
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Hemalata S Shedad1 , Deeksha G Nadig2
1Bachelor of Engineering, Information Science and Engineering, Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology, Karnataka, India
2Bachelor of Engineering, Information Science and Engineering, Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology, Karnataka, India [3]
Abstract – New opportunities for improving accessibility for people with hearing impairments have been made possible by the development of Bluetooth technology. Throughwirelessaudiotransmission,intuitivecontrols,and device interoperability this study investigates the possibilitiesof
utilizing Bluetooth connections to enhance hearing accessibility. Bluetooth-enhanced headphones, hearing aids, andotheraudiosourceswithease.Thegoaloftheprojectis to create effective Bluetooth protocols and algorithms that guarantee high-quality, low-latency audio streaming while upholding strong security and power efficiency. Furthermore,
welookintohowBluetooth-basedsystemscanbeintegrated with smartphone apps that offer real-time sound amplification, noise reduction, and customized sound profilestomeettheindividualhearingdemandsoftheuser.
Key Words: Bluetooth technology, Wireless audio transmission, Hearing aids, Assistive listening devices, Low-latency audio, Real-time sound amplification, Noise reduction,Smartphoneintegration.
Millions of people worldwide suffer from hearing problems, which make engagement and communication difficult in a variety of contexts. In order to help people with hearing impairments participate more completely in everyday life, new solutions are being developed as technology advances. Bluetooth connectivity is one such technology development that presents a promising foundation for improving accessibility for those with hearing impairments. Due to its popularity and ability to facilitatewirelesscommunication,Bluetoothtechnologyis now a standard feature of many contemporary audio products, including computers, televisions, and smartphones.
In order to improve the auditory experience for people with hearing impairments. Bluetooth -enabled equipment such as assistive listening devices, headphones, and hearing aids have been developed recent years. These gadgets take advantage of Bluetooth’s capacity to send high-qualitymusicwirelessly,enablinguserstoconnectto
a range of audio sources without the hassle of bulky connections. The creation of Bluetooth protocols and algorithms that guarantee minimal latency and highquality audio transmission while upholding robust securityandpowerefficiencyareimportantareasoffocus.
Bluetooth technology has the potential to have a big influenceonhearingaccessibility.Itencouragesinclusivity in social, educational, and professional contexts in addition to empowering those with hearing impairments by enabling improved communication. This study also exploreshowBluetoothtechnologycanbeintegratedwith mobile applications that provide configurable features including noise reduction, real-time sound amplification, and customized sound settings. These developments seek to provide a customized auditory experience by catering each user’s particular hearing requirements. It looks at present trends, assesses technical difficulties, and offers predictions on where Bluetooth-based solutions for hearing aids will go in the future. The objective is to pinpoint areas in need of development and offer creative fixesthatwillincreasetheefficacyandusabilityofhearing accessibilityforawiderangeofpeople.
The idea behind improving hearing accessibility with Bluetoothtechnology istousewirelesscommunication to give those with hearing impairments a better auditory experience. Devices can connect and interact across short distancesusingBluetooth,apopularwirelessprotocolthat transmitsdata,includingaudiosignals,whenlittlelatency. With this feature, Bluetooth is a great option for hearing accessibility applications where clear, high-quality audio transmissionisessential.
Bluetooth technology allows for the wireless transmissionofaudiosignalsfromvarioussourcessuchas smartphones, televisions, computers, and audio systems directlytoBluetooth-enabledhearingaids,headphones,or assistive listening devices. This wireless capability eliminates the need for physical connections, enhancing convenience and enabling individuals to access audio content in a wide range of environments, from home to publicspaces.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Chart-1: DifferenthearingdevicesusingBluetooth technology
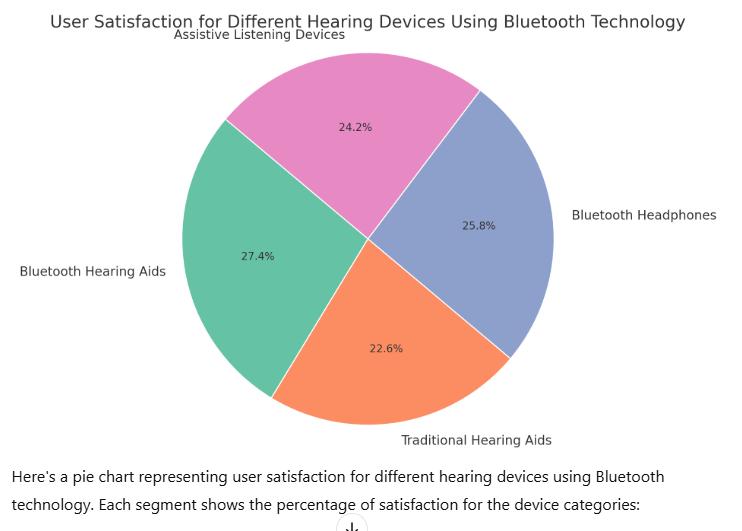
To enhance the auditory experience, Bluetooth connections need to support low-latency and high-quality audio transmission. Low-latency and high-quality audio transmission. Low-latency ensures that audio signals are transmitted withminimal delay,synchronicity withvisual content or in real time communication scenarios. Highquality audio streaming is essential for clarity, especially for individuals with hearing impairments who rely on clear sound to discern speech and other important auditory cues. Advanced Bluetooth protocols and algorithms are developed to prioritize these factors, aiming to minimize signal delays and preserve audio fidelity.
OneofBluetooth’sstrengthsisitscompatibilitywitha widerangeofdevices.Bluetooth-enabledhearingaidsand headphones can seamlessly connect to multiple audio sources, making it easier for users to switch between devices without manual configuration. This interoperabilityallowsindividualstoengagewithavariety of media, such as streaming services, phone calls, or inperson conversations, without the need for separate equipmentorcomplexadjustments.
Modern Bluetooth-based hearing devices are often paired with smartphone applications that offer advanced customization options. These apps allow users to adjust volumes, select sound profiles, manage noise cancellation, and even apply real-time sound amplification based on
their individual hearing needs. Customizable settings enable users to tailor their auditory experience to specific environments,whethertheyareinaquietroomoranoisy publicspace,providinggreaterautonomyandcontrol.
Bluetooth-based systems are increasingly incorporating advanced features like noise reduction and real-time sound amplification. These features use algorithms to filter out background noise, enhance speech clarity, and amplify desired sounds, making communicationmoreeffectiveforindividualswithhearing impairments. Such technology adapts to the user’s environment, offering a dynamic listening experience that addressessituationalchallenges.
Table-1: DataforBluetooth-basedHearingAccessibility Enhancement
Ease of Use (1-10) 8 7 5
Real-time Sound Amplification Yes Yes Yes
Thedataandvisualizationfocussesonkeymetricssuchas usersatisfaction,audiolatency,powerconsumption,device compatibility, providing insights into the benefits and challengesofBluetooth-enabledhearingdevices.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
For Bluetooth hearing devices to be effective, they need to operate with optimal power efficiency, ensuring that they are usable throughout the day without frequent charging. Additionally, security measures must be implemented to protect user data and maintain privacy, especially when connecting to personal devices like smartphones. This research examines hoe Bluetooth protocols can balance these requirements, ensuring that devicesarebothefficientandsecure.
The concept of using Bluetooth to enhance hearing accessibility extends beyond personal hearing aids to include broader applications, such as public hearing assistance systems in theaters, conference rooms, and educational institutions. Bluetooth’s ability to connect multiple devices to a single source can facilitate group listening experiences or provide targeted assistance in publicenvironments.ThepotentialscalabilityofBluetoothbased solutions makes it a versatile option for addressing accessibilitychallengesonalargerscale.
1. Wireless convenience Eliminates cables: Users can connect hearing aids to multiple devices like smartphones,TV’sandcomputerswithoutthehassle ofwires.
2. Hands -Free Functionality: Bluetooth-enabled hearingaidsallowuserstotakecalls,listentomusic, orusevoiceassistantsseamlessly.
3. Better Audio Quality High-fidelity audio: More natural and clear sound is produced using sophisticated Bluetooth codecs, which are essential for improved hearing, Customizable Sound Profiles: Through apps, users can modify sound settings to improve hearing in various contexts, such as noisy placesandquitrooms.
4. Adaptability to a Variety of devices, Connectivity to intelligent ecosystems: By Connecting to a range of smart devices, Bluetooth-enabled hearing aids can improveproductivityandeverydayinteractions.
5. Featuresofassistivetechnology: Theycanbeusedin conjunction with alert systems or captioning devices toincreaseaccessibilityforpeople
1. HighCostExpensiveDevices:Someusersmayfind itdifficulttoaffordBluetooth-enabledhearingaids because they are typically more expensive than conventionaldevices.
2. AdditionalCosts:Thetotalcostmaygoupifusers requirecompatibledevicesoraccessories.
3. Dependencies on Batteries Regular Recharging: Bluetooth technology can still deplete batteries more quickly even with increased efficiency, necessitating frequent charging or battery replacements.
4. Dependency on Power: When gadgets run out of battery in urgent situations, users may find it inconvenient.
5. Dependencies on Devices Smartphone Requirement: Many sophisticated functions are dependent on smartphones or other gadgets, which less tech-savvy users may find difficult to utilize.
6. Limited functionality Without Connectivity: If the Bluetooth connection is lost or interfered with, somefeaturesmightnotfunction.
1. Review of Literature: The goal is to compile and summarize the body of knowledge regarding accessibility technologies, Bluetooth-enabled hearing aids, and how they affect people with hearingimpairments.
Techniques:
Examine white papers, conference reports, and scholarlypublications.
ExaminecasestudiesofPSAPs,Bluetoothearbuds, and associated technology. List the latest innovations in technology, market trends, and regulations.
2. Quantitative Approaches : The goal is to compile quantifiable data regarding the performance, usability and efficiency of Bluetooth-enabled hearingaids.
Techniques:
Questionaries & Surveys: Create tools to gather information from caregivers, audiologists, and usersofhearingaids.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Track improvements in hearing experiences, devicesusability,andusersatisfaction.
InvestigationsthroughExperiments:
Test the latency, noise reduction, and sound quality of Bluetooth devices in controlled experiments. When comparing various devices or settings,usestatisticalanalysis(suchasANOVAor t-tests).
3. QualitativeApproaches:
The goal is to investigate user perceptions, experiences,andobstaclesrelatedtotheadoption ofBluetoothhearingtechnology.
Techniques:
Interviews: Interview users, audiologists, and product developers in a semi-structured manner. Pay attention to obstacles, experiences and ideas forenhancement.
FocusGroups:
Arrange conversations amongst various user groups, such as young individuals, senior citizens, and tech-savvy users. Examine the views and thoughts of the general public on Bluetooth hearingtechnology.
4. AnalysisbyComparison:Thegoalistoassessand contrastseveralBluetooth-basedhearingaids.
Techniques:
Determine the most important performance indicators, such as battery life, sound quality, and usability.
Examine the features, prices, and reviews of different products. Utilize benchmarking methods toevaluateeachdevice’srespectivebenefits.
5. Technical Assessment: The goal is evaluate Bluetooth’stechnologicalcapabilitiesandlimitsin termsofhearingaccessibility.
Techniques:
Analyze signal processing by testing data transmissionstability,signal range, andlatencyin varioussettings.
BatteryPerformanceTesting:
Assess how Bluetooth streaming affects the batterylifeofyoursmartphone.
CompatibilityTesting:LookathowwellBluetooth headphoneswork withTVs,cellphones,andother accessories.
6. MethodsofUser-centeredDesign(UCD):
Involving end users in the creation of Bluetooth hearingaidsisthegoal.
Techniques:
Usabilitytestingandprototyping:Createworking models of Bluetooth apps or devices. To improve thedesigninresponsetouser input,runusability testing.
IterativeDesign: Useagiletechniquestointegrate ongoingcriticismandenhancements.
7. Examples of Cases: The goal is to investigate the practical uses and results of Bluetooth hearing technologies.
Techniques:
Choose particular instances, such as companies, schools,ormedicalfaculties.
Recordthebenefits,difficulties,andproceduresof implementation.
Analyze success stories and lessons learned in detail.
8. AnalysisofPoliciesandRegulations:Thegoalisto investigate how standards and laws affect the uptake and advancement of Bluetooth hearing aids.
Methods: Examine regulations from international standards bodies, the FDA, and the FCC. Examine howrulesaffecttheaffordability,accessibility,and innovationofdevices.
Enhancing hearing accessibility using Bluetooth technology essentially entails building a wireless environment in which people with hearing loss may interact with a variety of audio sources with ease, change sound settings in real-time, and take in crystal clear, high quality audio. In order to overcome current constraints and make Bluetooth protocols and devices more efficient, user-friendly, and environment-adaptable, our research focuses on optimizing them. The objective is to offer an inclusive and accessible solution that enables people with hearing impairments to live more connected and communicative lives by fusing Bluetooth technology with cutting-edgeaudiofeaturesandsmartphoneapplications.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 12 | Dec 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
I want to sincerely thank Hemashree ma’am for all of her helpandassistanceduringtheresearchandwritingofthis article. This work has greatly benefited from her knowledge, support. This endeavor would not have been possible without her guidance. I am incredibly appreciative of the chance to study under her guidance andherunwaveringdrivetoadvancethefieldofresearch in Enhancing the accessibility of hearing using Bluetooth connection.
[1] VermaRR,KonkimallaA,ThakarA,SikkaK,SinghAC, Khanna T. Prevalence of hearing loss in India. The NationalMedicalJournalofIndia.2022;34-216.
[2] Humes LE. The World Health Organization’s hearingimpairmentgradingsystem;anevaluationforunaided communication in age-related hearing loss. Internationaljournalofaudiology.2019;58(1):12-20.
[3] Lasak JM, Allen P, McVay T, Lewis D. Hearing loss: Diagnosis and management. Primary Care – Clinics in OfficePractice.2014;41(1):19-31.
[4] Alshuaib WB, Al-Kandari JM, Hasan SM. Classification of hearing loss. In Update on Hearing Loss. In Tech;2015.
[5] ClarkJG.Usesandabusesofhearinglossclassification. In Asha. A Journal of the American Speech-LanguageHearingAssociation;1981.
[6] Olusanya BO, Davis AC, Hoffman HJ. Hearing loss grades and the International classification of functioning, disability and health. Bulletin of the WorldHealthOrganisation.2019;97(10):725.
[7] Hearing Aids | FDA. (n.d.). Retrieved November 23; 2022.
[8] Kim MB, Chung WH, Choi J, Hong SH, Cho YS, Park G, Lee S. Effect of a Bluetooth-implemented hearing aid on speech recognition performance: subjective and objective measurement. Annals of Otology, Rhinology andLaryngology.2014;123(6):396-401.
[9] Smith P, Davis A. The benefits of using Bluetooth accessorieswithhearingaids.InternationalJournalof Audiology.2014;53(10):770-773.
[10] Wall Hagen MI. The stigma of hearing loss. The Gerontologist.2010;50(1):66.