
Volume: 11 Issue: 09 | Sep 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


Volume: 11 Issue: 09 | Sep 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
LISSEAU THERESA, VIGNESH T R
Lisseau Theresa , Department of Computer Application, St. Thomas College (Autonomous)Thrissur, 680001, Kerala, India
Vignesh T R , Department of Computer Application, St. Thomas College(Autonomous)Thrissur, 680001, Kerala, India
ABSTRACT - Blockchain is an innovative technology that has the potential to revolutionize several industries, such as supply chain management, banking, education, and healthcare. Blockchain technology has the ability to contribute to the development of a more transparent and safe educational system by facilitating the recording and authentication of students' academic achievements. This would enable students to more easily demonstrate their abilities and knowledge to prospective employers. The discussion of Blockchain technology's potential applications in education wraps up the study. It contends that while blockchain technology has the ability to completely transform education, more study and advancement are requiredtofullyunderstanditslimitations.
KEY WORDS: Blockchain, Education, Sustainability, Machine learning, Credential verification
Blockchain, a revolutionary digital ledger, has redefined how transactions are recorded, ensuring security, transparency, and immutability. The structure of blockchaining is designed in such a way that it ensures safety andprovidesfullprotectionandencryptionalongwiththe concernsoftamperingthatisperforminganysortofillegal activities can be thereby prevented using this technology. With features providing cryptographic algorithms and datasecurityBlock-chainingtechnologyhasraiseditsbars in cybersecurity and privacy providing trustworthy solutions and results. Beyond security, its potential to enable real-time transactions without intermediaries promises significant gains in efficiency, marking a paradigmshiftintransactionprocessing[1].
Education is one sector in which the blockchain is only now starting to gain traction. Very few educational institutions have embraced blockchain technology, therefore its application in the field is still in its infancy. Merely 2% of higher education institutions were utilizing blockchain, according to a 2019 poll conducted by the research firm Gartner, while another 18% intended to do sointhefollowingtwoyears[2].
In the realm of education, blockchain technology is not merelyatoolforstoringandsharingacademicrecords;it's
a catalyst for transformative change. Imagine a student seamlessly taking an exam on a laptop, their responses securely recorded through blockchain. While current blockchain adoption focuses on record-keeping, researchers envision a future where blockchain reshapes educationinprofoundways.
Leveraging blockchaincanrevolutionizeonline education, offeringsecureandtransparentsystemsfordeliveringand trackingcoursesandcertifications.Thisbreakthroughhas the potential to elevate the credibility and recognition of online learning, making it an appealing choice for both students and employers. The shift towards blockchainpowered platforms addresses fundamental challenges in the online education landscape, providing a robust solutiontoissuesoftrustandverification.
TheEducational institutions canlower expenses,expedite administrative procedures, and improve the credibility of credentialsandcertificationsbyutilizingthedecentralized and transparent characteristics of blockchain technology. Making education more trustworthy and accessible for both companies and students is one of the main advantages of implementing blockchain in the classroom. Students may confidently display their qualifications by using blockchain technology to help prevent fraud and guaranteethatcredentialsareauthentic.
Theforthcomingresearchonthetransformativeimpactof blockchain technology in the education sector sounds promising and addresses critical areas such as distance learning, data security, and certification processes. By exploring these dimensions, this research can contribute valuable insights and practical recommendations that guideeducationalinstitutionsandspecialistsineffectively harnessing the transformative potential of blockchain technology.
This research aims to contribute substantially to the evolving landscape of blockchain in education. As an integral part of the growing body of research in this domain, this work stands as a influence for future, providing a foundation for informed decision-making and effective integration of blockchain technology in education[3]. e-ISSN:2395-0056

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 09 | Sep 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Blockchain technology, originally designed for secure value transfer, has evolved into a decentralized powerhouse with applications across diverse sectors. In education,itoffersaparadigmshiftinthemanagementof records, fostering interoperability and decentralized control. This literature reviewaims to dissect the existing landscape, identify challenges faced by educational institutions, and explore how specific blockchain features canaddresstheseissues.
Blockchain's distributed ledger system, free from thirdparty control, forms the cornerstone of its applications. Beyond its initial use in value transfer, blockchain has founditswayintohealthcare,banking,andtheinternetof things. In education, it presents opportunities for decentralizedrecordmanagementwithinaninteroperable framework.
The analysis reveals three major challenges faced by educational institutions: manipulation risk, difficulties in verification, and the exchange of records between institutions. These issues, spanning physical, digital, and financial realms, underscore the need for transformative solutionsintheeducationallandscape.
In conclusion, this literature review unveils the transformative potential of blockchain in addressing prevalent challenges faced by educational institutions. By systematically categorizing issues and exploring blockchain features as viable solutions, this research contributestotheongoingdiscourseontheintersectionof blockchain and education. However, it also underscores the importance of addressing technical challenges to ensure a seamless integration and maximize the benefits ofthisrevolutionarytechnology.
The education sector has undergone several tremendous changes. From traditional classrooms to digital learning, thisindustryhasencounteredextensivegrowth,especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. The trend of e-learning has escalated during the COVID-19 pandemic and accelerated a new wave of revolution in the sector. Besides the introductionoftheeLearningsystem,theeducationsector also experienced significant growth with Blockchain adoption. Although Blockchain has not disrupted the educationsectorcompletely,itsimpactcanbeexperienced inthecomingyears.
According to Business Research Insights in 2021, the globalBlockchaintechnologyineducationmarketsizewas valuedat$118.73millionin2021andisexpectedtoreach $1055.98millionby2027,expandingataCAGRof43.94% during the forecast period. Many education institutions areplanningtointegratetheBlockchainintotheirexisting
systemforincreasedtransparency,streamlinedprocesses, andeasyrecordmanagement[4].
2.2
Blockchain technology empowers students by allowing them to own and manage their academic achievements. Unlike traditional models where universities control records, students now have the ability to independently access and share their academic history. Blockchain eliminates barriers like fees and bureaucratic processes associated with accessing physical records. Students can access their diplomas seamlessly at any time and from anywhere, offering convenience and immediate availability during job searches or further education pursuits. The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain reduces the risks associated with physical records. Students no longer face the threat of loss or destruction of their diplomas, ensuring the perpetual existence and integrity of their academic credentials. Graduates can easily share accurate and tamper-proof credentialswithemployersduringjobsearches.
2.3
Blockchain streamlines the diploma verification process for higher education institutions, saving them time and resources. The virtually tamper-proof nature of blockchain-issued diplomas simplifies and expedites the verification of a student's academic record. Institutions can realize substantial cost savings by leveraging blockchain for issuing and verifying diplomas. Adopting blockchain technology to store and authenticate diplomas essentially establishes a mutually beneficial partnership that gives institutions more efficiency and lower costs whileprovidingstudentswithmoreautonomy.Beyondits direct benefits, blockchain technology is revolutionizing theeducationsectorbyfosteringamorestreamlined,safe, andaccessibleacademicecosystem.
Storingstudentdataontheblockchainallowsforeasyand secure access to credentials and skills learned. Decentralized nature removes the need for a central administrator (e.g., a university), giving students control over their information throughout their lives. Ownership andcontrolofdatacanenhancecredibilitywithemployers, astheinformationonresumesisverifiable.
Blockchain provides potential solutions for protecting student data, ensuring identity, privacy, and security. Hashingandencryptioncanbe employedto enhancedata privacyandsecurity.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 09 | Sep 2024 www.irjet.net
The most durable feature of blockchaintechnology is that it performs its working in such a way that it provides a way to protect the exact grades, marks and credentials in suchawaythatitcannotbealteredbyanyone.Itactsasa building factor of maintaining trust and transparency in the employment sector, providing employers with a reliable and accurate means of verifying the educational backgrounds of job applicants. This can lead to more consistent and useful talent assessment, improved hiring decisions, and increased overall confidence in the hiring process meeting the selection criteria and making the job mucheasier.
Blockchain technology offers several opportunities for application in the field of education. Here are some potentialbenefits:-
Student Records: Blockchain provides a secure and decentralized platform for storing, tracking, and using students'credentials.Studentshave quick and convenient accesstotheirrecords,whichcanbesecurelysharedwith potential employers. Platforms like Blockcerts offer openstandard solutions for storing and verifying digital certificates, including academic transcripts and credentials.
E-Transcripts: Blockchain technology can streamline the process of issuing and verifying transcripts, reducing delays and costs associated with traditional methods. The useof distributedledgertechnologyminimizesthe risk of fraudulenteducationalcreditclaims.
Automated Learning Platforms: Teachers and students canusesmartcontractsontheblockchaintocreatedigital agreements for tasks and assignments. These agreements can include all the necessary details such as instructions, conditions, due dates, and deadlines, providing transparencyandaccountability.
Publishing & Copyright Protection: Blockchain facilitates secure and transparent publication of research work,protectingit fromplagiarism.Academicinstitutions can use blockchain to ensure the integrity of their students' and staff's research, allowing for a more trustworthyandaccessibleacademicenvironment.
Payment via Cryptocurrencies: Cryptocurrenciesenable faster and more efficient international transactions. Students, especially international ones, can make paymentstouniversitiesusingcryptocurrencies,reducing transaction times and costs. Some universities, such as Simon Fraser University, the University of Nicosia, and
p-ISSN:2395-0072
King’s College in New York, already accept cryptocurrenciesasaformofpaymentfromstudents.
Blockchain technology is often surrounded by plenty of hype, which makes many business leaders keenly interested in adopting it but also concerned about blockchain challengesandrisks. Some of the challenges thatarefacingineducationwhileusingblockchainare:
Successdependsonwidespreadacceptanceandtrustfrom educational institutions and employers. The legitimacy of blockchaincredentialsiscontingentonthe recognition by schools and firms. Building trust and making blockchain credentialsthenormratherthantheexceptioniscrucial.
Educational institutions handle large volumes of data, potentially posing scalability issues for blockchain. Peerto-peerverificationforeachtransactioncanleadtoslower transaction speeds as the volume of data grows. Permissioned blockchains may offer better transaction ratescomparedtopermissionlessones.
Adoption and implementation of new technology, including blockchain,canbe expensive.Costs mayinclude computer power, infrastructure modifications, and training for administrators. The financial investment needs to be weighed against potential savings in other areas.
While blockchain is known for its security features, the sensitive nature of educational records requires careful consideration. Compliance with state and federal data protectionrulescanbechallenging.Institutionsmayneed touseprivateorPermissionedblockchainsandimplement encryptionforaddedprivacysafeguards.
1. Record keeping
Blockchain simplifies the management of student records by storing credentials and certificates on a distributed ledger, eliminating the need for intermediaries in the verificationprocess.
2. Courses and Certificates
Blockchain facilitates certification of course contents and academic achievements, streamlining the process of obtainingcomplete,verifieddocumentation.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 09 | Sep 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
3. Credential Verification
Academic credentials which include degrees, diplomas, and certifications that can be securely stored and verified on the blockchain, ensuring authenticity and preventing fraud.
4. Fraud Prevention
Blockchainhelpspreventfraudbyensuringthatacademic qualificationsaregenuine,reducingtheriskofunqualified individualsbeinghiredbasedonfakecredentials.
5. Decentralized Online Learning
Introducing blockchain in online learning enhances realtimedataexchangeandinteractionsbetweenstudentsand teachers, providing a more dynamic and engaging educationalexperience.
6. Plagiarism Check
Blockchain technology with advanced encryption allows for secure storage of academic information, preventing plagiarism by enabling content creators to track, access, verify,andcontroltheusageoftheircontent.
7. Better Online Platforms
Blockchain enthusiasts are exploring the development of online learning platforms that leverage blockchain applications to connect students and teachers, facilitate token-based interactions, and make education more convenientandengaging.
8. Student Data Privacy
Blockchain can establish a decentralized and secure systemforstoringstudentdata,ensuringdataprivacyand protectingagainstdatabreaches.
6. MACHINE LEARNING AND BLOCKCHAIN IN EDUCATION
CombiningMachineLearningandBlockchaintechnologies canunlockinnovativesolutions,particularlyinareawhere data security, transparency, and decentralized control are critical. Some of the ways where machine learning and blockchaintechnologycanbeusedineducation:
Secure and private E-Learning environment: Blockchain Ensures secure and tamper-proof storage of student data. Machine Learning Enhances security by identifying patterns of unusual access or behaviour, providinganadditionallayerofprotection.
Personalized Learning Experiences: Machine Learning
Analyses vast amounts of data to understand individual learning patterns, preferences, and strengths and
weaknesses. Blockchain Safely stores this personalized learningdata,maintainingitsintegrityandprivacy.
Verification of Educational Achievements: Blockchain Creates a tamper-proof record of degrees and certifications, making it easier for employers and institutions to verify credentials. Machine Learning Could assist in analyzing patterns in the educational achievements data, ensuring accuracy and detecting anomalies.
Improved Evaluation and Assessment: Machine Learning Automates grading processes, providing quicker and more consistent evaluations. Blockchain Secures the integrity of grades and assessments, preventing unauthorizedchanges.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Machine Learning Analyses large datasets to provide insights into effective teachingmethodsandmaterials.BlockchainSafelyrecords andstoresthedata usedfordecision-making, ensuringits accuracyandtransparency.
"Blockchain-Based Credential Verification" is a cuttingedgecourse that equips students with the knowledge and skills to transform traditional credential verification processes. By embracing blockchain technology, educational institutions, employers, and other stakeholders can revolutionize the way academic credentials are verified, ensuring a more secure, efficient, andtransparenteducationalecosystem.
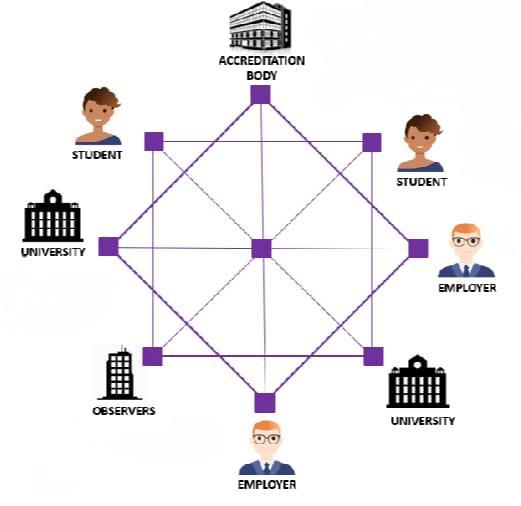
Fig-1: BlockchainInCredentialVerification
ACCREDIATION BODY:
Accredit academic credentials issued by issuing authorities.
Eliminateaccreditationfraudintheprocess.
Provideverificationservicetoemployers.
Providetransparencyintheprocess.
Administernetwork.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 09 | Sep 2024 www.irjet.net
STUDENT: Offer proof of credentials to prospective employees.
EMPLOYER: Ensure prospective employee has genuine credentialsthroughverification.
OBSERVERS: Actasaneutralwatchdogbody.
UNIVERSITY: Issue/revoke academic credentials to student.
An education needs to be long-lasting. In general, sustainable education (SE) is an important idea that encourages employability and incorporates equitable, inclusive, and continual learning. New techniques, technology, and practical abilities in instruction and evaluation could benefit from a digital transversal. Furthermore, all parties involved in SE are included: communities,universities,instructors,students,etc.When we take into consideration the disruptive forces, constantly shifting geopolitical powers, and the ongoing epidemic that has impacted over 1.6 billion learners, we can see that there has been a significant learning loss. Furthermore, compared to just 20% in high-income nations, 86% of students in low-income countries are effectively absent from school as a result of school closures. However, every crisis has fresh chances for teaching about sustainable development. Artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, 5G, machine learning, blockchain, e-learning, educational platforms, virtual classrooms, and other cutting-edge technology can providegenuinesupport.[5].
Insummary,theintegrationofblockchaindevelopmentin the education sector has emerged as a transformative force. Moreover,itsdecentralizednaturefacilitatesmore inclusive and equitable access to educational resources, opening doors for learners in regions with limited traditional educational infrastructure. As we continue to explore the applications of blockchain in education, fostering innovation, collaboration, and adaptability becomes crucial. Embracing these principles will allow us to fully leverage the benefits of blockchain technology, creating a future where education is not only more accessible but also more impactful for learners and institutions.Lookingahead,futurestudiescoulddelveinto the legal and ethical implications of implementing blockchain technology in education. Additionally, exploring the potential of blockchain to promote sustainabilityinothersectorscoulduncovernovelwaysin which this technology contributes to broader societal and environmental goals. Embracing such research avenues will further enrich our understanding and application of blockchain in shaping a more sustainable and inclusive educationallandscape.
p-ISSN:2395-0072
[1] D. Yaga, P. Mell, N. Roby, et al. Blockchain technology overview arXiv (2019) Preprint. arXiv:1906.110782019
[2] How Blockchain is used in Education (2021) Online.maryville.edu/blog/blockchain-in-education
[3]P.Bhaskar,C.K.Tiwari,A.JoshiBlockchainineducation management: present and future applications Interact. Technol. Smart Educ., 18 (1) (2020), pp. 117,10.1108/ITSE-07-2020-0102
[4] Mourtzis Dimitris, et al. A hybrid teaching factory model for supporting the educational process in COVID-19era.ProcediaCirp,2021,104:1626-1631.
[5] Anto,J.M.;Marti,J.L.;Casals,J.;Bou-Habib,P.;Casal,P.; Fleurbaey, M.; Frumkin, H.; Jimenez-Moales, M.; Jordana, J.; Lancelotti, C.; et al. The Planetary. N. Wellbeing Initiative: Pursuing the Sustainable. O.Development Goals in Higher Education. P. Sustainability2021,13,3372