot elimina on through hot/cold aisle containment, or air flow management. They will then assist operators with soluon deployment in the exis ng facility. Lastly, a detailed report on energy usage and reduc on will be presented, to show how the strategy and solu ons carried out address the gaps iden fied in the ini al analysis.
One of the solu ons that help achieve energy savings within the data centre cooling system is the Ver v Liebert iCOM-S, a data visualisa on so ware that provides facility and data centre management teams with advanced thermal management monitoring and control. It helps to reduce energy costs by using advanced algorithms but with a simplified user interface, for ease of use.
For heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, Vertiv utilises the External Digital Demand Response Technology or EDD-RT. The EDD-RT is an energy management device that combines IoT and AI technologies to reduce electricity consumption and maximise efficiency of chilled water systems without impacting the facility’s preset conditions. The EDD-RT maintains, then enhances, the manufacturer’s design characteristics, utilising live energy consumption patterns to optimise energy consumption.
Ver v
Ver v addresses important challenges facing data centres, communica on networks and commercial and industrial facili es, with a por olio of power, cooling and IT infrastructure solu ons and services, that extend from the cloud to the edge of the network.
by Er. Neo Poh Hong, Shinhan Tech-Engineering Pte Ltd (Principal Investigator), Mr George Ng, MET Engineering Services Pte Ltd (Industrial Collaborator), Associate Professor Steve Kardinal Jusuf (Lead SIT CoInvestigator), Associate Professor Aung Myat (SIT Co-Investigator), Associate Professor An Hui (SIT Co-Investigator), Associate Professor Victor Wang Peng Cheng (SIT Co-Investigator), Mr Soh Yong Loke (SIT Research Engineer) and Mr Jeggathishwaran S/O Panisilvam (SIT Research Engineer)
Passive Displacement Ven la on (PDV), also known as Passive Displacement Cooling (PDC), is an innova ve air distribu on system that has been recognised as an Alternate Cooling Technology (ACT). It relies on the principle of natural convec on to facilitate a con nuous heat transfer cycle without the need for mechanical fans to deliver the chilled air to the end-user and remove heat. These systems are typically installed at high levels from the ground to maximise convec onal cooling of the space.
In addi on, due to Singapore’s geography within the tropical and humid Southeast Asia region, the PDC system also excels in serving the dual func ons of dehumidificaon and cooling. This is due to the longer contact me between the hot air and the cooling surfaces of the PDC system, which allows be er cooling performances than that of the conven onal Fan Coil Unit (FCU) or Air Handling Unit (AHU) system. The configura on of dual cooling coils is an advancement from the single coil, in terms of efficiency and flexibility of design. Cooling surface area is maximised within a compact design coupled with a condensate tray for collec on. This significantly
boosts the cooling performance of a Dual PD Coil system with vast energy- and cost-saving poten al. Hence, the main objec ves of the research study were to redesign the Dual PD Coil system by evaluating its design parameters and the resul ng cooling performance.
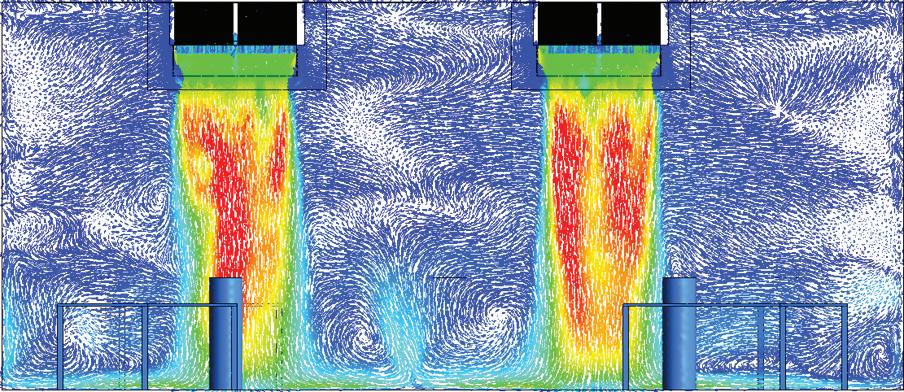
Prior to the first phase of experimenta on at the BCA SkyLab, an extensive preliminary study was conducted with Computa onal Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simula ons based on the layout of the space. These simula ons served to provide detailed informa on on the airflow velocity and temperature distribuon under the opera ons of a Dual PD Coil system. Based on a validated
and verified CFD model, parametric analyses were performed to examine the impacts of various parameters on the cooling performance. Based on the results from the CFD simula ons, an ideal design for the fall duct of the Dual PD Coil system was iden fied, to maximise its cooling capabili es. The design, with 300 mm in length and 0° taper angle, allowed the system to maintain the temperature of the space within a thermally comfortable range for most of the simula ons.
The experimenta on at the BCA SkyLab consisted of a Parametric Study of the Dual PD Coil system and a Subjec ve Study that involved par cipants comple ng a
Impressive results were obtained from the studies conducted in a laboratory and under a commercial se ng.
Experimental inves ga on of the cooling capacity and thermal performance of the passive displacement dual cooling coil system in tropical climatesFigure 1: The airflow pa ern, as determined by the CFD model based on the BCA SkyLab.
Thermal Comfort survey. A full set of the cooling system with two Dual PD Coil units were installed in the tes ng cell along with a comprehensive set of measurement instruments and suppor ng accessories. Throughout the Parametric Study, various cri cal parameters were varied, to test and evaluate the full spectrum of the system’s capabilies. These parameters include the intensity of heat loading and the temperature of the supplied chilled water.
From the analysis of the measured data, the Dual PD Coil system was able to maintain the condi ons of the space at a thermally comfortable environment for the majority of the experiment scenarios. The rela ve humidity measured at 1m above ground level was not higher than 56% at any point in me, displaying the strong dehumidifica on capability of the system. In addi on, thermal comfort was s ll achievable at a higher space temperature of 26.5˚C than the recommended 24˚C from Singapore Standards (SS) and ASHRAE Standards. Even at higher temperatures of the supplied chilled water, such as 9.5˚C and 10.5˚C, the system was s ll considerably effec ve in cooling the space.

A review of the collated results from the Subjec ve Study showed that the thermal comfort performance of the Dual PDC Coil system was generally favoured by the parcipants. The majority perceived the humidity condi ons of the space to be acceptable and thermally comfortable. This observa on was confirmed by the high overall sa sfac on value of 8 (out of 10) rated by 67% of the par cipants.
The subsequent and progressive phase of experimenta on was executed at Hotel 81 (Star), consisting of a format similar to that of the BCA SkyLab. An Evalua on Study of the Dual PD Coil system and a more extensive Subjec ve Study with an adapted Thermal Comfort survey were conducted. An objec ve for this phase was to determine the feasibility of implemen ng the system within the commercial se ng of an opera onal hotel with realis c oc-
cupancy. The other was to validate the system’s performance based on the ideal design parameters selected from the CFD simula on results.
A Dual PD Coil unit was installed in a hotel room along with the same comprehensive set of measurement instruments and suppor ng accessories.
A review of the measurements in the hotel room showed that the indoor condi ons could be maintained within the ideal range for thermal comfort as recommended by ASHRAE. The temperature on the surface of the bed was kept within the compact range of between 23˚C and 25˚C, with the humidity at approximately 70%. At the standing space of 1 m from the ground, the temperature was kept within the same range, with the humidity slightly lower at between 65% and 70%.

Correspondingly, the results from the Subjec ve Study displayed a generally posi ve outlook on the thermal comfort condi ons of the hotel room. Par cipants generally perceived the hotel room to be cool, with the humidity at an acceptable level. The overall sa sfac on ra ng the par cipants gave was considerably high, with an average value of 7.9 out of 10.
Addi onally, there is a significant energy-saving poten al with the elimina on of the fan that would
be cri cal in the conven onal FCU in typical hotel rooms. The replacement with the Dual PD Coil system also minimised unnecessary energy consump on from over-cooling.
[This paper is supported by the Na onal Research Founda on, Singapore, and Building and Construcon Authority, Singapore under its Green Buildings Innova on Cluster (GBIC) Programme (GBIC Award no. 94.23.1.12). Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommenda ons expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not reflect the views of Na onal Research Founda on, Singapore and Building and Construc on Authority, Singapore.]
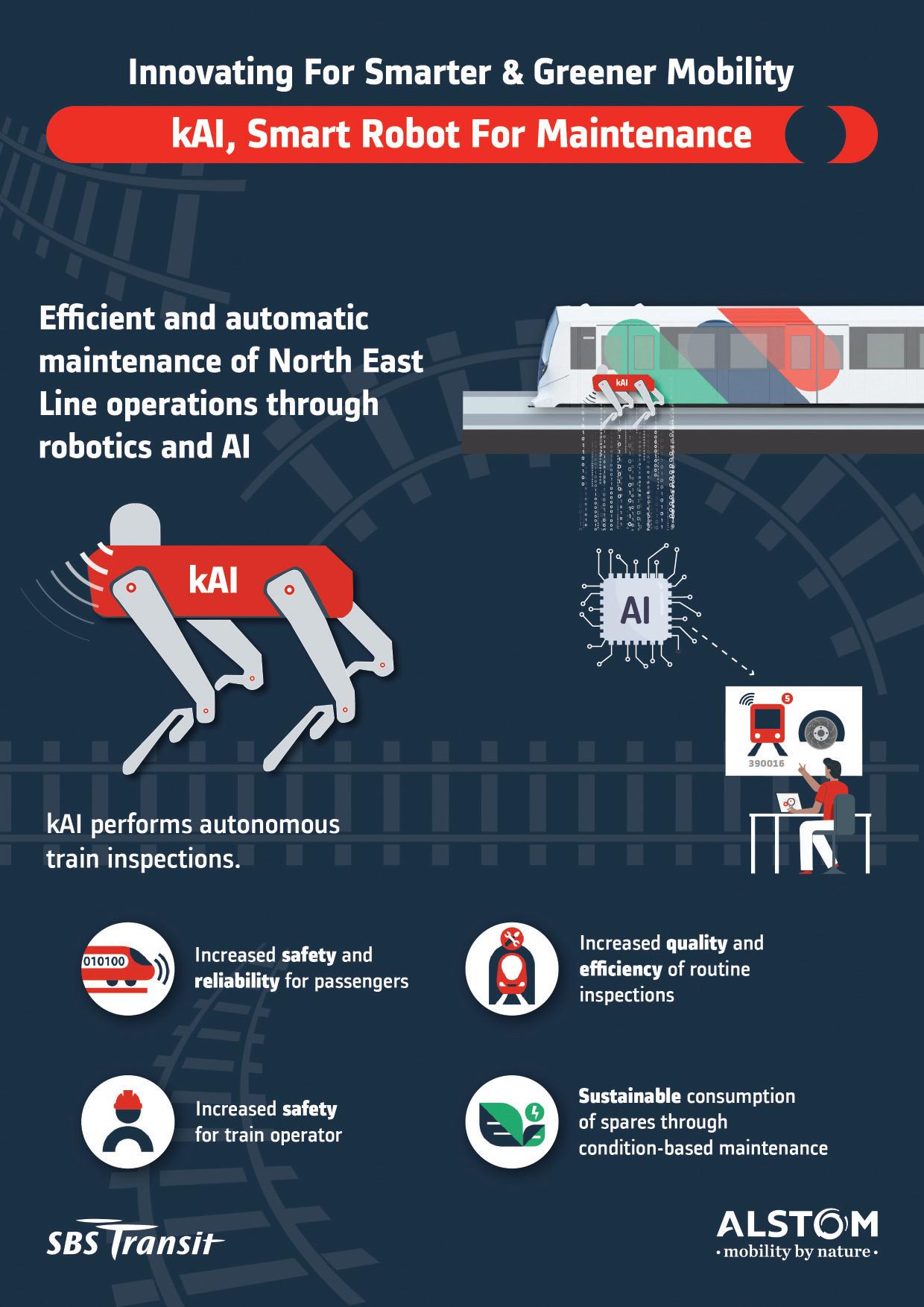
They are said to be a first for Singapore’s MRT networks.
SBS Transit and Alstom are working on a series of three transformave rail projects that are expected to contribute towards making Singapore’s railway system smart, modern and sustainable. They are the Op mised Timetable Energy Savings (OTES), 3D-prin ng of train parts, and AI-enabled robots for train inspec on.

All three solu ons are expected to be implemented on the North East Line by the first quarter of 2024. These projects are among the inia ves that SBS Transit and Alstom are pursuing to improve the rail transporta on sector.
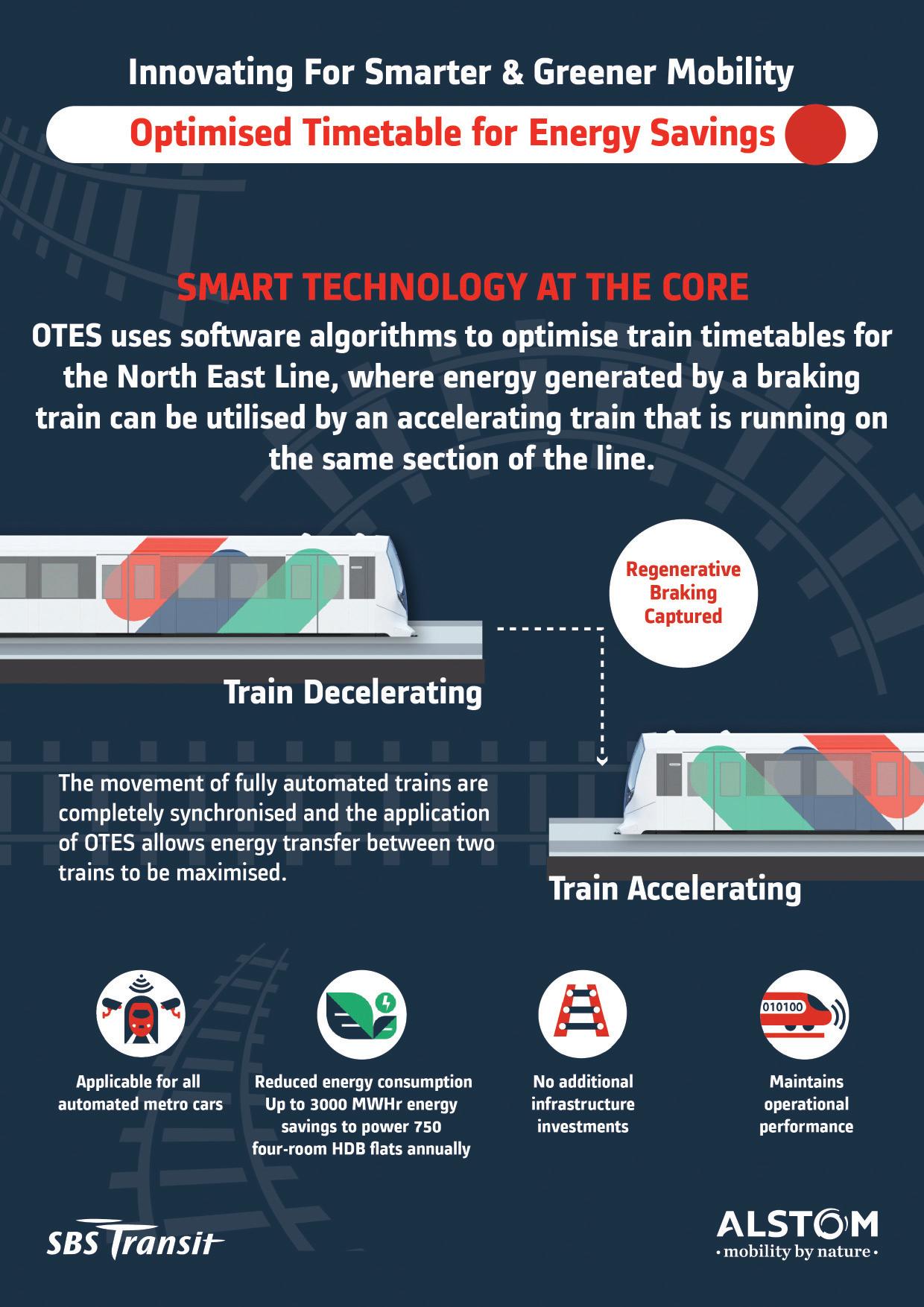
Op mised Timetable Energy Savings (OTES) is a solu on that uses an Ar ficial Intelligence (AI) so ware algorithm to orchestrate train frequencies such that one train arrives at the MRT sta on at the precise moment another train departs. This allows the harnessing of the kine c energy generated from the braking of a decelera ng train to power an accelera ng train, thus reducing the overall energy consump on of the accelera ng train.
With the implementa on of OTES, up to 3,000 megawa -hours (MWh) of energy are expected to be recovered, which can power some 750 four-room HDB flats annually.
With 3D-prin ng, it is possible to print selected train parts locally, on demand. As the required number of train parts can be printed at specific mes, there is no need to carry a huge volume of inventory, thus elimina ng the need to incur warehousing costs. It also dispenses with the need to import spare parts, transported over long distances as air or sea freight, thereby
reducing carbon emissions. The wastage of raw materials, resul ng from tradi onal manufacturing processes, is also eliminated.
3D-prin ng enables customisa on of the parts and improvement of their designs. This solu on contributes to sustainability in the maintenance of railway assets, reduces produc on costs and strengthens supply chain resilience.
For example, the 3-D prin ng of a coil nucleus offers several advantages. The coil nucleus is a key component of the propulsion control contactor that is used to establish an electrical connec on so that the train can run. If the neck of the coil nucleus breaks, the contactor fails and the train is not able to operate. Purchasing a new contactor would take several months and the cost is high.
With the op on of 3D-prin ng, SBS Transit in partnership with Alstom is able to customise and strengthen the neck of the coil nucleus such that it is less likely to break and it is able to last longer than the original part. This new design can be easily printed within three weeks and at a frac on of the original cost.
AI-enabled robots for train inspec on
kAI is an autonomous AI-enabled robo c dog that will conduct train inspec ons at the North East Line depot.
The robot is equipped with a camera and sensors, and has four legs that will allow it to navigate smoothly around the depot, and climb up and down the stairs, while avoiding any obstacles on the ground.
With the help of kAI, visual inspecon of a train can be completed in an hour – about half the me taken when manual inspec ons are carried out by technicians. This frees them to take on higher value-added roles and maintenance tasks. Furthermore, kAI can also detect anomalies that may not be visible to the naked eye, thus ensuring that inspec ons are conducted more effec vely and accurately.
With early detec on of anomalies through kAI, any issues or defects can be pre-emp vely rec fied, before they develop into major problems and poten ally disrupt train opera ons, thus saving on cost, manpower and resources.
3D-prin ng of train parts

Progress of Tuas Port a er its official opening in September 2022
When completed in the 2040s, Tuas Port will be the world’s largest fully-automated terminal, with a handling capacity of 65 million twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs), which is almost double the 37.3 million TEUs handled in 2022.
Development of Tuas Port is taking place over four phases. Reclamaon works for Phase 1 commenced in February 2015 and was completed in November 2021. Reclama on works for Phase 2 commenced in March 2018 and is currently about 60% completed. When the berths in both phases are fully opera onal, Tuas Port will reach an annual handling capacity of more than 40 million TEUs.
The Mari me and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA) has started planning and design works for Tuas Port Phase 3. Reclama on works for Phase 3 is expected to be completed in the mid-2030s.
To improve Tuas Port’s accessibility for its workers and users, MPA will collaborate with port operator PSA Singapore, government agencies, industry partners and unions, to form a tripar te commi ee, in 2023, to co-create various transporta on op ons for port workers and users.
To further mari me digitalisa on and development of the future concept of opera ons, MPA and Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) in August 2022 to provide full mari me 5G coverage in the major anchorages, fairways, terminals and boarding grounds, by mid-2025.
Twelve mari me 5G base sta ons will be set up to complement the onshore 5G communica on infrastructure. Three of the base sta ons will be ready by 2023 to support tes ng and development of new digital applica ons, such as remotely assisted pilotage advisory, digital bunkering, delivery drones, and telemedicine. The remaining nine base sta ons will be set up by 2025.
To further strengthen vessel naviga onal safety and efficiency of the port, as it con nues to grow, MPA is developing an ar ficial intelligence-enabled Next Genera on Vessel Traffic Management System (NGVTMS) to replace the exis ng Vessel Traffic Informa on System (VTIS).
With data analy cs and machine learning to iden fy traffic hotspots as well as advanced algorithms to predict poten al collisions, the NGVTMS will allow MPA to provide Ship Captains with more accurate and mely informa on to take early ac ons for naviga onal safety. As part of NGVTMS, secured and reliable data transfer between ship and ship and between ship and shore can be facilitated through connec vity pla orms such as the VHF Data Exchange System (VDES) and the mari me 5G network.
The NGVTMS will be developed in three phases.
• Phase 1 – Innova on Programme (2018- 2021): MPA completed a three-year Innova on Programme in 2021 to develop and test new opera ng concepts and technologies to enhance naviga on safety and efficiency of vessel traffic management.
• Phase 2 – Prototyping (2023 –2024): MPA will develop a system
prototype to test various vessel traffic management applica ons such as the Smart Collision Detecon and Proac ve Traffic Management in a real- me sandbox opera ng environment. This will enable MPA to gain insights on poten al new capabili es and scope the requirements and specifica ons for system implementa on.
• Phase 3 – System Implementa on (2024-2027): The final phase will consist of design, development, installa on, tes ng and commissioning of the NGVTMS. The system will be deployed from 2025 for 24/7 opera ons.
Phase 2 of digitalPORT@SG
With the successful implementaon of digitalPORT@SG Phase 1 as a one stop portal for port entry and departure, in 2020, MPA will roll out Phase 2 of digitalPORT@SG in 2023.
Phase 2 will provide port stakeholders with real- me informa on to facilitate just-in- me vessel arrivals to terminals, help vessels access marine services such as bunkering, supplies and repairs, as well as an Ac ve Anchorage Management System to op mise the usage of anchorage spaces. This will enhance port efficiency, reduce ship turnaround me, and cut greenhouse gas emissions by minimising ships’ idling me at anchorages.
Singapore Trade Data Exchange Pilot Data Sharing Ini a ve MPA will work with Singapore Trade Data Exchange (SGTraDex), Jurong Port and their partners to pilot a data sharing ini a ve under SGTraDex’s ship supplies and lighterage op misa on use case that focuses on supplies procurement, fulfilment and lighterage logis cs. The pilot aims to help large and small businesses op mise their ship supplies opera ons through digitalisa on,
The various ini a ves undertaken include digitalisa on, decarbonisa on and talent development.
and by encouraging data sharing between supply chain stakeholders in the ship supplies sector.
Mari me Cyber Assurance and Opera ons Centre
As mari me systems become increasingly digitalised, Singapore must also be prepared with the right tools to manage the risk of cyber incidents that could disrupt the movement of vessels and cargo at its ports.
MPA will establish the Mari me Cyber Assurance and Opera ons Centre (MCAOC) by 2025 to provide real- me security monitoring and disseminate informa on to mi gate cyber threats; advise on system recovery and measures to take, following an incident; and facilitate cyber threat informa on-sharing among mari me stakeholders such as port and terminal operators, shipping lines and marine services providers with digital systems.
The MCAOC will enable mari me stakeholders to pool financial and manpower resources and create economies of scale to tackle cyber threats in the mari me sector.
Equipped with analy cs capabilies, MCAOC will strengthen operaonal responses to evolving cyber threats by providing insights to mari me stakeholders on advanced malware and modes of a ack. MCAOC will also offer training and conduct cybersecurity exercises for the mari me industry.
Decarbonising domes c harbour
cra and pleasure cra
MPA will set the target for the harbour cra and pleasure cra sectors to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, in support of Singapore’s 2050 na onal net-zero target. To achieve this transi on, from 2030, MPA will require all new harbour cra opera ng in the country’s port waters to be fully electric, or be capable of using B100 biofuel or net-zero fuels such as hydrogen.
To help the industry meet the 2030 requirement, owners are encouraged to consult MPA on
their electric, B100 biofuel- or hydrogen-compa ble harbour cra designs, early. The consultaon process will be a compulsory requirement from 2027.
MPA will support the development of electrifica on technology through the following ini a ves:
• Research, design, build and operate full-electric vessels: Keppel
Offshore & Marine Consor um is working on the retrofit of Eng Hup Shipping’s 30 pax ferry to be fully electric, and a charging sta on with solid state transformer technology, which will be trialled later this year.
The ‘Goal Zero’ consor um, led by SeaTech Solu ons with partners such as Yinson Green Technologies and Lita Ocean, is building the first fully electric lighter cra with ba ery swapping technology, which will be trialled later this year. These consor ums, which comprise various industry enterprises and research ins tu ons, were awarded funding by MPA and the Singapore Mari me Ins tute in 2021, to research, design, build and operate a fully electric harbour cra by 2025.
• Conduct trials of full-electric vessels: Shell and Penguin Internaonal (Singapore’s homegrown aluminium shipbuilder and shipowner) will be commissioning their first fully electric ferries and rapid shore chargers, scheduled for opera onal deployment this year.
Concurrently, MPA is working with terminal and harbour cra operators to implement pilot charging sta ons. The first of these pilot charging sta ons was scheduled to be deployed by Shell at the Shell Energy and Chemicals Park Singapore on Pulau Bukom by Q2 2023.
• Work with research ins tutes to study the charging infrastructure required to support an electric harbour cra fleet: MPA aims to develop a charging infrastructure implementa on masterplan by 2025, and has commenced a study with research ins tutes to study the loca ons of charging infrastructure and the electrical power required to support electric vessels plying Singapore’s domes c waters.
The findings from the study will be released in 2024.
• Partnering with industry, financial ins tu ons, harbour cra operators and manufacturers, to lower costs of adop on and mobilise support for early adopters: An invita on for Expression of Interest in providing proposals for the design and development, demand aggrega on, and green financing for new electric harbour cra , was scheduled to be launched by MPA in Q2 2023.
• Collabora ng with industry to enhance energy efficiency and reduce emissions of exis ng harbour cra s in the near term.
MPA will work with the industry on energy management efforts and studies on the use of higher blends of biofuel for exis ng harbour cra Pathways for alterna ve fuels
To prepare Singapore for a mulfuel bunkering future, MPA has developed the world’s first marine biofuel provisional standard, in consulta on with the industry and researchers, for biofuel blends of up to 50% (B50). This standard will be updated progressively as trials for biofuel blends of up to 100% (B10) are carried out, and is expected to be completed by 2025. Singapore’s Mari me Energy and Sustainable Development Centre of Excellence was also scheduled to release the findings of its compa bility study on various biofuel types and percentage blends for harbour cra s, by end-March 2023.
Aside from biofuels, MPA is exploring the use of hydrogen and ammonia to support the decarbonisa on of interna onal shipping. In December 2022, MPA and the Energy Market Authority (EMA) launched an invita on for Expression of Interest (EOI) to build, own and operate low or zero-carbon ammonia power genera on and bunkering solu ons on Jurong Island.
In August 2022, MPA signed a MoU with the Port of Ro erdam to establish the world’s longest ‘Green and Digital Shipping Corridor (GDSC)’. The corridor will pilot the deployment of digital solu ons, support investment in green infra-
structure, and develop enablers to accelerate low and zero carbon shipping.
Singapore is ac vely engaging other like-minded ports and country partners to establish more corridors. Recently, MPA, Port of Los Angeles, Port of Long Beach and C40 Ci es started discussions to establish a GDSC between Singapore and the San Pedro Bay port complex in California, USA.
MPA has put in place several schemes to a ract and develop a steady pipeline of mari me talent who are equipped with the right skills and exper se, as the industry transforms.
Work-Study Diploma by the Instute of Technical Educa on (ITE). The programmes provide graduates with a head-start in their careers and deepen their skillsets in various roles including seafaring, port opera ons, cargo opera ons and shipboard opera ons.
Career conversion and mid-career development
Keppel Offshore & Marine Ltd (Keppel O&M), through its wholly owned subsidiary, Keppel FELS Limited, has formed a consor um to develop Singapore’s first comprehensive electric vessel supply chain. Keppel O&M’s Floa ng Living Lab will be used to testbed the electric vessel charging infrastructure, accelera ng pilot and scale up of Singapore’s harbour cra electrifica on adop on.
Internships,
Global Internship Award: Established by MPA in 2013, the Global Internship Award aims to help undergraduates be er understand the interna onal nature of the mari me industry. The 12-week programme gives selected undergraduates an opportunity to gain on-the-job experience, working in a leading mari me company. It sponsors the undergraduate for an overseas a achment of up to six weeks in the overseas office of the company. More than 300 undergraduates have benefi ed from the programme in the last 10 years.
Scholarships: In 2022, 54 Mari meONE scholarships, worth about SGD 1.7 million in value, were awarded. Since the launch in 2007, 524 recipients have received the scholarships. Addi onally, 12 Tripar te Mari me Scholarships (TMSS), valued at about SGD 1 million, were awarded in 2022 to seafaring cadets. Since the launch in 2002, more than 240 TMSS have been given out.
Work-Study Programmes: There are currently three mari me-related Work-Study Post-Diploma Programmes conducted by Singapore Polytechnic (SP) and targeted at fresh polytechnic graduates, and a
Career Conversion Programme: The Career Conversion Programme (CCP) for Sea Transport Professionals and Associates provides mari me and non-mari me mid-careerists with skills conversion opportuni es, to enable them to take on roles in Port Opera ons and Services, Shipping, and Mari me Services. Close to 220 mid-careerists have benefi ed from the Career Conversion Programmes for Sea Transport, since 2018.
Mari me Leadership Programme: Since its launch in 2021, more than 40 mari me professionals have a ended the Mari me Leadership Programme (MLP). The MLP aims to hone par cipants’ leadership skills, build global perspec ves on key mari me issues, and strengthen business networks locally and abroad. In 2022, MLP included, for the fi rst me, an overseas site visit to the Port of Ro erdam. MPA will hold the third run of MLP this year.
Eng Hup Shipping has a fleet of over 70 vessels suppor ng a variety of marine opera ons across Singapore and Asia. As a harbour cra owner-operator in this project, Eng Hup Shipping’s exis ng 30 pax ferry would be retrofi ed to become fully electric and fulfil the vessel’s new opera onal profile and technical requirements.

The Energy Research Ins tute @ NTU (ERI@N) and the Technology Centre for Offshore and Marine, Singapore (TCOMS) are part of the consor um and contribute to the research and development of charging sta ons with solid state transformer technology, marinised energy management system, energy storage performance, modelling and simula on tools.
Key industrial partners in the coali on including Envision Digital, Surbana Jurong and DNV are further
strengthening the overall supply chain value, by contribu ons in the areas of marinised smart ba ery solu on, land-based infrastructure standardisa on, and new technology qualifica ons, respec vely.
‘Goal Zero’ Consor um
SeaTech Solu ons Interna onal leads the Goal Zero Consor um and provides the op mised hull form design and detailed engineering of the zero-emission electric pilot vessel. This includes the vessel solu on development carried out in consulta on with the ba ery and charging solu on OEMs as well as detailed engineering of the pilot vessel, modelling, hydrodynamic analysis, and design integra on of OEM equipment including the electric propulsion system, energy management system and ba ery management system.
Yinson Green Technologies (YGT) leads the programme management of this project. The company leverages on its extensive supply chain network for the procurement, construc on and integra on of the pilot vessel and testbed facility, and aims to accelerate the commercial adop on of electric harbour cra in Singapore. YGT will also be the owner of this vessel and also the commercialisa on partner to produce more such vessels in Singapore’s harbour cra market.

SHIFT is responsible for the design and engineering of a new genera-

on energy storage system for electrifica on of vessels with charging infrastructure, along with a so ware management system designed for B2B and B2C aspects of the commercial opera on.

Lita Ocean supports analysis of vessels’ opera ng profiles for elec-
trifica on, contributes to the design of the vessel and its systems, and provides the costs associated with vessel construc on and onboard systems. Its role also covers construc on of the vessel, installa on of the electric propulsion system, and provision of the waterfront land area for test-bedding.
The winners will be selected and honoured at the ‘2023 Year in Infrastructure and Going Digital Awards’ event which will be held in Singapore, in October.
Bentley Systems Incorporated, the infrastructure engineering so ware company, recently announced the finalists of the ‘2023 Going Digital Awards in Infrastructure’. The annual awards programme honours the work of Bentley so ware users advancing infrastructure design, construc on and opera ons throughout the world. Twelve independent jury panels, represen ng 12 award categories, selected the 36 finalists from over 300 nominaons submi ed by 235 organisaons from 51 countries.
Representa ves from the finalists’ organisa ons will present their projects to a panel of independent judges to determine the winners and meet with global press and industry execu ves, at the ‘2023 Year in Infrastructure and Going Digital Awards’ event which will be held at Marina Bay Sands, Singapore, on 11 and 12 October 2023.
Chris Bradshaw, Bentley Systems’ Chief Marke ng Officer, said, “We are so excited to be back in Singapore to present the ‘Going Digital Awards’ finalists in front of our users and those a ending virtually, as well as invited press and analysts, at the ‘2023 Year in Infrastructure and Going Digital Awards’ event. These projects reflect how organisa ons have improved their workflows by embracing digital technologies to maximise efficiency and cost savings. I congratulate the finalists for advancing infrastructure intelligence by adop ng Bentley Infrastructure Cloud, iTwin Pla orm and products, and Bentley Open Applica ons, and I wish them success on their future projects.”
BRIDGES AND TUNNELS
• China Railway Changjiang Transporta on Design Group Co
Ltd, Road & Bridge Interna onal Co Ltd, Chongqing Expressway Group Co Ltd – Comprehensive Applica on of BIM-based Digital and Intelligent Design and Construcon for the Liaozi Grand Bridge, Chongqing City, China
• Collins Engineers Inc – Digital Twins and Ar ficial Intelligence for Historic Robert Street Bridge Rehabilita on, St Paul, Minnesota, United States
• WSP Australia Pty Ltd – Southern Program Alliance, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
• Dura Vermeer Infra Landelijke Projecten, Mobilis, Gemeente Amsterdam – Bruggen en Straten Oranje Loper, Amsterdam, Noord-Holland, Netherlands
• Laing O’Rourke – New Everton Stadium Project, Liverpool, Merseyside, United Kingdom
• Laing O’Rourke – SEPA Surrey Hills Level Crossing Removal Project, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
• Arcadis – RSAS - Carstairs, Glasgow, Scotland, United Kingdom
• Mo MacDonald – Standardizing Delivery of Phosphorus Removal Schemes for the UK Water Industry, United Kingdom
• Phocaz Inc – CAD Assets to GIS
– A CLIP Update, Atlanta, Georgia, United States
FACILITIES, CAMPUSES, AND CITIES
• Clarion Housing Group – Twins: Crea ng a Golden Thread across Digital Estates, London, United Kingdom
• Port Authority of New South Wales – Port Authority of New South Wales: A Case Study in Digital Transforma on, New South Wales, Australia
• vrame Consult GmbH – Siemensstadt Square - Digital Campus Twin in Berlin, Berlin, Germany
PROCESS AND POWER GENERATION
• MCC Capital Engineering & Research Incorpora on Limited
– Green and Digital Plant Construcon Project of Linyi 2.7 Million Tons of High-Quality Special Steel Base, Linyi, Shandong, China
• Shanghai Inves ga on, Design & Research Ins tute Co Ltd – Digital Asset Management of Hydropower Projects Based on Digital Twins, Liangshan, Yibin, and Zhaotong, Sichuan and Yunnan, China
• Shenyang Aluminum & Magnesium Engineering & Research Ins tute Co Ltd – Digital Twin Applica on Project of Electroly c Aluminum Engineering of Chinalco China Resources, Lvliang, Shanxi, China
RAIL AND TRANSIT
• AECOM Perunding Sdn Bhd
– Johor Bahru–Singapore Rapid Transit System Link, Malaysia and Singapore
• IDOM – Value Engineering Stage for Detailed Design & Supervision of the Rail Bal ca Project, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania
• Italferr SpA – New High Speed Line Salerno – Reggio Calabria, Ba paglia, Campania, Italy
ROADS AND HIGHWAYS
• Atkins – I-70 Floyd Hill to Veterans Memorial Tunnels Project, Idaho Springs, Colorado, United States
• Hunan Provincial Communicaons Planning, Survey & Design Ins tute Co Ltd – Hengyang-Yongzhou Expressway in Hunan Province, Hengyang and Yongzhou, Hunan, China
• SMEC South Africa – N4 Montrose Interchange, Mbombela, Mpumalanga, South Africa
STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING
• Hyundai Engineering – Automated Design of Civil and Architectural Structures with STAAD API, Seoul, South Korea

• L&T Construc on – Construc on of 318 MLD (70 MGD) Wastewater Treatment Plant at Corona on Pillar, New Delhi, India
• RISE Structural Design Inc –Dhaka Metro Rail Line 1, Dhaka, Bangladesh
SUBSURFACE MODELING AND ANALYSIS
• Arcadis – South Dock Bridge, London, United Kingdom
• OceanaGold – Valida on of Digital Management Tools for OceanaGold’s Waihi Tailings Storage Facility, Waihi, Waikato, New Zealand
• Prof Quick und Kollegen GmbH
– Deutsche Bahn Neubaustrecke Gelnhausen – Fulda, Gelnhausen, Hessen, Germany
SURVEYING AND MONITORING
• Avineon India P Ltd – Provision of Services on the Genera on of CityGML Models of Kowloon East for the Lands Department, Hong Kong SAR, China
• Italferr SpA – The Digital Twin for Structural Monitoring of St Peter’s
Basilica, Va can City
• UAB IT logika (DRONETEAM) –
DBOX M2, Vilnius, Lithuania
TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
• Elia – Digital Transforma on and Connected iTwins in Smart Substaon Design, Brussels, Belgium
• PowerChina Hubei Electric Engineering Co Ltd – Full Life-cycle Digital Applica on on Xianning Chibi 500kV Substa on Project, Xianning, Hubei, China
• Qinghai Kexin Electric Power Design Ins tute Co Ltd – 110 kV Transmission and Transforma on Project in Deerwen, Guoluo Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai Province, China, Gande County, Guoluo Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai, China
WATER AND WASTEWATER
• Geoinfo Services – Achieving Drink from Tap 24x7 Water Supply System for Emerging Economies, Ayodhya, U ar Pradesh, India
• L&T Construc on – Rajghat Mul Village Rural Water Supply Scheme, Ashok Nagar and Guna, Madhya Pradesh, India
• Project Controls Cubed LLC –EchoWater Project, Sacramento, California, United States
Bentley Systems provides so ware to advance infrastructure - sustaining boththe global economy and the environment.
The company’s so ware solu ons are used by professionals, and organisa ons of every size, for the design, construc on, and opera ons of roads and bridges, rail and transit, water and wastewater, public works and u li es, buildings and campuses, mining, and industrial facili es. Bentley Systems’ offerings, powered by the iTwin Platform for infrastructure digital twins, include MicroSta on and Bentley Open applica ons for modelling and simula on, Seequent’s soware for geoprofessionals, and Bentley Infrastructure Cloud encompassing ProjectWise for project delivery, SYNCHRO for construc on management, and AssetWise for asset opera ons.







Organisa ons will be able to safely do more with less.
In a world where companies are under immense pressure to improve their bo om line, finding ways to boost produc vity while reducing costs has become a top priority.
A recent study by McKinsey has revealed that the US could grow its cumula ve GDP by a staggering USD 10 trillion by 2030, if produc vity is boosted to past historical rates. With the emergence of Robo c Process Automa on (RPA) 2.0, technology can help. This intelligent solu on, which combines the power of ar ficial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, is changing the game for businesses by automa ng more complex tasks and improving efficiency.
The adop on of Robo c Process Automa on (RPA) has revolu onised the way businesses operate, streamlining opera ons and reducing costs by automa ng repe ve and me-consuming tasks. However, as industries like Aerospace & Defence, and Healthcare, seek to comply with strict security mandates while maximising efficiency, the need for more intelligent and reliable process automa on has become increasingly apparent.
This is where RPA 2.0 comes in. Leveraging AI and machine learning, RPA 2.0 can automate even more complex workflows non-invasively, making it an ideal solu on for heavily regulated industries.
According to Gartner, almost 70% of human effort in management and processing will be automated by 2024, highligh ng the vast
poten al for RPA 2.0. With new capabili es like intelligent computer vision, RPA 2.0 can analyse elements on the screen and drive so ware just like humans, making automa on more reliable.
RPA 2.0 has advanced natural language processing (NLP). It understands the meaning and context of words and phrases, even when there are varia ons in language, dialect, or syntax. It learns from and adapts to new language pa erns and varia ons over me, improving its ability to understand and respond to human language more accurately and effec vely.
Using NLP, RPA can automate responses to inquiries on the website, pa ent registra on at kiosks, front-line administra ve queries and many other communica on services. This improves communicaon, significantly shortens the me to diagnosis, increases efficiency, and leads to be er outcomes, in healthcare se ngs.

Moreover, with machine learning algorithms, RPA 2.0 can adapt to changing requirements more efficiently, enhancing the organisaon’s agility and minimising risks. The result? An RPA 2.0 that evolves from a virtual assistant to a virtual workforce, capable of handling more complex tasks and freeing up human resources to focus on higher-value tasks.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, enterprises require an efficient way to manage complex workflows that span across mul -
ple teams, regions and pla orms. RPA 2.0 is a powerful tool that can help organisa ons manage these workflows seamlessly, quickly adap ng to changing factors and new requirements.
A good example is a London-based healthcare system which uses RPA 2.0 and intelligent test automa on to automate processes across mulple pla orms, including a student informa on management system, a me-tabling system, and electronic pa ent records.
By mapping different ac vity types to plan the best me for ac vi es, it achieved greater efficiency at scale, accelera ng digital innova ons.
Greater security with non-invasive automa on
Installing RPA tools on mission-critical applica ons is not an op on. It is a necessity. Because of intelligent computer vision, RPA 2.0 solu ons can interact with the so ware and systems without installing anything on the server or jeopardising security requirements.
A combina on of two techniques achieves non-invasive automa on:


• A two-system model allows the RPA 2.0 so ware to sit on a separate machine.
• Bots can drive the so ware via the user interface (UI) rather than through access to the source code or object layer, both of which can be obscured or unavailable to tradional RPA tools.
For example, non-invasive RPA has been used across the US Department of Defense (DoD) and mul ple
military branches to manage finances, data and cri cal office tasks.
At one defence contractor, one of its labs required a three-hour setup process every morning before any tes ng work could start. This process was a giant barrier to ge ng work done quickly, as it meant that the real tes ng work could only begin a er lunch.
However, the team could automate this setup and configura on process non-invasively. Instead of taking all morning, once ini ated, the setup was ready to go within 15 minutes.
In today’s hyper-compe ve landscape, organisa ons must con nuously drive opera onal efficiency and free up personnel for more strategic tasks, to remain ahead of the curve. RPA 2.0 can be a powerful tool for achieving these goals, but implemen ng it safely and securely is paramount to its success.
Here are some key considera ons for implemen ng RPA 2.0 safely:
• Understand the regulatory environment: Industries like Healthcare and Aerospace & Defence are highly regulated. Before implemen ng RPA 2.0, it is important to understand the regulatory environment

and ensure your tool complies with all relevant regula ons.
• Iden fy the right processes: Not all processes are suitable for automa on. Iden fying the right processes, based on complexity, repeatability and volume, is important. Common workflows such as database migra on, audit trails for federal organisa ons, and security patches for hospital servers are good star ng points.
• Implement strong security controls: Although RPA 2.0 can automate processes non-invasively, it is essen al to implement strong security controls such as user authenca on, data encryp on, and access controls to mi gate security risks.
• Ensure transparency and accountability: It is essen al to ensure
transparency and accountability in the implementa on process. This includes providing clear documenta on, training and communica on to all stakeholders and ensuring clear lines of responsibility and accountability for automa on.
Conclusion
In summary, RPA 2.0 arrives as a mely solu on for organisa ons aiming to do more with less, in highly secured environments. Compared to the first itera on, it can handle more complex tasks with greater reliability through AI and machine learning. This innova ve approach can unlock significant business value by addressing produc vity challenges and catalysing digital innova on on a larger scale.
The ar cle explains why lighter and closer-cu ng shoulder milling and face milling is the answer.
According to the ‘Fact Sheet: Europe’ report from the Internaonal Council of Clean Transporta on (ICCT), “reducing mass is an effec ve way to reduce a vehicle’s emissions.”
The onus is on automo ve manufacturers to produce more weight-efficient components. Yet heavy cast iron and forged steel remain popular, and manufacturers must design engineer these ‘heavy’ metals into being weight-efficient.

Further to the ICCT’s findings, McKinsey & Company’s ‘Lightweight, heavy impact’ report offers in-depth calcula ons that show how lighter vehicles have lower CO emissions. The report states that lightweight measures can help reduce CO emissions to a certain extent (the CO reduc on is approximately 0.08 g per kilogram of weight reduced). The report also states that if an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) manages to reduce the vehicle weight by 100 kg, it saves approximately 8.5 g CO per 100 km.
In response to findings like these, automo ve manufacturers are turning to ‘lightweigh ng’, which entails building cars and trucks that are less heavy, to facilitate be er fuel efficiency and handling.
Lighter metals like aluminium and magnesium can help in this regard, of course. But lightweighting is about more than simply choosing whichever material that weighs less, especially when heavier materials, like forged steels, cobalt chrome, Inconel or grey and nodular cast irons (NCIs) are s ll widely used in vehicle manufacturing.

Rather, manufacturers must design engineer these ‘heavy’ metals into being a weight-efficient and strong
alterna ve to lighter metals. This means producing more complex, near-net shaped parts based on more complex designs. However, it is tough when producing ISO-K materials that are more difficult to machine. What is more, all cast irons contain silicon carbide (SiC) which is very abrasive to the cu ng edge. A further challenge for OEMs is to manufacture these more complex components to the highest quality, with high produc vity and a low cost per part.
When there is a need to produce a variety of components, and for large amounts of material to be
removed quickly from the workpiece, shoulder milling is the best approach. This basic, yet versa le, milling applica on ensures a lighter cu ng ac on that, in turn, minimises impact on the tool and ensures the component stays in shape. With shoulder milling, the tool creates a plane and shoulder surface, simultaneously.
To achieve this, it is essen al that the right angle is used to avoid unwanted offsets between the cu er and workpiece. A 90° angle is definitely preferred, but other angles can be used depending on the applica on.
There are a number of shoulder milling tooling inserts on the market designed for a near-90° milling angle. Generally, these inserts have eight edges – four on the front and four on the back, to produce the shoulder and plane simultaneously, or six, in some cases.
Nevertheless, Sandvik Coromant felt there was room for a new shoulder milling concept – one that would bring greater produc vity, tool-life advantages and economic benefits, for OEMs.


In response to the above challenges, Sandvik Coromant developed its CoroMill MF80 family of inserts. Designed for automo ve milling applica ons in ISO-K and ISO-P materials, the inserts have eight cu ng edges, chip protec on and op mised micro geometry. In par cular, the tools are designed to be ideal for thin-walled components and machine setups with limited stability. The cu ng edge is inclined for smooth cu ng ac on and low cu ng forces. This gives be er security and chip evacua on, as well as a wiper edge for superior surface finish.
CoroMill MF80 is not en rely new, but based on a technology pla orm similar to Sandvik Coromant’s exis ng CoroMill 345. This new milling concept offers a 40% lighter cu er body with shim protec on and high number of inserts for secure and stable machining, even in vibra on-prone overhang applica ons.
With shoulder and face milling applica ons, cu ng tools with 90° lead angles are generally preferred because they generate radial cutng forces and, importantly, transfer more cu ng energy away from the part. This is especially ideal when machining parts with thinner walls or near-net-shapes. CoroMill MF80 actually enables an 89.5° approach angle, so that the muledge cu er can work even closer to the fixture while machining.
The near-90° angle also reduces axial forces for improved milling on thin wall components and weak fix-
tures, without vibra on and chatter. Key advantages here include improved accuracy and machine u lisa on, as well as longer tool life with less scrap.
In one case, CoroMill MF80 was run against a compe tor’s mill in a rough shoulder milling applica on to produce pump and valve components from an ISO-P carbon steel (DIN 1.0619) workpiece. The mills were run with iden cal cu ng data – a spindle speed (n) of 500 rpm, cu ng speed (vc ) of 125 m/min, radial depth of cut (ae ) of 15/50 mm, axial depth of cut (ap ) of 5 mm and feed per tooth (fz ) of 0.15 mm –with one excep on, the table feed (vf ). The compe ng mill was run at 375 mm/min and CoroMill MF80 was run at 600 mm/min.
In the end, CoroMill MF80 gave a produc vity increase of 60%. The compe ng mill produced nine components while CoroMill MF80 produced 15. As for tool life, a er 40 minutes of machining me, only chipping wear was visible on the CoroMill MF80 and the mill gave a tool life increase of 67%. The key advantage for the customer was that the mill’s shim protec on and the high number of insert edges can lower the cost per part in roughing or shoulder milling applica ons.
In another test, CoroMill MF80 and
a compe ng insert were used in a roughing applica on on an ISO-K workpiece. The mills were used to produce carriers and supports from an ISO-K spheroidal graphite (SG) iron (GJS400/K3.1.C.UT) workpiece. Again, both tools were run with the same cu ng data, including ae = 20 mm to 80 mm and ap = 2 mm to 3 mm. Each mill was run at n = 1000 rpm, vc = 250 m/min and vf = 1200 mm/min. There was a slight difference in fz which was 0.24 mm for the compe tor’s mill and 0.3 mm for the CoroMill MF80.
The end result was that the customer achieved a 54% increase in tool life with Sandvik Coromant’s mill. While the compe tor’s mill produced 10 components in 55 minutes before showing signs of wear, CoroMill MF80, on the other hand, ran for 82 minutes and produced 15 components in that me.
CoroMill MF80 can greatly benefit OEMs’ lightweigh ng applica ons, with longer-las ng and more produc ve performance, when machining heavier materials like ISO-K NCIs, Inconel or grey irons, forged steels and cobalt chrome. These advantages can also prove essen al in helping manufacturers produce vehicles that meet stringent CO emission regula ons while maintaining a lower cost per part and ensuring that, in the words of the ICCT’s report, “reducing mass is an effec ve way to reduce a vehicle’s emissions.”
For proper func oning and durability, orthopedic implants in the human body require precisely defined finishes.
For the targeted surface finishing of femur components at its new high-tech plant in Penang, Malaysia, Smith+Nephew is u lising two manufacturing cells, each with three R 6/1000 SF drag finishers from Rösler. Two fully automa c Z1000 centrifuges, equipped with the digital process water management system, ‘Advanced’, from Rösler Smart Solu ons, ensure that the process water is reliably and efficiently cleaned and recycled. Another contribu on towards the stability of the finishing opera on is the con nuous monitoring and classifica on of the grinding and pre-polishing media.
With the development and applica on of innova ve technologies, Smith+Nephew works to improve the products under three global business divisions – orthopedic reconstruc on, modern wound care management, and sports medicine. This commitment to excellent medical solu ons is reflected in the company’s new high-tech plant in Penang, Malaysia. The plant, as part of the orthopedic reconstrucon division, produces primarily endoprosthe c knee and hip implants.
For each implant, Smith+Nephew has specifica ons that precisely define the required quality of the surface finish. Surface finishing cells are installed at the company’s new Penang plant, for knee implants made from cobalt chrome alloys. For example, the inner surface areas of femur components must have a precisely defined surface roughness to promote op mal integra on with the bone.
On the other hand, the outer surface areas must have a very smooth, polished surface finish to prevent fric on that causes premature wear. Therefore, some targeted outer surface areas of the femur components must undergo an extremely demanding finishing opera on with absolutely consistent results.
For this demanding task, the customer chose the Rösler R 6/1000 SF drag finishers. These are special mass finishing systems that were developed for the precise and targeted surface finishing of high-value and delicate work pieces with complex shapes.
An extremely important requirement is that the femur components should not touch each other during the surface grinding and polishing opera on. All process parameters, precisely adapted to the stringent finishing requirements, are stored in the PLC control panel. This guarantees repeatable and consistent results.

Since Smith+Nephew has a plant in Memphis, USA, using iden cal finishing processes and machines for the same applica on, the company has considerable experience and know-how. This facilitates and expedites the approval for the respec ve equipment and finishing processes significantly. Another point in favor of Rösler was the company’s global presence with, for example, a distributor in Singapore. Moreover, Rösler develops and produces all its products in-house. This allows the op mal adapta on of equipment and consumables and guarantees a stable source of supply.
The plant in Malaysia is equipped with two manufacturing cells. Each cell contains three drag finishers for the process stages, namely, pre-grinding with ceramic media, pre-polishing with plas c media, and dry polishing with a specially prepared organic polishing medium. To prevent any disrup ons of the surface finishing opera on, all drag finishers can be used for running the dry polishing process. Furthermore, four of the six drag finishers are suitable for the pre-grinding and pre-polishing, as well as the dry polishing opera on.
The drag finishers consist of a processing bowl with a diameter of 1,000 mm and a carousel with six rotary spindles. These are equipped with specially designed workpiece fixtures, to which the femur components are mounted. The design of the fixtures allows clamping of the workpieces in a posi on that allows the finishing of precisely defined surface areas.
A redesign of the fixtures allows an increase in the number of femur components clamped to one fixture, from two to three, without jeopar-
components
highEach knee implant is subject to precise surface finishing specifica ons.
dizing the all-round treatment and finishing quality. Smith+Nephew is now able to process 18 femur components in a single batch compared to only 12 in the past. This increases the throughput by around 50 %.
During the start phase of the grinding and polishing process, the rota ng carousel is lowered. This causes the work pieces a ached to the rota ng spindles to be immersed in the media contained in the staonary processing bowl. The built-in immersion depth control system ensures that the specified immersion depth for the various work piece types is precisely maintained. Separate, independently controlled carousel and spindle drives allow the op mal adapta on of the processing intensity to the various femur types.
The Rösler drag finishers, including the drives for the carousel and spindles, are very sturdy by nature. Therefore, no design change was necessary to cope with the higher opera ng load, by clamping three work pieces to a spindle instead of two. Achieving all processing parameters, including the immersion depth of the work pieces, was not a problem.
When it comes to consistently achieving high finishing quali es, maintaining the op mal media fill level in the processing bowl and the op mal media opera ng mix is extremely important. The media level is monitored visually as well
as with special sensors. A message is displayed in the control panel, whenever an ac on by the operator is needed.
In addi on, to maintain a consistently high finishing quality, a media classifica on system was installed, consis ng primarily of a vibratory screening unit. Once a week, the ceramic and plas c media are passed through the screening unit, where all undersized media are discharged from the opera ng mix.

For cleaning and recycling of the process water from the ‘wet’ pre-grinding and pre-polishing opera ons in the two manufacturing cells, Smith+Nephew bought two automa c Z1000 centrifuges.
The dual centrifuge concept allows Smith+Nephew to operate two separate process water cycles, one for the finishing opera ons with ceramic and the other for the opera ons with plas c media. Maintaining two separate water cycles helps to prevent problems such as foaming.
The control panel of each centrifuge is equipped with the digital process water management system from Rösler Smart Solu ons. This interacve so ware allows the monitoring, data collec on and evalua on of up to 14, individually selectable, process parameters. These include the compound concentra on, pH value and microbiological contamina on. The parameter target values and their respec ve tolerance ranges are
stored in the so ware, and the actual values are entered for comparison purposes.
Whenever one or several parameters are dri ing out of the pre-defined range, the system displays an error message and issues easy-to-understand recommendaons, allowing a quick return to the specified tolerance range. This ensures a consistently high quality of the process water.
The digital management system not only helps to control the water cleaning and recycling opera on much be er, it also helps in the training of employees.
Moreover, the recording of the parameters over a longer me-period helps to iden fy long-term trends in the process water, so that necessary changes can be precisely scheduled, with minimal disrup on of the manufacturing opera ons. The digital process water management system also significantly reduces the consump on of compounds and fresh water. Further, the careful recording of all relevant water parameters, such as process quality and stability, is useful for quality audits and documenta on purposes.
The start of full-scale produc on was scheduled for early 2023, a er the valida on phase. Smith+Nephew is also planning to install two addi onal manufacturing cells.

Aerotech Inc, a global leader in precision mo on control and automa on, has made the Automaon1 mo on control pla orm more powerful and user friendly. Version 2.5 brings a TCP socket interface (beta), Automa on1 MachineApps HMI developments, new motor setup helper modules, machine setup improvements for galvo laser scan heads, and more.
Recent developments in the Automa on1 mo on control pla orm include:
• TCP socket interface – The TCP socket interface (beta) allows users to communicate between the Automa on1 controller and other devices over TCP. New AeroScript socket func ons make it easy to interact with other nodes on a computer network and provide the ability to send and receive binary and UTF-8 string data.

• Customisable HMI – Automaon1’s Access Control feature now allows users to customise access to specific MachineApps, making it easy for developers to create different MachineApps and limit access to specific HMI screens based on users or groups. The new MachineApps Camera Module makes it possible to display a live video feed with op onal crosshairs, capture images, display saved images and view axes’ posi ons. With the new Message Log Viewer, users can write custom date- and me-stamped messages to the Message Log and view them in their custom HMI.
• New and improved graphical helper modules – The Motor Hall and Signal Status module helps users visually verify proper hall sensor opera on. The Absolute Encoder Alignment module helps to set an offset in motor commuta on o en required for axes that have absolute encoders. Addi onal improvements have been made to other Studio applica on modules, including the Frequency Response module’s loop shaping controls, the Homing module and the Programming module.
• Laser scan head improvements
– Users can now change galvo calibra on and galvo power correc on files without rese ng the controller. Support for higher-deriva ve feedforward control was added with snap feedforward. Laser scan head drives now interpolate feedforward current automa cally, making this feature simpler to use.
• Improved gantry and encoder features – Expanded support for

gantries includes a new homing configura on wizard and the ability to output quadrature or clock and direc on signals from a specified encoder port.
• Increased documenta on and smoother setup – gantry setup is easier, thanks to a Checklist sidebar module that provides specific steps for configuring a gantry. Gantry configura on is now more streamlined within the Device Catalog, too. Automa on1 help documentaon now features full documentaon for the C API.
ADVERTISERS’ INDEX
IES Chartered Engineer ––––––––––––– Inside Front Cover IES Membership –––––––––––––––––– Inside Back Cover

