
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Pandya Drashti1 , Aakash Suthar2 ,
1M. Tech Student, L.J. University, Ahmedabad
2Aakash Suthar, Head of Department, Structural Engineering Department, L.J. University, Ahmedabad, India.
Abstract: -The torsional effects of seismic events on multistorybuildingsarecriticallyanalyzedinthisresearch paper. The twisting motion of buildings brought on by seismicforcesisknownastorsionaleffects,anditiscrucial to the structural integrity of buildings. In order to design structuresthatcanwithstandseismicactivityandguarantee occupantsafety,itisimperativetocomprehendtheseeffects. The study draws attention to the complexity of torsional responsesandhowtheyaffecthowwellbuildingsfunction during earthquakes. The study examines two different models that are symmetric and asymmetric high-rise buildingswithandwithoutshearwallsintheirstructurein differentIndianseismiczones.Analysishadbeencarriedby modellinginETABS.Itwasobservedthattheperformanceof anybuildingdependsverymuchonthetorsionalbehaviorof thestructure.
Key Words: (Modal analysis), (Shear Wall), (Torsion), (Mass participation ratio), (Frequency) & (High rise).
1.INTRODUCTION: -
India'svastandvariedterrainismarkedbydifferentdegrees of seismic hazard, which makes in-depth study of the evaluation of structures in seismic zones necessary. One frequentnaturalhazardintheareaisearthquakes,whichare extremelydangerousforbothinfrastructureandhumanlife. Reducingthedevastatingeffectsofearthquakesrequiresan understandingofhowvariousbuildingtypesreacttoseismic stressinvariousregions.Indiahasawiderangeofseismic risk,fromlow-riskregionstohigh-intensityzonesnearplate borders.Thisemphasizestheneedforthoroughstudiesto guidebuildingproceduresandretrofittingtechniques.
Thestudyofmodalanalysisofstructuresisafundamental aspect of structural engineering and seismic design, providing critical insights into the dynamic behavior of buildings and other constructions under various loading conditions.Thisanalyticaltechniqueinvolvesexaminingthe naturalfrequencies,modeshapes,anddampingratiosofa structure,whichareessentialforunderstandinghowitwill respond to dynamic forces such as wind, vibrations, and earthquakes.Byidentifyingtheprimarymodesofvibration and their associated mass participation factors, engineers can predict potential resonances and ensure that the structure can withstand and dissipate energy effectively. Additionally, parameters like storey drift and torsional
stability are assessed to evaluate the overall performance andsafetyofthestructure.
In the study of structural dynamics, modal analysis is an essentialmethodforunderstandinghowstructuresrespond tovibrations.Forthepurposeofcreatingsafeandeffective structures,thisanalysisiscrucial,especiallyinthefieldsof civil,mechanical,aerospace,andautomotiveengineering.
Understandingandenhancingthevibrationalcharacteristics ofstructuresismadeeasierwiththehelpofmodalanalysis, a fundamental component of structural engineering. Throughtheidentificationofinherentfrequenciesandmode shapes, engineers are able to create more durable and resilientstructuresthatguaranteeperformanceandsafetyin arangeofapplications.
Inconclusion,studiesontheevaluationofIndianseismically vulnerable structures are essential to the preservation of infrastructureandhumanlife.Thecountry'svariedseismic risk makes it necessary to take a nuanced approach to comprehending how different regions' buildings behave. Thesestudiesprovidevaluableinsightsthatnotonlyguide thedesignandconstructionofnewbuildings,butalsoplaya majorroleinthedevelopmentofrobustbuildingcodesand retrofittingstrategies.Theknowledgegainedfromseismic researchwill becrucial indevelopinga builtenvironment that is safer and more resilient as India continues to urbanizeandgrow
Thecurrentworkcanbecategorizedasaquantitativestudy since it primarily focuses on gathering numerical data for twodistinctbuildingplanconfigurationsthatareexposedto seismic loads. The analysis was carried out on reinforced concrete structures that were symmetrical and asymmetrical,measuring38x38mforsquarebuildingsand 68.5x48.5mforL-shapedbuildings.Theseplanshave13 standardstories,eachmeasuring3metersinheight,witha basestoryheightof3.5meters.Everystructuralelementis modeledexactly,includingtheplacementandsizeofshear walls.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
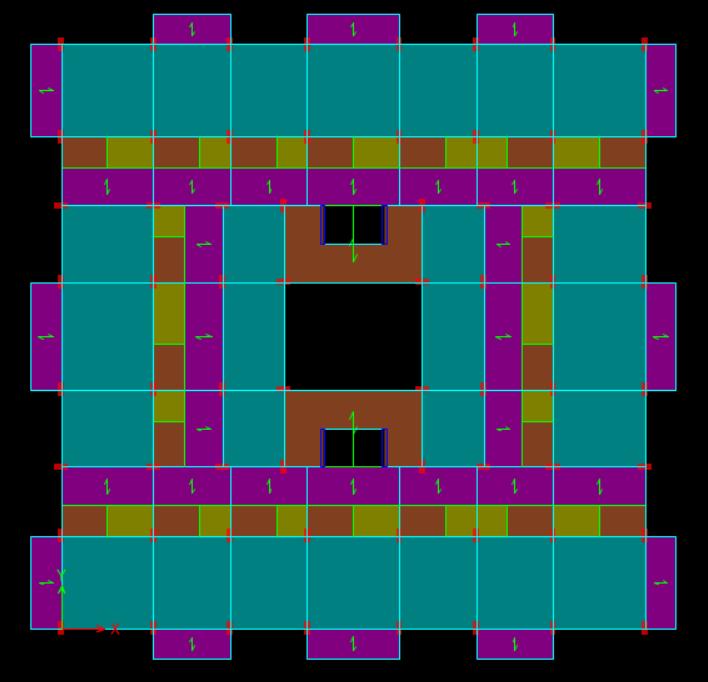
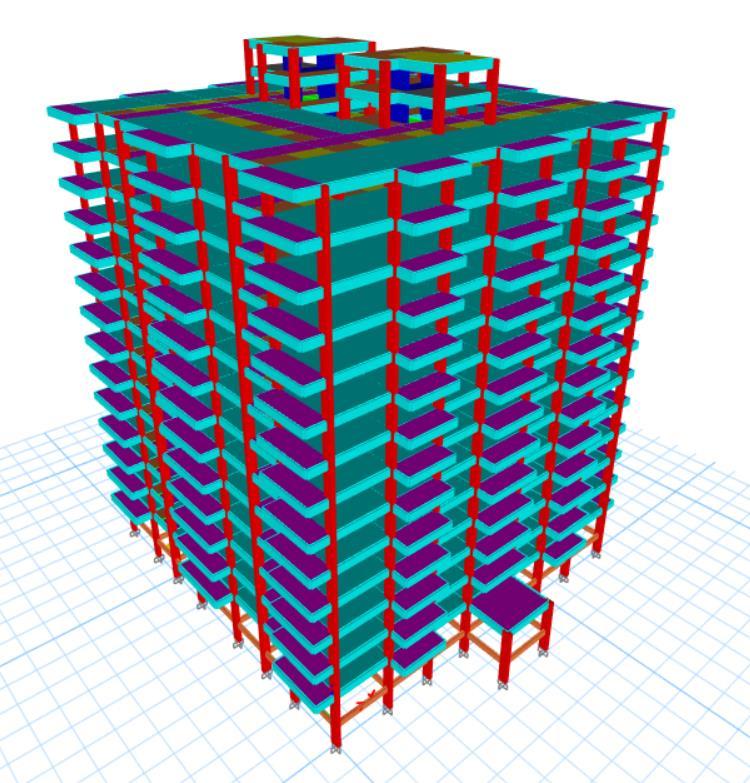
1(b):
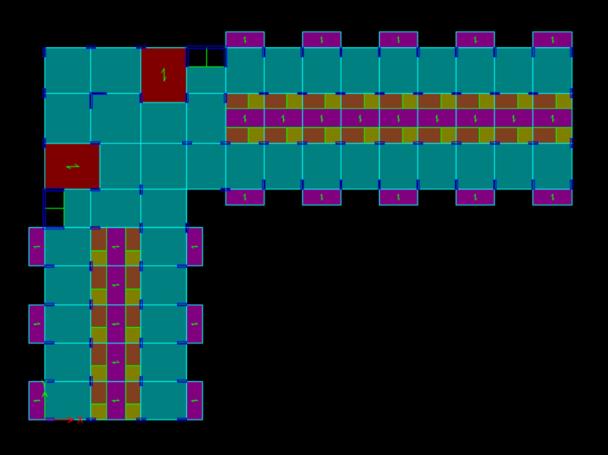
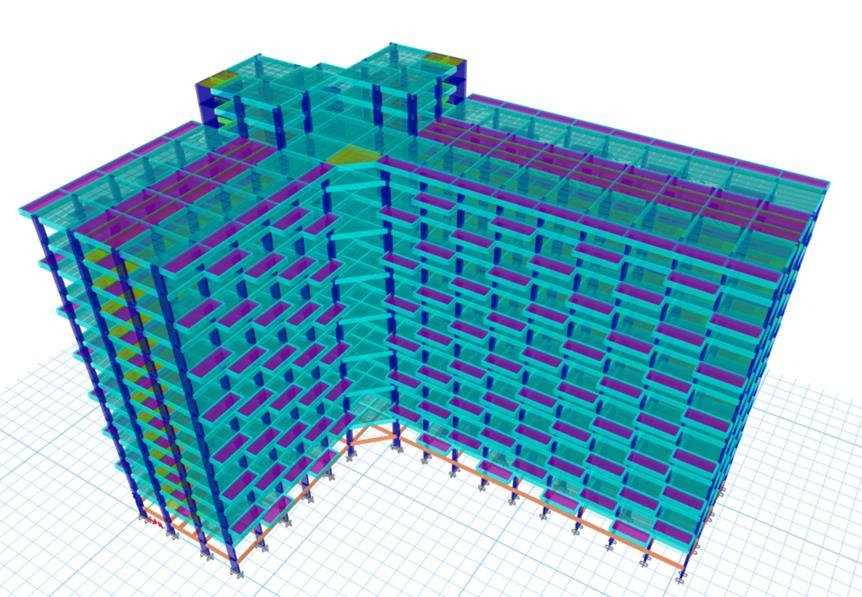
building
Table I: Properties and data: -
Numberofstories G+13
Storeyheight(Gf,typical) (3.5,3)m
GradeofConcreteinBeam&slab M25
GradeofConcreteinColumn M35
GradeofRebar Fe500
DepthofFoundation 12.7m
LiveLoad(rooms) 2KN/m2
Liveload(other) 3KN/m2
Liveload(terrace) 1.5KN/m
FloorFinishing 1.5KN/m2
Slab(Thickness) 125mm
Densityofblockmasonry 7.5kN/m3
DensityofPlaster 20KN/m3
DensityofConcrete 25KN/m3
Loadofwall(230mm) 6.75KN/m Loadofwall(100mm) 4.3KN/m
Parapetload(1.2m) 1.75KN/m Sunkload 3.15KN/m2
ImportanceFactor 1.5

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
TimeperiodforL-shape (Column)(X,Y) (0.5317,0.63 19)s
TimeperiodforL-shape(Shear wall)(X,Y) (0.5317,0.63 19)s
TimeperiodforSquare-shape (COLUMN) 0.6774s
TimeperiodforSquare(Shear wall)(X,Y) (0.7224,0.74 64)s
3.RESULTS & DISCUSSION: -
A. Base shear
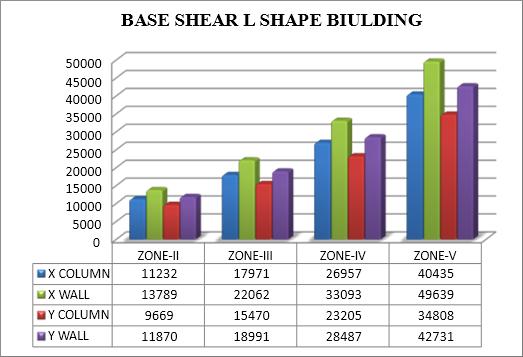
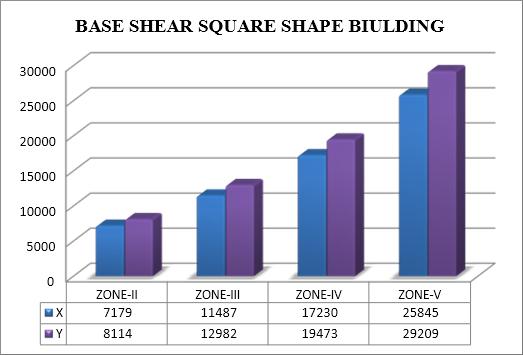
Baseshearintorsionalanalysisisthetotalhorizontalforce appliedtoastructure'sbaseasaresultofseismicactivity. When determining the building's response to torsional effects which happen when the center of mass and the centerofrigiditydonotlineup thisforceisessential.To effectively withstand seismic forces while minimizing damage,structuresmustbedesignedwithanunderstanding ofbaseshearintorsionalanalysis.
B. Storey Drift
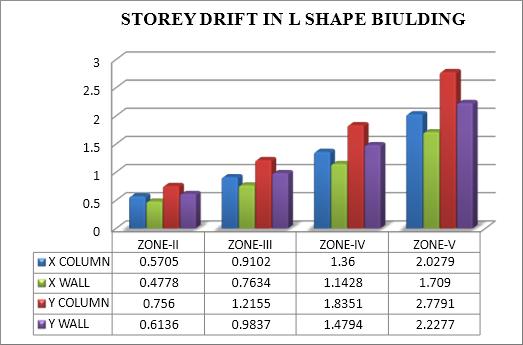
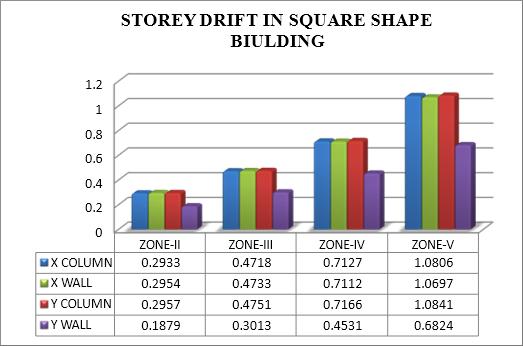
Storeydriftintorsionalanalysisisthedifferenceinlateral displacement between two floors that come after one another. It gauges the amount of movement caused by seismic forces between one floor and the next, which can causetorsionintheeventofanunevendisplacement.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The modal mass participation ratio in torsional analysis shows the percentage of a structure's total mass that is involvedineachmodeofvibration.Itassistsindetermining which modes have a major impact on how the building reacts to seismic forces. Even in asymmetrical buildings, torsionalmodescanshowlowerparticipationratiosandyet haveasubstantialeffect.Reducingtorsionalresponseand enhancingseismicperformancecanbeachievedbyensuring thatthedominantmodesaretakenintoaccountduringthe designphase.
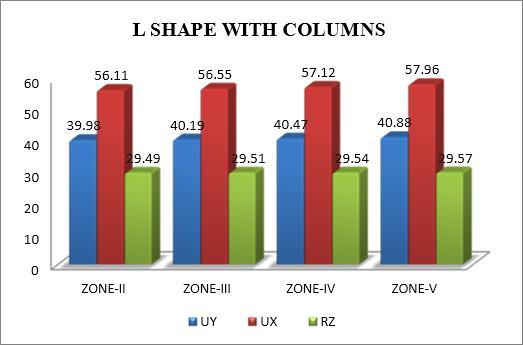
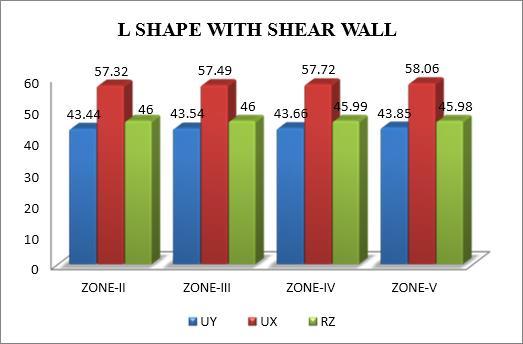
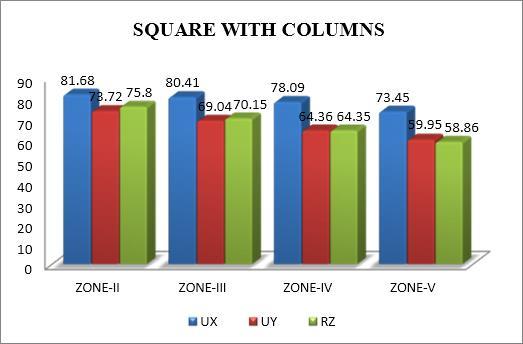
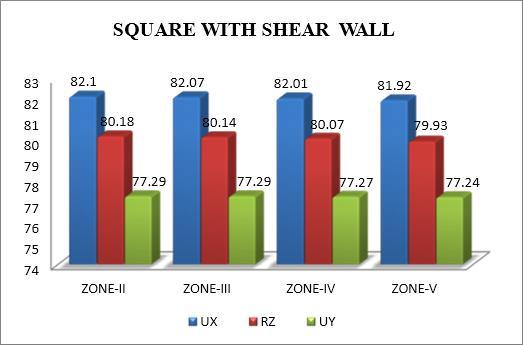
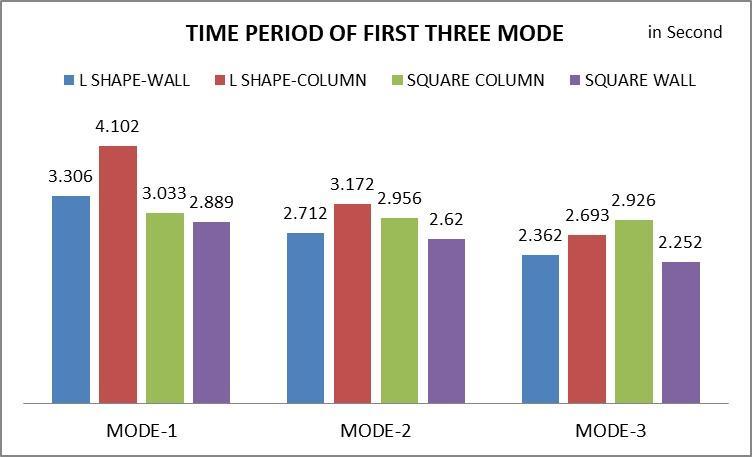
Themodaltimeperiodintorsionalanalysisisthelengthofa singlecycleoftorsional vibrationfora particularmode. It sheds light on how the structureresponds dynamicallyto seismic forces, especially when torsional effects are substantial.Longerperiodmodeshavethepotentialtocause thestructuretotwist
4.CONCLUSION: -
Thefollowingimportantconclusionscanbedrawnfromthe investigationthatwasdone:
Baseshearincreaseswithincreaseinseismiczone IITOV.
Base shear is observed to be greater in buildings withshearwallcomparedtobuildingswithcolumn intheirstructure.
Timeperiodiscomparativelylessinthefirstmodes inbuildingshavingshearwall.
Storeydriftinbothxandydirectionincreasewith increaseinseismiczoneinalltypesofbuildings.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 07 | July 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
It is observed that building with shear wall performsbetterthanbuildingwithcolumninterms ofstoreydrift.
Modal mass participation increases in each governingtop3modesinmodelshavingshearwall thanmodelshavingcolumns.
InL-shapebuildingmodalmassparticipationratio increases in each governing top 3 modes with increaseinseismiczones.
Thetotalofmassparticipationremainssameinall seismiczones.
Thetotalallfirstthreegoverningmodesstayssame inallseismiczones.
InSquareshapebuildingmodalmassparticipation ratiodecreasesineachgoverningtop3modeswith increaseinseismiczones.
InL-shapebuildingitisobservedthatbuildingwith shearwallperformsbetter.
Insquareshapebuildingitisobservedthatbuilding withcolumnsperformbetter.
Itisnotalwaysnecessarythatbuildingwithshear wall will perform better. Each and every other factor like orientation, structural grid, symmetry, etc.playsitsroleinperformanceofthebuildingand equallyaffectstheperformance.
1. Hossain, S., & Singh, S. K. (2023, February). ComparativeanalysisofirregularRCCbuildingsin differentzones.InIOPConferenceSeries:Earthand Environmental Science (Vol. 1110, No. 1, p. 012035).IOPPublishing.
2. DeepaliVasudev,AnjaliRai."ComparativeStudyon Seismic Analysis of Multi Storied RC Framed Structure with and without Diaphragm Discontinuity", Volume 9, Issue X, International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology (IJRASET) Page No: 657662,ISSN:2321-9653
3. Vasave, S. D., Vhankade, G. N., Kumbhar, A. S., Damse, A. R., Bhusare, V. P., & Khadake, N. V. Comparative Study Of Dynamic Behavior Of G+ 4 Building With Different Configurations In Seismic ZoneIiiUsingEtabsSoftware.
4. Prathap, G. V., & Radha, D. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Behaviour Of Horizontal And Vertical
IrregularBuildingsWithAndWithoutUsingShear Walls By Etabs Software. Journal Of Engineering Sciences,14(02).
5. Devi,K.,&Petal,S.(2023).AComparativeStudyon Seismic Analysis of Multistorey Buildings in DifferentSeismicZones.JournalofSmartBuildings andConstructionTechnology,5(2),9-16.
6. Mourya,V.,&Vyas,J N.(2020).SEISMICANALYSIS OF RC MULTI-STORIED IRREGULAR BUILDING WITH TORSIONAL EFFECTS Global Journal Of AdvancedEngineeringTechnologiesAndSciences, 7(11),1-11.
7. SB, M. S., & Uday, M. A. K. Determination of Appropriate Time Period to be used Analyzing MultiblockTallBuildings.
8. Konapure, C. G., & Muddiddi, M. S. (2018). Determination Of Time Period And Evaluation Of Seismic Response Of Framed Structure With Different Approaches. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (Irjet), 5(04),956-960.
9. IS1893(Part1):2016
10. IS16700:2023