UNIT
6
MODULE • Chemistry FORM 4
ACIDS AND BASES ASID DAN BES
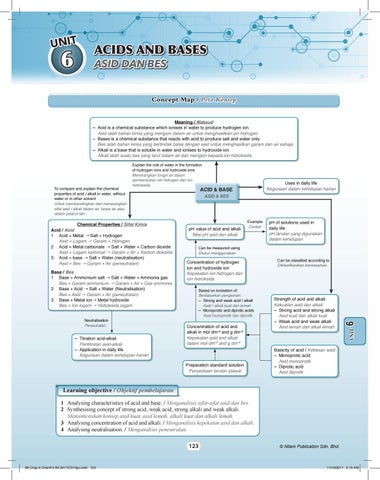
Concept Map / Peta Konsep Meaning / Maksud – Acid is a chemical substance which ionises in water to produce hydrogen ion. Asid ialah bahan kimia yang mengion dalam air untuk menghasilkan ion hidrogen. – Bases is a chemical substance that reacts with acid to produce salt and water only. Bes ialah bahan kimia yang bertindak balas dengan asid untuk menghasilkan garam dan air sahaja. – Alkali is a base that is soluble in water and ionises to hydroxide ion. Alkali ialah suatu bes yang larut dalam air dan mengion kepada ion hidroksida.
Base / Bes 1 Base + Ammonium salt ➝ Salt + Water + Ammonia gas Bes + Garam ammonium ➝ Garam + Air + Gas ammonia 2 Base + Acid ➝ Salt + Water (Neutralisation) Bes + Asid ➝ Garam + Air (peneutralan) 3 Base + Metal ion➝ Metal hydroxide Bes + Ion logam ➝ Hidroksida logam Neutralisation Peneutralan
– Titration acid-alkali Pentitratan asid-alkali – Application in daily life Kegunaan dalam kehidupan harian
ASID & BES
pH value of acid and alkali Nilai pH asid dan alkali
Example Contoh
pH of solutions used in daily life pH larutan yang digunakan dalam kehidupan
Can be measured using Diukur menggunakan
Concentration of hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion Kepekatan ion hidrogen dan ion hidroksida Based on ionisation of: Berdasarkan pengionan: – Strong and weak acid / alkali Asid / alkali kuat dan lemah – Monoprotic and diprotic acids Asid monoprotik dan diprotik
Concentration of acid and alkali in mol dm–3 and g dm–3 Kepekatan asid and alkali dalam mol dm–3 and g dm–3
Preparation standard solution Penyediaan larutan piawai
Can be classified according to Diklasifikasikan berdasarkan
Strength of acid and alkali Kekuatan asid dan alkali – Strong acid and strong alkali Asid kuat dan alkali kuat – Weak acid and weak alkali Asid lemah dan alkali lemah
6
Chemical Properties / Sifat Kimia Acid / Asid 1 Acid + Metal ➝ Salt + Hydrogen Asid + Logam ➝ Garam + Hidrogen 2 Acid + Metal carbonate ➝ Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide Asid + Logam karbonat ➝ Garam + Air + Karbon dioksida 3 Acid + base ➝ Salt + Water (neutralisation) Asid + Bes ➝ Garam + Air (peneutralan)
Uses in daily life Kegunaan dalam kehidupan harian
ACID & BASE
UNIT
To compare and explain the chemical properties of acid / alkali in water, without water or in other solvent Untuk membandingkan dan menerangkan sifat asid / alkali dalam air, tanpa air atau dalam pelarut lain
Explain the role of water in the formation of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions Menerangkan fungsi air dalam pembentukan ion hidrogen dan ion hidroksida
Basicity of acid / Kebesan asid: – Monoprotic acid Asid monoprotik – Diprotic acid Asid diprotik
Learning objective / Objektif pembelajaran 1 2 3 4
Analysing characteristics of acid and base. / Menganalisis sifat-sifat asid dan bes. Synthesising concept of strong acid, weak acid, strong alkali and weak alkali. Mensintesiskan konsep asid kuat, asid lemah, alkali kuat dan alkali lemah. Analysing concentration of acid and alkali. / Menganalisis kepekatan asid dan alkali. Analysing neutralisation. / Menganalisis peneutralan.
123
06 Chap 6 ChemF4 Bil 2017(CSY5p).indd 123
© Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
11/10/2017 9:15 AM