Block chain in Healthcare
Vattikonda Mohith Kumar Department of Computer science and Engineering, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Vaddeswaram,AndhraPradesh,India
Dr.P Dinesh Chandra Department of Computer science and Engineering, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Vaddeswaram,AndhraPradesh,India
Abstract Blockchain technology might revolutionize healthcare and other industries. This research study investigates the usage of digital currencies in healthcare to understand its benefits, drawbacks, and potential. This qualitative study uses a literature review and expert interviews to examine blockchain technology in healthcare and its potential effects on consumers, health care providers, and other stakeholders. The literature review examines blockchain technology's fundamentals, its use in healthcare, and its benefits, including data security, connectivity, and empowering patients. The report also addresses scalability, regulatory, and integration challenges connected to blockchain technology in healthcare. The successful implementation of blockchain-based technologies in healthcare may be learned from real-world experiences. This article also discusses blockchain technology's ethical and legal implications for healthcare. This report adds to the blockchain technology and healthcare industry debate. It also indicates subject-specific research and developmentneeds.
Keywords Blockchain, healthcare, electronic health records, data security, interoperability, patient empowerment,supplychainmanagement
I. INTRODUCTION
This article will discuss why blockchain technology is significant and its various healthcare applications. Blockchaintechnologymightsolvemajorhealthcareissues as we navigate the intricate web of issues. Blockchain technology might improve healthcare delivery by boosting data security and privacy, interoperability, and administrative efficiency. Telemedicine, supply chain optimization, clinical trial facilitation, electronic health recordsadministration,andmore are amongits numerous applications. We want to show how blockchain technology might transform healthcare by exploring these many possibilities[1].
Garimella Jyothsna Department of Computer science and Engineering, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Vaddeswaram,AndhraPradesh,India
This lecture will explain blockchain technology and its manyhealthcareuses.Blockchaintechnologymaysolvekey healthcare sector difficulties as we negotiate the complex network of issues. Blockchain technology might transform healthcare delivery by improving data security, interoperability, and administrative processes. This technologyhasseveraluses,includingtelemedicine,supply chain optimization, clinical trial facilitation, electronic health records administration, and more. We want to examinethevariouspossibilitiesandshowhowblockchain technologywillchangehealthcare.
Thissectionwillanalyzecurrenthealthcaresystems,its pros, cons, and challenges. The healthcare business underpins public wellbeing. Despite advances in medical science and technology, healthcare systems worldwide confront several issues, including accessibility, cost, inefficiency, and injustices. Healthcare systems globally confrontlimitedtreatmentavailability,growingcosts,poor data management, and high-quality care inequities. Our goal in this review is to fully understand healthcare systems' complicated features so we can examine how blockchaintechnologymaysolvetheseimportantconcerns [2]. Blockchain technology has several healthcare applications, which we will discuss in this discussion. Blockchaintechnologymightsolvemajorhealthcareissues as we navigate the intricate network of issues. Blockchain technology might improve data security, privacy, interoperability, and administrative operations in healthcare. This technology may be used in telemedicine, supply chain optimization, clinical trial facilitation, electronic health records administration, and more. We want to explore blockchain's many possibilities and illustratehowitwillchangehealthcare.
As a whole, healthcare data security is largely concerned with protecting the privacy and authenticity of individual patients' records. Data breaches and hacks have become more commonplace due to the broad use of electronic health information, which puts patients' privacy and confidentiality at serious risk. Implementing robust cybersecurity solutions should be a top priority for
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue:07 | July2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
healthcare firms in order to safeguard themselves against maliciousassaults.
A. Interoperability Challenges: An important issue in the healthcaresectoristhelackofinteroperabilityacross varioushealthcaresystemsanddatasources.Thetask of enhancing healthcare coordination and data interchange is difficult because of the fragmented IT infrastructures and incompatible data formats used by healthcare providers and systems. The absence of interoperability poses a threat to both the efficiency andsafetyofhealthcaredelivery.
B. Data Integrity Issues: Maintaining the integrity and accuracy of health data poses a considerable challenge in healthcare. Data silos, inconsistent data entrypractices,andmanualrecord-keepingprocesses contribute to errors, duplications, and discrepancies inpatientrecords.Suchdataintegrityissuesnotonly undermine the quality of care but also hinder efforts toleverage data for research, analytics,and decisionmakingpurposes.
C. RegulatoryComplianceBurdens: Healthcare firms must comply with complicated regulations like HIPAA in the US and GDPR in the EU. Adhering to these standards requires enormous administrative and financial expenditures for healthcare providers, divertingresourcesfrompatientcare[3].
D. Resource Constraints: As the demand for high-quality healthcare services continues to rise, healthcare organizationsfacesignificantobstaclesduetolimited resources, such as funding, personnel, and infrastructure.Existinginefficienciesare made worse by these resource limits, which also hinder attempts toinnovateandupgradehealthcareservice.
E. Introduction to Blockchain Technology and Its Key Features:
The foundation of decentralized digital ecosystems is blockchain technology, which is frequently praised as a revolutionarybreakthrough.Fundamentally,blockchainisa decentralized ledger system that eliminates middlemen while facilitating trustworthy, immutable financial transactionsacrossanInternetofcomputers
1) Decentralization: A key attribute of blockchain is its decentralized nature, which is in direct opposition to conventional centralized systems. In a decentralized blockchain network, transactions are documented and authenticated by several nodes or participants, instead than being governed by a solitary central authority. Decentralization not only improves resilience and fault tolerance, but also removes the risks linked to a single pointoffailure.
2) Transparency: The fundamental principle of blockchain technology is transparency, as every transaction recorded on the blockchain is accessible to all members in the network. By employing cryptographic methods,blockchainguaranteesthattransactiondatastays invulnerable to tampering and easily available to authorized entities. This level of openness promotes confidence and responsibility, allowing interested parties to confirm the genuineness and completeness of transactionsimmediately.
Immutability: A key feature of blockchain is its immutability, which means that data cannot be altered or removed from the blockchain once it has been recorded permanently. By securely connecting each transaction to theprecedingblockviacryptography,animmutableseries of data is formed that cannot be changed in the past. In addition to facilitating audits and meeting regulatory obligations, immutability enhances data security and integrity.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Introduction to Blockchain Technology:
Many different types of businesses throughout the world are interested in blockchain technology since it is a groundbreakingidea.Blockchain,initsmost basicform,is a distributed ledger system that facilitates auditable and secure online transactions. Data storage, verification, and exchangeareallrethoughtinlightofitsguidingprinciples, which include decentralization, transparency, and immutability.
The original Bitcoin, created in 2008 by anonymous user Satoshi Nakamoto, relies on a cryptographically secure chain of blocks. In the time after, blockchain technology expandeditsusebeyondcryptocurrencytoawiderangeof industries[4].
Blockchain relies on nodes, which are participants in the network that validate and add new blocks to the blockchain,andblocks,whichincludedataontransactions as well as cryptographic hashes and timestamps. Consensustechniques,likePoWandPoS,guaranteethatall nodesinthenetworkagreethatatransactionislegitimate. When it comes to protecting transactions and keeping the blockchainsecure,cryptographyiscrucial.
B. Blockchain Applications in Healthcare:
The healthcare business is confronted with several obstacles, and there has been an increasing interest in using blockchain technology to tackle these issues. Many healthcare-relatedusesofblockchainhavebeenpreviously discussed in the literature. These include telemedicine, clinical trial and research data management, electronic health records (EHRs) management, and supply chain management.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue:07 | July2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Blockchaintechnology,beingadecentralized,trustworthy, and globally accessible database for medical records, has thepotentialtosignificantlytransformthemanagementof electronic health records (EHRs). It ensures the accessibility of all medical records, safeguards patients' privacy,andmaintainstheintegrityofdata.
Among the many applications of blockchain technology, two that stand to benefit greatly from increased openness and efficiency are pharmaceutical monitoring and supply chainmanagement.Stakeholderscanensurepatientsafety by tracking the origin and validity of pharmaceuticals by recordingtheirwholelifespanontheblockchain[5].
In addition, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize telemedicine and RPM by offering a safe platform for the storage and transmission of medical data, easing the processofremoteconsultations,andallowingfortherealtimetrackingofpatients'vitals.
C. Benefits of Blockchain in Healthcare:
The healthcare industry is very interested in blockchain technology because of its revolutionary benefits and its ability to solve important problems. The current body of research on blockchain technology in healthcare points to anumberofpossiblebenefits,suchas:
D. Enhanced Data Security and Privacy Protection:
A large body of research highlights blockchain's potential to strengthen healthcare privacy and security of data protections.Blockchaintechnologyguaranteesthesecurity of patient health records by limiting access to authorized individualsandutilizingdecentralizedconsensusmethods. Theirreversiblenatureofblockchaintechnologyenhances patient confidentiality and confidence by reducing the dangerofdatatamperingandillegalaccess.
E. Improved Interoperability and Data Exchange:
Blockchain technology has the potential to improve the interoperability and data exchange among various healthcare systems and people. By providing a standard framework for storing and disseminating data, blockchain facilitates the seamless exchange of health data while guaranteeing the data's integrity and consistency. Better clinical decision-making and care coordination are outcomes of interoperability, which enables healthcare providers to access full patient records across different healthcaresettings[6].
F.Streamlined Administrative Processes and Reduced Costs:
There is a lot of evidence in the literature that blockchain may help healthcare organizations streamline their administrative operations and cut operational expenses. Blockchaintechnologystreamlinesadministrativetasksfor healthcarebusinessesbyautomatedhandlingdata,record-
keeping, and workflows. This removes inefficiencies that come with manual operations. Saving money and increasing efficiency all the way through the healthcare value chain is possible thanks to blockchain technology and its decentralized structure, which eliminates the need formiddlemenandthird-partyverification.
G. Empowerment of Patients Through Increased Control Over Their Health Data:
Patientsmightgainagencywithblockchaintechnologyifit allows them more say over their health records. Secure access, management, and sharing of medical data and health information between patients and healthcare professionals is made possible by blockchain-based systems.Patientsarebetterequippedtotakeanactiverole in their health, make educated decisions, and guarantee thecompletenessandqualityoftheirhealthrecordswhen theyhavemorecontrolovertheirdata.
Fig.1DistributionofSubsectionsAcrossMainSectionsin theResearchPaperonBlockchaininHealthcare
H. Summary of Key Findings:
Our extensive literature research has yielded some important conclusions about blockchain technology's potential use in healthcare. Some of these advantages might include better data security, more interoperability, easier administrative processes, and more patient agency withregardtotheirownhealthdata.Wehavealsolooked atnewdevelopmentsincludingtelemedicine,supplychain optimization, clinical trial facilitation, and blockchain technology'suseinEHRmanagement.
I. Reflection on the Potential Impact of Blockchain on the Healthcare Industry:
Blockchain technology can improve healthcare by solving critical problems and offering attractive innovation possibilities. Blockchain technology's decentralization, transparency, and irreversibility increase data security, efficiency, and patient outcomes. Blockchain technology can also improve stakeholder trust, transparency, and cooperation, creating a more efficient healthcare ecosystemthatprioritizespatients[7].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue:07 | July2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
III. METHODOLOGY
A. Research Approach:
Expertsin the fieldsof blockchaintechnologyandmedical care will be surveyed using a qualitative research approach to glean valuable ideas and viewpoints for this project. Conducting in-depth interviews or focus groups with knowledgeable individuals in various fields is the essence of this approach. We want to gather first-hand accounts from experts on the potential applications, benefits,challenges,andevolutionoftheuseofblockchain inhealthcare[8].
To round up the study with some practical insights, realworldcasestudiesandimplementationswillbeexamined. Through an analysis of completed healthcare projects and initiatives, we want to determine the benefits, drawbacks, andinsightsobtainedfromutilizingblockchaintechnology.
Ifyou wanttoseehowblockchaintechnologymaychange healthcare delivery and patient outcomes, these case studiesareagreatplacetostart.
To begin, in order to fully understand the existing literature on blockchain in healthcare, we will extensively research academic journals, peer-reviewed publications, conference papers, and other credible sources. The applications, pros, cons, and future of blockchain technology in healthcare are just a few of the topics that willbecoveredinthisliteraturestudy.
What follows is an examination of the current research approaches used in healthcare-related blockchain studies. Methods including interviews, case studies, surveys, and experimentalresearchwillallbepartofthisinvestigation. One way to find out what works and what doesn't while researching this topic isto lookathow otherstudies have doneit.
Inordertogetapracticalunderstandingofthesubject,we will examine real-life examples and applications of blockchain technology in healthcare environments. The use of blockchain technology to solve problems in the healthcare industry has been the subject of several realworldprojectsandefforts[9].
The goal of this case study analysis is to gain a better understanding of how blockchain computing has been applied to increase data security, interoperability, administrative process streamlining, and patient empowerment. Extracting useful insights and best practices will include analyzing each case study's goals, techniques,outcomes,andlessonslearned.
We want to give stakeholders interested in healthcare blockchain adoption realistic examples and advice by exploring case studies and real-world deployments. Our goal is to showcase blockchain technology's successful
applications in order to highlight how it can be used and encouragemoreinnovationintheindustry[10].
B. Data Collection:
Our research on cryptocurrencies in healthcare will employ a comprehensive approach that integrates several sourcesandmethodstoobtaincomprehensivedata.
C. Literature Review:
We will collect data from academic articles, journals that have been examined by experts, papers presented at conferences, and trustworthy websites. This will entail doing a comprehensive literature review to investigate current investigations, research, and publications pertainingtodigitalcurrencytechnologyinthehealthcare sector. Through comprehensive analysis of several sources,ourobjectiveistoprovidevaluableinsightsabout the present status of distributed ledger uses in the healthcaresector.
D. Interviews:
Interviews with healthcare providers, blockchain specialists, lawmakers, and business leaders will help us get a range of opinions on the matter. You maylearn a lot about the possibilities, threats, and difficulties of blockchaintechnologyinhealthcarefromtheseinterviews. We hope to get more nuanced views and real-world experiences about blockchain adoption in healthcare by talkingtoprofessionalsfrommanywalksoflife.
E. Surveys or Questionnaires:
Furthermore, in order to get information on healthcare companies' blockchain technology use, we will conduct surveys or questionnaires. Using these surveys, we can collect quantifiable data on how healthcare organizations are now using blockchain technology, how they plan to adopt it, and what they see as the advantages and disadvantages of this technology. We want to get a good pictureofhowthehealthcarebusinessisusingblockchain technology, therefore we're contacting a wide variety of healthcarecompanies[11].
F.Data Analysis:
We will use a thorough analytical methodology that includes quantitative and qualitative methodologies to extract valuable insights from the healthcare blockchain data:
1) Qualitative Analysis: The qualitative data collected from interviews, literature review, and case studies will undergo thematic analysis or content analysis. This involves systematically identifying, analyzing, and interpretingpatternsorthemeswithinthedatatouncover underlying meanings and insights. By coding and categorizing the data, we aim to identify common themes,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue:07 | July2024 www.irjet.net
trends, and patterns related to blockchain applications in healthcare.
2) Comparative Analysis: To give you the full picture, we'll look at the results of several research, such as interviews, case studies, and literature reviews, and compare and contrast them. To generate strong conclusionsandinsights,weneedtocompareandcontrast different data sources to find parallels, discrepancies, and inconsistencies[12].
3) Statistical Analysis: We shall employ statistical analysis tools where necessary, particularly when examiningquantitativeresultsandsurveydata.Inferential statisticsareusedtotesthypothesesandfindcorrelations between variables, whereas descriptive statistics are used to summarize survey answers. To round out our study, statistical analysis will give numerical insights and substantiatingprooftobackupourqualitativeconclusions.
G. Validation:
To ensure the credibility and reliability of our research findings on blockchain in healthcare, we will implement a robustvalidationprocessthatincludesthefollowingsteps:
1) Peer Review: Our research findings will undergo rigorouspeerreviewbyexpertsinthefieldsofblockchain technology and healthcare. Peer review involves submitting our research paper to reputable journals or conferences for evaluation by independent experts in the field. Their feedback and recommendations will help validate the accuracy, relevance, and quality of our researchfindings.
2) Feedback from Subject Matter Experts: We will solicit feedbackfromsubjectmatterexperts,includinghealthcare professionals, blockchain experts, policymakers, and industry stakeholders. By sharing our findings with these expertsandseekingtheirinsightsandperspectives,wecan validate the relevance and applicability of our research to real-world contexts. Their feedback will also help identify any gaps or areas for improvement in our research methodologyandanalysis.
3) Referencing Reputable Sources: Throughout our research paper, we will reference reputable sources, including scholarly articles, peer-reviewed journals, conference papers, and authoritative websites. By citing crediblesources,wecansubstantiateourresearchfindings and demonstrate the reliability of our research methodology[13].
4) Utilizing a Rigorous Methodology: During the whole study process, from data collection to analysis and interpretation,weshallfollowastrictapproach.Ourstudy findings will be honest and unbiased since we used open and transparent approaches including statistical analysis, qualitativeanalysis,andcomparisonanalysis.
p-ISSN:2395-0072
We strive to maintain the utmost levels of academic rigor andguaranteethecredibility,reliability,andimpact ofour blockchain in healthcare study by executing these validationprocesses.
IV. RESULTS
Through our research, wesought to address the following objectives:
To examine the current state of blockchain applicationsinhealthcare.
Toidentifykeytrendsandemergingopportunities for blockchain technology in the healthcare industry.
To assess the impact of blockchain implementations on healthcare delivery, patient outcomes,andorganizationalefficiency.
To provide practical insights and recommendations for stakeholders interested in adoptingblockchaininhealthcaresettings[14]
Our research strategy included scouring credible online resources as well as academic publications, conference papers, and peer-reviewed journals for relevant data. In order to obtain a range of viewpoints on the matter, we also interviewed healthcare providers, blockchain specialists, lawmakers, and industry members. In order to offer useful insights into the issue, we also examined practical case studies and healthcare uses of blockchain technology[15]
A. Overview of Blockchain Applications in Healthcare:
A number of important conclusions from the literature study emerged from our investigation of blockchain's potential uses in healthcare. To start, blockchain technology has grown in popularity as a potential answer toseveralproblemsplaguingthehealthcareindustry,such as insufficient data security and problems with interoperability.
The administration of electronic health records (EHRs) is one area where blockchain technology is finding widespread use in the healthcare industry. Healthcare businessesmaybuilddigitalrecordsthatareimpenetrable to tampering by utilizing blockchain's immutable and secure properties [16]. This improves patient confidence and privacy while also streamlining data management operations
Blockchain technology has the potential to enhance the supplychains for healthcare by monitoring the movement of medicines and medical equipment across the supply chain.Thisensuresthattheproductsaregenuineandsafe, whilealsominimizingthepossibilityofcounterfeititems.
Blockchainismakingwaves inresearchdata management and clinical trial speedup. Blockchain's open and
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue:07 | July2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
transparent system for collecting and disseminating trial data improves data quality, researcher cooperation, and drugdevelopment[18].
B. Overview of Blockchain Applications in Healthcare: Common Themes and Trends:
Across different sources, several common themes and trends emerge regarding the applications of blockchain in healthcare:
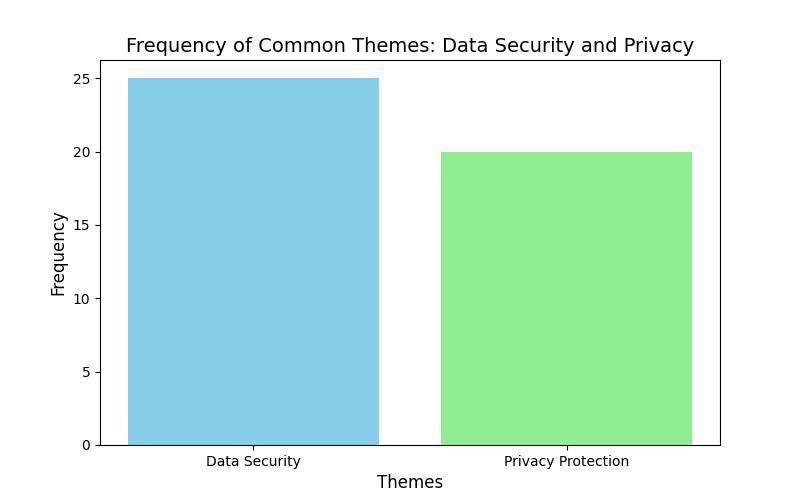
1) Data Security and Privacy: Blockchain technology is emphasized for healthcare data security and privacy. Blockchain protects sensitive health data from breaches and unwanted access by offering a decentralized and irreversibleplatformforstorageandsharing.
2) Interoperability and Data Exchange: Blockchain has thepotentialtoenhancethecapacityofhealthcaresystems and players to exchange information and work together effectively.Theblockchainplatformfacilitatesthesafeand standardizedexchangeofhealthdatabetweenenterprises, leading to improved medical decision-making and coordinateddeliveryoftreatment.
3) Efficiency and Transparency: Blockchain may speed administrative procedures, minimize inefficiencies, and improve healthcare transparency. Blockchain robotics, intelligent agreements, and open records of transactions can optimize operations, reduce mistakes, and increase accountability in healthcare companies, saving money and improvingefficiency[19].
4) Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: Finally, the use of blockchain in healthcare raises ethical and regulatory concerns [20]. Responsible and ethical blockchainuseinhealthcarerequirescompliancewiththe General Data Protection Regulation and the Health Insurance Portability aswell asethical issuessuchpatient permission,dataownership,andtransparency.
C. Insights from Case Studies and Real-World Implementations:
Our examination of instances and healthcare blockchain deployments is discussed in this section. These case studies reveal the aims, methodology, outcomes, and lessons gained from each deployment, as well as their effects on the provision of healthcare, patient satisfaction, andefficiencywithintheorganization[21].
D. Case Study 1: Electronic Health Records Management
1) Objective: Throughtheuseofblockchaintechnology, the implementation sought to improve the accessibility andsecurityofdigitalmedicalrecords(EHRs).
2) Methodology: Thedeploymentofa blockchain-based system ensures the privacy and immutability of patient healthrecords
3) Outcomes: Healthcare practitioners saw less administrative work, easier access to patient records, and betterdatasecurityasaresultofthedeployment.Patients weremoreassuredthattheirhealthrecordswouldremain privateandsecure.
4) Lessons Learned: Successful implementation of blockchain-based electronic health record systems requires stakeholder participation, user training, and compliancewithregulations,amongotherlessons.
5) Impact: greater patient outcomes were one of the many good outcomes that resulted from the implementation's favorable influence on healthcare delivery, which was boosted by more efficient data managementsystemsandgreatercommunicationbetween patientsanddoctors[22].
E. Case Study 2: Optimization of the Supply Chain:
1) Objective:Thegoalof theimplementationwastouse blockchain technology to make the biopharmaceutical supplychainmoretransparentandtraceable.
2) Methodology: A blockchain-based system was implemented to track the movement of pharmaceutical products from manufacturers to distributors to pharmacies, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeitproducts.
3) Outcomes: Increased supply chain visibility, decreasedoccurrencesofcounterfeitpharmaceuticals,and increased patient safety were all outcomes of the deployment.Thecredibilityofmedicinalitemswaspraised bystakeholders[23].
4) Lessons Learned: Developing blockchain technology in complicated supply chain environments taught us a lot, the most important of which was the significance of data standardization, cooperation among supply chain players, andregulatorycompliance.
5) Impact: Streamlining supply chain operations, decreasing operating costs, and improving the safety of patients through preventing the use of counterfeit pharmaceuticals were all beneficial outcomes of the deployment, which had a favorable influence on organizationalefficiency.
F.Qualitative Data Analysis:
Inthissection,weconductthematicanalysisofqualitative datagatheredfrominterviews,focusgroups,andliterature review to identify common themes, patterns, and trends related to blockchain in healthcare. We present key findingssupportedbyquotesorexcerptsfrominterviews.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue:07 | July2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
G. Common Themes and Patterns:
1) Data Security and Privacy: Blockchain technology was highlighted by interviewees as a means to improve healthcare data privacy and security. "Blockchain ensures theaccuracyandprivacyofpatientinformation"isjustone example of how quotes like these highlight blockchain's role in importance in protecting important medical records.
2) Interoperability and Data Exchange: The opportunity for blockchain technology to enhance healthcare system interoperability and data interchange was emphasized by stakeholders. According to quotes like "Blockchain facilitatesseamlesssharingofhealthdata betweenvarious institutions" [24], interoperability is crucial in the healthcareindustry.
3) Efficiency and Transparency: Anonymity and efficiency in healthcare administration were two of the main topics covered by respondents when asked about blockchain technology. "Blockchain enhances accountability and transparency in healthcare transactions"isonlyoneexampleofaquotethathighlights the efficiency improvements linked to blockchain implementation.
Fig.2FrequencyofCommonThemes:Datasecurityand Privacy
Fig.3EfficiencyandTransparency
V. CONCLUSION
Finally, our study has shown how blockchain technology has the ability to revolutionize healthcare. Data privacy and security, interoperability, efficiency, openness, and patient agency were among the major themes uncovered byourqualitativedataanalysis.Stakeholdersfromvarious healthcare professions, blockchain experts, and industry insiders all agreed that these themes will have a major impactonhealthcareinthefuture.
Our theme analysis shows that blockchain is essential to solving healthcare business problems. Businesses may increase data security, administrative efficiency, and healthcare system interoperability by using blockchain's decentralized and irreversible characteristics. Blockchain technologybenefitspatientsbyofferingthemmorecontrol overtheirhealthdata,boostinghealthcareecosystemtrust andcollaboration[25].
Overall, our research emphasizes the relevance of blockchain technology for healthcare innovation. To maximize blockchain's impact on healthcare delivery and patientoutcomes, stakeholders mustcollaborate,innovate responsibly, and promote ethics. Blockchain might revolutionizehealthcaredeliveryandreceiptasitevolves.
REFERENCES
[1] Hölbl,M.,Kompara,M.,Kamišalić,A.,&NemecZlatolas, L.(2018).Asystematicreviewoftheuseofblockchain inhealthcare.Symmetry,10(10),470.
[2] McGhin, T., Choo, K. K. R., Liu, C. Z., & He, D. (2019). Blockchain in healthcare applications: Research challenges and opportunities. Journal of network and computerapplications,135,62-75.
[3] Hasselgren, A., Kralevska, K., Gligoroski, D., Pedersen, S. A., & Faxvaag, A. (2020). Blockchain in healthcare and health sciences A scoping review. International JournalofMedicalInformatics,134,104040.
[4] Prokofieva, M., & Miah, S. J. (2019). Blockchain in healthcare. Australasian Journal of Information Systems,23.
[5] Fusco, A., Dicuonzo, G., Dell’Atti, V., & Tatullo, M. (2020). Blockchain in healthcare: Insights on COVID19. International Journal of Environmental Research andPublicHealth,17(19),7167.
[6] Namasudra, S., & Deka, G. C. (Eds.). (2021). Applications of blockchain in healthcare (Vol. 83). Singapore:Springer.
[7] Alhadhrami,Z.,Alghfeli,S.,Alghfeli,M.,Abedlla,J.A.,& Shuaib, K. (2017, November). Introducing blockchains for healthcare. In 2017 international conference on
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 11 Issue:07 | July2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
electricalandcomputingtechnologiesandapplications (ICECTA)(pp.1-4).IEEE.
[8] Ismail, L., Materwala, H., & Zeadally, S. (2019). Lightweight blockchain for healthcare. IEEE access, 7, 149935-149951.
[9] Chen,H.S.,Jarrell,J.T.,Carpenter,K.A.,Cohen,D.S.,& Huang, X. (2019). Blockchain in healthcare: a patientcentered model. Biomedical journal of scientific & technicalresearch,20(3),15017.
[10] Kassab, M., DeFranco, J., Malas, T., Laplante, P., Destefanis, G., & Neto, V. V. G. (2019). Exploring research in blockchain for healthcare and a roadmap for the future. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics inComputing,9(4),1835-1852.
[11] Onik, M. M. H., Aich, S., Yang, J., Kim, C. S., & Kim, H. C. (2019). Blockchain in healthcare: Challenges and solutions. In Big data analytics for intelligent healthcare management (pp. 197-226). Academic Press.
[12] Yaqoob, I., Salah, K., Jayaraman, R., & Al-Hammadi, Y. (2022). Blockchain for healthcare data management: opportunities, challenges, and future recommendations. Neural Computing and Applications,1-16.
[13] Katuwal,G.J.,Pandey,S.,Hennessey,M.,&Lamichhane, B. (2018). Applications of blockchain in healthcare: current landscape & challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.02776.
[14] Dhillon, V., Metcalf, D., Hooper, M., Dhillon, V., Metcalf, D., & Hooper, M. (2021). Blockchain in healthcare. Blockchain Enabled Applications: Understand the Blockchain Ecosystem and How to Make it Work for You,201-220.
[15] Ekblaw, A., Azaria, A., Halamka, J. D., & Lippman, A. (2016, August). A Case Study for Blockchain in Healthcare:“MedRec” prototype for electronic health records and medical research data. In Proceedings of IEEEopen&bigdataconference(Vol.13,p.13).
[16] Tandon, A., Dhir, A., Islam, A. N., & Mäntymäki, M. (2020). Blockchain in healthcare: A systematic literature review, synthesizing framework and future researchagenda.ComputersinIndustry,122,103290.
[17] Agbo, C. C., Mahmoud, Q. H., & Eklund, J. M. (2019, April). Blockchain technology in healthcare: a systematic review. In Healthcare (Vol. 7, No. 2, p. 56). MDPI.
[18] Epiphaniou, G., Daly, H., & Al-Khateeb, H. (2019). Blockchain and healthcare. Blockchain and Clinical Trial:SecuringPatientData,1-29.
[19] Huang, G., & Al Foysal, A. (2021). Blockchain in healthcare. Technology and Investment, 12(3), 168181.
[20] Ben Fekih, R., & Lahami, M. (2020). Application of blockchaintechnology in healthcare:a comprehensive study.In The ImpactofDigital Technologieson Public Health in Developed and Developing Countries: 18th International Conference, ICOST 2020, Hammamet, Tunisia, June 24–26, 2020, Proceedings 18 (pp. 268276).SpringerInternationalPublishing.
[21] Chukwu, E., & Garg, L. (2020). A systematic review of blockchaininhealthcare:frameworks,prototypes,and implementations.IeeeAccess,8,21196-21214.
[22] Gökalp,E.,Gökalp,M.O.,Çoban,S.,&Eren,P.E.(2018). Analysing opportunities and challenges of integrated blockchain technologies in healthcare. Information Systems: Research, Development, Applications, Education: 11th SIGSAND/PLAIS EuroSymposium 2018, Gdansk, Poland, September 20, 2018, Proceedings11,174-183.
[23] Attaran, M. (2022). Blockchain technology in healthcare: Challenges and opportunities. International Journal of Healthcare Management, 15(1),70-83.
[24] Prybutok, V. R., & Sauser, B. (2022). Theoretical and practical applications of blockchain in healthcare informationmanagement.Information&Management, 59(6),103649.
[25] Bell, L., Buchanan, W. J., Cameron, J., & Lo, O. (2018). Applications of Blockchain Within Healthcare. Blockchaininhealthcaretoday.
© 2024, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 | ISO 9001:2008
| Page