
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1 Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, Assam Engineering College, Jalukbari, Guwahati, 781013, Assam, India
2 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering Assam Engineering College, Jalukbari, Guwahati, 781013, Assam, India
Abstract - Piled-raft foundations, known also as piled rafts, are a combination of a shallow foundation (raft) and a deep foundation (pile group). Study of the influence of different parameters of piled raft foundation is the objective of this research work. To analyze piled-raft foundations on layered soil., a numerical model has been developed using the software PLAXIS 3D Parametric study of piled raft foundation has been carried out at geological province of Alluvium (Phanerozoics) of India such as Guwahati (Assam, India). As the pile length increases in individual piled raft foundation in layered soil of Guwahati, the settlement decreases. Introduction of 4 nos. of piles, 9 nos. of piles to raft placed directly below the column position, 16 nos. of piles to raft placed at one-third of bay in between the column positions and 24 nos. of piles to raft placed at column center line in addition to one third of bay can reduce the total settlement in layered soil of Guwahati. Increasing the number of piles up to 16 numbers in piled raft foundation has considerable effect in reducing settlement in layered soil. However, increasing the number of piles to 24 does not significantly reduce the settlement of the piled raft foundation. The thickness of raft has nominal effect on the settlement of piled raft foundation. In case of pile groups, position of piles has much effect to the reduction of settlement of piled raft foundation.
Key Words: Foundation,piled-raft,settlement,layeredsoil,
A piled raft is a foundation that is made up of three loadbearing components: piles, raft, and subsoil. Piled-raft foundations,knownalsoaspiledrafts,areacombinationofa shallowfoundation(raft)andadeepfoundation(pilegroup). Inthistypeoffoundations,theroleoftheraftistoprovide therequiredbearingcapacityandthepilesareusedmainly assettlementreducersbutcanalsocontributetothebearing capacity. Generally, the raft by itself can provide the necessary bearing capacity but it cannot regulate the settlement.Asaresult,thepilesareessentialtoreducethe raft settlement. Pile-raft foundations are considered extremely complex systems since they combine piles and raftsintoasinglestructure.
ThemethodbyPoulosandDavisisaconvenientmethodof hand calculations that can be used as preliminary design tool.Poulosmodeledpiledraftfoundationasaspring-loaded stripwherethestriprepresentstheraftinonedirectionand thespringsrepresentthepiles AnbazhaganP.et.al.in2014 while development of any earthquake resistant design, presented the soil classification for different geological provinces of India as per National Disaster Management Authority.
Using a software finite element package for soil and foundationanalysis,a16mx16mraftwithmassivecircular pilesofvarieddiameterswasanalyzed.Tomodelthepiled raftfoundationaplanestrainfiniteelementmodelwasused. Itwasassumedthatpilesandraftswerelinearlyelastic.The Mohr-Coulombyieldcriterionwasusedtorepresentthesoil typeaselastic-perfectlyplasticmaterial.Heretotalvertical displacementwascalculatedusingplasticcalculationsanda drainedconditionwasassumed. A15-nodedtriangularsoil elementwasdiscretized.Plateelementswereusedtomodel thepilesandraft. Thesideskinfrictioninpileswastaken intoaccountbyapplyinginterfacereductionfactorRinter.The piledraftissubjectedtoa non-uniformvertical loadingin theformofconcentratedcolumnloads.
Generally, India can be naturally divided into three geological provinces, namely, the Himalayas, the IndoGangeticPlainandtheIndianShield.India'sgeologymaybe splitinto 20 provinces, and theGeological SurveyofIndia (GSI) publishes comprehensive geological publications complete with maps. In India, sixteen major types of soils have been recognized. Parametric study of piled raft foundation has been carried out at geological province of Alluvium(Phanerozoics)ofIndiasuchasGuwahati(Assam). Altogether,147nos.ofmodelshavebeendevelopedtocarry outtheparametricstudy
Thepropertiesofdifferentlayerssoilbeingusedinthestudy aretabulatedinTable1.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Table -1: Propertiesofthesoilbeingusedinthestudy
Particulars
Layer1 (0-2)m depth
Layer2(24)mdepth
Layer3(44.8)m depth
Soiltype SiltyClay SandyClay SiltyClay
Materialmodel MohrCoulomb MohrCoulomb MohrCoulomb
Angleoffriction (ϕu) 80 100 80
Stiffness(Eref) 4750 kN/m2 7500 kN/m2 6250
Dilatancyangle (Ѱ) 00 00 00
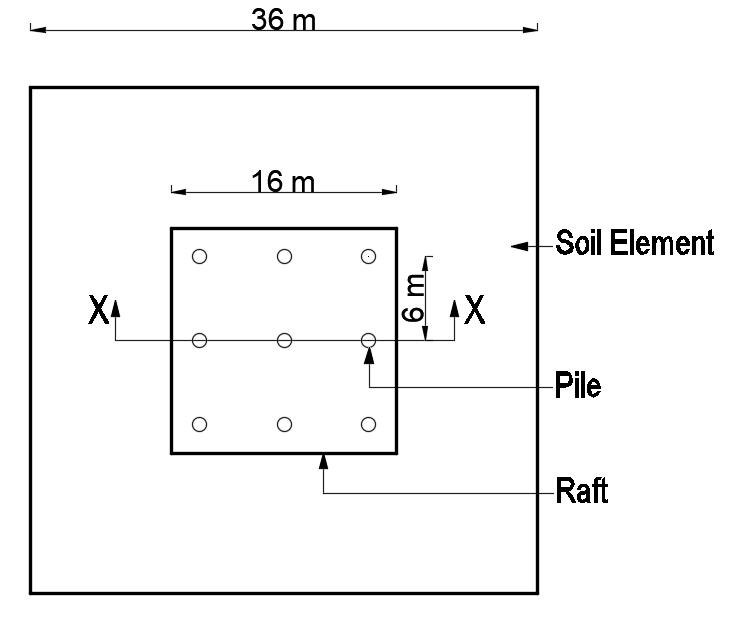
Fig -1:PositionofPilesinPiledRaftFoundation-TypeARaftonly(Nopile)
Drainage condition Drained Drained Drained Permeability
Particulars Layer4 (4.8-16.5) mdepth Layer5 (16.5-17.8) mdepth Layer6 (17.8-30.0) mdepth
Soiltype Sandy Clay SiltyClay SandyClay
Materialmodel MohrCoulomb MohrCoulomb MohrCoulomb
Stiffness(Eref)
Cohesion(Cu ) 24kN/m2 96kN/m2 20kN/m2
Poisson’s
Dilatancyangle (Ѱ) 0
Drainage condition Drained Drained Drained
Permeability (kx=ky=kz)
m/day
Figures1to5belowshowsthepositionofpilesin themodelsofpiledraftfoundation
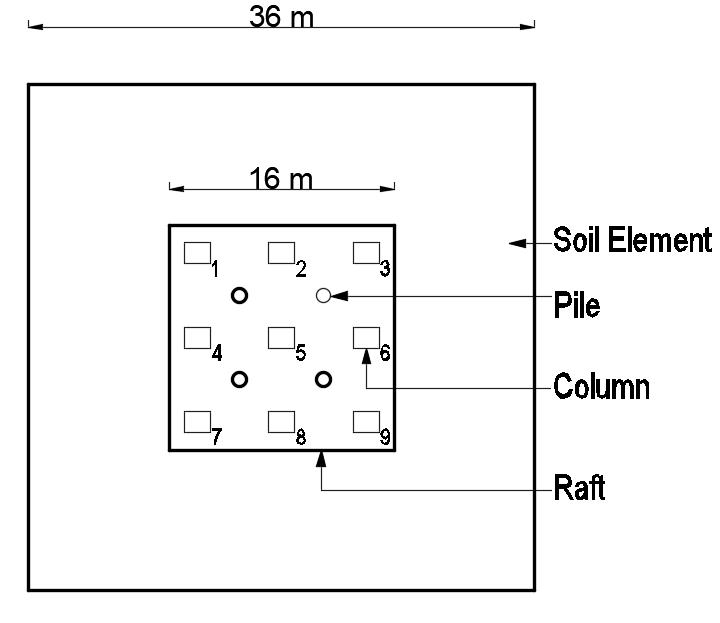
Fig -2:PositionofPilesinPiledRaftFoundation-TypeBPileathalfofbay(4nos.ofpiles)
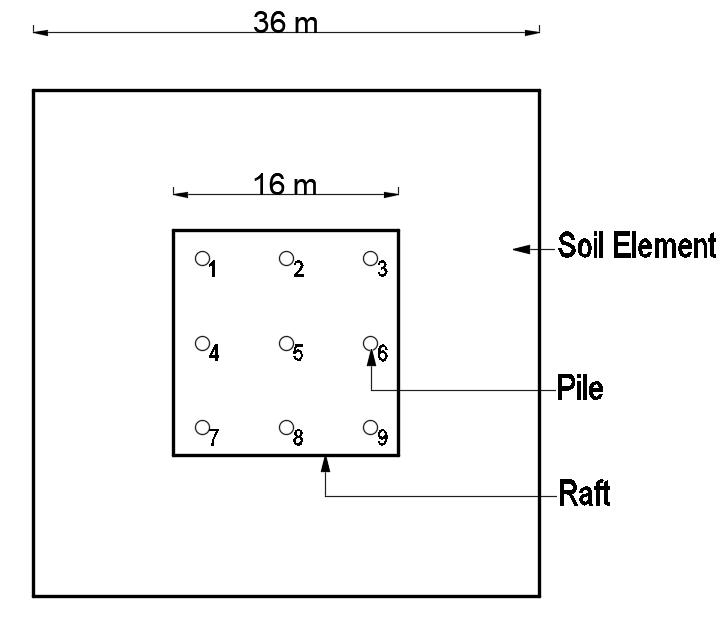
Fig -3:PositionofPilesinPiledRaftFoundation-TypeCPiledirectlybelowthecolumn(9nos.ofpiles)

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
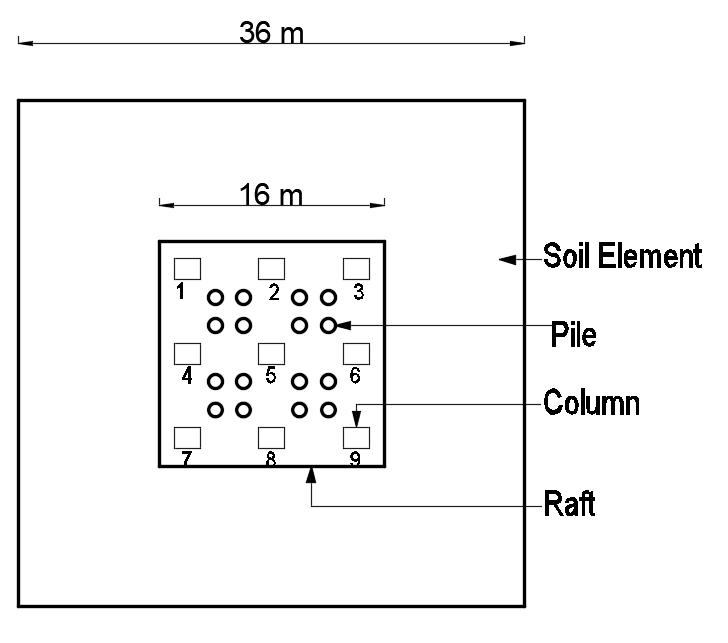
Fig -4:PositionofPilesinPiledRaftFoundation-TypeDPileatone-thirdofbay(16nos.ofpiles)
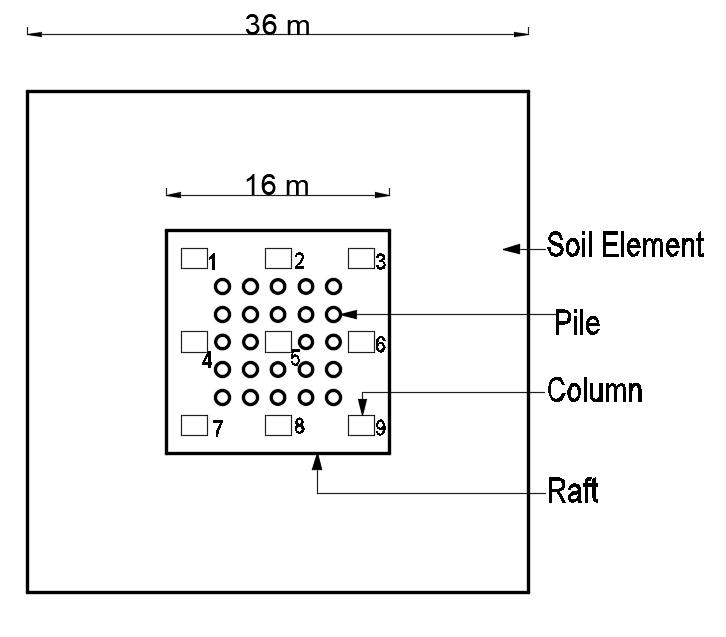
Fig -5:PositionofPilesinPiledRaftFoundation-TypeEPileatone-thirdofbay+pileatcolumncenter-line(24 Nos.ofPiles)
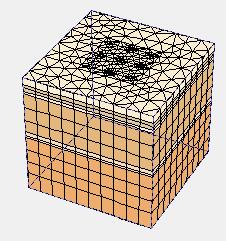
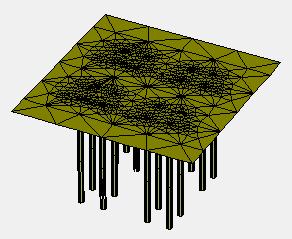
Thetypical3DmodelofPiledraftareshowninfigure6to 10:
-6: (a)TypicalmodelofRaftonly(withoutpiles);(b) generated3DmeshforGuwahati
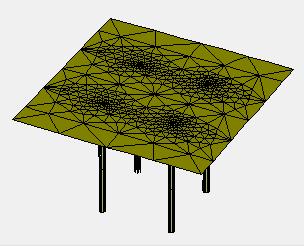
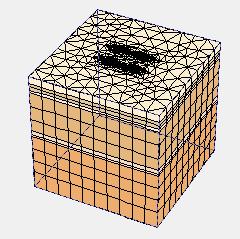
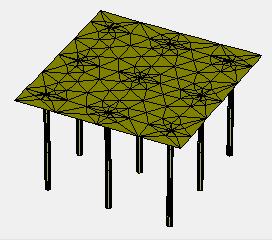
Typical
Piled
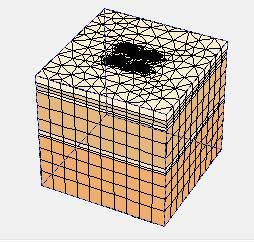


-10: (a)TypicalmodelofPiledRaftwith24piles;(b) generated3Dmeshfor

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thetotalverticalloadappliedis2470kNwhichisunequally distributed on nine equally spaced columns with 250kN vertical load each on 4 nos. of corner columns, 280kN on each 4 nos. of intermediate and 350kN on a single center column. This distribution of vertical load is based on the generalpatternofloaddistributionindifferentcolumnsofa building.
Here(i)ArepresentsNp=0(ii)BrepresentsNp=4&Pp=Pile athalfofbay(iii)CrepresentsNp=9&Pp=Piledirectlybelow thecolumn(iv)DrepresentsNp=16&Pp=Pileatone-thirdof bay (16 no. of piles) (v) E represents Np=24 & Pp= Pile at one-thirdofbay+pileatcolumncenter-line(24no.ofpiles)
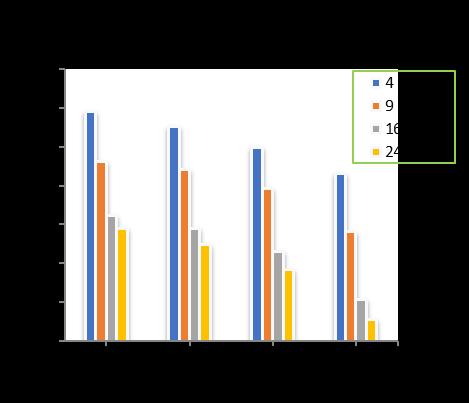
Chart-1showsthevariationoftotalsettlementofpiledraft foundation after loading at varied number of piles at pile diameter of 300 mm, pile length of 10m for varied raft thicknessoffrom300to400mm.
The maximum settlement of the piled raft foundation decreasesasthenumberofpilesincreases.Forraftthickness of300mm,introductionof4-piles,showsadecreaseintotal settlement up-to 4.23 %. Increasing the pile number to 9 (nine),totalsettlementdecreaseup-to12.60%withrespect to 4 (four) number of piles. Further increasing the pile number to 16 (sixteen), shows as decrease in total settlementup-to17.48%withrespectto9(nine)numberof piles.Again,increasingthepilenumberto24(twenty-four), there is a decrease in total settlement up-to 6.34 % with respect to 16 (sixteen) number of piles. Also, the total settlement reduces upto 35.30 % with introduction of 24 (twenty-four) numbers in comparison to unpiled raft of 300mmthickness.
Forraftthicknessof350mm,introductionof4-piles,showsa decreaseintotalsettlementup-to6.00%.Increasingthepile numberto9(nine),totalsettlementdecreaseup-to9.00% withrespectto4(four)numberofpiles.Furtherincreasing thepilenumberto16(sixteen),showsasdecreaseintotal settlementup-to20.36%withrespectto9(nine)numberof piles.Again,increasingthepilenumberto24(twenty-four), there is a decrease in total settlement up-to 6.20 % with respect to 16 (sixteen) number of piles. Also, the total settlement reduces upto 36.14 % with introduction of 24 (twenty-four) numbers in comparison to unpiled raft of 350mmthickness.
Forraftthicknessof400mm,introductionof4-piles,showsa decreaseintotalsettlementup-to6.81%.Increasingthepile numberto9(nine),totalsettlementdecreaseup-to11.64% withrespectto4(four)numberofpiles.Furtherincreasing thepilenumberto16(sixteen),showsasdecreaseintotal
settlementup-to19.67%withrespectto9(nine)numberof piles.Again,increasingthepilenumberto24(twenty-four),
there is a decrease in total settlement up-to 6.27 % with respect to 16 (sixteen) number of piles. Also, the total settlement reduces upto 38.01 % with introduction of 24 (twenty-four) numbers in comparison to unpiled raft of 400mmthickness.
Afterincreasingtheraftthicknessfrom300to400mmata pilediameterof300mm,thepilelengthincreasedfrom10 to18m,alongwithincreaseinthenumberofpilesfrom4 (four) to 24 (Twenty-four) shows a decrease in the settlementupto29.36%forpilelengthof10m,30.22%for pilelengthof12m,34.41%forpilelengthof15mand36.84 %forpilelengthof18mrespectivelyincomparisontounpiledraft.(Chart-1,Chart-2,Chart-3&Chart-4)
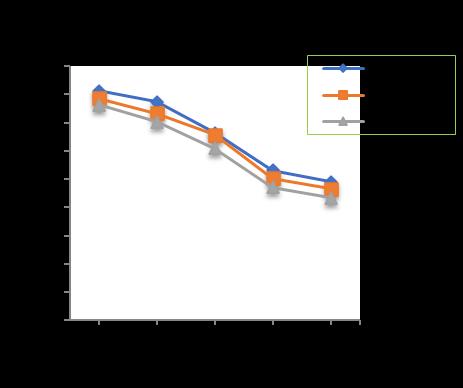
-1: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.
300 mmandPilelength=10m
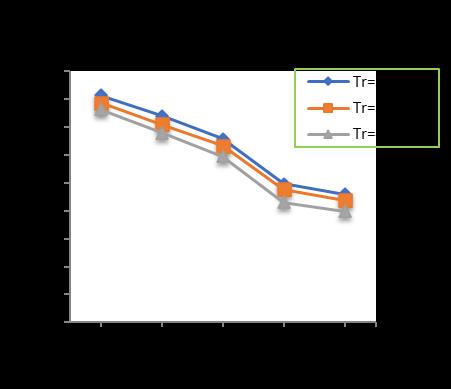
-2: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=300 mmandPilelength=12m

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
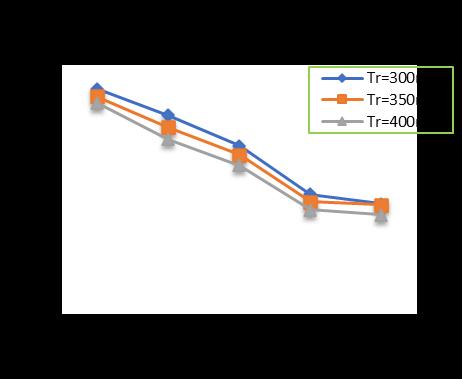
-3: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=300 mmandPilelength=15m
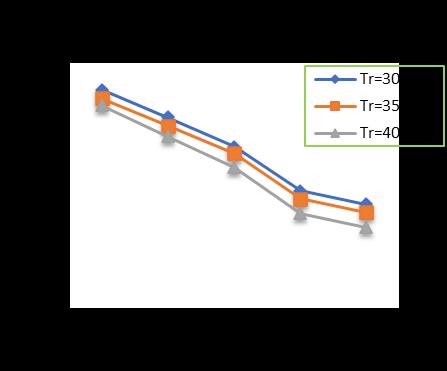
-4: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=300 mmandPilelength=18m
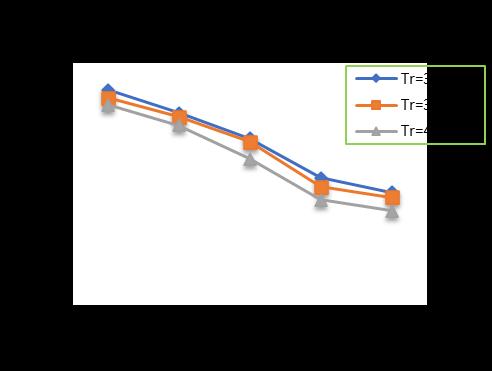
-5: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=400 mmandPilelength=10m

-6: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=400 mmandPilelength=12m
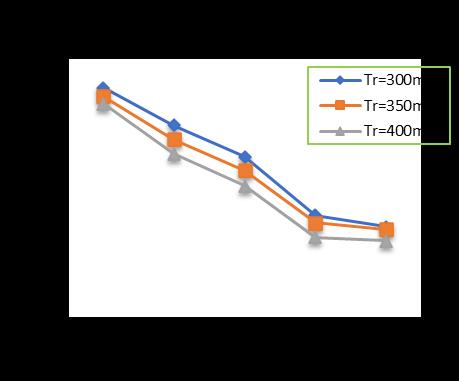
Chart -7: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=400 mmandPilelength=15m
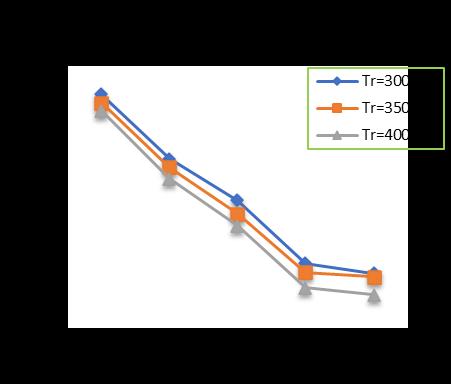
Chart -8: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=400 mmandPilelength=18m

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
At pile diameter 400 mm, with increase in raft thickness from 300 to 400 mm and subsequently increase in pile lengthfrom10mto18malongwithincreaseinthenumber ofpilesfrom4(four)to24(Twenty-four)showsadecrease inthesettlementupto32.81%forpilelengthof10m,35.79 %forpilelengthof12m,40.93%forpilelengthof15mand 42.58%forpilelengthof18mrespectivelyincomparisonto un-piledraft.(Chart-5,Chart-6,Chart-7,Chart-8)
At pile diameter 500 mm, with increase in raft thickness from 300 to 400 mm and subsequently increase in pile lengthfrom10mto18malongwithincreaseinthenumber ofpilesfrom4(four)to24(Twenty-four)showsadecrease inthesettlementupto35.52%forpilelengthof10m,37.21 %forpilelengthof12m,44.74%forpilelengthof15mand 49.17%forpilelengthof18mrespectivelyincomparisonto un-piledraft.(Chart-9,Chart-10,Chart-11,Chart-12)
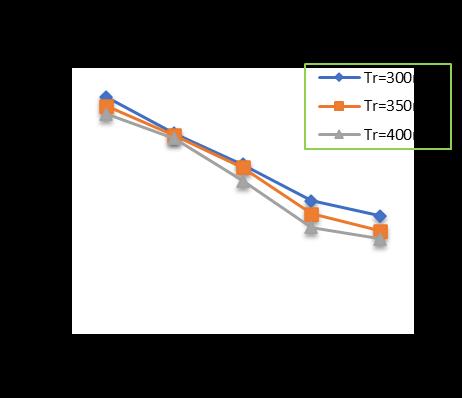
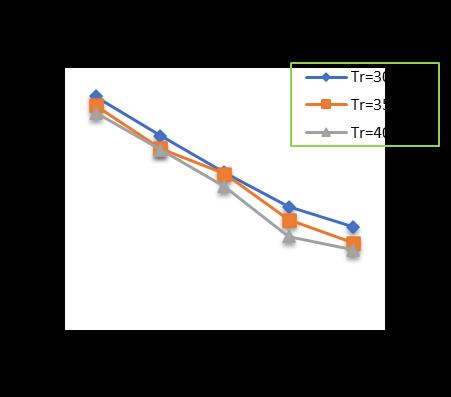
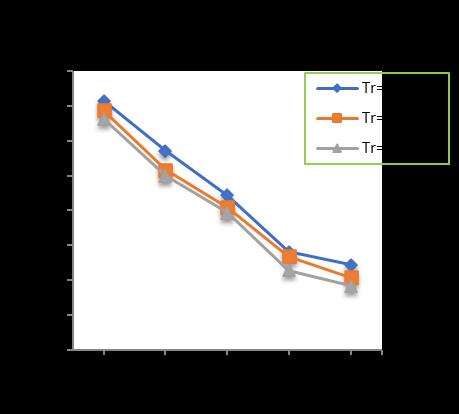
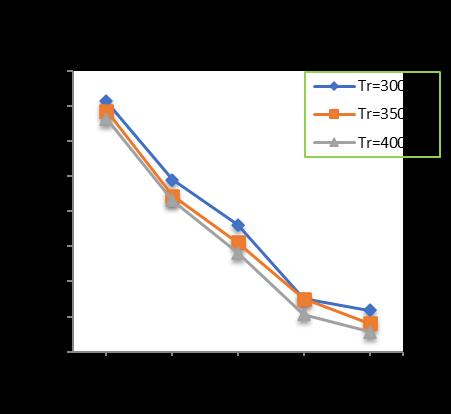
-12: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=500 mmandPilelength=18m
Figures below shows the variation of total settlement of piledraftfoundationafterloadingwithincreaseinthelength ofpilesfrom10mto18matvariednumberofpilesfrom4to 24numbersataparticulardiameterofpileandthicknessof raft. From chart-13, 14 & 15, it is significant that as the lengthofpileincreases,totalsettlementdecrease.
Atpilediameterof300mm,raftthicknessof300mmwith increase of pile length from 10m to 18 m, increase in the number of piles shows a decrease in the total settlement upto9.24%for4nos.ofpiles,17.08%for9nos.ofpiles, 32.06%for16nos.ofpilesand32.52%for24nos.ofpiles respectivelyincomparisontounpiledraft.(Chart-13)
Atpilediameterof300mm,raftthicknessof350mmwith increase of pile length from 10m to 18 m, increase in the

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
number of piles shows a decrease in the total settlement upto11.19%for4nos.ofpiles,26.81%for9nos.ofpiles, 32.89%for16nos.ofpilesand35.15%for24nos.ofpiles respectivelyincomparisontounpiledraft.(Chart-14)
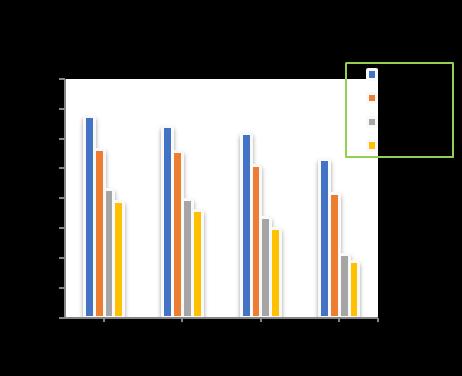
Chart -13: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=300 mmandRaftthickness=300mm
Atpilediameterof300mm,raftthicknessof400mmwith increase of pile length from 10m to 18 m, increase in the number of piles shows a decrease in the total settlement upto11.87%for4nos.ofpiles,29.89%for9nos.ofpiles, 34.75%for16nos.ofpilesand36.84%for24nos.ofpiles respectivelyincomparisontounpiledraft.(Chart-15)
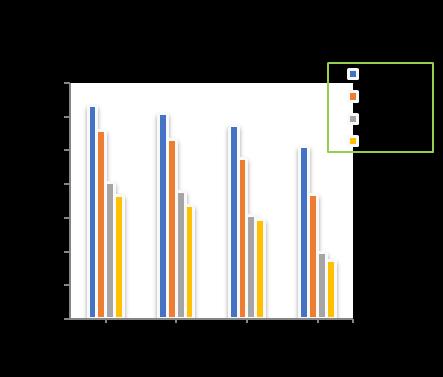
Chart -14: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=300 mmandRaftthickness=350mm
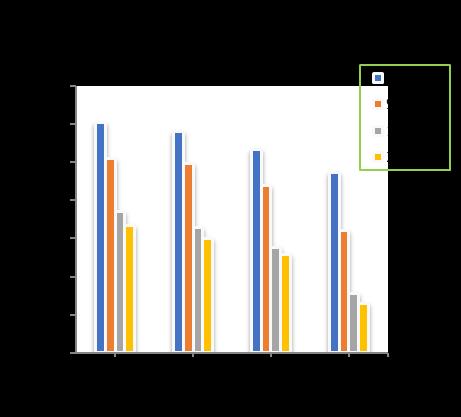
Chart -15
Atpilediameterof 400mm, raftthicknessof300 mmwithincreaseofpilelengthfrom10mto18m,increase in the number of piles shows a decrease in the total settlement upto 10.97 % for 4 nos. of piles, 28.97 % for 9 nos.ofpiles,33.38%for16nos.ofpilesand38.81%for24 nos. of piles respectively in comparison to unpiled raft. (Chart-16)
Atpilediameterof 400mm, raftthicknessof350 mmwithincreaseofpilelengthfrom10mto18m,increase in the number of piles shows a decrease in the total settlement upto 12.19 % for 4 nos. of piles, 30.33 % for 9 nos.ofpiles,39.55%for16nos.ofpilesand41.02%for24 nos. of piles respectively in comparison to unpiled raft. (Chart-17)
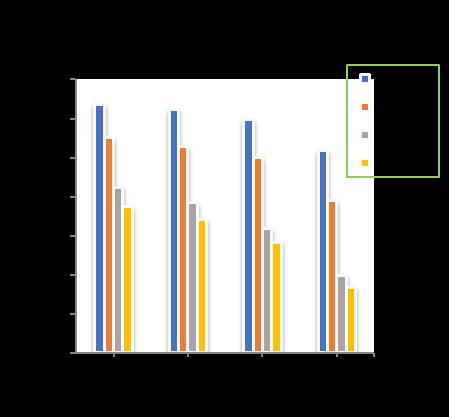
-16: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=400 mmandRaftthickness=300mm

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
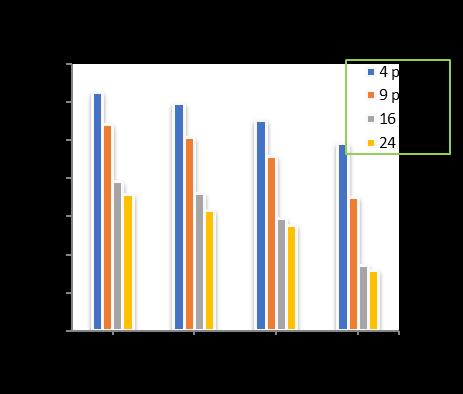
-17: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=400 mmandRaftthickness=350mm
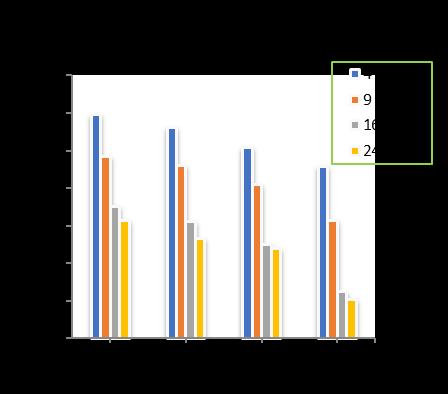
Chart -18: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=400 mmandRaftthickness=400mm
Atpilediameterof400mm,raftthicknessof400mmwith increase of pile length from 10m to 18 m, increase in the number of piles shows a decrease in the total settlement upto15.55%for4nos.ofpiles,30.66%for9nos.ofpiles, 40.99%for16nos.ofpilesand42.57%for24nos.ofpiles respectivelyincomparisontounpiledraft.(Chart-18)
Atpilediameterof 500mm, raftthicknessof300 mmwithincreaseofpilelengthfrom10mto18m,increase in the number of piles shows a decrease in the total settlement upto 13.53 % for 4 nos. of piles, 34.21 % for 9 nos.ofpiles,35.26%for16nos.ofpilesand42.51%for24 nos. of piles respectively in comparison to unpiled raft. (Chart-19)
Atpilediameterof 500mm, raftthicknessof350 mmwithincreaseofpilelengthfrom10mto18m,increase
in the number of piles shows a decrease in the total settlement upto 16.32 % for 4 nos. of piles, 35.26 % for 9 nos.ofpiles,37.56%for16nos.ofpilesand42.55%for24 nos. of piles respectively in comparison to unpiled raft. (Chart-20)
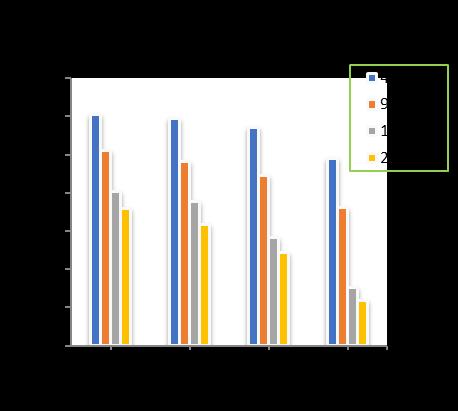
-19: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=500 mmandRaftthickness=300mm
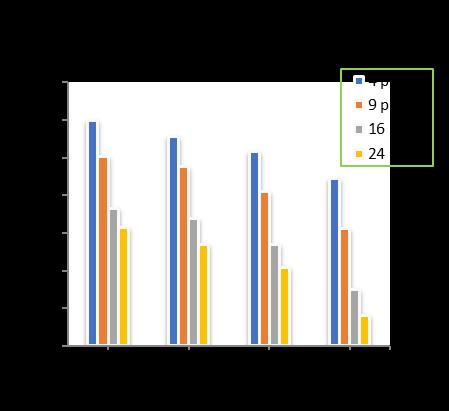
-20: VariationofTotalSettlementforPileDia.=500 mmandRaftthickness=350mm
Atpilediameterof 500mm, raftthicknessof400 mmwithincreaseofpilelengthfrom10mto18m,increase in the number of piles shows a decrease in the total settlementupto17.76%for4nos.ofpiles,38.5%for9nos. ofpiles,46.78%for16nos.ofpilesand49.17%for24nos. ofpilesrespectivelyincomparisontounpiledraft.(Chart21)

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1) Asthepilelengthincreasesinindividualpiledraft foundation in layered soil of Guwahati, the settlementdecreases.Introductionof4(four)piles can reduce the total settlement up-to nearly 17% (seventeenpercent)inlayeredsoil.Increasingthe numberofpilesup-to9(nine)canreducethetotal settlementup-tonearly38%(thirtyeightpercent) inlayeredsoil.However,furtherincreaseinnumber of piles up-to 16 (sixteen), can reduce the total settlementup-tonearly46(fortysixpercent).When thenumberofpilesis24(twenty-four),settlement reducesup-to49%(fortyninepercent).
2) Increaseinthenumberofpilesup-to16(sixteen) has considerable contribution in decreasing the settlementofpiledraftfoundationinlayeredsoil. However, further increase in the number of piles doesnotcontributemuchinreducingsettlement
3) The thickness of raft has nominal effect on the settlementofpiledraftfoundation.Asthethickness of raft increases, the settlement of the piled raft foundation decreases. However, the decrement is verynominalduetotheincreaseinself-weight.So, itcanbeconcludedthatincreasingthethicknessof raft does not contribute much to the reduction of settlement.
4) In case of pile groups, position of piles has much effect to the reduction of settlement of piled raft foundation.Introductionofpilesbelowcolumnata considerable distance from column center shows good results than piles positioned just below the column.
[1] AnbazhaganP.et.al.(2014)“ProvisionsforGeotechnical aspectsandSoilClassificationinIndianSeismicDesign CodeIS-1893,”DisasterAdvances,Vol7(3)March2014.
[2] Banerjee, R., Bandyopadhyay, S., Sengupta, A., and Reddy,G.R.,(2020)“Settlementbehaviourofapileraft subjected to vertical loadings in multilayered soil”, GeomechanicsandGeoengineering,Volume-17,Issue-1, Pages-282-296.
[3] Bowles,J.E.(1997).“FoundationAnalysisandDesign” Fifth Edition, Mc Graw Hill and Design, ISBN-0-07118844-4
[4] NDMA, “Development of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Map of India” Technical Report of the Working Committee of Experts (WCE) Constituted by The NationalDisasterManagementAuthorityGovt.ofIndia, New Delhi. Published in web page: http://ndma.gov.in/ndma/eqinfomation.
[5] Patowary,B.N.,Nath,U.K.,(2023).“StudyofPiledRaft Foundation on Layered Soil subjected to Vertical Loading,”SustainableCivilInfrastructureDevelopmentCaseStudies.ISBN-979-8-9884971-0-3(e-book),979-89884971-1-0(print)
[6] Patowary, B. N., Nath, U.K., (2022, December 15-17). “Study of Piled Raft Foundation on Layered Soil,” GEOLEAP-Geotechnics: Learning, Evaluation, Analysis and Practice, Indian Geotechnical Conference (IGC2022),Kochi.
[7] Poulos, H.G. and Davis, E.H. (1980). “Pile Foundation AnalysisandDesign,”JohnWiley. New York.
[8] Poulos, H.G. (1994), “An Approximate Numerical Analysis of Pile-raft Interaction,” Int. Jl. for Numerical andAnalyticalMethodsinGeomechanics,Vol.18,pp.5772.

Bhaskarendra Nath Patowary is a PhD scholaratAssamEngineeringCollegeunder GauhatiUniversity,Assam,India.Heholdsa Bachelor’sdegreeinCivilEngineeringanda Masters degree in Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. He has over 5 years of academic experience. His field of study is Foundation Engineering. His research interests include piled raft foundation, bank stability analysis and compressedstabilisedearthblock.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | June 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

Prof.U.K.Nathhasthirtyyearsofteaching experience in different State Engineering College under the Directorate Technical Education of Govt. of Assam. His field of research interest are foundation engineering, concrete technology, neural network etc. He published total forty-six number of papers in different field of his interested.