
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Mihir Dungria1 , Kishan jayswal2 , Aakash suthar3
1M.Tech Student, L.J. University, Ahmedabad
2Kishan Jayswal, Assistance Professor, Civil Engineering Department, L.J. University, Ahmedabad, India.
Abstract – Intoday'srapidlyevolvinggloballandscape,the constructionsectorstandsasalinchpinofeconomicgrowth. While high-rise buildings are esteemed symbols of modernity,traditionalReinforcedConcrete(RCC)methods often prove cost-prohibitive. This study delves into the advantages of employing Post-Tensioning technology to enhancestructuralrobustness,withstandlateralforces,and optimizefinancialoutlay.Post-Tensionedconstructionsare renowned for their superior cost-efficiency and durability over RCC, minimizing steel and concrete usage while maximizingroomclearspans.TheresearchutilizesETABS (ExtendedThree-DimensionalAnalysisofBuildingSystems) to design a Post-Tensioned high-rise in compliance with IndianStandarddesigncodes.Acomprehensivecomparative analysis is conducted for a G+25 floor asymmetrical plan, accountingforwindandseismicloads.
Key Words: P.T. slab, R.C. slab, E-tabs, Overturning Moments, Displacements along both x and z axes..
Buildingsmustbedesignedtowithstandnaturalforceslike earthquakes and wind to ensure structural integrity and safety.ETABSsoftwareisintegral inthis process,offering advancedtoolsforcomprehensiveanalysisanddesign.For seismic analysis, ETABS employs Response Spectrum AnalysisandTimeHistoryAnalysismethods.Thesepredict how buildings will react to various frequencies and durationsofgroundshaking,aligningwithIndianStandard IS1893forearthquakeresistance.Simultaneously,ETABS addresseswindeffectsthroughstaticanddynamicwindload analysesperIS875(Part3).Staticanalysiscalculatesforces basedonbuildinggeometryandexposure,assumingsteady wind pressure. Dynamic analysis considers wind's fluctuating nature, assessing responses to varying speeds andgustsovertime.Byintegratingtheseanalyses,ETABS facilitatesdetailed3DmodelingofG+25reinforcedconcrete buildings,applyingloadstosimulateresponsesandidentify vulnerabilities. This approach ensures compliance with safetystandards,optimizingdesignforstructuralresilience andcostefficiency.

An RCC slab is crucial in construction projects such as buildingsandbridges,providingaflat,horizontalsurfacefor floorsandroofs.Ittypicallyconsistsofconcretereinforced withsteelrebarstoenhanceitstensilestrength.Construction beginswithsettingupformworktodefinetheslab'sshape anddimensions.Structuraldrawingsguidetheplacementof steelreinforcementtoresistbendingandshearforces.Once the reinforcement is inspected and approved, concrete is pouredintotheformworkandcompactedtoremovevoids and air pockets. Curing follows to ensure the concrete reachesitsrequiredstrength.Aftercuring,theformworkis removed,unveilingastronganddurableRCCslabcapableof supporting designated loads and serving as a functional surfaceforthestructure.
PT(post tensioning ) slab:
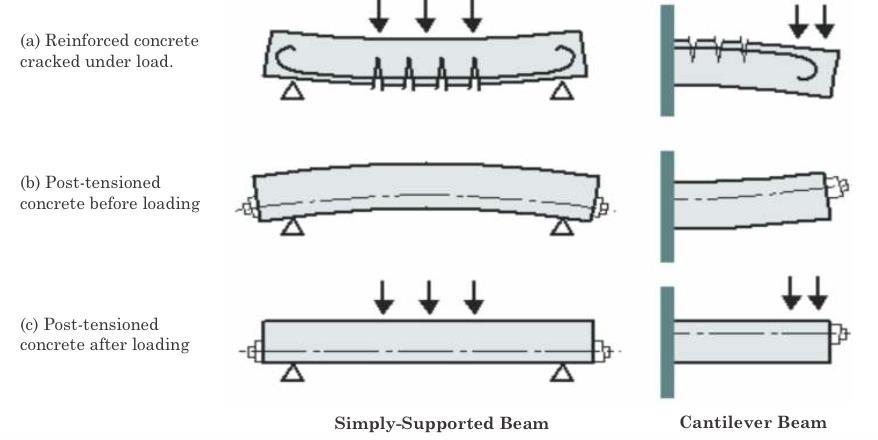
APost-Tensioned(PT)slabiscrucialinconstructionprojects suchasbuildingsandbridges,providingalevel,horizontal surfaceforfloorsandroofs.UnliketraditionalRCCslabs,PT

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
slabsusehigh-strengthsteeltendonsthataretensionedafter the concrete has set to enhance load-bearing capacity. Construction begins by erecting formwork to define the slab'sdimensionsandshape.Structuraldrawingsguidethe preciseplacementofhigh-strengthsteeltendonswithinthe formwork to effectively resist bending and shear forces. Afterinspectionandapprovalofthetendonlayout,concrete is poured into the formwork and compacted to eliminate voidsandairpockets.Curingfollowstoensuretheconcrete reachesitsrequiredstrength.Subsequently,hydraulicjacks are used to tension the tendons and anchor them at the slab'sends,placingtheslabundercompressiontoimprove resistancetocrackingandincreaseloadcapacity.Oncecured andtensioned,theformworkisremoved,revealingadurable PT slab capable of supporting designated loads and providingafunctionalsurfaceforthestructure.
Evaluate and compare structural performance of tensioned slabs vs. traditional RCC slabs under seismicandwindloads.
AssessresilienceoftensionedslabsandRCCslabs toseismicandwindforces.
Analyzeefficiencyofbothapproachesinenhancing seismicandwindresistance,consideringstrength, flexibility,anddeformability.
Identify strengths and weaknesses of tensioned slabs versus RCC methods for slab design and construction.
UtilizeETABSsoftwareforstructuralanalysis
2. Literature Review
[1] Bahoria, Boskey Vishal, and Dhananjay K. Parbat. "Analysis and design of RCC and post-tensioned flat slabs considering seismic effect." International journal of engineering and technology 5.1 (2013): 10.
The post-tensioning method is increasingly favored in modern construction for its economic and safe design applications. This study focuses on designing a posttensioned flat slab for a G+4 office building using load balancing and an equivalent frame method. Four different floorsystemsareevaluated,andcalculationsforquantitiesof reinforcingsteel,prestressingsteel,andconcreteneededfor slabs,beams,andcolumnsarepresentedintabularformat. Eachcase'stotalbuildingcostpersquaremeterisdetermined for a comprehensive cost comparison. The introduction highlightstheimportanceoffloorsystemsinoverallbuilding costsandintroducespost-tensioningasanefficientsolution, listing technical and economic advantages. The conclusion underscores additional benefits of post-tensioned construction, emphasizing its versatility across different buildingscenariosandoutliningspecificadvantagesofposttensioned slabs over traditional reinforced concrete slabs, includingcost-effectivenessandincreasedspancapabilities.
[2] Satwika, Vanteddu, and Mohit Jaiswal."Comparison of RCC and Post-Tensioned Flat Slabs Using ETABS." IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. Vol. 982. No. 1. IOP Publishing, 2022.
This study focuses on addressing the issue of insufficient punching shear capacity in flat slabs, a common structural challenge. Conventional methods such as increasing slab thickness or column size often conflict with architectural objectives. The research introduces post-tensioning as a solution to enhance flat slab strength, comparing conventionallyreinforcedconcrete(RCC)flatslabswithposttensioned flat slabs using various tendon profiles. Posttensioned slabs demonstrate superior punching shear capacityevenwithshallowerdepths,resultinginenhanced cost-effectiveness.Thestudyhighlightsseveraladvantagesof post-tensioning,includingincreasedclearspans,reducedslab thickness,minimizedcrackinganddeflection,lighterbuilding structures, accelerated construction timelines, improved water resistance, and decreased reliance on traditional reinforcement. It explores technical details, benefits, and contrastswithtraditionalflatslabs,emphasizingthepotential ofpost-tensioningtoimprovestructuralperformance.
[3 Nighot¹, Shubham, Sopan Chinchole, Rohan Kapgate, and Sujesh D. Ghodmare⁴. "Analysis and design of post tension slab using ETABS software." (2020).
The construction industry is increasingly adopting posttensioningforitsnumerousadvantages,althoughcountries like India have yet to fully appreciate its benefits, particularly in the context of flat slabs. This study utilizes ETABSsoftwaretoevaluatethecost-effectiveness,strength, and serviceability of post-tensioned flat slabs in a commercialbuilding(G+7).Findingsindicatesignificantcost advantagescomparedtotraditionalRCflatslabs,positioning post-tensioningashighlysuitableformulti-storystructures. This method not only enhances structural strength and durabilitybutalsoimprovesaestheticappealwhileoffering aneconomicalalternative.Thestudyunderscoresthebroad applicability of post-tensioned slabs and concludes with a favorablecomparisonoverRCslabsintermsofconcreteand steelutilization.
[4] Chou, Chung-Che, and Jun-Hen Chen. "Seismic tests of post-tensioned self-centering building frames with column and slabrestraints." FrontiersofArchitectureand Civil Engineering in China 5 (2011): 323-334.
This study explores post-tensioned (PT) self-centering moment frames as a seismic-resistant alternative to conventionalmoment-resistingframes(MRFs).Itintroduces a methodology to assess column restraint and beam compressionforcesbasedoncolumndeformationandgap openings across all stories of a PT frame. Cyclic tests conducted on a full-scale, two-bay by one-story PT frame validatethisapproach.Additionally,thepaperproposesusing

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
aslidingslabtominimizerestraintsonPTframeexpansion andpresentsshakingtabletestsonareduced-scale,two-bytwo bay one-story PT building structure. The findings illustrateself-centeringbehaviorwithminimalvariationsin peak drifts, even during earthquake simulations, underscoring the seismic resilience potential of PT structures.Thestudyaddresseschallengesassociatedwith column and slab restraints in PT self-centering frames, offering insights and testing methodologies for further advancementandpracticalapplicationinconstruction
[5] Prajapati, Deepak, and Komal Bedi. "Post Tensioning Building Analysis Considering Seismic Zone V using Analysis Tools ETABS." (2019).
Intoday'srapidlyevolvingandcompetitiveenvironment,the construction sector plays a crucial role in national development,particularlywiththewidespreadadmiration forhigh-risebuildings.WhileReinforcedConcrete(RCC)has traditionally dominated construction methods, there is a growing shift towards Post-Tensioning for high-rise structures. Post-Tensioned buildings offer significant economic and durable advantages, reducing the required quantities of steel and concrete compared to RCC and enablinglargerclearspansinrooms.Thisstudyfocuseson the design of a Post-Tensioned building using ETABS software, which is specialized for systematic multistoried building designconforming toIndian Standardcodes. The comparative analysis includes an asymmetrical G+9 floor plan,accountingforwindloadsandsoilconditionstypicalof black cotton soil. Parameters evaluated include storey displacement,axialandshearforces,bendingmoments,drift, stiffness,overturningmoments,andcostanalysisbasedon ScheduleofRates(S.O.R).Theresearchaimstodemonstrate theeconomicandstructuralbenefitsofPost-Tensioningin theconstructionofhigh-risebuildings.
[6] Yogesh Poptani ,Prerna Girepunje Lokesh Singh” Analysis of Behavior of Post Tensioning Slab for Various Framing Under the Influence of Lateral Load” International Journal of Scientific Research in Civil Engineering January-February-2019, Volume 3, Issue 1
Inmodernconstructionpractices,post-tensioningsystems are preferred over pre-stressing systems due to their reduced losses and flexibility in tendon shaping. PostTensioned(PT)tendonsarecommonlyutilizedinflatslabs to enhance crack and deflection control, enabling larger span-to-thickness ratios (typically 35 to 45), compared to Reinforced Concrete (RC) slabs which typically achieve ratiosupto30.PTsystemsalsocontributetoreducingfloorto-floorheightsandoverallstructuralweight.Additionally, post-tensioning enhances construction efficiency, sustainability, and durability. However, it is crucial to understand and analyze the behavior of flat slab systems under lateral forces, particularly in seismic regions. Evaluatingtheseismicresistanceofsuchbuildings,withor without a Lateral Force Resisting System, is essential.
Nonlinear static analysis serves as a valuable tool in this context,providingapracticalandintermediatesolutionto predictforcesanddeformationdemandscausedbyseismic motions. This approach assists in accurately assessing structural strength and is particularly beneficial for performance-baseddesign.
International journal of research in engineering and technology January-February2019, Volume 3, Issue 1
Incontemporaryconstructionpractices,reinforcedconcrete (RC) frame buildings are prevalent, but flat slab buildings offer distinct advantages such as architectural flexibility, efficient space utilization, simplified formwork, and expeditedconstructiontimelines.However,theirstructural efficiency under seismic loading is a concern. This study investigates six buildings with varying heights (G+3, G+8, andG+12storeys)usingE-Tabssoftwaretoevaluatetheir performanceunderseismiczoneIVconditions.Comparing conventionalRCframestructureswithflatslabstructures, the study analyzes parameters including lateral displacement,storeydrift,storeyshear,columnmoments, axial forces, and natural time periods. The findings underscoretheneedforenhancedseismicdesignmeasures inflatslabconstructionstooptimizetheirperformancein earthquake-prone regions. Key conclusions highlight that momentspeakatlowerlevelsandvarywithheight,column behavior shifts with increased height, and columns are designed for combined dead and earthquake loads, with seismic load combinations being critical. Additionally, columnmomentsaregenerallyhigherinflatslabbuildings, ranging from 10% to 20% more than in RCC frames dependingonstoreyheight.Baseshearpeaksatlowerlevels anddecreaseswithheightbutincreasessignificantlyoverall withbuildingheight,withflatslabbuildingsexhibiting8%to 13%lowerbaseshearcomparedtoRCCbuildings.Lateral displacementincreaseswithstoreyheight,beinghighestat thetopstoreyand28%to57%greaterinflatslabbuildings, while natural time periods increase with building height, being14%to33%longerinflatslabbuildings,peakingat modes1and2anddecreasingnotablythereafter.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
DESIGNDATAOF BUILDING DATA
NUMBEROFSTORY G+15,G+20,G+25
TYPICALSTRORYHIGHT 3,3.2,3.5
COLUMNSIZE 300X600mm
SHEARWALLSIZE 375X1500mm
BEAMSIZE 375X900mm
THICKNESSOFSLAB 200mm
GRADEOFCONCRETE M35
GRADEOFSTEEL FE500
WALLTHICKNESS 230mm

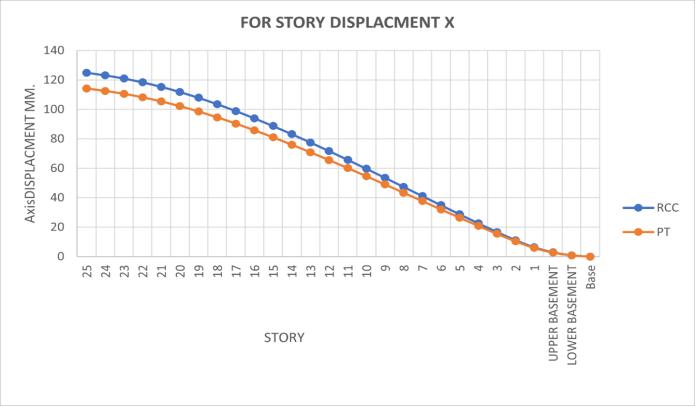
FIG 5: DISPLACMENT IN X DIRECTION
2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
3. CONCLUSIONS
Introduction of post-tensioning reduces bending moments, allowing for more economical section designscomparedtobareframes.
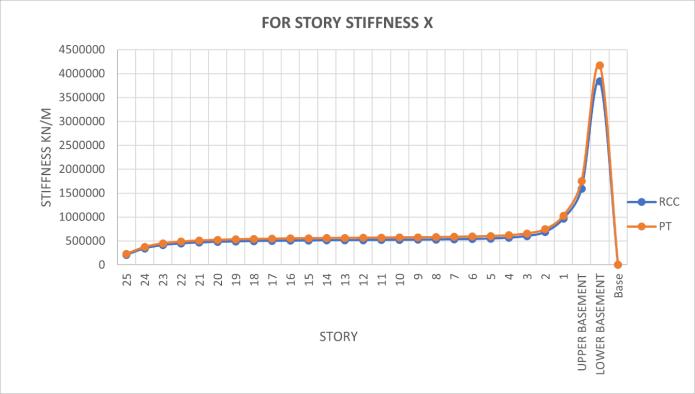
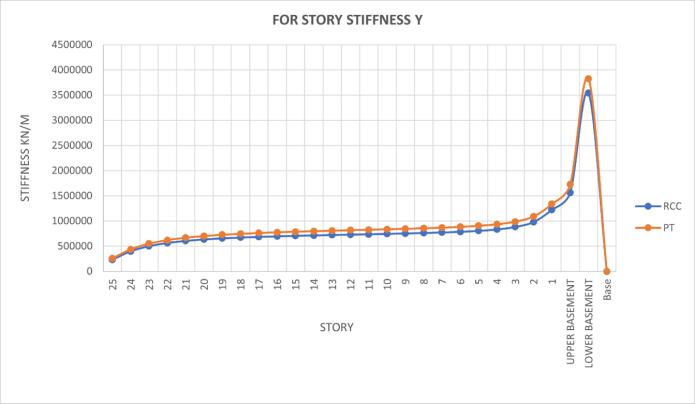
Post-tensioned structures minimize storey shear, therebyreducingtheriskofunbalancedforcesand enhancing structural stability against wind pressures.
Axialforcesinpost-tensionedframesareefficiently distributed in vertical members, contributing to structuralefficiency.
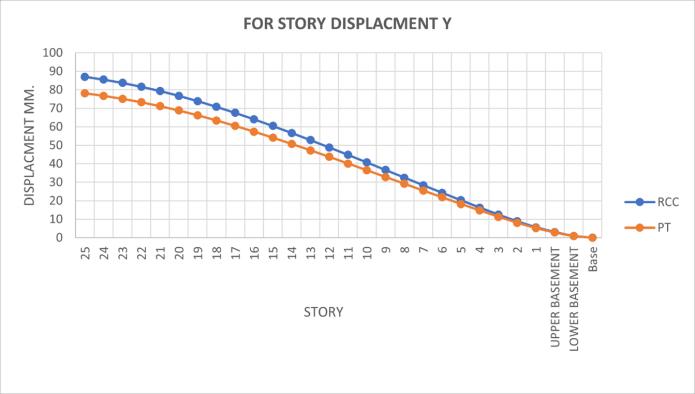
Post-tensioning significantly reduces relative displacement,improvingoverallstabilitycompared tobareframestructures.
Comparativeanalysisacrossaxialforcedistribution, storey stiffness, shear response, displacement characteristics,andbendingmomentsconsistently favorsPTslabsystemsoverRCCslabframes.
PT slabs exhibit approximately 20% less displacementunderappliedloadscomparedtoRCC slabs,indicatingsuperiorstability.
PTslabsdemonstrateapproximately12%greater stiffnessthanRCCslabs,highlightingtheirenhanced structuralrigidityandabilitytoresistdeformation.
In summary, PT slabs offer superior structural stability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness comparedtotraditionalRCCslabs.
[1] Bahoria, Boskey Vishal, and Dhananjay K. Parbat. "Analysis and design of RCC and post-tensioned flat slabsconsideringseismiceffect." International journal of engineering and technology 5.1(2013):10.
[2] Satwika,Vanteddu,andMohitJaiswal."Comparisonof RCC and Post-Tensioned Flat Slabs Using ETABS." IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.Vol. 982.No.1.IOPPublishing,2022.
[3] Nighot¹,Shubham,SopanChinchole,RohanKapgate,and Sujesh D. Ghodmare⁴. "Analysis and design of post tensionslabusingETABSsoftware."(2020)..
[4] Chou, Chung-Che, and Jun-Hen Chen. "Seismic tests of post-tensioned self-centering building frames with columnandslabrestraints." Frontiers of Architecture and Civil Engineering in China 5(2011):323-334.
[5] Prajapati, Deepak, and Komal Bedi. "Post Tensioning Building Analysis Considering Seismic Zone V using AnalysisToolsETABS."(2019).
[6] www.reinforcementproductsonline.co.uk was first indexedbyGoogleinJanuary2018
[7] https://sanfieldindia.in/browse/page/BuildingPostTen sionedSlab
[8] Poptani, Yogesh, K. Divya Kotecha, and Lokesh Singh. "Analysis of Behavior of Post Tensioning Slab for

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
VariousFramingUnderTheInfluenceofLateralLoad:A Review." International Journal of Scientific Research in Civil Engineering 4.1(2020):57-62.
[9] Navyashree, K., and T. S. Sahana. "Use of flat slabs in multi-storey commercial building situated in high seismic zone." International journal of research in engineering and technology 3.08(2014):439-451.
[10] Arkadiusz Mordak and Zbigniew Zee Manko (2016) “Effectiveness of Post-tensioned prestressed concrete road bridge realization in the light of research under dynamicloading”,“9thInternationalconference,Bridge inDanubeBaisn”Vol1,ISSN3463-4521
[11] Alpa Sheth“Effect of perimeter frames in seismic performanceoftallconcretebuildingswithshearwall coreandflatslabsystem”The14thWorldConference onEarthquake
[12] Rafal Szydlowski and Barbara Labuzek (2017),“PostTensioned Concrete Long-Span Slabs in Projects of Modern Building Construction”, “IOP Conf. Series: MaterialsScienceand Engineering”,Vol3,ISSN 45622132,pp245.
2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 |