
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Siddhi Shinde1 , Hingade Arpita2, Thite Swarup3 Dherange Prem4 Prof. shelke B.N
1student of Dept. Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering
2 student Dept. Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering
3 student Dept. Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering
4 student Dept. Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering
5Prof. Dept. Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering
Abstract –
Awirelessfrequencymeterisanessentialtoolusedforthe detection,measurement,andanalysisoffrequencysignalsin wireless communication system This device operates by capturingelectromagneticsignalstransmittedovertheair and accurately determining their frequency. Traditional frequencymetersrequireawiredconnection,butwireless frequency meters eliminate the need for physical connections,improvingconvenienceandmobilityinvarious applications, including telecommunications, signal processing,andspectrummanagementme.hedevelopment ofawirelessfrequencymeterinvolvesintegratingareceiver withsignalprocessingcomponents,capableofanalyzingand displayingthemeasuredfrequenciesinreal-time.Advances in digital technology allow these devices to cover a wide rangeoffrequencies,fromlow-frequencybandstogigahertz ranges used in modern wireless communication. Key features often include high precision, low power consumption, and the ability to operate in environments whereinterferenceandnoisearecommon.
Introduction of wireless frequency meter As wireless technologies continue to expand across industries, from telecommunicationstoaerospace,thedemandforprecise, portable, and efficient tools to analyze and manage frequencies has increased. Wireless frequency meters are used to measure radio frequencies (RF), microwaves, and other electromagnetic waves transmitted through air, typicallyindevicessuchasradios,cellphones,Wi-Firouters, andradarsystems.Theyplayanessentialroleinoptimizing communicationsystemsbyensuringsignalsareoperatingat their intended frequencies and helping identify potential interferenceorbandwidthissues.KeyFeatures:
1. FrequencyDetection:Itmeasuresthefrequencyof radio signals, electromagnetic waves, or wireless communicationsignals.
2. Wireless Functionality: Some wireless frequency meters can detect signals without direct contact with the source, using antennas to capture radio wavesorsignalsemittedbywirelessdevices.
3. PortableDesign:Manywirelessfrequency meters are portable and handheld, making them suitable for field testing in various environments, such as telecom, radio broadcasting, and other wireless systems.
4. DigitalDisplay:Mostdeviceshaveadigitalreadout, whichprovidespreciseandeasy-to-readfrequency measurements.
5. BroadFrequencyRange:Wirelessfrequencymeters canoftenmeasureawiderangeoffrequencies,from low-frequency radio waves to higher frequencies usedinWi-Fi,Bluetooth,orcellularnetworks.
6. Applications: These devices are useful for technicians and engineers working in telecommunications,signalprocessing,andwireless networking, allowing them to monitor and troubleshoot signal interference, stability, and performance.
2 CommunicationSystems
1)RadioFrequencies:METARdataisoftentransmittedvia VHFradiofrequencies,allowingforreal-timeupdates. This particularly important for aviation operations, wheretimelyweatherinformationiscritical.Satellite Communication: For remote areas where terrestrial communication is limited, METAR data can be transmittedviasatellitefrequencies,ensuringglobal coverage.2 Data Encoding and Transmission Data Format: METAR reports are encoded in a specific format, which is then modulated onto radio frequenciesfortransmission.Digitalvs.Analog:While traditional METAR broadcasts might utilize analog signals,manysystemsnowemploydigitalmodulation techniques, enhancing reliability and reducing interference. Spectrum Analysis: It aids in analyzing the frequency spectrum, allowing users to see how different frequencies are utilized and identify any unauthorized or unexpected signals. Compliance Testing:Ensuresthatdevicescomplywithregulatory standardsregardingfrequencyuse,whichisvitalfor

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
legal operation in telecommunications. Troubleshooting:Techniciansusefrequencymetersto diagnoseissuesinwirelesscommunicationsystems, helpingtoidentifymalfunctionsormisconfigurations. TestingandCalibration
In laboratories, research, and development environments, wireless frequency meters are used to test and calibrate devicesthatrelyonwirelesscommunication.Engineerscan fine-tune devices to operate on specific frequencies, and measure parameters such as signal strength, modulation, andstability.Forexample,duringtheproductionofmobile phonesorWi-Firouters,wirelessfrequencymetersareused to verify that devices meet the required performance standards.
Wirelessdevicesoperatingonoverlappingfrequenciescan causeinterference,leadingtopoorperformanceorcomplete communication breakdown. Frequency meters can help identify such issues in environments where multiple wirelesssystemsareoperating.Forexample:
Wi-Fi Networks: In an office with many Wi-Fi routers, a frequency meter can help avoid signal congestionbyidentifyingthebestchannelstouse.
BluetoothDevices:Afrequencymetercanmonitor and help reduce interference between Bluetooth andotherwirelessdevices.
3)7.
Wireless frequency meters are portable, making them essential tools for field technicians and engineers performingsitesurveys.Thesesurveysinvolvemeasuring the signal strength, frequency, and interference in a given area to assess network performance and coverage. For example:
Cellular Networks: Technicians use wireless frequency meters to check network coverage in differentlocations,ensuringstrongsignalpresence.
Wi-Fi Coverage: A frequency meter helps identify Wi-Fi dead zones or areas with weak coverage, allowing network optimization by placing access pointsstrategically.
Wirelessfrequencymetersplayacriticalroleinmaintaining large-scalecommunicationinfrastructure.Theyareusedby telecommunications companies, broadcasters, and other serviceproviderstoensurethat:
Wirelesstransmitters(celltowers,radiostations) areoperatingwithintherequiredfrequencylimits.
Signalqualityremainsconsistentovertime.
Nounauthorizedordisruptivesignalsarecausing interferenceintheirnetworks.
Wireless frequency meters are frequently used in educationalinstitutionsandresearchlabstoteachstudents about electromagnetic theory, signal processing, and wirelesscommunications.Researchersusethesedevicesto conduct experiments on signal propagation, frequency response,andnewwirelesstechnologies.
Wirelessfrequencymetersarealsoemployedinsecurityand surveillance applications. They can detect unauthorized transmissions or the presence of covert wireless devices (such as hidden cameras or unauthorized communication devices) in secure environments. Security personnel use themtoscanforunknownfrequenciesinsensitivelocations like government buildings, data centers, or conference rooms.
Navigation frequency bands are designated ranges of frequenciesusedforvariousnavigationsystems,including GPS and other global navigation satellite systems (GNSS). Here’sanoverview:
KeyFrequencyBands
L1Band:
Frequency:1575.42MHz
Use: The primary frequency for civilian GPS signals. It transmitstheC/A(Coarse/Acquisition)codeandiswidely usedforpositioning.
L2Band:Frequency:1227.60MHz
Use: Primarily used for military signals but also supports dual-frequencyGPSreceivers.IttransmitstheP(Y)codeand isimportantforaccuracyandionosphericcorrection.
L5Band: Frequency:1176.45MHz
Use: Designed for safety-of-life applications, L5 offers higher power and improved signal integrity. It is being integratedintovariousnewGNSSsystems.
L3Band:Frequency:1381.05MHz
Use: Used by the Nuclear Detonation Detection System (NDS).Nottypicallyusedforciviliannavigation.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
L4Band:
Frequency:1268.52MHz
2. Detailed Block Diagram Information
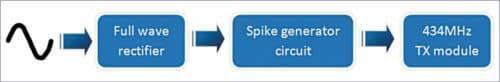
BlockDiagramofTransmitterSide
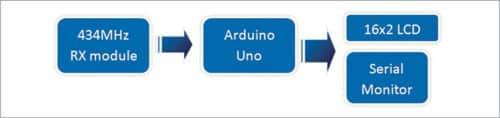
BlockDiagramofReceiverSide
1.Working of Transmitter side: -
1.Full wave Rectifier: -
Afull-waverectifieriscrucialina wirelessfrequencymeterforconvertingalternatingcurrent (AC)signalstodirectcurrent(DC)signals.
MainFunctionsofaFull-WaveRectifier:
ACtoDCConversion:
The full-wave rectifier allows both halves of the AC waveformtobeutilized,convertingthemintoapulsatingDC output. This ensures that the signal is always in the same direction,whichisessentialforaccuratemeasurement.
IncreasedEfficiency:
Byusing both halvesof the ACsignal,a full-waverectifier effectivelydoublestheoutputfrequencycomparedtoahalfwaverectifier.Thisresultsinmoreefficientpowerusageand better performance in applications requiring rapid signal changes.
2. Spike generator Circuit:-
Inawirelessfrequencymeter,aspikegeneratorisusedto produce short-duration voltage spikes that can help in various measurement and calibration tasks. Here’s how it worksanditsmainfunctions:
MainFunctionsofaSpikeGeneratorinWirelessFrequency Meters:
Calibration:
The spike generator can be used to create referencepulsesthathelpcalibratethefrequencymeter.By providing known spike frequencies, the meter can be adjustedforaccuracy.
SignalTesting:
It allows for the testing of the meter's responsetosuddenchangesinsignal,whichisimportantfor assessingthedynamicperformanceofthedevice.
PulseModulation:
The generator can create pulse-widthmodulated signals that can be used to simulate various communication scenarios, enabling the meter to evaluate howwellitrespondstodifferenttypesofsignals.
InterferenceSimulation:
Bygeneratingspikes,thecircuitcan simulatepotentialinterferenceinwirelesscommunication systems, allowing for the assessment of the meter's robustnessandreliabilityunderdifferentconditions.
TriggeringMechanism:
The spike generator can serve as a triggering source for other circuits within the frequency meter, enabling precise timing and synchronization for measurements.
3. 434MHz TX module:-
The434MHzTX(transmitter)moduleiscommonlyusedin wireless communication systems, including wireless frequencymeters.
MainFunctionsofthe434MHzTXModule:
SignalTransmission:
The primary function is to transmit datawirelesslyatafrequencyof434MHz.Thisissuitable forshort-rangecommunicationapplications,suchasremote controlsandsensordatatransmission.
DataEncoding:
The module can encode data (like sensor readings)intoaformatsuitableforwirelesstransmission, ensuringthattheinformationsentiscorrectlyinterpretedby thereceivingmodule.
Modulation:
The TX module uses modulation techniques (oftenamplitudemodulationorfrequencyshiftkeying)to convertdigitalsignalsintoradiowavesfortransmission.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
IntegrationwithMicrocontrollers:
The module typically interfaceswithamicrocontrollerormicroprocessor,which sends the data to be transmitted. This allows various applications.
LowPowerConsumption:
Designed for battery-operated devices, these modules often feature low power consumptiontoprolongbatterylife,makingthemidealfor portableapplications.
2.Working of Receiver Side: -
1.434MHz RX Module: -
The434MHzRX(receiver)moduleinawirelessfrequency meter is crucial for receiving data transmitted wirelessly fromtheTX(transmitter)module.Here’sanoverviewofits mainfunctionsandoperation:
MainFunctions:
1.SignalReception:
The primary function is to receive the 434 MHz radio frequency signals transmitted by the TX module.
2.Demodulation:
TheRXmoduledemodulatesthereceived signal, extracting the encoded data (like frequency measurements)fromthemodulatedcarrierwave.
3.DataDecoding:
After demodulation, the module decodes the data into a format that can be processed by the microcontrollerordisplayunit.
4.Integration:
The RX module interfaces with a microcontroller,allowingittoprocessthereceiveddataand display the frequency readings or other relevant information.
5.LowPowerOperation:
Similar to the TX module, the RX module is often designed for low power consumption, makingitsuitableforbattery-poweredapplications.
2.Arduino UNO:-
The Arduino Uno plays a central role in a wireless frequency meter by acting as the main
microcontrollerthatprocessesdataandcontrolsthesystem. Here’s an overview of its main functions and operation withinthecontextofawirelessfrequencymeter:
Main Functions of Arduino Uno:
1.DataAcquisition:
TheArduinocollectsfrequencydatafrom sensorsorotherinputdevices.Thisdatacouldcomefroma frequencydetectororasignalprocessingmodule.
2.ProcessingandCalculation:
It processes the incoming frequency signals, converting them into meaningful measurements.Thismayinvolvecalculationstodetermine frequency,signalstrength,orotherparameters.
3.ControlLogic:
The Arduino implements the control logic needed for the meter, such as initiating measurements, handlinguserinputs,andmanagingtimingoperations.
4.Communication:
It manages communication with other components,suchasthe434MHzTXmoduleforwireless transmission and the RX module for receiving data, if applicable.
5.UserInterface:
TheArduinocaninterfacewithanLCDor OLED display to show the frequency readings and other relevantinformation.Itcanalsohandleuserinputthrough buttonsorrotaryencoders.
6.DataTransmission:
If the meter is designed to send data wirelessly,theArduinocontrolstheTXmoduletotransmit frequencyreadingstoaremotereceiver.
3.16*2LCDDisplayandSerialMonitor:-
Inawirelessfrequencymeter,the16x2LCDdisplayandthe serialmonitorserveimportantrolesforuserinteractionand datavisualization.Here’showeachworksinthiscontext:
16x2LCDDisplay
Main Functions:
1.DataDisplay:
The LCD displays real-time frequency measurements and other relevant information, such as signalstrengthorsystemstatus.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
UserInterface:
Itprovidesasimpleinterfaceforuserstosee readings without needing a computer, making the device moreportableanduser-friendly.
MultipleLines:
With 16 characters per line and 2 lines, it allows for displaying a variety of information simultaneously,likethecurrentfrequencyononelineand additionalparameters(likemodeorbatterystatus)onthe other.
Table -1: SampleTableformat
FrequencyBand FrequencyRange TypicalUses
LF(LowFrequency) 30kHz-300kHz AM radio, navigation
MF (Medium Frequency)
HF(HighFrequency)
VHF(very high frequency)
UHF(Ultra high frequency)
SHF(Super high frequency)
300kHz-3MHz AM radio Broadcasting
3MHz-30MHz Shortwaveradio, aviation
30MHz-300MHz FM radio ,TV broadcasting, marine
300MHz-3GHz TV Broadcasting ,mobilephones,WiFi
3GHz-30GHz Radar, satellite communications
EHF(Extremelyhigh frequency) 30GHz-300GHz Research, millimeter wave communication
Here’sasimpleoverviewofcommonwirelessfrequency bands,theirpurposes,andtypicalusesintheformofa tableandchart:
Conclusions of Wireless Frequency Meter Analysis:
1.BroadFrequencyRange:
Wireless frequency bands span from extremely low frequencies (ELF) to extremely high frequencies (EHF), covering a massive range from a few Hertz(Hz)tohundredsofGigahertz(GHz).Eachfrequency rangehasdistinctpropertiesthatdetermineitseffectiveness fordifferentcommunicationtechnologies.
LowerFrequencies(ELFtoMF):
2.Characteristics:
Longwavelengths,lowerdatatransmission rates,andextendedsignalranges.
3.Applications:
Bestsuitedforlong-rangecommunicationsuch asAMradio,maritime,andaeronauticalnavigation.These frequencies can penetrate water and the ground, making them ideal for submarine communication and navigation systems.
4.Mid-Frequencies(HFtoVHF):
Characteristics: Shorter wavelengths, higher data transmission capacity, and moderaterange.
5.Applications:
UsedforFMradio,TVbroadcasts,landmobile radio, and aviation communication. These bands strike a balancebetweenrangeanddatathroughput,makingthem crucialformedium-rangecommunicationsystemslikeVHF (VeryHighFrequency)andHF(HighFrequency)bands.
HigherFrequencies(UHFtoEHF):
6.Characteristics:
Short wavelengths, high data rates, but limitedrangeduetosignalattenuation.
7.Applications:
Ideal for high-speed data communication suchascellularnetworks(4G,5G),Wi-Fi,satellite,radar,and microwavesystems.Thesebandsallowformuchhigherdata throughput, but their shorter wavelengths require more infrastructure,likecellulartowers,tomaintaincoverage.
Wewouldliketoexpressourgratitudetothepioneersand researchers in the field of wireless communication whose workhaslaidthefoundationforunderstandingandutilizing the wireless frequency spectrum. The development of wireless frequency meters and the exploration of various frequency bands have been instrumental in advancing moderncommunicationtechnologies.
Specialthanksareduetotheregulatorybodiessuchasthe InternationalTelecommunicationUnion(ITU)andFederal Communications Commission (FCC) for their continuous efforts in defining and allocating frequency spectrums globally,ensuringtheharmonioususeoftheelectromagnetic spectrumforawiderangeofwirelessapplications.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
1. https://www.itu.int/
2. https://www.fcc.gov
3. https://www.electronicsforu.com/electronicsprojects/arduino-based-wireless-frequency-mete
4. Alan P. Nebrida1, Chavelita D. Amador 1, Clyed M Madiam1, Glenn John S. Ranche1, Niel Carlo P. Nieves1,VOL4,NO.02,FEBRUARY2023.
BIOGRAPHIES




Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified
(Dept.ofElectronicsand TelecommunicationEngineering)
Dept.ofElectronicsand TelecommunicationEngineering
Dept.ofElectronicsand TelecommunicationEngineering
Dept.ofElectronicsand TelecommunicationEngineering