
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Shaktisinh Raol1 , Aakash Suthar2
,
1M.Tech Student, L.J. University, Ahmedabad
2Aakash Suthar, Professor, Structural Engineering Department, L.J. University, Ahmedabad, India
Abstract - This study provides a detailed comparative analysis of three different foundation systems: Raft Foundation, Raft with Drop, and Pile Raft Foundation. Utilizing advanced structural analysis and design software, the research explores the structural and geotechnical behaviorsofthesefoundations.Theperformanceisevaluated undervariousloadingconditionsandsoilprofiles,focusingon critical factors such as soil pressure, punching shear, settlement, and overall structural integrity. CSI SAFE software'sfiniteelementanalysiscapabilitiesareemployedto model bearing capacity, settlement characteristics, and the interaction between the foundation and soil. This approach offers a comprehensive understanding of the geotechnical aspectsinvolved
Key Words: Foundation Design, Raft Foundation, Pile Raft foundation, Raft with Top Cap, Structural Design, Seismic Load, CSI SAFE, Etabs.
Choosing the appropriate foundation system for high-rise buildings is crucial for their stability and resilience in structural engineering. As urban landscapes continue to develop vertically, a deeper understanding of foundation designbecomesincreasinglyimportant.Thisstudyutilizes ETABSandCSISAFEsoftwaretoperformacomprehensive comparativeanalysisofRaftFoundation,RaftwithTopCap, andPileRaftFoundation,withthemainobjectivebeingto evaluate and compare their geotechnical responses and structuralperformanceinhigh-risebuildings.
By focusing on the complex interactions between these foundationsystemsunderdifferentseismiczonesandsoil types, this research aims to provide valuable insights for practitionersandstakeholders.Theseinsightswillfacilitate informeddecision-makinginselectingfoundationsystems that effectively address the challenges of various seismic conditionsandsoilprofiles.Theultimateaimistocontribute to the ongoing enhancement of foundation design techniques,ensuringthestructuralintegrityandlong-term resilience of high-rise buildings in dynamic urban environments.
Theapplication ofETABS forstructural analysisreflects a commitment to utilizing advanced computational tools to
improve the structural components of tall buildings. This includes assessing structural responses to diverse loads, ensuringcompliancewithsafetyregulations,andoptimizing overall performance. Simultaneously, detailed foundation modelling with CSI SAFE software highlights the essential roleoffoundationsinmaintainingthestructuralintegrityof high-risebuildings.
TocompareRaftFoundation,RaftwithTopCap,and PileRaftFoundationusingstructuralanalysisand designsoftware.
To support ongoing advancements in high-rise buildingfoundationdesignmethodologies,ensuring long-term resilience and structural integrity in dynamicurbanenvironments.
To provide a comprehensive understanding of different foundation types, their advantages and disadvantages,suitableapplications,anddesignand constructionconsiderations.
Toresearchandevaluatevariousfoundationtypes used in the construction industry, exploring their designs and the use of alternative materials to enhance firmness, durability, and environmental sustainability.
To develop robust, cost-effective, and environmentallyfriendlyfoundationbasesforboth bungalowsandtallbuildings.
To examine factors such as soil bearing capacity, settlement, and seismic behaviour in relation to Raft,RaftwithTopCap,andPileRaftfoundations.
The multistory building with a different seismic zone and soilconditionanalyzed and designed fromEtabssoftware after that export base reactionsfilefor CSI SAFEsoftware then import this file to safe software. In safe there are majorlyfivestepsfordesignedandanalysisoffoundation: Import ETABS Data File Define, Draw, Assign, Analysis, Design.ForanalysisofRCCstructurestheremustberequire goodamountofknowledgeofIScodesandFundamentalof structures. Total 27 models are made for the exact data validationandforcomparison

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Table-1: Data Input in Etabs Model
Densityofblockmasonry
kN/m3 DensityofPlaster
GradeofConcreteinBeam&slab M25
GradeofConcreteinColumn M30
GradeofRebar Fe500

SoilSubgradeModuluswillbeSoilBearingCapacity ofsoilforanallowablesettlement,soifthesoilis soft soil and allowable settlement is 125 mm for SBC22Tonthen,
SoilSubgradeModulus= SBC/Allowablesettlement=220/0.125 =1760kN/m/m2
DefinedPileasaPointSpringPropertyandvalue ofthispropertywillbe,
PointSpringvalue=EcXApXH
Where,
Ec=4700X(Fc′)1/2
Fc′=Specified28-DayCompressive StrengthofConcrete
Ap=Cross-SectionAreaofPile
H=DepthofPile
ConsideredPileDiameter600mm,14mDepth& M25Gradeofconcrete.
SovalueofPointSpring, PointSpringValue=(2.35X106)X(0.28)X(14) =474604.89KN/m
Table-2: Data Input in Safe Model
SoilBearingCapacity 22Ton AreaofRaftFoundation 59.51mX39.27m
DepthofRaft 1200mm
DepthofRaftinRaftwith TopCap 1050mm
DepthoftopCap 750mm
AreaofRaftTopCap 2000mmX2000mm
NumberofRaftTopCap 30
DepthofRaftinPileRaft 1200mm
DiameterofPile 600mm
DepthofPile 14m
CompressiveCapacityofPile 825kN
NumberofPile 368
GradeofRaft&RafttopCap M25
GradeofPile M25
GradeofSteel FE500
AllowableSettlementinSoft Soil 125mm
AllowableSettlementin MediumSoil 100mm
AllowableSettlementin HardSoil 75mm
SoilSubgradeModulusin SoftSoil 1760kN/m2/m
SoilSubgradeModulusin MediumSoil 2200kN/m2/m
SoilSubgradeModulusin HardSoil 2933.34kN/m2/m
PointSpringforPile 474604.89KN/m
Usingtheabovedate,total27Safemodelswerepreparedfor allthreetypeoffoundationconcurringseismiczoneIII,IV andVwithdifferenttypeofsoil.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072



WithuseofSafesoftwaredifferenttypesoffoundationssuch asraftfoundation,Raftwithtop-capfoundationand pileraft foundationondifferenttypesofsoiltypeanddifferenttypes ofIndianseismiczonewerepreparedso therewas total27 foundation model observed and mainly, soil pressure, Average punching shear and settlement was noted. Those observationsarebelowinachartform.




International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
5.2 Settlement
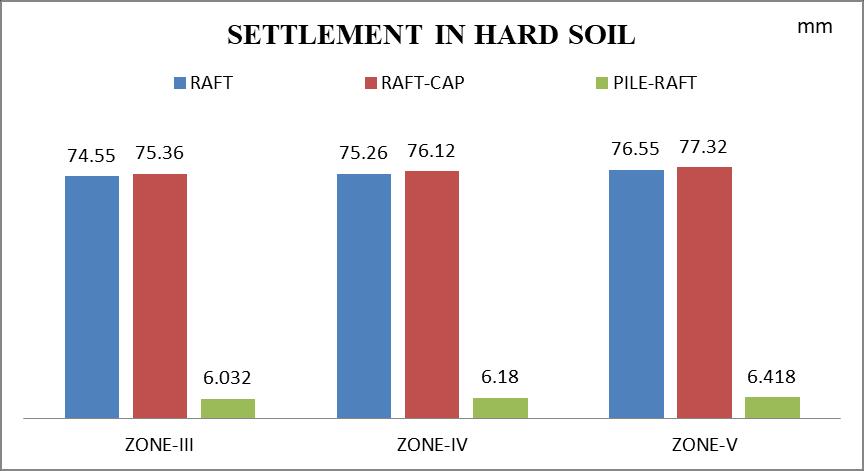


Average


6. Conclusions
Soilpressureincreasewithincreaseinseismiczone IIItoVinallthreetypeoffoundation.
SoilPressureisobservedlittlehighinraftwithtop cap foundation compare to raft foundation in all seismiczones.
Soilpressureinpileraftfoundationobservedvery less compare to raft foundation and raft with top capfoundation.
SettlementincreasewithincreaseinseismiczoneIII toVinallthreetypeoffoundation.
Settlement increases as all three types of foundationsmovefromhardtosoftsoil.
Settlement is observed little high in raft with top cap foundation compare to raft foundation in all seismiczones.
Settlement in pile raft foundation observed very less compare to raft foundation and raft with top capfoundation.
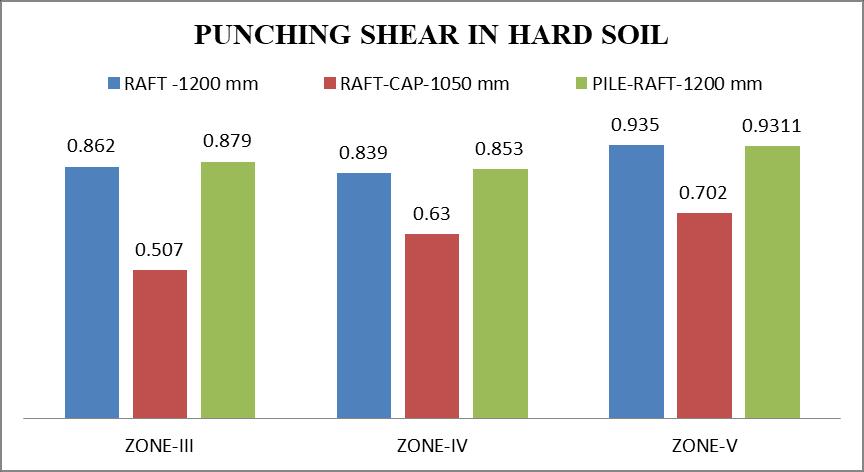
Punching shear increase with increase in seismic zoneIIItoVinallthreetypeoffoundation.
Punching shear increases as all three types of foundationsmovefromhardtosoftsoil.
Punching shear is observed very high in raft and pileraftfoundation.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 06 | Jun 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Punchingisobservedverylessinraftwithtopcap foundationcomparetoraftfoundationandpileraft foundationinallseismiczonesandsoiltype.
Pile raft foundation performed better in soil pressureandsettlementcomparetoraftfoundation andraftwithtopcapfoundationbutwhencomesto punchingshearinpileraftobservedhigh.
Pile with top cap with less thickness (1050mm) comparetoraftfoundation(1200mm)andpileraft foundation(1200mm).
[1] Magar, J., Kudtarkar, A., Pachpohe, J., & Nagargoje, P. (2020).Study andanalysisoftypesoffoundationand designconstruction.IRJET,7,3301-3307.
[2] Srivastava, R. K. Structural Design of Raft Foundation For30storyhighrisebuilding-AcasestudyinLucknow, UttarPradeshregion,India.
[3] Krishna,A.M.,Teja,A.P.,Bhattacharya,S.,&Ghosh,B. SeismicDesignofPileFoundationsforDifferentGround Conditions. In 15 World Conferences on Earthquake Engineering,Lisboa2012.
[4] Azhar, S., Patidar, A., & Jaurker, S. (2020). Parametric StudyofPiledRaftFoundationforHighRiseBuildings. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology,9(12),548-555.
[5] Dhage, A., & Solanke, S. S. (2023, June). Comparative Analysis of Raft, Pile & Piled Raft Foundation using DesigningSoftware.InIOPConferenceSeries:Earthand EnvironmentalScience(Vol.1193,No.1,p.012006).IOP Publishing.
[6] Shakir,S.,Mudassir,S.,&Abdullah,S.(2020).Analysisof Raft&PileRaftFoundationusingSafeSoftware.
[7] ReinforcedConcrete Vol.II.India,CharotarPublishing HousePvt.Limited,2008.
[8] IS 1904 (1986): Code of practice for design and construction of foundations in soils: General requirements [CED 43: Soil and Foundation Engineering]
[9] IS 2911-1-4 (2010): Code of practice for design and constructionofpilefoundations,Part1:Concretepiles, Section4:Boredprecastconcretepiles[CED43:Soiland FoundationEngineering]