
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
512x + 1728y = z3 and 271x + 9y = z3
Parakram Singh
Department of Mathematics, Planetskool Research centre, Sonipat, (HR) India
Abstract – The aim of the present paper is to demonstrate the problem of existence of the solution of exponential nonlinear Diophantine equation as there are no general methods to find solution with natural number. This is an attempt to find numerical solutions (if any) of the equations 512x + 1728 y = z3 , and the 271x + 9y = z3 , where (x, y, z) are non-negative integers.
Keywords: Exponential Diophantine equation, Number Theory, Non-Negative Integers Solution
Mathematics Subject Classification (ASM): 11D61, 11D79
1. INTRODUCTION
ThetheoryofNumberisanelegantbranchofmathematics that primarily concerned with the study of non-negative integers,orcountingnumbers,andtheirpropertiesaswell as the solvability of equations in whole numbers It has a veritablylonganddifferenthistory,andsomeofthetopmost mathematicians of all time, similar as Euclid, Euler, and Gauss,havemadesignificantbenefactionstoit. Hardyand Wright,[9]discussedagreatdiversityofdifferenttopicsof theoreticalnumbertheoryandfoundaremarkableselection ofarithmeticproblemstreatedwithconsummateclarityand distinction.Burton[7]suggestedthestudyofElementary& classicalnumbertheoryandtoimpartsomeofthehistorical backgroundinwhichthesubjectevolved. Nivenetal.[11] havediscussedthe introductiontothetheoryofnumbers andexpandthebinomialtheorem,calculationmethods for numericalandapublickeycryptographysection.Contains anoutstandingsetofproblems.Baker,[1]and[2]provided comprehensive initiation to all the major branches of number theory including elements of cryptography and primality testing, an account of number fields in the arithmetic of elliptic curves. The particular type of Exponential Diophantine equation is analyzed and generalized by the method of Catalan's conjecture, its primaryCyclotomicunits,andproofwasgivenbyMihailescu [15].
Algebraic equations with non-negative integer amounts having integer solutions are Diophantine equations. For findingthesolutiontotheseequations,there'snouniversal manner available yet, so the investigators are keenly interested in developing new techniques for unravelling theseequations.Whilehandlinganycognateequation,three issuesarise,that'swhethertheproblemisresolvableornot;
ifresolvable,possiblenumberofsolutionsandfinallytofind thecompleteresults.Diophantineequationsarefrequently usedinthefieldofAbstractalgebra,Coordinategeometry, Grouptheory,Linearalgebra,Trigonometry,Cryptography andasunderaswellaswecandefinethenumberofrational pointsonacircle.IninvestigationsonDiophantineequations ofsteps,twosignificantsuccesseswerescoredonlyinthe 20thcentury.ItwasprovedbyA.Thue[4].Diophantusfrom Alexandria such equations are vociferated Diophantine equations.Mordell[12]studiedtheDiophantineequations. Acu [6] has studied the elementary solutions for the Diophantineequationofax +by =cz Suvarnamanietal [3] analyzedtwoDiophantineequations4x+7y=z2and4x+11y = z2. Sroysang [5] obtained the solutions for Diophantine Equations 2x + 3y = z2. Cohen [10] studied the Number Theory and also gave its tools he also dealt with many aspectsofnumbertheory, mainlythecentral theme being thesolutionofDiophantineequations Cipuetal [13]have revealedthenumberofextensionsforafixedDiophantine triple. Burshtein [14], considered the general equation of threeconsecutiveprimeintegersoftheformpx +(p+1)y + (p+2)z =M3 ,whereMrepresentsapositiveintegerandp represents prime with p ≥ 2, x, y ≥ 1, & z ≤ 2, also he determined all solutions of the above exponential Diophantine equations. Janaki and Shankari [8] have discussed various implementable ways to tackle multivariableandmulti-degreeDiophantineproblemsand obtain the solution of these exponential Diophantine equations.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the Preliminary work of the paper by using Lemma and theorems.Section3and4,presentstheworkingstrategyto solve the main exponential Diophantine equations of this paper. The conclusions about the obtained solutions are containinsection5.Therestofthepaperlistedtherelated workasreferences.
2.1 Lemma: (Miheailescu’sTheorem)[15]TheDio-phantine equationax by =1hastheuniquesolution(a,b,x,y)= (3,2,2,3),wherea,b,xandyareintegerswithmin{a, b,x,y}>1.
2.2 Lemma: Therearenosolutionsinintegerx,y,zwithx, y, z > 0, of xn + yn = zn when n ≥ 3, also known as Fermat'sLastTheorem,wasprovedbyWiles[16]

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
3. Main work for Equation 1: 512x +1728y =z3
Theorem 3: The Diophantine 512x + 1728y = z3, has no solutioninnon-negativeintegers,wherex,y,z>0
Proof: letwefindthetrivialsolutionfor 512x +1728y =z3 (3)
Letx=0
1+1728y =z3,thenz3 >1orz>1
or z3 – 1728y = 1, byLemma 2.1,ycanonlytakethe value 0 and1, for y = 0 and 1, the equation 1 + 1728y = z3 giveszhasnointegervalue
Nowlety=0
512x+1=z3,alsoherez3>1orz>1,thenequationz3–512x =1,byLemma2.1,says,xcantakethevaluelessthan2in integersthatarex=0,1 forx=0and1equation512x +1= z3 implyingz3 =2and513respectively,itgiveszhasnota positiveintegervalue.Hence,theequation512x+1728y=z3 hasnotrivialsolution.
Nowfindthenontrivialsolutionforequation,(3) or 512x +1728y =z3
canberewriteoftheform
83x +123y =z3 (3.1)
⟹ 2|z
zisevenbecauseLHSiseven,ifzisoddthenz3 isalsoodd
Dividingequation(3.1)by8weget
83x-1 +123y-3 ∙63 =(z/2)3
Ingeneral,ifwedivide(3.1)by8, i timesthen

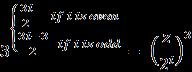
fori>1 (3.2)
We cannot divide by 8 infinitely many times. In equation (3.2) when i = min {3x, 2y, L} where L is the logarithm of highestpowerof2dividingzonbase2,itcannotbedivided by8.Weassumein(3.1)thatthetermisreducedifitstops theequationtodivideby8andcanbeaninteger,first.
Case 3.1: if123yreducesbeforeorwithz3 or83x
Afterkeepondividingby8,2ytimes,then
83x-2y +33y =(z/22y)3
3x-2y≥0
83x-2y+33y=t3 [t=z/22y]
(23x-2y)3+(3y)3=t3
Leta=23x-2y,b=33y
a3 +b3 =t3 whichtakesformofx3 +y3 =z3 andhasnosolutionduetoLemma2.2.
if123y willnotreducefirstgotothenextcase
Case 3.2: let83x reducesfirstbeforez3
1+123y-9x ∙69x =(z/8x)3
Put,m=3x 1+(12y-m ∙6m)3 =(z/2m)3` (3.2.1)
z/2m >1
as z/2m iseven
As123y hasnotreduced,soy-m>0ory>m
12y-m ∙6m>1andbyCatalanconjectureLemma2.1,wehave nosolutionforthiscase.
Case 3.3: ifz3 reducesfirsttoletsayk3 andbefore83x
Let z=2mk,
Dividingby8uptomtimesofequation(3.1)
83x-m +123y-3m ∙ 63m =k3
And it can be clearly seen that parity of LHS and RHS are different
Case 3.4: ifz3 and83x reduceboth
Afterreducing,weget 1+(63x ∙12y-3x)3 =k3 , wherez=23xk
(8isdivided3xtimes)
If n=63x ∙123y-3x , 1+n3 =k3
Now, n>1,k>0
Ifkis1thennis0whichisnotpossiblesok>1whichhas nosolutionbyLemma2.1.
Hence, the equation 512x + 1728y =z3 has no solution in non-negativeintegers.
Main work for Equation 2: 271x +9y=z3
Theorem 4: Let x, y, z be non-negative integers then the equation271x +9y=z3 hasasolution(1,3,10).
Proof: Now initially check the trivial solution for the equation
271x +9y=z3 (4)
Letx=0,
1+9y =z3 Sincez3 >1,soz>1

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
or z3 –9y =1,
BytheLemma2.1,ycantakethevalueonlylessthan2,that is,y=0,1.ify=0,theequation1+9y =z3 givesz3 =2,which showszisnotanintegervalue.Similarly,fory=1,then1+ 91 =z3 orz3 =10whichgivesagain,zisnotanintegervalue Nowlety=0
271x +1=z3 Sincez3 >1,z>1 or z3 –271x =1
ByLemma2.1,ifanequationoftheformax –by =1then(a, b,x,y)canonlytakethepossiblesolutionis(3,2,2,3)for min {a, b, x, y} > 1. So, x can take the value less than 2 in integers,thatare x=0,1.
forx=0and1,theequation271x +1=z3 ,implyz3 =2and 272 respectively for both cases shows z is not a positive integer. Hence the equation 271x + 9y = z3 has no trivial solution.
Nowcheckthenontrivialsolutionforequation(4) x,yandz are the non-negative integers and the equation as given below-
Let, 271x +9y=z3 zisevenso, z3 ≡0(mod8), 9y ≡1(mod8), 271≡-1(mod8),hencexisodd
Nowforfindingy,consideritundermodulo3thenthereare followingcasesarise:
Case 4.1: Lety=3k,thenequation(4)becomes
271x +93k =z3
271x =z3 –(9k)3
271x =(z–9k)(z2 +9kz+92k)
Letx=u+v.forfactoring271x togetvaluesofz–9k andz2 +9kz+92k .
271u =z–9k (4.1.1)
271v =z2 +9kz+92k (4.1.2)
From(4.1.1),z=271u +9k
substitutingthisinequation(4.1.2)
271v =(271u +9k)2 +9k(271u +9k)+92k =2712u +3∙9k(271u +9k)=2712u +3∙9kz
32k+1 ∙z=271v –2712u =2712u(271v-2u –1)
Obviously,v>2uand271 LHShenceu=0andv=x
∵ x=u+v;
Then, 32k+1 ∙z+1=271x
or z3 –32k+1 ∙z–(36k +1)=0
whichgives, z=(32k +1),(-32k –1±√(-4∙32k+1))
Now,consideronlyrealvalueofz=32k +1,then
32k+1(32k +1)+1=271x
34k+1 +32k+1 =271x -1x
34k-2 +32k-2 =10(271x–1 +271x–2 +…+2712 +271+1)
Ifk=1,then34–2 +32–2 =10=10*1
Hence,x=1andz=10so,(1,3,10)isasolution
Ifk>1,then3|271x–1 +271x–2 +…+2712 +271+1
Sincealltermsare1(mod3)so3|x, let x=3m
(271m)3+(9k)3 =z3 ,whichisnotpossiblebyLemma2.2or Fermat’s last theorem represents no solution would be appearforthiscase.
Case 4.2: Lety=3k+1forequation(4),then
271x +93k+1 =z3 (4 2.1)
here,weconsidertwocasesfork,eitherithasthevaluek>0 orat,k=0
Subcase 4.2 (A): k>0
93k+1 ≡0(mod81)
Letx=2m+1andz=2t,
∵xisoddandziseven
Thenequation(4.2.1)becomes
2712m+1 +81∙93k-1 =8t3
2712m+1 +271∙93k-1 -190∙93k-1 =8t3
271(2712m +93k-1)=2(4t3 +95∙93k-1)
((2712m +93k-1)/2)=((4t3 +95∙93k-1)/271)=a (say) (4.2.A.1)
from1&3ratioofequation(4.2.A.1)
2712m +93k-1 =2a
⇒ 93k-1 =2a–2712m (4.2.A.2)
Alsoconsiderfrom2&3ratioofequation(4.2.A.1)
271a=4t3 +95∙93k-1 =4t3 +190a-95∙2712m by(4.2.A.2)
81a =4t3 -95∙2712m
0≡4t3 -14∙282m(mod81)
or 0≡4t3 -14∙55m(mod81) (4.2.A.3)
Weconstructthetablestofindthevaluefordifferentm andt,of14∙55mand4t3 modulo81

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Table -1: ToFindallthepossiblevaluesof1455m (mod 81)
Find all the possible values of 14∙55m (mod 81)
m 55m (mod81) 14∙55m (mod81)
form>3,repeatthevaluesunder(mod81)
Table -2: ToFindallthepossiblevaluesof4t3 (mod81)
Find all the possible values of 4t3 (mod 81)
t t3(mod81) 4t3(mod81)
Subcase 4.2 (B): k=0
Lettheequation(4.2.1)at,k=0
271x +9=z3 (4.2.B.1)
We consider different modulo for the equation (4.2. B.1), Firstconsidermodulo5,then
271x +9≡z3 (mod5)
271x +9≡0(mod5), [∵271≡1(mod5)]
⇒ z≡0(mod5)
⇒ z3 ≡0(mod25)
From,(4.2.B.1),considermodulo25,then
⇒ 21x ≡16(mod25),
∵ 271≡21(mod25)
271x can be 21, 16, 11, 6, 1 (mod 25), if x takes the value from1,2,3,4and5resp.so,hereweseex>5,itwillrepeat thevalues.
Hence x≡2(mod5)
Nowfromequation(4.2.B.1),
271x +9≡z3 (mod31)
23x +9≡z3 (mod31)
(23x +9)canbe1,11,24,13,8,17,7,25,5,10(mod31),ifx takesthevaluefrom1to10respectivelyandmore So,we takex>10,itwillrepeatthevalues.
∵ x≡2,7(mod10)
Hence, z3≡7,11(mod31) Whichcontradicts,becausez3can nevertakesthevalue7or11under(mod31),sosubcase42 (B)unabletoshowthesolutionatk=0.
fort>8,repeatthevaluesunder(mod81)
wecan compare these values of t and m, according to the congruence (4.2.A.3) then here, z = 2t and t ≡ 5(mod 9) becauset>8,repeatthevaluesunder(mod81)
z≡1(mod9)andm≡0(mod3)
⇒ z3 ≡1(mod81)andx≡1(mod3).
Letx=3n+1
Sincez3 ≡1(mod81)and93k+1 ≡0(mod81),fromequation (4.2.1)
⇒ 271x ≡1(mod81)
⇒ 271∙(2713)n ≡1(mod81)
While,
271≡28(mod81)
which is a contradiction as 1 and 28 are not congruent to eachotherundermodulo81.So,the equation(42.1)hasno solutionforthiscase.
Case 4.3: y=3k+2,thenequation(4)becomes
Let 271x +93k+2 =z3 (4.3.1)
93k+2 ≡0(mod81)
Letx=2m+1andz=2t [∵xisoddandziseven]
Thenequation(4.3.1)becomes
2712m+1 +81∙93k =z3
271(2712m +93k)=2(4t3 +95∙93k)
Tofactorout542because271isafactorof542,Sinceboth sideoftheaboveequationisdivisibleby542,letitbe542a then,
2712m +93k =2a
⇒ 93k =2a–2712m
Also,271a=4t3 +95∙93k =4t3 +95(2a–2712m)
© 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page535

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
=4t3 +190a-95∙2712m
81a=4t3 -95∙2712m
Usingsubcase4.2(A);ithasnosolution.
Hencetheequation271x +9y=z3 hasasolution(1,3,10).
5. CONCLUSIONS
We have examined the equation 512x + 1728y = z3 has no solution in Z+ and also obtained the solution of the nonlinear exponential Diophantine equation 271x + 9y = z3 , where(x,y,z)=(1,3,10)arenon-negativeintegers.
REFERENCES
[1] A. Baker, “A Concise Introduction to the Theory of Numbers”, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1994.
[2] A.Baker,“AComprehensiveCourseinNumberTheory” , CambridgeUniversityPress,Cambridge,2012
[3] A.Suvarnamani,A.Singta,andS.Chotchaisthit,“Ontwo diophantineequations4x+7y=z2and4x+11y =z2”,Sci. andTech.RMUTTJour,Vol.1,No.1,2011,pp.25–28.
[4] A. Thue,“Über Annäherungswerte algebraischer” , Zahlen.J.reineangew.Math.,Vol.135,1909,pp.284–305.
[5] B.Sroysang,“MoreontheDiophantineEquations2x+3y = z2” , Int. Jour. of Pure and Appl. Math., Vol. 84, No. 2, 2013,pp.133-137
[6] D.Acu,“Onthediophantineequationoftypeax+by=cz,” GeneralMath.,Vol.13,No.1,2005,pp.67-72.
[7] D.M. Burton, “Elementary Number Theory”, Allyn and Bacon,Inc.,1980.
[8] G.Janaki,andA.G.Shankari,“Exponentialdiophantine equation(n2 -1)u +n2v =w2,n=2,3,4,5”,Ind.J.ofSci. andTech.,Vol.17,No.2,2024,pp.166-170.
[9] G.H. Hardy and E. M. Wright, “An Introduction to the TheoryofNumbers”,OxfordSci.Pub.,1979.
[10] H. Cohen, “Number Theory. Volume I: Tools and DiophantineEquations”,SpringerVerlag,Berlin,2007
[11] I. Niven, H.S. Zuckerman and H.L. Montgomery, “An introduction to the theory of numbers”, fifth edition. JohnWileyandSons,Inc,1991.
[12] L.J.Mordell,“Diophantineequations”,AcademicPress, NewYork,1969.
[13] M. Cipu, Y. Fujita, T. Miyazaki, “On the number of extensions of a Diophantine triple”, Int. J. Number Theory,Vol.14,2018, pp.899–917.
[14] N Burshtein, “All the solutions of the diophantine equationspx +(p+1)y +(p+2)z=M3whenpisprime and1≤x,y,z≤2”,Anls.ofPureandAppl.Math.,Vol.22, No.1,2021,pp.7-15.
[15] P.Mihailescu,“OnprimaryCyclotomicunitsandaproof ofCatalan'sconjecture”,J.ReineAngew.Math.,Vol.27, 2004,pp.167-195.
[16] A. Wiles,“ Modular elliptic curves and Fermat's Last Theorem”,Ann.ofMath.,Vol.141,No.3,1995,pp.443551.
Volume: 11 Issue: 10 | Oct 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified