
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Sailesh Oduri

Abstract:
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force in cloud infrastructure management, offering a decentralized,secure,andtransparentapproachtoprovisioning,monitoring,andoptimizingcloudresources.Thisarticle explores the revolutionary potential of blockchain-based cloud infrastructure management, highlighting its key benefits, such as enhanced security, increased efficiency, and improved trust. The article delves into the fundamental concepts of blockchain technology, including decentralization, immutability, consensus mechanisms, and smart contracts, and examinestheirapplicationinthecontextofcloudcomputing.Itdiscusseshowblockchainenablesautomatedandtamperproofresourcemanagement,decentralizedidentitymanagement,andgranulartrackingofresourceusageandbilling.The article also explores the potential of tokenization, incentivization mechanisms, and decentralized cloud marketplaces in driving cost optimization and resource efficiency. Additionally, it addresses the challenges and future directions of blockchain-based cloud infrastructure management, including scalability, regulatory compliance, interoperability, and adoption efforts. Through case studies and practical applications, the article demonstrates the real-world impact of blockchaininvariousindustriesand providesinsightsintothebenefitsandlessons learnedfromearlyadopters.Overall, this article presents a comprehensive overview of how blockchain technology is revolutionizing cloud infrastructure management,pavingthewayforamoresecure,efficient,andtrustworthycloudecosystem.
Keywords: Blockchain technology, Cloud infrastructure management, Smart contracts, Decentralized identity management,Tokenization
1. Introduction
Cloudcomputinghasemergedasatransformativetechnology,enablingorganizationstoleveragescalableandon-demand computing resources. However, traditional cloud infrastructure management faces challenges related to security,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
transparency, and efficiency [1]. Centralized control and reliance on intermediaries introduce vulnerabilities and hinder trust in cloud environments. Moreover, the lack of granular tracking and the presence of intermediaries lead to inefficienciesandincreasedcosts[2].
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable nature, presents a promising solution to address these challenges. By integrating blockchain into cloud infrastructure management, organizations can establish trust, enhance security, and improve efficiency [3]. Blockchain enables the creation of a transparent and tamper-proof record of transactions,eliminatingtheneedforintermediariesandreducingtheriskofunauthorizedaccessormanipulation.
Thisarticleexplorestherevolutionarypotentialofblockchain-basedcloudinfrastructuremanagement.Itaimstoprovide acomprehensiveoverviewofhowblockchainprinciplescanbeappliedtoenhancesecurity,efficiency,andtrustincloud environments. The article delves into the fundamentals of blockchain technology, including decentralization, consensus mechanisms,andsmartcontracts.Itdiscusseshowtheseconceptscanbeleveragedtoestablishtrust,automateresource management,andenabledecentralizedidentitymanagementincloudinfrastructures.
Furthermore,thearticleexaminestheefficiencyandcost-effectivenessaspectsofblockchain-basedcloudmanagement.It explorestheconceptoftokenization,whichallowsforgranulartrackingofresourceusageandfacilitatesaccuratebilling. Thearticlealsodiscussesthepotentialofdecentralizedcloudmarketplaces,whereorganizationscantradeexcesscapacity andprocureresourceswithouttheneedforintermediaries.
Thechallengesandfuturedirectionsofblockchain-basedcloudinfrastructuremanagementarealsoaddressed.Thearticle explores scalability and performance considerations, regulatory compliance, interoperability with existing cloud infrastructures, and adoption efforts. It presents case studies and practical applications, highlighting real-world implementationsandthebenefitsrealizedbyearlyadopters.
Overall, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how blockchain technology revolutionizes cloud infrastructuremanagement,pavingthewayforamoresecure,efficient,andtrustworthycloudecosystem.
Blockchain technology, at its core, is built upon the principles of decentralization, immutability, and consensus mechanisms. These fundamental concepts enable blockchain to establish trust, security, and transparency in various applications,includingcloudinfrastructuremanagement.
Aspect
Traditional Cloud Infrastructure Management
Blockchain-based Cloud Infrastructure Management
Security Centralizedcontrol,singlepointof failure Decentralized,enhancedsecurity
Transparency Limitedvisibility,lackoftrust Transparentandauditabletransactions
ResourceManagement Manualprocesses,pronetoerrors Automatedandtamper-proofthroughsmart contracts
IdentityManagement Centralizedidentityrepositories Decentralized,self-sovereignidentitysolutions
CostOptimization Limitedgranularity,inefficiencies Tokenization,granulartracking,incentivization
Marketplace Centralized,intermediary-dependent Decentralized,peer-to-peertrading
Table1:ComparisonofTraditionalandBlockchain-basedCloudInfrastructureManagement[1-3]
2.1. Decentralization and Immutability
Decentralization is a key characteristic of blockchain technology. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single authoritymaintainscontrol,blockchainoperatesonadistributednetworkofnodes[4].Eachnodeinthenetworkholdsa copyoftheblockchainledger,whichcontainsarecordofalltransactions.Thisdecentralizedstructureeliminatestheneed forintermediariesandreducestheriskofsinglepointsoffailure.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Immutability is another crucial property of blockchain. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes virtually tamper-proof. The cryptographic techniques used in blockchain ensure that any attempt to modify or delete a transaction would require an enormous amount of computational power, making it practically infeasible [5]. This immutabilityguaranteestheintegrityandtransparencyoftherecordeddata.
Consensusmechanismsarethealgorithmsthatgovernhowparticipantsinablockchainnetworkreachagreementonthe stateoftheledger.These mechanisms ensurethatall nodesinthe network havea consistentviewoftheblockchainand preventdouble-spendingorunauthorizedmodifications[6].
Oneofthemostwell-knownconsensusmechanismsisProofofWork(PoW),usedbyBitcoin.InPoW,minerscompeteto solvecomplexmathematicalpuzzlestovalidatetransactionsandaddnewblockstothechain.Thefirstminer tosolvethe puzzleisrewardedwithcryptocurrency.OtherconsensusmechanismsincludeProofofStake(PoS),wherevalidatorsare selectedbasedontheirstakeinthenetwork,andDelegatedProofofStake(DPoS),wheretokenholderselectdelegatesto validatetransactions.
Smartcontractsareself-executingagreementswiththetermsoftheagreementdirectlywrittenintocode.Theyarestored andreplicatedontheblockchainnetwork,enablingautomatedandtrustlessexecutionofcontractualterms[4].
In the context of cloud infrastructure management, smart contracts can be used to automate resource allocation, billing, and access control. They can define the rules and conditions under which cloud resources are provisioned, ensuring transparency and eliminating the need for manual interventions. Smart contracts can also facilitate the creation of decentralizedcloudmarketplaces,enablingpeer-to-peertradingofcloudresources.
The combination of decentralization, immutability, consensus mechanisms, and smart contracts forms the foundation of blockchain technology. These principles enable the creation of secure, transparent, and efficient systems, making blockchainapromisingsolutionforrevolutionizingcloudinfrastructuremanagement
Blockchain technology offers significant potential to enhance security in cloud environments. By leveraging the inherent propertiesofblockchain,suchasdecentralization,immutability,andcryptographictechniques,organizationscanestablish trust, ensure transparency, and mitigate various security risks associated with traditional cloud infrastructure management.
One of the primary challenges in cloud computing is establishing trust between cloud service providers and users. Blockchain technology addresses this issue by providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of transactions [7]. By recording all interactions and resource provisioning activities on the blockchain, stakeholders can verify and audit the actionsofcloudserviceproviders.Thistransparencyenhancesaccountabilityandfosterstrustinthecloudenvironment.
Moreover, the decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of data manipulation or unauthorized access. The distributed ledger ensures that all participants have a consistent view of the systemstate,makingitdifficultforanysingleentitytocompromisetheintegrityofthecloudinfrastructure[8].
Smart contracts play a crucial role in automating and securing resource management in blockchain-based cloud environments.Theseself-executingcontractscandefinetherulesandconditionsforresourceallocation,usage,andbilling [9].Byencodingthetermsofserviceandservicelevelagreements(SLAs)intosmartcontracts,cloudserviceproviderscan ensureautomatedandtamper-proofenforcementofresourceprovisioningpolicies.
Smart contracts can also facilitate the creation of decentralized marketplaces for cloud resources. Through these marketplaces, organizations can trade excess capacity and acquire additional resources on demand, without relying on

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
intermediaries. The automated execution of smart contracts ensures fair and transparent resource trading, reducing the riskoffraudormanipulation.
Identity management and access control are critical aspects of cloud security. Blockchain technology enables the implementationofdecentralizedidentitymanagementsystems,whereusershavefull control overtheirdigital identities [7].Decentralizedidentifiers(DIDs)andverifiablecredentialscanbeused toestablish secureandself-sovereignidentity solutions.
By leveraging blockchain-based identity management, cloud service providers can ensure that only authorized users can accesscloudresources.Smartcontractscanbeutilizedtodefineandenforceaccesscontrolpolicies,grantingorrevoking permissions based on predefined conditions. This decentralized approach eliminates the need for centralized identity repositories,reducingtheriskofdatabreachesandunauthorizedaccess.
Traditionalcloudinfrastructuresoftenrelyoncentralizedcomponents,suchascontrolplanesandmanagementsystems, which can introduce single points of failure. If these critical components are compromised or experience downtime, the entirecloudenvironmentcanbedisrupted.
Blockchain-basedcloudinfrastructuremanagementmitigatesthisriskbydistributingcontrolanddecision-makingacross anetworkofnodes[8].Thedecentralizedarchitectureensuresthatnosingleentityhascompletecontroloverthesystem, making it more resilient to failures and attacks. Even if a subset of nodes is compromised, the overall integrity and availabilityofthecloudenvironmentremainintact.
Furthermore,theuseofconsensusmechanismsinblockchainnetworksensuresthatallparticipantsagreeonthestateof the system. This distributed consensus helps prevent malicious actors from manipulating or corrupting the cloud infrastructure,enhancingoverallsecurityandreliability.
Blockchaintechnologyofferssignificantopportunitiestoenhanceefficiencyandcost-effectivenessincloudinfrastructure management.Byleveragingtokenization,granulartracking,incentivizationmechanisms,anddecentralizedmarketplaces, organizationscanoptimizeresourceutilization,streamlinebillingprocesses,andreduceoperationalcosts.
4.1.
Tokenization is the process of representing cloud resources as digital assets on the blockchain. Each token represents a specific unit of computing power, storage, or network bandwidth [10]. By tokenizing cloud resources, organizations can achieveamoregranularandflexibleapproachtoresourceallocationandmanagement.
Tokenizationenablesthecreationofatransparentandauditablerecordofresourceownershipandusage.Itallowsforthe fractional allocation of resources, enabling organizations to acquire and utilize resources in smaller increments. This granularity optimizes resource utilization and reduces waste, as organizations can precisely match their resource requirementswiththeavailabletokenizedassets.
Blockchaintechnologyenablesgranulartrackingofresourceusageandbillingincloudenvironments.Smartcontractscan beemployedtoautomaticallyrecordandvalidateresourceconsumptiondataontheblockchain[11].Thisimmutableand transparentrecordeliminatestheneedformanualreconciliationandensuresaccuratebillingbasedonactualusage.
Moreover,blockchain-basedsystemscanfacilitatereal-timetrackingandmonitoringofresourceutilization.Organizations cangaininsightsintotheircloudusagepatterns,identifyinefficiencies,andmakedata-drivendecisionstooptimizetheir resource allocation. This granular tracking also enables more precise cost allocation and chargeback mechanisms, ensuringfairandtransparentbillingpractices.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Blockchain-based incentivization mechanisms can be employed to encourage resource optimization in cloud environments. Smart contracts can define reward systems that incentivize users to adopt efficient resource utilization practices [12]. For example, users who release underutilized resources back to the pool or contribute excess capacity to thenetworkcanberewardedwithtokensordiscountedpricing.
Incentivization schemes can also promote the adoption of energy-efficient practices, such as using renewable energy sourcesoroptimizing workloadplacement. Byaligning incentives with resource efficiencygoals,organizations candrive behaviorchangeandfosteramoresustainableandcost-effectivecloudecosystem.
Decentralized cloud marketplaces, powered by blockchain technology, enable peer-to-peer trading of cloud resources. These marketplaces allow organizations to monetize their excess capacity by offering it to other participants in the network [10]. Buyers can acquire resources on demand from multiple providers, ensuring competitive pricing and reducingdependenceonasinglevendor.
Smart contracts automate the trading process, ensuring trustless and secure transactions. The decentralized nature of these marketplaces eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and enabling more efficient resource allocation. Organizations can dynamically adjust their resource procurement based on real-time market conditions,optimizingcostsandensuringoptimalutilizationofavailableresources.
Thecombinationoftokenization,granulartracking,incentivizationmechanisms,anddecentralizedmarketplacescreatesa more efficient and cost-effective cloud infrastructure management ecosystem. By leveraging these blockchain-based solutions, organizations can optimize resource utilization, reduce waste, and achieve significant cost savings while maintaininghighlevelsofperformanceandreliability.
While blockchain-based cloud infrastructure management offers numerous benefits, there are several challenges and futuredirectionsthatneedtobeaddressedtorealizeitsfullpotential.Scalability,regulatorycompliance,interoperability, andadoptionareamongthekeyconsiderationsthatwillshapethefutureofblockchaininthecloudcomputinglandscape.
Scalability is a significant challenge in blockchain-based systems, particularly when applied to cloud infrastructure management. As the number of transactions and participants in the network grows, the performance and throughput of theblockchainnetworkmaybeimpacted[13].Theconsensusmechanismsusedinblockchainnetworks,suchasProofof Work(PoW),canintroducelatencyandlimitthetransactionprocessingcapacity.
To address scalability issues, researchers are exploring various solutions, such as sharding, off-chain transactions, and layer-2scalingtechniques.Shardinginvolvespartitioningtheblockchainnetworkintosmaller,moremanageablesubsets, allowing for parallel processing and improved scalability. Off-chain transactions, such as payment channels or state channels, enable faster and more efficient processing of transactions outside the main blockchain. Layer-2 solutions, like side chains or nested blockchains, aim to offload some of the transaction processing from the main chain to improve overallperformance.
The adoption of blockchain-based cloud infrastructure management raises regulatory compliance and legal considerations. The decentralized nature of blockchain networks can pose challenges in terms of data privacy, security, and jurisdiction [14]. Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation(GDPR)intheEuropeanUnion,requirescarefuldesignandimplementationofblockchainsolutions.
Moreover, the legal implications of smart contracts and their enforceability need to be addressed. The automated executionofsmartcontractsmayraisequestionsregardingliability,disputeresolution,andthelegal status oftheseselfexecuting agreements. Establishing clear legal frameworks and guidelines for blockchain-based cloud systems will be crucialtofostertrustandadoption.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Integrating blockchain-based solutions with existing cloud infrastructures poses interoperability challenges. Many organizations have invested heavily in traditional cloud platforms and have established workflows and systems in place. Seamless integration and compatibility between blockchain-based solutions and existing cloud infrastructures are essentialforwidespreadadoption[15].
Efforts are being made to develop standards and protocols that enable interoperability between different blockchain networks and traditional cloud systems. Initiatives such as the Interledger Protocol (ILP) and the Blockchain InteroperabilityAlliance(BIA)aimtoestablishcommonstandardsandpromotecollaborationamongblockchainprojects. Addressing interoperability issues will be key to unlocking the full potential of blockchain in the cloud computing ecosystem.
The adoption of blockchain-based cloud infrastructure management depends on various factors, including awareness, technical maturity, and standardization efforts. Educating stakeholders about the benefits and potential use cases of blockchain in cloud computing is crucial to drive adoption. Collaborative efforts among industry players, academia, and regulatory bodies are necessary to establish best practices and guidelines for implementing blockchain solutions in the cloud.
Standardization efforts play a vital role in promoting interoperability, security, and trust in blockchain-based systems. OrganizationssuchastheIEEE,ISO,andITUareactivelyworkingondevelopingstandardsforblockchaintechnology.The IEEE has established the IEEE Blockchain Initiative to foster collaboration and standardization in various domains, including cloud computing [13]. These standardization efforts will provide a foundation for the development and deploymentofreliableandinteroperableblockchainsolutionsinthecloud.
















International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The potential of blockchain-based cloud infrastructure management has attracted attention from various industries, leading to real-world implementations and pilot projects. Exploring case studies and practical applications helps to understand the benefits, challenges, and lessons learned from early adopters, as well as to identify potential use cases acrossdifferentsectors.
Several organizations have already embarked on the journey of implementing blockchain-based solutions for cloud infrastructure management. One notable example is the collaboration between IBM and Maersk, which resulted in the development of TradeLens, a blockchain-based platform for the global shipping industry [16]. TradeLens utilizes blockchain technology to enable secure and transparent tracking of shipping containers, streamlining supply chain processesandreducingadministrativecosts.
Another real-world implementation is the Energy Web Foundation's Energy Web Chain, a blockchain platform designed for the energy sector [17]. The Energy Web Chain enables decentralized energy trading, renewable energy certificate (REC) tracking, and grid balancing, leveraging blockchain's transparency and immutability to create a more efficient and sustainableenergyecosystem.
Earlyadoptersof blockchain-based cloudmanagement havereportedseveral benefits,includingincreased transparency, enhancedsecurity,andimprovedefficiency.Forinstance,theimplementationofTradeLenshasreducedthetimerequired for document processing and container tracking, leading to significant cost savings and operational efficiencies for participantsintheshippingindustry[16].
However,earlyadoptershavealsoencounteredchallengesandlearnedvaluablelessonsalongtheway.Onekeylessonis theimportanceofstakeholdercollaborationandalignment.Blockchain-basedsolutionsoftenrequiretheparticipationand buy-in of multiple stakeholders, including industry partners, regulators, and technology providers. Building trust, establishing governance frameworks, and ensuring interoperability are critical success factors for blockchain projects [18].
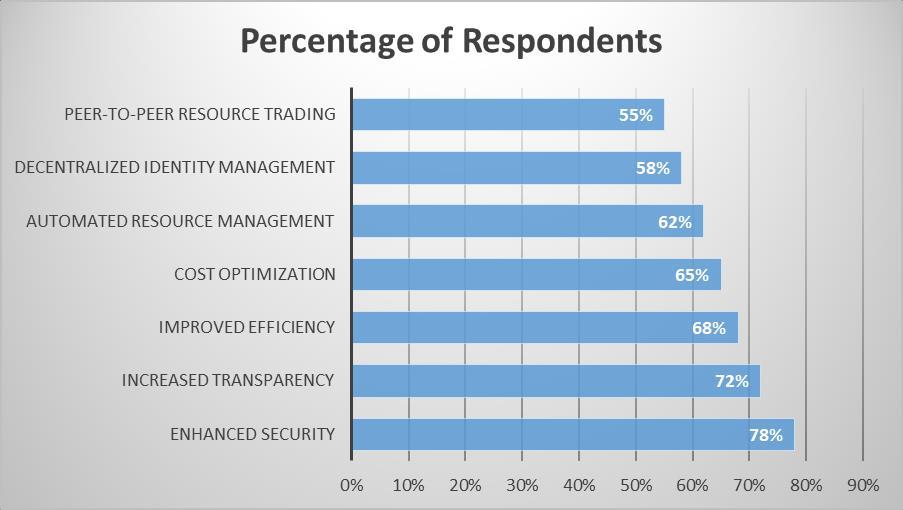
2:BenefitsofBlockchain-basedCloudInfrastructureManagement(SurveyResults)[16-18]

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Another lesson learned is the need for careful consideration of data privacy and security. While blockchain provides inherentsecurityfeatures,suchasimmutabilityandcryptographictechniques,implementingproperaccesscontrols,data encryption, and privacy-preserving mechanisms is essential to protect sensitive information and comply with regulatory requirements.
The potential use cases for blockchain-based cloud infrastructure management extend across various industries. In the healthcaresector,blockchaincanenablesecureandinteroperablesharingofpatientrecords,improvingcarecoordination andresearchcapabilities[18].Smartcontractscanautomatetheverificationofmedicalcredentialsandensurecompliance withdataprivacyregulations.
In the financial services industry, blockchain-based cloud solutions can streamline cross-border payments, reduce settlement times, and enhance fraud detection [16]. Decentralized identity management systems can provide secure and portabledigitalidentities,enablingseamlessandtrustedinteractionsbetweenfinancialinstitutionsandcustomers.
The supply chain and logistics industry can benefit from blockchain-based cloud management through improved traceability, provenance tracking, and counterfeit prevention [17]. Blockchain-based systems can create an immutable recordofproductjourneys,enablingtransparencyandtrustthroughoutthesupplychain.
Healthcare
FinancialServices
SupplyChain&Logistics
Energy
Gaming
Manufacturing
Government
Securesharingofpatientrecords,credentialverification
Cross-borderpayments,frauddetection,digitalidentities
Traceability,provenancetracking,counterfeitprevention
Decentralizedenergytrading,renewableenergycertificatetracking
Decentralizedgamingplatforms,ownershipofin-gameassets
Securedatasharing,intellectualpropertyprotection
Securerecord-keeping,transparentpublicservices
Table2:PotentialUseCasesofBlockchain-basedCloudInfrastructureManagementAcrossIndustries[16-18]
Otherpotentialusecasesincludedecentralizedcloudstorage,whereblockchainensuresdataintegrityandenablessecure and resilient storage solutions. In the gaming industry, blockchain-based cloud infrastructure can support decentralized gamingplatforms,enablingplayerownershipofin-gameassetsandfacilitatingsecureandtransparenttransactions.
Blockchain-based cloud infrastructure management represents a paradigm shift in the way organizations provision, monitor, and secure their cloud resources. By leveraging the inherent properties of blockchain technology, such as decentralization, immutability, and transparency, organizations can establish trust, enhance security, and improve efficiency in their cloud environments. The use of smart contracts enables automated and tamper-proof resource management, while decentralized identity management solutions provide secure and self-sovereign access control. Tokenization of cloud resources, granular tracking of usage, and incentivization mechanisms facilitate cost optimization and drive resource efficiency. Decentralized cloud marketplaces, powered by blockchain, enable peer-to-peer trading of resources, promoting a more competitive and resilient cloud ecosystem. However, challenges related to scalability, regulatory compliance, interoperability, and adoption need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of blockchain in cloud computing. Ongoing research, standardization efforts, and collaborative initiatives are crucial to overcome these hurdlesandpavethewayforwidespreadadoption.Asmoreorganizationsembraceblockchain-basedcloudsolutions,the future of cloud infrastructure management looks promising, with the potential to revolutionize various industries and unlocknewpossibilitiesforsecure,efficient,andtrustworthycloudcomputing.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
References:
[1] S. Nakamoto, "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System," 2008. [Online]. Available: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
[2] M. Ali, J. Nelson, R. Shea, and M. J. Freedman, "Blockstack: A Global Naming and Storage System Secured by Blockchains,"inProceedingsofthe2016USENIXAnnualTechnicalConference(USENIXATC'16),2016,pp.181-194.
[3] X. Xu et al., "A Taxonomy of Blockchain-Based Systems for Architecture Design," in Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE InternationalConferenceonSoftwareArchitecture(ICSA),2017,pp.243-252.
[4]M.Crosby,P.Pattanayak,S.Verma,andV.Kalyanaraman,"Blockchaintechnology:Beyondbitcoin,"AppliedInnovation Review,no.2,pp.6-19,2016.
[5] Z. Zheng, S. Xie, H. Dai, X. Chen, and H. Wang, "An Overview of Blockchain Technology: Architecture, Consensus, and FutureTrends,"inProceedingsofthe2017IEEE6thInternationalCongressonBigData,2017,pp.557-564.
[6]Y.Xiao,N.Zhang,W.Lou,andY.T.Hou,"ASurveyof DistributedConsensusProtocolsforBlockchainNetworks,"IEEE CommunicationsSurveys&Tutorials,vol.22,no.2,pp.1432-1465,2020.
[7] Q. Zhang, L. Cheng, and R. Boutaba, "Cloud computing: state-of-the-art and research challenges," Journal of Internet ServicesandApplications,vol.1,no.1,pp.7-18,2010.
[8] A. Bahga and V. K. Madisetti, "Blockchain Platform for Industrial Internet of Things," Journal of Software Engineering andApplications,vol.9,no.10,pp.533-546,2016.
[9]K.ChristidisandM.Devetsikiotis,"BlockchainsandSmartContractsfortheInternetofThings,"IEEEAccess,vol.4,pp. 2292-2303,2016.
[10] M. Andoni et al., "Blockchain technology in the energy sector: A systematic review of challenges and opportunities," RenewableandSustainableEnergyReviews,vol.100,pp.143-174,2019.
[11] J. Gu, B. Sun, X. Du, J. Wang, Y. Zhuang, and Z. Wang, "Consortium blockchain-based malware detection in mobile devices,"IEEEAccess,vol.6,pp.12118-12128,2018.
[12] Z. Li, J. Kang, R. Yu, D. Ye, Q. Deng, and Y. Zhang, "Consortium blockchain for secure energy trading in industrial internetofthings,"IEEETransactionsonIndustrialInformatics,vol.14,no.8,pp.3690-3700,2018.
[13] T. T. A. Dinh, R. Liu, M. Zhang, G. Chen, B. C. Ooi, and J. Wang, "Untangling blockchain: A data processing view of blockchainsystems,"IEEETransactionsonKnowledgeandDataEngineering,vol.30,no.7,pp.1366-1385,2018.
[14] M. Kuperberg, "Blockchain-based identity management: A survey from the enterprise and ecosystem perspective," IEEETransactionsonEngineeringManagement,vol.67,no.4,pp.1008-1027,2020.
[15]J.Sikorski,J.Haughton,andM.Kraft,"Blockchaintechnologyinthechemicalindustry:Machine-to-machineelectricity market,"AppliedEnergy,vol.195,pp.234-246,2017.
[16] M. Francisconi, "An explorative study on blockchain technology in application to port logistics," Procedia Computer Science,vol.160,pp.318-325,2019.
[17] J. Golosova and A. Romanovs, "The advantages and disadvantages of the blockchain technology," 2018 IEEE 6th WorkshoponAdvancesinInformation,ElectronicandElectricalEngineering(AIEEE),2018,pp.1-6.
[18]P.Zhang,J. White,D.C. Schmidt,andG.Lenz,"Applyingsoftwarepatternstoaddressinteroperabilityin blockchainbasedhealthcareapps,"arXivpreprintarXiv:1706.03700,2017.
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072 © 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page872